Amphipolis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Amphipolis ( ell, Αμφίπολη, translit=Amfipoli; grc, Ἀμφίπολις, translit=Amphipolis) is a municipality in the Serres regional unit, Macedonia,
Amphipolis ( ell, Αμφίπολη, translit=Amfipoli; grc, Ἀμφίπολις, translit=Amphipolis) is a municipality in the Serres regional unit, Macedonia,
 Throughout the 5th century BC,
Throughout the 5th century BC,
 The city itself kept its independence until the reign of king Philip II () despite several Athenian attacks, notably because of the government of Callistratus of Aphidnae. In 357 BC, Philip succeeded where the Athenians had failed and conquered the city, thereby removing the obstacle which Amphipolis presented to Macedonian control over Thrace. According to the historian Theopompus, this conquest came to be the object of a secret accord between Athens and Philip II, who would return the city in exchange for the fortified town of Pydna, but the Macedonian king betrayed the accord, refusing to cede Amphipolis and laying siege to Pydna as well.
The city was not immediately incorporated into the Macedonian kingdom, and for some time preserved its institutions and a certain degree of autonomy. The border of Macedonia was not moved further east; however, Philip sent a number of Macedonian governors to Amphipolis, and in many respects the city was effectively "Macedonianized". Nomenclature, the calendar and the currency (the
The city itself kept its independence until the reign of king Philip II () despite several Athenian attacks, notably because of the government of Callistratus of Aphidnae. In 357 BC, Philip succeeded where the Athenians had failed and conquered the city, thereby removing the obstacle which Amphipolis presented to Macedonian control over Thrace. According to the historian Theopompus, this conquest came to be the object of a secret accord between Athens and Philip II, who would return the city in exchange for the fortified town of Pydna, but the Macedonian king betrayed the accord, refusing to cede Amphipolis and laying siege to Pydna as well.
The city was not immediately incorporated into the Macedonian kingdom, and for some time preserved its institutions and a certain degree of autonomy. The border of Macedonia was not moved further east; however, Philip sent a number of Macedonian governors to Amphipolis, and in many respects the city was effectively "Macedonianized". Nomenclature, the calendar and the currency (the
 During the period of
During the period of

 In 2012 Greek archaeologists unearthed a large tomb within the Kasta Hill, the biggest burial mound in Greece, northeast of Amphipolis. The large size and quality of the tumulus indicates the prominence of the burials made there, and its dating and the connections of the city with Alexander the Great suggest important occupants. The perimeter wall of the tumulus is long, and is made of limestone covered with marble.
The tomb comprises three chambers separated by walls. There are two
In 2012 Greek archaeologists unearthed a large tomb within the Kasta Hill, the biggest burial mound in Greece, northeast of Amphipolis. The large size and quality of the tumulus indicates the prominence of the burials made there, and its dating and the connections of the city with Alexander the Great suggest important occupants. The perimeter wall of the tumulus is long, and is made of limestone covered with marble.
The tomb comprises three chambers separated by walls. There are two 
 The original 7.5 km long walls are generally visible, particularly the northern section which is preserved to a height of 7.5m. 5 preserved gates can be seen and notably the gate in front of the wooden bridge.
In early Christian times another, inner, wall was built around the acropolis.
The original 7.5 km long walls are generally visible, particularly the northern section which is preserved to a height of 7.5m. 5 preserved gates can be seen and notably the gate in front of the wooden bridge.
In early Christian times another, inner, wall was built around the acropolis.
 The ancient bridge that crossed the river Strymon was mentioned by Thucydides, was strategic as it controlled access between Macedonia and the Chalkidike in the west to Thrace in the east, and was important for the economy and trade. It was therefore incorporated into the city walls.
It was discovered in 1977 and is a unique find for Greek antiquity. The hundreds of wooden piles have been carbon-dated and show the vast life of the bridge with some piles dating from 760 BC, and others used till about 1800 AD.
The ancient bridge that crossed the river Strymon was mentioned by Thucydides, was strategic as it controlled access between Macedonia and the Chalkidike in the west to Thrace in the east, and was important for the economy and trade. It was therefore incorporated into the city walls.
It was discovered in 1977 and is a unique find for Greek antiquity. The hundreds of wooden piles have been carbon-dated and show the vast life of the bridge with some piles dating from 760 BC, and others used till about 1800 AD.
 This was a major public building for the military and gymnastic training of youth as well as for their artistic and intellectual education. It was built in the 4th c. BC and includes a
This was a major public building for the military and gymnastic training of youth as well as for their artistic and intellectual education. It was built in the 4th c. BC and includes a
Official site about Amphipolis
Demographic Information from Greek Travel Pages
The tomb of Amphipolis
{{Second Journey of Paul of Tarsus 437 BC 5th-century BC establishments 8th-century disestablishments in the Byzantine Empire Ancient Amphipolis Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Greece Archaeological sites in Macedonia (Greece) Athenian colonies Former populated places in Greece Municipalities of Central Macedonia Populated places established in the 5th century BC Populated places disestablished in the 8th century Populated places in ancient Macedonia Populated places in ancient Thrace Populated places in Serres (regional unit) Roman sites in Greece Populated places of the Byzantine Empire
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
. The seat of the municipality is Rodolivos
Rodolivos ( el, Ροδoλίβος) is a town and a former municipality in the Serres regional unit, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Amfipoli, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal ...
. It was an important ancient Greek polis (city), and later a Roman city, whose large remains can still be seen.
Amphipolis was originally a colony
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state' ...
of ancient Athenians and was the site of the battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and for ...
between the Spartans and Athenians
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
in 422 BC. It was later the place where Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
prepared for campaigns leading to his invasion of Asia in 335 BC. Alexander's three finest admirals, Nearchus, Androsthenes and Laomedon, resided in Amphipolis. After Alexander's death, his wife Roxana
Roxana (c. 340 BC – 310 BC, grc, Ῥωξάνη; Old Iranian: ''*Raṷxšnā-'' "shining, radiant, brilliant"; sometimes Roxanne, Roxanna, Rukhsana, Roxandra and Roxane) was a Sogdian or a Bactrian princess whom Alexander the Great married ...
and their son Alexander IV were imprisoned and murdered in 311 BC.
Excavations in and around the city have revealed important buildings, ancient walls and tombs. The finds are displayed at the archaeological museum of Amphipolis. At the nearby vast Kasta burial mound, an ancient Macedonian tomb has recently been revealed. The Lion of Amphipolis monument nearby is a popular destination for visitors.
It was located within the region of Edonis
The B Engineering Edonis is a sports car developed in the year 2000 and manufactured by Italian automobile manufacturer B Engineering with overall engineering by Nicola Materazzi (ex Lancia, Ferrari & Bugatti) and styling by Marc Deschamps (e ...
.
History
Origins
 Throughout the 5th century BC,
Throughout the 5th century BC, Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
sought to consolidate its control over Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
, which was strategically important because of its raw materials (the gold and silver of the Pangaion hills and the dense forests that provided timber for naval construction), and the sea routes vital for Athens' supply of grain from Scythia
Scythia ( Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
...
.
A first unsuccessful attempt at colonisation was in 497 BC by the Milesian Tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to ...
Histiaeus. After the defeat of the Persians in 490 BC, the Athenian general Kimon
Cimon or Kimon ( grc-gre, Κίμων; – 450BC) was an Athenian ''strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician.
He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Battl ...
managed to occupy Eion a few km south on the coast in 476 BC, and turned it into a military base and commercial port. The Athenians founded a first colony at ''Ennea-Hodoi'' (‘Nine Ways’) in 465 BC, but the first ten thousand colonists were massacred by the Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
. A second attempt took place in 437 BC on the same site under general Hagnon which was successful. The city and its first impressive and elaborately built walls of 7.5 km length date from this time. The new Athenian colony became quickly of considerable size and wealth.
The new settlement took the name of Amphipolis (literally, "around the city"), a name which is the subject of much debate about its etymology
Etymology () The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words ...
. Thucydides claims the name comes from the fact that the Strymon River flows "around the city" on two sides; however a note in the ''Suda
The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; grc-x-medieval, Σοῦδα, Soûda; la, Suidae Lexicon) is a large 10th-century Byzantine encyclopedia of the ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas (Σούδας) or Souida ...
'' (also given in the lexicon of Photius) offers a different explanation apparently given by Marsyas, son of Periander: that a large proportion of the population lived "around the city". However, a more probable explanation is the one given by Julius Pollux: that the name indicates the vicinity of an isthmus.
Amphipolis quickly became the main power base of the Athenians in Thrace and, consequently, a target of choice for their Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referr ...
n adversaries. In 424 BC during the Peloponnesian War the Spartan general Brasidas
Brasidas ( el, Βρασίδας, died 422 BC) was the most distinguished Spartan officer during the first decade of the Peloponnesian War who fought in battle of Amphipolis and Pylos. He died during the Second Battle of Amphipolis while winning ...
captured Amphipolis.
Two years later in 422 BC, a new Athenian force under the general Kleon
Cleon (; grc-gre, wikt:Κλέων, Κλέων, ; died 422 BC) was an Classical Athens, Athenian strategos, general during the Peloponnesian War. He was the first prominent representative of the commercial class in Athenian politics, although he w ...
failed once more during the Battle of Amphipolis at which both Kleon and Brasidas lost their lives. Brasidas survived long enough to hear of the defeat of the Athenians and was buried at Amphipolis with impressive pomp. From then on he was regarded as the founder of the city and honoured with yearly games and sacrifices.
The Athenian population remained very much in the minority in the city and hence Amphipolis remained an independent city and an ally of the Athenians, rather than a colony or member of the Athens-led Delian League. It entered a new phase of prosperity as a cosmopolitan centre.
Macedonian rule
 The city itself kept its independence until the reign of king Philip II () despite several Athenian attacks, notably because of the government of Callistratus of Aphidnae. In 357 BC, Philip succeeded where the Athenians had failed and conquered the city, thereby removing the obstacle which Amphipolis presented to Macedonian control over Thrace. According to the historian Theopompus, this conquest came to be the object of a secret accord between Athens and Philip II, who would return the city in exchange for the fortified town of Pydna, but the Macedonian king betrayed the accord, refusing to cede Amphipolis and laying siege to Pydna as well.
The city was not immediately incorporated into the Macedonian kingdom, and for some time preserved its institutions and a certain degree of autonomy. The border of Macedonia was not moved further east; however, Philip sent a number of Macedonian governors to Amphipolis, and in many respects the city was effectively "Macedonianized". Nomenclature, the calendar and the currency (the
The city itself kept its independence until the reign of king Philip II () despite several Athenian attacks, notably because of the government of Callistratus of Aphidnae. In 357 BC, Philip succeeded where the Athenians had failed and conquered the city, thereby removing the obstacle which Amphipolis presented to Macedonian control over Thrace. According to the historian Theopompus, this conquest came to be the object of a secret accord between Athens and Philip II, who would return the city in exchange for the fortified town of Pydna, but the Macedonian king betrayed the accord, refusing to cede Amphipolis and laying siege to Pydna as well.
The city was not immediately incorporated into the Macedonian kingdom, and for some time preserved its institutions and a certain degree of autonomy. The border of Macedonia was not moved further east; however, Philip sent a number of Macedonian governors to Amphipolis, and in many respects the city was effectively "Macedonianized". Nomenclature, the calendar and the currency (the gold stater
The stater (; grc, , , statḗr, weight) was an ancient coin used in various regions of Greece. The term is also used for similar coins, imitating Greek staters, minted elsewhere in ancient Europe.
History
The stater, as a Greek silver curr ...
, created by Philip to capitalise on the gold reserves of the Pangaion hills, replaced the Amphipolitan drachma) were all replaced by Macedonian equivalents. In the reign of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, Amphipolis was an important naval base, and the birthplace of three of the most famous Macedonian admirals: Nearchus, Androsthenes and Laomedon, whose burial place is most likely marked by the famous lion of Amphipolis.
The importance of the city in this period is shown by Alexander the Great's decision that it was one of the six cities at which large luxurious temples costing 1,500 talents were built. Alexander prepared for campaigns here against Thrace in 335 BC and his army and fleet assembled near the port before the invasion of Asia. The port was also used as naval base during his campaigns in Asia. After Alexander's death, his wife Roxana
Roxana (c. 340 BC – 310 BC, grc, Ῥωξάνη; Old Iranian: ''*Raṷxšnā-'' "shining, radiant, brilliant"; sometimes Roxanne, Roxanna, Rukhsana, Roxandra and Roxane) was a Sogdian or a Bactrian princess whom Alexander the Great married ...
and their young son Alexander IV were exiled by Cassander and later murdered here.
Throughout Macedonian sovereignty Amphipolis was a strong fortress of great strategic and economic importance, as shown by inscriptions. Amphipolis became one of the main stops on the Macedonian royal road (as testified by a border stone found between Philippi and Amphipolis giving the distance to the latter), and later on the ''Via Egnatia
The Via Egnatia was a road constructed by the Romans in the 2nd century BC. It crossed Illyricum, Macedonia, and Thracia, running through territory that is now part of modern Albania, North Macedonia, Greece, and European Turkey as a con ...
'', the principal Roman road which crossed the southern Balkans. Apart from the ramparts of the lower town, the gymnasium and a set of well-preserved frescoes from a wealthy villa are the only artifacts from this period that remain visible. Though little is known of the layout of the town, modern knowledge of its institutions is in considerably better shape thanks to a rich epigraphic documentation, including a military ordinance of Philip V and an ephebarchic law from the gymnasium.
Conquest by the Romans
After the final victory ofRome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
over Macedonia in the Battle of Pydna
The Battle of Pydna took place in 168 BC between Rome and Macedon during the Third Macedonian War. The battle saw the further ascendancy of Rome in the Hellenistic world and the end of the Antigonid line of kings, whose power traced back ...
in 168 BC, Amphipolis became the capital of one of the four mini-republics, or ''merides'', which were created by the Romans out of the kingdom of the Antigonids
The Antigonid dynasty (; grc-gre, Ἀντιγονίδαι) was a Hellenistic dynasty of Dorian Greek provenance, descended from Alexander the Great's general Antigonus I Monophthalmus ("the One-Eyed") that ruled mainly in Macedonia.
History
...
which succeeded Alexander's empire in Macedon. These ''merides'' were gradually incorporated into the Roman client state, and later province, of Thracia. According to the '' Acts of the Apostles'', the apostles Paul and Silas
Silas or Silvanus (; Greek: Σίλας/Σιλουανός; fl. 1st century AD) was a leading member of the Early Christian community, who according to the New Testament accompanied Paul the Apostle on his second missionary journey.
Name and et ...
passed through Amphipolis in the early AD 50s, on their journey between Philippi and Thessalonica; where hence they proselytized to the Greeks, including Epicurean and Stoic philosophers.
In the 1st c. BC the city was badly damaged in the Thracian revolt against Roman rule.
Revival in Late Antiquity
 During the period of
During the period of Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English h ...
, Amphipolis benefited from the increasing economic prosperity of Macedonia, as is evidenced by the large number of Christian churches that were built. Significantly however, these churches were built within a restricted area of the town, sheltered by the walls of the acropolis. This has been taken as evidence that the large fortified perimeter of the ancient town was no longer defendable, and that the population of the city had considerably diminished.
Nevertheless, the number, size and quality of the churches constructed between the 5th and 6th centuries are impressive. Four basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its nam ...
s adorned with rich mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
floors and elaborate architectural sculptures (such as the ram-headed column capitals – see picture) have been excavated, as well as a church with a hexagonal central plan which evokes that of the basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its nam ...
of St Vitalis in Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the c ...
. It is difficult to find reasons for such municipal extravagance in such a small town. One possible explanation provided by the historian André Boulanger
André Boulanger (26 July 1886 – 9 September 1958) was a French professor of literature and Latin scholar who shared his activity between archaeology and the teaching profession.
He was a professor of Latin language and literature at Fribourg, ...
is that an increasing ‘willingness’ on the part of the wealthy upper classes in the late Roman period to spend money on local gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and planning. Gentrification often increases the ...
projects (which he terms '' euergetism'', from the Greek verb ; meaning 'I do good') was exploited by the local church to its advantage, which led to a mass gentrification of the urban centre and of the agricultural riches of the city's territory. Amphipolis was also a diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associ ...
under the metropolitan see
Metropolitan may refer to:
* Metropolitan area, a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories
* Metropolitan borough, a form of local government district in England
* Metropolitan county, a t ...
of Thessalonica – the Bishop of Amphipolis is first mentioned in 533. The bishopric is today listed by the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
as a titular see
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbi ...
.
Final decline of the city
The Slavic invasions of the late 6th century gradually encroached on the back-country Amphipolitan lifestyle and led to the decline of the town, during which period its inhabitants retreated to the area around the acropolis. The ramparts were maintained to a certain extent, thanks to materials plundered from the monuments of the lower city, and the large unused cisterns of the upper city were occupied by small houses and the workshops of artisans. Around the middle of the 7th century, a further reduction of the inhabited area of the city was followed by an increase in the fortification of the town, with the construction of a new rampart with pentagonal towers cutting through the middle of the remaining monuments. The acropolis, the Roman baths, and especially the episcopal basilica were crossed by this wall. The city was probably abandoned in the eighth century, as the last bishop was attested at the Second Council of Nicaea in 787. Its inhabitants probably moved to the neighbouring site of ancient Eion, port of Amphipolis, which had been rebuilt and refortified in theByzantine period
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
under the name “ Chrysopolis”. This small port continued to enjoy some prosperity, before being abandoned during the Ottoman period. The last recorded sign of activity in the region of Amphipolis was the construction of a fortified tower to the north in 1367 by the ''megas primikerios The Latin term ''primicerius'', hellenized as ''primikērios'' ( el, πριμικήριος), was a title applied in the later Roman Empire and the Byzantine Empire to the heads of administrative departments, and also used by the Church to denote th ...
'' John and the '' stratopedarches'' Alexios to protect the land that they had given to the monastery of Pantokrator on Mount Athos.

Archaeology
The site was discovered and described by many travellers and archaeologists during the 19th century, including E. Cousinéry (1831) (engraver), Leon Heuzey (1861), and P. Perdrizet (1894–1899). However, excavations did not truly begin until after the Second World War. The Greek Archaeological Society under D. Lazaridis excavated in 1972 and 1985, uncovering a necropolis, the city wall (see photograph), the basilicas, and the acropolis. Further excavations have since uncovered the river bridge, the gymnasium, Greek and Roman villas and numerous tombs etc. Parts of the lion monument and tombs were discovered during World War I by Bulgarian and British troops whilst digging trenches in the area. In 1934, M. Feyel, of theÉcole française d'Athènes
The French School at Athens (french: École française d’Athènes, EfA; el, Γαλλική Σχολή Αθηνών ''Gallikí Scholí Athinón'') is one of the seventeen foreign archaeological institutes operating in Athens, Greece.
Histor ...
(EfA), led an epigraphical mission to the site and uncovered further remains of the lion monument (a reconstruction was given in the ''Bulletin de Correspondance Hellénique'', a publication of the EfA which is available on line).
The silver ossuary containing the cremated remains of Brasidas
Brasidas ( el, Βρασίδας, died 422 BC) was the most distinguished Spartan officer during the first decade of the Peloponnesian War who fought in battle of Amphipolis and Pylos. He died during the Second Battle of Amphipolis while winning ...
and a gold crown (see image) was found in a tomb in pride of place under the Agora.
The Tomb of Amphipolis
 In 2012 Greek archaeologists unearthed a large tomb within the Kasta Hill, the biggest burial mound in Greece, northeast of Amphipolis. The large size and quality of the tumulus indicates the prominence of the burials made there, and its dating and the connections of the city with Alexander the Great suggest important occupants. The perimeter wall of the tumulus is long, and is made of limestone covered with marble.
The tomb comprises three chambers separated by walls. There are two
In 2012 Greek archaeologists unearthed a large tomb within the Kasta Hill, the biggest burial mound in Greece, northeast of Amphipolis. The large size and quality of the tumulus indicates the prominence of the burials made there, and its dating and the connections of the city with Alexander the Great suggest important occupants. The perimeter wall of the tumulus is long, and is made of limestone covered with marble.
The tomb comprises three chambers separated by walls. There are two sphinxes
A sphinx ( , grc, σφίγξ , Boeotian: , plural sphinxes or sphinges) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of a falcon.
In Greek tradition, the sphinx has the head of a woman, the haunches of ...
just outside the entrance to the tomb. Two of the columns supporting the roof in the first section are in the form of Caryatids, in the 4th century BC style. The excavation revealed a pebble mosaic directly behind the Caryatids and in front of the Macedonian marble door leading to the "third" chamber. The mosaic shows the allegory of the abduction of Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld aft ...
by Hades, but the persons depicted are Philip and Olympias of Macedon. Hades' chariot is drawn by two white horses and led to the underworld by Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orat ...
. The mosaic verifies the Macedonian character of the tomb. As the head of one of the sphinxes was found inside the tomb behind the broken door, it is clear that there were intruders, probably in antiquity.
Fragments of bones from 5 individuals were found in the cist tomb, the most complete of which is a 60+ year old woman in the deepest layer. Dr. Katerina Peristeri, the archaeologist heading the excavation of the tomb, dates the tomb to the late 4th century BC, the period after the death of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
(323 BC). One theory is that the tomb was built for the mother of Alexander the Great, Olympias.
Restoration of the tomb is due for completion in 2023 in the course of which building materials of the grave site which were later used by the Romans elsewhere will be rebuilt in their original location.

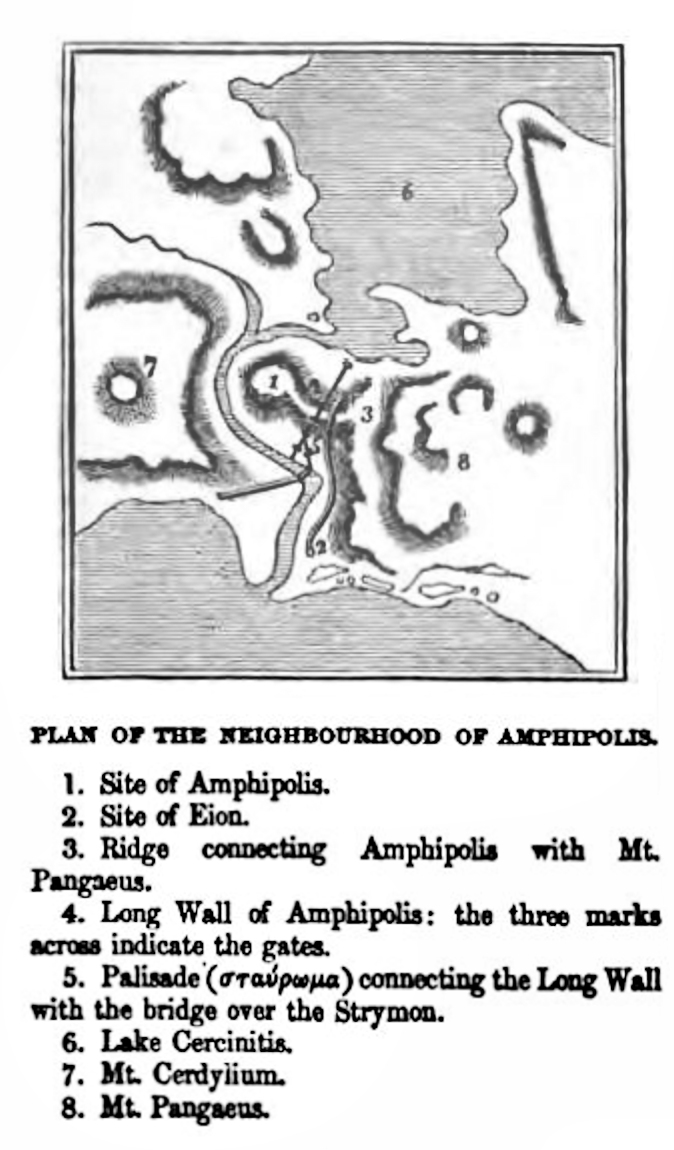
The city walls
 The original 7.5 km long walls are generally visible, particularly the northern section which is preserved to a height of 7.5m. 5 preserved gates can be seen and notably the gate in front of the wooden bridge.
In early Christian times another, inner, wall was built around the acropolis.
The original 7.5 km long walls are generally visible, particularly the northern section which is preserved to a height of 7.5m. 5 preserved gates can be seen and notably the gate in front of the wooden bridge.
In early Christian times another, inner, wall was built around the acropolis.
The ancient wooden bridge of Amphipolis
 The ancient bridge that crossed the river Strymon was mentioned by Thucydides, was strategic as it controlled access between Macedonia and the Chalkidike in the west to Thrace in the east, and was important for the economy and trade. It was therefore incorporated into the city walls.
It was discovered in 1977 and is a unique find for Greek antiquity. The hundreds of wooden piles have been carbon-dated and show the vast life of the bridge with some piles dating from 760 BC, and others used till about 1800 AD.
The ancient bridge that crossed the river Strymon was mentioned by Thucydides, was strategic as it controlled access between Macedonia and the Chalkidike in the west to Thrace in the east, and was important for the economy and trade. It was therefore incorporated into the city walls.
It was discovered in 1977 and is a unique find for Greek antiquity. The hundreds of wooden piles have been carbon-dated and show the vast life of the bridge with some piles dating from 760 BC, and others used till about 1800 AD.
The Gymnasium
 This was a major public building for the military and gymnastic training of youth as well as for their artistic and intellectual education. It was built in the 4th c. BC and includes a
This was a major public building for the military and gymnastic training of youth as well as for their artistic and intellectual education. It was built in the 4th c. BC and includes a palaestra
A palaestra ( or ;
also (chiefly British) palestra; grc-gre, παλαίστρα) was any site of an ancient Greek wrestling school. Events requiring little space, such as boxing and wrestling, took place there. Palaestrae functioned both in ...
, the rectangular court surrounded by colonnades with adjoining rooms for many athletic functions. The covered stoa or xystos for indoor training in inclement weather is a long portico 75m long and 7m wide to allow 6 runners to compete simultaneously. There was also a parallel outdoor track, ''paradromida'', for training in good weather and a system of cisterns for water supply.
During the Macedonian era it became a major institution.
The stone stela bearing the rules of the gymnasium was found in the north wing, detailing the duties and powers of the master and the education of the athletes.
After it was destroyed in the 1st c. BC in the Thracian rebellion against Roman rule, it was rebuilt in Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
's time in the 1st c. AD along with the rest of the city.
Amphipolitans
* Demetrius of Amphipolis, student of Plato *Zoilus
Zoilus ( el, Ζωΐλος ''Zoilos''; c. 400320 BC) was a Greek grammarian, Cynic philosopher, and literary critic from Amphipolis in Eastern Macedonia, then known as Thrace. He took the name Homeromastix (Ὁμηρομάστιξ "Homer whippe ...
(400–320 BC), grammarian, cynic philosopher
* Pamphilus (painter), head of Sicyonian school and teacher of Apelles
* Aetion, sculptor
* Philippus of Amphipolis, historian
* Nearchus, admiral
*Erigyius Erigyius (in Greek Ἐριγυιoς; died 328 BC), a Mytilenaean, son of Larichus, was an officer in Alexander the Great's army. He had been driven into banishment by Philip II, king of Macedon, because of his faithful attachment to Alexander, and ...
, general
*Damasias of Amphipolis
The following is a list of winners of the Stadion race at the Olympic Games from 776 BC to 225 AD. It is based on the list given by Eusebius of Caesarea using a compilation by Sextus Julius Africanus. The Stadion race was the first and most importa ...
320 BC Stadion Olympics
* Hermagoras of Amphipolis (), stoic philosopher, follower of Persaeus
* Apollodorus of Amphipolis, appointed joint military governor of Babylon and the other satrapies as far as Cilicia by Alexander the GreatDiodorus Siculus Library of History Book XVII
* Xena - In the television series Xena Warrior Princess, Amphipolis is the main character's home village.
Municipality
The municipality Amfipoli was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following four former municipalities, that became municipal units: *Amfipoli *Kormista
Kormista ( el, Κορμίστα) is a village and a former municipality in the Serres regional unit, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Amfipoli
Amphipolis ( ell, Αμφίπολη, translit=Amfipoli; ...
* Proti
*Rodolivos
Rodolivos ( el, Ροδoλίβος) is a town and a former municipality in the Serres regional unit, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Amfipoli, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal ...
The municipality has an area of 411.773 km2, the municipal unit 152.088 km2.
See also
* Archaeological Museum of AmphipolisReferences
External links
Official site about Amphipolis
Demographic Information from Greek Travel Pages
The tomb of Amphipolis
{{Second Journey of Paul of Tarsus 437 BC 5th-century BC establishments 8th-century disestablishments in the Byzantine Empire Ancient Amphipolis Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Greece Archaeological sites in Macedonia (Greece) Athenian colonies Former populated places in Greece Municipalities of Central Macedonia Populated places established in the 5th century BC Populated places disestablished in the 8th century Populated places in ancient Macedonia Populated places in ancient Thrace Populated places in Serres (regional unit) Roman sites in Greece Populated places of the Byzantine Empire