Aedes aegypti on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Aedes aegypti'', the yellow fever mosquito, is a
 ''Aedes aegypti'' is a long, dark
''Aedes aegypti'' is a long, dark
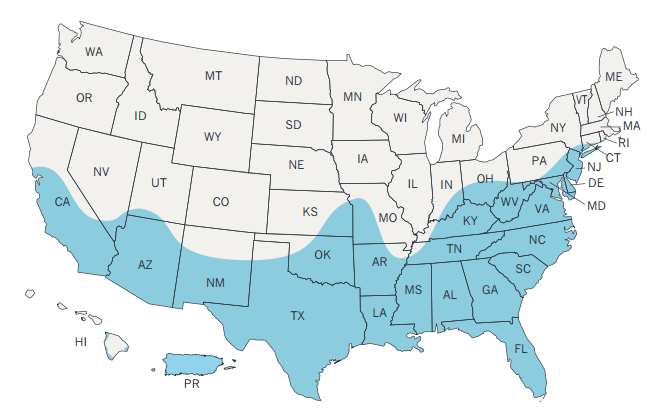 ''Aedes aegypti'' originated in Africa and was spread to the New World through slave trade, but is now found in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world.
''Ae. aegypti'' distribution has increased in the past two to three decades worldwide, and it is considered to be among the most widespread mosquito species.
In 2016, Zika virus-capable mosquito populations have been found adapting for persistence in warm temperate climates. Such a population has been identified to exist in parts of
''Aedes aegypti'' originated in Africa and was spread to the New World through slave trade, but is now found in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world.
''Ae. aegypti'' distribution has increased in the past two to three decades worldwide, and it is considered to be among the most widespread mosquito species.
In 2016, Zika virus-capable mosquito populations have been found adapting for persistence in warm temperate climates. Such a population has been identified to exist in parts of
 To stabilise the nomenclature, a petition to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature was made by P. F. Mattingly, Alan Stone, and Kenneth L. Knight in 1962. It also transpired that, although the name ''Aedes aegypti'' was universally used for the yellow fever mosquito, Linnaeus had actually described a species now known as ''Aedes'' (''Ochlerotatus'') ''caspius''. In 1964, the commission ruled in favour of the proposal, validating Linnaeus' name, and transferring it to the species for which it was in general use.
The yellow fever mosquito belongs to the tribe Aedini of the dipteran family Culicidae and to the genus ''Aedes'' and subgenus ''Stegomyia''. According to one recent analysis, the subgenus '' Stegomyia'' of the genus ''
To stabilise the nomenclature, a petition to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature was made by P. F. Mattingly, Alan Stone, and Kenneth L. Knight in 1962. It also transpired that, although the name ''Aedes aegypti'' was universally used for the yellow fever mosquito, Linnaeus had actually described a species now known as ''Aedes'' (''Ochlerotatus'') ''caspius''. In 1964, the commission ruled in favour of the proposal, validating Linnaeus' name, and transferring it to the species for which it was in general use.
The yellow fever mosquito belongs to the tribe Aedini of the dipteran family Culicidae and to the genus ''Aedes'' and subgenus ''Stegomyia''. According to one recent analysis, the subgenus '' Stegomyia'' of the genus ''
''Aedes aegypti''
on the entomology Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences Featured Creatures Web site
''Aedes aegypti'' University of Sydney, Australia
very brief, undated
microscopy-uk.org.uk, undated
United States CDC page on dengue fever containing information on prevalence of ''Aedes aegypti'' worldwide and past efforts to eradicate it
''Aedes aegypti'' on Walter Reed Hospital page
Distribution, taxonomy, references etc.
The ecology and biology of ''Aedes aegypti'' (L.) and ''Aedes albopictus''and the resistance of ''Aedes albopictus'' against organophosphates in Penang, Malaysia
M.S. thesis, June 2006
January 2019 * ttps://www.vectorbase.org/organisms/aedes-aegypti VectorBase's genomic resource for ''Aedes aegypti''
''Aedes aegypti'' at GeoChemBio.com
09/01/14 {{Authority control aegypti Insects described in 1762 Dengue fever Insect vectors of human pathogens Yellow fever Chikungunya Diptera of Africa Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
that can spread
Spread may refer to:
Places
* Spread, West Virginia
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Spread'' (film), a 2009 film.
* ''$pread'', a quarterly magazine by and for sex workers
* "Spread", a song by OutKast from their 2003 album ''Speakerboxxx/T ...
dengue fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, Mayaro and yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. ...
viruses, and other disease agents. The mosquito can be recognized by black and white markings on its legs and a marking in the form of a lyre on the upper surface of its thorax. This mosquito originated in Africa, but is now found in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world.
Biology
 ''Aedes aegypti'' is a long, dark
''Aedes aegypti'' is a long, dark mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
which can be recognized by white markings on its legs and a marking in the form of a lyre on the upper surface of its thorax. Females are larger than males. Microscopically females possess small palps tipped with silver or white scales, and their antennae have sparse short hairs, whereas those of males are feathery. ''Aedes aegypti'' can be mixed up with Aedes albopictus
''Aedes albopictus'' (''Stegomyia albopicta''), from the mosquito (Culicidae) family, also known as the (Asian) tiger mosquito or forest mosquito, is a mosquito native to the tropical and subtropical areas of Southeast Asia. In the past few cen ...
without a magnifying glass: The latter have a white stripe on the top of the mid thorax.
Males live off fruit and only the female bites for blood, which she needs to mature her eggs. To find a host, she is attracted to chemical compounds emitted by mammals, including ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
lactic acid, and octenol. Scientists at The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Agricultural Research Service studied the specific chemical structure of octenol to better understand why this chemical attracts the mosquito to its host and found the mosquito has a preference for "right-handed" (dextrorotatory
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circul ...
) octenol molecules. The preference for biting humans is dependent on expression of the odorant receptor ''AaegOr4''.
The white eggs are laid separately into water and not together, unlike most other mosquitoes, and soon turn black. The larvae feed on bacteria, grow over a period of weeks until they reach the pupa stage.
The lifespan of an adult ''Ae. aegypti'' is two to four weeks depending on conditions, but the eggs can be viable for over a year in a dry state, which allows the mosquito to re-emerge after a cold winter or dry spell.
Hosts
Mammalian hosts includedomesticated horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
s, and feral
A feral () animal or plant is one that lives in the wild but is descended from domesticated individuals. As with an introduced species, the introduction of feral animals or plants to non-native regions may disrupt ecosystems and has, in some ...
and wild horses and equids more generally.
As of 2009 birds were found to be the best food supply for ''Ae. aegypti'' among all taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
.
Distribution
 ''Aedes aegypti'' originated in Africa and was spread to the New World through slave trade, but is now found in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world.
''Ae. aegypti'' distribution has increased in the past two to three decades worldwide, and it is considered to be among the most widespread mosquito species.
In 2016, Zika virus-capable mosquito populations have been found adapting for persistence in warm temperate climates. Such a population has been identified to exist in parts of
''Aedes aegypti'' originated in Africa and was spread to the New World through slave trade, but is now found in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world.
''Ae. aegypti'' distribution has increased in the past two to three decades worldwide, and it is considered to be among the most widespread mosquito species.
In 2016, Zika virus-capable mosquito populations have been found adapting for persistence in warm temperate climates. Such a population has been identified to exist in parts of Washington, DC
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan ...
, and genetic evidence suggests they survived at least the last four winters in the region. One of the study researchers noted, " ...some mosquito species are finding ways to survive in normally restrictive environments by taking advantage of underground refugia".
As the world's climate becomes warmer, the range of ''Aedes aegypti'' and a hardier species originating in Asia, the tiger mosquito ''Aedes albopictus
''Aedes albopictus'' (''Stegomyia albopicta''), from the mosquito (Culicidae) family, also known as the (Asian) tiger mosquito or forest mosquito, is a mosquito native to the tropical and subtropical areas of Southeast Asia. In the past few cen ...
'', which can expand its range to relatively cooler climates, will inexorably spread north and south. Sadie Ryan of the University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its ...
was the lead author in a 2019 study that estimated the vulnerability of naïve populations in geographic regions that currently do not harbor vectors i.e., for Zika in the Old World. Ryan's co-author, Georgetown University's Colin Carlson remarked,"Plain and simple, climate change is going to kill a lot of people." As of 2020, the Northern Territory Government Australia and the Darwin City Council have recommended tropical cities initiate rectification programs to rid their cities of potential mosquito breeding stormwater sumps. A 2019 study found that accelerating urbanization and human movement would also contribute to the spread of ''Aedes'' mosquitoes.
In continental Europe, ''Aedes aegypti'' is not established but it has been found in localities close to Europe such as the Asian part of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
. However, a single adult female specimen was found in Marseille
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern Fra ...
(Southern France) in 2018. On the basis of a genetic study and an analysis of the movements of commercial ships, the origin of the specimen could be traced as coming from Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the C ...
, in Central Africa. Genomics
In 2007, the genome of ''Aedes aegypti'' was published, after it had been sequenced and analyzed by a consortium including scientists at The Institute for Genomic Research (now part of the J. Craig Venter Institute), the European Bioinformatics Institute, the Broad Institute, and theUniversity of Notre Dame
The University of Notre Dame du Lac, known simply as Notre Dame ( ) or ND, is a private Catholic university, Catholic research university in Notre Dame, Indiana, outside the city of South Bend, Indiana, South Bend. French priest Edward Sorin fo ...
. The effort in sequencing its DNA was intended to provide new avenues for research into insecticides and possible genetic modification to prevent the spread of virus. This was the second mosquito species to have its genome sequenced in full (the first was '' Anopheles gambiae''). The published data included the 1.38 billion base pairs containing the insect's estimated 15,419 protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
-encoding genes. The sequence indicates the species diverged from '' Drosophila melanogaster'' (the common fruit fly) about , and ''Anopheles gambiae'' and this species diverged about . Matthews ''et al.'', 2018 finds ''A. aegypti'' to carry a large and diverse number of transposable elements. Their analysis suggests this is common to all mosquitoes.
Vector of disease
''Aedes aegypti'' is avector
Vector most often refers to:
*Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
*Vector (epidemiology), an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematic ...
for transmitting numerous pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
s. According to the Walter Reed Biosystematics Units as of 2022, it is associated with the following 54 viruses and 2 species of Plasmodium:
Aino virus (AINOV), African horse sickness virus (AHSV), Bozo virus (BOZOV), Bussuquara virus (BSQV), Bunyamwera virus (BUNV), Catu virus (CATUV), Chikungunya virus
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the ''Chikungunya virus'' (CHIKV). Symptoms include fever and joint pains. These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a ra ...
(CHIKV), Chandipura vesiculovirus (CHPV), Cypovirus (unnamed), Cache Valley virus (CVV), Dengue virus (DENV), Eastern Equine Encephalitis virus (EEEV), Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV), Guaroa virus (GROV), Hart Park virus
Hart Park virus, or HP virus, is a single-stranded RNA arbovirus that is primarily transmitted through mosquitoes. The HP virus is classified in the Rhabdoviridae family and is related to the viral agents that cause rabies and vesicular stomatiti ...
(HPV), Ilheus virus (ILHV), Irituia virus (IRIV), Israel Turkey Meningoencephalitis virus (ITV), Japanaut virus (JAPV), Joinjakaka (JOIV), Japanese encephalitis virus
Japanese encephalitis (JE) is an infection of the brain caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). While most infections result in little or no symptoms, occasional inflammation of the brain occurs. In these cases, symptoms may include he ...
(JBEV), Ketapang virus (KETV), Kunjin virus (KUNV), La Crosse virus (LACV), Mayaro virus (MAYV), Marburg virus (MBGV), Marco virus (MCOV), Melao virus (MELV) Marituba virus (MTBV), Mount Elgon bat virus (MEBV), Mucambo virus (MUCV), Murray Valley Encephalitis virus (MVEV), Navarro virus (NAVV), Nepuyo virus (NEPV), Nola virus (NOLV), Ntaya virus (NTAV), Oriboca virus (ORIV), Orungo virus (ORUV), Restan virus (RESV), Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV), Semliki Forest virus (SFV), Sindbis virus (SINV), Tahyna virus (TAHV), Tsuruse virus (TSUV), Tyuleniy virus (TYUV), Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus is a mosquito-borne viral pathogen that causes Venezuelan equine encephalitis or encephalomyelitis (VEE). VEE can affect all equine species, such as horses, donkeys, and zebras. After infection, equines m ...
(VEEV), Vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana serotype), Warrego virus (WARV), West Nile virus (WNV), Wesselsbron virus (WSLV), Yaounde virus (YAOV)
Yellow fever virus (YFV), Zegla virus (ZEGV), Zika virus, as well as Plasmodium gallinaceum and Plasmodium lophurae.
This mosquito also mechanically transmits some veterinary disease
The following are lists of animal diseases:
* List of aquarium diseases
* List of dog diseases
* List of feline diseases
* List of diseases of the honey bee
* List of diseases spread by invertebrates
* Poultry disease
* Zoonosis#Lists of disea ...
s. In 1952 Fenner ''et al.'', found it transmitting the myxoma virus
''Myxoma virus'' is a poxvirus in the genus ''Leporipoxvirus''. The two broad geographic types of ''myxoma virus'' are Californian and South American. Californian ''myxoma virus'' is found on the West Coast of the United States, the Baja Penins ...
between rabbits and in 2001 Chihota ''et al.'', the lumpy skin disease virus
Lumpy skin disease (LSD) is an infectious disease in cattle caused by a virus of the family ''Poxviridae'', also known as Neethling virus. The disease is characterized by large fever, enlarged superficial lymph nodes and multiple nodules (measuri ...
between cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ma ...
.
The yellow fever mosquito can contribute to the spread of reticular cell sarcoma
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal ( connective tissue) origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sar ...
among Syrian hamster
The golden hamster or Syrian hamster (''Mesocricetus auratus'') is a rodent belonging to the hamster subfamily, Cricetinae. Their natural geographical range is in an arid region of northern Syria and southern Turkey. Their numbers have been de ...
s.
Bite prevention methods
TheCenters for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
traveler's page on preventing dengue fever suggests using mosquito repellents that contain DEET (N, N-diethylmetatoluamide, 20% to 30%). It also suggests:
# Although ''Aedes aegypti'' mosquitoes most commonly feed at dusk and dawn, indoors, in shady areas, or when the weather is cloudy, "they can bite and spread infection all year long and at any time of day."
# Once a week, scrub off eggs sticking to wet containers, seal and/or discard them. The mosquitoes prefer to breed in areas of stagnant water, such as flower vases, uncovered barrels, buckets, and discarded tires, but the most dangerous areas are wet shower floors and toilet tanks, as they allow the mosquitos to breed in the residence. Research has shown that certain chemicals emanating from bacteria in water containers stimulate the female mosquitoes to lay their eggs. They are particularly motivated to lay eggs in water containers that have the correct amounts of specific fatty acids associated with bacteria involved in the degradation of leaves and other organic matter in water. The chemicals associated with the microbial stew are far more stimulating to discerning female mosquitoes than plain or filtered water in which the bacteria once lived.
# Wear long-sleeved clothing and long pants when outdoors during the day and evening.
# Use mosquito netting over the bed if the bedroom is not air conditioned or screened, and for additional protection, treat the mosquito netting with the insecticide permethrin.
Insect repellents containing DEET (particularly concentrated products) or ''p''-menthane-3,8-diol (from lemon eucalyptus) were effective in repelling ''Ae. aegypti'' mosquitoes, while others were less effective or ineffective in a scientific study. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
article on "Protection against Mosquitoes, Ticks, & Other Arthropods" notes that "Studies suggest that concentrations of DEET above approximately 50% do not offer a marked increase in protection time against mosquitoes; DEET efficacy tends to plateau at a concentration of approximately 50%". Other insect repellents recommended by the CDC include Picaridin (KBR 3023/ icaridin), IR3535
Ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate (trade name IR3535) is an insect repellent which is applied topically to prevent bites and stings from mosquitos, ticks, and other insects. It is a colorless and almost odorless oil, has efficacy against a broad ran ...
, and 2-undecanone.
Population control efforts
Insecticides
Pyrethroids are commonly used. This widespread use of pyrethroids andDDT
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, commonly known as DDT, is a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochloride. Originally developed as an insecticide, it became infamous for its environmental impacts. ...
has caused Knockdown resistance Knockdown resistance, also called kdr, describes cases of resistance to diphenylethane (e.g. DDT) and pyrethroid insecticides in insects and other arthropods that result from reduced sensitivity of the nervous system caused by point mutations in ...
(''kdr'') mutations. Almost no research has been done on the fitness implications. studies by Kumar ''et al.'', 2009 on deltamethrin in India, Plernsub ''et al.'', 2013 on permethrin in Thailand, by Jaramillo-O ''et al.'', 2014 on λ-cyhalothrin in Colombia, by Alvarez-Gonzalez ''et al.'', 2017 on deltamethrin in Venezuela, are all substantially confounded. As of 2019, understanding of selective pressure under withdrawal of insecticide is hence limited.
Genetic modification
''Ae. aegypti'' has beengenetically modified
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including ...
to suppress its own species in an approach similar to the sterile insect technique
The sterile insect technique (SIT) is a method of biological insect control, whereby overwhelming numbers of sterile insects are released into the wild. The released insects are preferably male, as this is more cost-effective and the females ma ...
, thereby reducing the risk of disease. The mosquitoes, known as , were developed by Oxitec, a spinout of Oxford University
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to th ...
. Field trials in the Cayman Islands, in Juazeiro
Juazeiro, formerly also known as Joazeiro, is a municipality in the state of Bahia, in the northeastern region of Brazil.
The city is twinned with Petrolina, in the state of Pernambuco. The two cities are connected by a modern bridge crossing ...
Brazil by Carvalho ''et al.'', 2015, and in Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
by Neira ''et al.'', 2014 have shown that the OX513A mosquitoes reduced the target mosquito populations by more than 90%. This mosquito suppression effect is achieved by a self-limiting gene that prevents the offspring from surviving. Male modified mosquitoes, which do not bite or spread disease, are released to mate with the pest females. Their offspring inherit the self-limiting gene and die before reaching adulthood—before they can reproduce or spread disease. The OX513A mosquitoes and their offspring also carry a fluorescent marker for simple monitoring. To produce more OX513A mosquitoes for control projects, the self-limiting gene is switched off (using the Tet-Off system) in the mosquito production facility using an antidote (the antibiotic tetracycline), allowing the mosquitoes to reproduce naturally. In the environment, the antidote is unavailable to rescue mosquito reproduction, so the pest population is suppressed.
The mosquito control effect is nontoxic and species-specific, as the OX513A mosquitoes are ''Ae. aegypti'' and only breed with ''Ae. aegypti''. The result of the self-limiting approach is that the released insects and their offspring die and do not persist in the environment.
In Brazil, the modified mosquitoes were approved by the National Biosecurity Technical Commission for releases throughout the country. Insects were released into the wild populations of Brazil, Malaysia, and the Cayman Islands in 2012. In July 2015, the city of Piracicaba, São Paulo, started releasing the OX513A mosquitoes. In 2015, the UK House of Lords called on the government to support more work on genetically modified insects in the interest of global health. In 2016, the United States Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
granted preliminary approval for the use of modified mosquitoes to prevent the spread of the Zika virus.
Another proposed method consists in using radiation to sterilize male larvae so that when they mate, they produce no progeny. Male mosquitoes do not bite or spread disease.
Using CRISPR/Cas9 based genome editing to engineer the genome of ''Aedes aegypti'' genes like ECFP (enhanced cyan fluorescent protein), Nix (male-determining factor gene), Aaeg-wtrw (Ae. aegypti water witch locus), Kmo (kynurenine 3-monoxygenase), loqs (loquacious), r2d2 (r2d2 protein), ku70 (ku heterodimer protein gene) and lig4 (ligase4) were targeted to modify the genome of ''Aedes aegypti''. The new mutant will become incapable of pathogen transmission or result in population control.
Infection with Wolbachia
In 2016 research into the use of a bacterium called ''Wolbachia
''Wolbachia'' is a genus of intracellular bacteria that infects mainly arthropod species, including a high proportion of insects, and also some nematodes. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes, and is possibly the most common reproducti ...
'' as a method of biocontrol was published showing that invasion of ''Ae. aegypti'' by the endosymbiotic bacteria allows mosquitos to be resistant to certain arboviruses such as dengue fever and Zika virus strains currently circulating. In 2017 Alphabet, Inc. started the Debug Project to infect males of this species with ''Wolbachia
''Wolbachia'' is a genus of intracellular bacteria that infects mainly arthropod species, including a high proportion of insects, and also some nematodes. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes, and is possibly the most common reproducti ...
'' bacteria, interrupting the reproductive cycle of these animals.
Taxonomy
The species was first named (as ''Culex aegypti'') in 1757 by Fredric Hasselquist in his treatise '. Hasselquist was provided with the names and descriptions by his mentor,Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his Nobility#Ennoblement, ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalise ...
. This work was later translated into German and published in 1762 as '. Since the latter is an uncritical reproduction of the former, they are both considered to antedate the starting point for zoological nomenclature
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the ICZN Code, for its publisher, the In ...
in 1758. Nonetheless, the name ''Aedes aegypti'' was frequently used, starting with H. G. Dyar in 1920.
 To stabilise the nomenclature, a petition to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature was made by P. F. Mattingly, Alan Stone, and Kenneth L. Knight in 1962. It also transpired that, although the name ''Aedes aegypti'' was universally used for the yellow fever mosquito, Linnaeus had actually described a species now known as ''Aedes'' (''Ochlerotatus'') ''caspius''. In 1964, the commission ruled in favour of the proposal, validating Linnaeus' name, and transferring it to the species for which it was in general use.
The yellow fever mosquito belongs to the tribe Aedini of the dipteran family Culicidae and to the genus ''Aedes'' and subgenus ''Stegomyia''. According to one recent analysis, the subgenus '' Stegomyia'' of the genus ''
To stabilise the nomenclature, a petition to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature was made by P. F. Mattingly, Alan Stone, and Kenneth L. Knight in 1962. It also transpired that, although the name ''Aedes aegypti'' was universally used for the yellow fever mosquito, Linnaeus had actually described a species now known as ''Aedes'' (''Ochlerotatus'') ''caspius''. In 1964, the commission ruled in favour of the proposal, validating Linnaeus' name, and transferring it to the species for which it was in general use.
The yellow fever mosquito belongs to the tribe Aedini of the dipteran family Culicidae and to the genus ''Aedes'' and subgenus ''Stegomyia''. According to one recent analysis, the subgenus '' Stegomyia'' of the genus ''Aedes
''Aedes'' is a genus of mosquitoes originally found in tropical and subtropical zones, but now found on all continents except perhaps Antarctica. Some species have been spread by human activity: '' Aedes albopictus'', a particularly invasive sp ...
'' should be raised to the level of genus. The proposed name change has been ignored by most scientists; at least one scientific journal, the ''Journal of Medical Entomology
A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to:
*Bullet journal, a method of personal organization
*Diary, a record of what happened over the course of a day or other period
*Daybook, also known as a general journal, a ...
'', has officially encouraged authors dealing with aedile mosquitoes to continue to use the traditional names, unless they have particular reasons for not doing so. The generic name comes from the Ancient Greek ἀηδής, ''aēdēs'', meaning "unpleasant" or "odious".
Subspecies
Two subspecies are commonly recognized: * * This classification is complicated by the results of Gloria-Soria ''et al.'', 2016. Although confirming the existence of these two major subspecies, Gloria-Sora ''et al.'' finds greater worldwide diversity than previously recognized and a large number of distinct populations separated by various geographic factors.References
External links
''Aedes aegypti''
on the entomology Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences Featured Creatures Web site
University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its ...
, March 2019.
''Aedes aegypti'' University of Sydney, Australia
very brief, undated
microscopy-uk.org.uk, undated
United States CDC page on dengue fever containing information on prevalence of ''Aedes aegypti'' worldwide and past efforts to eradicate it
''Aedes aegypti'' on Walter Reed Hospital page
Distribution, taxonomy, references etc.
The ecology and biology of ''Aedes aegypti'' (L.) and ''Aedes albopictus''and the resistance of ''Aedes albopictus'' against organophosphates in Penang, Malaysia
M.S. thesis, June 2006
January 2019 * ttps://www.vectorbase.org/organisms/aedes-aegypti VectorBase's genomic resource for ''Aedes aegypti''
''Aedes aegypti'' at GeoChemBio.com
09/01/14 {{Authority control aegypti Insects described in 1762 Dengue fever Insect vectors of human pathogens Yellow fever Chikungunya Diptera of Africa Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus