Alpha 21264 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Alpha 21264 is a
The Alpha 21264 is a
 The Alpha 21264A, code-named EV67 was a shrink of the Alpha 21264 introduced in late 1999. There were six versions: 600, 667, 700, 733, 750, 833 MHz. The EV67 was the first Alpha microprocessor to implement the count extension (CIX), which extended the instruction set with instructions for performing population count. It was fabricated by Samsung Electronics in a 0.25 μm CMOS process that had 0.25 μm transistors but 0.35 μm metal layers. The die had an area of 210 mm². The EV68 used a 2.0 V power supply. It dissipated a maximum of 73 W at 600 MHz, 80 W at 667 MHz, 85 W at 700 MHz, 88 W at 733 MHz and 90 W at 750 MHz.
The Alpha 21264A, code-named EV67 was a shrink of the Alpha 21264 introduced in late 1999. There were six versions: 600, 667, 700, 733, 750, 833 MHz. The EV67 was the first Alpha microprocessor to implement the count extension (CIX), which extended the instruction set with instructions for performing population count. It was fabricated by Samsung Electronics in a 0.25 μm CMOS process that had 0.25 μm transistors but 0.35 μm metal layers. The die had an area of 210 mm². The EV68 used a 2.0 V power supply. It dissipated a maximum of 73 W at 600 MHz, 80 W at 667 MHz, 85 W at 700 MHz, 88 W at 733 MHz and 90 W at 750 MHz.
"A 1 GHz Alpha microprocessor"
''ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers'', pp. 86–87. * Clouser, J. et al. (July 1999)
"A 600-MHz superscalar floating-point processor"
''IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits'' 34 (7): pp. 1026–1029. * Fischer, T.; Leibholz, D. (1998)
"Design trade offs in stall-control circuits for 600 MHz instruction queues"
''ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers'', pp. 232–234, 444. * Gieseke, B.A. et al. (1997). "A 600 MHz superscalar RISC microprocessor with out-of-order execution". ''ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers'', pp. 176–177, 451. * Gronowski, Paul E. et al. (May 1998). "High-performance microprocessor design". ''IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits'' 33 (5): pp. 676–686. * Hokinson, R. et al. (2001)
"Design and migration challenges for an Alpha microprocessor in a 0.18 μm copper process"
''ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers'', pp. 320–321, 460. {{Digital Equipment Corporation DEC microprocessors Superscalar microprocessors 64-bit microprocessors
 The Alpha 21264 is a
The Alpha 21264 is a Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president un ...
RISC
In computer engineering, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set comp ...
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circ ...
launched on 19 October 1998. The 21264 implemented the Alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ''álpha'', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , whi ...
instruction set architecture
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA), also called computer architecture, is an abstract model of a computer. A device that executes instructions described by that ISA, such as a central processing unit (CPU), is called an ...
(ISA).
Description
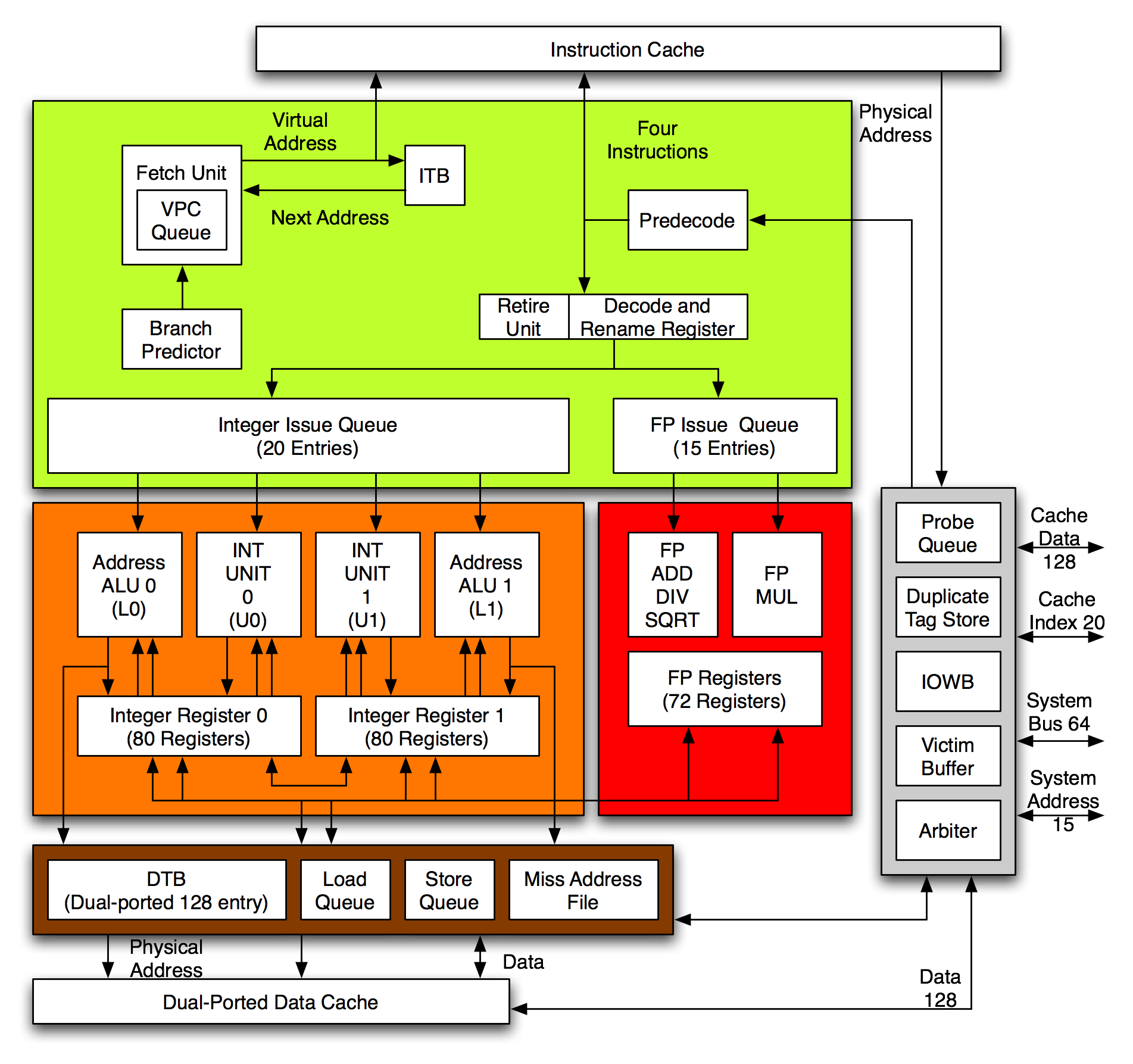
The Alpha 21264 is a four-issuesuperscalar
A superscalar processor is a CPU that implements a form of parallelism called instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. In contrast to a scalar processor, which can execute at most one single instruction per clock cycle, a sup ...
microprocessor with out-of-order execution
In computer engineering, out-of-order execution (or more formally dynamic execution) is a paradigm used in most high-performance central processing units to make use of instruction cycles that would otherwise be wasted. In this paradigm, a proces ...
and speculative execution
Speculative execution is an optimization technique where a computer system performs some task that may not be needed. Work is done before it is known whether it is actually needed, so as to prevent a delay that would have to be incurred by doing ...
. It has a peak execution rate of six instructions per cycle and could sustain four instructions per cycle. It has a seven-stage instruction pipeline
In computer engineering, instruction pipelining or ILP is a technique for implementing instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. Pipelining attempts to keep every part of the processor busy with some instruction by dividing inco ...
.
Out of order execution
At any given stage, the microprocessor could have up to 80 instructions in various stages of execution, surpassing any other contemporary microprocessor. Decoded instructions are held in instruction queues and are issued when their operands are available. The integer queue contained 20 entries and the floating-point queue 15. Each queue could issue as many instructions as there were pipelines.Ebox
The Ebox executes integer, load and store instructions. It has two integer units, two load store units and two integerregister file
A register file is an array of processor registers in a central processing unit (CPU). Register banking is the method of using a single name to access multiple different physical registers depending on the operating mode. Modern integrated circuit- ...
s. Each integer register file contained 80 entries, of which 32 are architectural registers, 40 are rename registers and 8 are PAL shadow registers. There was no entry for register R31 because in the Alpha architecture, R31 is hardwired to zero and is read-only.
Each register file served an integer unit and a load store unit, and the register file and its two units are referred to as a "cluster". The two clusters were designated U0 and U1. This scheme was used as it reduced the number of write and read ports required to serve operands and receive results, thus reducing the physical size of the register file, enabling the microprocessor to operate at higher clock frequencies. Writes to any of the register files thus have to be synchronized, which required a clock cycle to complete, negatively impacting performance by one percent. The reduction of performance resulting from the synchronization was compensated in two ways. Firstly, the higher clock frequency achievable offset the loss. Secondly, the logic responsible for instruction issue avoided creating situations where the register file had to be synchronized by issuing instructions that were not dependent on data held in other register file where possible.
The clusters are near identical except for two differences: U1 has a seven-cycle pipelined multiplier while U0 has a three-cycle pipeline for executing Motion Video Instructions (MVI), an extension to the Alpha Architecture defining single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instructions for multimedia.
The load store units are simple arithmetic logic unit
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a combinational digital circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on floating point num ...
s used to calculate virtual addresses for memory access. They are also capable of executing simple arithmetic and logic instructions. The Alpha 21264 instruction issue logic utilized this capability, issuing instructions to these units when they were available for use (not performing address arithmetic).
The Ebox therefore has four 64-bit adders, four logic units, two barrel shifter
A barrel shifter is a digital circuit that can shift a data word by a specified number of bits without the use of any sequential logic, only pure combinational logic, i.e. it inherently provides a binary operation. It can however in theory also ...
s, byte-manipulation logic, two sets of conditional branch logic equally divided between U1 and U0.
Fbox
The Fbox is responsible for executingfloating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can ...
instructions. It consists of two floating-point pipelines and a floating-point register file. The pipelines are not identical, one executes the majority of instructions and the other only multiply instructions. The adder pipeline has two non-pipelined units connected to it, a divide unit and a square root unit. Adds, multiplies and most other instructions have a 4-cycle latency, a double-precision divide has 16-cycle latency and a double-precision square root has a 33-cycle latency. The floating point register file contains 72 entries, of which 32 are architectural registers and 40 are rename registers.
Cache
The Alpha 21264 has two levels of cache, a primary cache and secondary cache. The level three (L3, or "victim") cache of the Alpha 21164 was not used due to problems with bandwidth.Primary caches
The primary cache is split into separate caches for instructions and data ("modified Harvard architecture
The modified Harvard architecture is a variation of the Harvard computer architecture that, unlike the pure Harvard architecture, allows the contents of the instruction memory to be accessed as data. Most modern computers that are documented as ...
"), the I-cache and D-cache, respectively. Both caches have a capacity of 64 KB. The D-cache is dual-ported by transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This method of dual-porting enabled any combination of reads or writes to the cache every processor cycle. It also avoided duplication the cache so there are two, as in the Alpha 21164. Duplicating the cache restricted the capacity of the cache, as it required more transistors to provide the same amount of capacity, and in turn increased the area required and power consumed.
B-cache
The secondary cache, termed the B-cache, is an external cache with a capacity of 1 to 16 MB. It is controlled by the microprocessor and is implemented by synchronousstatic random access memory
Static random-access memory (static RAM or SRAM) is a type of random-access memory (RAM) that uses latching circuitry (flip-flop) to store each bit. SRAM is volatile memory; data is lost when power is removed.
The term ''static'' differ ...
(SSRAM) chips that operate at two thirds, half, one-third or one-fourth the internal clock frequency, or 133 to 333 MHz at 500 MHz. The B-cache was accessed with a dedicated 128-bit bus that operates at the same clock frequency as the SSRAM or at twice the clock frequency if double data rate
In computing, a computer bus operating with double data rate (DDR) transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in ...
SSRAM is used. The B-cache is direct-mapped.
Branch prediction
Branch prediction
In computer architecture, a branch predictor is a digital circuit that tries to guess which way a branch (e.g., an if–then–else structure) will go before this is known definitively. The purpose of the branch predictor is to improve the flow ...
is performed by a tournament branch prediction algorithm. The algorithm was developed by Scott McFarling at Digital's Western Research Laboratory (WRL) and was described in a 1993 paper. This predictor was used as the Alpha 21264 has a minimum branch misprediction penalty of seven cycles. Due to the instruction cache's two cycle latency and the instruction queues, the average branch misprediction penalty is 11 cycles. The algorithm maintains two history tables, Local and Global, and the table used to predict the outcome of a branch is determined by a Choice predictor.
The local predictor is a two-level table which records the history of individual branches. It consists of a 1,024-entry by 10-bit branch history table. A two-level table was used as the prediction accuracy is similar to that of a larger single-level table while requiring fewer bits of storage. It has a 1,024-entry branch prediction table. Each entry is a 3-bit saturating counter. The value of the counter determines whether the current branch is taken or not taken.
The global predictor is a single-level, 4096-entry branch history table. Each entry is a 2-bit saturating counter; the value of this counter determines whether the current branch is taken or not taken.
The choice predictor records the history of the local and global predictors to determine which predictor is the best for a particular branch. It has a 4,096-entry branch history table. Each entry is a 2-bit saturating counter. The value of the counter determines if the local or global predictor is used.
External interface
The external interface consisted of a bidirectional 64-bitdouble data rate
In computing, a computer bus operating with double data rate (DDR) transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in ...
(DDR) data bus
In computer architecture, a bus (shortened form of the Latin '' omnibus'', and historically also called data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This ...
and two 15-bit unidirectional time-multiplexed address and control
Control may refer to:
Basic meanings Economics and business
* Control (management), an element of management
* Control, an element of management accounting
* Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization
* Controlli ...
buses, one for signals originating from the Alpha 21264 and one for signals originating from the system. Digital licensed the bus to Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufact ...
(AMD), and it was subsequently used in their Athlon
Athlon is the brand name applied to a series of x86-compatible microprocessors designed and manufactured by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). The original Athlon (now called Athlon Classic) was the first seventh-generation x86 processor and the fi ...
microprocessors, where it was known as the EV6 bus.
Memory addressing
Alpha 21264 CPU supports 48-bit or 43-bit virtual address (256 TiB or 8 TiB virtual address space respectively), selectable under IPR control (using VA_CTL control register). Alpha 21264 supports a 44-bit physical address (up to 16 TiB of physical memory). This is an increase from previous Alpha CPUs (43-bit virtual and 40-bit physical for Alpha 21164, and 43-bit virtual and 34-bit physical for Alpha 21064).Fabrication
The Alpha 21264 contained 15.2 million transistors. The logic consisted of approximately six million transistors, with the rest contained in the caches and branch history tables. The die measured 16.7 mm by 18.8 mm (313.96 mm²). Gronowski, "High Performance Microprocessor Design", p. 676. It was fabricated in a 0.35 μmcomplementary metal–oxide–semiconductor
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
(CMOS) process with six levels of interconnect.
Packaging
The Alpha 21264 was packaged in a 587-pin ceramic interstitialpin grid array
A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") a ...
(IPGA).
Alpha Processor, Inc. later sold the Alpha 21264 in a Slot B package containing the microprocessor mounted on a printed circuit board with the B-cache and voltage regulators. The design was intended to use the success of slot-based microprocessors from Intel and AMD. Slot B was originally developed to be used by AMD's Athlon as well, so that API could obtain materials for the Slot B at commodity prices in order to reduce the cost of the Alpha 21264 to gain a wider market share. This never materialized as AMD chose to use Slot A for their slot-based Athlons.
Derivatives
Alpha 21264A
 The Alpha 21264A, code-named EV67 was a shrink of the Alpha 21264 introduced in late 1999. There were six versions: 600, 667, 700, 733, 750, 833 MHz. The EV67 was the first Alpha microprocessor to implement the count extension (CIX), which extended the instruction set with instructions for performing population count. It was fabricated by Samsung Electronics in a 0.25 μm CMOS process that had 0.25 μm transistors but 0.35 μm metal layers. The die had an area of 210 mm². The EV68 used a 2.0 V power supply. It dissipated a maximum of 73 W at 600 MHz, 80 W at 667 MHz, 85 W at 700 MHz, 88 W at 733 MHz and 90 W at 750 MHz.
The Alpha 21264A, code-named EV67 was a shrink of the Alpha 21264 introduced in late 1999. There were six versions: 600, 667, 700, 733, 750, 833 MHz. The EV67 was the first Alpha microprocessor to implement the count extension (CIX), which extended the instruction set with instructions for performing population count. It was fabricated by Samsung Electronics in a 0.25 μm CMOS process that had 0.25 μm transistors but 0.35 μm metal layers. The die had an area of 210 mm². The EV68 used a 2.0 V power supply. It dissipated a maximum of 73 W at 600 MHz, 80 W at 667 MHz, 85 W at 700 MHz, 88 W at 733 MHz and 90 W at 750 MHz.
Alpha 21264B
The Alpha 21264B is a further development for increased clock frequencies. There were two models, one fabricated by IBM, code-named EV68C, and one by Samsung, code-named EV68A. The EV68A was fabricated in a 0.18 μm CMOS process with aluminium interconnects. It had a die size of 125 mm², a third smaller than the Alpha 21264A, and used a 1.7 V power supply. It was available in volume in 2001 at clock frequencies of 750, 833, 875 and 940 MHz. The EV68A dissipated a maximum of 60 W at 750 MHz, 67 W at 833 MHz, 70 W at 875 MHz and 75 W at 940 MHz. Compaq, "21264/EV68A Microprocessor Hardware Reference Manual". The EV68C was fabricated in a 0.18 μm CMOS process with copper interconnects. It was sampled in early 2000 and achieved a maximum clock frequency of 1.25 GHz. In September 1998, Samsung announced they would fabricate a variant of the Alpha 21264B in a 0.18 μm fully depletedsilicon-on-insulator
In semiconductor manufacturing, silicon on insulator (SOI) technology is fabrication of silicon semiconductor devices in a layered silicon–insulator–silicon substrate, to reduce parasitic capacitance within the device, thereby improving perfo ...
(SOI) process with copper interconnects
In semiconductor technology, copper interconnects are interconnects made of copper. They are used in silicon integrated circuits (ICs) to reduce propagation delays and power consumption. Since copper is a better conductor than aluminium, ICs usin ...
that was capable of achieving a clock frequency of 1.5 GHz. This version never materialized.
Alpha 21264C
The Alpha 21264C, code-named EV68CB was a derivative of the Alpha 21264. It was available at clock frequencies of 1.0, 1.25 and 1.33 GHz. The EV68CB contained 15.5 million transistors and measured 120 mm². It was fabricated by IBM in a 0.18 μm CMOS process with seven levels of copper interconnect and low-Kdielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the ma ...
. It was packaged in a 675-pad flip-chip ceramic land grid array (CLGA) measuring 49.53 by 49.53 mm. The EV68CB used a 1.7 V power supply, dissipating a maximum of 64 W at 1.0 GHz, 75 W at 1.25 GHz and 80 W at 1.33 GHz. Compaq, "21264/EV68CB and 21264/EV68DC Hardware Reference Manual".
Alpha 21264D
The Alpha 21264D, code-named EV68CD is a faster derivative fabricated by IBM.Alpha 21264E
The Alpha 21264E, code-named EV68E, was a cancelled derivative developed by Samsung first announced on 10 October 2000 at Microprocessor Forum 2000 slated for introduction at around mid-2001. Improvements were a higher operating frequency of 1.25 GHz and the addition of an on-die 1.85 MB secondary cache. It was to be fabricated in a 0.18 micrometre CMOS process with copper interconnects.Chipsets
Digital andAdvanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufact ...
(AMD) both developed chipsets for the Alpha 21264.
21272/21274
The Digital 21272, also known as the Tsunami, and the 21274, also known as the Typhoon, were the first chipset for the Alpha 21264. The 21272 chipset supported one- or two-way multiprocessing and up to 8GB of memory, while the 21274 supported one-, two-, three- or four-way multiprocessing, up to 64GB of memory, and both supported one or two 64-bit 33 MHz PCI buses. They had 128- to 512-bit memory bus which operated at 83 MHz, yielding a maximum bandwidth of 5,312 MB/s. The chipset supported 100 MHz registered ECC SDRAM. The chipset consisted of three devices, a C-chip, a D-chip and a P-chip. The number of devices which made up the chipset varied as it was determined by the configuration of the chipset. The C-chip is the control chip containing the memory controller. One C-chip was required for every microprocessor. The P-chip is the PCI controller, implementing a 33 MHz PCI bus. The 21272 could have one or two P-chips. The D-chip is the DRAM controller, implementing access to/from the CPUs, and to/from the P-chip. The 21272 could have two or four D-chips and the 21274 could have two, four, or eight D-chips. The 21272 and 21274 were used extensively by Digital, Compaq and Hewlett Packard in their entry-level to mid-range AlphaServers and in all models of the AlphaStation. It was also used in third-party products from Alpha Processor, Inc. (later known as API NetWorks) such as their UP2000+ motherboard.Irongate
AMD developed two Alpha 21264-compatible chipsets, the Irongate, also known as the AMD-751, and its successor, Irongate-2, also known as the AMD-761. These chipsets were developed for their Athlon microprocessors but due to AMD licensing the EV6 bus used in the Alpha from Digital, the Athlon and Alpha 21264 were compatible in terms of bus protocol. The Irongate was used by Samsung in their UP1000 and UP1100 motherboards. The Irongate-2 was used by Samsung in their UP1500 motherboard.See also
* AlphaVM: A fullDEC Alpha
Alpha (original name Alpha AXP) is a 64-bit reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). Alpha was designed to replace 32-bit VAX complex instruction set compute ...
system emulator running on Windows or Linux. It contains a high-performance emulator of the Alpha CPU.
* Clustered Multi-threading
* Alpha 21364
* Alpha 21464
The Alpha 21464 is an unfinished microprocessor that implements the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Digital Equipment Corporation and later by Compaq after it acquired Digital. The microprocessor was also known as EV8 (codenam ...
Notes
References
*Compaq Computer Corporation
Compaq Computer Corporation (sometimes abbreviated to CQ prior to a 2007 rebranding) was an American information technology company founded in 1982 that developed, sold, and supported computers and related products and services. Compaq produced ...
(July 1999). ''Alpha 21264 Microprocessor Hardware Reference Manual''.
* Compaq Computer Corporation
Compaq Computer Corporation (sometimes abbreviated to CQ prior to a 2007 rebranding) was an American information technology company founded in 1982 that developed, sold, and supported computers and related products and services. Compaq produced ...
(June 2001). ''21264/EV68CB and 21264/EV68DC Hardware Reference Manual''.
* Compaq Computer Corporation
Compaq Computer Corporation (sometimes abbreviated to CQ prior to a 2007 rebranding) was an American information technology company founded in 1982 that developed, sold, and supported computers and related products and services. Compaq produced ...
(March 2002). ''21264/EV67 Microprocessor Hardware Reference Manual''.
* Compaq Computer Corporation
Compaq Computer Corporation (sometimes abbreviated to CQ prior to a 2007 rebranding) was an American information technology company founded in 1982 that developed, sold, and supported computers and related products and services. Compaq produced ...
(March 2002). ''21264/EV68A Microprocessor Hardware Reference Manual''.
* Gronowski, Paul E. et al. (1998). "High Performance Microprocessor Design". ''IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits'', Volume 33, Number 5, pp. 676–686.
* Gwennap, Linley (28 October 1996). "Digital 21264 Sets New Standard". '' Microprocessor Report'', Volume 10, Number 14. MicroDesign Resources.
* Kessler, R. E.; McLellan, E. J. and Webb, D. A. (1998) "The Alpha 21264 Microprocessor Architecture". ''Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Design: VLSI in Computers and Processors''. pp. 90–95.
* Kessler, R. E. (1999). "The Alpha 21264 Microprocessor". ''IEEE Micro
''IEEE Micro'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the IEEE Computer Society covering small systems and semiconductor chips, including integrated circuit processes and practices, project management, development tools and infrastruc ...
'', March–April 1999. pp. 24–36.
* Leibholz, Daniel and Razdan, Rahul (1997). "The Alpha 21264: A 500 MHz Out-of-Order Execution Microprocessor". ''Proceedings of Compcon '97''. pp. 28–36.
* Matson, M. et al. "Circuit Implementation of a 600MHz Superscalar RISC Microprocessor". ''Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Design: VLSI in Computers and Processors''. pp. 104–110.
Further reading
* Benschneider, B.J. et al. (2000)"A 1 GHz Alpha microprocessor"
''ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers'', pp. 86–87. * Clouser, J. et al. (July 1999)
"A 600-MHz superscalar floating-point processor"
''IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits'' 34 (7): pp. 1026–1029. * Fischer, T.; Leibholz, D. (1998)
"Design trade offs in stall-control circuits for 600 MHz instruction queues"
''ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers'', pp. 232–234, 444. * Gieseke, B.A. et al. (1997). "A 600 MHz superscalar RISC microprocessor with out-of-order execution". ''ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers'', pp. 176–177, 451. * Gronowski, Paul E. et al. (May 1998). "High-performance microprocessor design". ''IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits'' 33 (5): pp. 676–686. * Hokinson, R. et al. (2001)
"Design and migration challenges for an Alpha microprocessor in a 0.18 μm copper process"
''ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers'', pp. 320–321, 460. {{Digital Equipment Corporation DEC microprocessors Superscalar microprocessors 64-bit microprocessors