Allison J33 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The General Electric/Allison J33 is a development of the
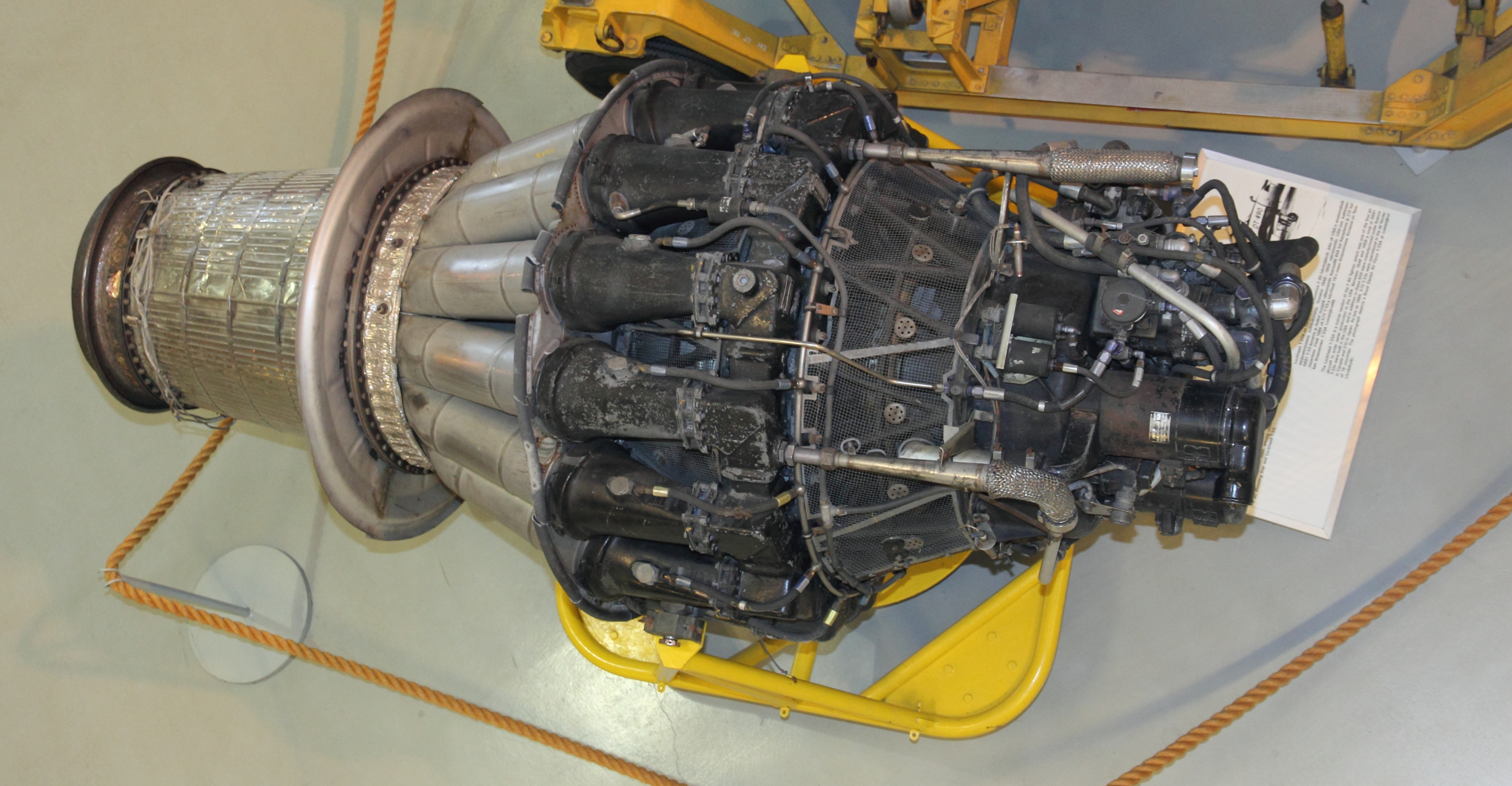

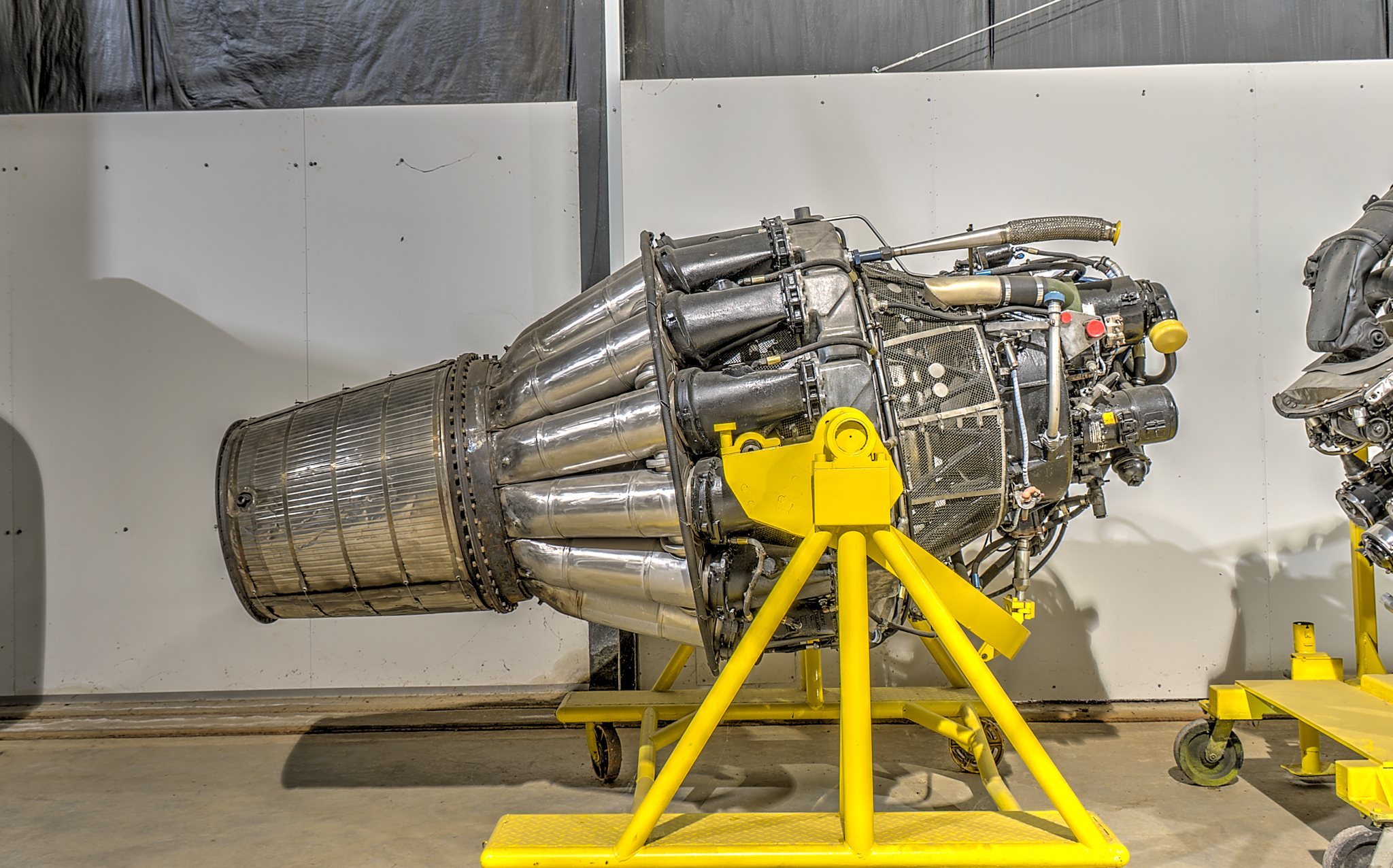 ''Data from:'' Aircraft engines of the World 1953, Aircraft engines of the World 1957, Aircraft engines of the World 1953,
;J33-A-4: similar to -21 without water injection.
;J33-A-6: ,
''Data from:'' Aircraft engines of the World 1953, Aircraft engines of the World 1957, Aircraft engines of the World 1953,
;J33-A-4: similar to -21 without water injection.
;J33-A-6: ,
J33 on LeteckeMotory.cz
(cs) {{USAF gas turbine engines J33 1940s turbojet engines Centrifugal-flow turbojet engines
General Electric J31
The General Electric J31 was the first jet engine to be mass-produced in the United States.
Design and development
After a visit to England mid-1941, General Henry H. Arnold was so impressed by flight demonstrations of the Gloster E.28/39 je ...
, enlarged to produce significantly greater thrust, starting at and ending at with an additional low-altitude boost to with water-alcohol injection.
Development
The J33 was originally developed byGeneral Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable en ...
as a follow-on to their work with the designs of Frank Whittle
Air Commodore Sir Frank Whittle, (1 June 1907 – 8 August 1996) was an English engineer, inventor and Royal Air Force (RAF) air officer. He is credited with inventing the turbojet engine. A patent was submitted by Maxime Guillaume in 1921 fo ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. Their first engine was known as the General Electric I-A
The General Electric I-A was the first working jet engine in the United States, manufactured by General Electric (GE) and achieving its first run on April 18, 1942.
The engine was the result of receiving an imported Power Jets W.1X that was flo ...
, but after major changes to adapt it to US production and to increase thrust, it started limited production as the I-16 in 1942, the 16 referring to its thrust. Full production started as the J31 when the United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
introduced common naming for all their engine projects.
Along with the I-16, GE also started work on an enlarged version, known as the I-40. As the name implied, the engine was designed to provide . Apart from size, the main difference between I-16 and the I-40 was the combustion system: the I-16 had ten reverse-flow cans, whereas the I-40 had 14 straight-through combustors. The development cycle was remarkably rapid. Design work started in mid-1943 and the first prototype underwent static testing on 13 January 1944.
Lockheed was in the midst of the XP-80 project at the time, originally intending to power their design with a US-produced version of the Halford H-1 of about . Production of the H-1 by Allis-Chalmers
Allis-Chalmers was a U.S. manufacturer of machinery for various industries. Its business lines included agricultural equipment, construction equipment, power generation and power transmission equipment, and machinery for use in industrial set ...
ran into delays, and since the I-40 would dramatically improve performance, plans were made to fit the prototypes with the I-40 instead.
The I-40 became important to the USAAF's plans when the I-16 powered P-59 was skipped over in favor of the I-40 powered P-80 as the US's first production jet fighter. In 1945, the license to actually produce the engine was not given to General Electric, but to Allison instead. Allison, working largely from government-owned wartime factories, could produce the engine in quantity more quickly and cheaply.
By the time the production lines were shut down, Allison had built over 6,600 J33's and General Electric another 300 (mostly the early runs).
In 1958, surplus J33s were used in jet donkeys pushing dead loads at 200 knots to test aircraft carrier arresting gear
An arresting gear, or arrestor gear, is a mechanical system used to rapidly decelerate an aircraft as it lands. Arresting gear on aircraft carriers is an essential component of naval aviation, and it is most commonly used on CATOBAR and STOB ...
cables and tailhook
A tailhook, arresting hook, or arrester hook is a device attached to the empennage (rear) of some military fixed-wing aircraft. The hook is used to achieve rapid deceleration during routine landings aboard aircraft carrier flight decks at sea, ...
s at Lakehurst.
A model of the J33 intended for civil use, designated the Allison 400-C4, in 1948 became the first US gas turbine certificated for commercial transport use.
Variants
 ''Data from:'' Aircraft engines of the World 1953, Aircraft engines of the World 1957, Aircraft engines of the World 1953,
;J33-A-4: similar to -21 without water injection.
;J33-A-6: ,
''Data from:'' Aircraft engines of the World 1953, Aircraft engines of the World 1957, Aircraft engines of the World 1953,
;J33-A-4: similar to -21 without water injection.
;J33-A-6: , United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
(USN)
;J33-A-8: , (USN)
;J33-A-10: , (USN) Used as mixed propulsion engine system with P&W R-4360 on Martin P4M
;J33-A-14: A short life engine powering the Chance-Vought Regulus
The SSM-N-8A Regulus or the Regulus I was a United States Navy-developed ship-and-submarine-launched, nuclear-capable turbojet-powered second generation cruise missile, deployed from 1955 to 1964. Its development was an outgrowth of U.S. Navy ...
, thrust.
;J33-A-16: Similar to the -16A,
;J33-A-16A: Powering the Grumman F9F-7
The Grumman F9F/F-9 Cougar is a carrier-based fighter aircraft for the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. Based on Grumman's earlier F9F Panther, the Cougar replaced the Panther's straight wing with a more modern swept wing. Thr ...
, thrust.
;J33-A-17:similar to -21 without water injection
;J33-A-17A:
;J33-A-18A: A short life engine powering the Chance-Vought Regulus
The SSM-N-8A Regulus or the Regulus I was a United States Navy-developed ship-and-submarine-launched, nuclear-capable turbojet-powered second generation cruise missile, deployed from 1955 to 1964. Its development was an outgrowth of U.S. Navy ...
.
;J33-A-20:
;J33-A-21: thrust.
;J33-A-22: Powering the Lockheed T2V-1
The Lockheed T2V SeaStar, later called the T-1 SeaStar, is a carrier-capable jet trainer for the United States Navy that entered service in May 1957. Developed from the Lockheed T-33 (itself derived from the Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star), it ...
with bleed air for boundary-layer control.
;J33-A-23: similar to -35, thrust.
;J33-A-24: thrust, powers the Lockheed T2V.
;J33-A-24A: thrust, powers the Lockheed T2V.
;J33-A-25: similar to -35
;J33-A-27: United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
(USAF), similar to the -16A,
;J33-A-29: re-heat thrust.
;J33-A-31: similar to -35
;J33-A-33: re-heat thrust.
;J33-A-35: thrust / with water-alcohol injection, powers the Lockheed T2V and Lockheed T-33
The Lockheed T-33 Shooting Star (or T-Bird) is an American subsonic jet trainer. It was produced by Lockheed and made its first flight in 1948. The T-33 was developed from the Lockheed P-80/F-80 starting as TP-80C/TF-80C in development, then d ...
.
;J33-A-37: A short life engine powering the Martin Matador, thrust.
;Model 400-C4:Company designation, for commercial use, similar to J33-A-21.
;Model 400-C5:Company designation of J33-A-23.
;Model 400-C13:Company designation of the -35
;Model 400-D9:Company designation of the -33
Applications
*Convair XF-92
The Convair XF-92 (re-designated from XP-92 in 1948) was an American, delta wing, first-generation jet prototype. Originally conceived as a point-defence interceptor, the design was later used purely for experimental purposes and only one w ...
* Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star
The Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star was the first jet fighter used operationally by the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) during World War II. Designed and built by Lockheed in 1943 and delivered just 143 days from the start of design, prod ...
* Lockheed T-33 Shooting Star
The Lockheed T-33 Shooting Star (or T-Bird) is an American subsonic jet trainer. It was produced by Lockheed and made its first flight in 1948. The T-33 was developed from the Lockheed P-80/F-80 starting as TP-80C/TF-80C in development, then d ...
* Lockheed F-94A / F-94B Starfire
* North American AJ Savage
The North American AJ Savage (later A-2 Savage) is an American carrier-based medium bomber built for the United States Navy by North American Aviation. The aircraft was designed shortly after World War II to carry atomic bombs and this meant th ...
* Martin P4M Mercator
The Martin P4M Mercator was a maritime reconnaissance aircraft built by the Glenn L. Martin Company. The Mercator was an unsuccessful contender for a United States Navy requirement for a long-range maritime patrol bomber, with the Lockheed P2V ...
* MGM-1 Matador
The Martin MGM-1 Matador was the first operational surface-to-surface cruise missile designed and built by the United States. It was developed after World War II, drawing upon their wartime experience with creating the Republic-Ford JB-2, a ...
* MGM-13 Mace
The Martin Mace was a ground-launched cruise missile developed from the earlier Martin TM-61 Matador. It used a new self-contained navigation system that eliminated the need to get updates from ground-based radio stations, and thereby allowed i ...
* SSM-N-8 Regulus
Specifications (Allison J33-A-35)
See also
References
Further reading
* * *External links
J33 on LeteckeMotory.cz
(cs) {{USAF gas turbine engines J33 1940s turbojet engines Centrifugal-flow turbojet engines