
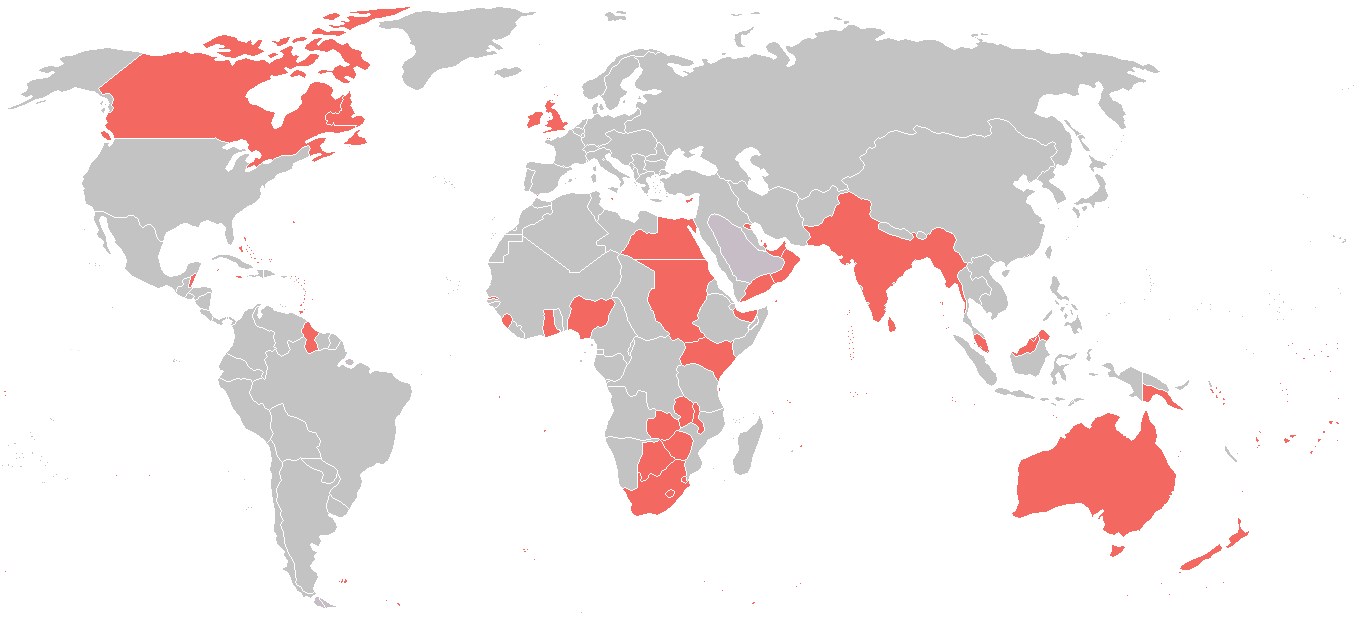
The Allies of World War I,
Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a
coalition of countries led by
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
,
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
,
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
,
Japan, and the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
against the
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
of
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
,
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
,
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, and their colonies during the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1914–1918).
By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major
European powers
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power inf ...
were divided between the
Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French '' entente'' meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland as well a ...
and the
Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of France, Britain, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and after proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although France, Britain, Russia, and Italy were also referred to as the Quadruple Entente and, together with Japan, as the Quintuple Entente. The colonies administered by the countries that fought for the allies were also part of the Entente Powers such as
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
,
French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China),; vi, Đông Dương thuộc Pháp, , lit. 'East Ocean under French Control; km, ឥណ្ឌូចិនបារាំង, ; th, อินโดจีนฝรั่งเศส, ...
, and
Japanese Korea
Between 1910 and 1945, Korea was ruled as a part of the Empire of Japan. Joseon Korea had come into the Japanese sphere of influence with the Japan–Korea Treaty of 1876; a complex coalition of the Meiji government, military, and business offici ...
.
The United States joined near the end of the war in 1917 (the same year in which Russia withdrew from the conflict) as an "associated power" rather than an official ally. Other "associated members" included
Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
,
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
,
Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
,
Asir,
Nejd and Hasa,
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
,
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
,
Hejaz,
Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
,
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
,
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
,
China,
Siam
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
(now
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
),
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
,
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
,
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
,
Guatemala,
Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the countr ...
,
Costa Rica,
Haiti,
Liberia,
Bolivia,
Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
,
Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
, and
Honduras. The treaties signed at the
Paris Peace Conference recognised Great Britain, France, Italy, Japan and the United States as 'the Principal Allied and Associated Powers'.
Background

When the war began in 1914, the
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
were opposed by the
Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French '' entente'' meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland as well a ...
, formed in 1907 when the agreement between Britain and the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
complemented existing agreements between Britain, Russia, and France.
Fighting commenced when Austria invaded
Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
on 28 July 1914, purportedly in response to the
assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, heir presumptive to the Austro-Hungarian throne, and his wife, Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, were assassinated on 28 June 1914 by Bosnian Serb student Gavrilo Princip. They were shot at close range whil ...
, heir to Emperor
Franz Joseph
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I (german: Franz Joseph Karl, hu, Ferenc József Károly, 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 2 December 1848 until his ...
; this brought Serbia's ally
Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
into the war on 8 August and it attacked the Austrian naval base at
Cattaro
Kotor (Montenegrin Cyrillic: Котор, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian: ), is a coastal town in Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has a population of 13,510 and is the administrative ...
, modern Kotor. At the same time, German troops carried out the
Schlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan (german: Schlieffen-Plan, ) is a name given after the First World War to German war plans, due to the influence of Field Marshal Alfred von Schlieffen and his thinking on an invasion of France and Belgium, which began on ...
, entering neutral
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
and
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
; over 95% of Belgium was occupied but the Belgian Army held their lines on the
Yser Front
The Yser Front (french: Front de l'Yser, nl, Front aan de IJzer or ), sometimes termed the West Flemish Front in British writing, was a section of the Western Front during World War I held by Belgian troops from October 1914 until 1918. The front ...
throughout the war. This allowed Belgium to be treated as an Ally, in contrast to Luxembourg which retained control over domestic affairs but was
occupied by the German military.

In the East, between 7 and 9 August the Russians entered German
East Prussia on 7 August, Austrian
Eastern Galicia
Eastern Galicia ( uk, Східна Галичина, Skhidna Galychyna, pl, Galicja Wschodnia, german: Ostgalizien) is a geographical region in Western Ukraine (present day oblasts of Lviv, Ivano-Frankivsk and Ternopil), having also essential h ...
.
Japan joined the Entente by declaring war on Germany on 23 August, then Austria on 25 August. On 2 September, Japanese forces surrounded the German
Treaty Port
Treaty ports (; ja, 条約港) were the port cities in China and Japan that were opened to foreign trade mainly by the unequal treaties forced upon them by Western powers, as well as cities in Korea opened up similarly by the Japanese Empire.
...
of
Tsingtao
Qingdao (, also spelled Tsingtao; , Mandarin: ) is a major city in eastern Shandong Province. The city's name in Chinese characters literally means " azure island". Located on China's Yellow Sea coast, it is a major nodal city of the One Belt ...
(now Qingdao) in China and occupied German colonies in the Pacific, including the
Mariana,
Caroline, and
Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
.
Despite its membership of the
Triple Alliance,
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
remained neutral until 23 May 1915 when it joined the Entente, declaring war on Austria but not Germany. On 17 January 1916,
Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
capitulated and left the Entente; this was offset when Germany declared war on
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
in March 1916, while
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
commenced hostilities against Austria on 27 August.
On 6 April 1917, the United States entered the war as a co-belligerent, along with the associated allies of
Liberia,
Siam
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
and
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
. After the 1917
October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
, Russia left the Entente and agreed to a separate peace with the Central Powers with the signing of the
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's ...
on 3 March 1918. Romania was forced to do the same in the May 1918
Treaty of Bucharest but on 10 November, it repudiated the Treaty and once more declared war on the Central Powers.
These changes meant the Allies who negotiated the
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
in 1919 included France, Britain, Italy, Japan and the US; Part One of the Treaty agreed to the establishment of the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
on 25 January 1919. This came into being on 16 January 1920 with Britain, France, Italy and Japan as permanent members of the Executive Council; the
US Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and po ...
voted against ratification of the treaty on 19 March, thus preventing the US from joining the League.
Statistics

Principal powers
Britain and its Empire
For much of the 19th century, Britain sought to maintain the European balance of power without formal alliances, a policy known as
splendid isolation
''Splendid isolation'' is a term used to describe the 19th-century British diplomatic practice of avoiding permanent alliances, particularly under the governments of Lord Salisbury between 1885 and 1902. The concept developed as early as 1822, ...
. This left it dangerously exposed as Europe divided into opposing power blocs and the
1895–1905 Conservative government negotiated first the 1902
Anglo-Japanese Alliance, then the 1904
Entente Cordiale
The Entente Cordiale (; ) comprised a series of agreements signed on 8 April 1904 between the United Kingdom and the French Republic which saw a significant improvement in Anglo-French relations. Beyond the immediate concerns of colonial de ...
with France. The first tangible result of this shift was British support for France against Germany in the
1905 Moroccan Crisis.
The
1905–1915 Liberal government continued this re-alignment with the 1907
Anglo-Russian Convention
The Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907 (russian: Англо-Русская Конвенция 1907 г., translit=Anglo-Russkaya Konventsiya 1907 g.), or Convention between the United Kingdom and Russia relating to Persia, Afghanistan, and Tibet (; ...
. Like the Anglo-Japanese and Entente agreements, it focused on settling colonial disputes but by doing so paved the way for wider co-operation and allowed Britain to refocus resources in response to
German naval expansion.

Since control of Belgium allowed an opponent to threaten invasion or blockade British trade, preventing it was a long-standing British strategic interest. Under Article VII of the 1839
Treaty of London, Britain guaranteed Belgian neutrality against aggression by any other state, by force if required. Chancellor
Bethmann Hollweg
Theobald Theodor Friedrich Alfred von Bethmann Hollweg (29 November 1856 – 1 January 1921) was a German politician who was the chancellor of the German Empire from 1909 to 1917. He oversaw the German entry into World War I. According to biog ...
later dismissed this as a 'scrap of paper,' but British law officers routinely confirmed it as a binding legal obligation and its importance was well understood by Germany.
The 1911
Agadir Crisis
The Agadir Crisis, Agadir Incident, or Second Moroccan Crisis was a brief crisis sparked by the deployment of a substantial force of French troops in the interior of Morocco in April 1911 and the deployment of the German gunboat to Agadir, a ...
led to secret discussions between France and Britain in case of war with Germany. These agreed that within two weeks of its outbreak, a
British Expeditionary Force of 100,000 men would be landed in France; in addition, the
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
would be responsible for the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
, the
Channel and protecting Northern France, with the French navy concentrated in the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
. Britain was committed to support France in a war against Germany but this was not widely understood outside government or the upper ranks of the military.
As late as 1 August, a clear majority of the Liberal government and its supporters wanted to stay out of the war. While Liberal leaders
H. H. Asquith
Herbert Henry Asquith, 1st Earl of Oxford and Asquith, (12 September 1852 – 15 February 1928), generally known as H. H. Asquith, was a British statesman and Liberal Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom f ...
and
Edward Grey considered Britain legally and morally committed to support France regardless, waiting until Germany triggered the 1839 Treaty provided the best chance of preserving Liberal party unity.

The German high command was aware entering Belgium would lead to British intervention but decided the risk was acceptable; they expected a short war while their ambassador in London claimed troubles in Ireland would prevent Britain from assisting France. On 3 August, Germany demanded unimpeded progress through any part of Belgium and when this was refused, invaded early on the morning of 4 August.
This changed the situation; the invasion of Belgium consolidated political and public support for the war by presenting what appeared to be a simple moral and strategic choice. The Belgians asked for assistance under the 1839 Treaty and in response, Britain declared war on Germany on 4 August 1914. Although Germany's violation of Belgium neutrality was not the only cause of British entry into the war, it was used extensively in government propaganda at home and abroad to make the case for British intervention. This confusion arguably persists today.
The declaration of war automatically involved all dominions and colonies and protectorates of the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, many of whom made significant contributions to the Allied war effort, both in the provision of troops and civilian labourers. It was split into
Crown Colonies
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Council ...
administered by the
Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created to deal with the colonial affairs of British North America but required also to oversee the increasing number of c ...
in London, such as
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
, and the self-governing
Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 192 ...
s of
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
,
Newfoundland,
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
,
Australia and
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
. These controlled their own domestic policies and military expenditure but not foreign policy.
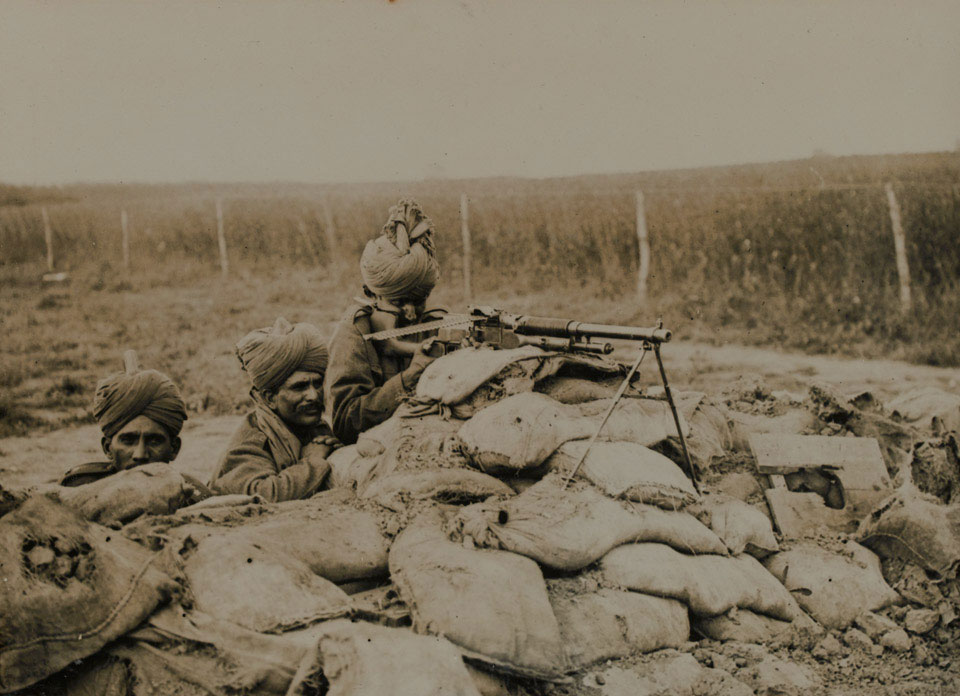

In terms of population, the largest component (after Britain herself) was the
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
or British India, which included modern
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
,
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
,
Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
and
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
. Unlike other colonies which came under the
Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created to deal with the colonial affairs of British North America but required also to oversee the increasing number of c ...
, it was governed directly by the
India Office or by
princes loyal to the British; it also controlled British interests in the
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bod ...
, such as the
Trucial States
The Trucial States ( '), also known as the Trucial Coast ( '), the Trucial Sheikhdoms ( '), Trucial Arabia or Trucial Oman, was the name the British government gave to a group of tribal confederations in southeastern Arabia whose leaders had s ...
and
Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
. Over one million soldiers of the
British Indian Army served in different theatres of the war, primarily France and the
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
.
From 1914 to 1916, overall Imperial diplomatic, political and military strategy was controlled by the
British War Cabinet
A war cabinet is a committee formed by a government in a time of war to efficiently and effectively conduct that war. It is usually a subset of the full executive cabinet of ministers, although it is quite common for a war cabinet to have senio ...
in London; in 1917 it was superseded by the
Imperial War Cabinet
The Imperial War Cabinet (IWC) was the British Empire's wartime coordinating body. It met over three sessions, the first from 20 March to 2 May 1917, the second from 11 June to late July 1918, and the third from 20 or 25 November 1918 to early Jan ...
, which included representatives from the Dominions. Under the War Cabinet were the
Chief of the Imperial General Staff or CIGS, responsible for all Imperial ground forces, and the
Admiralty
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
*Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
*Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
* Admiralty, Traf ...
that did the same for the
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
. Theatre commanders like
Douglas Haig
Field Marshal Douglas Haig, 1st Earl Haig, (; 19 June 1861 – 29 January 1928) was a senior officer of the British Army. During the First World War, he commanded the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) on the Western Front from late 1915 until ...
on the
Western Front or
Edmund Allenby
Field Marshal Edmund Henry Hynman Allenby, 1st Viscount Allenby, (23 April 1861 – 14 May 1936) was a senior British Army officer and Imperial Governor. He fought in the Second Boer War and also in the First World War, in which he led th ...
in Sinai and Palestine Campaign, Palestine then reported to the CIGS.
After the Indian Army, the largest individual units were the Australian Corps and Canadian Corps in France, which by 1918 were commanded by their own generals, John Monash and Arthur Currie. Contingents from South Africa, New Zealand and Newfoundland served in theatres including France, Gallipoli Campaign, Gallipoli, German East Africa and the Middle East. Australian troops separately occupied German New Guinea, with the South Africans doing the same in German South West Africa; this resulted in the Maritz rebellion by former Boers, which was quickly suppressed. After the war, New Guinea and South-West Africa became Protectorates, held until 1975 and 1990 respectively.
Russian Empire

Between 1873 and 1887, Russia was allied with Germany and Austria-Hungary in the League of the Three Emperors, then with Germany in the 1887–1890 Reinsurance Treaty; both collapsed due to the competing interests of Austria and Russia in the Balkans. While France took advantage of this to agree the 1894 Franco-Russian Alliance, Britain viewed Russia with deep suspicion; in 1800, over 3,000 kilometres separated the Russian Empire and British India, by 1902, it was 30 km in some areas. This threatened to bring the two into direct conflict, as did the long-held Russian objective of gaining control of the Bosporus, Bosporus Straits and with it access to the British-dominated Mediterranean Sea.

Defeat in the 1905 Russo-Japanese War and Britain's isolation during the 1899–1902 Second Boer War led both parties to seek allies. The
Anglo-Russian Convention
The Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907 (russian: Англо-Русская Конвенция 1907 г., translit=Anglo-Russkaya Konventsiya 1907 g.), or Convention between the United Kingdom and Russia relating to Persia, Afghanistan, and Tibet (; ...
of 1907 settled disputes in Asia and allowed the establishment of the Triple Entente with France, which at this stage was largely informal. In 1908, Austria annexed the former Ottoman province of Bosnia and Herzegovina; Russia responded by creating the Balkan League in order to prevent further Austrian expansion.
In the 1912–1913 First Balkan War,
Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
,
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
and
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
captured most of the remaining Ottoman possessions in Europe; disputes over the division of these resulted in the Second Balkan War, in which Bulgaria was comprehensively defeated by its former allies.
Russia's industrial base and railway network had significantly improved since 1905, although from a relatively low base; in 1913, Nicholas II of Russia, Tsar Nicholas approved an increase in the Russian Army of over 500,000 men. Although there was no formal alliance between Russia and Serbia, their close bilateral links provided Russia with a route into the crumbling Ottoman Empire, where Germany also had significant interests. Combined with the increase in Russian military strength, both Austria and Germany felt threatened by Serbian expansion; when Austria invaded Serbia on 28 July 1914, Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Sazonov viewed it as an Austro-German conspiracy to end Russian influence in the Balkans.
In addition to its own territory, Russia viewed itself as the defender of its fellow Pan-Slavism, Slavs and on 30 July, mobilised in support of Serbia. In response, Germany declared war on Russia on 1 August, followed by Austria-Hungary on 6th; after Ottoman warships bombarded Odessa in late October, the Entente declared war on the Ottoman Empire in November 1914.
French Republic

French defeat in the 1870–1871 Franco-Prussian War led to the loss of the two provinces of Alsace-Lorraine and the establishment of the French Third Republic, Third Republic. The suppression of the Paris Commune by the new regime caused deep political divisions and led to a series of bitter political struggles, such as the Dreyfus affair. As a result, aggressive nationalism or Revanchism was one of the few areas to unite the French.
The loss of Alsace-Lorraine deprived France of its natural defence line on the Rhine, while it was weaker demographically than Germany, whose 1911 population was 64.9 million to 39.6 in France, which had the lowest birthrate in Europe. This meant that despite their very different political systems, when Germany allowed the Reinsurance Treaty to lapse, France seized the opportunity to agree the 1894 Franco-Russian Alliance. It also replaced Germany as the primary source of financing for Russian industry and the expansion of its railway network, particularly in border areas with Germany and Austria-Hungary.

However, Russian defeat in the 1904–1905 Russo-Japanese War damaged its credibility, while Britain's isolation during the Second Boer War meant both countries sought additional allies. This resulted in the 1904
Entente Cordiale
The Entente Cordiale (; ) comprised a series of agreements signed on 8 April 1904 between the United Kingdom and the French Republic which saw a significant improvement in Anglo-French relations. Beyond the immediate concerns of colonial de ...
with Britain; like the 1907
Anglo-Russian Convention
The Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907 (russian: Англо-Русская Конвенция 1907 г., translit=Anglo-Russkaya Konventsiya 1907 g.), or Convention between the United Kingdom and Russia relating to Persia, Afghanistan, and Tibet (; ...
, for domestic British consumption it focused on settling colonial disputes but led to informal co-operation in other areas. By 1914, both the British army and
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
were committed to support France in the event of war with Germany but even in the British government, very few were aware of the extent of these commitments.

In response to Germany's declaration of war on Russia, France issued a general mobilisation in expectation of war on 2 August and on 3 August, Germany also declared war on France. Germany's ultimatum to Belgium brought Britain into the war on 4 August, although France did not declare war on Austria-Hungary until 12 August.
As with Britain, France's French colonial empire, colonies also became part of the war; pre-1914, French soldiers and politicians advocated using French African recruits to help compensate for France's demographic weakness. From August to December 1914, the French lost nearly 300,000 dead on the Western Front, more than Britain suffered in the whole of WWII and the gaps were partly filled by colonial troops, over 500,000 of whom served on the Western Front over the period 1914–1918. Colonial troops also fought at Gallipoli Campaign, Gallipoli, occupied Togo and Kamerun in West Africa and had a minor role in the Middle East, where France was the traditional protector of Christians in the Ottoman provinces of Ottoman Syria, Syria, History of Palestine#Early Ottoman rule, Palestine and History of Lebanon under Ottoman rule, Lebanon.
Japanese Empire
Prior to the Meiji Restoration in 1868, Japan was a semi-feudal, largely agrarian state with few natural resources and limited technology. By 1914, it had transformed itself into a modern industrial state, with a powerful military; by defeating China in the First Sino-Japanese War during 1894–1895, it established itself as the primary power in East Asia and colonised the then-unified Korea and Republic of Formosa, Formosa, now modern Taiwan.
Concerned by Russian expansion in Korea and Manchuria, Britain and Japan signed the
Anglo-Japanese Alliance on 30 January 1902, agreeing if either were attacked by a third party, the other would remain neutral and if attacked by two or more opponents, the other would come to its aid. This meant Japan could rely on British support in a war with Russia, if either France or Germany, which also had interests in China, decided to join them. This gave Japan the reassurance needed to take on Russia in the 1905 Russo-Japanese War; victory established Japan in the Chinese province of Manchuria.
With Japan as an ally in the Far East, John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, John Fisher, First Sea Lord from 1904 to 1910, was able to refocus British naval resources in the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
to counter the threat from the Imperial German Navy. The Alliance was renewed in 1911; in 1914, Japan joined the Entente in return for German territories in the Pacific, greatly annoying the Australian government which also wanted them.
On 7 August, Britain officially asked for assistance in destroying German naval units in China and Japan formally declared war on Germany on 23 August, followed by Austria-Hungary on 25th. On 2 September 1914, Japanese forces surrounded the German
Treaty Port
Treaty ports (; ja, 条約港) were the port cities in China and Japan that were opened to foreign trade mainly by the unequal treaties forced upon them by Western powers, as well as cities in Korea opened up similarly by the Japanese Empire.
...
of Qingdao, then known as Tsingtao, which surrendered on 7 November. The Imperial Japanese Navy simultaneously occupied German colonies in the
Mariana,
Caroline, and
Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Intern ...
, while in 1917, a Japanese naval squadron was sent to support the Allies in the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
.
Japan's primary interest was in China and in January 1915, the Chinese government was presented with a secret ultimatum of Twenty-One Demands, demanding extensive economic and political concessions. While these were eventually modified, the result was a surge of anti-Japanese nationalism in China and an economic boycott of Japanese goods. In addition, the other Allies now saw Japan as a threat, rather than a partner, lead to tensions first with Russia, then the US after it entered the war in April 1917. Despite protests from the other Allies, after the war Japan refused to return Qingdao and the province of Shandong to China.
Kingdom of Italy


The 1882
Triple Alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy was renewed at regular intervals, but was compromised by conflicting objectives between Italy and Austria in the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Aegean Sea, Aegean seas. Italian nationalists referred to Austrian-held Istria (including Trieste and Rijeka, Fiume) and Trento as Italian irredentism, 'the lost territories', making the Alliance so controversial that the terms were kept secret until it expired in 1915.
Alberto Pollio, the pro-Austrian Chief of Staff of the Italian Army, died on 1 July 1914, taking many of the prospects for Italian support with him. The Italian Prime Minister Antonio Salandra argued that as the Alliance was defensive in nature, Austria's aggression against Serbia and Italy's exclusion from the decision-making process meant it was not obliged to join them.
[Hamilton, Richard F; Herwig, Holger H. Decisions for War, 1914–1917. P194.]
His caution was understandable because France and Britain either supplied or controlled the import of most of Italy's raw materials, including 90% of its coal.
Salandra described the process of choosing a side as 'sacred egoism,' but as the war was expected to end before mid-1915 at the latest, making this decision became increasingly urgent. In line with Italy's obligations under the Triple Alliance, the bulk of the army was concentrated on Italy's border with France; in October, Pollio's replacement, Luigi Cadorna, General Luigi Cadorna, was ordered to begin moving these troops to the North-Eastern one with Austria.
Under the April 1915 Treaty of London (1915), Treaty of London, Italy agreed to join the Entente in return for Italian-populated territories of Austria-Hungary and other concessions; in return, it declared war on Austria-Hungary in May 1915 as required, although not on Germany until 1916.
[Hamilton, Richard F; Herwig, Holger H. Decisions for War, 1914–1917. P194-198.] Italian resentment at the difference between the promises of 1915 and the actual results of the 1919
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
would be powerful factors in the rise of Benito Mussolini.
Affiliated state combatants
Kingdom of Serbia
In 1817, the Principality of Serbia became an autonomous province within the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
; with Russian support, it gained full independence after the 1877–1878 Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878), Russo-Turkish War. Many Serbs viewed Russia as protector of the South Slavs in general but also specifically against Bulgaria, where Russian objectives increasingly collided with Bulgarian nationalism.
When Austria annexed Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1908, Russia responded by creating the Balkan League to prevent further Austrian expansion.
Austria viewed Serbia with hostility partly due to its links with Russia, whose claim to be the protector of South Slavs extended to those within the Austro-Hungarian Empire, such as the Czechs and Slovaks. Serbia also potentially gave Russia the ability to achieve their long-held objective of capturing Constantinople and the Dardanelles.

Austria backed the Albanian revolt of 1910 and the idea of a Greater Albania, since this would prevent Serbian access to the Austrian-controlled Adriatic Sea. Another Albanian revolt of 1912, Albanian revolt in 1912 exposed the weakness of the Ottoman Empire and led to the 1912–1913 First Balkan War, with
Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
,
Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
,
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
and
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
capturing most of the remaining Ottoman possessions in Europe. Disputes over the division of these resulted in the Second Balkan War, in which Bulgaria was comprehensively defeated by its former allies.
As a result of the 1913 Treaty of Bucharest (1913), Treaty of Bucharest, Serbia increased its territory by 100% and its population by 64%. However, it now faced a hostile Austria-Hungary, a resentful Bulgaria and opposition by Albanian nationalists. Germany too had ambitions in the Ottoman Empire, the centrepiece being the planned Berlin–Baghdad railway, with Serbia the only section not controlled by a pro-German state.
The exact role played by Serbian officials in the
assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, heir presumptive to the Austro-Hungarian throne, and his wife, Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, were assassinated on 28 June 1914 by Bosnian Serb student Gavrilo Princip. They were shot at close range whil ...
is still debated but despite complying with most of their demands, Austria-Hungary invaded on 28 July 1914. While Serbia successfully repulsed the Austro-Hungarian army in 1914, it was exhausted by the two Balkan Wars and unable to replace its losses of men and equipment. In 1915, Bulgaria joined the Central Powers and by the end of the year, a combined Bulgar-Austrian-German army occupied most of Serbia. Between 1914 and 1918, Serbia suffered the greatest proportional losses of any combatant, with over 25% of all those mobilised becoming casualties; including civilians and deaths from disease, over 1.2 million died, nearly 30% of the entire population.
Kingdom of Belgium
In 1830, the southern provinces of the Netherlands broke away to form the Belgium, Kingdom of Belgium and their independence was confirmed by the 1839
Treaty of London. Article VII of the Treaty required Belgium to remain perpetually neutral and committed Austria, France, Germany and Russia to guarantee that against aggression by any other state, including the signatories.


While the French and German militaries accepted Germany would almost certainly violate Belgian neutrality in the event of war, the extent of that was unclear. The original
Schlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan (german: Schlieffen-Plan, ) is a name given after the First World War to German war plans, due to the influence of Field Marshal Alfred von Schlieffen and his thinking on an invasion of France and Belgium, which began on ...
only required a limited incursion into the Belgian Ardennes, rather than a full-scale invasion; in September 1911, the Belgian Foreign Minister told a British Embassy official they would not call for assistance if the Germans limited themselves to that.
While neither Britain or France could allow Germany to occupy Belgium unopposed, a Belgian refusal to ask for help would complicate matters for the Liberal government, 1905–1915, British Liberal government, which contained a significant isolationist element.
However, the key German objective was to avoid war on two fronts; France had to be defeated before Russia could fully mobilise and give time for German forces to be transferred to the East. The growth of the Russian railway network and increase in speed of mobilisation made rapid victory over France even more important; to accommodate the additional 170,000 troops approved by the 1913 Army Bill, the 'incursion' now became a full-scale invasion. The Germans accepted the risk of British intervention; in common with most of Europe, they expected it to be a short war while their London Ambassador claimed civil war in Ireland would prevent Britain from assisting its Entente partners.
On 3 August, a German ultimatum demanded unimpeded progress through any part of Belgium, which was refused. Early on the morning of 4 August, the Germans invaded and the Belgian government called for British assistance under the 1839 Treaty; by the end of 1914, over 95% of the country was occupied but the Belgian Army held their lines on the
Yser Front
The Yser Front (french: Front de l'Yser, nl, Front aan de IJzer or ), sometimes termed the West Flemish Front in British writing, was a section of the Western Front during World War I held by Belgian troops from October 1914 until 1918. The front ...
throughout the war.
In the Belgian Congo, 25,000 Congolese troops plus an estimated 260,000 porters joined British forces in the 1916 East African Campaign (World War I), East African Campaign. By 1917, they controlled the western part of German East Africa which would become the Belgian League of Nations mandate, League of Nations Mandate of Ruanda-Urundi or modern-day Rwanda and Burundi.
Kingdom of Greece


Greece almost doubled in size as a result of the Balkan Wars of 1912 and 1913, but the success masked deep divisions within the political elite. In 1908, the island of Crete, formally part of the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
but administered by Greek officials, declared union with Greece, led by the charismatic nationalist Eleftherios Venizelos. A year later, young army officers formed the Military League to advocate for an aggressive and expansionist foreign policy; with their backing, Venizelos won a majority in the 1910 Parliamentary elections, followed by another in 1912. He had effectively broken the power of the pre-1910 political class and his position was then further strengthened by success in the Balkan Wars.
In 1913, the Greek monarch George I of Greece, George I was assassinated; he was succeeded by his son Constantine I of Greece, Constantine who had attended Heidelberg University, served in a Prussian regiment and married Sophia of Prussia, sister of Emperor Wilhelm II, German Emperor, William II. These links and a belief the Central Powers would win the war combined to make Constantine pro-German.
Venizelos himself favoured the Entente, partly due to their ability to block the maritime trade routes required for Greek imports.

Other issues adding complexity to this decision included disputes with Bulgaria and Serbia over the regions of Thrace and Macedonia (region), Macedonia as well as control of the Aegean Islands. Greece captured most of the islands during the Balkan Wars but Italy occupied the Dodecanese in 1912 and was in no hurry to give them back, while the Ottomans demanded the return of many others. In general, the Triple Entente favoured Greece, the Triple Alliance backed the Ottomans; Greece ultimately gained the vast majority but Italy did not cede the Dodecanese until 1947, while others remain Aegean dispute, disputed even today.
As a result, Greece initially remained neutral but in March 1915, the Entente offered concessions to join the Dardanelles campaign. Arguments over whether to accept led to the National Schism, with an Entente-backed administration under Venizelos in Crete, and a Royalist one led by Constantine in Athens that supported the Central Powers.
In September 1915, Bulgaria joined the Central Powers; in October, Venizelos allowed Entente forces to land at Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki or Salonica to support the Serbs, although they were too late to prevent their defeat. In August 1916, Bulgarian troops advanced into Greek-held Macedonia and Constantine ordered the army not to resist; anger at this led to a coup and he was eventually forced into exile in June 1917. A new national government under Venizelos joined the Entente, while the Greek National Defence Army Corps fought with the Allies on the Macedonian front.
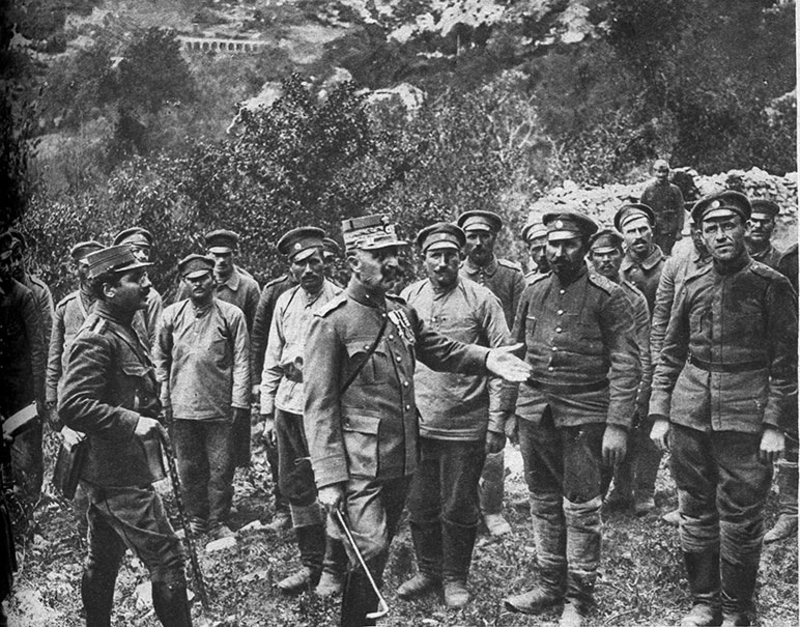
Kingdom of Montenegro

Unlike Serbia, with whom it shared close cultural and political connections, the Kingdom of Montenegro gained little from its participation in the 1912–1913 Balkan Wars. The main Montenegrin offensive was in Albanian Vilayet, Ottoman-controlled Albania, where it suffered heavy losses during the seven month Siege of Scutari (1912–13), Siege of Scutari. Austria-Hungary opposed Serb or Montenegrin control of Albania, since it provided access to the Adriatic Sea; despite Scutari's surrender, Montenegro was forced to relinquish it by the Treaty of London (1913), 1913 Treaty of London and it became capital of the short-lived Principality of Albania. This was largely an Austrian creation; the new ruler, William, Prince of Albania, was a German who was forced into exile in September, only seven months after taking up his new position and later served with the Imperial German Army.

In addition to the lack of substantive gains from the Balkan Wars, there were long-running internal divisions between those who like Nicholas I of Montenegro, Nicholas I preferred an independent Montenegro and those who advocated union with Serbia. In July 1914, Montenegro was not only militarily and economically exhausted, but also faced a multitude of political, economic and social issues.
At meetings held in March 1914, Austria-Hungary and Germany agreed union with Serbia must be prevented; Montenegro could either remain independent or be divided, its coastal areas becoming part of Albania, while the rest could join Serbia.
Nicholas seriously considered neutrality as a way to preserve his dynasty and on 31 July notified the Russian Ambassador Montenegro would only respond to an Austrian attack. He also held discussions with Austria, proposing neutrality or even active support in return for territorial concessions in Albania.
However, close links between the Serbian and Montenegrin militaries as well as popular sentiment meant there was little support for remaining neutral, especially after Russia joined the war; on 1 August, the National Assembly declared war on Austria-Hungary in fulfilment of its obligations to Serbia. After some initial success, in January 1916, the Montenegrin Army was forced to surrender to an Austro-Hungarian force.
Beda Sultanate
The Beda Sultanate was invaded by Ottoman forces in February 1915 and March 1916.
Britain assisted the Beda Sultanate in defeating the Ottoman invasions by sending arms and ammunition.
Idrisid Emirate of Asir
The Idrisid Emirate of Asir participated in the Arab Revolt. Its Emir, Muhammad ibn Ali al-Idrisi, signed an agreement with the British and joined the Allies in May 1915.
Emirate of Nejd and Hasa
The Emirate of Nejd and Hasa Battle of Jarrab, launched a failed offensive against the Ottoman aligned Emirate of Jabal Shammar in January 1915. It then agreed to enter the war as an ally of Britain in the Treaty of Darin on 26 December 1915.
Kingdom of Romania



Equal status with the main Entente Powers was one of the primary conditions for Romania's entry into the War. The Powers officially recognised this status through the Treaty of Bucharest (1916), 1916 Treaty of Bucharest. Romania fought on three of the four European Fronts: Eastern Front (World War I), Eastern, Balkans Campaign (World War I), Balkan and Italian Front (World War I), Italian, fielding in total over 1,200,000 troops.
Romanian military industry was mainly focused on converting various fortification guns into field and anti-aircraft artillery. Up to 334 German 53 mm Fahrpanzer guns, 93 French 57 mm Hotchkiss guns, 66 Krupp 150 mm guns, and dozens more 210 mm guns were mounted on Romanian-built Gun carriage, carriages and transformed into mobile field artillery, with 45 Krupp 75 mm guns and 132 Hotchkiss 57 mm guns being transformed into anti-aircraft artillery. The Romanians also 10.5 cm Feldhaubitze M.12, upgraded 120 German Krupp 105 mm howitzers, the result being the most effective field howitzer in Europe at that time. Romania even managed to design and build from scratch its own model of mortar, the 250 mm Negrei Model 1916.
Other Romanian technological assets include the building of A Vlaicu III, Vlaicu III, the world's first aircraft made of metal. The Romanian Navy possessed the largest warships on the Danube. They were a class of four river monitors, built locally at the Galați shipyard using parts manufactured in Austria-Hungary. The first one launched was ''Lascăr Catargiu'', in 1907. The Romanian monitors displaced almost 700 tons, were armed with three 120 mm naval guns in three turrets, two 120 mm naval howitzers, four 47 mm anti-aircraft guns and two 6.5 machine guns. The monitors took part in the Battle of Turtucaia and the First Battle of Cobadin. The Romanian-designed Schneider 150 mm Model 1912 howitzer was considered one of the most modern field guns on the Western Front.
Romania's entry into the War in August 1916 provoked major changes for the Germans. General Erich von Falkenhayn was dismissed and sent to command the Central Powers forces in Romania, which enabled Paul von Hindenburg, Hindenburg's subsequent ascension to power. Due to having to fight against all of the Central Powers on the longest front in Europe (1,600 km) and with little foreign help (only 50,000 Russians aided 650,000 Romanians in 1916), Battle of Bucharest, the Romanian capital was conquered that December. Vlaicu III was also captured and shipped to Germany, being last seen in 1942. The Romanian administration established a new capital at Iași and continued to fight on the Allied side in 1917. Despite being relatively short, the Romanian campaign of 1916 provided considerable respite for the Western Allies, as the Germans ceased all their other offensive operations in order to deal with Romania. After suffering a tactical defeat against the Romanians (aided by Russians) in July 1917 at Battle of Mărăști, Mărăști, the Central Powers launched two counterattacks, at Battle of Mărășești, Mărășești and Third Battle of Oituz, Oituz. The German offensive at Mărășești was soundly defeated, with German prisoners later telling their Romanian captors that German casualties were extremely heavy, and that they "had not encountered such stiff resistance since the battles of Somme and Verdun". The Austro-Hungarian offensive at Oituz also failed. On 22 September, the Austro-Hungarian Enns-class river monitor, ''Enns''-class river monitor SMS Inn, SMS ''Inn'' was sunk by a Romanian mine near Brăila. After Russia signed the
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's ...
and dropped out of the War, Romania was left surrounded by the Central Powers and eventually signed a Treaty of Bucharest (1918), similar treaty on 7 May 1918. Despite being forced to cede land to Austria-Hungary and Bulgaria, Romania ended up with a net gain in territory due to the Union of Bessarabia with Romania, Union with Bessarabia. On 10 November, Romania re-entered the War and fought a Hungarian-Romanian War, war with Hungary that lasted until August 1919.
Republic of the United States of Brazil
Brazil entered the war in 1917 after the United States intervened on the basis of Germany's unrestricted submarine warfare sinking its merchant ships, which Brazil also cited as a reason to enter the war fighting against Germany and the Central Powers. The First Brazilian Republic sent the Naval Division in War Operations that joined the British fleet in Gibraltar and made the first Brazilian naval effort in international waters. In compliance with the commitments made at the Inter-American Conference, held in Paris from 20 November to 3 December 1917, the Brazilian Government sent a medical mission composed of civilian and military surgeons to work in field hospitals of the European theatre, a contingent of sergeants and officers to serve with the French army; Airmen from the Army and Navy to join the Royal Air Force, and the employment of part of the Fleet, primarily in the anti-submarine war.
Co-belligerents: the United States
The
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
declared war on Germany in April 1917 on the grounds that Germany violated US neutrality by attacking international shipping with its unrestricted submarine warfare campaign.
The remotely connected Zimmermann Telegram of the same period, within which the Germans promised to help Mexico regain some of its territory Mexican Cession, lost to the U.S nearly seven decades before in the event of the United States entering the war, was Zimmermann Telegram#U.S, response, also a contributing factor. American entry into World War I, The US entered the war as an "associated power", rather than a formal ally of
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, in order to avoid "foreign entanglements".
[Tucker&Roberts pp. 1232, 1264, 1559] Although the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
and
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
severed relations with the United States, neither declared war,
[Tucker&Roberts p. 1559] nor did
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
. Eventually, however, the United States also United States declaration of war on Austria-Hungary, declared war on Austria-Hungary in December 1917, predominantly to help hard-pressed Italy.
Non-state combatants
Three non-state combatants, which voluntarily fought with the Allies and seceded from the constituent states of the Central Powers at the end of the war, were allowed to participate as winning nations to the peace treaties:
* First Republic of Armenia, Armenian Armenian fedayi, irregulars and Armenian volunteer units, volunteers: seceded from the Russian Empire in the aftermath of the Russian Revolution and fought against the Ottoman Empire.
* Assyrian volunteers under Mar Shimun XIX Benyamin and the Assyrian people, Assyrian tribal chiefs decided to side with the Allies, first with Russia, and next with the British, in the hope that they might secure after the victory, self-government for the Assyrians. The French also joined the alliance with the Assyrians, offering them 20,000 rifles, and the Assyrian army grew to 20,000 men co-led by Agha Petros of the Bit-Baz, Turkey, Bazi tribe, and Malik Khoshaba of the Bit-Tiyari tribe
[Paul Bartrop, Encountering Genocide: Personal Accounts from Victims, Perpetrators, and Witnesses, ABC-CLIO, 2014]
* Polish Legions in World War I, Polish Legions
* Czechoslovak Legions: armed by Czechoslovak Legion in France, France, Czechoslovak Legion in Italy, Italy and Russia
Additionally, there were also several Kurdish rebellions during World War I. Most of these, except for the uprisings of August 1917, were not supported by any of the Allied powers.
Leaders

Serbia
* Peter I of Serbia, Peter I – King of Serbia
* Alexander I of Yugoslavia, Crown Prince Alexander – Regent, Commander-in-Chief
* Nikola Pašić – Prime Minister of Serbia
* Field marshal (Serbia and Yugoslavia), Field Marshal Radomir Putnik – Chief of the General Staff (Serbia), Chief of the General Staff of the Serbian Army (1914–1915)
* General/Field marshal (Serbia and Yugoslavia), Field Marshal Živojin Mišić – Deputy Chief of General Staff (1914), Commander of First Army (Serbia), First Army (1914–1915; 1917), later Chief of General Staff (1918)
* General/Field marshal (Serbia and Yugoslavia), Field Marshal Petar Bojović – Commander of First Army (Serbia), First Army (1914), Deputy Chief of General Staff (1915–1916), Chief of General Staff (1916–1917) later Commander of First Army (1918)
* General/Field marshal (Serbia and Yugoslavia), Field Marshal Stepa Stepanović – Commander of Second Army (Serbia), Second Army (1914–1918)
* General Pavle Jurišić Šturm – Commander of Third Army (Serbia), Third Army (1914–1916)
* Colonel – Minister of Defence (Serbia), Minister of War (1914)
* Colonel – Minister of War (1914–1915)
* Colonel/General – Minister of War (1915–1918)
* General Mihailo Rašić – Minister of War (1918)
* Colonel/General Miloš Vasić (general), Miloš Vasić – Commander of First Army (Serbia), First Army (1916; 1917), Commander of Third Army (Serbia), Third Army (1916)
Montenegro
* Nicholas I of Montenegro, Nicholas I – King of Montenegro, Commander-in-Chief
* General Serdar (Ottoman rank), Serdar Janko Vukotić – Prime Minister of Montenegro, Prime Minister, Commander of 1st Montenegrin Army
* General Božidar Janković – Chief of the General Staff of the Montenegrin Army (1914–1915)
* Colonel Petar Pešić – Deputy Chief of the General Staff of the Montenegrin Army (1914–1915), later Chief of the General Staff of the Montenegrin Army (1915–1916)
* Danilo, Crown Prince of Montenegro, Crown Prince Danilo II Petrović-Njegoš – In the staff of the 1st Montenegrin Army
* Brigadier Krsto Popović – In the staff of the 1st Montenegrin Army, Aide-de-camp to Serdar (Ottoman rank), Serdar Janko Vukotić
* General Anto Gvozdenović – King's Aide-de-camp
* General Mitar Martinović – Commander of several detachments in the Montenegrin army (Drina and Herzegovina detachments together in 1914–1915, Kotor detachment in 1916)
Russia (1914–1917)
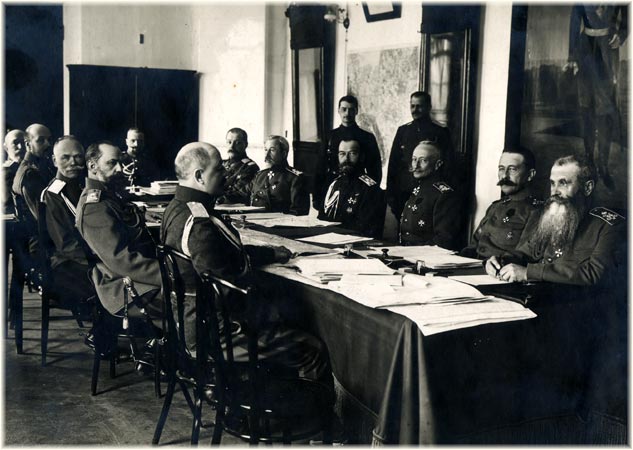

* Nicholas II of Russia, Nicholas II – Russian Emperor, King of Poland, and Grand Prince of Finland (until 15 March 1917)
* Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolaevich of Russia (1856–1929), Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolaevich – Commander-in-chief (1 August 1914 – 5 September 1916) and viceroy in the Caucasus
* Ivan Goremykin – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (1 August 1914 – 2 February 1916)
* Boris Stürmer – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (2 February 1916 – 23 November 1916)
* Alexander Trepov – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (23 November 1916 – 27 December 1916)
* Nikolai Golitsyn – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (27 December 1916 – 9 January 1917)
* General of the Cavalry Alexander Samsonov – Commander of the Russian Second Army for the invasion of East Prussia (1 August 1914 – 29 August 1914)
* General of the Cavalry Paul von Rennenkampf – Commander of the Russian First Army for the invasion of East Prussia (1 August 1914 – November 1914)
* General of the Artillery (Imperial Russia), General of the Artillery Nikolay Iudovich Ivanov, Nikolay Ivanov – Commander of the Imperial Russian Army, Russian army on the Southwestern Front, (1 August 1914 – March 1916) responsible for much of the action in Galicia (Eastern Europe), Galicia

* Adjutant general, General Adjutant Aleksei Brusilov – Commander of the South-West Front, then provisional Commander-in-Chief after the Tsar's abdication (February 1917 – August 1917)
* General of the Infantry (Imperial Russia), General of the Infantry Lavr Kornilov, Lavr Georgievich Kornilov – Commander of the South-West Front, then Commander-in-Chief (August 1917)
* General of the Infantry (Imperial Russia), General of the Infantry Aleksey Kuropatkin – Commander of the Northern Front (October 1915 – 1917)
* General of the Infantry (Imperial Russia), General of the Infantry Nikolai Yudenich – Commander of the Caucasus (January 1915 – May 1917)
* Admiral Andrei Eberhardt – Commander of Black Sea Fleet (1914–16)
* Admiral Alexander Kolchak – Commander of Black Sea Fleet (1916–17)
* Admiral Nikolai Essen – Commander of Baltic Fleet (1913 – May 1915)
Belgium
* Albert I of Belgium – King of the Belgians (23 December 1909 – 17 February 1934) and Commander-in-chief of the Belgian army
* Charles de Broqueville – Prime Minister of Belgium, Prime Minister (1912–1918); replaced by Gérard Cooreman in June 1918 shortly before the end of the war.
* Félix Wielemans – Chief of Staff of the Belgian Army
* Gérard Leman – general commanding the Battle of Liège, defense of Liège
* Charles Tombeur – commander of the colonial ''Force Publique'' in the East African Campaign (World War I), East African theatre
France
* Raymond Poincaré – President of France
* René Viviani – Prime Minister of France (13 June 1914 – 29 October 1915)
* Aristide Briand – Prime Minister of France (29 October 1915 – 20 March 1917)
* Alexandre Ribot – Prime Minister of France (20 March 1917 – 12 September 1917)
* Paul Painlevé – Prime Minister of France (12 September 1917 – 16 November 1917)
* Georges Clemenceau – Prime Minister of France (from 16 November 1917)
* Divisional General/Marshal of France, Marshal Joseph Joffre – Commander-in-Chief of the French Army (3 August 1914 – 13 December 1916)
* Divisional General Robert Nivelle – Commander-in-Chief of the French Army (13 December 1916 – April 1917)
* Divisional General/Marshal of France, Marshal Philippe Pétain – Commander-in-Chief of the French Army (April 1917 – 11 November 1918)
* Divisional General/Marshal of France, Marshal Ferdinand Foch – Supreme Allied Commander (26 March 1918 – 11 November 1918)
* Divisional General Maurice Sarrail – Commander of the Allied armies at Salonika front (1915–1917)
* Army general (France), Army General Adolphe Guillaumat – Commander of the Allied armies at Salonika front (1917–1918)
* Divisional General/Marshal of France, Marshal Louis Franchet d'Espèrey – Commander of the Allied armies at Salonika front (1918)
* Brigadier General Milan Rastislav Štefánik – General of French Army, Commander of Czechoslovak Legions
Britain and the British Empire
United Kingdom
* George V – Monarchy of the United Kingdom, King of the United Kingdom, and the British Dominions, Emperor of India
*
H. H. Asquith
Herbert Henry Asquith, 1st Earl of Oxford and Asquith, (12 September 1852 – 15 February 1928), generally known as H. H. Asquith, was a British statesman and Liberal Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom f ...
– Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (until 5 December 1916)
* David Lloyd George – Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (from 7 December 1916)
* Field marshal (United Kingdom), Field Marshal Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener, Horatio Herbert Kitchener – Secretary of State for War (5 August 1914 – 5 June 1916)
*Edward Stanley, 17th Earl of Derby – Secretary of State for War (1916– )
* General (United Kingdom), General Sir William Robertson, 1st Baronet, William Robertson – Chief of the Imperial General Staff (23 December 1915 – February 1918)
* General Sir Henry Wilson, 1st Baronet, Henry Wilson – Chief of the Imperial General Staff (February 1918 – February 1922)
* Field marshal (United Kingdom), Field Marshal John French, 1st Earl of Ypres, John French – Commander-in-Chief of the
British Expeditionary Force (4 August 1914 – 15 December 1915)
* General / Field marshal (United Kingdom), Field Marshal
Douglas Haig
Field Marshal Douglas Haig, 1st Earl Haig, (; 19 June 1861 – 29 January 1928) was a senior officer of the British Army. During the First World War, he commanded the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) on the Western Front from late 1915 until ...
– Commander-in-Chief of the British Expeditionary Force (15 December 1915 – 11 November 1918)
* General David Henderson (British Army officer), Sir David Henderson – Director-General of Military Aeronautics
* General Hugh Trenchard, 1st Viscount Trenchard, Hugh Trenchard – Commander of Royal Flying Corps – (August 1915 – January 1918) and Chief of the Air Staff (United Kingdom), Chief of the Air Staff of the combined Royal Air Force – 1 April 1918 – 13 April 1918
* Brigadier (United Kingdom)#Historical rank of brigadier general, Brigadier General Sir Frederick Sykes – Chief of the Air Staff (United Kingdom), Chief of the Air Staff – 13 April 1918 through 11 November 1918 (post-war to 31 March 1919)
* Winston Churchill – First Lord of the Admiralty – (1911 – May 1915)
* Arthur Balfour- First Lord of the Admiralty – (May 1915 – December 1916)
* Edward Carson – First Lord of the Admiralty – (10 December 1916 – 17 July 1917)
* Eric Campbell Geddes, Eric Geddes – First Lord of the Admiralty – (July 1917 – January 1919)
* Admiral of the Fleet (Royal Navy), Admiral of the Fleet John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, John "Jackie" Fisher – First Sea Lord – (1914 – May 1915)
* Admiral (Royal Navy), Admiral Henry Jackson (Royal Navy officer), Henry Jackson – First Sea Lord – (May 1915 – November 1916)
* Admiral John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, John Jellicoe – Commander of the Grand Fleet (August 1914 – November 1916); First Sea Lord (November 1916 – December 1917)
* Admiral Rosslyn Wemyss, 1st Baron Wester Wemyss, Rosslyn Wemyss – First Sea Lord (December 1917 – November 1919)
* Admiral David Beatty, 1st Earl Beatty, David Beatty – Commander of the Grand Fleet (November 1916 – April 1919)
* General Archibald Murray – Commander of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (January 1916 – June 1917)
* General
Edmund Allenby
Field Marshal Edmund Henry Hynman Allenby, 1st Viscount Allenby, (23 April 1861 – 14 May 1936) was a senior British Army officer and Imperial Governor. He fought in the Second Boer War and also in the First World War, in which he led th ...
– Commander of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (June 1917 – November 1918)
* Eric John Eagles Swayne – Commander of the British forces in the Somaliland Campaign
* William Peyton – commander and military secretary to the British Expeditionary Force
* Colonel T. E. Lawrence - A main leader of the Arab Revolt
Dominion of Canada
* Robert Borden – Prime Minister of Canada (1914–18)
* Sam Hughes – Minister of Militia and Defence (Canada), Minister of Militia and Defence (1914 – January 1915)
* Joseph Flavelle – Chairman of Imperial Munitions Board (1915–19)
* Lieutenant-General (UK), Lieutenant-General Edwin Alderson – Commander of the unified Canadian Corps of the Canadian Expeditionary Force (26 January 1915 – September 1915)
* General (United Kingdom), General Julian Byng, 1st Viscount Byng of Vimy, Julian Byng – Commander of the unified Canadian Corps of the Canadian Expeditionary Force (June 1916 – June 1917)
* General (United Kingdom), General Arthur Currie – Commander of the unified Canadian Corps of the Canadian Expeditionary Force (June 1917 – August 1919)
[first Canadian to attain the rank of full general]
Commonwealth of Australia
* Joseph Cook – Prime Minister of Australia (until 17 September 1914)
* Andrew Fisher – Prime Minister of Australia (17 September 1914 – 27 October 1915)
* Billy Hughes – Prime Minister of Australia (from 27 October 1915)
* General (United Kingdom), General William Birdwood – Commander of the Australian Corps (all five Australian infantry divisions serving on the Western Front) (November 1917 – May 1918)
* Lieutenant General (Australia), Lieutenant General Sir John Monash – Commander of the Australian Corps (May 1918 –)
* Major general (Australia), Major General William Holmes (Australian general), William Holmes – Commander of the Australian Naval and Military Expeditionary Force (August 1914 – February 1915)
* Lieutenant General (Australia), Lieutenant General Sir Harry Chauvel – Commander of Desert Mounted Corps (Sinai and Palestine) (August 1917 –)
British India
* Charles Hardinge, 1st Baron Hardinge of Penshurst – Viceroy of India 1910–1916
* Frederic Thesiger, 1st Viscount Chelmsford – Viceroy of India 1916–1921
* Robert Crewe-Milnes, 1st Marquess of Crewe – Secretary of State for India (May 1911 – May 1915)
* Austen Chamberlain – Secretary of State for India (May 1915 – July 1917)
* Edwin Samuel Montagu – Secretary of State for India (July 1917 – March 1922)
* Beauchamp Duff – Commander-in-Chief, India, Commander-in-Chief, India (March 1914 – October 1916)
* Sir Charles Monro, 1st Baronet, Charles Monro – Commander-in-Chief, India, Commander-in-Chief, India (October 1916 – November 1920)
* Lieutenant-General John Nixon (Indian Army officer), John Nixon commander of the
British Indian Army (active in the Middle East)
Union of South Africa
* General (United Kingdom), General Louis Botha – Prime Minister of South Africa
* General (United Kingdom), General Jan Smuts – Led forces in South-West Africa Campaign and East African Campaign (World War I), East African Campaign, later member of the
Imperial War Cabinet
The Imperial War Cabinet (IWC) was the British Empire's wartime coordinating body. It met over three sessions, the first from 20 March to 2 May 1917, the second from 11 June to late July 1918, and the third from 20 or 25 November 1918 to early Jan ...
Dominion of New Zealand
* William Massey – Prime Minister of New Zealand
* General Sir Alexander Godley – Commandant of New Zealand Military Forces (to October 1914); Commander of the New Zealand Expeditionary Force
* Major General Sir Alfred William Robin – Quartermaster-General and Commandant of New Zealand Military Forces (from October 1914)
* Major General Sir Andrew Hamilton Russell – Commander of the New Zealand Division
Dominion of Newfoundland
* Edward Morris, 1st Baron Morris, Sir Edward Morris – List of Newfoundland Prime Ministers#Dominion Prime Ministers, Prime Minister of Newfoundland (1909–1917)
* John Chalker Crosbie, Sir John Crosbie – Prime Minister of Newfoundland (1917–1918)
* William F. Lloyd, Sir William Lloyd – Prime Minister of Newfoundland (1918–1919)
Japan
* Emperor Taishō – Emperor of Japan
* Ōkuma Shigenobu – Prime Minister of Japan (16 April 1914 – 9 October 1916)
* Terauchi Masatake – Prime minister of Japan (9 October 1916 – 29 September 1918)
* Hara Takashi – Prime minister of Japan (29 September 1918 – 4 November 1921)
* Katō Sadakichi – Commander-in-chief of the 2nd Fleet (Imperial Japanese Navy), Second Fleet deployed to the Siege of Tsingtao
* Kōzō Satō – Commander of the Second Special Task Fleet
* Kamio Mitsuomi – Commander of Allied land forces Siege of Tsingtao, at Tsingtao
Italy (1915–1918)
* Victor Emmanuel III of Italy, Victor Emmanuel III – King of Italy
* Antonio Salandra – Prime Minister of Italy, Prime Minister (until 18 June 1916)
* Paolo Boselli – Prime Minister of Italy, Prime Minister (18 June 1916 – 29 October 1917)
* Vittorio Emanuele Orlando – Prime Minister of Italy, Prime Minister (from 29 October 1917)
* Luigi Cadorna – Commander-in-Chief of the Royal Italian Army
* Armando Diaz – Chief of General Staff of the Royal Italian army
* Prince Luigi Amedeo, Duke of the Abruzzi, Luigi, Duke of Abruzzi – Commander-in-Chief of the Adriatic Fleet of Italy (1914–17)
* Paolo Thaon di Revel – Admiral of the Royal Italian Navy
Romania (1916–1918)
* Ferdinand I of Romania, Ferdinand I – King of Romania
* General officer, General Constantin Prezan – Chief of the General Staff of Romania
* Ion I. C. Brătianu – Prime Minister of Romania
* Vintilă Brătianu – Secretary of War
* Mareşal (Romania), Field Marshal Alexandru Averescu – Commander of the Second Army (Romania), 2nd Army, 3rd Army, then Army Group South
* General officer, General Eremia Grigorescu – Commander of the 1st Territorial Army Corps, 1st Army
Portugal (1916–1918)
* Bernardino Machado – President of Portugal (until 12 December 1917)
* Afonso Costa – Prime Minister of Portugal (until 15 March 1916; then again 25 April 1917 – 10 December 1917)
* António José de Almeida – Prime Minister of Portugal (15 March 1916 – 25 April 1917)
* Sidónio Pais – Prime Minister of Portugal and War Minister (11 December 1917 – 9 May 1918) and President of Portugal (from 9 May 1918)
* José Norton de Matos – War Minister (until 10 December 1917)
* João Tamagnini Barbosa – Interim War Minister (9 May 1918 – 15 May 1918)
* Amílcar Mota – Secretary of State for War (15 May 1918 – 8 October 1918)
* Álvaro de Mendonça – Secretary of State for War (from 8 October 1918)
* Fernando Tamagnini de Abreu e Silva, Fernando Tamagnini de Abreu – Commander of the Portuguese Expeditionary Corps, Portuguese Expeditionary Corps (CEP)
* José Augusto Alves Roçadas – Commander of the Portuguese Forces in Southern Angola
* José Luís de Moura Mendes – Commander of the Portuguese Forces in Eastern Africa (until June 1916)
* José César Ferreira Gil – Commander of the Portuguese Forces in Eastern Africa (from June 1916)
* Sousa Rosa – Commander of the Portuguese Forces in Eastern Africa (from 1917)
Greece (1916/17–1918)

* Constantine I of Greece, Constantine I: King of Greece, he retired from the throne in June 1917, due to Allied pressure, without formally abdicating.
* Alexander of Greece, Alexander: King of Greece, he became King in 1917 after his father and brother retired from the throne
* Eleftherios Venizelos: Prime minister of Greece after 13 June 1917
* Panagiotis Danglis: Greek general of the Hellenic Army
United States (1916–1918)

* Woodrow Wilson – President of the United States/Commander-In-Chief of the US armed forces
* Newton D. Baker – US Secretary of War
* Josephus Daniels – United States Secretary of the Navy
* Major General/General John J. Pershing – Commander of the American Expeditionary Force
* Rear Admiral/Vice Admiral William Sims – Commander of United States Navy, US Naval Forces in European Waters
* Brigadier General Mason Patrick – Commander of the United States Army Air Service
Siam (Thailand) (1917–1918)

* Vajiravudh, Rama VI – King of Siam
* Field marshal (Thailand), Field Marshal Chao Phraya Bodindechanuchit – List of Defence Ministers of Thailand, Minister of Defence
* Chakrabongse Bhuvanath, Prince Chakrabongse Bhuvanath – Supreme Commander of the Siamese Expeditionary Forces in World War I
* General Phraya Bijai Janriddhi – Commander of the Siamese Expeditionary Forces in the
Western Front
Brazil (1917–1918)

* Venceslau Brás – President of Brazil
* Pedro Max Fernando Frontin, Pedro Frontin, Chief of the ''Divisão Naval em Operações de Guerra'' (Naval Division in War Operations)
* José Pessoa Cavalcanti de Albuquerque, Lieutenant of the Brazilian Army in France
* Napoleão Felipe Aché, Chief of Brazilian Military Mission in France (1918–1919)
* Doctor of Medicine, M.D. Nabuco Gouveia – Chief of Brazilian Military Medical Commission
Armenia (1917–1918)
* Hovhannes Kajaznuni – first Prime Minister of Armenia, Prime Minister of the First Republic of Armenia
* Andranik, General Andranik – military commander and statesman of the Caucasus Campaign
* Aram Manukian – Minister of Internal Affairs of the First Republic of Armenia
* Drastamat Kanayan – Military commander and member of the Armenian Revolutionary Federation
* Tovmas Nazarbekian – Commander-in-chief of the First Republic of Armenia
* Movses Silikyan – Army general and National hero
Czechoslovakia (1918)
* Tomáš Masaryk – first List of presidents of Czechoslovakia, President of First Czechoslovak Republic, Czechoslovakia
* Milan Rastislav Štefánik – Commander of the Czechoslovak Legion
* Edvard Beneš – Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Czechoslovakia), Minister of Foreign Affairs and Ministry of the Interior (Czechoslovakia), the Interior
Personnel and casualties

These are estimates of the cumulative number of different personnel in uniform 1914–1918, including army, navy and auxiliary forces. At any one time, the various forces were much smaller. Only a fraction of them were frontline combat troops. The numbers do not reflect the length of time each country was involved.
See also
* Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War
* Causes of World War I
* Color books, transcripts of official documents released by each nation early in the war
* Diplomatic history of World War I
** British entry into World War I
** French entry into World War I
* Historiography of the causes of World War I
* Home front during World War I
** Belgium in World War I
** French Third Republic#First World War, France in World War I
** History of Germany during World War I, Germany in World War I
** Military history of Italy during World War I, Italy in World War I
** Romania during World War I, Romania in World War I
** History of the United Kingdom during World War I, United Kingdom in World War I
** United States home front during World War I, United States in World War I
**Japan during World War I, Japan in World War I
* International relations of the Great Powers (1814–1919)
* July Crisis
Footnotes
References
Bibliography
* Ellis, John and Mike Cox. ''The World War I Databook: The Essential Facts and Figures for All the Combatants'' (2002)
* Esposito, Vincent J. ''The West Point Atlas of American Wars: 1900–1918'' (1997); despite the title covers entire war
online maps from this atlas* Falls, Cyril. ''The Great War'' (1960), general military history
*
* Gooch, G. P. ''Recent Revelations Of European Diplomacy'' (1940), 475pp; summarises memoirs of major participants
* Higham, Robin and Dennis E. Showalter, eds. ''Researching World War I: A Handbook'' (2003); historiography, stressing military themes
* Pope, Stephen and Wheal, Elizabeth-Anne, eds. ''The Macmillan Dictionary of the First World War'' (1995)
* Strachan, Hew. ''The First World War: Volume I: To Arms'' (2004)
* Trask, David F. ''The United States in the Supreme War Council: American War Aims and Inter-Allied Strategy, 1917–1918'' (1961)
*
* Tucker, Spencer, ed. ''The Encyclopedia of World War I: A Political, Social, and Military History'' (5 volumes) (2005); online at eBook.com
* United States. War Dept. General Staff. ''Strength and organisation of the armies of France, Germany, Austria, Russia, England, Italy, Mexico and Japan (showing conditions in July, 1914)'' (1916
online*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Allies Of World War I
1919 in law
20th-century military alliances
Aftermath of World War I
Military alliances involving Australia
Military alliances involving Canada
Military alliances involving France
Military alliances involving New Zealand
Military alliances involving South Africa
Military alliances involving the United Kingdom
Military alliances involving the United States
World War I by country
History of diplomacy
 When the war began in 1914, the
When the war began in 1914, the  In the East, between 7 and 9 August the Russians entered German East Prussia on 7 August, Austrian
In the East, between 7 and 9 August the Russians entered German East Prussia on 7 August, Austrian  For much of the 19th century, Britain sought to maintain the European balance of power without formal alliances, a policy known as
For much of the 19th century, Britain sought to maintain the European balance of power without formal alliances, a policy known as  Since control of Belgium allowed an opponent to threaten invasion or blockade British trade, preventing it was a long-standing British strategic interest. Under Article VII of the 1839 Treaty of London, Britain guaranteed Belgian neutrality against aggression by any other state, by force if required. Chancellor
Since control of Belgium allowed an opponent to threaten invasion or blockade British trade, preventing it was a long-standing British strategic interest. Under Article VII of the 1839 Treaty of London, Britain guaranteed Belgian neutrality against aggression by any other state, by force if required. Chancellor  The German high command was aware entering Belgium would lead to British intervention but decided the risk was acceptable; they expected a short war while their ambassador in London claimed troubles in Ireland would prevent Britain from assisting France. On 3 August, Germany demanded unimpeded progress through any part of Belgium and when this was refused, invaded early on the morning of 4 August.
This changed the situation; the invasion of Belgium consolidated political and public support for the war by presenting what appeared to be a simple moral and strategic choice. The Belgians asked for assistance under the 1839 Treaty and in response, Britain declared war on Germany on 4 August 1914. Although Germany's violation of Belgium neutrality was not the only cause of British entry into the war, it was used extensively in government propaganda at home and abroad to make the case for British intervention. This confusion arguably persists today.
The declaration of war automatically involved all dominions and colonies and protectorates of the
The German high command was aware entering Belgium would lead to British intervention but decided the risk was acceptable; they expected a short war while their ambassador in London claimed troubles in Ireland would prevent Britain from assisting France. On 3 August, Germany demanded unimpeded progress through any part of Belgium and when this was refused, invaded early on the morning of 4 August.
This changed the situation; the invasion of Belgium consolidated political and public support for the war by presenting what appeared to be a simple moral and strategic choice. The Belgians asked for assistance under the 1839 Treaty and in response, Britain declared war on Germany on 4 August 1914. Although Germany's violation of Belgium neutrality was not the only cause of British entry into the war, it was used extensively in government propaganda at home and abroad to make the case for British intervention. This confusion arguably persists today.
The declaration of war automatically involved all dominions and colonies and protectorates of the  In terms of population, the largest component (after Britain herself) was the
In terms of population, the largest component (after Britain herself) was the  Between 1873 and 1887, Russia was allied with Germany and Austria-Hungary in the League of the Three Emperors, then with Germany in the 1887–1890 Reinsurance Treaty; both collapsed due to the competing interests of Austria and Russia in the Balkans. While France took advantage of this to agree the 1894 Franco-Russian Alliance, Britain viewed Russia with deep suspicion; in 1800, over 3,000 kilometres separated the Russian Empire and British India, by 1902, it was 30 km in some areas. This threatened to bring the two into direct conflict, as did the long-held Russian objective of gaining control of the Bosporus, Bosporus Straits and with it access to the British-dominated Mediterranean Sea.
Between 1873 and 1887, Russia was allied with Germany and Austria-Hungary in the League of the Three Emperors, then with Germany in the 1887–1890 Reinsurance Treaty; both collapsed due to the competing interests of Austria and Russia in the Balkans. While France took advantage of this to agree the 1894 Franco-Russian Alliance, Britain viewed Russia with deep suspicion; in 1800, over 3,000 kilometres separated the Russian Empire and British India, by 1902, it was 30 km in some areas. This threatened to bring the two into direct conflict, as did the long-held Russian objective of gaining control of the Bosporus, Bosporus Straits and with it access to the British-dominated Mediterranean Sea.
 Defeat in the 1905 Russo-Japanese War and Britain's isolation during the 1899–1902 Second Boer War led both parties to seek allies. The
Defeat in the 1905 Russo-Japanese War and Britain's isolation during the 1899–1902 Second Boer War led both parties to seek allies. The  French defeat in the 1870–1871 Franco-Prussian War led to the loss of the two provinces of Alsace-Lorraine and the establishment of the French Third Republic, Third Republic. The suppression of the Paris Commune by the new regime caused deep political divisions and led to a series of bitter political struggles, such as the Dreyfus affair. As a result, aggressive nationalism or Revanchism was one of the few areas to unite the French.
The loss of Alsace-Lorraine deprived France of its natural defence line on the Rhine, while it was weaker demographically than Germany, whose 1911 population was 64.9 million to 39.6 in France, which had the lowest birthrate in Europe. This meant that despite their very different political systems, when Germany allowed the Reinsurance Treaty to lapse, France seized the opportunity to agree the 1894 Franco-Russian Alliance. It also replaced Germany as the primary source of financing for Russian industry and the expansion of its railway network, particularly in border areas with Germany and Austria-Hungary.
French defeat in the 1870–1871 Franco-Prussian War led to the loss of the two provinces of Alsace-Lorraine and the establishment of the French Third Republic, Third Republic. The suppression of the Paris Commune by the new regime caused deep political divisions and led to a series of bitter political struggles, such as the Dreyfus affair. As a result, aggressive nationalism or Revanchism was one of the few areas to unite the French.
The loss of Alsace-Lorraine deprived France of its natural defence line on the Rhine, while it was weaker demographically than Germany, whose 1911 population was 64.9 million to 39.6 in France, which had the lowest birthrate in Europe. This meant that despite their very different political systems, when Germany allowed the Reinsurance Treaty to lapse, France seized the opportunity to agree the 1894 Franco-Russian Alliance. It also replaced Germany as the primary source of financing for Russian industry and the expansion of its railway network, particularly in border areas with Germany and Austria-Hungary.
 However, Russian defeat in the 1904–1905 Russo-Japanese War damaged its credibility, while Britain's isolation during the Second Boer War meant both countries sought additional allies. This resulted in the 1904
However, Russian defeat in the 1904–1905 Russo-Japanese War damaged its credibility, while Britain's isolation during the Second Boer War meant both countries sought additional allies. This resulted in the 1904  In response to Germany's declaration of war on Russia, France issued a general mobilisation in expectation of war on 2 August and on 3 August, Germany also declared war on France. Germany's ultimatum to Belgium brought Britain into the war on 4 August, although France did not declare war on Austria-Hungary until 12 August.
As with Britain, France's French colonial empire, colonies also became part of the war; pre-1914, French soldiers and politicians advocated using French African recruits to help compensate for France's demographic weakness. From August to December 1914, the French lost nearly 300,000 dead on the Western Front, more than Britain suffered in the whole of WWII and the gaps were partly filled by colonial troops, over 500,000 of whom served on the Western Front over the period 1914–1918. Colonial troops also fought at Gallipoli Campaign, Gallipoli, occupied Togo and Kamerun in West Africa and had a minor role in the Middle East, where France was the traditional protector of Christians in the Ottoman provinces of Ottoman Syria, Syria, History of Palestine#Early Ottoman rule, Palestine and History of Lebanon under Ottoman rule, Lebanon.
In response to Germany's declaration of war on Russia, France issued a general mobilisation in expectation of war on 2 August and on 3 August, Germany also declared war on France. Germany's ultimatum to Belgium brought Britain into the war on 4 August, although France did not declare war on Austria-Hungary until 12 August.
As with Britain, France's French colonial empire, colonies also became part of the war; pre-1914, French soldiers and politicians advocated using French African recruits to help compensate for France's demographic weakness. From August to December 1914, the French lost nearly 300,000 dead on the Western Front, more than Britain suffered in the whole of WWII and the gaps were partly filled by colonial troops, over 500,000 of whom served on the Western Front over the period 1914–1918. Colonial troops also fought at Gallipoli Campaign, Gallipoli, occupied Togo and Kamerun in West Africa and had a minor role in the Middle East, where France was the traditional protector of Christians in the Ottoman provinces of Ottoman Syria, Syria, History of Palestine#Early Ottoman rule, Palestine and History of Lebanon under Ottoman rule, Lebanon.
 With Japan as an ally in the Far East, John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, John Fisher, First Sea Lord from 1904 to 1910, was able to refocus British naval resources in the
With Japan as an ally in the Far East, John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, John Fisher, First Sea Lord from 1904 to 1910, was able to refocus British naval resources in the 
 The 1882 Triple Alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy was renewed at regular intervals, but was compromised by conflicting objectives between Italy and Austria in the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Aegean Sea, Aegean seas. Italian nationalists referred to Austrian-held Istria (including Trieste and Rijeka, Fiume) and Trento as Italian irredentism, 'the lost territories', making the Alliance so controversial that the terms were kept secret until it expired in 1915.
Alberto Pollio, the pro-Austrian Chief of Staff of the Italian Army, died on 1 July 1914, taking many of the prospects for Italian support with him. The Italian Prime Minister Antonio Salandra argued that as the Alliance was defensive in nature, Austria's aggression against Serbia and Italy's exclusion from the decision-making process meant it was not obliged to join them.Hamilton, Richard F; Herwig, Holger H. Decisions for War, 1914–1917. P194.
His caution was understandable because France and Britain either supplied or controlled the import of most of Italy's raw materials, including 90% of its coal. Salandra described the process of choosing a side as 'sacred egoism,' but as the war was expected to end before mid-1915 at the latest, making this decision became increasingly urgent. In line with Italy's obligations under the Triple Alliance, the bulk of the army was concentrated on Italy's border with France; in October, Pollio's replacement, Luigi Cadorna, General Luigi Cadorna, was ordered to begin moving these troops to the North-Eastern one with Austria.
Under the April 1915 Treaty of London (1915), Treaty of London, Italy agreed to join the Entente in return for Italian-populated territories of Austria-Hungary and other concessions; in return, it declared war on Austria-Hungary in May 1915 as required, although not on Germany until 1916.Hamilton, Richard F; Herwig, Holger H. Decisions for War, 1914–1917. P194-198. Italian resentment at the difference between the promises of 1915 and the actual results of the 1919
The 1882 Triple Alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy was renewed at regular intervals, but was compromised by conflicting objectives between Italy and Austria in the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Aegean Sea, Aegean seas. Italian nationalists referred to Austrian-held Istria (including Trieste and Rijeka, Fiume) and Trento as Italian irredentism, 'the lost territories', making the Alliance so controversial that the terms were kept secret until it expired in 1915.
Alberto Pollio, the pro-Austrian Chief of Staff of the Italian Army, died on 1 July 1914, taking many of the prospects for Italian support with him. The Italian Prime Minister Antonio Salandra argued that as the Alliance was defensive in nature, Austria's aggression against Serbia and Italy's exclusion from the decision-making process meant it was not obliged to join them.Hamilton, Richard F; Herwig, Holger H. Decisions for War, 1914–1917. P194.
His caution was understandable because France and Britain either supplied or controlled the import of most of Italy's raw materials, including 90% of its coal. Salandra described the process of choosing a side as 'sacred egoism,' but as the war was expected to end before mid-1915 at the latest, making this decision became increasingly urgent. In line with Italy's obligations under the Triple Alliance, the bulk of the army was concentrated on Italy's border with France; in October, Pollio's replacement, Luigi Cadorna, General Luigi Cadorna, was ordered to begin moving these troops to the North-Eastern one with Austria.
Under the April 1915 Treaty of London (1915), Treaty of London, Italy agreed to join the Entente in return for Italian-populated territories of Austria-Hungary and other concessions; in return, it declared war on Austria-Hungary in May 1915 as required, although not on Germany until 1916.Hamilton, Richard F; Herwig, Holger H. Decisions for War, 1914–1917. P194-198. Italian resentment at the difference between the promises of 1915 and the actual results of the 1919  Austria backed the Albanian revolt of 1910 and the idea of a Greater Albania, since this would prevent Serbian access to the Austrian-controlled Adriatic Sea. Another Albanian revolt of 1912, Albanian revolt in 1912 exposed the weakness of the Ottoman Empire and led to the 1912–1913 First Balkan War, with
Austria backed the Albanian revolt of 1910 and the idea of a Greater Albania, since this would prevent Serbian access to the Austrian-controlled Adriatic Sea. Another Albanian revolt of 1912, Albanian revolt in 1912 exposed the weakness of the Ottoman Empire and led to the 1912–1913 First Balkan War, with 
 While the French and German militaries accepted Germany would almost certainly violate Belgian neutrality in the event of war, the extent of that was unclear. The original
While the French and German militaries accepted Germany would almost certainly violate Belgian neutrality in the event of war, the extent of that was unclear. The original 
 Greece almost doubled in size as a result of the Balkan Wars of 1912 and 1913, but the success masked deep divisions within the political elite. In 1908, the island of Crete, formally part of the
Greece almost doubled in size as a result of the Balkan Wars of 1912 and 1913, but the success masked deep divisions within the political elite. In 1908, the island of Crete, formally part of the  Other issues adding complexity to this decision included disputes with Bulgaria and Serbia over the regions of Thrace and Macedonia (region), Macedonia as well as control of the Aegean Islands. Greece captured most of the islands during the Balkan Wars but Italy occupied the Dodecanese in 1912 and was in no hurry to give them back, while the Ottomans demanded the return of many others. In general, the Triple Entente favoured Greece, the Triple Alliance backed the Ottomans; Greece ultimately gained the vast majority but Italy did not cede the Dodecanese until 1947, while others remain Aegean dispute, disputed even today.
As a result, Greece initially remained neutral but in March 1915, the Entente offered concessions to join the Dardanelles campaign. Arguments over whether to accept led to the National Schism, with an Entente-backed administration under Venizelos in Crete, and a Royalist one led by Constantine in Athens that supported the Central Powers.
In September 1915, Bulgaria joined the Central Powers; in October, Venizelos allowed Entente forces to land at Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki or Salonica to support the Serbs, although they were too late to prevent their defeat. In August 1916, Bulgarian troops advanced into Greek-held Macedonia and Constantine ordered the army not to resist; anger at this led to a coup and he was eventually forced into exile in June 1917. A new national government under Venizelos joined the Entente, while the Greek National Defence Army Corps fought with the Allies on the Macedonian front.
Other issues adding complexity to this decision included disputes with Bulgaria and Serbia over the regions of Thrace and Macedonia (region), Macedonia as well as control of the Aegean Islands. Greece captured most of the islands during the Balkan Wars but Italy occupied the Dodecanese in 1912 and was in no hurry to give them back, while the Ottomans demanded the return of many others. In general, the Triple Entente favoured Greece, the Triple Alliance backed the Ottomans; Greece ultimately gained the vast majority but Italy did not cede the Dodecanese until 1947, while others remain Aegean dispute, disputed even today.
As a result, Greece initially remained neutral but in March 1915, the Entente offered concessions to join the Dardanelles campaign. Arguments over whether to accept led to the National Schism, with an Entente-backed administration under Venizelos in Crete, and a Royalist one led by Constantine in Athens that supported the Central Powers.
In September 1915, Bulgaria joined the Central Powers; in October, Venizelos allowed Entente forces to land at Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki or Salonica to support the Serbs, although they were too late to prevent their defeat. In August 1916, Bulgarian troops advanced into Greek-held Macedonia and Constantine ordered the army not to resist; anger at this led to a coup and he was eventually forced into exile in June 1917. A new national government under Venizelos joined the Entente, while the Greek National Defence Army Corps fought with the Allies on the Macedonian front.
 Unlike Serbia, with whom it shared close cultural and political connections, the Kingdom of Montenegro gained little from its participation in the 1912–1913 Balkan Wars. The main Montenegrin offensive was in Albanian Vilayet, Ottoman-controlled Albania, where it suffered heavy losses during the seven month Siege of Scutari (1912–13), Siege of Scutari. Austria-Hungary opposed Serb or Montenegrin control of Albania, since it provided access to the Adriatic Sea; despite Scutari's surrender, Montenegro was forced to relinquish it by the Treaty of London (1913), 1913 Treaty of London and it became capital of the short-lived Principality of Albania. This was largely an Austrian creation; the new ruler, William, Prince of Albania, was a German who was forced into exile in September, only seven months after taking up his new position and later served with the Imperial German Army.
Unlike Serbia, with whom it shared close cultural and political connections, the Kingdom of Montenegro gained little from its participation in the 1912–1913 Balkan Wars. The main Montenegrin offensive was in Albanian Vilayet, Ottoman-controlled Albania, where it suffered heavy losses during the seven month Siege of Scutari (1912–13), Siege of Scutari. Austria-Hungary opposed Serb or Montenegrin control of Albania, since it provided access to the Adriatic Sea; despite Scutari's surrender, Montenegro was forced to relinquish it by the Treaty of London (1913), 1913 Treaty of London and it became capital of the short-lived Principality of Albania. This was largely an Austrian creation; the new ruler, William, Prince of Albania, was a German who was forced into exile in September, only seven months after taking up his new position and later served with the Imperial German Army.
 In addition to the lack of substantive gains from the Balkan Wars, there were long-running internal divisions between those who like Nicholas I of Montenegro, Nicholas I preferred an independent Montenegro and those who advocated union with Serbia. In July 1914, Montenegro was not only militarily and economically exhausted, but also faced a multitude of political, economic and social issues.
At meetings held in March 1914, Austria-Hungary and Germany agreed union with Serbia must be prevented; Montenegro could either remain independent or be divided, its coastal areas becoming part of Albania, while the rest could join Serbia.
Nicholas seriously considered neutrality as a way to preserve his dynasty and on 31 July notified the Russian Ambassador Montenegro would only respond to an Austrian attack. He also held discussions with Austria, proposing neutrality or even active support in return for territorial concessions in Albania.
However, close links between the Serbian and Montenegrin militaries as well as popular sentiment meant there was little support for remaining neutral, especially after Russia joined the war; on 1 August, the National Assembly declared war on Austria-Hungary in fulfilment of its obligations to Serbia. After some initial success, in January 1916, the Montenegrin Army was forced to surrender to an Austro-Hungarian force.
In addition to the lack of substantive gains from the Balkan Wars, there were long-running internal divisions between those who like Nicholas I of Montenegro, Nicholas I preferred an independent Montenegro and those who advocated union with Serbia. In July 1914, Montenegro was not only militarily and economically exhausted, but also faced a multitude of political, economic and social issues.
At meetings held in March 1914, Austria-Hungary and Germany agreed union with Serbia must be prevented; Montenegro could either remain independent or be divided, its coastal areas becoming part of Albania, while the rest could join Serbia.
Nicholas seriously considered neutrality as a way to preserve his dynasty and on 31 July notified the Russian Ambassador Montenegro would only respond to an Austrian attack. He also held discussions with Austria, proposing neutrality or even active support in return for territorial concessions in Albania.
However, close links between the Serbian and Montenegrin militaries as well as popular sentiment meant there was little support for remaining neutral, especially after Russia joined the war; on 1 August, the National Assembly declared war on Austria-Hungary in fulfilment of its obligations to Serbia. After some initial success, in January 1916, the Montenegrin Army was forced to surrender to an Austro-Hungarian force.

 Equal status with the main Entente Powers was one of the primary conditions for Romania's entry into the War. The Powers officially recognised this status through the Treaty of Bucharest (1916), 1916 Treaty of Bucharest. Romania fought on three of the four European Fronts: Eastern Front (World War I), Eastern, Balkans Campaign (World War I), Balkan and Italian Front (World War I), Italian, fielding in total over 1,200,000 troops.
Romanian military industry was mainly focused on converting various fortification guns into field and anti-aircraft artillery. Up to 334 German 53 mm Fahrpanzer guns, 93 French 57 mm Hotchkiss guns, 66 Krupp 150 mm guns, and dozens more 210 mm guns were mounted on Romanian-built Gun carriage, carriages and transformed into mobile field artillery, with 45 Krupp 75 mm guns and 132 Hotchkiss 57 mm guns being transformed into anti-aircraft artillery. The Romanians also 10.5 cm Feldhaubitze M.12, upgraded 120 German Krupp 105 mm howitzers, the result being the most effective field howitzer in Europe at that time. Romania even managed to design and build from scratch its own model of mortar, the 250 mm Negrei Model 1916.
Other Romanian technological assets include the building of A Vlaicu III, Vlaicu III, the world's first aircraft made of metal. The Romanian Navy possessed the largest warships on the Danube. They were a class of four river monitors, built locally at the Galați shipyard using parts manufactured in Austria-Hungary. The first one launched was ''Lascăr Catargiu'', in 1907. The Romanian monitors displaced almost 700 tons, were armed with three 120 mm naval guns in three turrets, two 120 mm naval howitzers, four 47 mm anti-aircraft guns and two 6.5 machine guns. The monitors took part in the Battle of Turtucaia and the First Battle of Cobadin. The Romanian-designed Schneider 150 mm Model 1912 howitzer was considered one of the most modern field guns on the Western Front.
Romania's entry into the War in August 1916 provoked major changes for the Germans. General Erich von Falkenhayn was dismissed and sent to command the Central Powers forces in Romania, which enabled Paul von Hindenburg, Hindenburg's subsequent ascension to power. Due to having to fight against all of the Central Powers on the longest front in Europe (1,600 km) and with little foreign help (only 50,000 Russians aided 650,000 Romanians in 1916), Battle of Bucharest, the Romanian capital was conquered that December. Vlaicu III was also captured and shipped to Germany, being last seen in 1942. The Romanian administration established a new capital at Iași and continued to fight on the Allied side in 1917. Despite being relatively short, the Romanian campaign of 1916 provided considerable respite for the Western Allies, as the Germans ceased all their other offensive operations in order to deal with Romania. After suffering a tactical defeat against the Romanians (aided by Russians) in July 1917 at Battle of Mărăști, Mărăști, the Central Powers launched two counterattacks, at Battle of Mărășești, Mărășești and Third Battle of Oituz, Oituz. The German offensive at Mărășești was soundly defeated, with German prisoners later telling their Romanian captors that German casualties were extremely heavy, and that they "had not encountered such stiff resistance since the battles of Somme and Verdun". The Austro-Hungarian offensive at Oituz also failed. On 22 September, the Austro-Hungarian Enns-class river monitor, ''Enns''-class river monitor SMS Inn, SMS ''Inn'' was sunk by a Romanian mine near Brăila. After Russia signed the
Equal status with the main Entente Powers was one of the primary conditions for Romania's entry into the War. The Powers officially recognised this status through the Treaty of Bucharest (1916), 1916 Treaty of Bucharest. Romania fought on three of the four European Fronts: Eastern Front (World War I), Eastern, Balkans Campaign (World War I), Balkan and Italian Front (World War I), Italian, fielding in total over 1,200,000 troops.
Romanian military industry was mainly focused on converting various fortification guns into field and anti-aircraft artillery. Up to 334 German 53 mm Fahrpanzer guns, 93 French 57 mm Hotchkiss guns, 66 Krupp 150 mm guns, and dozens more 210 mm guns were mounted on Romanian-built Gun carriage, carriages and transformed into mobile field artillery, with 45 Krupp 75 mm guns and 132 Hotchkiss 57 mm guns being transformed into anti-aircraft artillery. The Romanians also 10.5 cm Feldhaubitze M.12, upgraded 120 German Krupp 105 mm howitzers, the result being the most effective field howitzer in Europe at that time. Romania even managed to design and build from scratch its own model of mortar, the 250 mm Negrei Model 1916.
Other Romanian technological assets include the building of A Vlaicu III, Vlaicu III, the world's first aircraft made of metal. The Romanian Navy possessed the largest warships on the Danube. They were a class of four river monitors, built locally at the Galați shipyard using parts manufactured in Austria-Hungary. The first one launched was ''Lascăr Catargiu'', in 1907. The Romanian monitors displaced almost 700 tons, were armed with three 120 mm naval guns in three turrets, two 120 mm naval howitzers, four 47 mm anti-aircraft guns and two 6.5 machine guns. The monitors took part in the Battle of Turtucaia and the First Battle of Cobadin. The Romanian-designed Schneider 150 mm Model 1912 howitzer was considered one of the most modern field guns on the Western Front.
Romania's entry into the War in August 1916 provoked major changes for the Germans. General Erich von Falkenhayn was dismissed and sent to command the Central Powers forces in Romania, which enabled Paul von Hindenburg, Hindenburg's subsequent ascension to power. Due to having to fight against all of the Central Powers on the longest front in Europe (1,600 km) and with little foreign help (only 50,000 Russians aided 650,000 Romanians in 1916), Battle of Bucharest, the Romanian capital was conquered that December. Vlaicu III was also captured and shipped to Germany, being last seen in 1942. The Romanian administration established a new capital at Iași and continued to fight on the Allied side in 1917. Despite being relatively short, the Romanian campaign of 1916 provided considerable respite for the Western Allies, as the Germans ceased all their other offensive operations in order to deal with Romania. After suffering a tactical defeat against the Romanians (aided by Russians) in July 1917 at Battle of Mărăști, Mărăști, the Central Powers launched two counterattacks, at Battle of Mărășești, Mărășești and Third Battle of Oituz, Oituz. The German offensive at Mărășești was soundly defeated, with German prisoners later telling their Romanian captors that German casualties were extremely heavy, and that they "had not encountered such stiff resistance since the battles of Somme and Verdun". The Austro-Hungarian offensive at Oituz also failed. On 22 September, the Austro-Hungarian Enns-class river monitor, ''Enns''-class river monitor SMS Inn, SMS ''Inn'' was sunk by a Romanian mine near Brăila. After Russia signed the 
 * Nicholas II of Russia, Nicholas II – Russian Emperor, King of Poland, and Grand Prince of Finland (until 15 March 1917)
* Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolaevich of Russia (1856–1929), Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolaevich – Commander-in-chief (1 August 1914 – 5 September 1916) and viceroy in the Caucasus
* Ivan Goremykin – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (1 August 1914 – 2 February 1916)
* Boris Stürmer – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (2 February 1916 – 23 November 1916)
* Alexander Trepov – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (23 November 1916 – 27 December 1916)
* Nikolai Golitsyn – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (27 December 1916 – 9 January 1917)
* General of the Cavalry Alexander Samsonov – Commander of the Russian Second Army for the invasion of East Prussia (1 August 1914 – 29 August 1914)
* General of the Cavalry Paul von Rennenkampf – Commander of the Russian First Army for the invasion of East Prussia (1 August 1914 – November 1914)
* General of the Artillery (Imperial Russia), General of the Artillery Nikolay Iudovich Ivanov, Nikolay Ivanov – Commander of the Imperial Russian Army, Russian army on the Southwestern Front, (1 August 1914 – March 1916) responsible for much of the action in Galicia (Eastern Europe), Galicia
* Nicholas II of Russia, Nicholas II – Russian Emperor, King of Poland, and Grand Prince of Finland (until 15 March 1917)
* Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolaevich of Russia (1856–1929), Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolaevich – Commander-in-chief (1 August 1914 – 5 September 1916) and viceroy in the Caucasus
* Ivan Goremykin – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (1 August 1914 – 2 February 1916)
* Boris Stürmer – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (2 February 1916 – 23 November 1916)
* Alexander Trepov – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (23 November 1916 – 27 December 1916)
* Nikolai Golitsyn – List of heads of government of Russia, Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (27 December 1916 – 9 January 1917)
* General of the Cavalry Alexander Samsonov – Commander of the Russian Second Army for the invasion of East Prussia (1 August 1914 – 29 August 1914)
* General of the Cavalry Paul von Rennenkampf – Commander of the Russian First Army for the invasion of East Prussia (1 August 1914 – November 1914)
* General of the Artillery (Imperial Russia), General of the Artillery Nikolay Iudovich Ivanov, Nikolay Ivanov – Commander of the Imperial Russian Army, Russian army on the Southwestern Front, (1 August 1914 – March 1916) responsible for much of the action in Galicia (Eastern Europe), Galicia  * Adjutant general, General Adjutant Aleksei Brusilov – Commander of the South-West Front, then provisional Commander-in-Chief after the Tsar's abdication (February 1917 – August 1917)
* General of the Infantry (Imperial Russia), General of the Infantry Lavr Kornilov, Lavr Georgievich Kornilov – Commander of the South-West Front, then Commander-in-Chief (August 1917)
* General of the Infantry (Imperial Russia), General of the Infantry Aleksey Kuropatkin – Commander of the Northern Front (October 1915 – 1917)
* General of the Infantry (Imperial Russia), General of the Infantry Nikolai Yudenich – Commander of the Caucasus (January 1915 – May 1917)
* Admiral Andrei Eberhardt – Commander of Black Sea Fleet (1914–16)
* Admiral Alexander Kolchak – Commander of Black Sea Fleet (1916–17)
* Admiral Nikolai Essen – Commander of Baltic Fleet (1913 – May 1915)
* Adjutant general, General Adjutant Aleksei Brusilov – Commander of the South-West Front, then provisional Commander-in-Chief after the Tsar's abdication (February 1917 – August 1917)
* General of the Infantry (Imperial Russia), General of the Infantry Lavr Kornilov, Lavr Georgievich Kornilov – Commander of the South-West Front, then Commander-in-Chief (August 1917)
* General of the Infantry (Imperial Russia), General of the Infantry Aleksey Kuropatkin – Commander of the Northern Front (October 1915 – 1917)
* General of the Infantry (Imperial Russia), General of the Infantry Nikolai Yudenich – Commander of the Caucasus (January 1915 – May 1917)
* Admiral Andrei Eberhardt – Commander of Black Sea Fleet (1914–16)
* Admiral Alexander Kolchak – Commander of Black Sea Fleet (1916–17)
* Admiral Nikolai Essen – Commander of Baltic Fleet (1913 – May 1915)
 * Constantine I of Greece, Constantine I: King of Greece, he retired from the throne in June 1917, due to Allied pressure, without formally abdicating.
* Alexander of Greece, Alexander: King of Greece, he became King in 1917 after his father and brother retired from the throne
* Eleftherios Venizelos: Prime minister of Greece after 13 June 1917
* Panagiotis Danglis: Greek general of the Hellenic Army
* Constantine I of Greece, Constantine I: King of Greece, he retired from the throne in June 1917, due to Allied pressure, without formally abdicating.
* Alexander of Greece, Alexander: King of Greece, he became King in 1917 after his father and brother retired from the throne
* Eleftherios Venizelos: Prime minister of Greece after 13 June 1917
* Panagiotis Danglis: Greek general of the Hellenic Army
 * Woodrow Wilson – President of the United States/Commander-In-Chief of the US armed forces
* Newton D. Baker – US Secretary of War
* Josephus Daniels – United States Secretary of the Navy
* Major General/General John J. Pershing – Commander of the American Expeditionary Force
* Rear Admiral/Vice Admiral William Sims – Commander of United States Navy, US Naval Forces in European Waters
* Brigadier General Mason Patrick – Commander of the United States Army Air Service
* Woodrow Wilson – President of the United States/Commander-In-Chief of the US armed forces
* Newton D. Baker – US Secretary of War
* Josephus Daniels – United States Secretary of the Navy
* Major General/General John J. Pershing – Commander of the American Expeditionary Force
* Rear Admiral/Vice Admiral William Sims – Commander of United States Navy, US Naval Forces in European Waters
* Brigadier General Mason Patrick – Commander of the United States Army Air Service
 * Vajiravudh, Rama VI – King of Siam
* Field marshal (Thailand), Field Marshal Chao Phraya Bodindechanuchit – List of Defence Ministers of Thailand, Minister of Defence
* Chakrabongse Bhuvanath, Prince Chakrabongse Bhuvanath – Supreme Commander of the Siamese Expeditionary Forces in World War I
* General Phraya Bijai Janriddhi – Commander of the Siamese Expeditionary Forces in the Western Front
* Vajiravudh, Rama VI – King of Siam
* Field marshal (Thailand), Field Marshal Chao Phraya Bodindechanuchit – List of Defence Ministers of Thailand, Minister of Defence
* Chakrabongse Bhuvanath, Prince Chakrabongse Bhuvanath – Supreme Commander of the Siamese Expeditionary Forces in World War I
* General Phraya Bijai Janriddhi – Commander of the Siamese Expeditionary Forces in the Western Front
 * Venceslau Brás – President of Brazil
* Pedro Max Fernando Frontin, Pedro Frontin, Chief of the ''Divisão Naval em Operações de Guerra'' (Naval Division in War Operations)
* José Pessoa Cavalcanti de Albuquerque, Lieutenant of the Brazilian Army in France
* Napoleão Felipe Aché, Chief of Brazilian Military Mission in France (1918–1919)
* Doctor of Medicine, M.D. Nabuco Gouveia – Chief of Brazilian Military Medical Commission
* Venceslau Brás – President of Brazil
* Pedro Max Fernando Frontin, Pedro Frontin, Chief of the ''Divisão Naval em Operações de Guerra'' (Naval Division in War Operations)
* José Pessoa Cavalcanti de Albuquerque, Lieutenant of the Brazilian Army in France
* Napoleão Felipe Aché, Chief of Brazilian Military Mission in France (1918–1919)
* Doctor of Medicine, M.D. Nabuco Gouveia – Chief of Brazilian Military Medical Commission