Miscegenation ( ) is the interbreeding of people who are considered to be members of different
races. The word, now usually considered pejorative, is derived from a combination of the Latin terms ''miscere'' ("to mix") and ''genus'' ("race") from the Hellenic γένος.
The word first appeared in ''
Miscegenation: The Theory of the Blending of the Races, Applied to the American White Man and Negro'', a pretended anti-abolitionist pamphlet
David Goodman Croly
David Goodman Croly (November 3, 1829 – April 29, 1889) was an American journalist, born in New York City and educated at New York University. He was associated with the ''Evening Post'' and the '' Herald'' (1854–58), and then became an edito ...
and others published anonymously in advance of the 1864 U.S. presidential election.
The term came to be associated with laws that banned interracial marriage and sex, which were known as
anti-miscegenation laws.
Opposition to miscegenation, framed as preserving so-called
racial purity
The term racial hygiene was used to describe an approach to eugenics in the early 20th century, which found its most extensive implementation in Nazi Germany (Nazi eugenics). It was marked by efforts to avoid miscegenation, analogous to an animal ...
, is a typical theme of racial supremacist movements.
Although the notion that racial mixing is undesirable has arisen at different points in history, it gained particular prominence among white communities in
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
during the colonial period.
Although the term "miscegenation" was formed from the Latin ''miscere'' "to mix" plus ''genus'' "race" or "kind", and it could therefore be perceived as being value-neutral, it is almost always a pejorative term which is used by people who believe in
racial superiority or
purity
Purity may refer to:
Books
* ''Pureza'' (novel), a 1937 Brazilian novel by José Lins do Rego
* ''Purity'' (novel), a 2015 novel by Jonathan Franzen
** ''Purity'' (TV series), a TV series based on the novel
*''Purity'', a 2012 novel by Jackson P ...
. Less loaded terms for multiethnic relationships, such as interethnic or
interracial marriage
Interracial marriage is a marriage involving spouses who belong to different races or racialized ethnicities.
In the past, such marriages were outlawed in the United States, Nazi Germany and apartheid-era South Africa as miscegenation. In 1 ...
s, and mixed-race, multiethnic, or
multiracial people
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
, are more common in contemporary usage.
Usage
In the present day, the use of the word ''miscegenation'' is avoided by many scholars, because the term suggests that race is a concrete biological phenomenon, rather than a categorization which is imposed on certain relationships. The term's historical usage in contexts which typically implied disapproval is also a reason why more unambiguously neutral terms such as ''interracial'', ''interethnic'' or ''cross-cultural'' are more common in contemporary usage. The term remains in use among scholars when referring to past practices concerning
multiraciality, such as anti-miscegenation laws that banned interracial marriages.
In Spanish, Portuguese, and French, the words used to describe the mixing of races are ''mestizaje'', ''mestiçagem'' and ''métissage''. These words, much older than the term ''miscegenation'', are derived from the
Late Latin
Late Latin ( la, Latinitas serior) is the scholarly name for the form of Literary Latin of late antiquity.Roberts (1996), p. 537. English dictionary definitions of Late Latin date this period from the , and continuing into the 7th century in t ...
''mixticius'' for "mixed", which is also the root of the Spanish word ''
mestizo''. (Portuguese also uses ''miscigenação'', derived from the same Latin root as the English word.) These non-English terms for "race-mixing" are not considered as offensive as "miscegenation", although they have historically been tied to the
caste system (
casta) that was established during the colonial era in Spanish-speaking Latin America.
Today, the mixes among races and ethnicities are diverse, so it is considered preferable to use the term "mixed-race" or simply "mixed" (''mezcla''). In Portuguese-speaking Latin America (i.e.,
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
), a milder form of caste system existed, although it also provided for legal and social discrimination among individuals belonging to different races, since
slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
for black people existed until the late 19th century. Intermarriage occurred significantly from the very first settlements, with their descendants achieving high rank in government and society. To this day, there are controversies if Brazilian class system would be drawn mostly around socio-economic lines, not racial ones (in a manner similar to other former
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
colonies). Conversely, people classified in censuses as black, brown ("
pardo
''Pardos'' (feminine ''pardas'') is a term used in the former Portuguese and Spanish colonies in the Americas to refer to the triracial descendants of Southern Europeans, Amerindians and West Africans. In some places they were defined as ne ...
") or indigenous have disadvantaged social indicators in comparison to the white population.
The concept of miscegenation is tied to concepts of racial difference. As the different connotations and etymologies of miscegenation and ''mestizaje'' suggest, definitions of
race
Race, RACE or "The Race" may refer to:
* Race (biology), an informal taxonomic classification within a species, generally within a sub-species
* Race (human categorization), classification of humans into groups based on physical traits, and/or s ...
, "race mixing" and
multiraciality have diverged globally as well as
historically, depending on changing social circumstances and cultural perceptions. Mestizo are people of mixed white and indigenous, usually
Amerindian
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
ancestry, who do not self-identify as indigenous peoples or
Native Americans. In Canada, however, the
Métis, who also have partly Amerindian and partly white, often French-Canadian, ancestry, have identified as an ethnic group and are a constitutionally recognized
aboriginal people
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
.
Interracial marriages are often disparaged in racial minority communities as well. Data from the
Pew Research Center has shown that
African Americans are twice as likely as
white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
Americans to believe that interracial marriage "is a bad thing". There is a considerable amount of scientific literature that demonstrates similar patterns. However, most of the scientific research that is conducted on public attitudes towards miscegenation is almost exclusively interested in white people's attitudes on the matter; very little of the research is focused on the attitudes that non-white ethnic groups have towards miscegenation.
The differences between related terms and words which encompass aspects of racial admixture show the impact of different historical and cultural factors leading to changing
social interpretations of race and ethnicity. Thus the
Comte de Montlosier, in exile during the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
, the equated class difference in 18th-century France with racial difference. Borrowing
Boulainvilliers' discourse on the "
Nordic race
The Nordic race was a racial concept which originated in 19th century anthropology. It was considered a race or one of the putative sub-races into which some late-19th to mid-20th century anthropologists divided the Caucasian race, claiming tha ...
" as being the French aristocracy that invaded the plebeian "Gauls", he showed his contempt for the lowest
social class, the
Third Estate
The estates of the realm, or three estates, were the broad orders of social hierarchy used in Christendom (Christian Europe) from the Middle Ages to early modern Europe. Different systems for dividing society members into estates developed and ...
, calling it "this new person born of slaves ... a mixture of all races and of all times".
Etymological history

''Miscegenation'' comes from the
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''
miscere'', "to mix" and ''
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
'', "kind". The word was coined in the U.S. in 1863 in an anonymous hoax pamphlet, and the
etymology
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the Phonological chan ...
of the word is tied up with political conflicts during the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
over the
abolition of
slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
and over the
racial segregation
Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crimes against hum ...
of
African-Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of enslav ...
. The reference to ''genus'' was made to emphasize the supposedly distinct biological differences between whites and non-whites, though all humans belong to the same
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
, ''
Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely relat ...
'', and the same
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
, ''
Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
''.
The word was coined in an anonymous
propaganda pamphlet published in New York City in December 1863, during the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
. The pamphlet was entitled ''
Miscegenation: The Theory of the Blending of the Races, Applied to the American White Man and Negro''.
It purported to advocate the intermarriage of whites and blacks until they were indistinguishably mixed, as desirable, and further asserted that this was a goal of the
Republican Party. The pamphlet was a hoax, concocted by
Democrats to discredit the Republicans by imputing to them what were then radical views that would offend the vast majority of whites, even those who opposed slavery. The issue of miscegenation, raised by the opponents of
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
, featured prominently in the election campaign of 1864. In his fourth debate with
Stephen A. Douglas, Lincoln took great care to emphasise that he supported the law of
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
which forbade "the marrying of white people with negroes".
The pamphlet and variations on it were reprinted widely in both the North and
South by Democrats and Confederates. Only in November 1864, after Lincoln had won the election, was the pamphlet exposed in the United States as a hoax. It was written by
David Goodman Croly
David Goodman Croly (November 3, 1829 – April 29, 1889) was an American journalist, born in New York City and educated at New York University. He was associated with the ''Evening Post'' and the '' Herald'' (1854–58), and then became an edito ...
, managing editor of the ''
New York World
The ''New York World'' was a newspaper published in New York City from 1860 until 1931. The paper played a major role in the history of American newspapers. It was a leading national voice of the Democratic Party. From 1883 to 1911 under pub ...
'', a Democratic Party paper, and George Wakeman, a ''World'' reporter. By then, the word ''miscegenation'' had entered the common language of the day as a popular
buzzword in political and social discourse.
Before the publication of ''Miscegenation'', the terms ''racial intermixing'' and ''amalgamation'', the latter borrowed from
metallurgy, were used as a general terms for ethnic and racial genetic mixing. Contemporary usage of the ''amalgamation'' metaphor was that of
Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, abolitionist, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champ ...
's private vision in 1845 of America as an ethnic and racial smelting-pot, a variation on the concept of the
melting pot.
Opinions in the U.S on the desirability of such intermixing, including that between white
Protestants and
Irish Catholic
Irish Catholics are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland whose members are both Catholic and Irish. They have a large diaspora, which includes over 36 million American citizens and over 14 million British citizens (a quarter of the Briti ...
immigrants, were divided. The term ''miscegenation'' was coined to refer specifically to the intermarriage of blacks and whites, with the intent of galvanizing opposition to the war.
In
Spanish America
Spanish America refers to the Spanish territories in the Americas during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term "Spanish America" was specifically used during the territories' imperial era between 15th and 19th centuries. To the e ...
, the term ''
mestizaje
(; ; fem. ) is a term used for racial classification to refer to a person of mixed European and Indigenous American ancestry. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though thei ...
'', which is derived from ''
mestizo'', is a term used to describe a person who is the offspring of an
indigenous American and a European. The primary reason why there are so few
indigenous peoples of Central and
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
remaining is because of the persistent and pervasive miscegenation between the
Iberian colonists and the indigenous American population, which is the most common admixture of ethnicities found in the genetic tests of present-day Latinos. This explains why Latinos in North America, the vast majority of whom are immigrants or descendants of immigrants from Central and South America, carry an average of 18% Native American ancestry, and 65.1% European ancestry (mostly from the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
).
Laws banning miscegenation
Laws banning "race-mixing" were enforced in certain U.S. states until 1967 (but they were still on the books in some states until 2000),
in
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
(the
Nuremberg Laws
The Nuremberg Laws (german: link=no, Nürnberger Gesetze, ) were antisemitic and racist laws that were enacted in Nazi Germany on 15 September 1935, at a special meeting of the Reichstag convened during the annual Nuremberg Rally of ...
) from 1935 until 1945, and in South Africa during the
Apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
era (1949–1985). All of these laws primarily banned marriage between persons who were members of different racially or ethnically defined groups, which was termed "amalgamation" or "miscegenation" in the U.S. The laws in Nazi Germany and the laws in many U.S. states, as well as the laws in South Africa, also banned sexual relations between such individuals.
In the United States, various state laws prohibited marriages between
whites
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as ...
and
blacks
Black is a racialized classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin; in certain countries, often in ...
, and in many states, they also prohibited marriages between whites and
Native Americans as well as marriages between whites and
Asians. In the U.S., such laws were known as
anti-miscegenation laws. From 1913 until 1948, 30 out of the then 48 states enforced such laws. Although an "Anti-Miscegenation Amendment" to the
United States Constitution was proposed in 1871, in 1912–1913, and again in 1928, no nationwide law against racially mixed marriages was ever enacted. In 1967, the
United States Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
unanimously ruled in ''
Loving v. Virginia'' that anti-miscegenation laws are
unconstitutional
Constitutionality is said to be the condition of acting in accordance with an applicable constitution; "Webster On Line" the status of a law, a procedure, or an act's accordance with the laws or set forth in the applicable constitution. When l ...
. With this ruling, these laws were no longer in effect in the remaining 16 states which still had them.
The Nazi ban on interracial sexual relations and marriages was enacted in September 1935 as part of the
Nuremberg Laws
The Nuremberg Laws (german: link=no, Nürnberger Gesetze, ) were antisemitic and racist laws that were enacted in Nazi Germany on 15 September 1935, at a special meeting of the Reichstag convened during the annual Nuremberg Rally of ...
, the ''Gesetz zum Schutze des deutschen Blutes und der deutschen Ehre'' (The Law for the Protection of German Blood and German Honour). The Nuremberg Laws classified
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
as a race, and they also forbade extramarital sexual relations and marriages between persons who were classified as "
Aryans
Aryan or Arya (, Indo-Iranian *''arya'') is a term originally used as an ethnocultural self-designation by Indo-Iranians in ancient times, in contrast to the nearby outsiders known as 'non-Aryan' (*''an-arya''). In Ancient India, the term ...
" and persons who were classified as "
non-Aryans". Violations of these laws were condemned as ''
Rassenschande
''Rassenschande'' (, "racial shame") or ''Blutschande'' ( "blood disgrace") was an anti-miscegenation concept in Nazi German racial policy, pertaining to sexual relations between Aryans and non-Aryans. It was put into practice by policies like ...
'' (lit. "race-disgrace/race-shame") and they could be punished by imprisonment (usually followed by
deportation
Deportation is the expulsion of a person or group of people from a place or country. The term ''expulsion'' is often used as a synonym for deportation, though expulsion is more often used in the context of international law, while deportation ...
to a
concentration camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simpl ...
) and they could even be punished by death.
The
Prohibition of Mixed Marriages Act
The Prohibition of Mixed Marriages Act, Act No. 55 of 1949, was an apartheid law in South Africa that prohibited marriages between "whites" and "non-whites". It was among the first pieces of apartheid legislation to be passed following the Nation ...
in South Africa, enacted in 1949, banned intermarriages between members of different racial groups, including intermarriages between
whites
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as ...
and non-whites. The
Immorality Act, enacted in 1950, also made it a criminal offense for a white person to have any sexual relations with a person who was a member of a different race. Both of these laws were repealed in 1985.
History of ethnoracial admixture and attitudes towards miscegenation
Africa
Africa has had a long history of mixing with non-Africans since prehistoric times. The
Eurasian Backflow
The term ''Eurasian backflow'', or ''Eurasian back-migrations'', has been used to describe several pre-Neolithic and Neolithic migration events of humans from western Eurasia back to Africa. ''Homo sapiens'' had left Africa about 70-50,000 years a ...
which happened in prehistoric times saw a huge migration from the
Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
entering the region and these migrants mixing with the native Africans. Signs of this migration can be found among the people inhabiting the
Horn of Africa and
Sudan. Africa in antiquity, also has had long history of interracial mixing with male
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and European explorers, traders and soldiers having sexual relations with black African women as well as taking them as
wives.
Sir
Richard Francis Burton
Sir Richard Francis Burton (; 19 March 1821 – 20 October 1890) was a British explorer, writer, orientalist scholar,and soldier. He was famed for his travels and explorations in Asia, Africa, and the Americas, as well as his extraordinary kn ...
writes, during his expedition to Africa, about relationships between black women and white men: "The women are well disposed toward strangers of fair complexion, apparently with the permission of their husbands." There are several mixed race populations throughout Africa mostly the results of interracial relationships between Arab and European men and black women. In South Africa, there are big mixed race communities like the Coloureds and
Griqua formed by White colonists taking native African wives. In Namibia there is a community called the
Rehoboth Basters formed by the interracial marriage of
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
/
German men and black African women.
In the former
Portuguese Africa (now known as
Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
,
Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
and
Cape Verde) racial mixing between white
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
and black Africans was fairly common, especially in Cape Verde where the majority of the population is of mixed descent.
There have been some recorded cases of
Chinese merchants and labourers taking African wives throughout Africa as many
Chinese workers were employed to build railways and other infrastructural projects in Africa. These labour groups were made up completely of men with very few Chinese women coming to Africa.
In West Africa, especially Nigeria there are many cases of non-African men taking African women. Many of their offspring have gained prominent positions in Africa. Flight Lieutenant
Jerry John Rawlings
Jerry John Rawlings (22 June 194712 November 2020) was a Ghanaian military officer and politician who led the country for a brief period in 1979, and then from 1981 to 2001. He led a military junta until 1992, and then served two terms as the de ...
, who had a
Scottish father and a black Ghanaian mother became the president of Ghana.
Jean Ping
Jean Ping (; born 24 November 1942 in Omboué)[UN profile page]
[Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the nort ...]
and was the Chairperson of the Commission of the
African Union from 2009 to 2012. The president of
Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalaha ...
,
Ian Khama
Seretse Khama Ian Khama (born 27 February 1953) is a Botswana politician and former military officer who was the fourth President of the Republic of Botswana from 1 April 2008 to 1 April 2018. After serving as Commander of the Botswana Defence ...
, is the son of Botswana's first president,
Seretse Khama
Sir Seretse Goitsebeng Maphiri Khama, GCB, KBE (1 July 1921 – 13 July 1980) was a Motswana politician who served as the first President of Botswana, a post he held from 1966 to his death in 1980.
Born into an influential royal fa ...
, and a white British student,
Ruth Williams Khama
Ruth Williams Khama, Lady Khama (9 December 1923 – 22 May 2002) was the wife of Botswana's first president Sir Seretse Khama, the Paramount Chief of its Bamangwato tribe. She served as the inaugural First Lady of Botswana from 1966 to 1980.
...
.
Nicolas Grunitzky, who was the son of a white
German father and a
Togolese mother, became the second president of
Togo
Togo (), officially the Togolese Republic (french: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its c ...
after a
coup.
Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
men, who have long been traders in
East Africa, sometimes married among local African women. The
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
brought many Indian workers into East Africa to build the
Uganda Railway
The Uganda Railway was a metre-gauge railway system and former British state-owned railway company. The line linked the interiors of Uganda and Kenya with the Indian Ocean port of Mombasa in Kenya. After a series of mergers and splits, the li ...
. Indians eventually populated South Africa,
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
,
Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The sou ...
,
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
,
Malawi
Malawi (; or aláwi Tumbuka: ''Malaŵi''), officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa that was formerly known as Nyasaland. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northeas ...
,
Rwanda,
Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are t ...
,
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
and
Zaire
Zaire (, ), officially the Republic of Zaire (french: République du Zaïre, link=no, ), was a Congolese state from 1971 to 1997 in Central Africa that was previously and is now again known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Zaire was, ...
in small numbers. These interracial unions were mostly unilateral marriages between Indian men and East African women.
Mauritius
In the late 19th to early 20th century,
Chinese men in Mauritius married local
Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
and Creole women due to both the lack of Chinese women, and the higher numbers of Indian women on the island. When the very first Chinese men arrived in Mauritius, they were reluctant to marry local women due to their customary endogamy rules. But with no Chinese women in sight, the Chinese men eventually began to integrate themselves and mix with the local Creole and Indian populations on the island and establish households en ménage. The 1921 census in Mauritius counted that Indian women there had a total of 148 children fathered by Chinese men. These Chinese were mostly traders.
Congo
During the 1970s, an increased demand for
copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
and
cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
attracted
Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
investments in the mineral-rich southeastern region of
Katanga Province. Over a 10-year period, more than 1,000 Japanese miners relocated to the region, confined to a strictly male-only camp. Arriving without family or spouses, the men often sought social interaction outside the confines of their camps. In search of intimacy with the opposite sex, resulting in cohabitation, the men openly engaged in
interracial dating
Interracial marriage is a marriage involving spouses who belong to different races or racialized ethnicities.
In the past, such marriages were outlawed in the United States, Nazi Germany and apartheid-era South Africa as miscegenation. In 19 ...
and relationships, a practice embraced by the local society. As a result, a number of Japanese miners fathered children with Native Congolese women. However, most of the mixed race infants resulting from these unions died, soon after birth. Multiple testimonies of local people suggest that the infants were poisoned by a Japanese lead physician and nurse working at the local mining hospital. Subsequently, the circumstances would have brought the miners shame as most of them already had families back in their native Japan. The practice forced many native Katangan mothers to hide their children by not reporting to the hospital to give birth.
Today, fifty Afro-Japanese have formed an association of ''Katanga Infanticide'' survivors. The organization has hired legal counsel seeking a formal investigation into the killings. The group submitted an official inquiry to both the
Congolese and
Japanese governments, to no avail. Issues specific to this group include having no documentation of their births since not having been born in the local hospital spared their lives. The total number of survivors is unknown.
Réunion
The majority of the population of
Réunion is defined as mixed race. In the last 350 years, various ethnic groups (
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
ns, Chinese,
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
,
French,
Gujarati Indians,
Tamil Indians) have arrived and settled on the island. There have been mixed race people on the island since its first permanent inhabitation in 1665.
The Native
Kaf population has a diverse range of ancestry stemming from colonial Indian and Chinese peoples. They also descend from African slaves brought from countries like
Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
,
Guinea,
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 ...
,
Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
,
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
and
Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are t ...
to the island.
Most population of Réunion Creoles who are of mixed ancestry and make up the majority of the population. Mixed unions between European men and Chinese men with African women, Indian women, Chinese women, Madagascar women were also common. In 2005, a genetic study on the racially mixed people of Réunion found the following. For maternal (
mitochondrial) DNA, the haplogroups are Indian (44%), East Asian (27%), European/Middle Eastern (19%) or African (10%). The Indian lineages are
M2,
M6 and
U2i, the East Asian ones are
E1,
D5a,
M7c, and
F (E1 and M7c also found only in South East Asia and in Madagascar), the European/Middle Eastern ones are
U2e,
T1,
J,
H, and
I, and the African ones are
L1b1,
L2a1,
L3b, and
L3e1.
For paternal (
Y-chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abs ...
) DNA, the haplogroups are European/Middle Eastern (85%) or East Asian (15%). The European lineages are
R1b and
I, the Middle Eastern one
E1b1b1c (formerly E3b3) (also found in Northeast Africa), and the East Asian ones are
R1a (found in many parts of the world including Europe and Central and Southern Asia but the particular sequence has been found in Asia) and
O3.
Madagascar
There was frequent intermixing between the Austronesian and Bantu-speaking populations of Madagascar. A large number of the Malagasy today are the result of admixture between Austronesians and Africans. This is most evident in the
Mikea
The Mikea are a group of Malagasy-speaking horticulturalists and foragers who are often described as the lowland hunter-gatherers of Madagascar. They inhabit the Mikea Forest, a patch of mixed spiny forest and dry deciduous forest along ...
, who are also the last known Malagasy population to still practice a hunter-gatherer lifestyle. In the study of "The Dual Origin of the Malagasy in Island Southeast Asia and East Africa: Evidence from Maternal and Paternal Lineages" shows the Bantu maternal origin to be 38% and Paternal 51% while the Southeast Asian paternal to be 34% and maternal 62%. In the study of Malagasy, autosomal DNA shows the highlanders ethnic group like
Merina
The Merina people (also known as the Imerina, Antimerina, or Hova) are the largest ethnic group in Madagascar.[Merina ...]
are almost an even mixture of Southeast Asian and Bantu origin, while the coastal ethnic group have much higher Bantu mixture in their autosomal DNA suggesting they are mixture of new Bantu migrants and the already established highlander ethnic group. Maximum-likelihood estimates favour a scenario in which Madagascar was settled approximately 1200 years ago by a very small group of women of approximately 30.
[A small cohort of Island Southeast Asian women founded Madagascar](_blank)
by Murray P. Cox, Michael G. Nelson, Meryanne K. Tumonggor, François-X. Ricaut and Herawati Sudoyo The Malagasy people existed through intermarriages between the small founding population.
Intermarriage between Chinese men and native
Malagasy women was not uncommon. Several thousand
Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
men intermarried and cohabited with Malagasy women. 98% of the Chinese traced their origin from Guangdong – more specifically, the Cantonese district of Shunde. For example, the 1954 census found 1,111 "irregular" Chinese-Malagasy unions and 125 legitimate, i.e., legally married. Children were registered by their mothers under a Malagasy name. Intermarriage between French men and Native Malagasy women was not uncommon either.
Uganda
The topic of mixed race Ugandans continues to resurface, in the public arena, with the growing number of multiracial Ugandans (
Multiracial Ugandans in Uganda).
North America
Canada
Canada had no explicit laws against mixed marriage, but anti-miscegenation was often enforced through different laws and upheld by the Supreme Court of Canada as valid.
Velma Demerson, for example, was imprisoned in 1939 for carrying the child of a Chinese father; she was deemed "incorrigible" under the
Female Refuges Act, and was physically experimented on in prison to discover the causes of her behaviour.
Ultimately, an informal and extra-legal regime ensured that the social taboo of racial intermixing was kept to a minimum (Walker, 1997; Backhouse, 1999; Walker, 2000). And, from 1855 until the 1960s, Canada chose its immigrants on the basis of their racial categorization rather than the individual merits of the applicant, with preference being given to immigrants of Northern European (especially British, Scandinavian and French) origin over the so-called "black and Asiatic races", and at times over central and southern European races.
It is arguable that Canada's various manifestations of the federal Indian Act were designed to regulate interracial (in this circumstance, Aboriginal and non- Aboriginal) marital relations and the categorization of mixed-race offspring.
The
Canadian Ku Klux Klan burned crosses at a gathering in
Moose Jaw
Moose Jaw is the fourth largest city in Saskatchewan, Canada. Lying on the Moose Jaw River in the south-central part of the province, it is situated on the Trans-Canada Highway, west of Regina. Residents of Moose Jaw are known as Moose Javian ...
, Saskatchewan, to discourage mixed marriages, and in 1930 were enlisted in
Oakville,
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
, to intimidate
Isabella Jones and Ira Junius Johnson out of marrying.
United States

The historical taboo surrounding white–black relationships among American whites can be seen as a historical consequence of the oppression and
racial segregation
Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crimes against hum ...
of African Americans. In many U.S. states, interracial marriage was already illegal when the term ''miscegenation'' was coined in 1863. (Before that, it was called "amalgamation".) The first laws banning interracial marriage were introduced in the late 17th century in the slave-holding colonies of Virginia (1691) and Maryland (1692). Later these laws also spread to colonies and states where slavery did not exist.
Although vehemently opposed to miscegenation in public,
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was previously the natio ...
fathered his slave
Sally Hemings
Sarah "Sally" Hemings ( 1773 – 1835) was an enslaved woman with one-quarter African ancestry owned by president of the United States Thomas Jefferson, one of many he inherited from his father-in-law, John Wayles.
Hemings's mother Elizabet ...
child. Regarding blacks as "inferior to the whites in the endowments of both body and mind", Jefferson, in his ''
Notes on the State of Virginia
''Notes on the State of Virginia'' (1785) is a book written by the American statesman, philosopher, and planter Thomas Jefferson. He completed the first version in 1781 and updated and enlarged the book in 1782 and 1783. It originated in Jeffers ...
'' published in 1785, would also write: "The improvement of the blacks in body and mind, in the first instance of their mixture with the whites, has been observed by every one, and proves that their inferiority is not the effect merely of their condition of life".
In the early nineteenth century, the Quaker planter
Zephaniah Kingsley
Zephaniah Kingsley Jr. (December 4, 1765 – September 14, 1843) was a Quaker, born in England, who moved as a child with his family to South Carolina, and became a planter, slave trader, and merchant. He built four plantations in the Spanish co ...
published a pamphlet, which defended miscegenation, the pamphlet was reprinted three times. According to him, mixed-race children are healthier and more beautiful. He also claimed to be married to
a slave who he bought in Cuba at the age of 13, though the marriage did not take place in the United States, and there is no evidence of it other than Kingsley's statement. He was eventually forced to leave the United States and move to the
Mayorasgo de Koka plantation in Haiti (now
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
).

In 1918, there was considerable controversy in
Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
when an Asian-Indian farmer B. K. Singh married the sixteen-year-old daughter of one of his white tenants.
During and after slavery, most American whites regarded interracial marriage between whites and blacks as taboo. However, during slavery, many white American men and women did conceive children with black partners. Some children were freed by their slave-holding fathers or bought to be emancipated if the father was not the owner. Most mixed-raced descendants merged into the African-American ethnic group during the
Jim Crow era.
Initially,
Filipino Americans
Filipino Americans ( fil, Mga Pilipinong Amerikano) are Americans of Filipino ancestry. Filipinos and other Asian ethnicities in North America were first documented in the 16th century as slaves and prisoners on ships sailing to and from New ...
were considered white and were not barred from interracial marriage, with documented instances of interracial marriage of Filipino men and White women in Louisiana and Washington, D.C. However, by the late 19th century and early 20th century in California, Filipinos were barred from marrying white women through a series of court cases that redefined their racial interpretation under the law. During World War II, Filipino servicemen in California had to travel with their White fiancees to New Mexico, to be able to marry.
After the Civil War and the
abolition of slavery in 1865, the marriage of white and black Americans continued to be taboo, particularly in the former slave states.
The Motion Picture
Production Code
The Motion Picture Production Code was a set of industry guidelines for the self-censorship of content that was applied to most motion pictures released by major studios in the United States from 1934 to 1968. It is also popularly known as the ...
of 1930, also known as
Hays Code
The Motion Picture Production Code was a set of industry guidelines for the self-censorship of content that was applied to most motion pictures released by major studios in the United States from 1934 to 1968. It is also popularly known as the ...
, explicitly stated that the depiction of "miscegenation ... is forbidden".
One important strategy intended to discourage the marriage of white Americans and Americans of partly African descent was the promulgation of the
one-drop theory
The one-drop rule is a legal principle of racial classification that was prominent in the 20th-century United States. It asserted that any person with even one ancestor of black ancestry ("one drop" of "black blood")Davis, F. James. Frontlin"W ...
, which held that any person with any known African ancestry, however remote, must be regarded as black. This definition of blackness was encoded in the anti-miscegenation laws of various U.S. states, such as Virginia's
Racial Integrity Act of 1924
In 1924, the Virginia General Assembly enacted the Racial Integrity Act. The act reinforced racial segregation by prohibiting interracial marriage and classifying as "white" a person "who has no trace whatsoever of any blood other than Caucasia ...
. The plaintiffs in ''
Loving v. Virginia'',
Mildred Jeter and
Richard Loving
Mildred Delores Loving (née Jeter; July 22, 1939 – May 2, 2008) and her husband Richard Perry Loving (October 29, 1933 – June 29, 1975) were an American married couple who were the plaintiffs in the landmark U.S. Supreme Court case '' Lov ...
became the historically most prominent interracial couple in the US through their legal struggle against this act.

Throughout
American history
The history of the lands that became the United States began with the arrival of Settlement of the Americas, the first people in the Americas around 15,000 BC. Native American cultures in the United States, Numerous indigenous cultures formed ...
, there has been frequent mixing between Native Americans and black Africans. When Native Americans invaded the European colony of Jamestown, Virginia in 1622, they killed the Europeans but took the African slaves as captives, gradually integrating them. Interracial relationships occurred between African Americans and members of other tribes along coastal states. During the transitional period of Africans becoming the primary race enslaved, Native Americans were sometimes enslaved with them. Africans and Native Americans worked together, some even intermarried and had mixed children. The relationship between Africans and Native-Americans was seen as a threat to Europeans and European-Americans, who actively tried to divide Native-Americans and Africans and put them against each other.
During the 18th Century, some Native American women turned to freed or runaway African men due to a major decline in the male population in Native American villages. At the same time, the early slave population in America was disproportionately male. Records show that some Native American women bought African men as slaves. Unknown to European sellers, the women freed and married the men into their tribe. Some African men chose Native American women as their partners because their children would be free, as the child's status followed that of the mother. The men could marry into some of the matrilineal tribes and be accepted, as their children were still considered to belong to the mother's people. As European expansion increased in the Southeast, African and Native American marriages became more numerous.
From the mid 19th to the mid 20th century, many black people and ethnic Mexicans intermarried with each other in the Lower Rio Grande Valley in South Texas (mostly in Cameron County and Hidalgo County). In Cameron County, 38% of black people were interracially married (7/18 families) while in Hidalgo County the number was 72% (18/25 families). These two counties had the highest rates of interracial marriages involving at least one black spouse in the United States. The vast majority of these marriages involved black men marrying ethnic Mexican women or first generation Tejanas (Texas-born women of Mexican descent). Since ethnic Mexicans were considered white by Texas officials and the U.S. government, such marriages were a violation of the state's anti-miscegenation laws. Yet, there is no evidence that anyone in South Texas was prosecuted for violating this law. The rates of this interracial marriage dynamic can be traced back to when black men moved into the Lower Rio Grande Valley after the Civil War ended. They married into ethnic Mexican families and joined other black people who found sanctuary on the U.S./Mexico border.

From the mid 19th century to the 20th century, the several hundred thousand Chinese men who migrated were almost entirely of Cantonese origin, mostly from Taishan.
Anti-miscegenation laws prohibited Chinese men from marrying white women in many states. After the
Emancipation Proclamation, many intermarriages in some states were not recorded and historically, Chinese American men married African American women in proportions that were higher than their total marriage numbers due to the fact that few Chinese American women lived in the United States. After the Emancipation Proclamation, many Chinese Americans migrated to the
Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
, particularly to
Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
, to work on plantations. For example, in 1880, the tenth
US Census of
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
alone noted 57% of all interracial marriages were between Chinese men and black women and 43% of them were between Chinese men and white women.
Between 20 and 30 percent of the Chinese who lived in Mississippi married black women before 1940. In a genetic study of 199 samples from African American males found one belong to haplogroup O2a ( or 0.5% ) It was discovered by historian
Henry Louis Gates, Jr
Henry Louis "Skip" Gates Jr. (born September 16, 1950) is an American literary critic, professor, historian, and filmmaker, who serves as the Alphonse Fletcher University Professor and Director of the Hutchins Center for African and African Amer ...
in the ''
African American Lives'' documentary miniseries that
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
astronaut
Mae Jemison has a significant (above 10%) genetic
East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
n admixture. Gates speculated that the intermarriage/relations between migrant Chinese workers and black, or African-American slaves or ex-slaves during the 19th century might have contributed to her ethnic and genetic make-up.
In the mid 1850s, 70 to 150 Chinese were living in New York City and 11 of them married Irish women. In 1906 the ''New York Times'' (6 August) reported that 300 white women (Irish American) were married to Chinese men in New York, with many more cohabiting. In 1900, based on Liang's research, of the 120,000 men in more than 20 Chinese communities in the United States, he estimated that one out of every twenty Chinese men (Cantonese) was married to a white woman. In the 1960s census showed 3500 Chinese men married to white women and 2900 Chinese women married to white men.
Before the Civil War, accusations of support for miscegenation were commonly made against Abolitionists by defenders of slavery. After the war, similar charges were made against advocates of equal rights for African Americans by white
segregationists
Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into racial or other ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crime against humanity under the Statute of the Internati ...
. According to these accusations, they were said to be
secretly plotting the destruction of the white race through the promotion of miscegenation. In the 1950s, segregationists alleged that a
Communist plot to promote miscegenation in order to hasten the takeover of the United States was being funded by the government of the Soviet Union. In 1957, segregationists cited the
anti-semitic hoax ''
A Racial Program for the Twentieth Century
''A Racial Program for the Twentieth Century'' (occasionally ''A Radical Program for the Twentieth Century'') was a hoax that first gained public notoriety on June 7, 1957, during a debate on the Civil Rights Act of 1957, when Rep. Thomas Abern ...
'' as a source of evidence which proved the supposed validity of these claims.
Anti-amalgamation cartoons, such as those which were published by
Edward William Clay, were "elaborately exaggerated anti-abolitionist fantasies" in which black and white people were depicted as "fraternizing and socializing on equal terms."
[Bateman, David A. "Transatlantic Anxieties: Democracy and Diversity in Nineteenth-Century Discourse." Studies in American Political Development, 33 (October 2019), 139–177. ] Jerome B. Holgate's ''
A Sojourn in the City of Amalgamation'' "painted a future in which sexual amalgamation was in fashion."
Bob Jones University
, motto_lang = Latin
, mottoeng = We seek, we trust
, top_free_label =
, top_free =
, type = Private university
, established =
, closed =
, f ...
banned interracial dating until 2000.
Asians were specifically included in the anti-miscegenation laws of some states. California continued to ban Asian/white marriages until the ''
Perez v. Sharp
''Perez v. Sharp'', also known as ''Perez v. Lippold'' or ''Perez v. Moroney'', is a 1948 case decided by the Supreme Court of California in which the court held by a 4–3 majority that the state's ban on interracial marriage violated the Fourteen ...
'' decision in 1948.

In the United States, segregationists, including modern-day
Christian Identity
Christian Identity (also known as Identity Christianity) is an interpretation of Christianity which advocates the belief that only Celtic and Germanic peoples, such as the Anglo-Saxon, Nordic nations, or Aryan people and people of kindred blood, ...
groups, have claimed that several passages in the
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts ...
,
such as the stories of
Phinehas
According to the Hebrew Bible, Phinehas or Phineas (; , ''Phinees'', ) was a priest during the Israelites’ Exodus journey. The grandson of Aaron and son of Eleazar, the High Priests (), he distinguished himself as a youth at Shittim with h ...
(see
Phineas Priesthood), the
Curse and mark of Cain
The curse of Cain and the mark of Cain are phrases that originated in the story of Cain and Abel in the Book of Genesis. In the stories, if someone harmed Cain, the damage would come back sevenfold. Some interpretations view this as a physical ...
, and the
curse of Ham
The curse of Ham is described in the Book of Genesis as imposed by the patriarch Noah upon Ham's son Canaan. It occurs in the context of Noah's drunkenness and is provoked by a shameful act perpetrated by Noah's son Ham, who "saw the nakedness o ...
, should be understood as referring to miscegenation and they also believe that certain verses in the Bible expressly forbid it.
Interracial marriage has gained more acceptance in the United States since the
civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional racial segregation, discrimination, and disenfranchisement throughout the Unite ...
.
Approval of mixed marriages in national opinion polls has risen from 4% in 1958, 20% in 1968 (at the time of the SCOTUS decision), 36% in 1978, to 48% in 1991, 65% in 2002, 77% in 2007, and 86% in 2011. The most notable American of mixed race is the former
President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
,
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the ...
, who is the product of a mixed marriage between a black father and a white mother. Nevertheless, as late as 2009, a
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
justice of the peace refused to issue a marriage license to an interracial couple, justifying the decision on grounds of concern for any future children which the couple might have.
=Hawaii
=
The majority of Hawaiian Chinese were Cantonese-speaking migrants from Guangdong but a minority of them were Hakka. If all people with Chinese ancestry in Hawaii (including the Chinese-Hawaiians) are included, they form about 1/3 of Hawaii's entire population. A large percentage of Chinese immigrants married native-Hawaiian, European, and multi-racial Hawaiians. Intermarriage started to decline in the 1920s.
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
Hawaiians and others of European ancestry often married Chinese immigrants and their descendants. Birth records and census data from the 1930s demonstrate that children of mixed-parentage were often classified by only their father's ethnic identity, such as with 38 recorded births in between 1932 and 1933 to Portuguese-Chinese where the father was Chinese, reflecting American attitudes on racial purity.
[ A large amount of mingling took place between the Chinese community in Hawaii, with many Chinese-Hawaiians marrying people from the Portuguese, Spanish, Hawaiian, Caucasian-Hawaiian, and other communities. Intermarrages in Hawaii were also documented between the Chinese and Puerto Rican, Portuguese, Japanese, Greek, and mixed-race individuals.
]
Mexico
 In Mexico, the concept of ''
In Mexico, the concept of ''mestizaje
(; ; fem. ) is a term used for racial classification to refer to a person of mixed European and Indigenous American ancestry. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though thei ...
'' (or ''the cultural and racial amalgamation'') is an integral part of the country's identity. While frequently seen as a mixture of the indigenous and Spanish, Mexico has had a notable admixture of indigenous and black Africans since the Colonial era. The Catholic Church never opposed interracial marriages, although individuals had to declare their racial classification in the parish marital register.
Cuba
120,000 Cantonese coolies (all males) entered Cuba under contract for 80 years. Most did not marry, but Hung Hui (1975:80) states there was a frequency of sexual activity between black women and Cantonese coolies. According to Osberg, (1965:69) the Chinese often bought slave women and freed them, expressly for marriage. In the 19th and 20th centuries, Chinese men (Cantonese) engaged in sexual activity with white and black Cuban women, resulting in many children. (For a British Caribbean model of Chinese cultural retention through procreation with black women, see Patterson, 322–31). In the 1920s an additional 30000 Cantonese and small groups of Japanese arrived. Both immigrations were exclusively male, and there was rapid mingling with white, black, and mulato populations. In the CIA World Factbook: Cuba (15 May 2008) the authors estimated 114,240 people with Chinese-Cuban ancestry and only 300 pure Chinese. In the study of genetic origin, admixture, and asymmetry in maternal and paternal human lineages in Cuba, 35 Y-chromosome SNPs were typed in the 132 male individuals of the Cuban sample. The study did not include any people with some Chinese ancestry. All the samples were white and black Cubans. 2 out of 132 male samples belong to East Asian Haplogroup O2 which is found in significant frequencies among Cantonese people.
El Salvador
In El Salvador, there was frequent intermarriage between black male slaves and Amerindian women. Many of these slaves intermarried with Amerindian women in hopes of gaining freedom (if not for themselves, then their offspring). Many mixed African and Amerindian children resulted from these unions. The Spanish tried to prevent such Afro-Amerindian unions, but the mixing of the two groups could not be prevented. Slaves continued to pursue natives with the prospect of freedom. According to Richard Price's book ''Maroon Societies'' (1979), it is documented that during the colonial period that Amerindian women would rather marry black men than Amerindian men, and that black men would rather marry Amerindian women than black women so that their children will be born free. Price quoted this from a history by H.H. Bancroft published in 1877 referring to colonial Mexico. El Salvador's African population lived under similar circumstances, and the mixing between black men and native women was common during colonial times.
Guatemala
There were many instances when black and mulatto men would intermarry with Mayan and other native women in Guatemala. These unions were more common in some regions than others. In Escuintla (called Escuintepeque at the time), the Pipil-speaking natives who lived at higher elevations tended to live away from the lowland coastal hot lands where black and mulatto men were concentrated. Yet, as black men grew in number during this period (1671–1701), a tendency developed for them to marry native women. In Zapotitlán (also known as Suchitepéquez), Spaniards were proportionately more significant than in Escuintla. Thus the smaller African population had less opportunity for endogamy
Endogamy is the practice of marrying within a specific social group, religious denomination, caste, or ethnic group, rejecting those from others as unsuitable for marriage or other close personal relationships.
Endogamy is common in many cultu ...
and was disappearing by the early 18th Century as blacks married Mayans and mulattoes married mestizos and lower-ranking Spaniards. Finally in Guazacapán, a Pipil district that was 10% non-native, church marriages between Mayas or Pipils and free mulattoes were rare. But black men frequently married Mayan women in informal unions, which resulted in a significant population of mestizaje here and throughout the coastal region. In the Valle de las Vacas, black male slaves also intermarried with Mayan women.
Costa Rica
The Chinese in Costa Rica originated from Cantonese male migrants. Pure Chinese make up only 1% of the Costa Rican population but, according to Jacqueline M. Newman, as much as ten percent of the people in Costa Rica are Chinese, if counting the people who are Chinese, married to a Chinese, or of mixed Chinese descent. Most Chinese immigrants since then have been Cantonese, but in the last decades of the 20th century, a number of immigrants have also come from Taiwan. Many men came alone to work, married Costa Rican women, and speak Cantonese. However, the majority of the descendants of the first Chinese immigrants no longer speak Cantonese and think of themselves as full Costa Ricans. They married Tican women (who are a blend of European, Castizo, Mestizo, Indian, Black). A Tican is also a white person with a small amount of non-white blood, like Castizo. The 1989 census shows about 98% of Costa Ricans were either White, Castizo, Mestizos, with 80% being White or Castizo. Up to the 1940s men made up the vast majority of the Costa Rican Chinese community. Males made up the majority of the original Chinese community in Mexico and they married Mexican women.
Jamaica and Haiti
In Haiti, there is a sizable percentage within the minority who are of Asian descent. Haiti is also home to Marabou peoples, a half East Indian and half African people who descent from East Indian immigrants who arrived from other Caribbean nations, such Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in ...
and Guadeloupe and African slave descendants. Most present-day descendants of the original Marabou are products of hypodescent
In societies that regard some races or ethnic groups of people as dominant or superior and others as subordinate or inferior, hypodescent refers to the automatic assignment of children of a mixed union to the subordinate group. The opposite pract ...
and, subsequently, mostly of African in ancestry.
The country also has a sizable Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
and Chinese Haitian population. One of the country's most notable Afro-Asians is the late painter Edouard Wah who was born to a Chinese immigrant father and Afro-Haitian mother.
When black and Indian women had children with Chinese men the children were called chaina raial in Jamaican English. The Chinese community in Jamaica was able to consolidate because an openness to marrying Indian women was present in the Chinese since Chinese women were in short supply. Women sharing was less common among Indians in Jamaica according to Verene A. Shepherd. The small number of Indian women were fought over between Indian men and led to a rise in the amount of wife murders by Indian men. Indian women made up 11 percent of the annual amount of Indian indentured migrants from 1845 to 1847 in Jamaica. Thousands of Chinese men and Indian men married local Jamaican women. The study "Y-chromosomal diversity in Haiti and Jamaica: Contrasting levels of sex-biased gene flow" shows the paternal Chinese haplogroup O-M175 at a frequency of 3.8% in local Jamaicans ( non-Chinese Jamaicans) including the Indian H-M69 (0.6%) and L-M20 (0.6%) in local Jamaicans. Among the country's most notable Afro-Asians are reggae
Reggae () is a music genre that originated in Jamaica in the late 1960s. The term also denotes the modern popular music of Jamaica and its diaspora. A 1968 single by Toots and the Maytals, " Do the Reggay" was the first popular song to use ...
singers Sean Paul, Tami Chynn
Tammar Annika Chin (born 14 June 1983), known by her stage name Tami Chynn, is a Jamaican singer, songwriter, and dancer.
Early life
Chynn was born in Kingston, Jamaica. Her father, Richard Chin, is of Jamaican and Chinese descent and her mother ...
and Diana King
Diana King (born 8 November 1970) is a Jamaican-American singer-songwriter who performs a mixture and fusion of reggae, reggae fusion and dancehall. They were born to an Indo-Jamaican mother and an Afro-Jamaican father. They are best known f ...
.
South America
Latin America and the Caribbean
 About 300,000 Cantonese
About 300,000 Cantonese coolie
A coolie (also spelled koelie, kuli, khuli, khulie, cooli, cooly, or quli) is a term for a low-wage labourer, typically of South Asian or East Asian descent.
The word ''coolie'' was first popularized in the 16th century by European traders acros ...
s and migrants (almost all males) migrated during 1849–1874 to Latin America; many of them intermarried and cohabited with the Black, Mestizo, and European population of Cuba, Peru, Guyana, and Trinidad.
In addition, Latin American societies also witnessed growth in both Church-sanctioned and common law marriages between Africans and the non-colored.
Argentina
In Buenos Aires in 1810, only 2.2 percent of African men and 2.5 percent of African women were married to the non-colored (white). In 1827, the figures increased to 3.0 percent for men and 6.0 percent for women. Racial mixing increased even further as more African men began enlisting in the army. Between 1810 and 1820 only 19.9% of African men were enlisted in the army. Between 1850 and 1860, this number increased to 51.1%. This led to a sexual imbalance between African men and women in Argentina. Unions between African women and non-colored men became more common in the wake of massive Italian immigration to the country. This led one African male editorial commentator to quip that, given to the sexual imbalance in the community, black women who "could not get bread would have to settle for pasta".
Bolivia
During the colonial period, many black people often intermarried with the native population (mostly Aymara
Aymara may refer to:
Languages and people
* Aymaran languages, the second most widespread Andean language
** Aymara language, the main language within that family
** Central Aymara, the other surviving branch of the Aymara(n) family, which today ...
). The result of these relationships was the blending between the two cultures (Aymara and Afro-Bolivian
Afro-Bolivians are Bolivian people of Sub-Saharan African heritage and therefore the descriptive "Afro-Bolivian" may refer to historical or cultural elements in Bolivia thought to emanate from their community. It can also refer to the combining of ...
).
After Bolivia's Agrarian Reform of 1953, black people (like indigenous people) migrated from their agricultural villages to the cities of La Paz, Cochabamba
Cochabamba ( ay, Quchapampa; qu, Quchapampa) is a city and municipality in central Bolivia in a valley in the Andes mountain range. It is the capital of the Cochabamba Department and the fourth largest city in Bolivia, with a population of 630 ...
, and Santa Cruz in search of better educational and employment opportunities. Related to this, black individuals began intermarrying with people of lighter skin coloring such as blancos (whites) and mestizos. This was done as a means of better integration for themselves, and especially their children, into Bolivian society.
Brazil
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
is the most populated country in Latin America as well as one of the most racially diverse. According to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, Brazil's racial composition is 48% white (92 million) 44% pardo
''Pardos'' (feminine ''pardas'') is a term used in the former Portuguese and Spanish colonies in the Americas to refer to the triracial descendants of Southern Europeans, Amerindians and West Africans. In some places they were defined as ne ...
(83 million) 7% black (13 million) 0.50% yellow (1.1 million).pardo
''Pardos'' (feminine ''pardas'') is a term used in the former Portuguese and Spanish colonies in the Americas to refer to the triracial descendants of Southern Europeans, Amerindians and West Africans. In some places they were defined as ne ...
category denotes a mixed or multiracial composition. However, it could be further broken down into terms based on the main racial influences on an individual's phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
.
Brazil's systematic collection of data on race is considered to be one of the most extensive in the region. However, the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) has been continuously criticized for its method of measuring racial demographics. An important distinction is that Brazil collects data based on color, not race. Thus the 'pardo' category does not actually pertain to a specific phenotype, only to the color of the individual. This means that a 'pardo' person can range from somebody with white and Amerindian ancestry to someone with African and Portuguese ancestry. There is an obvious difference between these two phenotypes
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or phenotypic trait, traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (biology), morphology or physical form and structure, its Developmental biology, dev ...
that are not represented by the umbrella term of 'pardo'. There have been many studies focusing on the significance of the IBGE's focus on color rather than race. Ellis Monk has published research illustrating the implications of this racial framework on Brazilian society from a sociological perspective. In a discussion of how the government's implementation of a dichotomous white – non-white (mixed races, along with black and Amerindians) He states: "The Brazilian government, beginning in the 1990s, even led campaigns urging Brazilians to view themselves as racially dichotomous, as black or white on the basis of African ancestry, regardless of the color of their skin".Casa-Grande & Senzala
''Casa-Grande e Senzala'' ( en, The Masters and the Slaves, italic=yes) is a book published in 1933 by Gilberto Freyre, about the formation of Brazilian society. The '' casa-grande'' ("big house") refers to the slave owner's residence on a sugarca ...
'', sociologists have looked at Brazil as having a unique colonial history where interracial relations were accepted without religious or class prejudices. Freyre says:The sentiment of nationality in the Brazilian has been deeply affected by the fact that the feudal system did not here permit of a State that was wholly dominant or a Church that was omnipotent, as well as by the circumstance of miscegenation as practiced under the wing of that system and at the same time practiced against it, thus rendering less easy the absolute identification of the ruling class with the pure or quasi-pure European stock of the principal conquerors, the Portuguese. The result is a national sentiment tempered by a sympathy for the foreigner that is so broad as to become, practically, universalism. It would, indeed, be impossible to conceive of a people marching onward toward social democracy that in place of being universal in its tendencies should be narrowly exclusive or ethnocentric.
For Freyre, lack of sexual prejudices incentivized racial mixing that produces the wide genetic variety we see today. Portuguese men married and had children with indigenous and African women. The societal consequences of this are that a marked diversification of skin colors occur, blurring the racial ancestry of those considered to have 'mixed race. The increase of influence of one race over another in producing a Brazilian phenotype happened in stages. For example, immigration policy loosened in the late 1940s resulting in the influx of multiple European communities that are now considered to have 'whitened' Brazilian communities in the north and northeast.
British West Indies
Miscegenation has never been illegal in the British West Indies, and the populations of Guyana, Belize, Jamaica,
Peru
About 100,000 Chinese coolies (almost all males) from 1849 to 1874 migrated to Peru and intermarried with Peruvian women of Mestizo, European, Amerindian, European/Mestizo, African and mulatto origin. Thus, many Peruvian Chinese today are of mixed Chinese, Spanish, African, or Amerindian ancestry. One estimate for the Chinese-Peruvian mixture is about 1.3–1.6 million. Asian Peruvians are estimated to be 3% of the population, but one source places the number of citizens with some Chinese ancestry at 4.2 million, which equates to 15% of the country's total population. In Peru, non-Chinese women married the mostly male Chinese coolies.
Among the Chinese migrants who went to Peru and Cuba there were almost no women. Some Peruvian women married Chinese male migrants.
Asia
Inter-ethnic marriage in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
dates back to the spread of Indian culture
Indian culture is the heritage of social norms, ethical values, traditional customs, belief systems, political systems, artifacts and technologies that originated in or are associated with the ethno-linguistically diverse India. The term al ...
, Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
to the region. From the 1st century onwards, mostly male traders and merchants from the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
frequently intermarried with the local female populations in Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
, Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, Champa, Central Siam, the Malay Peninsula, and Malay Archipelago. Many Indianized kingdoms arose in Southeast Asia during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
.
From the 9th century onwards, a large number of mostly male Arab traders from the Middle East settled down in the Malay Peninsula and Malay Archipelago, and they intermarried with the local Malay, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
n and female populations in the islands later called the Philippines. This contributed to the spread of Islam in Southeast Asia
Islam is the most widely practised religion in Southeast Asia, numbering approximately 240 million adherents which translate to about 42% of the entire population, with majorities in Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia as well parts of Southern Thail ...
.Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
and Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
traders settled down within the maritime kingdoms of Southeast Asia and intermarried with the local female populations. This tradition continued among Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
traders who also intermarried with the local populations. In the 16th and 17th centuries, thousands of Japanese people
The are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago."人類学上は,旧石器時代あるいは縄文時代以来,現在の北海道〜沖縄諸島(南西諸島)に住んだ集団を祖先にもつ人々。" () Jap ...
also travelled to Southeast Asia and intermarried with the local women there.[
From the tenth to twelfth century, ]Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
women were to be found in Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
(Canton), some of them in the tenth century like Mei Zhu in the harem of the Emperor Liu Chang, and in the twelfth century large numbers of Persian women lived there, noted for wearing multiple earrings and "quarrelsome dispositions".Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bod ...
lived in Guangzhou's foreign quarter, they were all called "Persian women" (波斯婦 Po-ssu-fu or Bosifu).
Some scholars did not differentiate between Persian and Arab, and some say that the Chinese called all women coming from the Persian Gulf "Persian Women".
The exact number of Amerasians in Vietnam are not known. The U.S soldiers stationed in Vietnam had relationships with locals females, many of the women had origins from clubs, brothels and pubs. The American Embassy once reported there were less than a 1,000 Amerasians. A report by the South Vietnamese Senate Subcommittee suggested there are 15,000 to 20,000 children of mixed American and Vietnamese blood, but this figure was considered low. Congress estimated 20,000 to 30,000 Amerasians by 1975 lived in Vietnam. According to ''Amerasians Without Borders'', they estimated about 25,000 to 30,000 Vietnamese Amerasians were born from American first participation in Vietnam in 1962, and lasted until 1975. Although during the Operation Babylift it was estimated at 23,000.
In the 19th century and early 20th century, there was a network of small numbers of Chinese and Japanese prostitutes being trafficked across Asia, in countries such as China, Japan, Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, in what was then known as the "Yellow Slave Traffic". There was also a network of prostitutes from continental Europe being trafficked to India, Ceylon, Singapore, China and Japan at around the same time, in what was then known as the "White Slave Traffic".Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
soldiers engaged in war rape
Wartime sexual violence is rape or other forms of sexual violence committed by combatants during armed conflict, war, or military occupation often as spoils of war, but sometimes, particularly in ethnic conflict, the phenomenon has broader so ...
during their invasions across East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
and Southeast Asia. Some Indo Dutch women, captured in Dutch colonies in Asia, were forced into sexual slavery. More than 20,000 Indonesian women and nearly 300 Dutch women were so treated. A estimated 1000 Timor
Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is divided between the sovereign states of East Timor on the eastern part and Indonesia on the western part. The Indonesian part, also ...
women and girls who also used as sexual slaves. Melanesian women from New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
were also used as comfort women by the Japanese military and as well married Japanese, forming a small number of mixed Japanese-Papuan women born to Japanese fathers and Papuan mothers.East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-west ...
and West Papua caused the murders of approximately 300,000 to 400,000 West Papuans and many thousands of women raped.
Sex tourism has emerged in the late 20th century as a controversial aspect of Western tourism and globalization. Sex tourism is typically undertaken internationally by tourists from wealthier countries. Author Nils Ringdal alleges that three out of four men between the ages of 20 and 50 who have visited Asia or Africa have paid for sex.
Female sex tourism
Female sex tourism is sex tourism by women who travel intending to engage in sexual activities with one or more locals, usually male sex workers. Female sex tourists may seek aspects of the sexual relationship not typically shared by male sex ...
also emerged in the late 20th century in Bali. Tens of thousands of single women throng the beaches of Bali in Indonesia every year. For decades, young Balinese men have taken advantage of the louche and laid-back atmosphere to find love and lucre from female tourists—Japanese, European and Australian for the most part—who by all accounts seem perfectly happy with the arrangement.
Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
ns have descended from a mixture of various peoples, such as the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
, Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
, and Iranians. The Mongol conquest of Central Asia in the 13th century resulted in the mass killings of the Iranian-speaking people and Indo-Europeans population of the region, their culture and languages being superseded by that of the Mongolian-Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging t ...
. The remaining surviving population intermarried with invaders. Genetic shows a mixture of East Asian and Caucasian ancestry in all Central Asian people.
Afghanistan
Genetic analysis of the Hazara people
The Hazaras ( fa, , Həzārə; haz, , Āzərə) are an ethnic group and the principal component of the population of Afghanistan, native to, and primarily residing in the Hazaristan (Hazarajat) region in central Afghanistan and generally scatt ...
indicate partial Mongolian ancestry. Invading Mongols and Turco-Mongol
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century, among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these Khanates eventuall ...
s mixed with the local Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
population, forming a distinct group. Mongols settled in what is now Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
and mixed with native populations who spoke Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
. A second wave of mostly Chagatai Mongols came from Central Asia and were followed by other Mongolic groups, associated with the Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm ...
and the Timurids
The Timurid Empire ( chg, , fa, ), self-designated as Gurkani ( Chagatai: کورگن, ''Küregen''; fa, , ''Gūrkāniyān''), was a PersianateB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Online Edition, 2006 Turco-Mongol empire ...
, all of whom settled in Hazarajat and mixed with the local, mostly Persian-speaking population, forming a distinct group.
The analysis also detected Sub-Saharan African lineages in both the paternal and maternal ancestry of Hazara. Among the Hazaras there are 7.5% of African mtDNA haplogroup L with 5.1% of African Y-DNA B.
China
Intermarriage was initially discouraged by the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdom ...
. In 836 Lu Chun was appointed as governor of Canton, he was disgusted to find Chinese living with foreigners and intermarriage between Chinese and foreigners. Lu enforced separation, banning interracial marriages, and made it illegal for foreigners to own property. Lu Chun believed his principles were just and upright.Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
allowed third-generation immigrants with official titles to intermarry with Chinese imperial princesses.Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
women were to be found in Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
(Canton), some of them in the tenth century like Mei Zhu in the harem of the Emperor Liu Chang, and in the twelfth century large numbers of Persian women lived there, noted for wearing multiple earrings and "quarrelsome dispositions".Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bod ...
lived in Guangzhou's foreign quarter; they were all called "Persian women" (波斯婦; Po-szu-fu or Bosifu). Iranian female dancers were in demand in China during this period. During the Sui dynasty, ten young dancing girls were sent from Persia to China. During the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdom ...
bars were often attended by Iranian or Sogdian waitresses who performed dances for clients.Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
in 1368, this led to a violent Chinese backlash against West and Central Asians. In order to contain the violence, both Mongol and Central Asian Semu Muslim women and men of both sexes were required by Ming Code to marry Han Chinese after the first Ming Emperor Hongwu
Hongwu () (23 January 1368 – 5 February 1399) was the era name of the Hongwu Emperor, the founder of the Ming dynasty of China. Hongwu was also the Ming dynasty's first era name.
Comparison table
Other eras contemporaneous with Hongwu
* C ...
passed the law in Article 122.
Han women who married Hui men became Hui, and Han men who married Hui women also became Hui.
Of the Han Chinese Li family in Quanzhou, Li Nu Lin Nu (林駑, Xiao'erjing: ) was a Chinese merchant and scholar in the early Ming dynasty. He is the ancestor of the philosopher Li Zhi. His family was Han Chinese in origin and the branch that remained true to Han culture cut off the Lin Nu's bra ...
, the son of Li Lu, visited Hormuz in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
in 1376, married a Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
or an Arab girl, and brought her back to Quanzhou. He then converted to Islam. Li Nu was the ancestor of the Ming Dynasty reformer Li Chih.Xunhua
Xunhua Salar Autonomous County ( zh, s=循化撒拉族自治县, p=Xúnhuà Sǎlázú Zìzhìxiàn; slr, Gökhdengiz Velayat Yisyr Salyr Özbashdak Yurt) is a Salar autonomous county in the southeast of Haidong Prefecture of Qinghai Province, C ...
, Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
in the early Ming dynasty, they converted Tibetan women to Islam and the Tibetan women were taken as wives by Salar men. A Salar wedding ritual where grains and milk were scattered on a horse by the bride was influenced by Tibetans. After they moved into northern Tibet, the Salars originally practiced the same Gedimu
Gedimu () or ''Qadim'' ( ar, قديم}) is the earliest school of Islam in China. It is a Hanafi, non-Sufi school of the Sunni tradition. Its supporters are centered on local mosques, which function as relatively independent units.
It is numerical ...
(Gedem) variant of Sunni Islam as the Hui people and adopted Hui practices like using the Hui Jingtang Jiaoyu Islamic education during the Ming dynasty which derived from Yuan dynasty Arabic and Persian primers. One of the Salar primers was called "Book of Diverse Studies" (雜學本本 Zaxue Benben) in Chinese. The version of Sunni Islam practiced by Salars was greatly impacted by Salars marrying with Hui who had settled in Xunhua. The Hui introduced new Naqshbandi Sufi orders like Jahriyya and Khafiyya to the Salars and eventually these Sufi orders led to sectarian violence involving Qing soldiers (Han, Tibetans and Mongols) and the Sufis which included the Chinese Muslims (Salars and Hui). Ma Laichi brought the Khafiyya Naqshbandi order to the Salars and the Salars followed the Flowered mosque order (花寺門宦) of the Khafiyya. He preached silent dhikr and simplified Qur'an readings bringing the Arabic text Mingsha jing (明沙經, 明沙勒, 明沙爾 Minshar jing) to China.
The Kargan Tibetans, who live next to the Salar, have mostly become Muslim due to the Salars. The Salar oral tradition recalls that it was around 1370 in which they came from Samarkand to China. The later Qing dynasty and Republic of China Salar General Han Youwen
Han Youwen (; October 1912 – February 22, 1998) was an ethnic Salar Muslim General in the National Revolutionary Army of the Republic of China, born in Hualong Hui Autonomous County, Qinghai. His Muslim name was Muhammad Habibullah ().
Caree ...
was born to a Tibetan woman named Ziliha (孜力哈) and a Salar father named Aema (阿额玛).
Tibetan women were the original wives of the first Salars to arrive in the region as recorded in Salar oral history. The Tibetans agreed to let their Tibetan women marry Salar men after putting up several demands to accommodate cultural and religious differences. Hui and Salar intermarry due to cultural similarities and following the same Islamic religion. Older Salars married Tibetan women but younger Salars prefer marrying other Salars. Han and Salar mostly do not intermarry with each other unlike marriages of Tibetan women to Salar men. Salars however use Han surnames. Salar patrilineal clans are much more limited than Han patrilineal clans in how much they deal with culture, society or religion. Salar men often marry a lot of non-Salar women and they took Tibetan women as wives after migrating to Xunhua according to historical accounts and folk histories. Salars almost exclusively took non-Salar women as wives like Tibetan women while never giving Salar women to non-Salar men in marriage except for Hui men who were allowed to marry Salar women. As a result, Salars are heavily mixed with other ethnicities.
Salars in Qinghai live on both banks of the Yellow river, south and north, the northern ones are called Hualong or Bayan Salars while the southern ones are called Xunhua Salars. The region north of the Yellow river is a mix of discontinuous Salar and Tibetan villages while the region south of the yellow river is solidly Salar with no gaps in between, since Hui and Salars pushed the Tibetans on the south region out earlier. Tibetan women who converted to Islam were taken as wives on both banks of the river by Salar men. The term for maternal uncle (ajiu) is used for Tibetans by Salars since the Salars have maternal Tibetan ancestry. Tibetans witness Salar life passages in Kewa, a Salar village and Tibetan butter tea is consumed by Salars there as well. Other Tibetan cultural influences like Salar houses having four corners with a white stone on them became part of Salar culture as long as they were not prohibited by Islam. Hui people started assimilating and intermarrying with Salars in Xunhua after migrating there from Hezhou in Gansu due to the Chinese Ming dynasty ruling the Xunhua Salars after 1370 and Hezhou officials governed Xunhua. Many Salars with the Ma surname appear to be of Hui descent since a lot of Salars now have the Ma surname while in the beginning the majority of Salars had the Han surname. Some example of Hezhou Hui who became Salars are the Chenjia (Chen family) and Majia (Ma family) villages in Altiuli where the Chen and Ma families are Salars who admit their Hui ancestry. Marriage ceremonies, funerals, birth rites and prayer were shared by both Salar and Hui as they intermarried and shared the same religion since more and more Hui moved into the Salar areas on both banks of the Yellow river. Many Hui married Salars and eventually it became far more popular for Hui and Salar to intermarry due to both being Muslims than to non-Muslim Han, Mongols and Tibetans. The Salar language and culture however was highly impacted in the 14th-16th centuries in their original ethnogenesis by marriage with Mongol and Tibetan non-Muslims with many loanwords and grammatical influence by Mongol and Tibetan in their language. Salars were multilingual in Salar and Mongol and then in Chinese and Tibetan as they trade extensively in the Ming, Qing and Republic of China periods on the yellow river in Ningxia and Lanzhou in Gansu.
Salars and Tibetans both use the term maternal uncle (ajiu in Salar and Chinese, azhang in Tibetan) to refer to each other, referring to the fact that Salars are descendants of Tibetan women marrying Salar men. After using these terms they often repeat the historical account how Tibetan women were married by 2,000 Salar men who were the First Salars to migrate to Qinghai. These terms illustrate that Salars were viewed separately from the Hui by Tibetans. According to legend, the marriages between Tibetan women and Salar men came after a compromise between demands by a Tibetan chief and the Salar migrants. The Salar say Wimdo valley was ruled by a Tibetan and he demanded the Salars follow four rules in order to marry Tibetan women. He asked them to install on their houses's four corners Tibetan Buddhist prayer flags, to pray with Tibetan Buddhist prayer wheels with the Buddhist mantra om mani padma hum and to bow before statues of Buddha. The Salars refused those demands saying they did not recite mantras or bow to statues since they believed in only one creator god and were Muslims. They compromised on the flags in houses by putting stones on their houses' corners instead of Tibetan Buddhist prayer flags. Some Tibetans do not differentiate between Salar and Hui due to their Islamic religion. In 1996, Wimdo township only had one Salar because Tibetans whined about the Muslim call to prayer and a mosque built in the area in the early 1990s so they kicked out most of the Salars from the region. Salars were bilingual in Salar and Tibetan due to intermarriage with Tibetan women and trading. It is far less likely for a Tibetan to speak Salar. Tibetan women in Xiahe also married Muslim men who came there as traders before the 1930s.
In eastern Qinghai and Gansu there were cases of Tibetan women who stayed in their Buddhist Lamaist religion while marrying Chinese Muslim men and they would have different sons who would be Buddhist and Muslims, the Buddhist sons became Lamas while the other sons were Muslims. Hui and Tibetans married Salars.
In the frontier districts of Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the ...
, numerous half Chinese-Tibetans were found. Tibetan women were glad to marry Chinese traders and soldiers. Some Chinese traders married Tibetan girls. Traders and officials in ancient times were often forbidden to bring Chinese women with them to Tibet, so they tended to marry Tibetan women; the male offspring were considered Chinese and female offspring as Tibetan. Special names were used for these children of Chinese fathers and Tibetan mothers. They often assimilated into the Tibetan population. Chinese and Nepalese in Tibet married Tibetan women.
Chinese men also married Turkic Uyghur women in Xinjiang from 1880 to 1949. Sometimes poverty influenced Uyghur women to marry Chinese. These marriages were not recognized by local mullahs since Muslim women were not allowed to marry non-Muslim men under Islamic law. This did not stop the women because they enjoyed advantages, such as not being subject to certain taxes. Uyghur women married to the Chinese also did not have to wear a veil
A veil is an article of clothing or hanging cloth that is intended to cover some part of the head or face, or an object of some significance. Veiling has a long history in European, Asian, and African societies. The practice has been prominent ...
and they received their husband's property upon his death. These women were forbidden from being buried in Muslim graves. The children of Chinese men and Uyghur women were considered as Uyghur. Some Chinese soldiers had Uyghur women as temporary wives, and after the man's military service was up, the wife was left behind or sold, and if it was possible, sons were taken, and daughters were sold.
After the Russian Civil War, a huge number of Russians settled in the Manchuria region of China. One Chinese scholar Zhang Jingsheng wrote essays in 1924 and 1925 in various Chinese journals praising the advantages of miscegenation between Russians and Chinese, saying that interracial sex would promote greater understandings between the two peoples, and produce children with the best advantages of both peoples.[Bong, Inyoung A "White Race" without Supremacy: Russians, Racial Hybridity, and Liminality in the Chinese Literature of Manchukuo pp. 137–190 from ''Modern Chinese Literature and Culture'', Volume 26, No. 1, Spring 2014 p. 147.] Zhang argued that Russians were taller and had greater physical strength than the Han, but the Chinese were gentler and kinder than the Russians, and so intermarriage between the two peoples would ensure children with the advantages of both.Nigerian
Nigerians or the Nigerian people are citizens of Nigeria or people with ancestry from Nigeria. The name Nigeria was taken from the Niger River running through the country. This name was allegedly coined in the late 19th century by British jour ...
) traders and local Chinese women in the city of Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
where it is estimated that in 2013 there are 400 African-Chinese families.[''Christian Science Monitor'': "In China, mixed marriages can be a labor of love – In one major Chinese city, marriages between Chinese and Africans are on the rise. In a country known for monoculture, it isn't easy" By Yepoka Yeebo]
21 September 2013 The rise in mixed marriages has not been without controversy. The state, fearing fraud marriages, has strictly regulated matters. In order to obtain government-issued identification (which is required to attend school), the children must be registered under the Chinese mother's family name. Many African fathers, fearing that in doing so, they would relinquish their parental rights, have instead chosen to not send their children to school. There are efforts to open an African-Chinese school but it would first require government authorization.
=Taiwan
=
During the Siege of Fort Zeelandia
The siege of Fort Zeelandia () of 1661–1662 ended the Dutch East India Company's rule over Taiwan and began the Kingdom of Tungning's rule over the island.
Prelude
From 1623 to 1624 the Dutch had been at war with Ming China over the Pescador ...
of 1661–1662 in which Chinese Ming
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
loyalist forces commanded by Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
besieged and defeated the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
and conquered Taiwan, the Chinese took Dutch women and children prisoner. Koxinga took Hambroek's teenage daughter as a concubine, and Dutch women were sold to Chinese soldiers to become their wives. In 1684 some of these Dutch wives were still captives of the Chinese.
Some Dutch physical looks like auburn and red hair among people in regions of south Taiwan are a consequence of this episode of Dutch women becoming concubines to the Chinese commanders.
=Hong Kong
=
Many Tanka women conceived children with foreign men. Ernest John Eitel mentioned in 1889 how an important change had taken place among Eurasian girls, the offspring of illicit connections: instead of becoming concubines, they were commonly brought up respectably and married to Hong Kong Chinese husbands. Many Hong Kong born Eurasians were assimilated into the Hong Kong society by intermarriage with the Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
population. A good example of a Cantonese Eurasian is Nancy Kwan
Nancy Kwan Ka-shen (; born May 19, 1939) is a Chinese-American actress, philanthropist, and former dancer. In addition to her personality and looks, her career was benefited by Hollywood's casting of more Asian roles in the 1960s, especially in ...
, a Hollywood sex symbol. Kwan was of Eurasian origin, born in 1939 in Hong Kong to a father who was a Cantonese architect and mother who is a model of British descent. The martial artist Bruce Lee had a Cantonese father and a Eurasian mother.
Ernest John Eitel controversially claimed that most "half caste" people in Hong Kong were descended exclusively from Europeans having a relationship with Tanka women. The theory that most of the Eurasian mixed race Hong Kong people are descended only from Tanka women and European men, and not ordinary Cantonese women, has been backed up by other researchers who pointed out that Tanka women freely consorted with foreigners due to the fact that they were not bound by the same Confucian traditions as the Cantonese, and having a relationship with a European man was advantageous for Tanka women, but Lethbridge criticized it as "a 'myth' propagated by xenophobic Cantonese to account for the establishment of the Hong Kong Eurasian community". Carl Smith's study in the late 1960s on the protected women seems, to some degree, to support Ernest John Eitel's theory. Smith says that the Tankas experienced certain restrictions within the traditional Chinese social structure. Being a group marginal to the traditional Chinese society of the Puntis (Cantonese), they did not have the same social pressure in dealing with Europeans. The ordinary Cantonese women did not sleep with European men, thus the Eurasian population was formed mostly from Tanka and European admixture.
They invaded Hongkong the moment the settlement was started, living at first on boats in the harbour with their numerous families, gradually settling on shore. They have maintained ever since almost a monopoly of the supply of pilots and ships' crews, of the fish trade and the cattle trade, but unfortunately also of the trade in girls and women. Strange to say, when the settlement was first started, it was estimated that some 2,000 of these Tan-ka people had flocked to Hongkong, but at the present time they are about the same number, a tendency having set in among them to settle on shore rather than on the water and to disavow their Tan-ka extraction in order to mix on equal terms with the mass of the Chinese community. The half-caste population in Hongkong was, from the earliest days of the settlement of the Colony and down to the present day, almost exclusively the off-spring of these Tan-ka people. But, like the Tan-ka people themselves, they are happily under the influence of a process of continuous re-absorption into the mass of the Chinese residents of the Colony.
South Asians have been living in Hong Kong throughout the colonial period, before the independence in 1947 into the nations of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
. They migrated to Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
and worked as police officers as well as army officers during colonial rule. 25,000 of the Muslims in Hong Kong trace their roots back to what is now Pakistan. Around half of them belong to 'local boy' families, Muslims of mixed Chinese and South Asian ancestry, descended from early Indian/Pakistani Muslim immigrants who took local Chinese wives and brought their children up as Muslims.
=Macao
=
The early Macanese ethnic group was formed from Portuguese men intermarrying with Malay, Japanese and Indian women. The Portuguese encouraged Chinese migration to Macao, and most Macanese in Macao were formed from intermarriages between Portuguese and Chinese. In 1810, the total population of Macao was about 4,033, of which 1,172 were white men, 1,830 were white women, 425 were male slaves, and 606 were female slaves. In 1830, the population increased to 4,480 and the breakdown was 1,202 white men, 2,149 white women, 350 male slaves, and 779 female slaves. There is reason to speculate that large numbers of white women were involved in some forms of prostitution which would probably explain the abnormality in the ratio between men and women among the white population.
Rarely did Chinese women marry Portuguese; initially, mostly Goans
Goans ( kok, गोंयकार, Romi Konkani: , pt, Goeses) is the demonym used to describe the people native to Goa, India, who form an ethno-linguistic group resulting from the assimilation of Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Indo-Portuguese, and ...
, Ceylonese (from today's Sri Lanka), Indochinese, Malay, and Japanese women were the wives of the Portuguese men in Macau. Japanese girls would be purchased in Japan by Portuguese men. Many Chinese became Macanese simply by converting to Catholicism, and had no ancestry from Portuguese, having assimilated into the Macanese people. The majority of the early intermarriages of people from China with Portuguese were between Portuguese men and women of Tanka
is a genre of classical Japanese poetry and one of the major genres of Japanese literature.
Etymology
Originally, in the time of the '' Man'yōshū'' (latter half of the eighth century AD), the term ''tanka'' was used to distinguish "short p ...
origin, who were considered the lowest class of people in China and had relations with Portuguese settlers and sailors, or low class Chinese women.[Society of Macau: Macanese People, Public Holidays in Macau, Tanka People](_blank)
Alibris. Retrieved 29 January 2012. Western men were refused by high class Chinese women, who did not marry foreigners.[João de Pina-Cabral, p. 165] In fact, in those days, the matrimonial context of production was usually constituted by Chinese women of low socio-economic status who were married to or concubines of Portuguese or Macanese men. Very rarely did Chinese women of higher status agree to marry a Westerner. As Deolinda argues in one of her short stories, "even should they have wanted to do so out of romantic infatuation, they would not be allowed to. Macanese men and women also married with the Portuguese and Chinese; as a result, some Macanese became indistinguishable from the Chinese or Portuguese population. Because the majority of the Chinese population who migrated to Macao was Cantonese, Macao became a Cantonese speaking society, and other ethnic groups became fluent in Cantonese. Most Macanese had paternal Portuguese heritage until 1974."
India
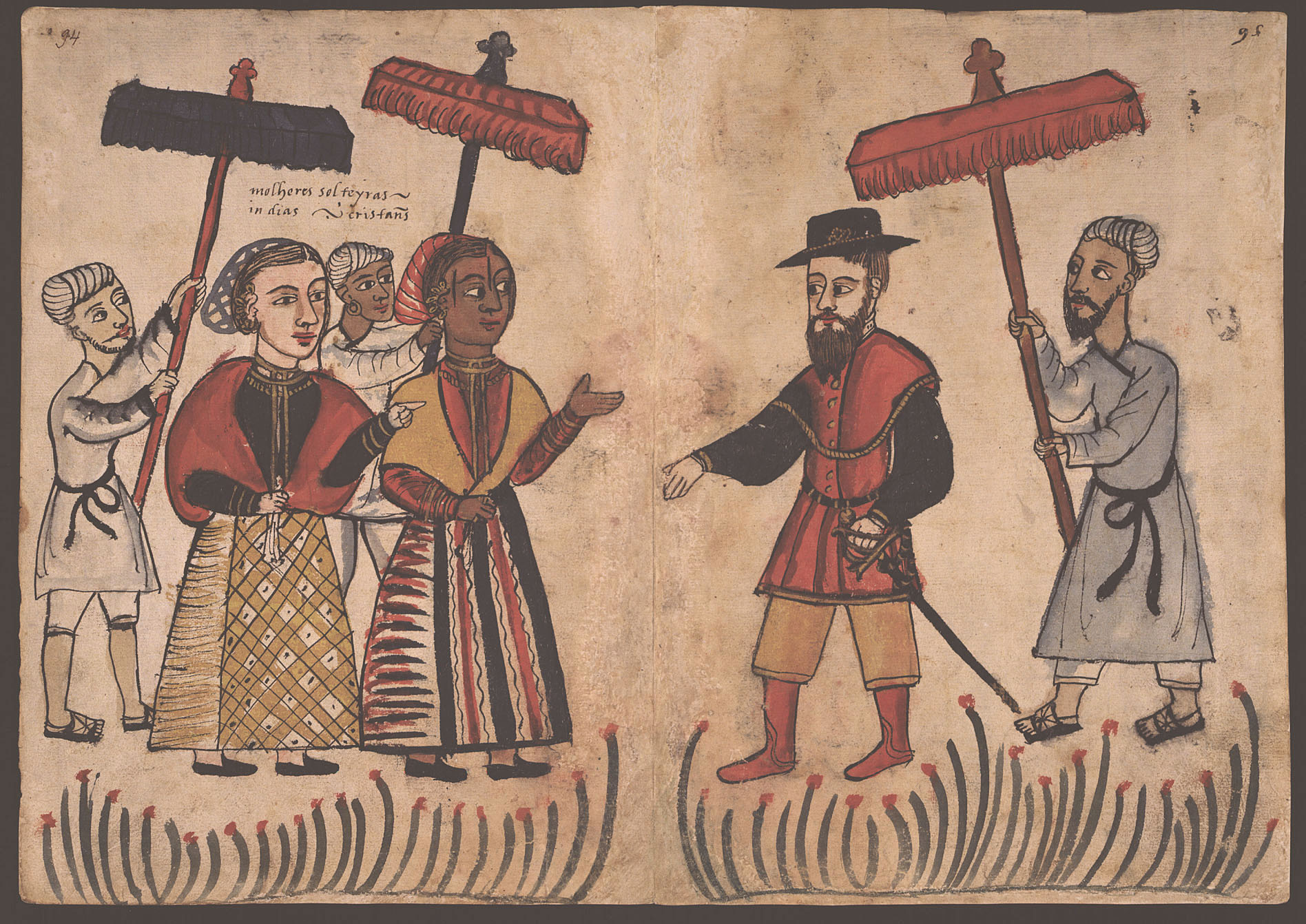

 Although the
Although the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
is virtually endogamous with wedding practices in India overwhelmingly occurring within the same caste and religion, interracial relationships have occurred predating recorded history and have been historically recorded since antiquity. Inter-marriage in the Indian subcontinent has historically been applied between different ethnolinguistic groups, varna, caste, and religions. One of the critical aspects of inter-marriage in India is inter-caste marriage, which is based around the construct of caste.
Various groups of people have been intermarrying between ethnolinguistic groups for millennia in the Indian subcontinent, including speakers of the Dravidian, Indo-Aryan, Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are th ...
, and Tibeto-Burman languages
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people sp ...
. This has often formed syncretic languages and regional dialects.
Intermarriage rates in India varies greatly among the states and union territories of India. In modern India, intermarriage is most likely to occur involving spouse from the same socioeconomic strata.
Afonso de Albuquerque conquered Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
in 1510. He inaugurated the policy of Portuguese men marrying Indian women who had converted to Catholicism, the consequence of which was a great miscegenation in Goa and other Portuguese territories in Asia. During the late 16th century and 17th century, there was a community of over thousand Japanese slaves
Japan had an official slave system from the Yamato period (3rd century A.D.) until Toyotomi Hideyoshi abolished it in 1590. Afterwards, the Japanese government facilitated the use of "comfort women" as sexual slavery, sex slaves from 1932 – 1945. ...
and traders in Goa, who were either Japanese Christians fleeing persecution in Japan,Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
women and girls brought or captured as sexual slaves by Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
traders and their South Asian ''lascar
A lascar was a sailor or militiaman from the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, the Arab world, British Somaliland, or other land east of the Cape of Good Hope, who was employed on European ships from the 16th century until the middle of the ...
'' crew members from Japan.James Achilles Kirkpatrick
Lieutenant-Colonel James Achilles Kirkpatrick (1764 – 15 October 1805) was an East India Company officer and diplomat who served as the Resident at Hyderabad Deccan from 1798 until 1805. Kirkpatrick also ordered the construction of the Koti Resi ...
.
The 600,000-strong Anglo-Indian
Anglo-Indian people fall into two different groups: those with mixed Indian and British ancestry, and people of British descent born or residing in India. The latter sense is now mainly historical, but confusions can arise. The '' Oxford English ...
community has been formed by British and Indian relationships, with significant amount of the diaspora living in Bangladesh, India, UK, Australia, and North America. Such syncretic relationships have had an influence on arts and culture.
As British women began arriving in India in large numbers around the early to mid-19th century, mostly as family members of officers and soldiers, British men became less likely to marry Indian women. Intermarriage declined after the events of the Rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against Company rule in India, the rule of the East India Company, British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the The Crown, British ...
, after which several anti-miscegenation laws were implemented.
The stereotype of the "Indian rapist" occurred frequently in English literature of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. This coincided with a period after the Indian Rebellion when the colonial government officially outlawed miscegenation, a decision which was influenced by the reports of rape supposedly committed by Indian rebels during the 1857 rebellion. These policies remained in effect until Indian independence in 1947.
The 1883 Ilbert Bill
The Ilbert Bill was a bill formally introduced on 9 February 1883 during the Viceroyship of the Marquess of Ripon, which was drafted by Sir Courtenay Peregine Ilbert, the legal member of the Council of the Governor-General of India. It concerne ...
, which would have granted Indian judges the right to judge British offenders, was opposed by many Britons in India on the grounds that Indian judges could not be trusted in dealing with cases involving British females, with miscegenation and ethnic tensions playing a large part in opposition to the bill.
The stereotype of Indian males as rapists who targeted British women in India was critiqued by several novels such as E. M. Forster
Edward Morgan Forster (1 January 1879 – 7 June 1970) was an English author, best known for his novels, particularly ''A Room with a View'' (1908), ''Howards End'' (1910), and ''A Passage to India'' (1924). He also wrote numerous short stori ...
's ''A Passage to India
''A Passage to India'' is a 1924 novel by English author E. M. Forster set against the backdrop of the British Raj and the Indian independence movement in the 1920s. It was selected as one of the 100 great works of 20th century English liter ...
'' (1924) and Paul Scott's '' The Jewel in the Crown'' (1966), both of which involve an Indian male being wrongly accused of raping a British female. Some activists argued that these stereotypes were wrong because Indians had proven to be more receptive to women's rights and progress, with the University of Calcutta
The University of Calcutta (informally known as Calcutta University; CU) is a public collegiate state university in India, located in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. Considered one of best state research university all over India every year, ...
becoming one of the first universities to admit female graduates to its degree programmes in 1878, before any of the universities in Britain did.
When Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
was ruled under the administration of British India, millions of Indians, mostly Muslims, migrated there. The small population of mixed descendants of Indian males and local Burmese females are called "Zerbadees", often in a pejorative sense implying mixed race.Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
, local Indians married several waves of Chinese migrants during the British colonial era, to the point where it became hard to physically differentiate Chinese in Assam from locals during the time of their internment during the 1962 war, and the majority of these Chinese in Assam were married to Indians, and some of these Indian women were deported to China with their husbands.
In the 19th century, when the British Straits Settlement shipped Chinese convicts to be jailed in India, the Chinese men then settled in the Nilgiri mountains
The Nilgiri Mountains form part of the Western Ghats in northwestern Tamil Nadu, Southern Karnataka, and eastern Kerala in India. They are located at the trijunction of three states and connect the Western Ghats with the Eastern Ghats. At le ...
near Naduvattam after their release and married Tamil Paraiyan women, having mixed Chinese-Tamil children with them. They were documented by Edgar Thurston
Edgar Thurston CIE (1855– 12 October 1935) was the British Superintendent at the Madras Government Museum from 1885 to 1908 who contributed to research studies in the fields of zoology, ethnology and botany of India, and later also publish ...
. Paraiyan is also anglicized as "pariah".
Thurston described the colony of the Chinese men with their Tamil pariah wives and children: "Halting in the course of a recent anthropological expedition on the western side of the Nilgiri plateau, in the midst of the Government Cinchona plantations, I came across a small settlement of Chinese, who have squatted for some years on the slopes of the hills between Naduvatam and Gudalur, and developed, as the result of ' marriage ' with Tamil pariah women, into a colony, earning an honest livelihood by growing vegetables, cultivating coffee on a small scale, and adding to their income from these sources by the economic products of the cow. An ambassador was sent to this miniature Chinese Court with a suggestion that the men should, in return for monies, present themselves before me with a view to their measurements being recorded. The reply which came back was in its way racially characteristic as between Hindus and Chinese. In the case of the former, permission to make use of their bodies for the purposes of research depends essentially on a pecuniary transaction, on a scale varying from two to eight annas. The Chinese, on the other hand, though poor, sent a courteous message to the effect that they did not require payment in money, but would be perfectly happy if I would give them, as a memento, copies of their photographs." Thurston further describe a specific family: "The father was a typical Chinaman, whose only grievance was that, in the process of conversion to Christianity, he had been obliged to 'cut him tail off.' The mother was a typical Tamil Pariah of dusky hue. The colour of the children was more closely allied to the yellowish tint of the father than to the dark tint of the mother; and the semimongol parentage was betrayed in the slant eyes, flat nose, and (in one case) conspicuously prominent cheek-bones." Thurston's description of the Chinese-Tamil families were cited by others, one mentioned "an instance mating between a Chinese male with a Tamil Pariah female" A 1959 book described attempts made to find out what happened to the colony of mixed Chinese and Tamils.
An increasing number of non-Tibetan Muslim men are marrying Ladakhi Tibetan Buddhist women in Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu ...
.
Pakistan
The Balti people of Baltistan in Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
and Kargil in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
are descendants of Tibetan Buddhists who converted to the Noorbakshia sect of Islam. With the passage of time a large number converted to Shia Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, m ...
, and a few converted to Sunni Islam. Their Balti language
Balti (Nastaʿlīq script: , Tibetan script: སྦལ་ཏི།, ) is a Tibetic language natively spoken by the ethnic Balti people in the Baltistan region of Gilgit−Baltistan, Pakistan, Nubra Valley of the Leh district and in the Kar ...
is highly archaic and conservative and closer to Classical Tibetan
Classical Tibetan refers to the language of any text written in Tibetic after the Old Tibetan period. Though it extends from the 12th century until the modern day, it particularly refers to the language of early canonical texts translated from ot ...
than other Tibetan languages
The Tibetic languages form a well-defined group of languages descended from Old Tibetan (7th to 9th centuries).Tournadre, Nicolas. 2014. "The Tibetic languages and their classification." In ''Trans-Himalayan linguistics, historical and descripti ...
. The Balti are speakers of a conservative Tibetan dialect in northern Pakistan, Baltistant. Most other Tibetan dialects lost Classical Tibetan consonant clusters that are preserved in Balti. However DNA testing revealed that while Tibetan mtDNA makes up the majority of the Balti's female ancestry, the Balti paternal ancestry has foreign Near Eastern Y haplogroups of non-Tibetan origin.
Sri Lanka
In Ceylon (present day Sri Lanka), interracial relationships between Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
men and local women were common. The 65,000-strong Burgher community was formed by the interracial marriages of Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
men with local Sinhalese and Tamil women. In addition to intermarriage, inter-ethnic prostitution in India
Prostitution is legal in India, but a number of related activities including soliciting, kerb crawling, owning or managing a brothel, prostitution in a hotel, child prostitution, pimping and pandering are illegal. There are, however, many b ...
was also fairly common at the time, when British officers would frequently visit Indian ''nautch
The nautch (; meaning "dance" or "dancing")Scott A. Kugle, 2016When Sun Meets Moon: Gender, Eros, and Ecstasy in Urdu Poetry p.230. was a popular court dance performed by girls (known as "nautch girls") in India. The culture of the performing ...
'' dancers. In the mid-19th century, there were around 40,000 British soldiers but fewer than 2,000 British officials present in India. Many British and other European officers had their own harems made up of Indian women similar to those the Nawabs and kings of India had. In the 19th century and early 20th century, thousands of women and girls from continental Europe were also trafficked into British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
(and Ceylon), where they worked as prostitutes servicing both British soldiers and local Indian (and Ceylonese) men.
Japan
 Inter-ethnic marriage in Japan dates back to the 7th century, when Chinese and
Inter-ethnic marriage in Japan dates back to the 7th century, when Chinese and Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
n immigrants began intermarrying with the local Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
population. In the 1590s, over 50,000 Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
were forcibly brought to Japan during Hideyoshi's invasions of Korea, where they intermarried with the local population. In the 16th and 17th centuries, around 58,000 Japanese travelled abroad, many of whom intermarried with the local women in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
.[Leupp, pp. 52–3] During the anti-Christian persecutions in 1596, many Japanese Christians fled to Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a p ...
and other Portuguese colonies
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the l ...
such as Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
, where there was a community of Japanese slaves and traders by the early 17th century. Intermarriage with the local populations in these Portuguese colonies also took place.[Leupp, p. 52] Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
traders in Japan also intermarried with the local Christian women.
From the 15th century, Chinese, Korean and other Far Eastern visitors frequented brothels in Japan. This practice later continued among visitors from the "Western Regions
The Western Regions or Xiyu (Hsi-yü; ) was a historical name specified in the Chinese chronicles between the 3rd century BC to the 8th century AD that referred to the regions west of Yumen Pass, most often Central Asia or sometimes more sp ...
", mainly European traders.[Leupp, p. 49] This began with the arrival of Portuguese ships to Japan in the 16th century. Portuguese visitors and their South Asian (and sometimes African) crewmembers often engaged in slavery in Japan
Japan had an official slave system from the Yamato period (3rd century A.D.) until Toyotomi Hideyoshi abolished it in 1590. Afterwards, the Japanese government facilitated the use of "comfort women" as sex slaves from 1932 – 1945. Prisoners of wa ...
, where they bought Japanese slaves who were then taken to Macau and other Portuguese colonies in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
,India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
.Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, also engaged in prostitution in Japan
Prostitution in Japan has existed throughout the country's history. While the Prostitution Prevention Law of 1956 states that "No person may either do prostitution or become the customer of it", loopholes, liberal interpretations and a loose ...
. Marriage and sexual relations between European merchants and Japanese women was usual during this period.
Many documents mention the large slave trade along with protests against the enslavement of Japanese. Although the actual number of slaves is debated, the proportions on the number of slaves tends to be exaggerated by the Japanese as part of anti-Portuguese propaganda. At least more than several hundreds of Japanese women were sold.
A large slave trade developed in which Portuguese purchased hundreds of Japanese as slaves in Japan and sold them to various locations overseas, including Portugal itself, throughout the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. Many documents mention the large slave trade along with protests against the enslavement of Japanese. Japanese slaves are believed to be the first of their nation to end up in Europe, and the Portuguese purchased large numbers of hundreds Japanese slave girls to bring to Portugal for sexual purposes, as noted by the Church in 1555. King Sebastian feared that it was having a negative effect on Catholic proselytization since the slave trade in Japanese was growing to massive proportions, so he commanded that it be banned in 1571.
Japanese slave women were even sold as concubine
Concubinage is an interpersonal and sexual relationship between a man and a woman in which the couple does not want, or cannot enter into a full marriage. Concubinage and marriage are often regarded as similar but mutually exclusive.
Concubi ...
s to black African crewmembers, along with their European counterparts serving on Portuguese ships trading in Japan, mentioned by Luis Cerqueira, a Portuguese Jesuit, in a 1598 document. Japanese slaves were brought by the Portuguese to Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a p ...
, where some of them not only ended up being enslaved to Portuguese, but as slaves to other slaves, with the Portuguese owning Malay and African slaves, who in turn owned Japanese slaves of their own.
Karayuki-san, literally meaning "Ms. Gone Abroad", were Japanese women who traveled to or were trafficked to East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
, Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
and as far as San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
in the second half of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century to work as prostitutes, courtesans and geisha
{{Culture of Japan, Traditions, Geisha
{{nihongo, Geisha, 芸者 ({{IPAc-en, ˈ, ɡ, eɪ, ʃ, ə; {{IPA-ja, ɡeːɕa, lang), also known as {{nihongo, , 芸子, geiko (in Kyoto and Kanazawa) or {{nihongo, , 芸妓, geigi, are a class of female J ...
. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, there was a network of Japanese prostitutes being trafficked across Asia, in countries such as China, Japan, Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
and British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
, in what was then known as the 'Yellow Slave Traffic'.
In the early part of the Shōwa era
The was the period of Japanese history corresponding to the reign of Emperor Shōwa (Hirohito) from December 25, 1926, until his death on January 7, 1989. It was preceded by the Taishō era.
The pre-1945 and post-war Shōwa periods are almos ...
, Japanese governments executed a eugenic policy to limit the birth of children with inferior traits, as well as aiming to protect the life and health of mothers. Family Center staff also attempted to discourage marriage between Japanese women and Korean men who had been recruited from the peninsula as laborers following its annexation by Japan in 1910. In 1942, a survey report argued that "the Korean laborers brought to Japan, where they have established permanent residency, are of the lower classes and therefore of inferior constitution ... By fathering children with Japanese women, these men could lower the caliber of the Yamato minzoku."
In 1928, journalist Shigenori Ikeda promoted 21 December as the blood-purity day (''junketsu de'') and sponsored free blood tests at the Tokyo Hygiene laboratory. By the early 1930s, detailed "eugenic marriage" questionnaires were printed or inserted in popular magazines for public consumption. Promoters like Ikeda were convinced that these marriage surveys would not only ensure the eugenic fitness of spouses but also help avoid class differences that could disrupt and even destroy marriage. The goal was to create a database of individuals and their entire households which would enable eugenicists to conduct in-depth surveys of any given family's genealogy.
Historian S. Kuznetsov, dean of the Department of History of the Irkutsk State University, one of the first researchers of the topic, interviewed thousands of former internees and came to the following conclusion: What is more, romantic relations between Japanese internees and Russian women were not uncommon. For example, in the city of Kansk
Kansk (russian: Канск) is a town in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located on both banks of the Kan River. Population:
History and economy
Founded in 1628 as a Russian fort, it was transferred to its current location in 1636 and granted town st ...
, Krasnoyarsk Krai
Krasnoyarsk Krai ( rus, Красноя́рский край, r=Krasnoyarskiy kray, p=krəsnɐˈjarskʲɪj ˈkraj) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai), with its administrative center in the city of Krasnoyarsk, the third-largest city in Si ...
, about 50 Japanese married locals and stayed. Today many Russian women married Japanese men, often for the benefit of long-term residence and work rights. Some of their mixed offspring stay in Japan while other's to Russia.
To prevent venereal diseases and rape by Japanese soldiers and to provide comfort to soldiers and head off espionage, the Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor o ...
established "comfort stations" in the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere
The , also known as the GEACPS, was a concept that was developed in the Empire of Japan and propagated to Asian populations which were occupied by it from 1931 to 1945, and which officially aimed at creating a self-sufficient bloc of Asian peo ...
where around 200,000 women, mostly from Korea and China, were recruited or kidnapped by the Kempeitai
The , also known as Kempeitai, was the military police arm of the Imperial Japanese Army from 1881 to 1945 that also served as a secret police force. In addition, in Japanese-occupied territories, the Kenpeitai arrested or killed those suspecte ...
or the Tokeitai as comfort women.
One of the last eugenic measures of the Shōwa regime was taken by the Higashikuni government. On 19 August 1945, the Home Ministry ordered local government offices to establish a prostitution service for Allied soldiers to preserve the "purity" of the "Japanese race". The official declaration stated that: "Through the sacrifice of thousands of " Okichis" of the Shōwa era
The was the period of Japanese history corresponding to the reign of Emperor Shōwa (Hirohito) from December 25, 1926, until his death on January 7, 1989. It was preceded by the Taishō era.
The pre-1945 and post-war Shōwa periods are almos ...
, we shall construct a dike to hold back the mad frenzy of the occupation troops and cultivate and preserve the purity of our race long into the future...."
According to Peter Schrijvers in ''The GI War against Japan: American Soldiers in Asia and the Pacific during World War II'',Okinawa
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city ...
n historian for the entire three-month period of the campaign exceeds 10,000. A figure that does not seem unlikely when one realizes that during the first 10 days of the occupation of Japan there were 1,336 reported cases of rape of Japanese women by American soldiers in Kanagawa
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Kanagawa Prefecture is the second-most populous prefecture of Japan at 9,221,129 (1 April 2022) and third-densest at . Its geographic area of makes it fifth-smallest. Kanagaw ...
prefecture alone".[A Heterology of American GIs during World War II]
by Xavier Guillaume, Department of Political Science, University of Geneva July 2003, (H-NET review of Peter Schrijvers. "The GI War against Japan: American Soldiers in Asia and the Pacific during World War II". New York: New York University Press, 2002) The citation is cited to p. 212 of "The GI War against Japan".
However, despite being told by the Japanese military that they would suffer rape, torture and murder at the hands of the Americans, Japanese civilians "were often surprised at the comparatively humane treatment they received from the American enemy." According to ''Islands of Discontent: Okinawan Responses to Japanese and American Power'' by Mark Selden, the Americans "did not pursue a policy of torture, rape, and murder of civilians as Japanese military officials had warned".
Japanese society
The culture of Japan has changed greatly over the millennia, from the country's prehistoric Jōmon period, to its contemporary modern culture, which absorbs influences from Asia and other regions of the world.
Historical overview
The ances ...
, with its ideology of homogeneity, has traditionally been intolerant of ethnic and other differences. Men or women of mixed ancestry, foreigners, and members of minority groups
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number o ...
face discrimination in a variety of forms. In 2005, a United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
report expressed concerns about racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonis ...
in Japan and that government recognition of the depth of the problem was not realistic.["Japan racism 'deep and profound.](_blank)
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
(11 July 2005). Retrieved 5 January 2007. In 2005, Japanese Minister Tarō Asō
is a Japanese politician serving as the Vice President of the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) since 2021. Asō previously served as Prime Minister of Japan from 2008 to 2009 and as Deputy Prime Minister of Japan and Minister of Finance from 2 ...
called Japan a "one-race" country.
The Japanese public was thus astounded by the sight of some 45,000 so-called "pan pan girls" ( prostitutes) fraternizing with American soldiers during the occupation. In 1946, the 200 wives of U.S. officers landing in Japan to visit their husbands also had a similar impact when many of these reunited couples were seen walking hand in hand and kissing in public. Both prostitution and marks of affection had been hidden from the public until then, and this "democratization of eroticism" was a source of surprise, curiosity, and even envy. The occupation set new relationship models for Japanese men and women: the practice of modern "dating" spread, and activities such as dancing, movies, and coffee were not limited to "pan pan girls" and American troops anymore and became popular among young Japanese couples.
Korea
Inter-ethnic marriage in Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
dates back to the arrival of Muslims in Korea during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, when Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
and Turkic navigators, traders and slaves settled in Korea and married local Korean people
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply refer ...
. Some assimilation into Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
and Shamanism eventually took place, owing to Korea's geographical isolation from the Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
.
There are several Korean clans that are descended from such intermarriages. For example, the Deoksu Jang clan
The Deoksu Jang clan () is one of the bon-gwan or Korean clans from Kaepung County, North Hwanghae Province.The clan was founded by , an Arab- Uiguric Muslim civil servant who served in the Goryeo court.
According to the research held in 2015, t ...
, claiming some 30,000 Korean members, views Jang Sunnyong, a Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
n who married a Korean female, as their ancestor.Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
. The average number of Korean women marrying US military personnel each year was about 1,500 per year in the 1960s and 2,300 per year in the 1970s. Since the beginning of the Korean War in 1950, Korean women have immigrated to the United States as the wives of American soldiers. Based on extensive oral interviews and archival research, Beyond the Shadow of the Camptowns tells the stories of these women, from their presumed association with U.S. military camptowns and prostitution to their struggles within the intercultural families they create in the United States.
International marriages now make up 13% of all marriages in South Korea. Most of these marriages are unions between a Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
male and a foreign female usually from China, Japan, Vietnam, the Philippines, United States, Mongolia, Thailand, or Russia. On the other hand, Korean females have married foreign males from Japan, China, the United States, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Philippines, and Nepal. Between 1990 and 2005, there have been 159,942 Korean males and 80,813 Korean females married to foreigners.
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and sharing a land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eas ...
is among the world's most ethnically homogeneous nations. Koreans have traditionally valued unmixed blood as the most important feature of Korean identity. The term "Kosian", referring to someone who has a Korean father and a non-Korean mother, is considered offensive by some who prefer to identify themselves or their children as Korean. Moreover, the Korean office of Amnesty International has claimed that the word "Kosian" represents racial discrimination. Kosian children, like those of other mixed-race backgrounds in Korea, often face discrimination.
Malaysia and Singapore
In West Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
and Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, the majority of inter-ethnic marriages are between Chinese and Indians. The offspring of such marriages are informally known as "Chindian
Chindian ( zh, c=中印人, p=Zhōngyìnrén, cy=Jūngyanyàn; ta, சிந்தியன்; is an informal term used to refer to a person of mixed Chinese and Indian ancestry; i.e. from any of the host of ethnic groups native to modern Ch ...
", although the Malaysian government only classifies them by their father's ethnicity. As the majority of these intermarriages usually involve an Indian groom and Chinese bride, the majority of Chindians in Malaysia are usually classified as "Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
" by the Malaysian government. As for the Malays, who are predominantly Muslim, legal restrictions in Malaysia make it uncommon for them to intermarry with either the Indians, who are predominantly Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, or the Chinese, who are predominantly Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
and Taoist
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Tao ...
. Non-Muslims are required to convert to Islam in order to marry Muslims. However, this has not entirely stopped intermarriage between the Malays and the Chinese and Indians. The Muslim Chinese community is small and has only a negligible impact on the socio-economy and demography of the region.
It is common for Arabs in Singapore and Malaysia to take local Malay and Jawi Peranakan
The Jawi Peranakan ( Jawi: ) is an elite ethnic group found primarily within the Malaysian state of Penang and in Singapore, both regions were part of the historical Straits Settlements where their culture and history is centred around. The t ...
wives, due to a common Islamic faith.Chitty
The Chitty, also known as the Chetty or Chetti Melaka, are a distinctive group of Tamil people found mainly and originally in Melaka, Malaysia, and in Singapore where they migrated to in the 18th and 19th centuries from Melaka, who are also kn ...
people, in Singapore and the Malacca state of Malaysia, are a Tamil people
The Tamil people, also known as Tamilar ( ta, தமிழர், Tamiḻar, translit-std=ISO, in the singular or ta, தமிழர்கள், Tamiḻarkaḷ, translit-std=ISO, label=none, in the plural), or simply Tamils (), are a Drav ...
with considerable Malay descent, which was due to the first Tamil settlers taking local wives, since they did not bring along any of their own women with them. According to government statistics, the population of Singapore as of September 2007 was 4.68 million, of whom multiracial people, including Chindians and Eurasians, formed 2.4%.
In the East Malaysian states of Sabah
Sabah () is a state of Malaysia located in northern Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah borders the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and the North Kalimantan province of Indonesia to the south. The Federal Territory o ...
and Sarawak
Sarawak (; ) is a state of Malaysia. The largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak is located in northwest Borneo Island, and is bordered by the Malaysian state of Sabah to the northeast, ...
, intermarriage is common between Chinese and native tribes such as the Murut and Dusun
Dusun is the collective name of a tribe or ethnic and linguistic group in the Malaysian state of Sabah of North Borneo. Collectively, they form the largest ethnic group in Sabah. Dusun has been recognised as among the indigenous community of ...
in Sabah, and the Iban
IBAN or Iban or Ibán may refer to:
Banking
* International Bank Account Number
Ethnology
* Iban culture
The Ibans or Sea Dayaks are a branch of the Dayak people, Dayak people on the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. It is believed that the ...
and Bisaya
Visayans ( Visayan: ''mga Bisaya''; ) or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. When taken as a single ethnic group, ...
in Sarawak. This has resulted in a potpourri of cultures in both states where many people claiming to be of native descent have some Chinese blood in them, and many Chinese have native blood in them. The offspring of these mixed marriages are called 'Sino-(name of tribe)', e.g. Sino-Dusun. Normally, if the father is Chinese, the offspring will adopt Chinese culture and if the father is native then native culture will be adopted, but this is not always the case. These Sino-natives are usually fluent in Malay and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
. A smaller number are able to speak Chinese dialects and Mandarin, especially those who have received education in vernacular Chinese schools.
The Eurasian
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Ja ...
s in West Malaysia and Singapore are descendants of Europeans and locals, mostly Portuguese or British colonial settlers who have taken local wives.
Myanmar (Burma)
Burmese Muslims
Islam is a minority religion in Myanmar, practiced by about 2.3% of the population, according to the 2014 Myanmar official statistics.
History
In the early Bagan era (AD 652-660), Arab Muslim merchants landed at ports such as Thaton and Marta ...
are the descendants of Bengalis
Bengalis (singular Bengali bn, বাঙ্গালী/বাঙালি ), also rendered as Bangalee or the Bengali people, are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the Bengal region of ...
, Indian Muslims
Islam is India's second-largest religion, with 14.2% of the country's population, approximately 172.2 million people identifying as adherents of Islam in 2011 Census. India is also the country with the second or third largest number of Muslim ...
, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
, Pathans
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
, Chinese Muslims
Islam has been practiced in China since the 7th century CE.. Muslims are a minority group in China, representing 1.6-2 percent of the total population (21,667,000- 28,210,795) according to various estimates. Though Hui Muslims are the most nume ...
, and Malays who settled in Burma and married members of the local Burmese population as well as members of other Burmese ethnic groups such as the Rakhine, Shan, Karen, and Mon.Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
(Myanmar) are the Rohingya people
The Rohingya people () are a stateless Indo-Aryan ethnic group who predominantly follow Islam and reside in Rakhine State, Myanmar (previously known as Burma). Before the Rohingya genocide in 2017, when over 740,000 fled to Bangladesh, an ...
, who some believe are descended from Bengalis who settled in Burma and married native females in Rakhine State
Rakhine State (; , , ; formerly known as Arakan State) is a state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Region to the east, the Bay of Ben ...
after the 7th century, but this is just a theory. When Burma was ruled by the British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
administration, millions of Indians, mostly Muslims, migrated there. The small group of people who are the mixed descendants of Indian males and local Burmese females are called "Zerbadees", a term which is frequently used in a pejorative way in order to imply that they are people of mixed race. The Panthays
Panthays () form a group of Chinese Muslims in Burma. Some people refer to Panthays as the oldest group of Muslims in Burma. The exact proportion of the Chinese Muslim group in the local Chinese population remains unknown due to a lack of data. H ...
, a group of Chinese Muslims
Islam has been practiced in China since the 7th century CE.. Muslims are a minority group in China, representing 1.6-2 percent of the total population (21,667,000- 28,210,795) according to various estimates. Though Hui Muslims are the most nume ...
descended from West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
ns and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
ns, migrated from China and also intermarried with local Burmese females.[Muslim Communities in Myanmar]
ColorQ World
In addition, Burma has an estimated 52,000 Anglo-Burmese people, descended from British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and Burmese people. Anglo-Burmese people frequently intermarried with Anglo-Indian
Anglo-Indian people fall into two different groups: those with mixed Indian and British ancestry, and people of British descent born or residing in India. The latter sense is now mainly historical, but confusions can arise. The '' Oxford English ...
immigrants, who eventually assimilated into the Anglo-Burmese community.
The ''All India Digest'' stated that when a Chinese man
Chinese Man is a French trip hop band formed in 2004 and originally from Aix-en-Provence.
History
They are influenced by hip-hop, funk, dub, reggae and jazz.
Chinese Man is composed of DJ Marseille Zé Mateo and High Ku and beatmaker SLY. Beatm ...
wanted to marry a Burmese woman, he needed to prove that he previously adopted and was currently following the Burmese form of Buddhism because it was assumed that even though he was currently using a Burmese name, he was still practicing Chinese Buddhism. Since many Chinese in Burma gave themselves Burmese names but continued to practice Chinese Buddhism, the adoption of a Burmese name was not proof that he had adopted Burmese Buddhism, therefore, Chinese Buddhist customary law must be followed in such cases.
Philippines
 Historically, admixture has been an ever-present and pervasive phenomenon in the Philippines. The
Historically, admixture has been an ever-present and pervasive phenomenon in the Philippines. The Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
were originally settled by Australoid
Australo-Melanesians (also known as Australasians or the Australomelanesoid, Australoid or Australioid race) is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to Melanesia and Australia. Controversially, groups from Southeast Asia an ...
peoples who are called Negritos
The term Negrito () refers to several diverse ethnic groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia and the Andaman Islands. Populations often described as Negrito include: the Andamanese peoples (including the Great Andamanese, the On ...
(different from other australoid groups) which now form the country's aboriginal community. Some admixture may have occurred between this earlier group and the mainstream Malayo-Polynesian
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeas ...
population.Cainta, Rizal
Cainta, officially the Municipality of Cainta ( fil, Bayan ng Cainta, ), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Rizal, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 376,933 people.
It is one of the oldest municipalit ...
, are descended from Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
soldiers who mutinied against the British Indian Army when the British briefly occupied the Philippines in 1762–63. These Indian soldiers, called Sepoy, settled in towns and intermarried with native women. Cainta residents of Indian descent are very visible today, particularly in Barrio Dayap near Brgy. Sto Niño.
There has been a Chinese presence in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
since the 9th century. However, large-scale migrations of Chinese to the Philippines only started during the Spanish colonial era, when the world market was opened to the Philippines. It is estimated that among Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or othe ...
, 10%–20% have some Chinese ancestry and 1.5% are "full-blooded" Chinese.[:: Overseas Compatriot Affairs Commission, R.O.C. ::]
. Ocac.gov.tw (24 August 2004). Retrieved 14 August 2010.
According to the American anthropologist Dr. H. Otley Beyer, the ancestry of Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or othe ...
is 2% Arab. This dates back to when Arab traders intermarried with the local Malay Filipina female populations during the pre-Spanish history of the Philippines.Sultanate of Sulu
The Sultanate of Sulu ( Tausūg: ''Kasultanan sin Sūg'', كاسولتانن سين سوڬ; Malay: ''Kesultanan Sulu''; fil, Sultanato ng Sulu; Chavacano: ''Sultanato de Sulu/Joló''; ar, سلطنة سولك) was a Muslim state that ruled ...
and the Sultanate of Maguindanao
The Sultanate of Maguindanao ( Maguindanaon: ''Kasultanan nu Magindanaw''; Old Maguindanaon: كاسولتانن نو ماڬينداناو; Jawi: کسلطانن ماڬيندناو; Iranun: ''Kesultanan a Magindanao''; ms, Kesultanan Magindan ...
claim Arab descent even going as far as claiming direct lineage from Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
. Such intermarriage mostly took place around the Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
island area, but the arrival of Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
Conquistadors
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, ...
to the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
abruptly halted the spread of Islam further north into the Philippines. Intermarriage with Spanish people
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex history, including a number of different languages, both i ...
later became more prevalent after the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
was colonized by the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
.
When the Spanish colonized the Philippines, a significant portion of the Filipino population mixed with the Spanish. When the United States took the Philippines from Spain during the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
, much intermixing of Americans, both white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
and black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ...
, took place on the island of Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as ...
where the US had a Naval Base and Air Force Base, even after the USA gave the Philippines independence after World War II. First children and descendants of the male Filipino population with Spanish surnames who intermarried with the white American female population may be considered Spanish mestizos. The descendants of Filipinos and Europeans are today known as mestizos, following the term used in other former Spanish colonies.
Much mixing with the Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
also took place due to the war rape
Wartime sexual violence is rape or other forms of sexual violence committed by combatants during armed conflict, war, or military occupation often as spoils of war, but sometimes, particularly in ethnic conflict, the phenomenon has broader so ...
s of Filipina women during World War II. Today there is an increasing number of Japanese men marrying Filipina women and fathering children by them whose family remains behind in the Philippines and are financially supported by their Japanese fathers who make regular visits to the Philippines. Today mixed-race marriages have a mixed perception in the Philippines. Most urban centers like Manila and Cebu are more willing to accept interracial marriages than rural areas.
Vietnam
Much of the business conducted with foreign men in Southeast Asia was done by the local women, who engaged in both sexual and mercantile intercourse with foreign male traders. A Portuguese and Malay speaking Vietnamese woman who lived in Macao for an extensive period of time was the person who interpreted for the first diplomatic meeting between Cochin-China and a Dutch delegation, she served as an interpreter for three decades in the Cochin-China court with an old woman who had been married to three husbands, one Vietnamese and two Portuguese. The cosmopolitan exchange was facilitated by the marriage of Vietnamese women to Portuguese merchants. Those Vietnamese woman were married to Portuguese men and lived in Macao which was how they became fluent in Malay and Portuguese.
Alexander Hamilton said that "The Tonquiners used to be very desirous of having a brood of Europeans in their country, for which reason the greatest nobles thought it no shame or disgrace to marry their daughters to English and Dutch seamen, for the time they were to stay in Tonquin, and often presented their sons-in-law pretty handsomely at their departure, especially if they left their wives with child; but adultery was dangerous to the husband, for they are well versed in the art of poisoning."
Europe
Germany
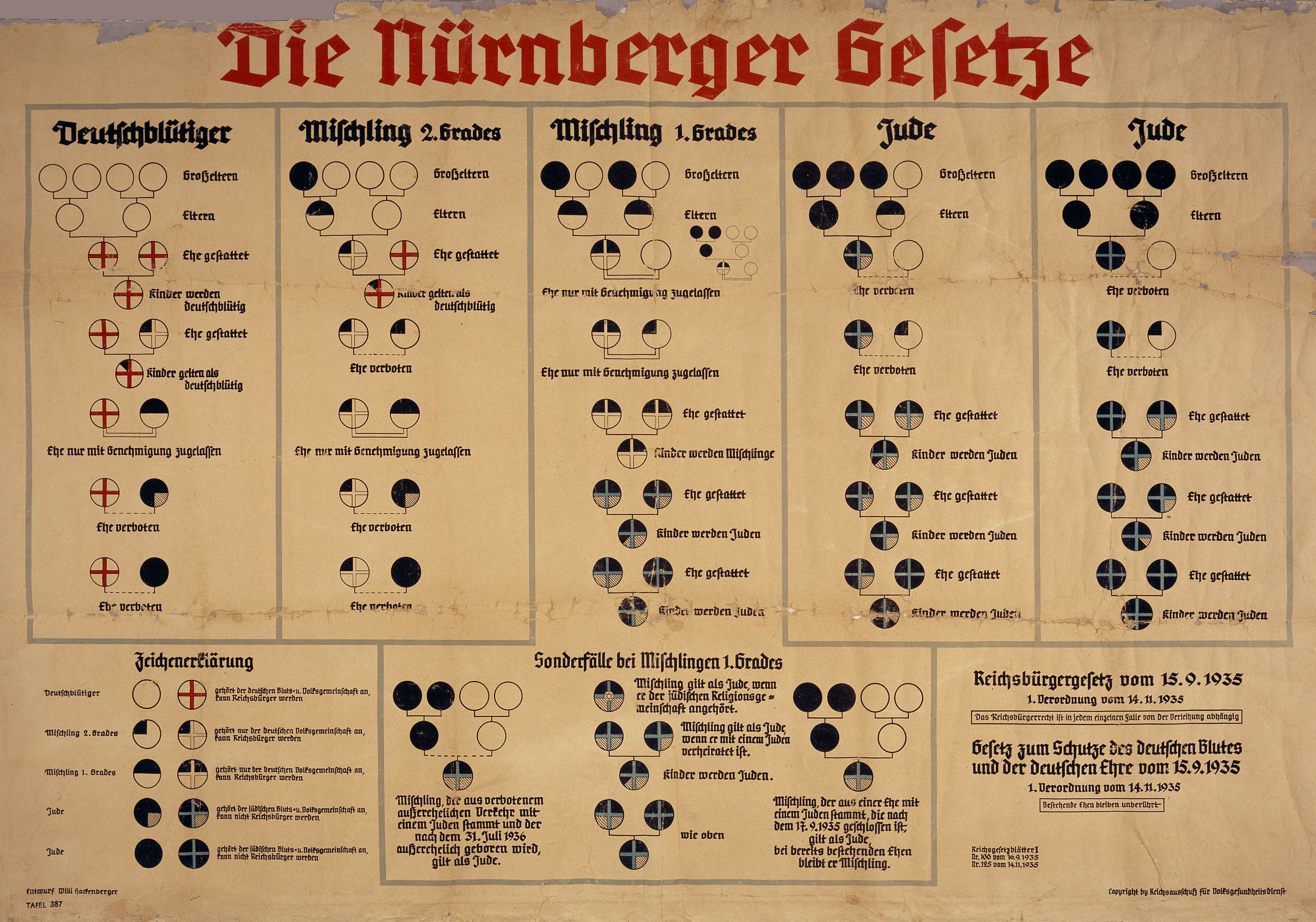
 In 1905 the local colonial administration banned civil marriages of "mixed" couples in German South West Africa. Three years later, all "mixed marriages" that had been contracted before 1905 were annulled retrospectively.
During the years which followed
In 1905 the local colonial administration banned civil marriages of "mixed" couples in German South West Africa. Three years later, all "mixed marriages" that had been contracted before 1905 were annulled retrospectively.
During the years which followed World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Force ...
occupied the Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
, utilizing African soldiers amongst their forces. Their children were known as "Rhineland Bastard
Rhineland Bastard (german: Rheinlandbastard) was a derogatory term used in Nazi Germany to describe Afro-Germans, believed fathered by French Army personnel of African descent who were stationed in the Rhineland during its occupation by France a ...
s".
Beginning in 1933, the Nazis declared that the Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
were a group of people who were bound to form a unit by their close, so-called genetic (blood) ties, a unit which a non-Jew could never join or secede from. The Nazis declared that the influence of Jews was detrimental in Germany, in order to justify the discrimination and persecution which they were then subjecting Germany's Jews to. In order to be spared from the discrimination and persecution, a person needed to prove his or her affiliation with the '' Aryan race
Race, RACE or "The Race" may refer to:
* Race (biology), an informal taxonomic classification within a species, generally within a sub-species
* Race (human categorization), classification of humans into groups based on physical traits, and/or s ...
'', as it was conceived by the Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
.
It was paradoxical that neither genetic tests nor allegedly outwardly racial features in a person's physiognomy determined his or her racial affiliation, although the Nazis talked a lot about physiognomy
Physiognomy (from the Greek , , meaning "nature", and , meaning "judge" or "interpreter") is the practice of assessing a person's character or personality from their outer appearance—especially the face. The term can also refer to the genera ...
, but only the records of the religious affiliations of a person's grandparents decided it. While a person's grandparents had previously been able to choose their religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, ...
, in the Nazi era, he or she would compulsorily be categorized as a Jew and persecuted, even if his or her grandparents had originally practiced Judaism but later converted to another religion, thus, if three or four grandparents had been enrolled as members of a Jewish congregation, their grandchildren would be considered Jews and persecuted, regardless of whether they were considered Jews according to the Halachah
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandm ...
(roughly meaning: they were Jewish by birth from a Jewish mother or they were Jewish by conversion), apostate
Apostasy (; grc-gre, ἀποστασία , 'a defection or revolt') is the formal religious disaffiliation, disaffiliation from, abandonment of, or renunciation of a religion by a person. It can also be defined within the broader context of emb ...
s, irreligionist
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and anti ...
s or Christians.
The Nuremberg Laws
The Nuremberg Laws (german: link=no, Nürnberger Gesetze, ) were antisemitic and racist laws that were enacted in Nazi Germany on 15 September 1935, at a special meeting of the Reichstag convened during the annual Nuremberg Rally of ...
of 1935 forbade marriages between persons who were considered ''racially superior'', so-called ''Aryans
Aryan or Arya (, Indo-Iranian *''arya'') is a term originally used as an ethnocultural self-designation by Indo-Iranians in ancient times, in contrast to the nearby outsiders known as 'non-Aryan' (*''an-arya''). In Ancient India, the term ...
'', and persons who were considered '' racially inferior'', so-called ''non-Aryans''; these laws forbade all marriages in which at least one partner was a German citizen. ''Non-Aryans'' mostly consisted of Jewish Germans and Gentile Germans who were of Jewish descent. The official definition of "Aryan" classified all non-Jewish Europeans as Aryans, sexual relations between Aryans and non-Aryans now became punishable as ''Rassenschande
''Rassenschande'' (, "racial shame") or ''Blutschande'' ( "blood disgrace") was an anti-miscegenation concept in Nazi German racial policy, pertaining to sexual relations between Aryans and non-Aryans. It was put into practice by policies like ...
'' (race defilement).Mischling
(; " mix-ling"; plural: ) was a pejorative legal term used in Nazi Germany to denote persons of mixed "Aryan" and non-Aryan, such as Jewish, ancestry as codified in the Nuremberg racial laws of 1935. In German, the word has the general denota ...
e or crossbreeds and discriminated against. However, children who were later born to mixed parents, parents who were not yet married when the Nuremberg Laws were passed, were considered Geltungsjuden and discriminated against, even if the parents had gotten married abroad or remained unmarried. Eventually, children who were enrolled in a Jewish congregation were also considered Geltungsjuden and discriminated against.
Geltungsjuden were subjected to varying degrees of forced labour in 1940, an order which was partially imposed on all Jewish-classified spouses, the only Jewish-classified spouses who were exempted from this order were Jewish-classified husbands and Jewish-classified wives who were taking care of their minor children. According to the documents, no mixed couples were ever exempted from persecution, this was especially the case with Jewish-classified spouses.
Systematic deportations of Jewish Germans and Gentile Germans of Jewish descent started on 18 October 1941. In fact, German Jews and German Gentiles of Jewish descent who were living in ''mixed marriages'' were mostly spared from deportation. In the event that a mixed marriage ended with the death of the so-called Aryan spouse or the divorce of the Jewish-classified spouse, the Jewish-classified spouse who was residing within Germany was usually deported soon afterward, this was not the case if the couple still had minor children who were not considered Geltungsjuden.[Beate Meyer, ''Die Verfolgung und Ermordung der Hamburger Juden 1933–1945'', Landeszentrale für politische Bildung (ed.), Hamburg: Landeszentrale für politische Bildung, 2006, p. 83. ]
In March 1943, an attempt to deport the Berlin-based Jews and Gentiles of Jewish descent who were living in non-privileged mixed marriages failed due to public protest by their in-laws who were of so-called ''Aryan'' kinship (see Rosenstraße protest). Also, the Aryan-classified husbands and the Mischling-classified children (starting at the age of 16) who were born as a result of their mixed marriages were taken for forced labour by the Organisation Todt
Organisation Todt (OT; ) was a civil and military engineering organisation in Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945, named for its founder, Fritz Todt, an engineer and senior Nazi. The organisation was responsible for a huge range of engineering pr ...
, starting in the autumn of 1944.
The last attempt, undertaken in February/March 1945, ended because the extermination camp
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (german: Vernichtungslager), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocaust. The v ...
s were already liberated. However, 2,600 people were deported to Theresienstadt from all over the Reich, most of them survived the last months of the war and lived to see their liberation.
After the war began, the race defilement law was extended to all foreigners.Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one orga ...
harshly persecuted sexual relations between Germans and workers from Eastern Europe on the grounds of "risk for the racial integrity of the German nation".abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pre ...
s were illegal in Germany (except for medical and eugenic reasons), such as when doctors opened up and started performing abortions on rape
Rape is a type of sexual assault usually involving sexual intercourse or other forms of sexual penetration carried out against a person without their consent. The act may be carried out by physical force, coercion, abuse of authority, or ...
victims. It was also typical for women to specify the reasons for their abortions. Many women who wanted to have abortions would claim that they had been raped by men who looked Asian or Mongolian. German women uniformly described the rapists in racialist terms. They never claimed that the rapists were blond, instead, they consistently claimed that the rapists were "of Mongolian or Asiatic type".
 With the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, the laws which banned so-called mixed marriages were lifted. If couples who had already lived together during the Nazi era had remained unmarried due to the legal restrictions then got married after the war, their date of marriage was legally retroactively backdated if they wished it to be the date when they formed a couple. Even if one spouse was already dead, the marriage could be retroactively recognised. In the West German Federal Republic of Germany 1,823 couples applied for recognition, which was granted in 1,255 cases.
With the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, the laws which banned so-called mixed marriages were lifted. If couples who had already lived together during the Nazi era had remained unmarried due to the legal restrictions then got married after the war, their date of marriage was legally retroactively backdated if they wished it to be the date when they formed a couple. Even if one spouse was already dead, the marriage could be retroactively recognised. In the West German Federal Republic of Germany 1,823 couples applied for recognition, which was granted in 1,255 cases.
France
During the early 20th century, some Vietnamese men married French women, but most of the time had to hide their relationships through casual sexual encounters, brothels and workplaces. According to official records in 1918, of the Vietnamese men and French women, 250 had married officially and 1363 couples were living together without the approval of the French parental consent and without the approval of French authorities.
Hungary
The Avars, Central Asian nomads who during the late 6th and 7th centuries had formed Avar Khaganate largely inhabited by conquered Slavs, used their wives and daughters as concubines.
The Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
are thought to have originated in an ancient Finno-Ugric
Finno-Ugric ( or ; ''Fenno-Ugric'') or Finno-Ugrian (''Fenno-Ugrian''), is a traditional grouping of all languages in the Uralic language family except the Samoyedic languages. Its formerly commonly accepted status as a subfamily of Uralic is ba ...
-speaking population that originally inhabited the forested area between the Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchme ...
and the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
. At the time of the Magyar migration in the 10th century, the present-day Hungary was inhabited by Slavs, numbering about 200,000,Russian campaign
The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign, the Second Polish War, the Army of Twenty nations, and the Patriotic War of 1812 was launched by Napoleon Bonaparte to force the Russian Empire back into the continental block ...
in the 13th century, the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
drove some 40,000 Cuman
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
families, a nomadic tribe, west of the Carpathian Mountains. The Iranian Jassic people came to Hungary together with the Cumans after they were defeated by the Mongols. Over the centuries they were fully assimilated into the Hungarian population. Rogerius of Apulia
Roger of Torre Maggiore or Master Roger ( hu, Rogerius mester; 1205 in Torre Maggiore – April 14, 1266 in Split) was an Italian prelate active in the Kingdom of Hungary in the middle of the 13th century. He was archbishop of Split in ...
, an Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
monk who witnessed and survived the First Mongol invasion of Hungary
The first Mongol invasion of Hungary ( hu, tatárjárás) started in March 1241, and the Mongols started to withdraw in late March 1242.
Background Mongol invasion of Europe
The Hungarians had first learned about the Mongol threat in 1229, when ...
, pointed out that the Mongols "found pleasure" in humiliating local women.
Starting in 1938, Hungary under Miklós Horthy
Miklós Horthy de Nagybánya ( hu, Vitéz nagybányai Horthy Miklós; ; English: Nicholas Horthy; german: Nikolaus Horthy Ritter von Nagybánya; 18 June 1868 – 9 February 1957), was a Hungarian admiral and dictator who served as the regent ...
passed a series of anti-Jewish measures in the emulation of Germany's Nuremberg Laws. The first, promulgated on 29 May 1938, restricted the number of Jews in each commercial enterprise, in the press, among physicians, engineers and lawyers to twenty percent. The second anti-Jewish law (5 May 1939), for the first time, defined Jews racially: people with 2, 3 or 4 Jewish-born grandparents were declared Jewish. Their employment in government at any level was forbidden, they could not be editors at newspapers, their numbers were restricted to six per cent among theater and movie actors, physicians, lawyers, and engineers. Private companies were forbidden to employ more than 12% Jews. 250,000 Hungarian Jews lost their income. Most of them lost their right to vote as well: before the second Jewish law, about 31% of the Jewish population of Borsod county (Miskolc excluded), 2496 people had this right. At the next elections, less than a month after this new anti-Jewish legislation, only 38 privileged Jews could vote.
Southwestern Europe
 In
In ancient history
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cove ...
, the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
was frequently invaded by foreigners who intermarried with the native population. One of the earliest foreign groups to arrive in the region were the Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
who intermarried with the pre-Indo-European Iberians
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (amo ...
in prehistoric Iberia
The prehistory of the Iberian Peninsula begins with the arrival of the first hominins 1.2 million years ago and ends with the Punic Wars, when the territory enters the domains of written history. In this long period, some of its most signific ...
creating Celtiberians. They were later followed by the Semitic Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns and Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
and the Indo-European Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
who intermarried with the pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula
This is a list of the pre- Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania, i. e., modern Portugal, Spain and Andorra). Some closely fit the concept of a people, ethnic group or tribe. Others are confederations or even unions of t ...
during Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
.
They were in turn followed by the Germanic Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
, Suebi and Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
and the Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
and Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
who also intermarried with the local population in Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
during late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
. In the 6th century, the region of Spania
Spania ( la, Provincia Spaniae) was a province of the Eastern Roman Empire from 552 until 624 in the south of the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands. It was established by the Emperor Justinian I in an effort to restore the western prov ...
was reconquered by the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
(Eastern Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
), when Byzantine Greeks
The Byzantine Greeks were the Greek-speaking Eastern Romans of Orthodox Christianity throughout Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. They were the main inhabitants of the lands of the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire), of Constantinople ...
also settled there, before the region was lost again to the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
less than a century later.
The offspring of marriages between Arabs and non-Arabs in Iberia (Berbers or local Iberians) were known as ''Muladi'' or '' Muwallad'', an Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
term still used in the modern Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
to refer to people with Arab fathers and non-Arab mothers. Some sources consider this term the origin for the Spanish word '' Mulatto''. However, the Real Academia Española does not endorse such etymology. This is because the term was mainly used during the time period of al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
to refer to local Iberians (Christians and pagans) who converted to Islam or whose ancestors had converted. An example is the Banu Qasi, a Muslim dynasty of Basque origin. In addition, many ''Muladi'' were also descended from ''Saqaliba
Saqaliba ( ar, صقالبة, ṣaqāliba, singular ar, صقلبي, ṣaqlabī) is a term used in medieval Arabic sources to refer to Slavs and other peoples of Central, Southern, and Eastern Europe, or in a broad sense to European slaves. The t ...
'' ( Slavic) slaves taken from Eastern Europe via the Arab slave trade
History of slavery in the Muslim world refers to various periods in which a slave trade has been carried out under the auspices of Arab peoples or Arab countries. Examples include:
* Trans-Saharan slave trade
* Indian Ocean slave trade
* Barbary s ...
. Collectively, Christian Europeans named all the Muslims of Iberia, "Moors", regardless of ethnic origin.
After the Reconquista
The ' (Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Nasrid ...
, which was completed in 1492, most of the Moors were forced to either flee to Islamic territories or convert to Christianity
Conversion to Christianity is the religious conversion of a previously non-Christian person to Christianity. Different Christian denominations may perform various different kinds of rituals or ceremonies initiation into their community of believe ...
. The ones who converted to Christianity were known as Morisco
Moriscos (, ; pt, mouriscos ; Spanish for "Moorish") were former Muslims and their descendants whom the Roman Catholic church and the Spanish Crown commanded to convert to Christianity or face compulsory exile after Spain outlawed the open ...
s, and they were often persecuted by the Spanish Inquisition
The Tribunal of the Holy Office of the Inquisition ( es, Tribunal del Santo Oficio de la Inquisición), commonly known as the Spanish Inquisition ( es, Inquisición española), was established in 1478 by the Catholic Monarchs, King Ferdinand ...
as suspects of heresy
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, in particular the accepted beliefs of a church or religious organization. The term is usually used in reference to violations of important religi ...
on the basis of the ''Limpieza de sangre
The concept of (), (, ) or (), literally "cleanliness of blood" and meaning "blood purity", was an early system of racialized discrimination used in early modern Spain and Portugal.
The label referred to those who were considered "Old Chri ...
'' ("Cleanliness of blood") doctrine, under which anti-miscegenation laws were implemented in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
.
Anyone whose ancestors had miscegenated with the Moors or Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
s were suspected of secretly practicing Islam or Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
, so were often particularly monitored by the Inquisition. The claim to universal '' hidalguía'' (lowest nobility) of the Basques was justified by erudites like Manuel de Larramendi (1690–1766)[de Larramendi, Manuel ''Corografía de la muy noble y muy leal provincia de Guipúzcoa'', Bilbao, 1986, facsimile edition of that from Editorial Ekin, Buenos Aires, 1950. (Also published by Tellechea Idígoras, San Sebastián, 1969.) Quoted in ]
La idea de España entre los vascos de la Edad Moderna
', by Jon Arrieta Alberdi, ''Anales 1997–1998'', Real Sociedad Económica Valenciana de Amigos del País because the Arab invasion had not reached the Basque territories, so it was believed that Basques had maintained their original purity, while the rest of Spain was suspect of miscegenation. Hidalguía helped many Basques to official positions in the administration.American Journal of Human Genetics
The ''American Journal of Human Genetics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of human genetics. It was established in 1948 by the American Society of Human Genetics and covers all aspects of heredity in humans, includin ...
'', estimated that about 10% have North African
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
ancestors and 20% have Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
as ancestors. Since there is no direct link between genetic makeup and religious affiliation, however, it is difficult to draw direct conclusions between their findings and forced or voluntary conversion.[ and by ]Stephen Oppenheimer
Stephen Oppenheimer (born 1947) is a British paediatrician, geneticist, and writer. He is a graduate of Balliol College, Oxford and an honorary fellow of the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine. In addition to his work in medicine and tropi ...
who estimates that much earlier migrations, 5000 to 10,000 years ago from the Eastern Mediterranean might also have accounted for the Sephardic estimates: "They are really assuming that they are looking at his migration of Jewish immigrants, but the same lineages could have been introduced in the Neolithic". The rest of genetic studies done in Spain estimate the North African contribution ranging from 2.5/3.4% to 7.7%.
Italy
 As was the case in other areas occupied by Muslims, it was acceptable in Islamic marital law for a Muslim male to marry Christian and
As was the case in other areas occupied by Muslims, it was acceptable in Islamic marital law for a Muslim male to marry Christian and Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
ish females in southern Italy when under Islamic rule – namely, the Emirate of Sicily between the 9th and 11th centuries; and, of least importance, the short-lived Emirate of Bari
The Emirate of Bari was a short-lived Islamic state in Apulia ruled by non-Arabs, probably Berbers and Black Africans. Controlled from the South Italian city of Bari, it was established about 847 when the region was taken from the Byzantine Empire, ...
between 847 and 871. In this case, most intermarriages were between Arab and Berber males from North Africa and the local Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
females. Such intermarriages were particularly common in the Emirate of Sicily, where one writer visiting the place in the 970s expressed shock at how common it was in rural areas. After the Norman conquest of southern Italy
The Norman conquest of southern Italy lasted from 999 to 1139, involving many battles and independent conquerors.
In 1130, the territories in southern Italy united as the Kingdom of Sicily, which included the island of Sicily, the southern ...
, all Muslim citizens (whether foreign, native or mixed) of the Kingdom of Sicily were known as "Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or ...
". After a brief period when the Arab-Norman culture had flourished under the reign of Roger II of Sicily, later rulers forced the Moors to either convert to Christianity
Conversion to Christianity is the religious conversion of a previously non-Christian person to Christianity. Different Christian denominations may perform various different kinds of rituals or ceremonies initiation into their community of believe ...
or be expelled from the kingdom to Muslim settlement of Lucera in 1224 CE/AD.
In Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, Arabs and Italians from neighbouring Sicily and Calabria intermarried with the local inhabitants, who were descended from Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
and Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
. There are Maltese people are descended from such unions, and the Maltese language
Maltese ( mt, Malti, links=no, also ''L-Ilsien Malti'' or '), is a Semitic language derived from late medieval Sicilian Arabic with Romance superstrata spoken by the Maltese people. It is the national language of Malta and the only offic ...
is descended from Siculo-Arabic
Siculo-Arabic ( ar, الْلهجَة الْعَرَبِيَة الْصَقلِيَة), also known as Sicilian Arabic, is the term used for varieties of Arabic that were spoken in the Emirate of Sicily (which included Malta) from the 9th century ...
.
At times, the Italian city-states also played an active role in the Arab slave trade, where Moorish and Italian traders occasionally exchanged slaves.
During World War II, France's Moroccan troops known as Goumier
The Moroccan Goumiers (french: Les Goumiers Marocains) were indigenous Moroccan soldiers who served in auxiliary units attached to the French Army of Africa, between 1908 and 1956. While nominally in the service of the Sultan of Morocco, they s ...
s committed war rape
Wartime sexual violence is rape or other forms of sexual violence committed by combatants during armed conflict, war, or military occupation often as spoils of war, but sometimes, particularly in ethnic conflict, the phenomenon has broader so ...
s in Italy, especially after the Battle of Monte Cassino, and also in smaller numbers in France and Germany. In Italy, victims of the mass rape
Rape is a type of sexual assault usually involving sexual intercourse or other forms of sexual penetration carried out against a person without their consent. The act may be carried out by physical force, coercion, abuse of authority, or ...
committed after the Battle of Monte Cassino by Goumiers are known as '' Marocchinate''. According to Italian sources, more than 7,000 Italian civilians, including women and children, were raped by Goumiers.
Russia
 Already in the 17th century there were many marriages between Russian settlers and aborigines of
Already in the 17th century there were many marriages between Russian settlers and aborigines of Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
.
The Metis Foundation estimates that there are about 40,000 mixed-race Russians.
Many Chinese men, even those who had left wives and children behind in China, married local women in the 1920s, especially those women who had been widowed during the wars and upheavals of the previous decade. Their mixed race
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
children tended to be given Russian forenames; some retained their fathers' Chinese surnames
Chinese surnames are used by Han Chinese and Sinicized ethnic groups in China, Taiwan, Korea, Vietnam, and among overseas Chinese communities around the world such as Singapore and Malaysia. Written Chinese names begin with surnames, unlike the W ...
, while others took on Russian surnames, and a large proportion also invented new surnames using their father's entire family name and given name as the new surname.
In 2017, ''The Moscow Times'' reported that "Mixed-race marriages are becoming more common in Russia."
Southeastern and Eastern Europe
Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and ...
explored and eventually settled in territories in Slavic-dominated areas of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
. By 950 AD these settlements were largely Slavicized through intermarriage with the local population. Eastern Europe was also an important source for the Arab slave trade at the time, when ''Saqaliba
Saqaliba ( ar, صقالبة, ṣaqāliba, singular ar, صقلبي, ṣaqlabī) is a term used in medieval Arabic sources to refer to Slavs and other peoples of Central, Southern, and Eastern Europe, or in a broad sense to European slaves. The t ...
'' (Slavic) slaves were taken to the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
, where the women and girls often served in harem
Harem ( Persian: حرمسرا ''haramsarā'', ar, حَرِيمٌ ''ḥarīm'', "a sacred inviolable place; harem; female members of the family") refers to domestic spaces that are reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A har ...
s, some of whom married their Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
masters. When the Mongol Empire annexed much of Eastern Europe in the 13th century, the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
also intermarried with the local population and often engaged in war rape
Wartime sexual violence is rape or other forms of sexual violence committed by combatants during armed conflict, war, or military occupation often as spoils of war, but sometimes, particularly in ethnic conflict, the phenomenon has broader so ...
and capturing sex slaves during the Mongol invasion of Europe
From the 1220s into the 1240s, the Mongols conquered the Turkic states of Volga Bulgaria, Cumania, Alania, and the Kievan Rus' federation. Following this, they began their invasion into heartland Europe by launching a two-pronged invasion of ...
.
United Kingdom
In the late 15th century, the Romani people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with sig ...
, who have Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
origins, arrived in Britain. The Romani in Britain intermarried with the local population and became known to the Romani as the Romanichal
Romanichal Travellers ( ; more commonly known as English Gypsies or English Travellers) are a Romani subgroup within the United Kingdom and other parts of the English-speaking world. There are an estimated 200,000 Romani in the United Kingdom ...
. In India, employees and officers of the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
, as well as other European soldiers, intermarried with Indian women. Children born in these marriages were called Anglo-Indian
Anglo-Indian people fall into two different groups: those with mixed Indian and British ancestry, and people of British descent born or residing in India. The latter sense is now mainly historical, but confusions can arise. The '' Oxford English ...
s. On some occasions, Indian women moved to Britain to live with their husbands. The British East India Company brought many South Asian lascar
A lascar was a sailor or militiaman from the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, the Arab world, British Somaliland, or other land east of the Cape of Good Hope, who was employed on European ships from the 16th century until the middle of the ...
s (maritime auxiliaries employed by British mercantile and shipping companies) to Britain, where many settled down with local white British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population ...
wives, due to a lack of Asian women in Britain at the time.Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
and African males, have white partners. As of 2009, one in 10 children in the UK lives in a mixed-race or mixed-ethnicity family (families headed by one white-British parent and one white parent not of British origin are included in the figure) and two out of five Chinese women have partners of a different race. One out of five Chinese men have partners of a different race. According to the UK 2001 census
A nationwide census, known as Census 2001, was conducted in the United Kingdom on Sunday, 29 April 2001. This was the 20th UK census and recorded a resident population of 58,789,194.
The 2001 UK census was organised by the Office for National ...
, black British males were around 50% more likely than black females to marry outside their race. British Chinese
British Chinese (also known as Chinese British or Chinese Britons) are people of Chineseparticularly Han Chineseancestry who reside in the United Kingdom, constituting the second-largest group of Overseas Chinese in Western Europe after France. ...
women (30%) were twice as likely as their male counterparts (15%) to marry someone from a different ethnic group.
Middle East
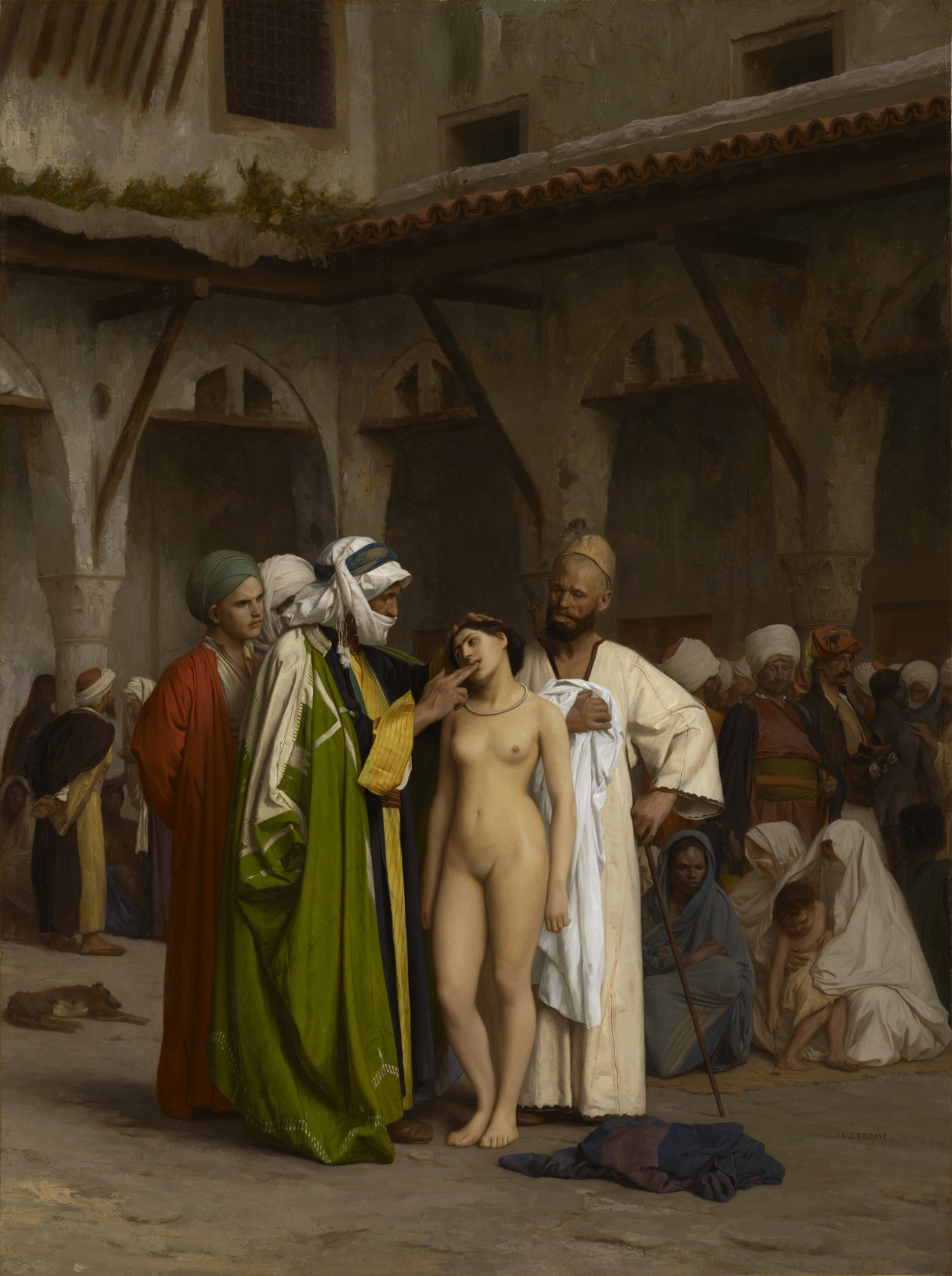 A Stanford team found the greatest diversity outside Africa among people living in the wide crescent of land stretching from the eastern shore of the Mediterranean to northern India. Not only was the region among the first colonized by the African migrants, they theorize, but a large number of European and East Asian genes among the population indicates that it has long been a human highway, with large numbers of migrants from both directions conquering, trading and generally reproducing along its entire length. The same team also found out that the Bedouin nomads of the Middle East actually have some similarities to Europeans and South Asians
Inter-ethnic sexual slavery was common during the
A Stanford team found the greatest diversity outside Africa among people living in the wide crescent of land stretching from the eastern shore of the Mediterranean to northern India. Not only was the region among the first colonized by the African migrants, they theorize, but a large number of European and East Asian genes among the population indicates that it has long been a human highway, with large numbers of migrants from both directions conquering, trading and generally reproducing along its entire length. The same team also found out that the Bedouin nomads of the Middle East actually have some similarities to Europeans and South Asians
Inter-ethnic sexual slavery was common during the Arab slave trade
History of slavery in the Muslim world refers to various periods in which a slave trade has been carried out under the auspices of Arab peoples or Arab countries. Examples include:
* Trans-Saharan slave trade
* Indian Ocean slave trade
* Barbary s ...
throughout the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and early modern period, when women and girls bought from warlords in non-Arab lands often ended up as concubines. Most of these slaves came from places such as Sub-Saharan Africa (mainly ''Zanj
Zanj ( ar, زَنْج, adj. , ''Zanjī''; fa, زنگی, Zangi) was a name used by medieval Muslim geographers to refer to both a certain portion of Southeast Africa (primarily the Swahili Coast) and to its Bantu inhabitants. This word is al ...
''), South Asia (Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
), the North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, ( ady, Темыр Къафкъас, Temır Qafqas; kbd, Ишхъэрэ Къаукъаз, İṩxhərə Qauqaz; ce, Къилбаседа Кавказ, Q̇ilbaseda Kavkaz; , os, Цӕгат Кавказ, Cægat Kavkaz, inh, ...
(mainly Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
), Central Asia (mainly Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
), and Central and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
(mainly ''Saqaliba
Saqaliba ( ar, صقالبة, ṣaqāliba, singular ar, صقلبي, ṣaqlabī) is a term used in medieval Arabic sources to refer to Slavs and other peoples of Central, Southern, and Eastern Europe, or in a broad sense to European slaves. The t ...
''). The Barbary pirate
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli. This area was known in Europe ...
s also captured a number of slaves from Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
and North America between the 16th and 19th centuries. It was also common for Arab conquerors, traders and explorers
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians.
Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most ...
to marry local females in the lands they conquered or traded with, in various parts of Africa, Asia (see Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
section) and Europe (see Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
section).
Inter-ethnic relationships were generally accepted in Arabic society and formed a fairly common theme in medieval Arabic literature
Arabic literature ( ar, الأدب العربي / ALA-LC: ''al-Adab al-‘Arabī'') is the writing, both as prose and poetry, produced by writers in the Arabic language. The Arabic word used for literature is '' Adab'', which is derived from ...
and Persian literature
Persian literature ( fa, ادبیات فارسی, Adabiyâte fârsi, ) comprises oral compositions and written texts in the Persian language and is one of the world's oldest literatures. It spans over two-and-a-half millennia. Its sources h ...
. For example, the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
poet Nizami, who had himself married his Kipchak slave girl, wrote ''The Seven Beauties'' (1196). Its frame story involves a Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
prince marrying seven foreign princesses, including Byzantine, Chinese, Indian, Khwarezmian, Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
ian, Slavic and Tartar princesses. '' Hadith Bayad wa Riyad'', a 12th-century Arabic tale from Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
, was a love story involving an Iberian girl and a Damascene man. The '' One Thousand and One Nights'' tale of "The Man of Al-Yaman and His Six Slave-Girls
''The'' () is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite ...
" involves a Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
i man's relationship with foreign slave girls, four of which are white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
, black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ...
, brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
and yellow
Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In the ...
. Another ''One Thousand and One Nights'' tale, " The Ebony Horse", involves the Prince of Persia, Qamar al-Aqmar, rescuing his lover, the Princess of Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
, from the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Emperor who also wishes to marry her.
One study found that some Arabic-speaking populations—Palestinians, Jordanians, Syrians, Iraqis, and Bedouins—have what appears to be substantial mtDNA gene flow from sub-Saharan Africa, amounting to 10–15% of lineages within the past three millennia. A genetic anthropological study known as the Genographic Project has found what is believed to be faint genetic traces left by medieval Crusaders in the Middle East. The team has uncovered a specific DNA signature in Syria, Lebanon, Palestine and Jordan that is probably linked to the 7th and 8th Christian crusades. The Crusaders originated from European kingdoms, mostly France, England and the Holy Roman Empire.
Human trafficking continues today in a smaller form in the Gulf Cooperation Council state, where women and children are trafficked from the post-Soviet states,
A genetic anthropological study known as the Genographic Project has found what is believed to be faint genetic traces left by medieval Crusaders in the Middle East. The team has uncovered a specific DNA signature in Syria, Lebanon, Palestine and Jordan that is probably linked to the 7th and 8th Christian crusades. The Crusaders originated from European kingdoms, mostly France, England and the Holy Roman Empire.
Human trafficking continues today in a smaller form in the Gulf Cooperation Council state, where women and children are trafficked from the post-Soviet states, Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
, Far East, Africa, South Asia and other parts of the Middle East.
Israel
Among the Jewish population in Israel as of 2014, over 25% of the schoolchildren and over 35% of all newborns are of mixed ancestry of both Ashkenazi and Sephardi/Mizrahi Jews, Mizrahi descent, which increases by 0.5% each year. Over 50% of the Jewish population is of at least partial Sephardi/Mizrahi descent.[''My Promised Land'', by Ari Shavit, (London 2014)]
In Israel, all marriages must be approved by religious authorities, while civil marriages are legally recognized if performed abroad. Rules governing marriage are based on strict religious guidelines of each religion. Under Israeli law, authority over all issues related to Judaism in Israel, including marriage, falls under the Chief Rabbinate of Israel, which is Orthodox. Orthodox Judaism is the only form of Judaism recognized by the state, and marriages performed in Israel by non-Orthodox rabbis are not recognized.
The Rabbinate prohibits marriage in Israel of halakhic Jews (i.e. people born to a Jewish mother or Jewish by conversion), whether they are Orthodox Jews or not, to partners who are non-Jewish or who are of Jewish descent that runs through the paternal line (i.e. not Jewish according to halakha), unless they undergo a formal conversion to Judaism. As a result, in the state of Israel, people of differing religious traditions cannot legally marry someone of another religion and multi-faith couples must leave the country to get married.
The only other option in Israel for the marriage of a halakhic Jew (Orthodox or not) to a non-Jew, or for that matter, a Christian to a non-Christian or Muslim to a non-Muslim, is for one partner to formally convert to the other's religion, be it to Orthodox Judaism, a Christian denomination or a denomination of Islam. As for persons with patrilineal Jewish descent (i.e. not recognized as Jewish according to halakha) who wish to marry a halakhic Jew (i.e., born to a Jewish mother or is Jewish by Orthodox conversion) who is Orthodox or otherwise, is also required to formally convert to Orthodox Judaism or they cannot legally marry.
According to a ''Haaretz'' article "Justice Ministry drafts civil marriage law for 'refuseniks 300,000 people, or 150,000 couples, are affected by marriage restrictions based on the partners' disparate religious traditions or non-halakhic Jewish status. A poll in 2014 found that three-quarters of Israeli Jews and two-thirds of Israeli Arabs would not marry someone from a different religion. Inter-faith relationships were opposed by 95 percent of Haredi Jews, 88 percent of traditional and religious Jews and 64 percent of Hiloni, secular Jews.
A group of 35 Jewish men, known as "Fire for Judaism", in Pisgat Ze'ev have started patrolling the town in an effort to stop Jewish women from dating Arab men. The municipality of Petah Tikva has also announced an initiative to prevent interracial relationships, providing a telephone hotline for friends and family to "inform" on Jewish girls who date Arab men as well as psychologists to provide counselling. The town of Kiryat Gat launched a school programme in schools to warn Jewish girls against dating local Bedouin men.
In February 2010 Maariv has reported that the Tel Aviv municipality has instituted an official, government-sponsored "counselling program" to discourage Jewish girls from dating and marrying Arab boys. ''The Times'' has also reported on a vigilante parents' group policing the Jerusalem neighborhood of Pisgat Ze'ev to intimidate and discourage local Arab-Jewish couples. The Jewish anti-missionary group Yad L'Achim has also performed paramilitary "rescue operations" of Jewish women from non-Jewish husbands and celebrates the "rescued women" on their website.
In 2014 the marriage of a Muslim groom and a bride who had converted from Judaism to Islam attracted attention when the wedding was protested by Lehava, an organisation opposing Jewish assimilation. An Israeli court allowed the protest to go ahead but ordered protesters to stay at least 200 metres away from the wedding venue in Rishon LeZion. In response, a demonstration in support for the couple was also held.
In 2005 Ben-Zion Gopstein, a disciple of the ultra-nationalist Meir Kahane, founded the anti-miscegenation organisation Lehava. The group's name is an acronym for "To Prevent Assimilation in the Holy Land". In November 2019, Gopstein was indicted on charges of incitement to terrorism, violence and racism.
Turkey

 In the 11th century, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine territory of Anatolia was conquered by the Seljuq dynasty, Seljuq Turks, who came from Turkestan in Central Asia. Their Ottoman Turks, Ottoman Turkish descendants went on to annex the Balkans and much of
In the 11th century, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine territory of Anatolia was conquered by the Seljuq dynasty, Seljuq Turks, who came from Turkestan in Central Asia. Their Ottoman Turks, Ottoman Turkish descendants went on to annex the Balkans and much of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
in the 15th and 16th centuries. Due to Islamic marital law allowing a Muslims, Muslim male to marry Christian and Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
ish females, it was common in the Ottoman Empire for Turkish males to intermarry with European females. For example, various sultans of the Ottoman Dynasty often had Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(''Rûm''), Slavic (''Saqaliba
Saqaliba ( ar, صقالبة, ṣaqāliba, singular ar, صقلبي, ṣaqlabī) is a term used in medieval Arabic sources to refer to Slavs and other peoples of Central, Southern, and Eastern Europe, or in a broad sense to European slaves. The t ...
''), Republic of Venice, Venetian, North Caucasus, Northcaucasian and French wives.
In the Ottoman Empire, in addition to the Ottoman elites often taking large numbers of European wives and concubines (see #Southeastern and Eastern Europe, Southeastern and Eastern Europe section), there were also opportunities for the reverse, when the empire recruited young Christian boys (Europeans and Christian Arabs) to become the elite troops of the Turkish Empire, the Janissaries. These Janissaries were stationed throughout the Turkish empire including the Middle-East and North Africa leading to inter-ethnic relationships between European men and women from the Middle East and North Africa.
The Ottoman Imperial Harem, concubines of the Ottoman Sultan consisted chiefly of purchased slaves. Because Islamic law forbade Muslims to enslave fellow Muslims, the Sultan's concubines were generally of Christian origin. The mother of a Sultan, though technically a slave, received the extremely powerful title of ''valide sultan'', and at times became effective ruler of the Empire (see Sultanate of women). One notable example was Kösem Sultan, daughter of a Greek Christian priest, who dominated the Ottoman Empire during the early decades of the 17th century. Another notable example was Roxelana, the favourite wife of Suleiman the Magnificent.
Some of these European wives exerted great influence upon the empire as ''valide sultan'' ("Mother-Sultan"), some famous examples including Roxelana, a Ukrainian harem slave who later became Suleiman the Magnificent's favourite wife, and Nakşidil Sultan, wife of Abdul Hamid I, who according to the legend may have been Aimée du Buc de Rivéry, cousin of French Empress Joséphine de Beauharnais, Josephine. Due to the common occurrence of such intermarriages in the Ottoman Empire, they have had a significant impact on the ethnic makeup of the modern Turkish people, Turkish population in Turkey, which now differs from that of the Turkic population in Central Asia. In addition to intermarriage, the large harems of Ottoman sultans often consisted almost entirely of female Concubinage, concubines who were of Christian European origin. Sultan Ibrahim the Mad, Ottoman ruler from 1640 to 1648, is said to have drowned 280 concubines of his harem in the Bosphorus. At least one of his concubines, Turhan Hatice, Ukrainian girl captured during one of the Crimean–Nogai slave raids in Eastern Europe, raids by Tatars and sold into Slavery in the Ottoman Empire, slavery, survived his reign.
Oceania

Australia
Miscegenation was a deliberate policy of the Western Australian Protector of Aborigines, A. O. Neville, who hoped to "breed out" Aboriginal characteristics from the growing "half caste" population of Aborigines in Western Australia. As a result, he failed to prosecute cases where half caste girls were sexually abused or raped by European Australians, who sought an evening on "the black velvet". The children of such unions were often taken from their mothers and confined to "concentration camps" at Moore River and Carrolup, as a part of the policy known as Stolen Generations.
The desire to avoid miscegenation was also a factor in the passage and continued enforcement of the White Australia policy. In 1949, Immigration Minister Arthur Calwell stated "I am sure we don't want half-castes running over our country", while justifying the government's decision to refuse entry to Lorenzo Gamboa (a Filipino man and U.S. Army veteran who had an Australian wife and children).
New Zealand
Mixed marriages are very common and almost universally accepted. People who identify as Māori typically have ancestors ('tīpuna') from at least two distinct ethnicities. Historically this lent itself to the belief that "real" Māori were gradually disappearing from New Zealand through mixed marriage. This view held sway in New Zealand until the late 1960s and 1970s, when a revival and re-establishment of Māori culture and tradition coincided with a rejection of the majority opinion.
The belief that Māori were disappearing was partially founded on the reality of high rates of intermarriage between Europeans and Māori since colonisation. During the revival of Māori culture and tradition, this belief was challenged by redefining "Māori" as an ethnic identity as opposed to a racial category. As a result, a person may have one European/Asian/Pacific parent and one Māori parent, but be considered no less "authentically Māori" than a descendant of two Māori.
As of 2010, two-thirds of Māori births, half of Pacific births, and a third of white and Asian births involved more than one ethnic group.
Portuguese colonies
According to Gilberto Freyre, a Brazilian sociologist, interracial marriage was commonplace in the Portuguese colonies
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the l ...
, and was even supported by the court as a way to boost low populations and guarantee a successful and cohesive settlement. Thus, settlers often released Atlantic slave trade, African slaves to become their wives. The children were guaranteed full Portuguese citizenship, provided the parents were married. Some former Portuguese colonies have large multiracial, mixed-race populations, for instance, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, Cape Verde, Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
, Timor Leste, Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a p ...
and São Tomé and Príncipe. In the case of Brazil, the influential "Indianist" novels of José de Alencar (O Guarany, Iracema, and Ubirajara (novel), Ubirajara) perhaps went farther than in the other colonies, advocating miscegenation in order to create a truly Brazilian race.
Mixed marriages between Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
and locals in former colonies were very common in all Portuguese colonies. Miscegenation was still common in Africa until the independence of the former Portuguese colonies in the mid-1970s. The case for miscegenation in Brazil started in the 1700s when gold was discovered in the heart of the country. This created a spectacular gold rush that lasted nearly 100 years. In this period close to a million men immigrated to Brazil in search of a quick fortune, mostly Portuguese. Since these men had no plans to bring their families, in the process they ended up fathering children with either African slaves or Native American women. Since immigration during this period was overwhelmingly by males, this created a less strict society in terms of enforcing anti-racial laws.
However, Brazil was the last country in the western hemisphere to grant freedom to the slaves, only happening in 1888. When the slaves were freed, the plantation owners encouraged immigration from Europe as a form to replace the slaves. At the beginning of the 20th century, eugenics set foot in Brazil, and although it stated that the white race was superior to the other races, in the end, it somehow contributed to the continuation of the miscegenation of Brazil. With the Politica do blanqueamiento, Branqueamento (Whitening Policy), the Eugenics encouraged mulatto women (daughter of black and white parents) to marry a white man. According to them, the child would be born much whiter than her mother. A famous painting by Modesto Brocos describes these hopes, showing a black grandmother with her arms to the sky, thanking God for white grandchildren. In the painting, a white man sits at the door, and his wife, a mulatto woman, is holding the child, while the mother is much darker than the daughter.
Demographics of ethnoracial admixture
U.S.
According to the U.S. Census, in 2000 there were 504,119 Asian–white marriages, 287,576 black-white marriages, and 31,271 Asian–black marriages. The black–white marriages increased from 65,000 in 1970 to 403,000 in 2006, and 558,000 in 2010, according to Census Bureau figures.
In the United States, rates of interracial cohabitation are significantly higher than those of marriage. Although only 7 percent of married African American men have Caucasian American wives, 13% of cohabitating African American men have Caucasian American partners. 25% of married Asian American women have Caucasian spouses, but 45% of cohabitating Asian American women are with Caucasian American men. Of cohabiting Asian men, slightly over 37% of Asian men have white female partners over 10% married White American women.[
] A Gallup poll on interracial dating in June 2006 found 75% of Americans approving of a white man dating a black woman, and 71% approving of a black man dating a white woman. Among people between the ages of 18 and 29, the poll found that 95% approved of blacks and whites dating, and about 60% said they had dated someone of a different race. 69% of Hispanics, 52% of blacks, and 45% of whites said they have dated someone of another race or ethnic group. In 1980, just 17% of all respondents said they had dated someone from a different racial background.
 However, according to a study from the University of California at Berkeley, using data from over 1 million profiles of singles from online dating websites, whites were far more reluctant to date outside their race than non-whites. The study found that over 80% of whites, including whites who stated no racial preference, contacted other whites, whereas about 3% of whites contacted blacks, a result that held for younger and older participants. Only 5% of whites responded to inquiries from blacks. Black participants were ten times more likely to contact whites than whites were to contact blacks, however black participants sent inquiries to other blacks more often than otherwise.
Interracial marriage is still relatively uncommon, despite the increasing rate. In 2010, 15% of new marriages were interracial, and of those only 9% of Whites married outside of their race. However, this takes into account inter ethnic marriages, this meaning it counts White Hispanic and Latino Americans, white Hispanics marrying non-Hispanic whites as interracial marriages, despite both bride and groom being racially white american, white. Of the 275,000 new interracial marriages in 2010, 43% were white-Hispanic, 14.4% were white-Asian, 11.9% were white-black and the rest were other combinations. However, interracial marriage has become more common over the past decades due to increasing racial diversity, and liberalizing attitudes toward the practice. The number of interracial marriages in the U.S. increased by 65% between 1990 and 2000, and by 20% between 2000 and 2010. "A record 14.6% of all new marriages in the United States in 2008 were between spouses of a different race or ethnicity from one another. ... Rates more than doubled among whites and nearly tripled among blacks between 1980 and 2008. But for both Hispanics and Asians, rates were nearly identical in 2008 and 1980", according to a Pew Research Center analysis of demographic data from the U.S. Census Bureau.
According to studies by Jenifer L. Bratter and Rosalind B. King made publicly available on the Education Resources Information Center, White female-Black male and White female-Asian male marriages are more prone to divorce than White-White pairings.
However, according to a study from the University of California at Berkeley, using data from over 1 million profiles of singles from online dating websites, whites were far more reluctant to date outside their race than non-whites. The study found that over 80% of whites, including whites who stated no racial preference, contacted other whites, whereas about 3% of whites contacted blacks, a result that held for younger and older participants. Only 5% of whites responded to inquiries from blacks. Black participants were ten times more likely to contact whites than whites were to contact blacks, however black participants sent inquiries to other blacks more often than otherwise.
Interracial marriage is still relatively uncommon, despite the increasing rate. In 2010, 15% of new marriages were interracial, and of those only 9% of Whites married outside of their race. However, this takes into account inter ethnic marriages, this meaning it counts White Hispanic and Latino Americans, white Hispanics marrying non-Hispanic whites as interracial marriages, despite both bride and groom being racially white american, white. Of the 275,000 new interracial marriages in 2010, 43% were white-Hispanic, 14.4% were white-Asian, 11.9% were white-black and the rest were other combinations. However, interracial marriage has become more common over the past decades due to increasing racial diversity, and liberalizing attitudes toward the practice. The number of interracial marriages in the U.S. increased by 65% between 1990 and 2000, and by 20% between 2000 and 2010. "A record 14.6% of all new marriages in the United States in 2008 were between spouses of a different race or ethnicity from one another. ... Rates more than doubled among whites and nearly tripled among blacks between 1980 and 2008. But for both Hispanics and Asians, rates were nearly identical in 2008 and 1980", according to a Pew Research Center analysis of demographic data from the U.S. Census Bureau.
According to studies by Jenifer L. Bratter and Rosalind B. King made publicly available on the Education Resources Information Center, White female-Black male and White female-Asian male marriages are more prone to divorce than White-White pairings.
Brazil
 Multiracial Brazilians make up Mixed-race Brazilian, 42.6% of Brazil's population, 79,782 million people, and they live in all regions of
Multiracial Brazilians make up Mixed-race Brazilian, 42.6% of Brazil's population, 79,782 million people, and they live in all regions of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
. Multiracial Brazilians are mainly people of mixed European, African, East Asian (mostly Japanese) and Amerindian
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
ancestry.
Interracial marriages constituted 22.6% of all marriages in 2000. 15.7% of blacks, 24.4% of whites and 27.6% of ''Pardos'' (mixed-race/brown) married someone whose race was different from their own.
Genetic admixture
Sexual reproduction between two populations reduces the genetic distance between the populations. During the Age of Discovery which began in the early 15th century, European explorers sailed all across the globe reaching all the major continents. In the process they came into contact with many populations that had been isolated for thousands of years. The Tasmanian Aboriginals were one of the most isolated groups on the planet.[ The colonization of the Americas brought Indigenous people of the Americas, Native Americans into contact with the distant populations of Europe, ]Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and Asia.[ As a result, many countries in the Americas have significant and complex multiracial populations.
]
Admixture in the United States
Genetic studies indicate that many African-Americans possess varying degrees of European admixture, although it is suggested that the Native American admixture in African-Americans is exaggerated. Some estimates from studies indicated that many of the African-Americans who took part, had European admixture ranging from 25-50% in the Northeast United States, Northeast and less than 10% in the South United States, South (where a vast majority of the population reside).
"Supplemental Tables and Figures"
p. 42. 18 September 2014. Retrieved 16 July 2015. A statistical analysis done in 1958 using historical census data and historical data on immigration and birth rates concluded that 21% of the white population had black ancestors. The growth in the White population could not be attributed to births in the White population and immigration from Europe alone, but had received significant contribution from the African American population as well.
The author states in 1958:
A 2003 study on Y-chromosomes and mtDNA detected no African admixture in the European-Americans who took part in it. The sample included 628 European-American Y-chromosomes and mtDNA from 922 European-Americans According to a genome-wide study by 23andMe, White Americans (European Americans) who participated were: "98.6 percent European, 0.19 percent African and 0.18 percent Native American on average."
A statistical analysis done in 1958 using historical census data and historical data on immigration and birth rates concluded that 21% of the white population had black ancestors. The growth in the White population could not be attributed to births in the White population and immigration from Europe alone, but had received significant contribution from the African American population as well.
The author states in 1958:
A 2003 study on Y-chromosomes and mtDNA detected no African admixture in the European-Americans who took part in it. The sample included 628 European-American Y-chromosomes and mtDNA from 922 European-Americans According to a genome-wide study by 23andMe, White Americans (European Americans) who participated were: "98.6 percent European, 0.19 percent African and 0.18 percent Native American on average."[
In the United States, intermarriage among Filipino Americans, Filipinos with other races is common. They have the largest number of interracial marriages among Asian immigrant groups, as documented in California. It is also noted that 21.8% of Filipino Americans are of mixed blood, second among Asian Americans, and is the fastest growing.
]
Admixture in Latin America
Background
Prior to the European conquest of the Americas the demographics of Latin America was naturally 100% Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American Indian. Today those who identify themselves as Native Americans are small minorities in many countries. For example, the CIA lists Demographics of Argentina#Indigenous peoples, Argentina's at 0.9%, Indigenous peoples in Brazil, Brazil's at 0.4%, and Uruguay's at 0%. However, the range varies widely from country to country in Latin America with some countries having significantly larger Amerindian
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
minorities.
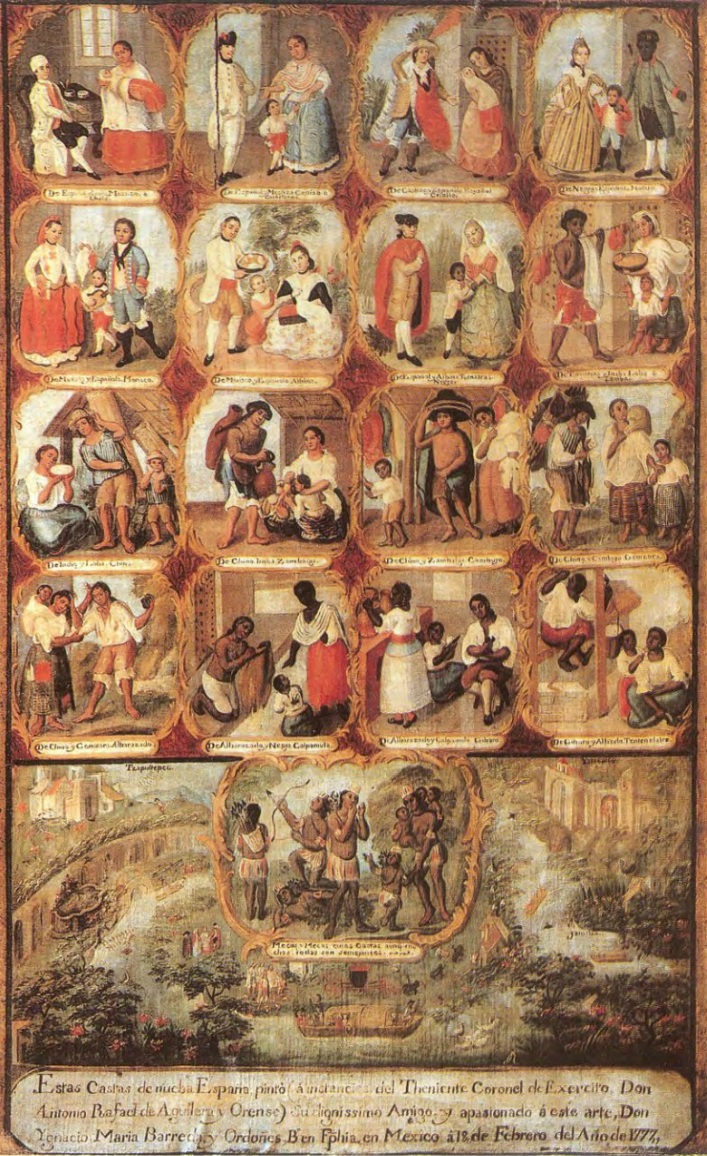 The early conquest of Latin America was primarily carried out by male soldiers and sailors from Spain and Portugal. Since they carried very few European women on their journeys the new settlers married and fathered children with Amerindian women and also with women taken by force from
The early conquest of Latin America was primarily carried out by male soldiers and sailors from Spain and Portugal. Since they carried very few European women on their journeys the new settlers married and fathered children with Amerindian women and also with women taken by force from Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. This process of miscegenation was even encouraged by the Spanish Monarchy and it led to the system of stratification known as the Casta. This system had Europeans (Spanish people, Spaniards and Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
) at the top of the hierarchy followed by those of mixed race
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
. Unmixed Blacks and Native Americans were at the bottom. A philosophy of Racial whitening, whitening, an example of scientific racism in favor of white supremacy, emerged in which Amerindian and African culture were stigmatized in favor of European values. Many Amerindian languages were lost as mixed race offspring adopted Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese as their first languages. Only towards the end of the 19th century and beginning of the 20th century did large numbers of Europeans begin to migrate to South America and consequently altering its Latin america#Demographics, demographics.
In addition many Ethnic groups of Africa, Africans were shipped to regions all over the Americas and were present in many of the early voyages of the conquistadors. Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
has the largest population of African descendants outside Africa. Other countries such as Jamaica, Cuba, Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, Haiti, Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador still have sizeable populations identified as Black people, Black. However countries such as Argentina do not have a visible African presence today. Census information from the early 19th century shows that people categorized as Black made up to 30% of the population, or around 400,000 people. Though almost completely absent today, their contribution to Argentine culture is significant and include the Argentine tango, tango, the Milonga (music), milonga and the Zamba (artform), zamba, words of Bantu languages, Bantu origin.
The ideology of whitening encouraged non-whites to seek white or lighter skinned partners. This dilution of non-white admixture would be beneficial to their offspring as they would face less stigmatization and find it easier to assimilate into mainstream society. After successive generations of European gene flow, non-white admixture levels would drop below levels at which skin color or physical appearance is not affected thus allowing individuals to identify as White. In many regions, the native and black populations were simply overwhelmed by a succession of waves of European immigration.
Historians and scientists are thus interested in tracing the fate of Native Americans and Africans from the past to the future. The questions remain about what proportion of these populations simply died out and what proportion still has descendants alive today including those who do not racially identify themselves as their ancestors would have. Admixture testing has thus become a useful objective tool in shedding light on the demographic history of Latin America.
Recent studies
 Unlike in the United States, there were no anti-miscegenation policies in Latin America. Though still a racially stratified society there were no significant barriers to gene flow between the three populations. As a result, admixture profiles are a reflection of the colonial populations of Africans, Europeans and Amerindians. The pattern is also sex biased in that the African and Amerindian maternal lines are found in significantly higher proportions than African or Amerindian Y chromosomal lines. This is an indication that the primary mating pattern was that of European males with Amerindian or African females. According to the study more than half the White populations of the Latin American countries studied have some degree of either Native American or African admixture (MtDNA or Y chromosome). In countries such as Chile and Colombia almost the entire white population was shown to have some non-white admixture.
Frank Moya Pons, a Dominican Republic, Dominican historian documented that Spanish colonists intermarried with Taíno women, and, over time, these mestizo descendants intermarried with Africans, creating a tri-racial Creole culture. 1514 census records reveal that 40% of Spanish men in the colony of Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, Santo Domingo had Taíno wives. A 2002 study conducted in Puerto Rico suggests that over 61% of the population possess Amerindian mtDNA.
Unlike in the United States, there were no anti-miscegenation policies in Latin America. Though still a racially stratified society there were no significant barriers to gene flow between the three populations. As a result, admixture profiles are a reflection of the colonial populations of Africans, Europeans and Amerindians. The pattern is also sex biased in that the African and Amerindian maternal lines are found in significantly higher proportions than African or Amerindian Y chromosomal lines. This is an indication that the primary mating pattern was that of European males with Amerindian or African females. According to the study more than half the White populations of the Latin American countries studied have some degree of either Native American or African admixture (MtDNA or Y chromosome). In countries such as Chile and Colombia almost the entire white population was shown to have some non-white admixture.
Frank Moya Pons, a Dominican Republic, Dominican historian documented that Spanish colonists intermarried with Taíno women, and, over time, these mestizo descendants intermarried with Africans, creating a tri-racial Creole culture. 1514 census records reveal that 40% of Spanish men in the colony of Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, Santo Domingo had Taíno wives. A 2002 study conducted in Puerto Rico suggests that over 61% of the population possess Amerindian mtDNA.
Admixture in the Philippines
Historically, admixture has been a common phenomenon in the Philippines. The Philippines were originally settled by Australoid
Australo-Melanesians (also known as Australasians or the Australomelanesoid, Australoid or Australioid race) is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to Melanesia and Australia. Controversially, groups from Southeast Asia an ...
peoples called Negritos
The term Negrito () refers to several diverse ethnic groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia and the Andaman Islands. Populations often described as Negrito include: the Andamanese peoples (including the Great Andamanese, the On ...
which now form the country's aboriginal community. Admixture occurred between this earlier group and the mainstream Malayo-Polynesian
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeas ...
population.[
There has been Indian Filipino, Indian migration to and influence in the Philippines since the precolonial era. About 25% of the words in the Tagalog language are Sanskrit terms and about 5% of the country's population possess Indian ancestry from antiquity.][Pre Colonial Period]
geocities.com There has been a Chinese presence in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
since the 9th century. However, large-scale migrations of Chinese to the Philippines only started during the Spanish colonial era, when the world market was opened to the Philippines. It is estimated that among Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or othe ...
, 10%–20% have some Chinese ancestry and 1.5% are "full-blooded" Chinese.[
According to the American anthropologist Dr. H. Otley Beyer, the ancestry of ]Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or othe ...
is 2% Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
. This dates back to when Arab traders intermarried with the local Malay Filipina female populations during the pre-Spanish history of the Philippines.[ A recent genetic study by Stanford University indicates that at least 3.6% of the population are European ethnic groups, European or of part European descent from both Spanish Empire, Spanish and United States colonization.
]
Admixture among the Romani people
Genetic evidence has shown that the Romani people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with sig ...
("Names of the Romani people, Gypsies") originated from the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
and mixed with the local populations in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, the Middle East, and Europe. In the 1990s, it was discovered that Romani populations carried large frequencies of particular Y chromosomes (inherited paternally) that otherwise exist only in populations from South Asia, in addition to fairly significant frequencies of particular mitochondrial DNA (inherited maternally) that is rare outside South Asia.
47.3% of Romani males carry Y chromosomes of Haplogroup H (Y-DNA), haplogroup H-M82 which is rare outside of the Indian subcontinent.
Admixture in South Africa
 Coloureds ( af, Kleurlinge or ''Bruinmense'', lit. "Brown people") are a multiracial ethnic group Indigenous peoples of Africa, native to Southern Africa who have ancestry from more than one of the various populations inhabiting the region, including Khoisan, Bantu peoples, Bantu, White South Africans, European, Austronesian peoples, Austronesian, East Asian people, East Asian or South Asian ethnic groups, South Asian. Because of the combination of ethnicities, different families and individuals within a family may have a variety of different physical features.
Coloureds ( af, Kleurlinge or ''Bruinmense'', lit. "Brown people") are a multiracial ethnic group Indigenous peoples of Africa, native to Southern Africa who have ancestry from more than one of the various populations inhabiting the region, including Khoisan, Bantu peoples, Bantu, White South Africans, European, Austronesian peoples, Austronesian, East Asian people, East Asian or South Asian ethnic groups, South Asian. Because of the combination of ethnicities, different families and individuals within a family may have a variety of different physical features.Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
an lineages contributed 37.3% to paternal components and South Asian/ Southeast Asian lineages 17.5%.[
]
See also
* Apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
* A Racial Program for the Twentieth Century
''A Racial Program for the Twentieth Century'' (occasionally ''A Radical Program for the Twentieth Century'') was a hoax that first gained public notoriety on June 7, 1957, during a debate on the Civil Rights Act of 1957, when Rep. Thomas Abern ...
* Discrimination based on skin color
* Exogamy
* First interracial kiss on television
* Heterosis
* Interracial marriage
* Interracial marriage in the United States
* Jim Crow laws
* Limpieza de sangre
The concept of (), (, ) or (), literally "cleanliness of blood" and meaning "blood purity", was an early system of racialized discrimination used in early modern Spain and Portugal.
The label referred to those who were considered "Old Chri ...
* List of interracial romance films
* Loving Day
* Lusotropicalism
* Mixed Race Day
* Melungeon
* Multiculturalism
* Multiracialism
* One-drop rule
* Outcrossing
* Plaçage
* Race and genetics
* Race and society
* Race of the future
* Racial antisemitism
* Racial Integrity Act of 1924
In 1924, the Virginia General Assembly enacted the Racial Integrity Act. The act reinforced racial segregation by prohibiting interracial marriage and classifying as "white" a person "who has no trace whatsoever of any blood other than Caucasia ...
* Racial segregation
* Racial segregation in the United States
* Racism
* Racism against Black Americans
* Racism by country
* Racism in the United States
References
Further reading
*
*Julie Novkov, Novkov, Julie, ''Racial union: law, intimacy, and the White state in Alabama, 1865–1954'', University of Michigan Press, 2008, pp. 125–128.
*
*
*Deschamps, Bénédicte, ''Le racisme anti-italien aux États-Unis (1880–1940)'', in ''Exclure au nom de la race (États-Unis, Irlande, Grande-Bretagne)'', Michel Prum (Éd.). Paris: Syllepse, 2000. 59–81.
*
*
*
*
* Jacobson, Matthew Frye,
Whiteness of a different color. European Immigrants and the Alchemy of Race
', Harvard University Press, 1998.
External links
*
*
{{Multiethnicity
Interracial relationships
 ''Miscegenation'' comes from the
''Miscegenation'' comes from the  The historical taboo surrounding white–black relationships among American whites can be seen as a historical consequence of the oppression and
The historical taboo surrounding white–black relationships among American whites can be seen as a historical consequence of the oppression and  Throughout
Throughout  From the mid 19th century to the 20th century, the several hundred thousand Chinese men who migrated were almost entirely of Cantonese origin, mostly from Taishan. Anti-miscegenation laws prohibited Chinese men from marrying white women in many states. After the Emancipation Proclamation, many intermarriages in some states were not recorded and historically, Chinese American men married African American women in proportions that were higher than their total marriage numbers due to the fact that few Chinese American women lived in the United States. After the Emancipation Proclamation, many Chinese Americans migrated to the
From the mid 19th century to the 20th century, the several hundred thousand Chinese men who migrated were almost entirely of Cantonese origin, mostly from Taishan. Anti-miscegenation laws prohibited Chinese men from marrying white women in many states. After the Emancipation Proclamation, many intermarriages in some states were not recorded and historically, Chinese American men married African American women in proportions that were higher than their total marriage numbers due to the fact that few Chinese American women lived in the United States. After the Emancipation Proclamation, many Chinese Americans migrated to the  In the United States, segregationists, including modern-day
In the United States, segregationists, including modern-day  In Mexico, the concept of ''
In Mexico, the concept of '' About 300,000 Cantonese
About 300,000 Cantonese 
 Although the
Although the  Inter-ethnic marriage in Japan dates back to the 7th century, when Chinese and
Inter-ethnic marriage in Japan dates back to the 7th century, when Chinese and  Historically, admixture has been an ever-present and pervasive phenomenon in the Philippines. The
Historically, admixture has been an ever-present and pervasive phenomenon in the Philippines. The 
 In 1905 the local colonial administration banned civil marriages of "mixed" couples in German South West Africa. Three years later, all "mixed marriages" that had been contracted before 1905 were annulled retrospectively.
During the years which followed
In 1905 the local colonial administration banned civil marriages of "mixed" couples in German South West Africa. Three years later, all "mixed marriages" that had been contracted before 1905 were annulled retrospectively.
During the years which followed  With the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, the laws which banned so-called mixed marriages were lifted. If couples who had already lived together during the Nazi era had remained unmarried due to the legal restrictions then got married after the war, their date of marriage was legally retroactively backdated if they wished it to be the date when they formed a couple. Even if one spouse was already dead, the marriage could be retroactively recognised. In the West German Federal Republic of Germany 1,823 couples applied for recognition, which was granted in 1,255 cases.
With the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, the laws which banned so-called mixed marriages were lifted. If couples who had already lived together during the Nazi era had remained unmarried due to the legal restrictions then got married after the war, their date of marriage was legally retroactively backdated if they wished it to be the date when they formed a couple. Even if one spouse was already dead, the marriage could be retroactively recognised. In the West German Federal Republic of Germany 1,823 couples applied for recognition, which was granted in 1,255 cases.
 In
In  As was the case in other areas occupied by Muslims, it was acceptable in Islamic marital law for a Muslim male to marry Christian and
As was the case in other areas occupied by Muslims, it was acceptable in Islamic marital law for a Muslim male to marry Christian and  Already in the 17th century there were many marriages between Russian settlers and aborigines of
Already in the 17th century there were many marriages between Russian settlers and aborigines of  A Stanford team found the greatest diversity outside Africa among people living in the wide crescent of land stretching from the eastern shore of the Mediterranean to northern India. Not only was the region among the first colonized by the African migrants, they theorize, but a large number of European and East Asian genes among the population indicates that it has long been a human highway, with large numbers of migrants from both directions conquering, trading and generally reproducing along its entire length. The same team also found out that the Bedouin nomads of the Middle East actually have some similarities to Europeans and South Asians
Inter-ethnic sexual slavery was common during the
A Stanford team found the greatest diversity outside Africa among people living in the wide crescent of land stretching from the eastern shore of the Mediterranean to northern India. Not only was the region among the first colonized by the African migrants, they theorize, but a large number of European and East Asian genes among the population indicates that it has long been a human highway, with large numbers of migrants from both directions conquering, trading and generally reproducing along its entire length. The same team also found out that the Bedouin nomads of the Middle East actually have some similarities to Europeans and South Asians
Inter-ethnic sexual slavery was common during the  A genetic anthropological study known as the Genographic Project has found what is believed to be faint genetic traces left by medieval Crusaders in the Middle East. The team has uncovered a specific DNA signature in Syria, Lebanon, Palestine and Jordan that is probably linked to the 7th and 8th Christian crusades. The Crusaders originated from European kingdoms, mostly France, England and the Holy Roman Empire.
Human trafficking continues today in a smaller form in the Gulf Cooperation Council state, where women and children are trafficked from the post-Soviet states,
A genetic anthropological study known as the Genographic Project has found what is believed to be faint genetic traces left by medieval Crusaders in the Middle East. The team has uncovered a specific DNA signature in Syria, Lebanon, Palestine and Jordan that is probably linked to the 7th and 8th Christian crusades. The Crusaders originated from European kingdoms, mostly France, England and the Holy Roman Empire.
Human trafficking continues today in a smaller form in the Gulf Cooperation Council state, where women and children are trafficked from the post-Soviet states, 

 However, according to a study from the University of California at Berkeley, using data from over 1 million profiles of singles from online dating websites, whites were far more reluctant to date outside their race than non-whites. The study found that over 80% of whites, including whites who stated no racial preference, contacted other whites, whereas about 3% of whites contacted blacks, a result that held for younger and older participants. Only 5% of whites responded to inquiries from blacks. Black participants were ten times more likely to contact whites than whites were to contact blacks, however black participants sent inquiries to other blacks more often than otherwise.
Interracial marriage is still relatively uncommon, despite the increasing rate. In 2010, 15% of new marriages were interracial, and of those only 9% of Whites married outside of their race. However, this takes into account inter ethnic marriages, this meaning it counts White Hispanic and Latino Americans, white Hispanics marrying non-Hispanic whites as interracial marriages, despite both bride and groom being racially white american, white. Of the 275,000 new interracial marriages in 2010, 43% were white-Hispanic, 14.4% were white-Asian, 11.9% were white-black and the rest were other combinations. However, interracial marriage has become more common over the past decades due to increasing racial diversity, and liberalizing attitudes toward the practice. The number of interracial marriages in the U.S. increased by 65% between 1990 and 2000, and by 20% between 2000 and 2010. "A record 14.6% of all new marriages in the United States in 2008 were between spouses of a different race or ethnicity from one another. ... Rates more than doubled among whites and nearly tripled among blacks between 1980 and 2008. But for both Hispanics and Asians, rates were nearly identical in 2008 and 1980", according to a Pew Research Center analysis of demographic data from the U.S. Census Bureau.
According to studies by Jenifer L. Bratter and Rosalind B. King made publicly available on the Education Resources Information Center, White female-Black male and White female-Asian male marriages are more prone to divorce than White-White pairings. Conversely, unions between White males and non-White females (and between Hispanics and non-Hispanic persons) have similar or lower risks of divorce than White-White marriages, unions between white male-black female last longer than white-white pairings or white-Asian pairings.
However, according to a study from the University of California at Berkeley, using data from over 1 million profiles of singles from online dating websites, whites were far more reluctant to date outside their race than non-whites. The study found that over 80% of whites, including whites who stated no racial preference, contacted other whites, whereas about 3% of whites contacted blacks, a result that held for younger and older participants. Only 5% of whites responded to inquiries from blacks. Black participants were ten times more likely to contact whites than whites were to contact blacks, however black participants sent inquiries to other blacks more often than otherwise.
Interracial marriage is still relatively uncommon, despite the increasing rate. In 2010, 15% of new marriages were interracial, and of those only 9% of Whites married outside of their race. However, this takes into account inter ethnic marriages, this meaning it counts White Hispanic and Latino Americans, white Hispanics marrying non-Hispanic whites as interracial marriages, despite both bride and groom being racially white american, white. Of the 275,000 new interracial marriages in 2010, 43% were white-Hispanic, 14.4% were white-Asian, 11.9% were white-black and the rest were other combinations. However, interracial marriage has become more common over the past decades due to increasing racial diversity, and liberalizing attitudes toward the practice. The number of interracial marriages in the U.S. increased by 65% between 1990 and 2000, and by 20% between 2000 and 2010. "A record 14.6% of all new marriages in the United States in 2008 were between spouses of a different race or ethnicity from one another. ... Rates more than doubled among whites and nearly tripled among blacks between 1980 and 2008. But for both Hispanics and Asians, rates were nearly identical in 2008 and 1980", according to a Pew Research Center analysis of demographic data from the U.S. Census Bureau.
According to studies by Jenifer L. Bratter and Rosalind B. King made publicly available on the Education Resources Information Center, White female-Black male and White female-Asian male marriages are more prone to divorce than White-White pairings. Conversely, unions between White males and non-White females (and between Hispanics and non-Hispanic persons) have similar or lower risks of divorce than White-White marriages, unions between white male-black female last longer than white-white pairings or white-Asian pairings.
 Multiracial Brazilians make up Mixed-race Brazilian, 42.6% of Brazil's population, 79,782 million people, and they live in all regions of
Multiracial Brazilians make up Mixed-race Brazilian, 42.6% of Brazil's population, 79,782 million people, and they live in all regions of  A statistical analysis done in 1958 using historical census data and historical data on immigration and birth rates concluded that 21% of the white population had black ancestors. The growth in the White population could not be attributed to births in the White population and immigration from Europe alone, but had received significant contribution from the African American population as well.
The author states in 1958:
A 2003 study on Y-chromosomes and mtDNA detected no African admixture in the European-Americans who took part in it. The sample included 628 European-American Y-chromosomes and mtDNA from 922 European-Americans According to a genome-wide study by 23andMe, White Americans (European Americans) who participated were: "98.6 percent European, 0.19 percent African and 0.18 percent Native American on average."
In the United States, intermarriage among Filipino Americans, Filipinos with other races is common. They have the largest number of interracial marriages among Asian immigrant groups, as documented in California. It is also noted that 21.8% of Filipino Americans are of mixed blood, second among Asian Americans, and is the fastest growing.
A statistical analysis done in 1958 using historical census data and historical data on immigration and birth rates concluded that 21% of the white population had black ancestors. The growth in the White population could not be attributed to births in the White population and immigration from Europe alone, but had received significant contribution from the African American population as well.
The author states in 1958:
A 2003 study on Y-chromosomes and mtDNA detected no African admixture in the European-Americans who took part in it. The sample included 628 European-American Y-chromosomes and mtDNA from 922 European-Americans According to a genome-wide study by 23andMe, White Americans (European Americans) who participated were: "98.6 percent European, 0.19 percent African and 0.18 percent Native American on average."
In the United States, intermarriage among Filipino Americans, Filipinos with other races is common. They have the largest number of interracial marriages among Asian immigrant groups, as documented in California. It is also noted that 21.8% of Filipino Americans are of mixed blood, second among Asian Americans, and is the fastest growing.
 The early conquest of Latin America was primarily carried out by male soldiers and sailors from Spain and Portugal. Since they carried very few European women on their journeys the new settlers married and fathered children with Amerindian women and also with women taken by force from
The early conquest of Latin America was primarily carried out by male soldiers and sailors from Spain and Portugal. Since they carried very few European women on their journeys the new settlers married and fathered children with Amerindian women and also with women taken by force from  Unlike in the United States, there were no anti-miscegenation policies in Latin America. Though still a racially stratified society there were no significant barriers to gene flow between the three populations. As a result, admixture profiles are a reflection of the colonial populations of Africans, Europeans and Amerindians. The pattern is also sex biased in that the African and Amerindian maternal lines are found in significantly higher proportions than African or Amerindian Y chromosomal lines. This is an indication that the primary mating pattern was that of European males with Amerindian or African females. According to the study more than half the White populations of the Latin American countries studied have some degree of either Native American or African admixture (MtDNA or Y chromosome). In countries such as Chile and Colombia almost the entire white population was shown to have some non-white admixture.
Frank Moya Pons, a Dominican Republic, Dominican historian documented that Spanish colonists intermarried with Taíno women, and, over time, these mestizo descendants intermarried with Africans, creating a tri-racial Creole culture. 1514 census records reveal that 40% of Spanish men in the colony of Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, Santo Domingo had Taíno wives. A 2002 study conducted in Puerto Rico suggests that over 61% of the population possess Amerindian mtDNA.
Unlike in the United States, there were no anti-miscegenation policies in Latin America. Though still a racially stratified society there were no significant barriers to gene flow between the three populations. As a result, admixture profiles are a reflection of the colonial populations of Africans, Europeans and Amerindians. The pattern is also sex biased in that the African and Amerindian maternal lines are found in significantly higher proportions than African or Amerindian Y chromosomal lines. This is an indication that the primary mating pattern was that of European males with Amerindian or African females. According to the study more than half the White populations of the Latin American countries studied have some degree of either Native American or African admixture (MtDNA or Y chromosome). In countries such as Chile and Colombia almost the entire white population was shown to have some non-white admixture.
Frank Moya Pons, a Dominican Republic, Dominican historian documented that Spanish colonists intermarried with Taíno women, and, over time, these mestizo descendants intermarried with Africans, creating a tri-racial Creole culture. 1514 census records reveal that 40% of Spanish men in the colony of Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, Santo Domingo had Taíno wives. A 2002 study conducted in Puerto Rico suggests that over 61% of the population possess Amerindian mtDNA.