Akrotiri and Dhekelia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Akrotiri and Dhekelia, officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA),, ''Periochés Kyríarchon Váseon Akrotiríou ke Dekélias'';
tr, Ağrotur ve Dikelya İngiliz Egemen Üs Bölgeleri is a
 The Sovereign Base Areas were created in 1960 by the
The Sovereign Base Areas were created in 1960 by the  In July and August 1961, there were a series of bomb attacks against the pipeline carrying fresh water to the Dhekelia Sovereign Base Area. The pipeline was breached by explosions twelve times.
In the early 1970s the U.S. built an
In July and August 1961, there were a series of bomb attacks against the pipeline carrying fresh water to the Dhekelia Sovereign Base Area. The pipeline was breached by explosions twelve times.
In the early 1970s the U.S. built an
 The SBAs were retained in 1960 to keep military bases in areas under British sovereignty, along with the rights retained to use other sites in what became the territory of the Republic. That makes them different from the other remaining
The SBAs were retained in 1960 to keep military bases in areas under British sovereignty, along with the rights retained to use other sites in what became the territory of the Republic. That makes them different from the other remaining
1960, p.111-112, p.116 According to the British Ministry of Defence: The territory is administered by an

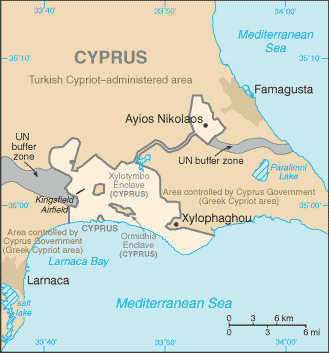 Akrotiri and Dhekelia cover 3% of the land area of Cyprus, a total of (split (48.5%) at Akrotiri and (51.5%) at Dhekelia). 60% of the land is privately owned as freeholds by Cypriot citizens; the other 40% is controlled by the Ministry of Defence as
Akrotiri and Dhekelia cover 3% of the land area of Cyprus, a total of (split (48.5%) at Akrotiri and (51.5%) at Dhekelia). 60% of the land is privately owned as freeholds by Cypriot citizens; the other 40% is controlled by the Ministry of Defence as
 Cyprus is an important migration flyway for birds between Africa and Europe and millions of birds are killed yearly as they migrate over the island. To protect resident and migratory birds,
Cyprus is an important migration flyway for birds between Africa and Europe and millions of birds are killed yearly as they migrate over the island. To protect resident and migratory birds,
 No economic statistics are gathered for Akrotiri and Dhekelia. The main economic activities are the provision of services to the military, as well as limited agriculture. When the territory under the effective control of the Republic of Cyprus switched currencies from the
No economic statistics are gathered for Akrotiri and Dhekelia. The main economic activities are the provision of services to the military, as well as limited agriculture. When the territory under the effective control of the Republic of Cyprus switched currencies from the 

Screens go blank as BFBS TV switches off transmitters.
'' The
Sovereign Base Areas Administration web-pages
BBC News – "UK offers to cede Cyprus land"
BBC News – "Cyprus protesters clash at UK base"
Cyprus Mail, Nathan Morley – "Mystery of Dhekelia Cemetery"
Cyprus Mail, Nathan Morley – "Dhekelia at 60"
Akrotiri
''
Dhekelia
''
The Princess Mary's Hospital RAF Akrotiri
Cyprus Independence Agreement – Hansard Official UK Parliament Record
* James Rogers and Luis Simón
The Status and Location of the Military Installations of the Member States of the European Union and Their Potential Role for the European Security and Defence Policy (ESDP).
Brussels: European Parliament, 2009. 25 pp. {{DEFAULTSORT:Akrotiri And Dhekelia Geography of Cyprus Cyprus and the Commonwealth of Nations English-speaking countries and territories 1960 establishments in the British Empire British Army deployments British military in Cyprus .Akrotiri and Dhekelia Dependent territories in Europe Royal Air Force deployments Sovereign Base Areas States and territories established in 1960 1960 establishments in Europe Military of Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia Enclaves and exclaves
tr, Ağrotur ve Dikelya İngiliz Egemen Üs Bölgeleri is a
British Overseas Territory
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remnants of the former Br ...
on the island of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
. The areas, which include British military bases and installations, as well as other land, were retained by the British under the 1960 treaty of independence, signed by the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
and representatives from the Greek and Turkish Cypriot communities, which granted independence to the (then) Crown colony of Cyprus. The territory serves an important role as a station for signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of '' signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ...
and provides a vital strategic part of the United Kingdom surveillance-gathering network in the Mediterranean and the Middle East.
History
 The Sovereign Base Areas were created in 1960 by the
The Sovereign Base Areas were created in 1960 by the London and Zürich Agreements
The London and Zürich Agreements ( el, Συμφωνίες Ζυρίχης–Λονδίνου; tr, Zürih ve Londra Antlaşmaları) for the constitution of Cyprus started with an agreement on 19 February 1959 in Lancaster House, London, between T ...
, when Cyprus achieved independence from the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, as recorded by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
in 1960 as treaty 5476. The United Kingdom desired to retain sovereignty over these areas, as this guaranteed the use of UK military bases on Cyprus, including RAF Akrotiri
RAF Akrotiri ( el, Βασιλική Πολεμική Αεροπορία Ακρωτηρίου) is a large Royal Air Force base on the Mediterranean island of Cyprus. It is located in the Western Sovereign Base Area, one of two areas which compri ...
, and a garrison of the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkha ...
. The importance of the bases to the British is based on the strategic location of the island, at the eastern edge of the Mediterranean, close to the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popula ...
and the Middle East; the ability to use the RAF base as staging post for military aircraft; and for training.
 In July and August 1961, there were a series of bomb attacks against the pipeline carrying fresh water to the Dhekelia Sovereign Base Area. The pipeline was breached by explosions twelve times.
In the early 1970s the U.S. built an
In July and August 1961, there were a series of bomb attacks against the pipeline carrying fresh water to the Dhekelia Sovereign Base Area. The pipeline was breached by explosions twelve times.
In the early 1970s the U.S. built an over-the-horizon radar
Over-the-horizon radar (OTH), sometimes called beyond the horizon radar (BTH), is a type of radar system with the ability to detect targets at very long ranges, typically hundreds to thousands of kilometres, beyond the radar horizon, which is ...
named Cobra Shoe, which could observe airplane operations and missile tests in southern Russia. This was operated by the RAF on behalf of the USAF
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
. This augmented an earlier British system built in the early 1960s named Project Sandra. The U.S. use of the base was hidden from the Cypriot government due to their sensitivities and an arguable breach of the limitations in the treaty establishing the bases.
In 1974, following a military coup by the Cypriot National Guard
, name2 = National Guard General Staff
, image = Emblem of the Cypriot National Guard.svg
, image_size = 100px
, caption = Emblem of the National Guard of Cyprus
, image2 = Flag of the ...
attempting to achieve ''enosis
''Enosis'' ( el, Ένωσις, , "union") is the movement of various Greek communities that live outside Greece for incorporation of the regions that they inhabit into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea, an irredentist conc ...
'' (union with Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
), Turkey invaded the north of Cyprus, leading to the establishment of the internationally unrecognised Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Reco ...
. This did not affect the status of the bases. Greek Cypriots
Greek Cypriots or Cypriot Greeks ( el, Ελληνοκύπριοι, Ellinokýprioi, tr, Kıbrıs Rumları) are the ethnic Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2011 census, 659,115 ...
fleeing from the Turkish forces were permitted to travel through the Dhekelia Sovereign Base Area and were given humanitarian aid, with those from Achna setting up a new village (Dasaki Achnas or Achna Forest) which is still in the Dhekelia Sovereign Base Area. The Turkish advance halted when it reached the edge of the Dhekelia Sovereign Base Area to avoid military conflict with the United Kingdom. In the Akrotiri Sovereign Base Area a tented refugee camp was set up at "Happy Valley" (part of the Episkopi Cantonment) to house Turkish Cypriots fleeing from Limassol and the villages surrounding the Area, until in 1975 they were flown out of RAF Akrotiri via Turkey to northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a '' de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Rec ...
. Some Greek Cypriot refugees remain housed on land in the parts of Trachoni
Trachoni ( el, Τραχώνι or tr, Trahon) is a large village lying partly in the Limassol District of Cyprus, and partly in the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia. , it had a population of 3,952. Prior to 1974, Trachoni was ...
and Kolossi
Kolossi ( el, Κολόσσι []) is a village on the outskirts of Limassol, Cyprus. It lies partly in the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia. Its population in 2011 was 5,651.
Kolossi is known for its Kolossi Castle, medieval castle.
...
villages that fall within the Akrotiri Sovereign Base Area.
In 1974, the British government decided that British forces would be entirely withdrawn from Cyprus, because the sprawling bases had become undefendable in the light of increasing troop demands in Northern Ireland, and because of pressure on the defence budget. The U.S. had lost access to its many signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of '' signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ...
bases in Turkey due to its political dispute with Turkey following the invasion of Cyprus, and it very strongly objected to any British withdrawal that would result in the United States losing access to GCHQ
Government Communications Headquarters, commonly known as GCHQ, is an intelligence and security organisation responsible for providing signals intelligence (SIGINT) and information assurance (IA) to the government and armed forces of the Uni ...
signals intelligence from Cyprus. The U.S. agreed to contribute to base costs, and the British cancelled the closure plan. U.S. use of the base increased, such as Lockheed U-2
The Lockheed U-2, nicknamed "''Dragon Lady''", is an American single- jet engine, high altitude reconnaissance aircraft operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) and previously flown by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). It provides d ...
spy flights on Syria, though flights were generally at night "to avoid local curiosity".
Politics
Current status
The territory is composed of two base areas. One is Akrotiri ( el, Ακρωτήρι ; tr, Ağrotur ), or the Western Sovereign Base Area (WSBA), which includes two main bases atRAF Akrotiri
RAF Akrotiri ( el, Βασιλική Πολεμική Αεροπορία Ακρωτηρίου) is a large Royal Air Force base on the Mediterranean island of Cyprus. It is located in the Western Sovereign Base Area, one of two areas which compri ...
and Episkopi Cantonment, plus all of Akrotiri Village's district (including Limassol Salt Lake) and parts of eleven other village districts. The other area is Dhekelia Cantonment
Dhekelia Cantonment ( el, Φρουρά Δεκέλεια, tr, Dikelya Cantonment) is a military base in Akrotiri and Dhekelia, a British Overseas Territory on the island of Cyprus, administered as the Sovereign Base Areas. It is located in the E ...
( ; ), or the Eastern Sovereign Base Area (ESBA), which includes a base at Ayios Nikolaos plus parts of twelve village districts.
As of 2022, based units include:
* RAF Akrotiri and Episkopi Cantonment:
** No. 903 Expeditionary Air Wing RAF
** No. 84 Squadron RAF
No. 84 Squadron of the Royal Air Force is at present a Search and Rescue Squadron based at RAF Akrotiri, using the Bell Griffin HAR.2 helicopter. It is currently one of the two operational parts of the RAF Search and Rescue Force left in ser ...
** 2nd Battalion, The Yorkshire Regiment
* Dhekelia Cantonment:
** 1st Battalion, Princess of Wales’ Royal Regiment
Ayios Nikolaos Station
Ayios Nikolaos Station (also spelled ''Agios Nikolaos''; el, Άγιος Νικόλαος, lit. "Saint Nicholas") is a British military station and part of in the British Sovereign Base Area of Dhekelia in Cyprus. It is a former village (Ayios ...
, in the ESBA, is an ELINT
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of '' signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ...
(electronic intelligence) listening station of the UKUSA Agreement
The United Kingdom – United States of America Agreement (UKUSA, ) is a multilateral agreement for cooperation in signals intelligence between Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The alliance of intellig ...
intelligence network. The UKUSA signals intelligence system is sometimes known as "ECHELON
ECHELON, originally a secret government code name, is a surveillance program (signals intelligence/SIGINT collection and analysis network) operated by the five signatory states to the UKUSA Security Agreement:Given the 5 dialects that use ...
".
Governance
British Overseas Territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remnants of the former Bri ...
.
The basic philosophy of their administration was declared by the British government in Appendix O to the 1960 treaty with Cyprus, which provided that the British government intended:
*Not to develop the Sovereign Base Areas for other than military purposes.
*Not to set up and administer "colonies".
*Not to create customs posts or other frontier barriers between the Sovereign Base Areas and the Republic.
*Not to set up or permit the establishment of civilian commercial or industrial enterprises except insofar as these are connected with military requirements, and not otherwise to impair the economic, commercial or industrial unity and life of the Island.
*Not to establish commercial or civilian seaports or airports.
*Not to allow new settlement of people in the Sovereign Base Areas other than for temporary purposes.
*Not to expropriate private property within the Sovereign Base Areas except for military purposes on payment of fair compensation.
Appendix O also provides that various ancient monuments in the SBAs (in particular the site and remains of Kourion
Kourion ( grc, Koύριov; la, Curium) was an important ancient Greek city-state on the southwestern coast of Cyprus. In the twelfth century BCE, after the collapse of the Mycenaean palaces, Greek settlers from Argos arrived on this site.
I ...
, the Sanctuary of Apollo Hylates near Kourion, the Stadium of Curium and the Church and remains of the Holy Monastery of St Nicholas of the Cats) should be administered by the Republic of Cyprus. The Cypriot government issues licences for antiquity excavation in the SBAs subject to British consent, and any movable antiquities found in excavations or otherwise discovered become Cypriot state property.Treaty of Establishment1960, p.111-112, p.116 According to the British Ministry of Defence: The territory is administered by an
Administrator
Administrator or admin may refer to:
Job roles Computing and internet
* Database administrator, a person who is responsible for the environmental aspects of a database
* Forum administrator, one who oversees discussions on an Internet forum
* N ...
, who is also the Commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain. ...
of British Forces Cyprus
British Forces Cyprus (BFC) is the name given to the British Armed Forces stationed in the UK Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia on the island of Cyprus and at a number of related 'retained sites' in the Republic of Cyprus. The United ...
, which is Air vice-marshal
Air vice-marshal (AVM) is a two-star air officer rank which originated in and continues to be used by the Royal Air Force. The rank is also used by the air forces of many countries which have historical British influence and it is sometimes ...
Peter J. M. Squires
Air Vice-Marshal Peter James Murray Squires, is a senior Royal Air Force officer, who currently serves as the Commander of British Forces Cyprus. From August 2016 to October 2019 he served as Commandant of RAF College Cranwell. He was formerly a ...
. The Administrator is officially appointed by the British monarch
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiw ...
on the advice of the Ministry of Defence. The Administrator has all the executive and legislative authority of a governor of an overseas territory. A Chief Officer is appointed, and is responsible to the Administrator for the day-to-day running of the civil government, with subordinate Area Officers responsible for the civil administration of the two areas. No elections are held in the territory, although British citizens are normally entitled to vote in United Kingdom elections (as British Forces or overseas electors).
The areas have their own legal system, distinct from the United Kingdom and the Republic of Cyprus. This consists of the laws of the Colony of Cyprus as of August 1960, amended as necessary. The laws of Akrotiri and Dhekelia are closely aligned with, and in some cases identical to, the laws operating within the Republic of Cyprus. The Court of the Sovereign Base Areas is concerned with non-military offences committed by any person within Akrotiri and Dhekelia, and law and order is maintained by the Sovereign Base Areas Police
The Sovereign Base Areas Police is the local civilian police force for the British controlled Sovereign Base Areas (SBA) of Akrotiri and Dhekelia in Cyprus.
Duties
Established in August 1960, the force has responsibility for all 15,000 residen ...
, while offences involving British Forces Cyprus and military law are dealt with by the Cyprus Joint Police Unit. Fire and rescue services are provided by the Defence Fire and Risk Management Organisation through stations at Episkopi, Akrotiri, Dhekelia and Ayios Nikolayos. The Defence Medical Services provide emergency ambulance cover based from medical centres in the main bases. All emergency services are accessible from any telephone using the Europe-wide emergency number 112.
Reviews
In January 2010, a newspaper article appeared in the British press claiming that as a result of budgetary constraints arising from theGreat Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At ...
, the British Ministry of Defence
The Ministry of Defence (MOD or MoD) is the department responsible for implementing the defence policy set by His Majesty's Government, and is the headquarters of the British Armed Forces.
The MOD states that its principal objectives are to d ...
drew up controversial plans to withdraw the United Kingdom's 3,000 strong garrison and end the use of Cyprus as a staging point for ground forces. The Labour government, under whom the proposal appeared, was replaced by the Cameron–Clegg coalition
The Cameron–Clegg coalition was formed by David Cameron and Nick Clegg when Cameron was invited by Queen Elizabeth II to form a new administration, following the resignation of Prime Minister Gordon Brown on 11 May 2010, after the gene ...
whose defence review did not mention the issue.
On 15 December 2012 in a written statement to the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
, the UK's Secretary of State for Defence
The secretary of state for defence, also referred to as the defence secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with overall responsibility for the business of the Ministry of Defence. The incumbent is a membe ...
, Philip Hammond
Philip Hammond, Baron Hammond of Runnymede (born 4 December 1955) is a British politician and life peer who served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 2016 to 2019, Foreign Secretary from 2014 to 2016, and Defence Secretary from 2011 to 2014. ...
, revealed the findings of a report on the SBA military bases following the completion of a review of their operations by Lord Ashcroft:
Dispute and controversies
TheRepublic of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
claims that the Sovereign Base Areas are a "remnant of colonialism". On 30 June 2005 the House of Representatives of Cyprus
The House of Representatives ( el, Βουλή των Αντιπροσώπων ; tr, Temsilciler Meclisi) is the national unicameral legislature of the Republic of Cyprus. Members and three observers representing Armenian, Latin, and Maronite Cy ...
unanimously adopted a resolution on the legal status of the base areas originally proposed by Vassos Lyssarides. The resolution refers to "relevant UN decisions on the abolition of colonialism, as well as the fundamental principles of international law, which forbid the occupation of territory within the domain of any other country." It claims that "the United Kingdom does not have substantial sovereignty over the British bases, but it has as much sovereignty as is necessary for military reasons and not for administrative, financial and / or any other reasons." The resolution urged the UK government "to fulfil its financial obligations towards the Republic of Cyprus, which derive from the Treaty of Establishment." It also argued that the UK does not have territorial waters in the areas.
The UK government does not recognise Cypriot claims that the UK's sovereignty in the areas is limited.
In July 2001, protests were held at the bases by local Cypriots, unhappy with British plans to construct radio masts
Radio masts and towers are typically tall structures designed to support antennas for telecommunications and broadcasting, including television. There are two main types: guyed and self-supporting structures. They are among the tallest human-mad ...
at the bases as part of an upgrade of British military communication posts around the world. Locals claimed the masts would endanger local lives and cause cancer, as well as have a negative impact on wildlife in the area. The British and Cypriot governments jointly commissioned health research from the University of Bristol
, mottoeng = earningpromotes one's innate power (from Horace, ''Ode 4.4'')
, established = 1595 – Merchant Venturers School1876 – University College, Bristol1909 – received royal charter
, type ...
and the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Cyprus, and that research project reported in 2005 that there was no evidence of health problems being caused by electromagnetic fields from the antennas. The Sovereign Base Areas Administration has carried out assessments and surveys into the effects on wildlife, which have fed into an "Akrotiri Peninsula Environmental Management Plan", published in September 2012.
In 2004, the UK offered to cede of farmland as part of the rejected Annan Plan for Cyprus.
On 29 August 2013, during the Syrian civil war, some Cypriot and British media sources speculated that long-range ballistic missiles, fired from Syria in retaliation for proposed British involvement in military intervention against the Syrian government of Bashar al-Assad
Bashar Hafez al-Assad, ', Levantine pronunciation: ; (, born 11 September 1965) is a Syrian politician who is the 19th president of Syria, since 17 July 2000. In addition, he is the commander-in-chief of the Syrian Armed Forces and the ...
, could hit Cyprus, and could potentially deliver chemical weapons. In some Cypriot media it was stated that the proposed interdiction of the Syrian civil war, utilising Akrotiri and Dhekelia, could recklessly endanger the Cypriot populations near to those bases. Two days earlier, on 27 August 2013, Cypriot foreign minister Ioannis Kasoulides
Ioannis Kasoulides ( el, Ιωάννης Κασουλίδης; born 10 August 1948 in Nicosia, Cyprus) is a Cypriot politician, party member of DISY and current Minister of Foreign Affairs of Cyprus. He has served in the same position from 1997 ...
had moved to calm Cypriot concerns, saying that the British bases were unlikely to play a major part in any intervention.
Travel documents
There is normally no passport check at the border from Akrotiri or Dhekelia to Cyprus. Possession of a passport, or an EU-compliant national identity card is generally needed in Cyprus. A passport is required to travel betweenCyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
/SBAs and Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a '' de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Rec ...
. Issues concerning the validity of car insurance and customs are specified by SBAs' administration.
Brexit implications
Under Article 2(1) of the Protocol, the SBAs are partially part of theEuropean Union Customs Union
The European Union Customs Union (EUCU), formally known as the Community Customs Union, is a customs union which consists of all the member states of the European Union (EU), Monaco, and the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekel ...
in three domains: VAT, agriculture and fisheries. However, the SBAs are already outside the EU. Therefore, concerns have been raised about the future status of about 15,000 Cypriots ( EU citizens) working in the SBA following the UK's 2020 departure from the EU. Cyprus, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
are the only three EU states that conducted bilateral talks with the UK on the Brexit issue. The talks between the UK and the Republic of Cyprus started in October 2017.
The Brexit withdrawal agreement
The Brexit withdrawal agreement, officially titled Agreement on the withdrawal of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland from the European Union and the European Atomic Energy Community, is a treaty between the European Uni ...
has a protocol on the SBAs, with provisions essentially maintaining their previous status.
Geography

 Akrotiri and Dhekelia cover 3% of the land area of Cyprus, a total of (split (48.5%) at Akrotiri and (51.5%) at Dhekelia). 60% of the land is privately owned as freeholds by Cypriot citizens; the other 40% is controlled by the Ministry of Defence as
Akrotiri and Dhekelia cover 3% of the land area of Cyprus, a total of (split (48.5%) at Akrotiri and (51.5%) at Dhekelia). 60% of the land is privately owned as freeholds by Cypriot citizens; the other 40% is controlled by the Ministry of Defence as The Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has differ ...
leasehold land. In January 2014, an agreement between the Cypriot and UK governments was signed, ensuring that residents and property owners in the British Bases will enjoy equal rights for the development of property. In addition to Akrotiri and Dhekelia, the Treaty of Establishment also provided for the continued use by the British Ministry of Defence and the British Armed Forces of certain facilities within the Republic of Cyprus, known as ''Retained Sites''.
Akrotiri is located in the south of the island, near the city of Limassol
Limassol (; el, Λεμεσός, Lemesós ; tr, Limasol or ) is a city on the southern coast of Cyprus and capital of the district with the same name. Limassol is the second largest urban area in Cyprus after Nicosia, with an urban populatio ...
(or Lemesos). Dhekelia is in the southeast, near Larnaca
Larnaca ( el, Λάρνακα ; tr, Larnaka) is a city on the south east coast of Cyprus and the capital of the district of the same name. It is the third-largest city in the country, after Nicosia and Limassol, with a metro population of ...
. Both areas include military bases, as well as farmland and some residential land. Akrotiri is surrounded by territory controlled by the Republic of Cyprus, but Dhekelia also borders on the United Nations (UN) buffer zone and the area controlled by the Turkish forces.
Ayia Napa
Ayia Napa ( el, Άγια Νάπα tr, Aya Napa, ), officially romanised Agia Napa, is a tourist resort at the far eastern end of the southern coast of Cyprus.
Etymology
The name Ayia Napa is derived from a Venetian-era monastery of the sam ...
lies to the east of Dhekelia. The villages of Xylotympou
Xylotymbou ( el, Ξυλοτύμπου [] or ) is a small town in Larnaca District in south-eastern Cyprus. It is one of the four Cyprus#Exclaves and enclaves, enclaves surrounded by the Eastern Sovereign Base Area of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, a Briti ...
and Ormideia
Ormideia ( el, Ορμήδεια []), sometimes also spelled ''Ormidhia'', is a village in Larnaca District in south-eastern Cyprus. It is one of the four Cyprus#Exclaves and enclaves, exclaves surrounded by the Eastern Sovereign Base Area of Akrot ...
, also in the Republic of Cyprus, are enclaves surrounded by Dhekelia. The Dhekelia Power Station
Dhekelia Power Station is one of three power plants belonging to the Electricity Authority of Cyprus. It is located approximately east of the city of Larnaca and it has a capacity of 460 MW.
History
The original plant was the first of the ...
, divided by a British road into two parts, also belongs to the Republic of Cyprus. The northern part is an enclave, like the two villages, whereas the southern part is located by the sea, and therefore not an enclave, though it has no territorial waters of its own.
Territorial waters of are claimed, and the right according to the laws of the UN to extend the claim of up to is reserved.
Wildlife and ecology
 Cyprus is an important migration flyway for birds between Africa and Europe and millions of birds are killed yearly as they migrate over the island. To protect resident and migratory birds,
Cyprus is an important migration flyway for birds between Africa and Europe and millions of birds are killed yearly as they migrate over the island. To protect resident and migratory birds, BirdLife Cyprus
BirdLife Cyprus (BLC) is an environmental non-governmental organisation dedicated to the conservation of birds and their habitats on the island of Cyprus in the eastern Mediterranean, for which it is the BirdLife International partner organisat ...
and the RSPB
The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) is a charitable organisation registered in England and Wales and in Scotland. It was founded in 1889. It works to promote conservation and protection of birds and the wider environment th ...
survey areas of illegal trapping. More than 150 species of birds, over half of conservation concern, have been trapped in nets, or on limesticks, and it is estimated that organised crime gangs earn over 15 million Euros yearly. The dead birds are sold to provide the main ingredient for ambelopoulia Ambelopoulia is a controversial dish of grilled, fried, pickled or boiled songbirds which is a traditional dish enjoyed by native Cypriots and served in some Cypriot restaurants. It is illegal in Cyprus as it involves trapping wild birds such as b ...
in the Republic of Cyprus; an illegal delicacy served to restaurant diners. The 2015 survey estimated a maximum of mist nets across both the Republic and the British Territories, and more than 5,300 limesticks removed, mainly in the Republic. It is estimated that over 2 million birds were killed in 2015 including over 800,000 on British Territories. Employing measures such as covert camera surveillance (including a drone), exclusion zones and impounding vehicles, trapping activity at Dhekelia fell by 77.5%. In 2016 an estimated 800,000 birds were killed at Dhekelia and in the following year trapping activity fell by 77.5% and bird deaths to an estimated 180,000.
The Episkopi Cliffs Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations.
IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife Inte ...
lies mostly within the western base area, and covers much of the peninsula. It was identified as an IBA in 1989, and became recognised under the Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands. It ...
in 2003. 60% was designated as a Special Protection Area in 2010. Over 300 bird species have been recorded in this area. The wetlands, including the large salt lake, are an important habitat and bird hotspot. These wetlands are an important breeding spot for the ferruginous duck
The ferruginous duck (''Aythya nyroca''), also known as ferruginous pochard, common white-eye or white-eyed pochard, is a medium-sized diving duck from Eurosiberia. The scientific name is derived from Greek '' aithuia'' an unidentified seabir ...
, which has nested there since 2005. Other species that nest in the wetlands include the black-winged stilt
The black-winged stilt (''Himantopus himantopus'') is a widely distributed very long-legged wader in the avocet and stilt family ( Recurvirostridae). The scientific name ''H. himantopus'' is sometimes applied to a single, almost cosmopolitan sp ...
, the Kentish plover
The Kentish plover (''Charadrius alexandrinus'') is a small cosmopolitan shorebird (40-44 g) of the family Charadriidae that breeds on the shores of saline lakes, lagoons, and coasts, populating sand dunes, marshes, semi-arid desert, and tundra.S ...
, the spur-winged lapwing
The spur-winged lapwing or spur-winged plover (''Vanellus spinosus'') is a lapwing species, one of a group of largish waders in the family Charadriidae.
It is one of several species of wader supposed to be the "trochilus" bird said by Herodotus ...
, and the stone-curlew
The stone-curlews, also known as dikkops or thick-knees, consist of 10 species within the family Burhinidae, and are found throughout the tropical and temperate parts of the world, with two or more species occurring in some areas of Africa, Asia, ...
. Black francolin
The black francolin (''Francolinus francolinus'') is a gamebird in the pheasant family Phasianidae of the order Galliformes, gallinaceous birds. It was formerly known as the black partridge. It is the state bird of Haryana state, India (locally ...
s, Cyprus wheatear
The Cyprus wheatear or Cyprus pied wheatear (''Oenanthe cypriaca'') is a small, 14–15 cm long passerine bird that was formerly classed as a member of the thrush family Turdidae, but is now more generally considered to be an Old World fly ...
s, Cyprus warbler
The Cyprus warbler (''Curruca melanothorax'') is a typical warbler which breeds only on Cyprus. This small passerine bird is a short-distance migrant, and winters in Israel, Jordan and Egypt.
Like most ''Curruca'' species, it has distinct ma ...
s, Eleonora's falcon
Eleonora's falcon (''Falco eleonorae'') is a medium-sized falcon. It belongs to the hobby group, a rather close-knit number of similar falcons often considered a subgenus ''Hypotriorchis''. The sooty falcon is sometimes considered its closest re ...
s, peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a cosmopolitan bird of prey (raptor) in the family Falconidae. A large, crow-sized falcon, it has a blue-grey bac ...
s, griffon vulture
The Eurasian griffon vulture (''Gyps fulvus'') is a large Old World vulture in the bird of prey family Accipitridae. It may also be known as the Griffon vulture, though it may be used for the genus as a whole. It is not to be confused with Rü ...
s, European shag
The European shag or common shag (''Gulosus aristotelis'') is a species of cormorant. It is the only member of the monotypic genus ''Gulosus''. It breeds around the rocky coasts of western and southern Europe, southwest Asia and north Africa, mai ...
s, European roller
The European roller (''Coracias garrulus'') is the only member of the roller family of birds to breed in Europe. Its overall range extends into the Middle East, Central Asia and the Maghreb.
The European roller is found in a wide variety of hab ...
s, blue rock thrush
The blue rock thrush (''Monticola solitarius'') is a species of chat. This thrush-like Old World flycatcher was formerly placed in the family Turdidae. It breeds in southern Europe, northwest Africa, and from Central Asia to northern China and ...
s, and wallcreeper
The wallcreeper (''Tichodroma muraria'') is a small passerine bird found throughout the high mountains of the Palearctic from southern Europe to central China. It is the only extant member of both the genus ''Tichodroma'' and the family Tichodr ...
s breed elsewhere in the area, especially around the cliffs.
The beaches in the British Sovereign Base Areas (SBAs) are important nesting sites for the endangered green ''Chelonia mydas'' and loggerhead ''Caretta caretta'' turtles. The SBA Environment Department, assisted by a large volunteer effort, has monitored turtle nesting success on SBA beaches since 1990. Disturbance to nesting turtles is an issue in some areas due to activities such as camping, driving on beaches and illegal fishing
Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing (IUU) is an issue around the world. Fishing industry observers believe IUU occurs in most fisheries, and accounts for up to 30% of total catches in some important fisheries.
Illegal fishing takes p ...
. Sea turtles in Cyprus are protected as priority species under the Protection and Management of Nature and Wildlife Ordinance (implementing the provisions of the Habitats Directive), enacted in 2007.
In December 2015, five Special Areas of Conservation
A Special Area of Conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the ''Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. They are to protect the 220 habitats and ap ...
(SACs) were designated in the Cyprus Sovereign Base Areas. The five SACs designated are Akrotiri, Episkopi, Cape Pyla, Dhekelia and Agios Nikolaos. The designations were made under the Protection and Management of Nature and Wildlife Ordinance and will support the existing network (NATURA 2000
Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respecti ...
) of SACs in Cyprus and across Europe.
Demographics
When the areas were being established, the boundaries were deliberately drawn to avoid centres of population. Approximately 18,195 people live in the areas. About 11,000 native Cypriots work in the areas themselves, or on farmland within the boundaries of the areas. The British military and their families make up the rest of the population. Persons related to the territory may in theory be eligible to claim theBritish Overseas Territories citizen
A British Overseas Territories citizen (BOTC), formerly called British Dependent Territories citizen (BDTC), is a member of a class of British nationality granted to people connected with one or more of the British Overseas Territories (previ ...
ship (BOTC status) through a personal connection to the areas (i.e., birth on the territory before 1983, or born after 1983 to a parent who was born on the territory before 1983). But unlike most other British Overseas Territories, there is no provision in the 2002 amendment of the British Nationality Act 1981
The British Nationality Act 1981 (c.61) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom concerning British nationality since 1 January 1983.
History
In the mid-1970s the British Government decided to update the nationality code, which had b ...
by which British citizenship (with the right of abode in the United Kingdom
The right of abode (ROA) is an immigration status in the United Kingdom that gives a person the right to enter and live in the UK. It was introduced by the Immigration Act 1971 which went into effect on 1 January 1973. This status is held by Bri ...
) can either be claimed through automatic entitlement or be applied for by means of registration, from or through a sole personal connection to the Base Areas (in comparison, the 2002 Act bestowed British citizenship on all other BOTCs). Hence, non-British and non-military personnel with the connection to the territory cannot live and work in the UK and must use their Cypriot passports to apply for visas to the UK.
Under the terms of the 1960 agreement with Cyprus establishing the Sovereign Base Areas, the United Kingdom is committed not to use the areas for civilian purposes. This was stated in 2002 as the primary reason for the exclusion of the areas from the scope of the British Overseas Territories Act 2002. , around 7,195 service personnel of British Forces Cyprus
British Forces Cyprus (BFC) is the name given to the British Armed Forces stationed in the UK Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia on the island of Cyprus and at a number of related 'retained sites' in the Republic of Cyprus. The United ...
are based at Akrotiri and Dhekelia.
Education
Service Children's Education
Service Children's Education (SCE) is an organisation of the United Kingdom government responsible for the education of the children of British Armed Forces families and Ministry of Defence (MoD) personnel serving outside of the United Kingdo ...
oversees education for children of personnel and MoD employees. The Eastern Sovereign Base Area is served by Dhekelia Primary School and Ayios Nikolaos Primary School, which are feeders for King Richard School. The Western Sovereign Base Area is served by Episkopi Primary School and Akrotiri Primary School, which are feeders for St. John's School.
Economy
 No economic statistics are gathered for Akrotiri and Dhekelia. The main economic activities are the provision of services to the military, as well as limited agriculture. When the territory under the effective control of the Republic of Cyprus switched currencies from the
No economic statistics are gathered for Akrotiri and Dhekelia. The main economic activities are the provision of services to the military, as well as limited agriculture. When the territory under the effective control of the Republic of Cyprus switched currencies from the Cypriot pound
The pound, or lira ( el, λίρα, plural , and tr, lira, ota, لیره, from the Latin via the Italian ; sign: £, sometimes £C for distinction), was the currency of Cyprus, including the Sovereign Base Areas in Akrotiri and Dhekelia, from 1 ...
to the euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
on 1 January 2008, Akrotiri and Dhekelia followed suit making the Sovereign Base Areas the only territory under British sovereignty to officially use the euro.

Transport
Cypriot motorways pass through both areas. There is no public airport within the areas, but theRAF Akrotiri
RAF Akrotiri ( el, Βασιλική Πολεμική Αεροπορία Ακρωτηρίου) is a large Royal Air Force base on the Mediterranean island of Cyprus. It is located in the Western Sovereign Base Area, one of two areas which compri ...
airbase is located there, which has a runway suitable for long-distance flights, but is not used for public flights.
Communications
The Base Areas form part of the Republic of Cyprustelephone numbering plan
A telephone numbering plan is a type of numbering scheme used in telecommunication to assign telephone numbers to subscriber telephones or other telephony endpoints. Telephone numbers are the addresses of participants in a telephone network, re ...
, using the international prefix +357. Landline numbers are in the same eight-digit format, with the last four digits being the line number. Numbers in Dhekelia begin with the digits 2474, while those in Akrotiri begin with the digits 2527.
Postal services are provided by the British Forces Post Office
The British Forces Post Office (BFPO) provides a postal service to HM Forces, separate from that provided by Royal Mail in the United Kingdom. BFPO addresses are used for the delivery of mail in the UK and around the world. BFPO moved from its ...
, with mail to Akrotiri being addressed to BFPO 57 and mail to Dhekelia and Ayios Nikolaos being addressed to BFPO 58. Cyprus Postal Services
Cyprus Postal Services, or Cyprus Post, is the postal operator of Cyprus and operates the government-operated Post Office. A legacy of British colonial rule is the use of pillar boxes (mail boxes) with the initials of the British monarch, alth ...
provides postal service for civilian homes and businesses within the Base Areas, then using Cypriot postal codes and "Cyprus" as country on letters from abroad.
The bases are issued different amateur radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency commu ...
call signs
In broadcasting and radio communications, a call sign (also known as a call name or call letters—and historically as a call signal—or abbreviated as a call) is a unique identifier for a transmitter station. A call sign can be formally assign ...
from the Republic of Cyprus. Amateur radio stations on the bases use the International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
prefix of "ZC4", which is assigned to Great Britain. There are about 52 amateurs licensed in this manner. Amateur radio direction finding
Direction finding (DF), or radio direction finding (RDF), isin accordance with International Telecommunication Union (ITU)defined as radio location that uses the reception of radio waves to determine the direction in which a radio stati ...
identified RAF Akrotiri as the location of the powerful but now defunct shortwave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using shortwave (SW) radio frequencies. There is no official definition of the band, but the range always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (100 to 10 me ...
numbers station " Lincolnshire Poacher". Several curtain antennas there have been identified as being used for these transmissions.
Culture

Media
BFBS Radio 1 and 2 are broadcast on FM and can be widely received across Cyprus. BFBS Television is now only available to viewers via satellite, having been confined to the SBAs or encrypted in 1997 for copyright reasons, before BFBS switched off its analogue transmitters in 2009.''
Cyprus Mail
The ''Cyprus Mail'' is the only English-language daily newspaper published in Cyprus. Established in 1945, it is published every day except Monday, and most of the local articles are available on its website.
History
With the demise of the '' ...
'', 8 January 2009British East Mediterranean Relay Station
The British East Mediterranean Relay Station (also known as BEMRS) was one of the most powerful broadcasting stations in Cyprus. The medium wave transmitters were situated south of Limassol west of Lady's Mile Beach on the area of Western Sovere ...
was situated locally.
See also
* Index of Akrotiri and Dhekelia-related articles *List of British Army installations
This is a list of British Army Installations in the United Kingdom and overseas. British overseas bases are concentrated in Cyprus, Brunei, Kenya, the South Atlantic and Germany.
Overseas installations
Belize
British Overseas Territories Berm ...
* List of British overseas territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remnants of the former Bri ...
* Murder of Louise Jensen
The killing of Louise Jensen happened on 16 September 1994 in Ayia Napa, Cyprus, when British soldiers Allan Ford, Justin Fowler, and Geoffrey Pernell attacked, abducted, raped, and killed Danish tour guide Louise Jensen.
Jensen
Louise Jen ...
* Sovereign Base Areas Customs
* United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus
The United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus is a demilitarized zone, patrolled by the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP), that was established in 1964 and extended in 1974 after the ceasefire of 16 August 1974, following the ...
* Overseas military bases of the United Kingdom
Overseas military bases of the United Kingdom enable the British Armed Forces to conduct expeditionary warfare and maintain a forward presence. Bases tend to be located in or near areas of strategic or diplomatic importance, often used for the bui ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*External links
*Sovereign Base Areas Administration web-pages
BBC News – "UK offers to cede Cyprus land"
BBC News – "Cyprus protesters clash at UK base"
Cyprus Mail, Nathan Morley – "Mystery of Dhekelia Cemetery"
Cyprus Mail, Nathan Morley – "Dhekelia at 60"
Akrotiri
''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is availabl ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.
Dhekelia
''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is availabl ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.
The Princess Mary's Hospital RAF Akrotiri
Cyprus Independence Agreement – Hansard Official UK Parliament Record
* James Rogers and Luis Simón
The Status and Location of the Military Installations of the Member States of the European Union and Their Potential Role for the European Security and Defence Policy (ESDP).
Brussels: European Parliament, 2009. 25 pp. {{DEFAULTSORT:Akrotiri And Dhekelia Geography of Cyprus Cyprus and the Commonwealth of Nations English-speaking countries and territories 1960 establishments in the British Empire British Army deployments British military in Cyprus .Akrotiri and Dhekelia Dependent territories in Europe Royal Air Force deployments Sovereign Base Areas States and territories established in 1960 1960 establishments in Europe Military of Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia Enclaves and exclaves