Amiga 4000 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The

Commodore
Commodore may refer to:
Ranks
* Commodore (rank), a naval rank
** Commodore (Royal Navy), in the United Kingdom
** Commodore (United States)
** Commodore (Canada)
** Commodore (Finland)
** Commodore (Germany) or ''Kommodore''
* Air commodore ...
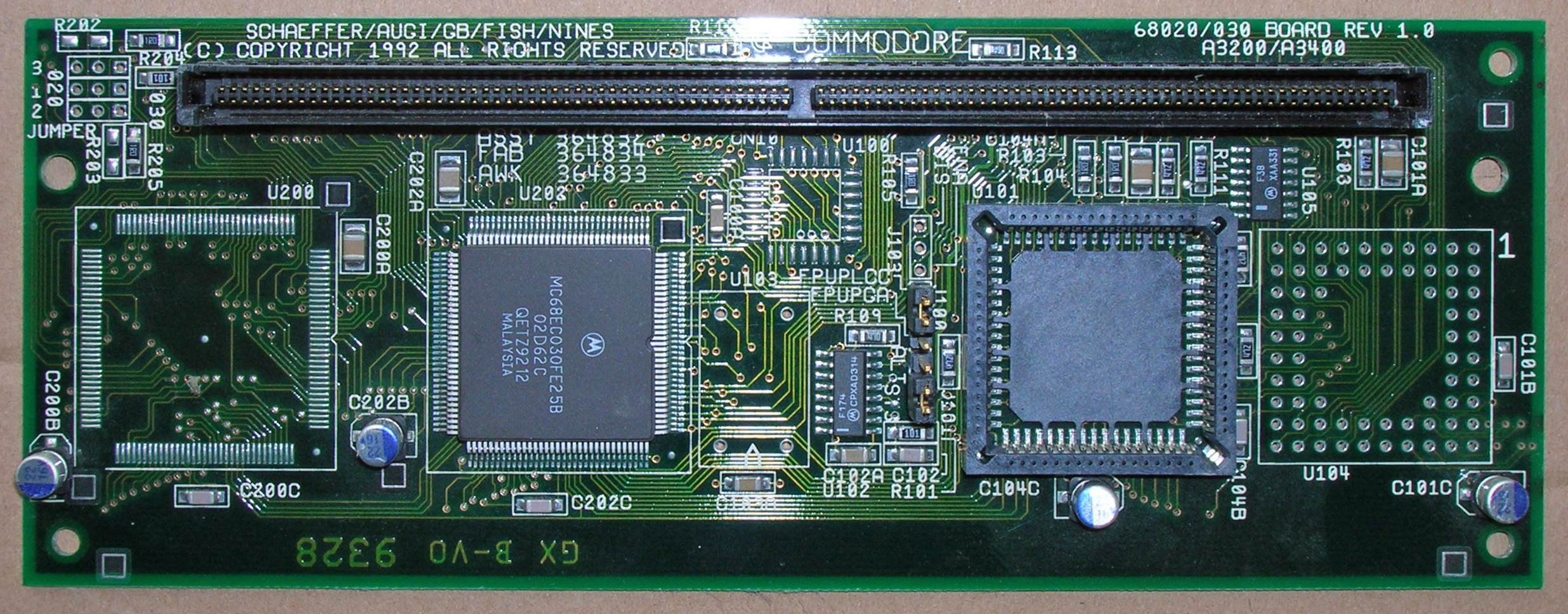
Amiga 4000, or A4000, is the successor of the A2000 and A3000 computers. There are two models: the A4000/040 released in October 1992 with a Motorola 68040
The Motorola 68040 ("''sixty-eight-oh-forty''") is a 32-bit microprocessor in the Motorola 68000 series, released in 1990. It is the successor to the 68030 and is followed by the 68060, skipping the 68050. In keeping with general Motorola na ...
CPU, and the A4000/030 released in April 1993 with a Motorola 68EC030.
The Amiga 4000 system design was generally similar to that of the A3000, but introduced the Advanced Graphics Architecture
Amiga Advanced Graphics Architecture (AGA) is the third-generation Amiga graphic chipset, first used in the Amiga 4000 in 1992. Before release AGA was codenamed Pandora by Commodore International.
AGA was originally called AA for Advanced Archit ...
(AGA) chipset with enhanced graphics. The SCSI system from previous Amigas was replaced by the lower-cost Parallel ATA.
The original A4000 is housed in a beige horizontal desktop box with a separate keyboard. Later, Commodore released an expanded tower
A tower is a tall structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting structures.
Towers are specifi ...
version called the A4000T.
Technical information
Processor and RAM
The stock A4000 shipped with either a Motorola 68EC030 or 68040 CPU, 2 MB of Amiga Chip RAM and up to 16 MB of additional RAM in 32-bitSIMM
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module containing random-access memory used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It differs from a dual in-line memory module (DIMM), the most predominant form of memory ...
s. There is a non-functional jumper that was intended to expand the "chip RAM" to 8MB. Later, third-party developers created various CPU expansion boards featuring higher-rated 68040, 68060 and PowerPC CPUs. Such hardware also typically offers faster and higher-capacity RAM (128 MB or greater).
A4000-CR version
Unlike previous Amiga models, early A4000 machines have the CPU mounted in an expansion board; the motherboard does not have an integrated CPU. Later revisions of the A4000 have the CPU and 2 MB RAM surface-mounted on the motherboard in an effort to reduce costs. These machines are known as the A4000-CR (cost-reduced) and the surface-mounted CPU is a 68EC030. The cost-reduced models also make use of a non-rechargeable lithium battery for real-time clock battery backup rather than a rechargeable NiCad battery. The NiCad backup battery is one of the most common causes of problems in an aging device that uses one because it has a tendency to eventually leak. The released fluids are somewhat corrosive and can eventually damage the circuitry.Graphics and sound
The A4000 is the first Amiga model to have shipped with Commodore's third-generation Amiga chipset, the 32-bitAdvanced Graphics Architecture
Amiga Advanced Graphics Architecture (AGA) is the third-generation Amiga graphic chipset, first used in the Amiga 4000 in 1992. Before release AGA was codenamed Pandora by Commodore International.
AGA was originally called AA for Advanced Archit ...
(AGA). As the name implies, AGA introduces improved graphical abilities, specifically, a palette expanded from 12-bit color depth (4,096 colors) to 24-bit (16.8 million colors) and new 64, 128, 256 and 262,144 ( HAM-8) color modes. Unlike earlier Amiga chipsets, all color modes are available at all display resolutions. AGA also improves sprite capacity and graphics performance. The on-board sound hardware remains identical to that of the original Amiga chipset (the Paula sound chip), namely, four DMA-driven 8-bit PCM channels, with two channels for the left speaker and two for the right.
Peripherals and expansion
The A4000 has a number of Amiga-specific connectors, including two DE-9 ports for joysticks, mice, andlight pen
A light pen is a computer input device in the form of a light-sensitive wand used in conjunction with a computer's cathode-ray tube (CRT) display.
It allows the user to point to displayed objects or draw on the screen in a similar way to a tou ...
s, a standard 25-pin RS-232
In telecommunications, RS-232 or Recommended Standard 232 is a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a ''DTE'' (''data terminal equipment'') such ...
serial port
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication interface through which information transfers in or out sequentially one bit at a time. This is in contrast to a parallel port, which communicates multiple bits simultaneously in parallel. ...
and a 25-pin Centronics
Centronics Data Computer Corporation was an American manufacturer of computer printers, now remembered primarily for the parallel interface that bears its name, the Centronics connector.
History
Foundations
Centronics began as a division ...
parallel port. As a result, at launch the A4000 was compatible with many existing Amiga peripherals, such as MIDI
MIDI (; Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a technical standard that describes a communications protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and ...
devices, serial modem
A modulator-demodulator or modem is a computer hardware device that converts data from a digital format into a format suitable for an analog transmission medium such as telephone or radio. A modem transmits data by Modulation#Digital modulati ...
s and sound samplers.
Like the just-earlier Amiga model, the 3000, the A4000 has four internal 32-bit Zorro III
Zorro (Spanish for 'fox') is a fictional character created in 1919 by American pulp writer Johnston McCulley, appearing in works set in the Pueblo of Los Angeles in Alta California. He is typically portrayed as a dashing masked vigilante who ...
expansion slots. This expansion bus allows the use of devices which comply with the AutoConfig standard, such as graphic cards, audio cards, network cards, SCSI controllers, and later even USB controllers. One of the most notable hardware items of the era is the NewTek
NewTek, Inc. is a San Antonio, Texas-based hardware and software company that produces live and post-production video tools and visual imaging software for personal computers. The company was founded in 1985 in Topeka, Kansas, United States, by T ...
Video Toaster system which became popular in the 1990s for amateur and commercial desktop video
Desktop video refers to a phenomenon lasting from the mid-1980s to the early 1990s when the graphics capabilities of personal computers such as Commodore's Amiga, the Apple Macintosh II and specially-upgraded IBM PC compatibles had advanced to th ...
production of standard-definition
Standard-definition television (SDTV, SD, often shortened to standard definition) is a television system which uses a resolution that is not considered to be either high or enhanced definition. "Standard" refers to it being the prevailing sp ...
broadcast quality Broadcast quality is a term stemming from quad videotape to denote the quality achieved by professional video cameras and time base correctors (TBC) used for broadcast television, usually in standard definition. As the standards for commercial tele ...
video, consisting of tools for video switching, chroma key
Chroma key compositing, or chroma keying, is a visual-effects and post-production technique for compositing (layering) two images or video streams together based on colour hues ( chroma range). The technique has been used in many fields to ...
ing, character generation, animation, and image manipulation
Image editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they are digital photographs, traditional photo-chemical photographs, or illustrations. Traditional analog image editing is known as photo retouching, using tools such as ...
.
The three ISA slots can be activated by use of a bridgeboard, which connects the Zorro and ISA buses. Such bridgeboards typically feature on-board IBM-PC-compatible hardware, including Intel 80286
The Intel 80286 (also marketed as the iAPX 286 and often called Intel 286) is a 16-bit microprocessor that was introduced on February 1, 1982. It was the first 8086-based CPU with separate, non- multiplexed address and data buses and also the ...
, 80386, or 80486 microprocessors allowing emulation of an entire IBM-PC system in hardware. Compatible ISA cards may then be installed into the two remaining ISA slots.
Later, in an effort to offer modern expansion options third-party developers created replacement expansion boards for the A4000 which provide PCI slots allowing use of higher performance and widely available PCI hardware, such as graphic, sound, and network cards.
Operating system
The A4000 shipped with AmigaOS 3.0, consisting of Workbench 3.0 and Kickstart 3.0, which together provide a single-user multi-tasking operating system and support for the built-in hardware. Following release of AmigaOS 3.1 it became possible to upgrade the A4000 by installing compatible Kickstart 3.1 ROM chips. The later AmigaOS 3.5 and 3.9 releases were software-only updates requiring Kickstart 3.1.AmigaOS 4
AmigaOS 4 (abbreviated as OS4 or AOS4) is a line of Amiga operating systems which runs on PowerPC microprocessors. It is mainly based on AmigaOS 3.1 source code developed by Commodore, and partially on version 3.9 developed by Haage & Partne ...
, a PowerPC-native release of the operating system, can be used with the A4000 provided a CyberStorm PPC board is installed. Likewise, MorphOS
MorphOS is an AmigaOS-like computer operating system (OS). It is a mixed proprietary and open source OS produced for the Pegasos PowerPC (PPC) processor based computer, PowerUP accelerator equipped Amiga computers, and a series of Freescale dev ...
, an alternative Amiga-compatible operating system, can be used with this hardware.
Variants of platform-independent operating systems, such as Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, w ...
and BSD, can also be used with the A4000.


Specifications
See also
* Amiga models and variantsReferences
{{commons category, Amiga 4000 Amiga Computer-related introductions in 1992