Afar Depression on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a
 Dallol in the Danakil Depression is one of the hottest places year-round anywhere on Earth. There is no rain for most of the year; the yearly rainfall averages range from , with even less rain falling closer to the coast. Daily mean temperatures at Dallol ranged from in January to in July in six years of observations from 1960 to 1966.
Dallol in the Danakil Depression is one of the hottest places year-round anywhere on Earth. There is no rain for most of the year; the yearly rainfall averages range from , with even less rain falling closer to the coast. Daily mean temperatures at Dallol ranged from in January to in July in six years of observations from 1960 to 1966.
 The
The
 The Afar Depression is the product of a
The Afar Depression is the product of a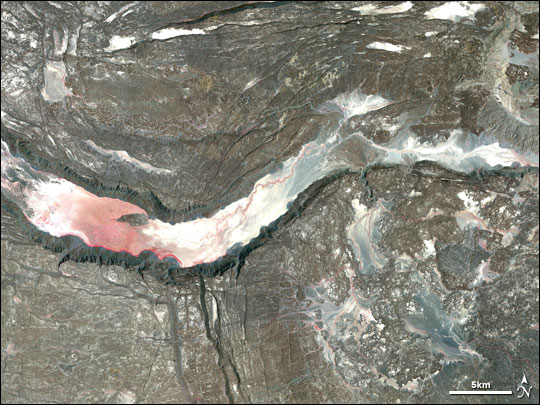  Related eruptions have taken place in Teru and Aura
Related eruptions have taken place in Teru and Aura
The Ethiopian state of Afar: Topography and Climate
Photos of Afars and Danakil
Huge collection of (3000) photos from different expeditions in the Dallol, Erta Ale and Danakil regions
Photos of Afar Depression: between Ethiopia and Djibouti
Web site of Main Ethiopian RiftScience news: Death of a Continent, Birth of an Ocean
{{Coord, 11.5, N, 41.0, E, display=title, source:frwiki Landforms of Djibouti Landforms of Eritrea Landforms of Ethiopia Afar Region Cenozoic rifts and grabens Landforms of Africa Endorheic basins of Africa Great Rift Valley
 The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a geological depression
In geology, a depression is a landform sunken or depressed below the surrounding area. Depressions form by various mechanisms.
Types
Erosion-related:
* Blowout: a depression created by wind erosion typically in either a partially vegetated san ...
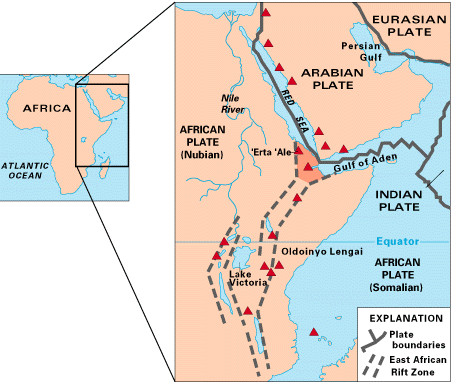
caused by the Afar Triple Junction
The Afar Triple Junction (also called the Afro-Arabian Rift System) is located along a divergent plate boundary dividing the Nubian, Somali, and Arabian plates. This area is considered a present-day example of continental rifting leading to ...
, which is part of the Great Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is a series of contiguous geographic trenches, approximately in total length, that runs from Lebanon in Asia to Mozambique in Southeast Africa. While the name continues in some usages, it is rarely used in geology as it ...
in East Africa. The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The t ...
; that is, the earliest of the human clade, and it is thought by some paleontologists to be the cradle of the evolution of humans. The Depression overlaps the borders of Eritrea, Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
and the entire Afar Region
The Afar Region (; aa, Qafar Rakaakayak; am, አፋር ክልል), formerly known as Region 2, is a regional state in northeastern Ethiopia and the homeland of the Afar people. Its capital is the planned city of Semera, which lies on the pave ...
of Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
; and it contains the lowest point in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, Lake Assal, Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
, at below sea level.
The Awash River
The Awash (sometimes spelled Awaash; Oromo: ''Awaash'', Amharic: አዋሽ, Afar: ''We'ayot'', Somali: ''Webiga Dir'') is a major river of Ethiopia. Its course is entirely contained within the boundaries of Ethiopia and empties into a chain of i ...
is the main waterflow into the region, but it runs dry during the annual dry season, and ends as a chain of saline lakes. The northern part of the Afar Depression is also known as the Danakil Depression
The Danakil Depression is the northern part of the Afar Triangle or Afar Depression in Ethiopia, a geological depression that has resulted from the divergence of three tectonic plates in the Horn of Africa.
Geology
The Danakil Depression lie ...
. The lowlands are affected by heat, drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
, and minimal air circulation, and contain the hottest places (year-round average temperatures) of anywhere on Earth.
The Afar Triangle is bordered as follows (see the topographic map): on the west by the Ethiopian Plateau
The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , while the summits reach heights of up to . ...
and escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
; to the north-east (between it and the Red Sea) by the Danakil block; to the south by the Somali Plateau and escarpment; and to the south-east by the Ali-Sabieh block (adjoining the Somali Plateau).
Many important fossil localities exist in the Afar region, including the Middle Awash
The Middle Awash is a paleoanthropological research area in the Afar Region along the Awash River in Ethiopia's Afar Depression. It is a unique natural laboratory for the study of human origins and evolution and a number of fossils of the earliest ...
region and the sites of Hadar, Dikika
The Dikika is an area of the Afar Region of Ethiopia where the hominin fossil named Selam was found (a specimen of the '' Australopithecus afarensis'' species). Dikika is located in Mille woreda.Based on the map of the findsite printed in Alemse ...
, and Woranso-Mille. These sites have produced specimens of the earliest (fossil) hominins and of human tool culture, as well as many fossils of various flora and fauna.
Environment
 Dallol in the Danakil Depression is one of the hottest places year-round anywhere on Earth. There is no rain for most of the year; the yearly rainfall averages range from , with even less rain falling closer to the coast. Daily mean temperatures at Dallol ranged from in January to in July in six years of observations from 1960 to 1966.
Dallol in the Danakil Depression is one of the hottest places year-round anywhere on Earth. There is no rain for most of the year; the yearly rainfall averages range from , with even less rain falling closer to the coast. Daily mean temperatures at Dallol ranged from in January to in July in six years of observations from 1960 to 1966.
 The
The Awash River
The Awash (sometimes spelled Awaash; Oromo: ''Awaash'', Amharic: አዋሽ, Afar: ''We'ayot'', Somali: ''Webiga Dir'') is a major river of Ethiopia. Its course is entirely contained within the boundaries of Ethiopia and empties into a chain of i ...
, flowing north-eastward through the southern part of the Afar Region, provides a narrow green belt which enables life for the flora and fauna in the area and for the Afars, the nomadic people living in the Danakil Desert
The Danakil Desert is a desert in northeast Ethiopia, southern Eritrea, and northwestern Djibouti. Situated in the Afar Triangle, it stretches across of arid terrain. It is inhabited by a few Afar, who engage in salt mining. The area is know ...
. About from the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
the Awash ends in a chain of salt lakes, where its waterflow evaporates as quickly as it is supplied. Some of the Afar Depression is covered by salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
deposits, and mining salt is a major source of income for many Afar groups.
The Afar Depression biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
is characterized as desert scrubland. Vegetation is mostly confined to drought-resistant plants such as small trees (e.g. species of the dragon tree), shrubs, and grasses. Wildlife includes many herbivores such as Gr éSoemmerring's gazelle
Soemmerring's gazelle (''Nanger soemmerringii''), also known as the Abyssinian mohr, is a gazelle species native to the Horn of Africa (Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Somalia and South Sudan). The species was described and given its binomen by ...
, beisa and, notably, the last viable population of African wild ass
The African wild ass (''Equus africanus'') or African wild donkey is a wild member of the horse family, Equidae. This species is thought to be the ancestor of the domestic donkey (''Equus asinus''), which is sometimes placed within the same spec ...
('' Equus africanus somalicus'').
Birds include the ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There ...
, the endemic Archer's lark
Archer's lark (''Heteromirafra archeri''), also known as the Liben lark, is a species of lark in the family Alaudidae. It is found in Somalia, Somaliland and Ethiopia. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry shrubland and subtrop ...
, the secretary bird
The secretarybird or secretary bird (''Sagittarius serpentarius'') is a large, mostly terrestrial bird of prey. Endemic to Africa, it is usually found in the open grasslands and savanna of the sub-Saharan region. John Frederick Miller describe ...
, Arabian and Kori bustard
The kori bustard (''Ardeotis kori'') is the largest flying bird native to Africa. It is a member of the bustard family, which all belong to the order Otidiformes and are restricted in distribution to the Old World. It is one of the four species ( ...
s, Abyssinian roller, and crested francolin
The crested francolin (''Ortygornis sephaena'') is a species of bird in the family Phasianidae.
It is found in southern Africa. One of its subspecies, ''Ortygornis sephaena rovuma'', is sometimes considered a separate species, Kirk's francolin.
...
. In the southern part of the plain lies the Mille-Serdo Wildlife Reserve
Mille-Serdo Wildlife Reserve () is a protected area in Ethiopia. It is located in Afar Region of Ethiopia. The reserve protects a portion of the Awash River and the surrounding desert.
Geography
Mille-Serdo Wildlife Reserve covers an area of 6503 ...
.
The Afar Triangle is a cradle source of the earliest hominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The ...
s. It contains a paleo-archaeological district that includes the Middle Awash
The Middle Awash is a paleoanthropological research area in the Afar Region along the Awash River in Ethiopia's Afar Depression. It is a unique natural laboratory for the study of human origins and evolution and a number of fossils of the earliest ...
region and numerous prehistoric sites of fossil hominin discoveries, including: the hominids
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the ...
and possible hominins, Ardi, or ''Ardipithecus ramidus
''Ardipithecus ramidus'' is a species of australopithecine from the Afar region of Early Pliocene Ethiopia 4.4 million years ago (mya). ''A. ramidus'', unlike modern hominids, has adaptations for both walking on two legs ( bipedality) and life i ...
'', and '' Ardipithecus kadabba'', see below; the Gawis cranium hominin from Gona; several sites of the world's oldest stone tools; Hadar, the site of Lucy
Lucy is an English feminine given name derived from the Latin masculine given name Lucius with the meaning ''as of light'' (''born at dawn or daylight'', maybe also ''shiny'', or ''of light complexion''). Alternative spellings are Luci, Luce, Lu ...
, the fossilized specimen of ''Australopithecus afarensis
''Australopithecus afarensis'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would not ...
''; and Dikika
The Dikika is an area of the Afar Region of Ethiopia where the hominin fossil named Selam was found (a specimen of the '' Australopithecus afarensis'' species). Dikika is located in Mille woreda.Based on the map of the findsite printed in Alemse ...
, the site of the fossilized child Selam, an australopithecine
Australopithecina or Hominina is a subtribe in the tribe Hominini. The members of the subtribe are generally ''Australopithecus'' (cladistically including the genera ''Homo'', '' Paranthropus'', and ''Kenyanthropus''), and it typically includ ...
hominin.
In 1994, near the Awash River in Ethiopia, Tim D. White found the then-oldest known human ancestor: 4.4 million-year-old ''Ar. ramidus''. A fossilized almost complete skeleton of a female hominin which he named "Ardi", it took nearly 15 years to safely excavate, preserve, and describe the specimen and to prepare publication of the event.
Geology
 The Afar Depression is the product of a
The Afar Depression is the product of a tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents ...
triple-rifts junction (the Afar Triple Junction
The Afar Triple Junction (also called the Afro-Arabian Rift System) is located along a divergent plate boundary dividing the Nubian, Somali, and Arabian plates. This area is considered a present-day example of continental rifting leading to ...
), where the spreading ridges forming the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
and the Gulf of Aden emerge on land and meet the East African Rift. The conjunction of these three plates of Earth's crust is near Lake Abbe
Lake Abbe, also known as Lake Abhe Bad, is a salt lake, lying on the Ethiopia-Djibouti border. It is one of a chain of six connected lakes, which also includes (from north to south) lakes Gargori, Laitali, Gummare, Bario and Afambo. The lake i ...
. The Afar Depression is one of two places on Earth where a mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a diver ...
can be studied on land, the other being Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
.
Within the triangle, the Earth's crust is slowly rifting apart at a rate of per year along each of the three rift zones
A rift zone is a feature of some volcanoes, especially shield volcanoes, in which a set of linear cracks (or rifts) develops in a volcanic edifice, typically forming into two or three well-defined regions along the flanks of the vent. Believed t ...
forming the "legs" of the triple junction. The immediate consequences are recurring sequences of earthquakes with deep fissures in the terrain hundreds of metres long, and the valley floor sinking broadly across the depression. During September and October 2005 some 163 earthquakes of magnitudes greater than 3.9 and a volcanic eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are oft ...
occurred within the Afar rift at the Dabbahu and Erta Ale
Erta Ale (or Ertale or Irta'ale; Amharic: ኤርታሌ) is a continuously active basaltic shield volcano in the Afar Region of northeastern Ethiopia. It is situated in the Afar Depression, a barren desert area. Erta Ale is the most active volcano ...
volcanoes. Some 2.5 cubic kilometers of molten rock was injected from below into the plate along a dyke between depths of , forcing open an wide gap on the surface, known as the Dabbahu fissure.
 Related eruptions have taken place in Teru and Aura
Related eruptions have taken place in Teru and Aura woredas
Districts of Ethiopia, also called woredas ( am, ወረዳ; ''woreda''), are the third level of the administrative divisions of Ethiopia – after ''zones'' and the '' regional states''.
These districts are further subdivided into a number of ...
. The rift has recently been recorded by means of three-dimensional laser mapping.
The region's salt deposits were created over time as water from the Red Sea periodically flooded the depression and evaporated; the most recent such flood was roughly 30,000 years ago.
Over the next millions of years, geologists expect erosion and the Red Sea to breach the highlands surrounding the Afar Depression and flood the valley. Geologists predict that in about 10 million years the whole length of the East African Rift will be submerged, forming a new ocean basin as large as today's Red Sea, and separating the Somali Plate
The Somali Plate is a minor tectonic plate which straddles the Equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is currently in the process of separating from the African Plate along the East African Rift Valley. It is approximately centered on the isl ...
and the Horn of Africa from the rest of the continent.
The floor of the Afar Depression is composed of lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
, mostly basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
. One of Earth's five lava lakes, Erta Ale is found here, as well as Dabbahu Volcano. It has been proposed that the Afar Depression is underlain by a mantle plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hot ...
,Hammond, J. O. S., J.- M. Kendall, G. W. Stuart, C. J. Ebinger, I. D. Bastow, D. Keir, A. Ayele, M. Belachew, B. Goitom, G. Ogubazghi, and T. J. Wright. "Mantle Upwelling and Initiation of Rift Segmentation beneath the Afar Depression." Geology 41.6 (2013): 635–38. DOI:10.1130/G33925.1 a great upwelling of mantle that melts to yield basalt as it approaches the surface.
See also
* * * in Djibouti * ''(with link directory)'' * ''(with images)'' *The who inhabit the regionReferences
Citations
Sources
* * Includes a photo essay of the region and its geologic changes. * * * Jon Kalb: ''Adventures in the Bone Trade. The Race to Discover Human Ancestors in Ethiopia's Afar Depression.'' Copernicus Books, New York 2001, *External links
The Ethiopian state of Afar: Topography and Climate
Photos of Afars and Danakil
Huge collection of (3000) photos from different expeditions in the Dallol, Erta Ale and Danakil regions
Photos of Afar Depression: between Ethiopia and Djibouti
Web site of Main Ethiopian Rift
{{Coord, 11.5, N, 41.0, E, display=title, source:frwiki Landforms of Djibouti Landforms of Eritrea Landforms of Ethiopia Afar Region Cenozoic rifts and grabens Landforms of Africa Endorheic basins of Africa Great Rift Valley