Alcácer Ceguer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ksar es-Seghir ( ar, القصر الصغير, ⵇⵙⴰⵔ ⵙⵖⵉⵔ, ''al-Qasr as-Seghir''), also known by numerous other spellings and names, is a small town on the
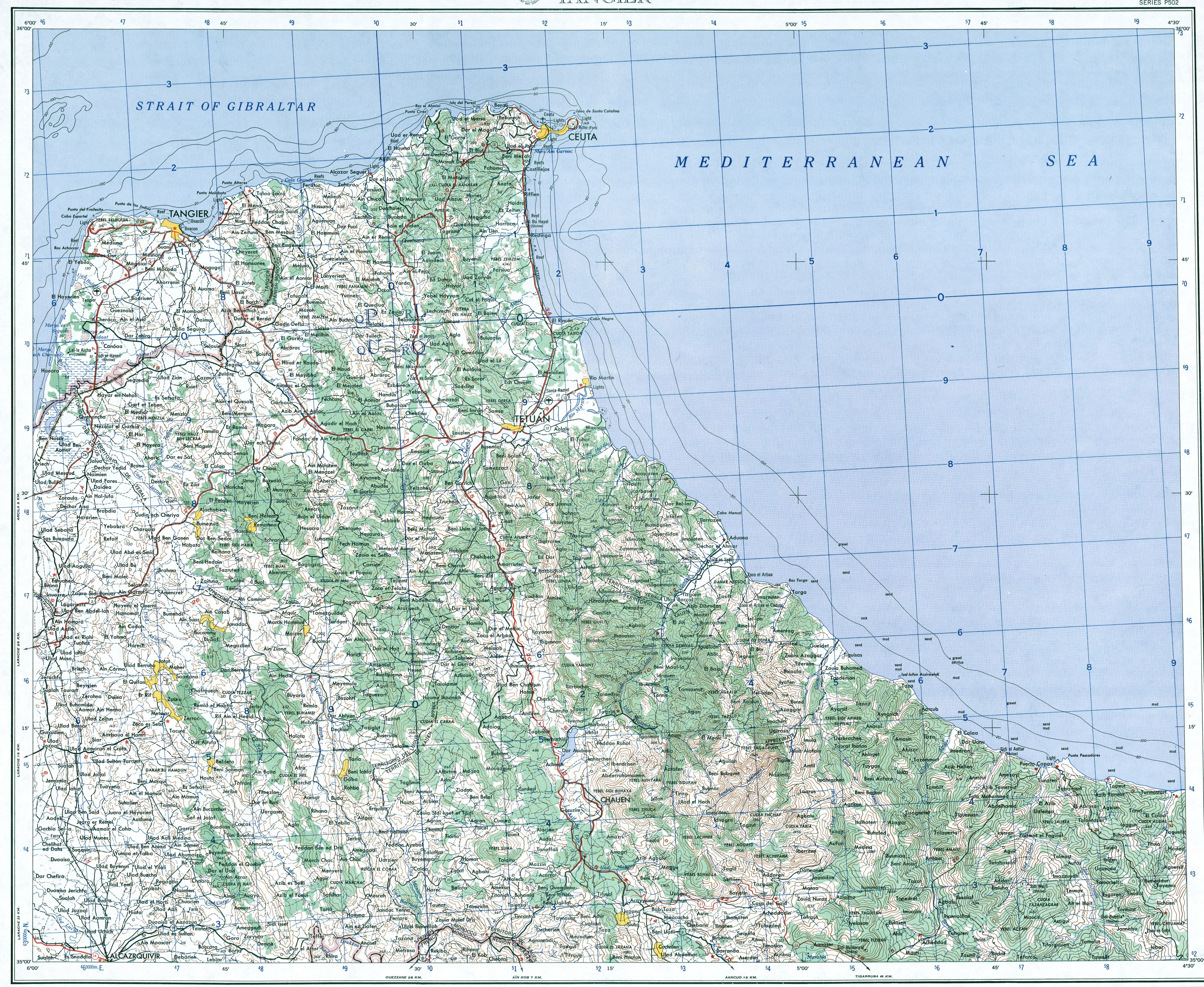 Ksar es-Seghir is located in the Strait of Gibraltar about halfway between
Ksar es-Seghir is located in the Strait of Gibraltar about halfway between
* . * Redman, Charles L. ''Qsar es-Seghir: an archaeological view of medieval life''. London, Academic Press, 1986. {{Authority control Phoenician colonies in Morocco Former Portuguese colonies Ksars Mediterranean port cities and towns in Morocco Populated places in Fahs-Anjra Province Populated places established in the 8th century 700s establishments 1458 establishments in the Portuguese Empire 1549 disestablishments in the Portuguese Empire 8th-century establishments in Africa
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
coast in the Jebala region of northwest Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, between Tangier
Tangier ( ; ; ar, طنجة, Ṭanja) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Moroccan coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel. The town is the capi ...
and Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territorie ...
, on the right bank of the river of the same name. Administratively, it belongs to Fahs-Anjra Province and the region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
of Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima
Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima ( ar, طنجة - تطوان - الحسيمة, ṭanja - tiṭwān - al-ḥusayma; ber, ⵟⴰⵏⵊⴰ ⵜⵉⵟⵡⴰⵏ ⵍⵃⵓⵙⵉⵎⴰ, ṭanja tiṭwan lḥusima) is the northernmost of the twelve regions of ...
. By the census of 2004, it had a population of 10,995 inhabitants.
The city is circular, a design unusual in medieval Moroccan town planning. It is built from brick and ashlar masonry and flanked by semi-circular masonry towers. There are three monumental doors in the wall, each flanked by square towers. The Bāb al-Bahr (door of the sea), has an elbowed entrance for defensive purposes. These doors were used both for communication and trade and for taxation purposes.
Names
TheMoroccan Arabic
Moroccan Arabic ( ar, العربية المغربية الدارجة, translit=al-ʻArabīya al-Maghribīya ad-Dārija ), also known as Darija (), is the dialectal, vernacular form or forms of Arabic spoken in Morocco. It is part of the Maghreb ...
name, meaning "The Small Castle", can be transcribed ''l-Qṣər ṣ-Ṣġir'' or ''Ksar Sghir''. The name distinguishes it from Ksar-el-Kebir
El-Ksar el Kebir (Arabic: القصر الكبير; ber, ⵍⵇⵚⵔ ⵍⴽⴱⵉⵔ, lqṣr lkbir) is a city in northwestern Morocco, about 160 km north of Rabat, 32 km east of Larache and 110 km south of Tangier. It recorded a ...
("The Big Castle"), which is farther south. The Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
name used to translate this as Castillejo but now transliterates it as Alcázar Seguir or '; its Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
equivalent is Alcácer-Ceguer. Under the Almoravid
The Almoravid dynasty ( ar, المرابطون, translit=Al-Murābiṭūn, lit=those from the ribats) was an imperial Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire in the 11th century that ...
s and Almohad
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the unity of God) was a North African Berber Muslim empire fou ...
s, it was known as , , or ("castle en route") because it was an important embarkation port for Moroccan troops on their way to Spain. Other names for the Muslim fortification include the 11th-century geographer al-Bakri
Abū ʿUbayd ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz ibn Muḥammad ibn Ayyūb ibn ʿAmr al-Bakrī ( ar, أبو عبيد عبد الله بن عبد العزيز بن محمد بن أيوب بن عمرو البكري), or simply al-Bakrī (c. 1040–1 ...
's al-Qasr al-Awwal ("The First Castle") and the 13th-century historian Abdelwahid al-Marrakushi
ʿAbd al-Wāḥid ibn ʿAlī al-Tamīmī al-Marrākushī (; born 7 July 1185 in Marrakech, died 1250) was a Moroccan historian who lived during the Almohad period.
Abdelwahid was born in Marrakech in 1185 during the reign of Yaqub al-Mansur, in ...
's ("Masmuda
The Masmuda ( ar, المصمودة, Berber: ⵉⵎⵙⵎⵓⴷⵏ) is a Berber tribal confederation of Morocco and one of the largest in the Maghreb, along with the Zanata and the Sanhaja. They were composed of several sub-tribes: Berghouat ...
Castle"), after the local Berber tribe.
In antiquity, it was known by the names Lissa and Exilissa ( grc-gre, Ἐξίλισσα), which Lipiński
Lipiński (feminine Lipińska, plural Lipińscy) is a Polish surname. Notable persons with the name include:
*Adam Lipiński (born 1956), Polish politician
*Anatoly Ivanovich Lipinsky (born 1959), Russian military leader
*Bill Lipinski (born 1937 ...
conjectures represent the survival of the Phoenician settlement's name ''Ḥiq'' or ''Ḥeq-še-Elišša'' ("Bay of Elissa"). Note, however, that Pliny
Pliny may refer to:
People
* Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE), ancient Roman nobleman, scientist, historian, and author of ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Pliny's Natural History'')
* Pliny the Younger (died 113), ancient Roman statesman, orator, w ...
and Lipiński place the ancient settlement further east, closer to Benzú
Benzú is a small settlement within the Spanish autonomous city of Ceuta. It has a population of 1,987 according to the 2011 census, divided into two units with Ceuta as its municipality.
Description
Benzú is in the northwest of the Spanish ex ...
.. The Byzantine Greek name was ''Exilýssa'' ().
Geography
 Ksar es-Seghir is located in the Strait of Gibraltar about halfway between
Ksar es-Seghir is located in the Strait of Gibraltar about halfway between Tangier
Tangier ( ; ; ar, طنجة, Ṭanja) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Moroccan coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel. The town is the capi ...
and Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territorie ...
. Situated in a bay on a stretch of coast that is relatively difficult to access by sea or land, Ksar es-Seghir never grew in size to rival the other north Moroccan ports. However, its sheltered position made it attractive as a military landing ground, a place for the safe and orderly embarkation and disembarkation of sea-borne troops, with little danger of disruption or molestation by enemy action.
History
Exilissa was probably established as aPhoenician colony
Colonies in antiquity were post-Iron Age city-states founded from a mother-city (its "metropolis"), not from a territory-at-large. Bonds between a colony and its metropolis remained often close, and took specific forms during the period of classic ...
, annexed by the Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
, and then lost to Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
control sometime after the Punic Wars. Under the Romans, it was a salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
ing post. It would've been overrun by the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
in the 5th century and then reconquered by the Byzantines in the 6th. Ksar Mesmouda was established after the Umayyad conquest of the area in 708-709 CE. In 971, the Umayyad Caliph
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
of al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
tried to capture the fort as a stepping stone to a projected conquest of Idrisid Morocco. During the Almoravid
The Almoravid dynasty ( ar, المرابطون, translit=Al-Murābiṭūn, lit=those from the ribats) was an imperial Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire in the 11th century that ...
and Almohad
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the unity of God) was a North African Berber Muslim empire fou ...
eras, it was used as a major shipyard.
In 1287, Marinid
The Marinid Sultanate was a Berber Muslim empire from the mid-13th to the 15th century which controlled present-day Morocco and, intermittently, other parts of North Africa (Algeria and Tunisia) and of the southern Iberian Peninsula (Spain) ar ...
sultan Abu Yaqub Yusuf
Abu Ya`qub Yusuf or Yusuf I ( ''Abū Ya‘qūb Yūsuf''; 1135 – 14 October 1184) was the second Almohad ''Amir'' or caliph. He reigned from 1163 until 1184 in Marrakesh. He was responsible for the construction of the Giralda in Seville, which ...
erected a new set of thick walls around the circular town, with 29 bastions and three monumental gates (Bab al-Bahr, Bab Sebta, Bab Fes). But with the end of Marinid adventures across the sea in Spain, it declined in use. By the 15th century, it had become a notorious corsair's nest, preying on shipping in the Straits of Gibraltar.
In 1458, a Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
expeditionary force of 25,000 men and 200 ships led by King Afonso V of Portugal
Afonso V () (15 January 1432 – 28 August 1481), known by the sobriquet the African (), was King of Portugal from 1438 until his death in 1481, with a brief interruption in 1477. His sobriquet refers to his military conquests in Northern Afri ...
, assaulted and captured the town after a two-day battle on 23–24 October. The Marinid
The Marinid Sultanate was a Berber Muslim empire from the mid-13th to the 15th century which controlled present-day Morocco and, intermittently, other parts of North Africa (Algeria and Tunisia) and of the southern Iberian Peninsula (Spain) ar ...
sultan Abd al-Haqq II of Morocco attempted to recover it immediately, laying sieges in late 1458 and again in the summer of 1459, to no avail. It would remain in Portuguese hands for much of the next century, known by the name of 'Alcácer-Ceguer'. In 1502, the Portuguese began a new set of fortifications that extended the town's walls well into the sea, thereby ensuring a shielded landing ground for Portuguese expeditionary forces in Africa. The resident population of the town under the Portuguese reached around 800 persons.
Finding Portuguese holdings in Morocco expensive to maintain, King John III of Portugal decided to abandon it in 1533, although the final evacuation of Ksar es-Seghir would be delayed until 1549. It was recovered by Morocco thereafter, but the departing Portuguese had taken the trouble to evacuate the population, dismantle much of the fortifications and town, and dump debris and sand into the harbor, diminishing its immediate usefulness. In 1609, Ksar es-Seghir became a destination for Moriscos expelled from Spain.
Having lost its role as a transit port, Ksar es-Seghir collapsed in size and importance thereafter, becoming a relatively insignificant fishing town, amid the ruins of the old Moroccan citadel and Portuguese fort. A more modern town arose later, on the right bank of the river, across from the old citadel. Ksar Sghir got a new lease on life in the 21st century, when it was slated as the site of a new naval base
A naval base, navy base, or military port is a military base, where warships and naval ships are docked when they have no mission at sea or need to restock. Ships may also undergo repairs. Some naval bases are temporary homes to aircraft that u ...
for the Royal Moroccan Navy
ber, ⴰⴷⵡⴰⵙ ⴰⴳⴻⵍⴷⴰⵏ ⵏ ⵢⵉⵍⴻⵍ
, image =
, caption = Royal Moroccan Navy Seal
, start_date = active since: 11th century
current form: 30 Apr ...
(construction begun 2008, operational 2010). In 2007, a new commercial cargo port, Tanger-Med
Tanger Med (in Arabic: طنجة المتوسط ) is a Moroccan industrial port complex, located 45 km northeast of Tanger and opposite of Tarifa, Spain (15 km north) on the Strait of Gibraltar, with handling capacities of 9 million containers, on ...
began being built nearby, around twelve kilometers to the northeast of Ksar Sghir.
See also
*European enclaves in North Africa before 1830
The European enclaves in North Africa (technically ‘ semi-enclaves’) were towns, fortifications and trading posts on the Mediterranean and Atlantic coasts of western North Africa (sometimes called also "Maghreb"), obtained by various European p ...
References
Citations
Bibliography
* Braga, Paulo Drumond. A Expansão no Norte de África. In: ''Nova História da Expansão Portuguesa (dir. de Joel Serrão e A. H. de Oliveira Marques)''. Lisboa: Editorial Estampa, 1998. Vol. II, A Expansão Quatrocentista. pp. 237–360. * Duarte, Luís Miguel. África. In: ''Nova História Militar de Portugal (dir. de Themudo Barata e Nuno Severiano Teixeira)''. Lisboa: Circulo de Leitores, 2003. vol. I, pp. 392–441. * Elbl, Martin Malcolm. "The Master-Builder, the Bureaucrat, and the Practical Soldier: Protecting Alcácer Seguer/Qasr al-Saghir (Morocco) in the Early Sixteenth Century," Portuguese Studies Review 12 (1) (2004/5), pp. 33–73* . * Redman, Charles L. ''Qsar es-Seghir: an archaeological view of medieval life''. London, Academic Press, 1986. {{Authority control Phoenician colonies in Morocco Former Portuguese colonies Ksars Mediterranean port cities and towns in Morocco Populated places in Fahs-Anjra Province Populated places established in the 8th century 700s establishments 1458 establishments in the Portuguese Empire 1549 disestablishments in the Portuguese Empire 8th-century establishments in Africa