Al-Burj, Ramle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Al-Burj ( ar, البرج) was a
 A
A
98
/ref> Just west of Al-Burj is ''Kŭlảt et Tantûrah'', "the castle of the peak." It is the remains of a tower, with 5 meter thick walls, and a door to the east. It is possible the Crusader castle called ''Tharenta'', under Muslim rule since 1187. While nearby


 In 1838 ''el-Burj'' was noted as a Muslim village, in the ''Ibn Humar'' area in the District of Er-Ramleh.Robinson and Smith, 1841, vol 3, Appendix 2, p.
In 1838 ''el-Burj'' was noted as a Muslim village, in the ''Ibn Humar'' area in the District of Er-Ramleh.Robinson and Smith, 1841, vol 3, Appendix 2, p.
121
/ref> It was also noted as a being small, "situated on an isolated hill surrounded by open vallies and plains." It was further noted that "there are here evident traces of an ancient site, apparently once fortified." In 1863
22
/ref> increasing in the 1931 census to 370, still all Muslims, in a total of 92 houses.Mills, 1932, p
19
In the 1945 statistics, the village had a population of 480 Muslims, with a total land area of 4,708 dunams. 6 dunams were either irrigated or used for orchards, 2,631 were used for cereals, while 12 dunams were built-up (urban) areas. An elementary school for boys was completed in 1947 with around 35 pupils.
34
/ref>
al-Burj
IAAWikimedia commons
at
Palestinian Arab
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
village 14 km east of Ramle
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
close to the highway to Ramallah, which was depopulated in 1948. Its name, "the tower", is believed to be derived from the crusader castle, Castle Arnold, built on the site. Victorian visitors in the 19th century recorded seeing crusader ruins close to the village.
History
 A
A Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
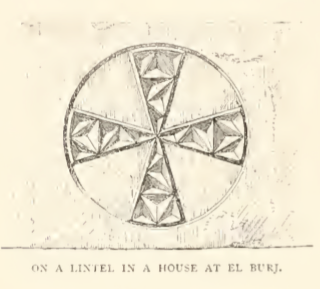
lintel was found in the village in the 1870s, with "a Greek cross inscribed in a circle, and having its four arms ornamented with curious facet-work."Clermont-Ganneau, 1896, ARP II, p98
/ref> Just west of Al-Burj is ''Kŭlảt et Tantûrah'', "the castle of the peak." It is the remains of a tower, with 5 meter thick walls, and a door to the east. It is possible the Crusader castle called ''Tharenta'', under Muslim rule since 1187. While nearby
Bayt Jiz
Bayt Jiz ( ar, بيت جيز) was a Palestinian Arab village situated on undulating land in the western foothills of the Jerusalem heights, southwest of Ramla. In 1945, it had a population of 550. It was occupied by Israeli forces in the 1948 Ar ...
often has been identified as the Crusader village of ''Gith'', some scholars (Schmitt, 1980; Fischer, Isaac and Roll, 1996) have suggested that ''Gith'' was actually at ''Kŭlảt et Tantûrah''.
Ottoman era


 In 1838 ''el-Burj'' was noted as a Muslim village, in the ''Ibn Humar'' area in the District of Er-Ramleh.Robinson and Smith, 1841, vol 3, Appendix 2, p.
In 1838 ''el-Burj'' was noted as a Muslim village, in the ''Ibn Humar'' area in the District of Er-Ramleh.Robinson and Smith, 1841, vol 3, Appendix 2, p.121
/ref> It was also noted as a being small, "situated on an isolated hill surrounded by open vallies and plains." It was further noted that "there are here evident traces of an ancient site, apparently once fortified." In 1863
Victor Guérin
Victor Guérin (15 September 1821 – 21 Septembe 1890) was a French intellectual, explorer and amateur archaeologist. He published books describing the geography, archeology and history of the areas he explored, which included Greece, Asia Min ...
found the village to have no more than 200 inhabitants, and noted that the Crusader fortress was in ruins.
An Ottoman village list from about 1870 showed that Al-Burj had a population of 139 in a total of 31 houses, though that population count included men, only. It was further noted that it was located one hour from Beit Ur al-Tahta.
In 1873-74 Clermont-Ganneau
Charles Simon Clermont-Ganneau (19 February 1846 – 15 February 1923) was a noted French Orientalist and archaeologist.
Biography
Clermont-Ganneau was born in Paris, the son of Simon Ganneau, a sculptor and mystic who died in 1851 when Cler ...
noted that the village was closely connected with Bir Ma'in.
In 1883, the PEF's ''Survey of Western Palestine
The PEF Survey of Palestine was a series of surveys carried out by the Palestine Exploration Fund (PEF) between 1872 and 1877 for the Survey of Western Palestine and in 1880 for the Survey of Eastern Palestine. The survey was carried out after the ...
'' (SWP) described Al-Burj as "a small village on a hill-top, with open ground beneath on all sides. There are remains of a Crusading fortress (Kulat et Tanturah), and the position is a strong one, near the main road to Lydda. It is possible that this is the site of the Castellum Arnoldi, near Beit Nuba, 'in primes auspices campestrum,' built in 1131 A.D. by the Patriarch of Jerusalem, to protect the approach to that city (William of Tyre
William of Tyre ( la, Willelmus Tyrensis; 113029 September 1186) was a medieval prelate and chronicler. As archbishop of Tyre, he is sometimes known as William II to distinguish him from his predecessor, William I, the Englishman, a former ...
)."
British Mandate era
In the 1922 census of Palestine conducted by the British Mandate authorities, Al Burj had a population of 344; all Muslims,Barron, 1923, Table VII, Sub-district of Ramleh, p22
/ref> increasing in the 1931 census to 370, still all Muslims, in a total of 92 houses.Mills, 1932, p
19
In the 1945 statistics, the village had a population of 480 Muslims, with a total land area of 4,708 dunams. 6 dunams were either irrigated or used for orchards, 2,631 were used for cereals, while 12 dunams were built-up (urban) areas. An elementary school for boys was completed in 1947 with around 35 pupils.
1948, aftermath
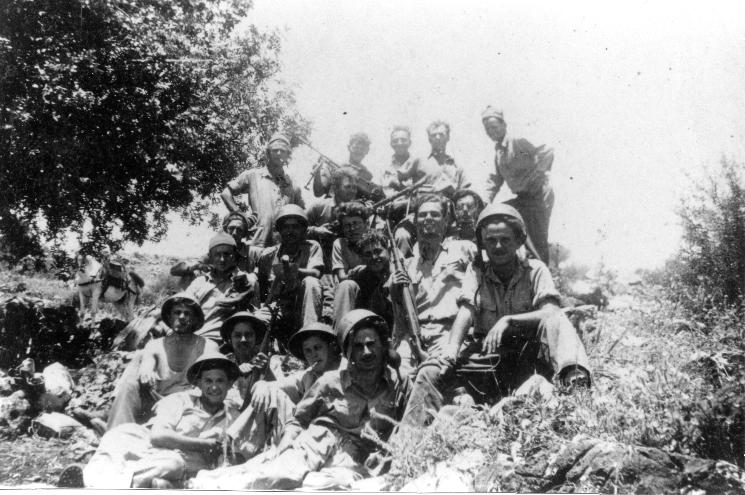
Al-Burj was occupied by the Israeli Army on July 15, 1948, during the second phase ofOperation Dani
Operation Danny ( he, מבצע דני, ''Mivtza Dani'') was an Israeli military offensive launched at the end of the first truce of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. The objectives were to capture territory east of Tel Aviv and then to push inland and ...
. The Arab Legion
The Arab Legion () was the police force, then regular army of the Emirate of Transjordan, a British protectorate, in the early part of the 20th century, and then of independent Jordan, with a final Arabization of its command taking place in 1 ...
counterattacked the following day with two infantry platoons and ten armoured cars but were forced to retreat. According to the Haganah 30 Arabs were killed and four armoured vehicles captured with 3 Israelis killed. Aref al-Aref
Aref al-Aref ( ar, عارف العارف, 1892–1973), variously spelled as Arif el Arif, 'Arif el-'Arif, etc., was a Palestinian journalist, historian and politician. He served as mayor of East Jerusalem in the 1950s during the Jordanian annex ...
records around 13 Legionaires killed.
Two elderly women and men remained. On the 23 July, one, a military cook, was sent out to pick vegetables. In his absence the other three were led to a house which, when an antitank shell missed, was blown up with six grenades. Two died: the surviving woman was then executed, and their bodies torched. The cook, on returning, didn't believe the story that they had been sent to a hospital in Ramallah, and some time later was executed with four bullets.
In 1992 the village site was described: "Only one crumbled house remains on the hilltop. Cactuses and wild plants grow on the site. The nearby settlements uses the village for hothouse agriculture."
In 2002 a woman, Kawthar al-Amir, published a 64 page long book about Al-Burj. According to Rochelle Davis, the book is "innovatively styled for children, the descendants of the village who do not know about the village," and it is a "question and answer format, as a conversation between her and her granddaughter Bahiyya."Davis, 2011, p34
/ref>
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Zochrot
Zochrot ( he, זוכרות; "Remembering"; ar, ذاكرات; "Memories") is an Israeli nonprofit organization founded in 2002. Based in Tel Aviv, its aim is to promote awareness of the Palestinian ''Nakba'' ("Catastrophe"), including the 1948 Pa ...
*Survey of Western Palestine, Map 17: IAA
at
Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center
Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center () is a leading Palestinian arts and culture organization that aims to create a pluralistic, critical liberating culture through research, query, and participation, and that provides an open space for the community ...
{{Palestinian Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Palestine War
Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
District of Ramla