Allison Engine Company on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Allison Engine Company was an American aircraft engine manufacturer. Shortly after the death of James Allison in 1929 the company was purchased by the
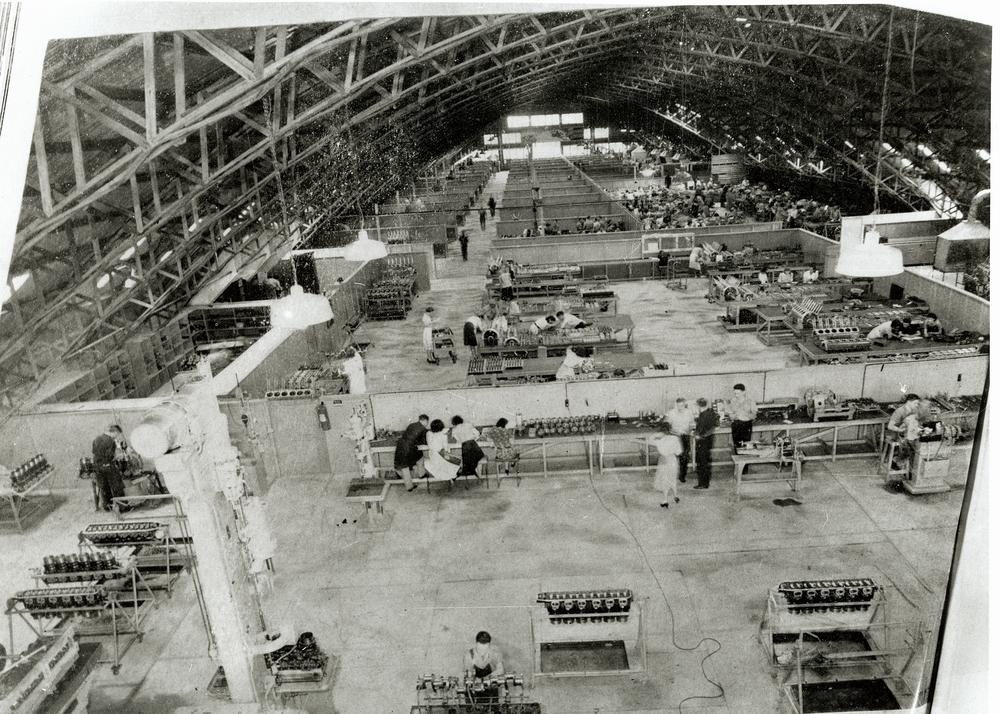
 The very first V-1710 was purchased by the U.S. Navy as their GV-1710-2, and appears to have had an Allison serial of number 1, suggesting that they restarted numbering for the V-1710. The first V-1710 engine purchased by the USAAC was AAC 33-42, Allison Serial No. 2, the XV-1710-1, while Serial Nos. 3, 4, 5 were V-1710-4 engines for U.S. Navy airships, followed by a batch of 11 Air Corps engines purchased with FY-1934 funds (34-4 through 34-14) that covered Allison serials 6 through 16. After these the production race was on, totaling over 70,000 V-1710s.
By this time the Army had become more interested in the design, and asked Allison to continue with a new "C" model. They had few funds of their own to invest, and Allison supported much of the development out of their own pocket. The V-1710-C first flew on 14 December 1936 in the
The very first V-1710 was purchased by the U.S. Navy as their GV-1710-2, and appears to have had an Allison serial of number 1, suggesting that they restarted numbering for the V-1710. The first V-1710 engine purchased by the USAAC was AAC 33-42, Allison Serial No. 2, the XV-1710-1, while Serial Nos. 3, 4, 5 were V-1710-4 engines for U.S. Navy airships, followed by a batch of 11 Air Corps engines purchased with FY-1934 funds (34-4 through 34-14) that covered Allison serials 6 through 16. After these the production race was on, totaling over 70,000 V-1710s.
By this time the Army had become more interested in the design, and asked Allison to continue with a new "C" model. They had few funds of their own to invest, and Allison supported much of the development out of their own pocket. The V-1710-C first flew on 14 December 1936 in the
The shaft driven Lift Fan propulsion system for the Joint Strike Fighter
" page 2, ''

Allison's work on turbine engines for automobiles
{{Authority control Defunct aircraft engine manufacturers of the United States Gas turbine manufacturers Companies disestablished in 1995 Engine manufacturers of the United States Former General Motors subsidiaries Rolls-Royce
Fisher brothers
Fisher Brothers is a real estate firm in New York City. It was formed by Martin Fisher in 1915, soon joined by his brothers Larry (born 1907), and Zachary (born 1910). The Fisher family has substantial real estate holdings in New York City and el ...
. Fisher sold the company to General Motors, which owned it for most of its history. It was acquired by Rolls-Royce plc
Rolls-Royce Holdings plc is a British multinational aerospace and defence company incorporated in February 2011. The company owns Rolls-Royce, a business established in 1904 which today designs, manufactures and distributes power systems for ...
in 1995 to become the US subsidiary, Rolls-Royce North America
Rolls-Royce North America, Inc. is a subsidiary of multinational corporation Rolls-Royce plc. The American unit operates under a Special Security Arrangement which allows it to work independently on some of the most sensitive United States def ...
.
History
A predecessor of Allison Engine Company, the Concentrated Acetylene Company, was founded in September 1904 by James Allison, Percy C. "Fred" Avery andCarl G. Fisher
Carl Graham Fisher (January 12, 1874 – July 15, 1939) was an American entrepreneur. He was an important figure in the automotive industry, in highway construction, and in real estate development.
In his early life in Indiana, despite fa ...
. Avery was the holder of the patent for the product. This company was the predecessor of the Prest-O-Lite Company, a manufacturer of acetylene headlights. An explosion at the acetylene gas works in downtown Indianapolis caused the company to relocate out of town, near the race track in Speedway, Indiana
Speedway is a town in Wayne Township, Marion County, Indiana, United States. The population was 11,812 at the 2010 U.S. Census. Speedway, which is an enclave of Indianapolis, is the home of the Indianapolis Motor Speedway.
History
Speedway was ...
. Allison and Fisher raced automobiles at that track, each owning a race car team. This hobby resulted in Allison building a shop at the track in Speedway where he maintained his fleet of race cars. This shop became the site for Allison Plant #1. Fisher and Allison sold their interest in Prest-O-Lite to Union Carbide
Union Carbide Corporation is an American chemical corporation wholly owned subsidiary (since February 6, 2001) by Dow Chemical Company. Union Carbide produces chemicals and polymers that undergo one or more further conversions by customers befo ...
for $9,000,000.
Allison Speedway Team Company
Allison started as an engine and car "hot rodding" company servicing the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Indianapolis. James Allison was the owner of the Indianapolis Speedway Team Company, a race car business in Indianapolis, Indiana. While it was founded as the Indianapolis Speedway Team Company, its name changed numerous times, first to the Allison Speedway Team Company, then the Allison Experimental Company and last as the Allison Engineering Company before becoming a division of General Motors. The company's only regular production item was a patented steel-backed lead bearing, which was used in various high performance engines. It also built various drive shafts, extensions and gear chains for high power engines, on demand. Later its main business was the conversion of olderLiberty engine
The Liberty L-12 is an American water-cooled 45° V-12 aircraft engine displacing and making designed for a high power-to-weight ratio and ease of mass production. It saw wide use in aero applications, and, once marinized, in marine use both ...
s to more powerful models, both for aircraft and marine use.
Allison needed a place where his race car engines could be modified and repaired. On January 1, 1917 Allison moved into a building at what was to become, in later years, the Indianapolis Motor Speedway. Along with the move, Allison hired Norman H. Gillman, a very talented engineer from a competing race team, as his chief engineer.
Allison's move to Florida
Allison moved to Florida to invest in real estate after World War I, leaving Gillman in charge. Allison did not want the company to wither, so he asked Gillman to build a V-12 marine engine worthy of the Allison name. Gillman then proceeded to build an engine that relied on what was learned from building and modifying the venerable Liberty engine. Allison's company was sold to CaptainEddie Rickenbacker
Edward Vernon Rickenbacker or Eddie Rickenbacker (October 8, 1890 – July 23, 1973) was an American fighter pilot in World War I and a Medal of Honor recipient.Fisher brothers
Fisher Brothers is a real estate firm in New York City. It was formed by Martin Fisher in 1915, soon joined by his brothers Larry (born 1907), and Zachary (born 1910). The Fisher family has substantial real estate holdings in New York City and el ...
. The Fishers sold the company to General Motors, who owned it for most of its history. The Allison Engine Company was acquired in 1995 by Rolls-Royce plc
Rolls-Royce Holdings plc is a British multinational aerospace and defence company incorporated in February 2011. The company owns Rolls-Royce, a business established in 1904 which today designs, manufactures and distributes power systems for ...
, and became the Rolls-Royce Corporation
Rolls-Royce North America, Inc. is a subsidiary of multinational corporation Rolls-Royce plc. The American unit operates under a Special Security Arrangement which allows it to work independently on some of the most sensitive United States defe ...
subsidiary.John Leonard's articles in various issues of the Allison Branch newsletters
Hyper engine
In the late 1920s theUnited States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land warfare, land military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight Uniformed services of the United States, U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army o ...
funded the development of a series of high-power engines, as part of its hyper engine
The hyper engine was a 1930s study project by the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) to develop a high-performance aircraft engine that would be equal to or better than the aircraft and engines then under development in Europe. The project goal ...
series, which it intended to produce on Continental Motors' production lines. Allison's manager, Norman Gilman, decided to experiment with his own high-power cylinder design. Allison's engine became Manufacturer Serial No. 1, AAC S/N 25-521. It was the X-4520, a 24-cylinder air-cooled 4-bank “X” configured engine designed by the Army Air Corps and built by the Allison Engineering Company in 1925. The result was presented to the Army in 1928, which turned down the development proposal.
General Motors
In 1929, shortly after the death of James Allison, the company was purchased by the Fisher brothers, who instructed it to use the cylinder design for a six-cylinder engine for a "family aircraft". Before work on this design had progressed very far, Fisher sold the company to General Motors, which ended development owing to financial pressures of the Great Depression. Nevertheless, Gilman pressed ahead with the cylinder design, building a "paper project" V-12 engine. The Army was once again uninterested, but instead suggested Allison try selling it to theUnited States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
. The Navy agreed to fund development of A and B models to a very limited degree for its airship
An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air.
In early ...
s, until the crash of the USS ''Macon'' in 1935, when the Navy's need for a engine disappeared.
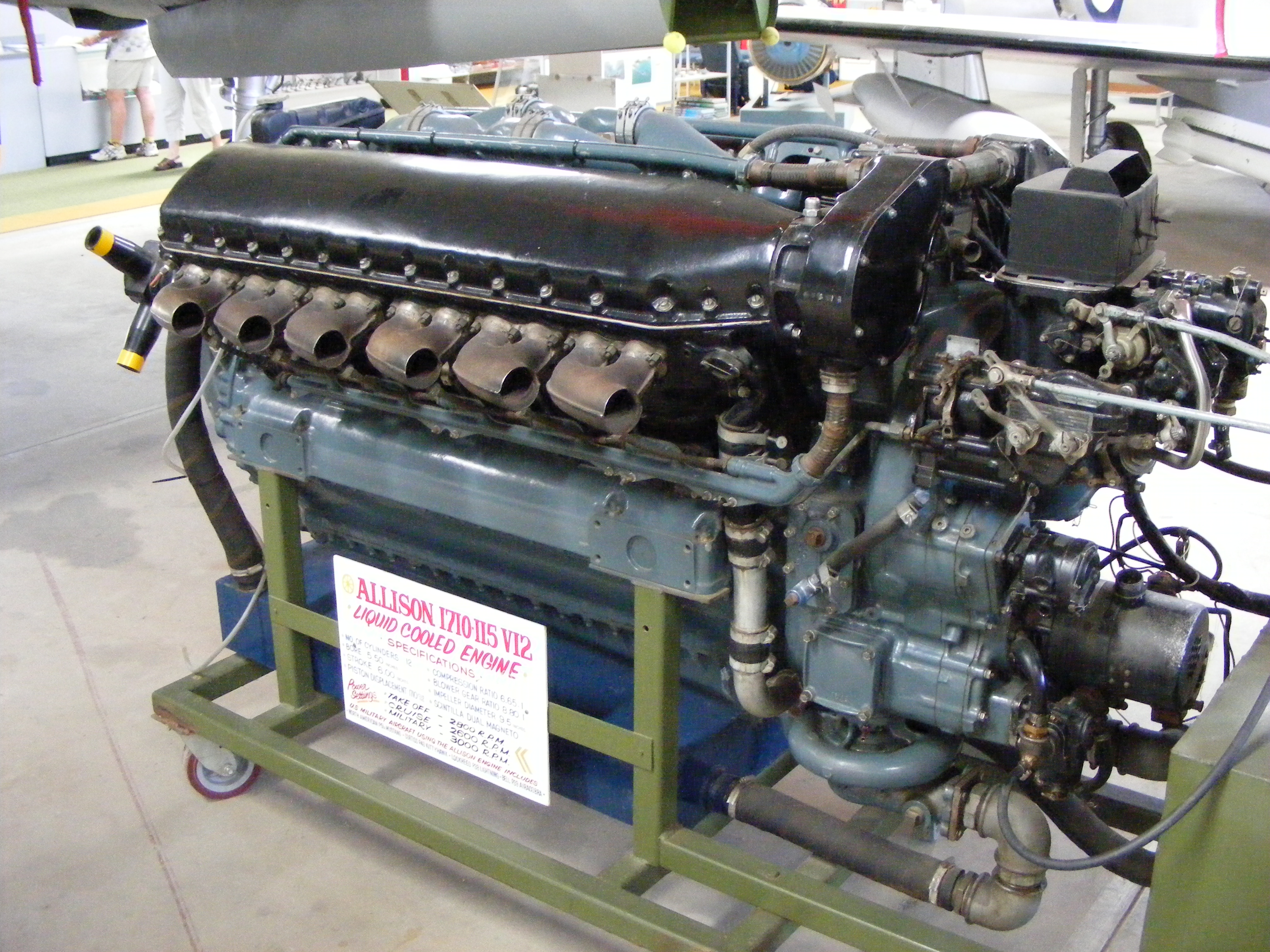
V-1710

 The very first V-1710 was purchased by the U.S. Navy as their GV-1710-2, and appears to have had an Allison serial of number 1, suggesting that they restarted numbering for the V-1710. The first V-1710 engine purchased by the USAAC was AAC 33-42, Allison Serial No. 2, the XV-1710-1, while Serial Nos. 3, 4, 5 were V-1710-4 engines for U.S. Navy airships, followed by a batch of 11 Air Corps engines purchased with FY-1934 funds (34-4 through 34-14) that covered Allison serials 6 through 16. After these the production race was on, totaling over 70,000 V-1710s.
By this time the Army had become more interested in the design, and asked Allison to continue with a new "C" model. They had few funds of their own to invest, and Allison supported much of the development out of their own pocket. The V-1710-C first flew on 14 December 1936 in the
The very first V-1710 was purchased by the U.S. Navy as their GV-1710-2, and appears to have had an Allison serial of number 1, suggesting that they restarted numbering for the V-1710. The first V-1710 engine purchased by the USAAC was AAC 33-42, Allison Serial No. 2, the XV-1710-1, while Serial Nos. 3, 4, 5 were V-1710-4 engines for U.S. Navy airships, followed by a batch of 11 Air Corps engines purchased with FY-1934 funds (34-4 through 34-14) that covered Allison serials 6 through 16. After these the production race was on, totaling over 70,000 V-1710s.
By this time the Army had become more interested in the design, and asked Allison to continue with a new "C" model. They had few funds of their own to invest, and Allison supported much of the development out of their own pocket. The V-1710-C first flew on 14 December 1936 in the Consolidated A-11
The Consolidated P-30 (PB-2) was a 1930s United States two-seat fighter aircraft. An attack version called the A-11 was also built, along with two Y1P-25 prototypes and YP-27, Y1P-28, and XP-33 proposals. The P-30 is significant for being the fi ...
A testbed. The V-1710-C6 completed the Army 150 hour Type Test on 23 April 1937, at 1,000 hp (750 kW), the first engine of any type to do so. By then all of the other Army engine projects had been cancelled or withdrawn, leaving the V-1710 as the only modern design available. It was soon found as the primary power plant of the new generation of United States Army Air Corps
The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical r ...
(USAAC) fighters, the P-38 Lightning
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinctive tw ...
, P-39 Airacobra
The Bell P-39 Airacobra is a fighter produced by Bell Aircraft for the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. It was one of the principal American fighters in service when the United States entered combat. The P-39 was used by the ...
and P-40 Warhawk
The Curtiss P-40 Warhawk is an American single-engined, single-seat, all-metal fighter and ground-attack aircraft that first flew in 1938. The P-40 design was a modification of the previous Curtiss P-36 Hawk which reduced development time and ...
.
The Army had been leaning heavily towards exhaust-driven turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pro ...
s, instead of the more common mechanically driven superchargers, favoring the theoretical advantage of using the otherwise wasted energy in the exhaust. Thus, little effort was invested in equipping the V-1710 with a complex two-stage supercharger, and when placed in aircraft designs like the P-39 or P-40, which lacked the room for a turbocharger, the engine suffered tremendously at higher altitudes. It was for this reason in particular that the V-1710 was later removed from the P-51 Mustang and replaced with the Rolls-Royce Merlin
The Rolls-Royce Merlin is a British liquid-cooled V-12 piston aero engine of 27-litres (1,650 cu in) capacity. Rolls-Royce designed the engine and first ran it in 1933 as a private venture. Initially known as the PV-12, it was late ...
.
Post-war
With the need for the V-1710 winding down at the end of the war, Allison found itself with a large production infrastructure that was no longer needed. For this reason, in 1947, the Army decided to takeGeneral Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable en ...
's versions of Frank Whittle
Air Commodore Sir Frank Whittle, (1 June 1907 – 8 August 1996) was an English engineer, inventor and Royal Air Force (RAF) air officer. He is credited with inventing the turbojet engine. A patent was submitted by Maxime Guillaume in 1921 fo ...
's jet engines and give them to Allison to produce instead. The main production model was GE's I-40, produced as the Allison J33
The General Electric/Allison J33 is a development of the General Electric J31, enlarged to produce significantly greater thrust, starting at and ending at with an additional low-altitude boost to with water-alcohol injection.
Development
Th ...
. By the time production ended in 1955, Allison had produced over 7,000 J33s.
Allison also took over GE's axial flow
An axial compressor is a gas compressor that can continuously pressurize gases. It is a rotating, airfoil-based compressor in which the gas or working fluid principally flows parallel to the axis of rotation, or axially. This differs from other ...
engine design, becoming the Allison J35
The General Electric/Allison J35 was the United States Air Force's first axial-flow (straight-through airflow) compressor jet engine. Originally developed by General Electric (GE company designation TG-180) in parallel with the Whittle-based c ...
. The J35 was the primary powerplant for the F-84 Thunderjet
The Republic F-84 Thunderjet was an American turbojet fighter-bomber aircraft. Originating as a 1944 United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) proposal for a "day fighter", the F-84 first flew in 1946. Although it entered service in 1947, the Thun ...
and F-89 Scorpion
The Northrop F-89 Scorpion was an American all-weather, twin-engined interceptor aircraft built during the 1950s, the first jet-powered aircraft designed for that role from the outset to enter service. Though its straight wings limited its per ...
, as well as appearing on numerous prototype designs. The J35 also finished production in 1955, by which point over 14,000 had been delivered.
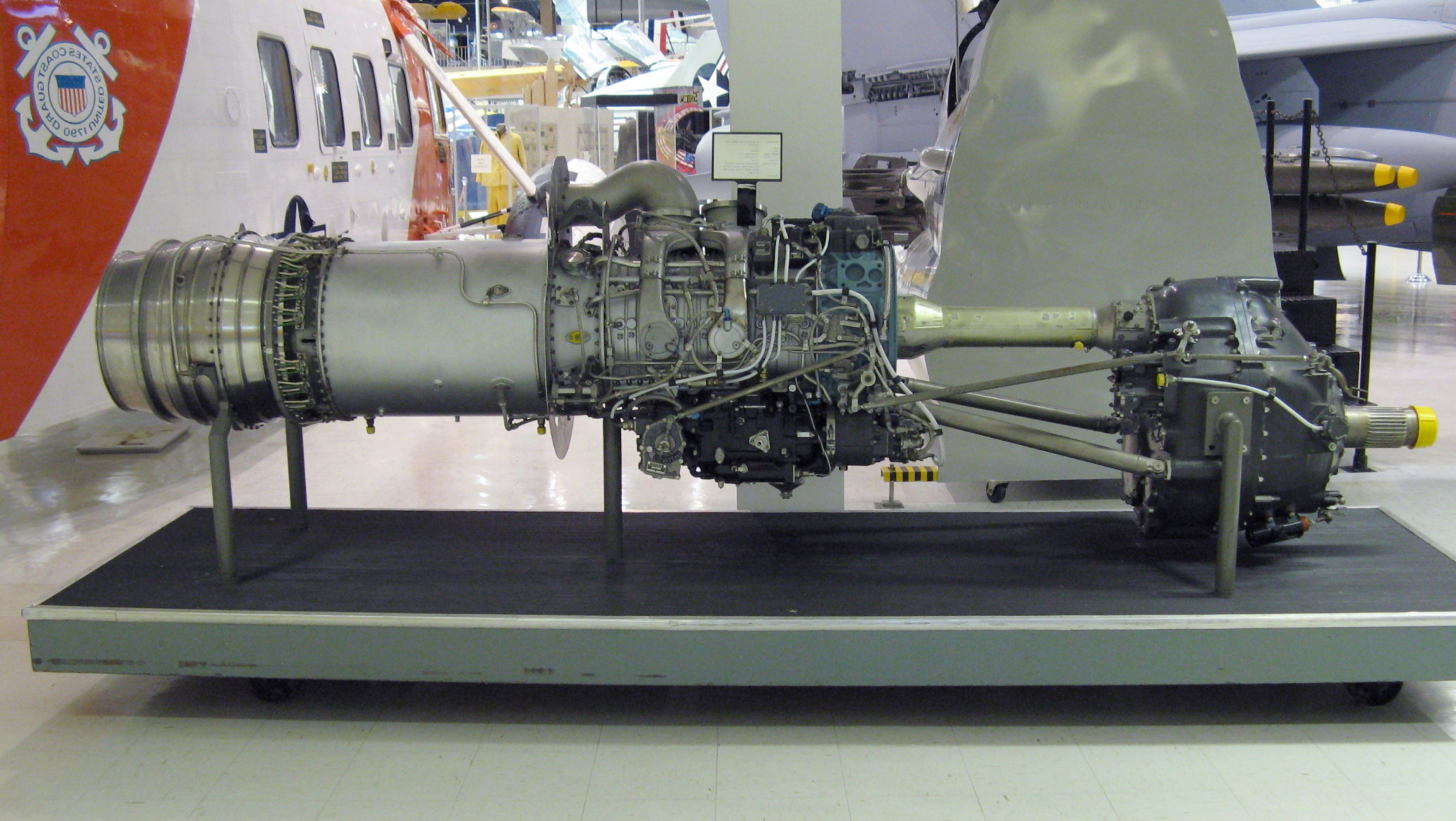
Allison also began development of a series of turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. ...
engines for the U.S. Navy, starting with the T38 and a "twinned" version as the T40. The Navy was interested only in the T40, but the complexities of the drive shaft arrangement doomed the engine and the project was eventually cancelled. Allison tried again with the T56, basically an enlarged T38 with the power of the T40, and was eventually rewarded when this engine was selected to power the C-130 Hercules. Allison turboprop engines were also used to re-engine Convair
Convair, previously Consolidated Vultee, was an American aircraft manufacturing company that later expanded into rockets and spacecraft. The company was formed in 1943 by the merger of Consolidated Aircraft and Vultee Aircraft. In 1953, i ...
prop airliners which resulted in the Convair 580
The Convair CV-240 is an American airliner that Convair manufactured from 1947 to 1954, initially as a possible replacement for the ubiquitous Douglas DC-3. Featuring a more modern design with cabin pressurization, the 240 series made some inroa ...
turboprop passenger aircraft which was widely used by local service and regional airlines in the U.S. such as Allegheny Airlines, the original Frontier Airlines, North Central Airlines
North Central Airlines was a regional airline in the Midwestern United States. Founded as Wisconsin Central Airlines in 1944 in Clintonville, Wisconsin, the company moved to Madison in 1947. This is also when the "Herman the duck" logo was bo ...
, as well as major carriers American, Eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
, United
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two f ...
, and Pan-Am
Pan American World Airways, originally founded as Pan American Airways and commonly known as Pan Am, was an American airline that was the principal and largest international air carrier and unofficial overseas flag carrier of the United State ...
.
Over the years a family of engines based on the T56 configuration was developed, culminating in the T406/ Allison AE1107 turboshaft for the V-22 Osprey, the Allison AE2100
Allison may refer to:
People
* Allison (given name)
* Allison (surname) (includes a list of people with this name)
* Eugene Allison Smith (1922-1980), American politician and farmer
Companies
* Allison Engine Company, American aircraft engine ...
turboprop, used on newer models of the C-130 and the Allison/Rolls-Royce AE 3007
The Rolls-Royce AE 3007 (US military: F137) is a turbofan engine produced by Rolls-Royce North America, sharing a common core with the Rolls-Royce T406 (AE 1107) and AE 2100. The engine was originally developed by the Allison Engine Company, he ...
turbofan which propels many regional airline aircraft, such as the Embraer ERJ 135, ERJ 140 and ERJ 145 family of regional passenger jets that continue to be widely used in the airline industry.
One of Allison's most successful projects is the Model 250 turboshaft/turboprop engine family, which was started by the company in the early 1960s, when helicopters started to be powered by turbine, rather than reciprocating, engines. Allison turbine engines were used to power Bell 206 Jet Ranger
The Bell 206 is a family of two-bladed, single- and twin-engined helicopters, manufactured by Bell Helicopter at its Mirabel, Quebec, plant. Originally developed as the Bell YOH-4 for the United States Army's Light Observation Helicopter progr ...
and Long Ranger helicopters as well as the initial version of the Sikorsky S-76 helicopter.
Experiments
In the mid-1970s the Allison Division ofGeneral Motors Corporation
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American multinational automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and was the largest in the world for 77 years bef ...
in Detroit designed ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
components into the Allison GT 404-4 turboshaft engine intended for trucks. Allison continued to work with General Motors on development of ceramic-turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating ...
powered engines until the early 1990s. During their work they were able to engineer fairly stable automobile engines that were capable of burning a variety of fuels, such as gasoline, Diesel, kerosene, alcohol, vegetable oil, and coal powder.
In the 1980s Allison collaborated with Pratt & Whitney on demonstrating the 578-DX propfan
A propfan, also called an open rotor engine, or unducted fan (as opposed to a ducted fan), is a type of aircraft engine related in concept to both the turboprop and turbofan, but distinct from both. The design is intended to offer the speed a ...
. Unlike the competing General Electric GE-36 UDF, the 578-DX was fairly conventional, having a reduction gearbox between the LP turbine and the propfan blades. Noise considerations, plus a significant reduction in the real cost of aviation fuel, brought the NASA funded program to a halt.
In 1995, Allison tested a prototype lift fan
Lift fan is an aircraft configuration in which lifting fans are located in large holes in an otherwise conventional fixed wing or fuselage. It is used for V/STOL operation.
The aircraft takes off using the fans to provide lift, then transitions ...
for the Joint Strike Fighter Program and a LiftFan nozzle was tested in 1997 at NASA's Lewis facility. By 1997, a complete prototype had been demonstrated Bevilaqua, Paul.The shaft driven Lift Fan propulsion system for the Joint Strike Fighter
" page 2, ''
American Helicopter Society (AHS) International
The Vertical Flight Society, formerly the American Helicopter Society (AHS), is the non-profit technical society for the advancement of vertical flight. It has 21 different technical committees and two dozen active chapters around the world. Ther ...
''. Presented May 1, 1997. DTIC.MIL Word document, 5.5 MB by the Rolls-Royce owned but American-controlled Allison Advanced Development Company.
Automotive use
In 1965 a drag racer, Jim Lytle, created a car known as ''Quad Al'' which incorporated four World War II surplus V-12 Allison aero-engines in a four-wheel drive configuration, and developing approximately . Although its engines started, it never ran; the creator could not afford the custom gearboxes and clutches required to handle the enormous torque generated by the engines. The car survives, without its engines, inIndiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
, USA.
Acquisition by Rolls-Royce
In 1992 General Motors tried to sell Allison to concentrate on rebuilding automobile market share. Rolls-Royce attempted to buy the company in 1993, but General Motors opted for a management buyout instead for $370 million. In 1995 US authorities approved, with restrictions on Joint Strike Fighter Program, the purchase of Allison by Rolls-Royce. The price was $525 million. In the year 2000, some of these restrictions were alleviated, and in 2001 the US government chose theF-35
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is an American family of single-seat, single-engine, all-weather stealth multirole combat aircraft that is intended to perform both air superiority and strike missions. It is also able to provide elect ...
with Rolls Royce LiftFan and Pratt & Whitney F135
The Pratt & Whitney F135 is an afterburning turbofan developed for the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II, a single-engine strike fighter. It has two variants; a Conventional Take-Off and Landing ( CTOL) variant used in the F-35A and F-35C, and a ...
engines.
Products


References
Footnotes
Notes
Bibliography
*External links
Allison's work on turbine engines for automobiles
{{Authority control Defunct aircraft engine manufacturers of the United States Gas turbine manufacturers Companies disestablished in 1995 Engine manufacturers of the United States Former General Motors subsidiaries Rolls-Royce