Amazon jungle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. or Amazonia is a moist broadleaf
 It is believed that the Amazon rainforest is over 55 million years old.
In the Amazonas, there has been fighting and wars between the neighboring tribes of the Jivaro. Several tribes of the Jivaroan group, including the
It is believed that the Amazon rainforest is over 55 million years old.
In the Amazonas, there has been fighting and wars between the neighboring tribes of the Jivaro. Several tribes of the Jivaroan group, including the

 The rainforest likely formed during the
The rainforest likely formed during the  During the mid-Eocene, it is believed that the drainage basin of the Amazon was split along the middle of the continent by the Púrus Arch. Water on the eastern side flowed toward the Atlantic, while to the west water flowed toward the Pacific across the Amazonas Basin. As the
During the mid-Eocene, it is believed that the drainage basin of the Amazon was split along the middle of the continent by the Púrus Arch. Water on the eastern side flowed toward the Atlantic, while to the west water flowed toward the Pacific across the Amazonas Basin. As the
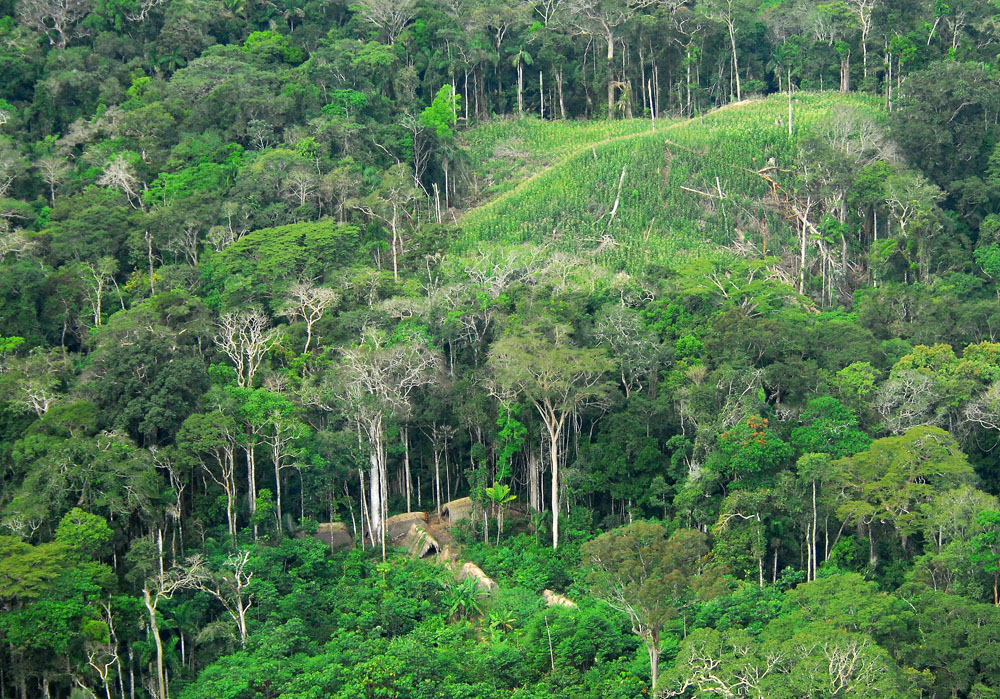

 Based on archaeological evidence from an excavation at Caverna da Pedra Pintada, human inhabitants first settled in the Amazon region at least 11,200 years ago. Subsequent development led to late-prehistoric settlements along the periphery of the forest by AD 1250, which induced alterations in the
Based on archaeological evidence from an excavation at Caverna da Pedra Pintada, human inhabitants first settled in the Amazon region at least 11,200 years ago. Subsequent development led to late-prehistoric settlements along the periphery of the forest by AD 1250, which induced alterations in the
 Wet tropical forests are the most species-rich
Wet tropical forests are the most species-rich
File:Hoatzins in Brazil.jpg,
File:DeforestationinBrazil2.jpg, NASA satellite observation of deforestation in the Mato Grosso state of Brazil. The transformation from forest to farm is evident by the paler square shaped areas under development.
File:Fires and Deforestation on the Amazon Frontier, Rondonia, Brazil - August 12, 2007.jpg, Fires and deforestation in the state of Rondônia
File:Fires and Deforestation on the Amazon Frontier, Rondonia, Brazil - September 30, 2007.jpg, One consequence of forest clearing in the Amazon: thick smoke that hangs over the forest
File:Deforestation of Rainforest.jpg, Impact of deforestation on natural habitat of trees
The increased area of fire-impacted forest coincided with a relaxation of environmental regulations from the Brazilian government. Notably, before those regulations were put in place in 2008 the fire-impacted area was also larger compared to the regulation period of 2009–2018. As these fire continue to move closer to the heart of the Amazon Basin, their impact on biodiversity will only increase in scale, as the cumulative fire-impacted area is correlated with the number of species impacted.
 Environmentalists are concerned about
Environmentalists are concerned about
"World may be warming up even faster"
. ''The Guardian''. However, simulations of Amazon basin climate change across many different models are not consistent in their estimation of any rainfall response, ranging from weak increases to strong decreases. Houghton, J.T. ''et al.'' 2001
"Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis"
. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. The result indicates that the rainforest could be threatened through the 21st century by climate change in addition to deforestation. In 1989, environmentalist C.M. Peters and two colleagues stated there is economic as well as biological incentive to protecting the rainforest. One hectare in the As indigenous territories continue to be destroyed by deforestation and
As indigenous territories continue to be destroyed by deforestation and
File:Greenhouse Gas by Sector.png, Anthropogenic emission of greenhouse gases broken down by sector for the year 2000.
File:September Smoke Over the Amazon from 2005-2008.png, Aerosols over the Amazon each September for four burning seasons (2005 through 2008). The aerosol scale (yellow to dark reddish-brown) indicates the relative amount of particles that absorb sunlight.
File:Roots by cesarpb.jpg, Aerial roots of red mangrove on an Amazonian river.
File:Climate change disturbances of rainforests infographic.jpg, Climate change disturbances of rainforests.
A 2009 study found that a 4 °C rise (above pre-industrial levels) in global temperatures by 2100 would kill 85% of the Amazon rainforest while a temperature rise of 3 °C would kill some 75% of the Amazon.
 A new study by an international team of environmental scientists in the Brazilian Amazon shows that protection of freshwater biodiversity can be increased by up to 600% through integrated freshwater-terrestrial planning
.
A new study by an international team of environmental scientists in the Brazilian Amazon shows that protection of freshwater biodiversity can be increased by up to 600% through integrated freshwater-terrestrial planning
.
 Available unde
Available unde
CC BY 4.0
. In 2022 the supreme court of Ecuador decided that "“under no circumstances can a project be carried out that generates excessive sacrifices to the collective rights of communities and nature.” It also required the government to respect the opinion of
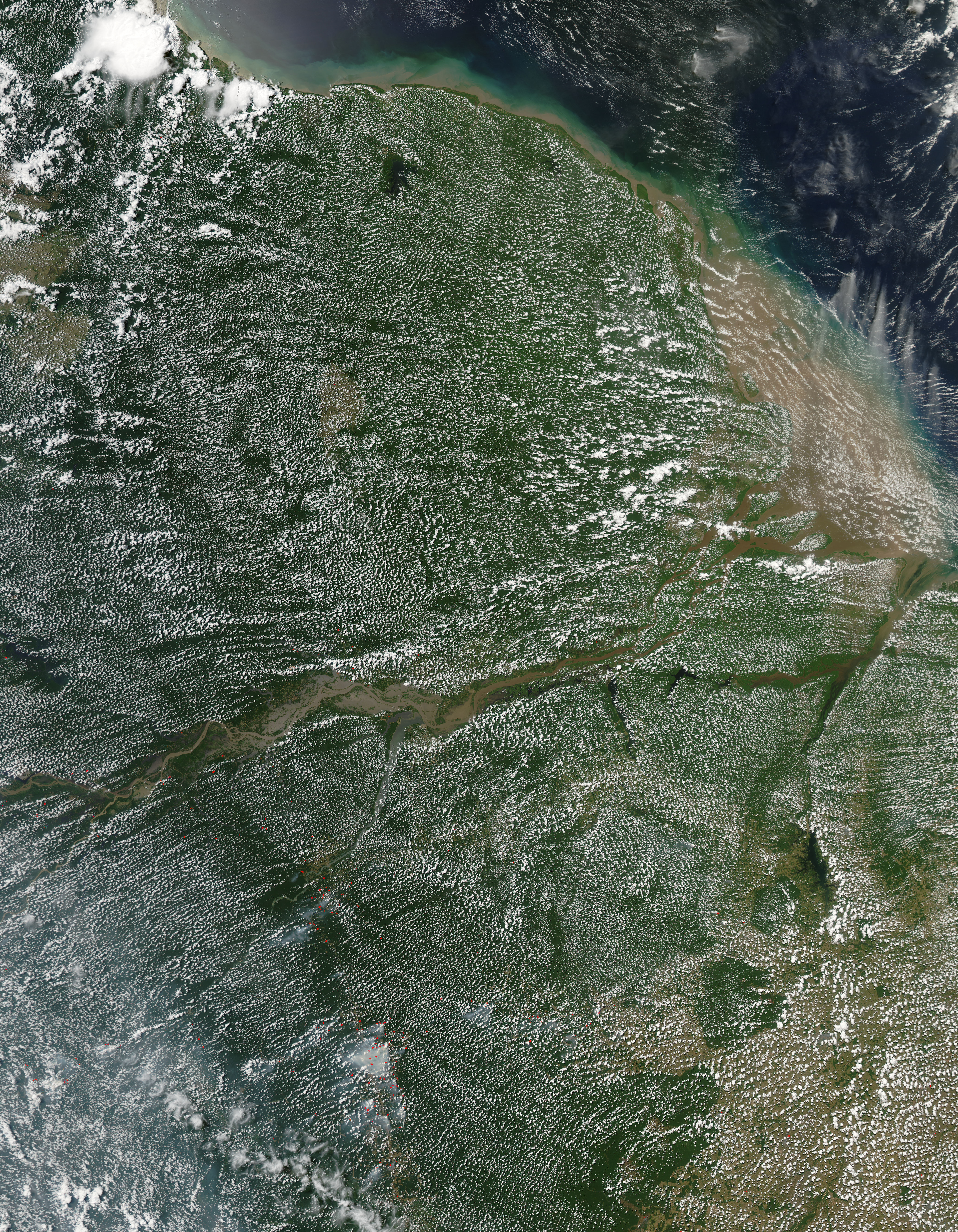 The use of remotely sensed data is dramatically improving conservationists' knowledge of the Amazon basin. Given the objectivity and lowered costs of satellite-based land cover and -change analysis, it appears likely that remote sensing technology will be an integral part of assessing the extents, locations and damage of deforestation in the basin. Furthermore, remote sensing is the best and perhaps only possible way to study the Amazon on a large scale.
The use of remote sensing for the conservation of the Amazon is also being used by the indigenous tribes of the basin to protect their tribal lands from commercial interests. Using handheld
The use of remotely sensed data is dramatically improving conservationists' knowledge of the Amazon basin. Given the objectivity and lowered costs of satellite-based land cover and -change analysis, it appears likely that remote sensing technology will be an integral part of assessing the extents, locations and damage of deforestation in the basin. Furthermore, remote sensing is the best and perhaps only possible way to study the Amazon on a large scale.
The use of remote sensing for the conservation of the Amazon is also being used by the indigenous tribes of the basin to protect their tribal lands from commercial interests. Using handheld
Journey into Amazonia
The Amazon: The World's Largest Rainforest
WWF in the Amazon rainforest
Amazonia.org.br
Good daily updated Amazon information database on the web, held by Friends of The Earth – Brazilian Amazon.
amazonia.org
Sustainable Development in the Extractive Reserve of the Baixo Rio Branco – Rio Jauaperi – Brazilian Amazon.
Original news updates on the Amazon.
Amazon-Rainforest.org
Information about the Amazon rainforest, its people, places of interest, and how everyone can help.
Conference: Climate change and the fate of the Amazon
Podcasts of talks given at
in the Amazon
{{Authority control Rainforest Amazon biome Rainforest Ecoregions of South America Natural history of Peru Natural history of Brazil Natural history of Ecuador Neotropical ecoregions Rainforests Regions of South America Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests Forestry in South America
tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equa ...
in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin encompasses , of which are covered by the rainforest. This region includes territory belonging to nine nations and 3,344 formally acknowledged indigenous territories.
The majority of the forest is contained within Brazil, with 60% of the rainforest, followed by Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
with 13%, Colombia with 10%, and with minor amounts in Bolivia, Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
, French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
, Guyana, Suriname, and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
. Four nations have " Amazonas" as the name of one of their first-level administrative regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
, and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
uses the name "Guiana Amazonian Park
Guiana Amazonian Park (french: Parc amazonien de Guyane) is the largest national park of France, aiming at protecting part of the Amazonian forest located in French Guiana which covers 41% of the region. It is the largest park in France as wel ...
" for its rainforest protected area. The Amazon represents over half of the planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
's remaining rainforests, and comprises the largest and most biodiverse
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity'') ...
tract of tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
rainforest in the world, with an estimated 390 billion individual trees
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are u ...
divided into 16,000 species.
More than 30 million people of 350 different ethnic groups live in the Amazon, which are subdivided into 9 different national political systems and 3,344 formally acknowledged indigenous territories. Indigenous peoples make up 9% of the total population with 60 of the groups remaining largely isolated.
Etymology
The name ''Amazon'' is said to arise from a warFrancisco de Orellana
Francisco de Orellana Bejarano Pizarro y Torres de Altamirano (; 1511 – November 1546) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador. In one of the most improbably successful voyages in known history, Orellana managed to sail the length of the Amaz ...
fought with the Tapuyas
The Pira-tapuya, or variations like Pira-Tapuia, Piratapuyo, etc., or Tapuya for short, are an indigenous people of the Amazon regions. They live along the Vaupés River in Colombia and in the state of Amazonas, Brazil.
Languages
The Pira-tapu ...
and other tribes. The women of the tribe fought alongside the men, as was their custom. Orellana derived the name ''Amazonas'' from the Amazons of Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities ...
, described by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
and Diodorus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
.
History
 It is believed that the Amazon rainforest is over 55 million years old.
In the Amazonas, there has been fighting and wars between the neighboring tribes of the Jivaro. Several tribes of the Jivaroan group, including the
It is believed that the Amazon rainforest is over 55 million years old.
In the Amazonas, there has been fighting and wars between the neighboring tribes of the Jivaro. Several tribes of the Jivaroan group, including the Shuar
The Shuar are an Indigenous people of Ecuador and Peru. They are members of the Jivaroan peoples, who are Amazonian tribes living at the headwaters of the Marañón River.
Name
Shuar, in the Shuar language, means "people". The people who spea ...
, practised headhunting
Headhunting is the practice of hunting a human and collecting the severed head after killing the victim, although sometimes more portable body parts (such as ear, nose or scalp) are taken instead as trophies. Headhunting was practiced in h ...
for trophies and headshrinking. The accounts of missionaries to the area in the borderlands between Brazil and Venezuela have recounted constant infighting in the Yanomami tribes. More than a third of the Yanomamo males, on average, died from warfare.
During the Amazon rubber boom it is estimated that diseases brought by immigrants, such as typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure. ...
and malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
, killed 40,000 native Amazonians.
The Matsés made their first permanent contact with the outside world in 1969. Before that date, they were effectively at-war with the Peruvian government.
Geography
Location
Nine countries share the Amazon basin—most of the rainforest, 58.4%, is contained within the borders of Brazil. The other eight countries include Peru with 12.8%, Bolivia with 7.7%, Colombia with 7.1%, Venezuela with 6.1%, Guyana with 3.1%, Suriname with 2.5%, French Guiana with 1.4%, and Ecuador with 1%.Natural

 The rainforest likely formed during the
The rainforest likely formed during the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
era (from 56 million years to 33.9 million years ago). It appeared following a global reduction of tropical temperatures when the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
had widened sufficiently to provide a warm, moist climate to the Amazon basin. The rainforest has been in existence for at least 55 million years, and most of the region remained free of savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
-type biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
s at least until the current ice age
The Late Cenozoic Ice Age,National Academy of Sciences - The National Academies Press - Continental Glaciation through Geologic Times https://www.nap.edu/read/11798/chapter/8#80 or Antarctic Glaciation began 33.9 million years ago at the Eocen ...
when the climate was drier and savanna more widespread.
Following the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
, the extinction of the dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s and the wetter climate may have allowed the tropical rainforest to spread out across the continent. From 66 to 34 Mya, the rainforest extended as far south as 45°. Climate fluctuations during the last 34 million years have allowed savanna regions to expand into the tropics. During the Oligocene, for example, the rainforest spanned a relatively narrow band. It expanded again during the Middle Miocene, then retracted to a mostly inland formation at the last glacial maximum. However, the rainforest still managed to thrive during these glacial periods
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
, allowing for the survival and evolution of a broad diversity of species.
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
Mountains rose, however, a large basin was created that enclosed a lake; now known as the Solimões Basin. Within the last 5–10 million years, this accumulating water broke through the Púrus Arch, joining the easterly flow toward the Atlantic.
There is evidence that there have been significant changes in the Amazon rainforest vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characte ...
over the last 21,000 years through the last glacial maximum (LGM) and subsequent deglaciation. Analyses of sediment deposits from Amazon basin paleolakes and the Amazon Fan indicate that rainfall in the basin during the LGM was lower than for the present, and this was almost certainly associated with reduced moist tropical vegetation cover in the basin. In present day, the Amazon receives approximately 9 feet of rainfall annually. There is a debate, however, over how extensive this reduction was. Some scientists argue that the rainforest was reduced to small, isolated refugia separated by open forest and grassland; other scientists argue that the rainforest remained largely intact but extended less far to the north, south, and east than is seen today. This debate has proved difficult to resolve because the practical limitations of working in the rainforest mean that data sampling is biased away from the center of the Amazon basin, and both explanations are reasonably well supported by the available data.
Sahara Desert dust windblown to the Amazon
More than 56% of the dust fertilizing the Amazon rainforest comes from theBodélé depression
The Bodélé Depression (), located at the southern edge of the Sahara Desert in north central Africa, is the lowest point in Chad. It is 500 km long, 150 km wide and around 160 m deep. Its bottom lies about 155 meters above sea leve ...
in Northern Chad in the Sahara desert. The dust contains phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
, important for plant growth. The yearly Sahara dust replaces the equivalent amount of phosphorus washed away yearly in Amazon soil from rains and floods.
NASA's CALIPSO satellite has measured the amount of dust transported by wind from the Sahara to the Amazon: an average of 182 million tons of dust are windblown out of the Sahara each year, at 15 degrees west longitude, across over the Atlantic Ocean (some dust falls into the Atlantic), then at 35 degrees West longitude at the eastern coast of South America, 27.7 million tons (15%) of dust fall over the Amazon basin (22 million tons of it consisting of phosphorus), 132 million tons of dust remain in the air, 43 million tons of dust are windblown and falls on the Caribbean Sea, past 75 degrees west longitude.
CALIPSO uses a laser range finder to scan the Earth's atmosphere for the vertical distribution of dust and other aerosols. CALIPSO regularly tracks the Sahara-Amazon dust plume. CALIPSO has measured variations in the dust amounts transported – an 86 percent drop between the highest amount of dust transported in 2007 and the lowest in 2011.
A possibility causing the variation is the Sahel, a strip of semi-arid land on the southern border of the Sahara. When rain amounts in the Sahel are higher, the volume of dust is lower. The higher rainfall could make more vegetation grow in the Sahel, leaving less sand exposed to winds to blow away.
Amazon phosphorus also comes as smoke due to biomass burning in Africa.
Human activity


 Based on archaeological evidence from an excavation at Caverna da Pedra Pintada, human inhabitants first settled in the Amazon region at least 11,200 years ago. Subsequent development led to late-prehistoric settlements along the periphery of the forest by AD 1250, which induced alterations in the
Based on archaeological evidence from an excavation at Caverna da Pedra Pintada, human inhabitants first settled in the Amazon region at least 11,200 years ago. Subsequent development led to late-prehistoric settlements along the periphery of the forest by AD 1250, which induced alterations in the forest cover
Forest cover is the amount of forest that covers a particular area of land. It may be measured as relative (in percent) or absolute (in square kilometres/square miles). Around a third of the world's surface is covered with forest, with closed-canop ...
.
For a long time, it was thought that the Amazon rainforest was never more than sparsely populated, as it was impossible to sustain a large population through agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
given the poor soil. Archeologist Betty Meggers was a prominent proponent of this idea, as described in her book ''Amazonia: Man and Culture in a Counterfeit Paradise''. She claimed that a population density of is the maximum that can be sustained in the rainforest through hunting, with agriculture needed to host a larger population. However, recent anthropological
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of behav ...
findings have suggested that the region was actually densely populated. Some 5 million people may have lived in the Amazon region in AD 1500, divided between dense coastal settlements, such as that at Marajó
Marajó () is a large coastal island in the state of Pará, Brazil. It is the main and largest of the islands in the Marajó Archipelago. Marajó Island is separated from the mainland by Marajó Bay, Pará River, smaller rivers (especially ...
, and inland dwellers. By 1900, the population had fallen to 1 million and by the early 1980s it was less than 200,000.
The first European to travel the length of the Amazon River was Francisco de Orellana
Francisco de Orellana Bejarano Pizarro y Torres de Altamirano (; 1511 – November 1546) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador. In one of the most improbably successful voyages in known history, Orellana managed to sail the length of the Amaz ...
in 1542. The BBC's '' Unnatural Histories'' presents evidence that Orellana, rather than exaggerating his claims as previously thought, was correct in his observations that a complex civilization was flourishing along the Amazon in the 1540s. It is believed that civilization was later devastated by the spread of diseases from Europe, such as smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
. This civilization was investigated by the British explorer Percy Fawcett in the early twentieth century. The results of his expeditions were inconclusive and he disappeared mysteriously on his last trip. His name for this lost civilization was the City of Z.
Since the 1970s, numerous geoglyph
A geoglyph is a large design or motif (generally longer than 4 metres) produced on the ground by durable elements of the landscape, such as stones, stone fragments, gravel, or earth. A positive geoglyph is formed by the arrangement and alignmen ...
s have been discovered on deforested land dating between AD 1–1250, furthering claims about Pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
civilizations. Ondemar Dias is accredited with first discovering the geoglyphs in 1977, and Alceu Ranzi is credited with furthering their discovery after flying over Acre. The BBC's ''Unnatural Histories'' presented evidence that the Amazon rainforest, rather than being a pristine wilderness, has been shaped by man for at least 11,000 years through practices such as forest gardening
Forest gardening is a low-maintenance, sustainable, plant-based food production and agroforestry system based on woodland ecosystems, incorporating fruit and nut trees, shrubs, herbs, vines and perennial vegetables which have yields directly us ...
and ''terra preta
''Terra preta'' (, locally , literally "black soil" in Portuguese) is a type of very dark, fertile anthropogenic soil ( anthrosol) found in the Amazon Basin. It is also known as "Amazonian dark earth" or "Indian black earth". In Portuguese its f ...
''. Terra preta is found over large areas in the Amazon forest; and is now widely accepted as a product of indigenous soil management
Soil management is the application of operations, practices, and treatments to protect soil and enhance its performance (such as soil fertility or soil mechanics). It includes soil conservation, soil amendment, and optimal soil health. In agricu ...
. The development of this fertile soil allowed agriculture and silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, and quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production.
The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests and wo ...
in the previously hostile environment; meaning that large portions of the Amazon rainforest are probably the result of centuries of human management, rather than naturally occurring as has previously been supposed. In the region of the Xingu tribe, remains of some of these large settlements in the middle of the Amazon forest were found in 2003 by Michael Heckenberger and colleagues of the University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its ...
. Among those were evidence of roads, bridges and large plazas.
Biodiversity, flora and fauna

 Wet tropical forests are the most species-rich
Wet tropical forests are the most species-rich biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
, and tropical forests in the Americas are consistently more species rich than the wet forests in Africa and Asia.Turner, I.M. (2001). ''The ecology of trees in the tropical rain forest''. Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer.
Cambridge University Pre ...
, Cambridge. As the largest tract of tropical rainforest in the Americas, the Amazonian rainforests have unparalleled biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
. One in ten known species in the world lives in the Amazon rainforest. This constitutes the largest collection of living plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclu ...
s and animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
in the world
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the worl ...
.
The region is home to about 2.5 million insect species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
, tens of thousands of plants, and some 2,000 birds and mammals. To date, at least 40,000 plant species, 2,200 fishes
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, 1,294 birds, 427 mammals, 428 amphibians, and 378 reptiles have been scientifically classified in the region. One in five of all bird species are found in the Amazon rainforest, and one in five of the fish species live in Amazonian rivers and streams. Scientists have described between 96,660 and 128,843 invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
species in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
alone.
The biodiversity of plant species is the highest on Earth with one 2001 study finding a quarter square kilometer (62 acres) of Ecuadorian rainforest supports more than 1,100 tree species. A study in 1999 found one square kilometer (247 acres) of Amazon rainforest can contain about 90,790 tonnes of living plants. The average plant biomass is estimated at 356 ± 47 tonnes per hectare. To date, an estimated 438,000 species of plants of economic and social interest have been registered in the region with many more remaining to be discovered or catalogued. The total number of tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
species in the region is estimated at 16,000.
The green leaf area of plants and trees in the rainforest varies by about 25% as a result of seasonal changes. Leaves expand during the dry season when sunlight is at a maximum, then undergo abscission in the cloudy wet season. These changes provide a balance of carbon between photosynthesis and respiration.
The rainforest contains several species that can pose a hazard. Among the largest predatory creatures are the black caiman, jaguar, cougar, and anaconda
Anacondas or water boas are a group of large snakes of the genus '' Eunectes''. They are found in tropical South America. Four species are currently recognized.
Description
Although the name applies to a group of snakes, it is often used ...
. In the river, electric eel
The electric eels are a genus, ''Electrophorus'', of neotropical freshwater fish from South America in the family Gymnotidae. They are known for their ability to stun their prey by generating electricity, delivering shocks at up to 860 volt ...
s can produce an electric shock that can stun or kill, while piranha
A piranha or piraña (, , or ; or , ) is one of a number of freshwater fish in the family Serrasalmidae, or the subfamily Serrasalminae within the tetra family, Characidae in order Characiformes. These fish inhabit South American rivers, fl ...
are known to bite and injure humans. Various species of poison dart frogs secrete lipophilic
Lipophilicity (from Greek λίπος "fat" and φίλος "friendly"), refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such non-polar solvents are themselves lipo ...
alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
toxins through their flesh. There are also numerous parasites and disease vectors. Vampire bat
Vampire bats, species of the subfamily Desmodontinae, are leaf-nosed bats found in Central and South America. Their food source is blood of other animals, a dietary trait called hematophagy. Three extant bat species feed solely on blood: the ...
s dwell in the rainforest and can spread the rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. Early symptoms can include fever and tingling at the site of exposure. These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, ...
virus. Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
, yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. ...
and dengue fever can also be contracted in the Amazon region.
The biodiversity in the Amazon is becoming increasingly threatened, primarily by habitat loss from deforestation as well as increased frequency of fires. Over 90% of Amazonian plant and vertebrate species (13,000-14,000 in total) may have been impacted to some degree by fires.
Hoatzin
The hoatzin ( ) or hoactzin ( ), (''Opisthocomus hoazin''), is the only species in the order Opisthocomiformes. It is a species of tropical bird found in swamps, riparian forests, and mangroves of the Amazon and the Orinoco basins in South Ameri ...
File:Avicularia-geroldi-subadult.jpg, Mygalomorphae
The Mygalomorphae, or mygalomorphs, are an infraorder of spiders, and comprise one of three major groups of living spiders with over 3000 species, found on all continents except Antarctica. Many members are known as trapdoor spiders due to the ...
File:Purus Red Howler Monkey.jpg, Howler monkey
Howler monkeys (genus ''Alouatta'', monotypic in subfamily Alouattinae) are the most widespread primate genus in the Neotropics and are among the largest of the platyrrhines along with the muriquis (''Brachyteles''), the spider monkeys (''Atele ...
File:Heliconia aemygdiana (14551077262).jpg, ''Heliconia
''Heliconia'', derived from the Greek word (), is a genus of flowering plants in the monotypic family Heliconiaceae. Most of the ca 194 known species are native to the tropical Americas, but a few are indigenous to certain islands of the we ...
''
File:Manuel Antonio (43).JPG, Brown-throated sloth
The brown-throated sloth (''Bradypus variegatus'') is a species of three-toed sloth found in the Neotropical realm of Central and South America.
It is the most common of the four species of three-toed sloth, and is found in the forests of South ...
File:Emperor Tamarin (EXPLORE) (9714001143).jpg, Emperor tamarin
The emperor tamarin (''Saguinus imperator'') is a species of tamarin allegedly named for its resemblance to the German emperor Wilhelm II. It lives in the west Brazilian states of Acre and Amazonas and the southwest Amazon Basin, in east Peru, ...
File:Dendrobates azureus (Dendrobates tinctorius) Edit.jpg, Blue poison dart frog
The blue poison dart frog or blue poison arrow frog (''Dendrobates tinctorius "azureus"'') is a poison dart frog found in the forests surrounded by the Sipaliwini Savanna, which is located in southern Suriname (known in Surinamese Dutch and adja ...
File:Standing jaguar.jpg, South American jaguar
The South American jaguar is a jaguar (''Panthera onca'') population in South America. Though a number of subspecies of jaguar have been proposed for South America, morphological and genetic research did not reveal any evidence for subspecific ...
is an apex predator in the Amazon Rainforest
File:Uakari male.jpg, Bald uakari
The bald uakari (''Cacajao calvus'') or bald-headed uakari is a small New World monkey characterized by a very short tail; bright, crimson face; a bald head; and long coat. The bald uakari is restricted to várzea forests and other wooded habitat ...
File:Isulas (8583611782).jpg, Bullet ants have an extremely painful sting
File:Many parrots -Anangu, Yasuni National Park, Ecuador -clay lick-8.jpg, Parrots at clay lick in Yasuni National Park Yasuni can mean:
* Yasuni National Park in Ecuador
* The Yasuní-ITT Initiative, a proposal to refrain from exploiting oil reserves within the park
* Lophostoma yasuni, a species of bat
* Osteocephalus yasuni, a species of frog
* Yasuni antwren, a ...
, Ecuador
File:Eunectes murinus.jpg, Green anaconda
File:Black caiman Macrofotografie 2.jpg, Black caiman
File:Pipa pipa01.jpg, Pipa pipa
The pipa, pípá, or p'i-p'a () is a traditional Chinese musical instrument, belonging to the plucked category of instruments. Sometimes called the "Chinese lute", the instrument has a pear-shaped wooden body with a varying number of frets ran ...
, a bizarre species of frog found within the Amazon.
Deforestation
Deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
is the conversion of forested areas to non-forested areas. The main sources of deforestation in the Amazon are human settlement and the development of the land. In 2018, about 17% of the Amazon rainforest was already destroyed. Research suggests that upon reaching about 20–25% (hence 3–8% more), the tipping point to flip it into a non-forest ecosystem – degraded savannah – (in eastern, southern and central Amazonia) will be reached.
Prior to the early 1960s, access to the forest's interior was highly restricted, and the forest remained basically intact. Farms established during the 1960s were based on crop cultivation and the slash and burn
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a farming method that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody plants in an area. The downed veget ...
method. However, the colonists were unable to manage their fields and the crops because of the loss of soil fertility and weed invasion.Watkins and Griffiths, J. (2000). Forest Destruction and Sustainable Agriculture in the Brazilian Amazon: a Literature Review (Doctoral dissertation, The University of Reading, 2000). Dissertation Abstracts International, 15–17 The soils in the Amazon are productive for just a short period of time, so farmers are constantly moving to new areas and clearing more land. These farming practices led to deforestation and caused extensive environmental damage. Deforestation is considerable, and areas cleared of forest are visible to the naked eye from outer space.
In the 1970s, construction began on the Trans-Amazonian highway
The Trans-Amazonian Highway (official designation BR-230, official name Rodovia Transamazônica), was introduced on September 27, 1972. It is 4,000 km long, making it the third longest highway in Brazil. It runs through the Amazon forest and ...
. This highway represented a major threat to the Amazon rainforest. The highway still has not been completed, limiting the environmental damage.
Between 1991 and 2000, the total area of forest lost in the Amazon rose from , with most of the lost forest becoming pasture for cattle.Centre for International Forestry Research (CIFOR) (2004) Seventy percent of formerly forested land in the Amazon, and 91% of land deforested since 1970, have been used for livestock pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep, or sw ...
. Currently, Brazil is the largest global producer of soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu a ...
s. New research however, conducted by Leydimere Oliveira et al., has shown that the more rainforest is logged in the Amazon, the less precipitation reaches the area and so the lower the yield per hectare becomes. So despite the popular perception, there has been no economical advantage for Brazil from logging rainforest zones and converting these to pastoral fields.
The needs of soy farmers have been used to justify many of the controversial transportation projects that are currently developing in the Amazon. The first two highways successfully opened up the rainforest and led to increased settlement and deforestation. The mean annual deforestation rate from 2000 to 2005 ( per year) was 18% higher than in the previous five years ( per year). Although deforestation declined significantly in the Brazilian Amazon between 2004 and 2014, there has been an increase to the present day.
Brazil's President, Jair Bolsonaro, has supported the relaxation of regulations placed on agricultural land. He has used his time in office to allow for more deforestation and more exploitation of the Amazon's rich natural resources.
Since the discovery of fossil fuel reservoirs in the Amazon rainforest, oil drilling activity has steadily increased, peaking in the Western Amazon in the 1970s and ushering another drilling boom in the 2000s. Oil companies have to set up their operations by opening new roads through the forests, which often contributes to deforestation in the region.
The European Union–Mercosur free trade agreement, which would form one of the world's largest free trade areas, has been denounced by environmental activists and indigenous rights campaigners. The fear is that the deal could lead to more deforestation of the Amazon rainforest as it expands market access to Brazilian beef.
According to a November 2021 report by Brazil's INPE, based on satellite data, deforestation has increased by 22% over 2020 and is at its highest level since 2006.
2019 fires
There have been 72,843 fires in Brazil in 2019, with more than half within the Amazon region. In August 2019 there were a record number of fires. Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon rose more than 88% in June 2019 compared with the same month in 2018.Conservation and climate change
 Environmentalists are concerned about
Environmentalists are concerned about loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity loss includes the worldwide extinction of different species, as well as the local reduction or loss of species in a certain habitat, resulting in a loss of biological diversity. The latter phenomenon can be temporary or permanent, de ...
that will result from destruction of the forest, and also about the release of the carbon contained within the vegetation, which could accelerate global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
. Amazonian evergreen forests account for about 10% of the world's terrestrial primary productivity and 10% of the carbon stores in ecosystems – of the order of 1.1 × 1011 metric tonnes of carbon. Amazonian forests are estimated to have accumulated 0.62 ± 0.37 tons of carbon per hectare per year between 1975 and 1996. In 2021 it was reported that the Amazon for the first time emitted more greenhouse gases than it absorbed. Though often referenced as producing more than a quarter of the Earth's oxygen, this often stated, but misused statistic actually refers to oxygen turnover. The net contribution of the ecosystem is approximately zero.
One computer model
Computer simulation is the process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be deter ...
of future climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
caused by greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
shows that the Amazon rainforest could become unsustainable under conditions of severely reduced rainfall and increased temperatures, leading to an almost complete loss of rainforest cover in the basin by 2100.Radford, T. 2002"World may be warming up even faster"
. ''The Guardian''. However, simulations of Amazon basin climate change across many different models are not consistent in their estimation of any rainfall response, ranging from weak increases to strong decreases. Houghton, J.T. ''et al.'' 2001
"Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis"
. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. The result indicates that the rainforest could be threatened through the 21st century by climate change in addition to deforestation. In 1989, environmentalist C.M. Peters and two colleagues stated there is economic as well as biological incentive to protecting the rainforest. One hectare in the
Peruvian Amazon
Peruvian Amazonia ( es, Amazonía del Perú) is the area of the Amazon rainforest included within the country of Peru, from east of the Andes to the borders with Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil and Bolivia. This region comprises 60% of the country ...
has been calculated to have a value of $6820 if intact forest
An intact forest landscape (IFL) is an unbroken natural landscape of a forest ecosystem and its habitat–plant community components, in an extant forest zone. An IFL is a natural environment with no signs of significant human activity or habitat f ...
is sustainably harvested for fruits, latex, and timber; $1000 if clear-cut for commercial timber (not sustainably harvested); or $148 if used as cattle pasture.
According to WWF, ecotourism
Ecotourism is a form of tourism involving responsible travel (using sustainable transport) to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. Its purpose may be to educate the traveler, to provide fund ...
could help the Amazon to reduce deforestation and climate change. Ecotourism is currently still little practiced in the Amazon, partly due to lack of information about places where implementation is possible. Ecotourism is a sector that can also be taken up by the Indigenous community in the Amazon as a source of income and revenue. An ecotourism project in the Brazilian-section of the Amazon rainforest had been under consideration by Brazil's State Secretary for the Environment and Sustainable Development in 2009, along the Aripuanã river
Aripuanã River ( pt, Rio Aripuanã) is a river in the Mato Grosso and Amazonas states in north-western Brazil. It is a tributary of the Madeira River in the Amazon Basin. The town of Novo Aripuanã is located on its banks where it merges into t ...
, in the Aripuanã Sustainable Development Reserve. Also, some community-based ecotourism exists in the Mamirauá Sustainable Development Reserve
The Mamirauá Sustainable Development Reserve ( pt, Reserva de Desenvolvimento Sustentável Mamirauá) in the Brazilian state of Amazonas, near the city of Tefé, is a reserve near the village of Boca do Mamirauá. It includes mostly Amazonian ...
. Ecotourism is also practiced in the Peruvian-section of the Amazon rainforest. A few ecolodges are for instance present between Cusco and Madre de Dios.
 As indigenous territories continue to be destroyed by deforestation and
As indigenous territories continue to be destroyed by deforestation and ecocide
Ecocide is human impact on the environment causing mass destruction to that environment.
Ten nations have codified ecocide as a crime. Activities that might constitute ecocide in these nations include substantially damaging or destroying ecos ...
, such as in the Peruvian Amazon
Peruvian Amazonia ( es, Amazonía del Perú) is the area of the Amazon rainforest included within the country of Peru, from east of the Andes to the borders with Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil and Bolivia. This region comprises 60% of the country ...
Dean, Bartholomew. (2003) State Power and Indigenous Peoples in Peruvian Amazonia: A Lost Decade, 1990–2000. In ''The Politics of Ethnicity Indigenous Peoples in Latin American States'' David Maybury-Lewis
David Henry Peter Maybury-Lewis (5 May 1929 – 2 December 2007) was a British anthropologist, ethnologist of lowland South America, activist for indigenous peoples' human rights, and professor emeritus of Harvard University.
Born in Hyderaba ...
, Ed. Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retir ...
indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
' rainforest communities continue to disappear, while others, like the Urarina continue to struggle to fight for their cultural survival and the fate of their forested territories. Meanwhile, the relationship between non-human primates in the subsistence and symbolism of indigenous lowland South American peoples has gained increased attention, as have ethno-biology and community-based conservation
Community-based conservation is a conservation movement that emerged in the 1980s, in response to escalating protests and subsequent dialogue with local communities affected by international attempts to protect the biodiversity of the earth. These ...
efforts.
From 2002 to 2006, the conserved land in the Amazon rainforest almost tripled and deforestation rates dropped up to 60%. About have been put onto some sort of conservation, which adds up to a current amount of .
In April 2019, the Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
ian court stopped oil exploration activities in of the Amazon rainforest.
In July 2019, the Ecuadorian court forbade the government to sell territory with forests to oil companies.
In September 2019, the US and Brazil agreed to promote private-sector development in the Amazon. They also pledged a $100m biodiversity conservation fund for the Amazon led by the private sector. Brazil's foreign minister stated that opening the rainforest to economic development was the only way to protect it.
 A new study by an international team of environmental scientists in the Brazilian Amazon shows that protection of freshwater biodiversity can be increased by up to 600% through integrated freshwater-terrestrial planning
.
A new study by an international team of environmental scientists in the Brazilian Amazon shows that protection of freshwater biodiversity can be increased by up to 600% through integrated freshwater-terrestrial planning
.
Deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
in the Amazon rainforest region has a negative impact on local climate. It was one of the main causes of the severe drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
of 2014–2015 in Brazil. This is because the moisture from the forests is important to the rainfall in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to th ...
and Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
. Half of the rainfall in the Amazon area is produced by the forests.
Results of a 2021 scientific synthesis indicate that, in terms of global warming, the Amazon basin with the Amazon rainforest is currently emitting more greenhouse gases than it absorbs overall. Climate change impacts and human activities in the area – mainly wildfires, current land-use and deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
– are causing a release of forcing agents that likely result in a net warming effect. CC BY 4.0
. In 2022 the supreme court of Ecuador decided that "“under no circumstances can a project be carried out that generates excessive sacrifices to the collective rights of communities and nature.” It also required the government to respect the opinion of
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
about different industrial projects on their land. Advocates of the decision argue that it will have consequences far beyond Ecuador. In general, ecosystems are in better shape when indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
own or manage the land.
Remote sensing
 The use of remotely sensed data is dramatically improving conservationists' knowledge of the Amazon basin. Given the objectivity and lowered costs of satellite-based land cover and -change analysis, it appears likely that remote sensing technology will be an integral part of assessing the extents, locations and damage of deforestation in the basin. Furthermore, remote sensing is the best and perhaps only possible way to study the Amazon on a large scale.
The use of remote sensing for the conservation of the Amazon is also being used by the indigenous tribes of the basin to protect their tribal lands from commercial interests. Using handheld
The use of remotely sensed data is dramatically improving conservationists' knowledge of the Amazon basin. Given the objectivity and lowered costs of satellite-based land cover and -change analysis, it appears likely that remote sensing technology will be an integral part of assessing the extents, locations and damage of deforestation in the basin. Furthermore, remote sensing is the best and perhaps only possible way to study the Amazon on a large scale.
The use of remote sensing for the conservation of the Amazon is also being used by the indigenous tribes of the basin to protect their tribal lands from commercial interests. Using handheld GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
devices and programs like Google Earth, members of the Trio Tribe, who live in the rainforests of southern Suriname, map out their ancestral lands to help strengthen their territorial claims. Currently, most tribes in the Amazon do not have clearly defined boundaries, making it easier for commercial ventures to target their territories.
To accurately map the Amazon's biomass and subsequent carbon-related emissions, the classification of tree growth stages within different parts of the forest is crucial. In 2006, Tatiana Kuplich organized the trees of the Amazon into four categories: mature forest, regenerating forest ess than three years regenerating forest etween three and five years of regrowth and regenerating forest leven to eighteen years of continued development The researcher used a combination of synthetic aperture radar
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide fine ...
(SAR) and Thematic Mapper A Thematic Mapper (TM) is one of the Earth observing sensors introduced in the Landsat program. The first was placed aboard Landsat 4 (decommissioned in 2001), and another was operational aboard Landsat 5 up to 2012. /sup> TM sensors feature seven ...
(TM) to accurately place the different portions of the Amazon into one of the four classifications.
In 2005, parts of the Amazon basin experienced the worst drought in one hundred years, and there were indications that 2006 may have been a second successive year of drought. A 2006 article in the UK newspaper ''
The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publish ...
'' reported the Woods Hole Research Center results, showing that the forest in its present form could survive only three years of drought. Scientists at the Brazilian National Institute of Amazonian Research
The National Institute of Amazonian Research (Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazônia or INPA) is a public educational and research institution headquartered in Manaus, Brazil. It was founded in 1952, with the purpose of furthering scientific ...
argued in the article that this drought response, coupled with the effects of deforestation on regional climate, are pushing the rainforest towards a " tipping point" where it would irreversibly start to die. It concluded that the forest is on the brink of being turned into savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
or desert, with catastrophic consequences for the world's climate. A study published in ''Nature Communications'' in October 2020 found that about 40% of the Amazon rainforest is at risk of becoming a savanna-like ecosystem due to reduced rainfall. A study published in ''Nature climate change
''Nature Climate Change'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature Publishing Group covering all aspects of research on global warming, the current climate change, especially its effects. It was established in 2011 as the ...
'' provided direct empirical evidence that more than three-quarters of the Amazon rainforest has been losing resilience since the early 2000s, risking dieback with profound implications for biodiversity, carbon storage and climate change at a global scale.
According to the World Wide Fund for Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the Wor ...
, the combination of climate change and deforestation increases the drying effect of dead trees that fuels forest fires
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identif ...
.
In 2010, the Amazon rainforest experienced another severe drought, in some ways more extreme than the 2005 drought. The affected region was approximately of rainforest, compared with in 2005. The 2010 drought had three epicenters where vegetation died off, whereas in 2005, the drought was focused on the southwestern part. The findings were published in the journal ''Science''. In a typical year, the Amazon absorbs 1.5 gigatons of carbon dioxide; during 2005 instead 5 gigatons were released and in 2010 8 gigatons were released. Additional severe droughts occurred in 2010, 2015, and 2016.
In 2019 Brazil's protections of the Amazon rainforest were slashed, resulting in a severe loss of trees. According to Brazil's National Institute for Space Research
The National Institute for Space Research ( pt, Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais, INPE) is a research unit of the Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovations, the main goals of which are fostering scientific research an ...
(INPE), deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon rose more than 50% in the first three months of 2020 compared to the same three-month period in 2019.
In 2020, a 17 percent rise was noted in the Amazon wildfires, marking the worst start to the fire season in a decade. The first 10 days of August 2020 witnessed 10,136 fires. An analysis of the government figures reflected 81 per cent increase in fires in federal reserves, in comparison with the same period in 2019. However, President Jair Bolsonaro turned down the existence of fires, calling it a "lie", despite the data produced by his own government. Satellites in September recorded 32,017 hotspots in the world's largest rainforest, a 61% rise from the same month in 2019. In addition, October saw a huge surge in the number of hotspots in the forest (more than 17,000 fires are burning in the Amazon's rainforest) - with more than double the amount detected in the same month last year.
See also
* Amanyé * Atlantic Forest * Bandeirantes * Deforestation of the Amazon rainforest *Environmental impact of meat production
The environmental impact of meat production varies because of the wide variety of agricultural practices employed around the world. All agricultural practices have been found to have a variety of effects on the environment. Some of the environmen ...
* Forest protection
Forest protection is a branch of forestry which is concerned with the preservation or improvement of a forest and prevention and control of damage to forest by natural or man made causes like forest fires, plant pests, and adverse climatic cond ...
* Indigenous peoples in Brazil
* Tapiche Ohara's Reserve
The Tapiche Reserve is a private conservation property located in Tapiche District, Requena Province, Loreto Region in Peru. The reserve is designated by the Peruvian government as a Private Conservation Area (PCA).
Geography
The reserve e ...
;Organizations
* Amazon Conservation Association
* Amazon Conservation Team (ACT)
* Amazon Watch
* Coordinator of Indigenous Organizations of the Amazon River Basin (COICA)
* Rainforest Action Network
Rainforest Action Network (RAN) is an environmental organization based in San Francisco, California, United States. The organization was founded by Randy "Hurricane" Hayes and Mike Roselle in 1985, and first gained national prominence with a gr ...
* Rainforest Alliance
* Rainforest Foundation Fund
The Rainforest Foundation Fund is a charitable foundation founded in 1987 and dedicated to drawing attention to rainforests and defending the rights of indigenous peoples living there.
The fund and its three sister organizations (Rainforest Fou ...
* Save the Amazon Rainforest Organisation (STARO)
;Technology
* Amazon Surveillance System
The Amazon Surveillance System (SIVAM, pt, Sistema de Vigilância da Amazônia), is a complex surveillance system used for monitoring Amazônia Legal ("legal Amazon area"). This area includes the Brazilian rainforest, to curb the trafficking of ...
(Sistema de Vigilância da Amazônia)
* Global Forest Watch
Global Forest Watch (GFW) is an open-source web application to monitor global forests in near real-time. GFW is an initiative of the World Resources Institute (WRI), with partners including Google, USAID, the University of Maryland (UMD), Esri, V ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*Bunker, S.G. (1985). ''Underdeveloping the Amazon: Extraction, Unequal Exchange, and the Failure of the Modern State''. University of Illinois Press. * * Dean, Warren (1976). ''Rio Claro: A Brazilian Plantation System, 1820–1920''. Stanford University Press. *Dean, Warren (1997). ''Brazil and the Struggle for Rubber: A Study in Environmental History''. Cambridge University Press. *Hecht, Susanna and Alexander Cockburn (1990). ''The Fate of the Forest: Developers, Destroyers, and Defenders of the Amazon''. New York: Harper Perennial. *Hochstetler, K. and M. Keck (2007). ''Greening Brazil: Environmental Activism in State and Society''. Duke University Press. *Revkin, A. (1990). ''The Burning Season: The Murder of Chico Mendes and the Fight for the Amazon Rain Forest''. Houghton Mifflin. * *Weinstein, Barbara (1983). ''The Amazon Rubber Boom 1850–1920''. Stanford University Press. *External links
Journey into Amazonia
The Amazon: The World's Largest Rainforest
WWF in the Amazon rainforest
Amazonia.org.br
Good daily updated Amazon information database on the web, held by Friends of The Earth – Brazilian Amazon.
amazonia.org
Sustainable Development in the Extractive Reserve of the Baixo Rio Branco – Rio Jauaperi – Brazilian Amazon.
Original news updates on the Amazon.
Amazon-Rainforest.org
Information about the Amazon rainforest, its people, places of interest, and how everyone can help.
Conference: Climate change and the fate of the Amazon
Podcasts of talks given at
Oriel College
Oriel College () is a constituent college of the University of Oxford in Oxford, England. Located in Oriel Square, the college has the distinction of being the oldest royal foundation in Oxford (a title formerly claimed by University College, w ...
, University of Oxford, 20–22 March 2007.
* Dead humpback whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh up to . The hu ...
calin the Amazon
{{Authority control Rainforest Amazon biome Rainforest Ecoregions of South America Natural history of Peru Natural history of Brazil Natural history of Ecuador Neotropical ecoregions Rainforests Regions of South America Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests Forestry in South America
Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...