Adriatic Sea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the

 }) along the basin's minor axis. Finally, Venice is increasingly vulnerable to flooding due to coastal area soil subsidence. Such unusually high tides resulting in flooding have also been observed elsewhere in the Adriatic Sea, and have been recorded in recent years in the towns of Koper, Zadar and
}) along the basin's minor axis. Finally, Venice is increasingly vulnerable to flooding due to coastal area soil subsidence. Such unusually high tides resulting in flooding have also been observed elsewhere in the Adriatic Sea, and have been recorded in recent years in the towns of Koper, Zadar and  It is estimated that the Adriatic's entire volume is exchanged through the Strait of Otranto in 3.4±0.4 years, a comparatively short period. (For instance, approximately 500 years are necessary to exchange all the
It is estimated that the Adriatic's entire volume is exchanged through the Strait of Otranto in 3.4±0.4 years, a comparatively short period. (For instance, approximately 500 years are necessary to exchange all the
 According to the
According to the

 Geophysical and geological information indicate that the Adriatic Sea and the Po Valley are associated with a tectonic
Geophysical and geological information indicate that the Adriatic Sea and the Po Valley are associated with a tectonic
 All types of
All types of
 The eastern Adriatic shore's Croatian part is the most indented Mediterranean coastline. Most of the eastern coast is characterised by a karst topography, developed from the Adriatic Carbonate Platform's exposure to weathering. Karstification there largely began after the Dinarides' final uplift in the Oligocene and the
The eastern Adriatic shore's Croatian part is the most indented Mediterranean coastline. Most of the eastern coast is characterised by a karst topography, developed from the Adriatic Carbonate Platform's exposure to weathering. Karstification there largely began after the Dinarides' final uplift in the Oligocene and the
Status and Conservation of Cetaceans in the Adriatic Sea
(pdf). United Nations Environment Programme. Mediterranean Action Plan. Regional Activity Centre for Specially Protected Areas. Retrieved on 4 September 2017 Largest of these live normally is the fin whale, and sperm whale, the largest of toothed whales also migrate but less common than fin whales, followed by Cuvier's beaked whales.
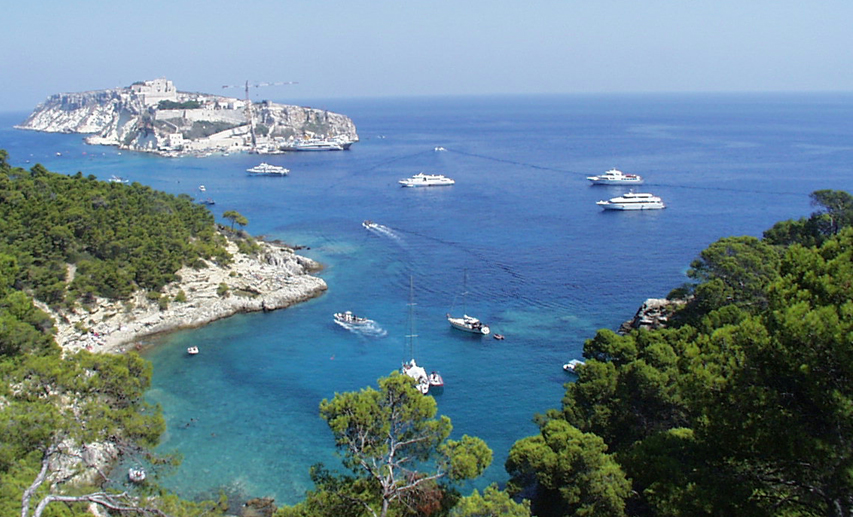 The biodiversity of the Adriatic is relatively high, and several marine protected areas have been established by countries along its coasts. In Italy, these are Miramare in the Gulf of Trieste (in the Northern Adriatic), Torre del Cerrano and Isole Tremiti in the Middle Adriatic basin and Torre Guaceto in southern Apulia. The Miramare protected area was established in 1986 and covers of coast and of sea. The area encompasses of coastline near the Miramare promontory in the Gulf of Trieste. The Torre del Cerrano protected area was created in 2009, extending into the sea and along of coastline. Various zones of the protected area cover of sea surface. The Isole Tremiti reserve has been protected since 1989, while the Tremiti islands themselves are part of the
The biodiversity of the Adriatic is relatively high, and several marine protected areas have been established by countries along its coasts. In Italy, these are Miramare in the Gulf of Trieste (in the Northern Adriatic), Torre del Cerrano and Isole Tremiti in the Middle Adriatic basin and Torre Guaceto in southern Apulia. The Miramare protected area was established in 1986 and covers of coast and of sea. The area encompasses of coastline near the Miramare promontory in the Gulf of Trieste. The Torre del Cerrano protected area was created in 2009, extending into the sea and along of coastline. Various zones of the protected area cover of sea surface. The Isole Tremiti reserve has been protected since 1989, while the Tremiti islands themselves are part of the  There are seven marine protected areas in Croatia:
There are seven marine protected areas in Croatia:  In Slovenia, the marine and coastal protected nature areas are the Sečovlje Salina Landscape Park, Strunjan Landscape Park, Škocjan Inlet Nature Reserve, and the Debeli Rtič, Cape Madona and Lakes in Fiesa natural monuments. The Sečovlje Salina Landscape Park was established in 1990, covers , and includes four nature reserves. In 1993, the area was designated a Ramsar site; it is also a site of international importance for waterbird species. The Strunjan Landscape Park was established in 2004 and comprises two nature reserves. It includes a long cliff, the northernmost Mediterranean salt field and the only Slovenian
In Slovenia, the marine and coastal protected nature areas are the Sečovlje Salina Landscape Park, Strunjan Landscape Park, Škocjan Inlet Nature Reserve, and the Debeli Rtič, Cape Madona and Lakes in Fiesa natural monuments. The Sečovlje Salina Landscape Park was established in 1990, covers , and includes four nature reserves. In 1993, the area was designated a Ramsar site; it is also a site of international importance for waterbird species. The Strunjan Landscape Park was established in 2004 and comprises two nature reserves. It includes a long cliff, the northernmost Mediterranean salt field and the only Slovenian
 Settlements along the Adriatic dating to between 6100 and 5900 BC appear in Albania and Dalmatia on the eastern coast, related to the Cardium pottery culture. During classical antiquity, Illyrians inhabited the eastern Adriatic coast, and the western coast was inhabited by the peoples of Ancient Italy, mainly Etruscans, before the
Settlements along the Adriatic dating to between 6100 and 5900 BC appear in Albania and Dalmatia on the eastern coast, related to the Cardium pottery culture. During classical antiquity, Illyrians inhabited the eastern Adriatic coast, and the western coast was inhabited by the peoples of Ancient Italy, mainly Etruscans, before the
 In the Early Middle Ages, after the Roman Empire's decline, the Adriatic's coasts were ruled by Ostrogoths, Lombards and the
In the Early Middle Ages, after the Roman Empire's decline, the Adriatic's coasts were ruled by Ostrogoths, Lombards and the  The
The
 In 1648, the Holy Roman Empire lost its claim on its former Italian lands, formally ending the Kingdom of Italy; however, its only outlet on the Adriatic Sea, the Duchy of Ferrara, was already lost to the Papal States. The 17th century's final territorial changes were caused by the Morean War, Morean or Sixth Ottoman–Venetian War, when in 1699 Venice slightly enlarged its possessions in Dalmatia. In 1797, the Republic of Venice was abolished after the Napoleonic Wars, French conquest. The Venetian territory was then handed over to Venetian Province, Austria and briefly ruled as part of the Archduchy of Austria. The territory was turned back over to France after the Peace of Pressburg (1805), Peace of Pressburg in 1805 when the territory in the Po Valley#Early modern, Po valley became an integral part of the new Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy. The new kingdom included the province of Romagna, thus removing the Papal State from the Adriatic coast; however, Trieste, Istria and Dalmatia were joined into a set of separate provinces of the First French Empire, French Empire: the Illyrian Provinces. These were created in 1809 through the Treaty of Schönbrunn; they represented the end of Venetian rule on the eastern Adriatic coast, as well as the end of the Republic of Ragusa. The Adriatic Sea was a minor Theater (warfare), theatre in the Napoleonic Wars; the Adriatic campaign of 1807–1814 involved the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British Royal Navy contesting the Adriatic's control by the combined navies of France, Italy and the Kingdom of Naples. During the campaign, the Royal Navy occupied Vis and established its base there in Vis (town), Port St. George. The campaign reached its climax in the 1811 Battle of Lissa (1811), Battle of Lissa, and ended with British and Austrian Empire, Austrian troops seizing the coastal cities on the eastern Adriatic coast from the French. Days before the Battle of Waterloo, the Congress of Vienna awarded the Illyrian Provinces (spanning from the Gulf of Trieste#History, Trieste to the Bay of Kotor) to Austria. The Congress of Vienna also created the Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia which encompassed the city of Venice, the surrounding coast and a substantial hinterland, and was controlled by Austria. In the Apennine peninsula's south, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was formed in 1816 by unifying the kingdoms of Naples and Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily.
In 1648, the Holy Roman Empire lost its claim on its former Italian lands, formally ending the Kingdom of Italy; however, its only outlet on the Adriatic Sea, the Duchy of Ferrara, was already lost to the Papal States. The 17th century's final territorial changes were caused by the Morean War, Morean or Sixth Ottoman–Venetian War, when in 1699 Venice slightly enlarged its possessions in Dalmatia. In 1797, the Republic of Venice was abolished after the Napoleonic Wars, French conquest. The Venetian territory was then handed over to Venetian Province, Austria and briefly ruled as part of the Archduchy of Austria. The territory was turned back over to France after the Peace of Pressburg (1805), Peace of Pressburg in 1805 when the territory in the Po Valley#Early modern, Po valley became an integral part of the new Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy. The new kingdom included the province of Romagna, thus removing the Papal State from the Adriatic coast; however, Trieste, Istria and Dalmatia were joined into a set of separate provinces of the First French Empire, French Empire: the Illyrian Provinces. These were created in 1809 through the Treaty of Schönbrunn; they represented the end of Venetian rule on the eastern Adriatic coast, as well as the end of the Republic of Ragusa. The Adriatic Sea was a minor Theater (warfare), theatre in the Napoleonic Wars; the Adriatic campaign of 1807–1814 involved the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British Royal Navy contesting the Adriatic's control by the combined navies of France, Italy and the Kingdom of Naples. During the campaign, the Royal Navy occupied Vis and established its base there in Vis (town), Port St. George. The campaign reached its climax in the 1811 Battle of Lissa (1811), Battle of Lissa, and ended with British and Austrian Empire, Austrian troops seizing the coastal cities on the eastern Adriatic coast from the French. Days before the Battle of Waterloo, the Congress of Vienna awarded the Illyrian Provinces (spanning from the Gulf of Trieste#History, Trieste to the Bay of Kotor) to Austria. The Congress of Vienna also created the Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia which encompassed the city of Venice, the surrounding coast and a substantial hinterland, and was controlled by Austria. In the Apennine peninsula's south, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was formed in 1816 by unifying the kingdoms of Naples and Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily.
 The process of Italian unification culminated in the Second Italian War of Independence, resulting in the Kingdom of Sardinia annexing all territories along the western Adriatic coast south of Venetia (region), Venetia in 1860, and the 1861 establishment of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946), Kingdom of Italy in its place. The Kingdom of Italy expanded in 1866: it Third Italian War of Independence, annexed Venetia, but Regia Marina, its navy was defeated in the Adriatic near Battle of Lissa (1866), Vis. Following the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 and the Croatian–Hungarian Settlement of 1868, the control of much of the eastern Adriatic coast was redefined. The cisleithanian (Austrian) part of Austria-Hungary spanned from the Austrian Littoral to the Bay of Kotor, with the exception of the Croatian Littoral mainland. In the territory outside the Austrian Littoral, Corpus separatum (Fiume), special status was given to Fiume (modern-day Rijeka) as a separate part of the Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen, Kingdom of Hungary. The rest of the territory was made a part of the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia, which in turn was also in the Transleithanian part of the dual monarchy. The Adriatic coastline controlled by the Ottoman Empire was reduced by the Congress of Berlin in 1878, through recognition of the independence of the Principality of Montenegro, which controlled the coast south of the Bay of Kotor to the Bojana River. The Ottoman Empire lost all territories along the Adriatic following the First Balkan War and consequent Treaty of London (1913), 1913 Treaty of London that established an independent Albania.
The process of Italian unification culminated in the Second Italian War of Independence, resulting in the Kingdom of Sardinia annexing all territories along the western Adriatic coast south of Venetia (region), Venetia in 1860, and the 1861 establishment of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946), Kingdom of Italy in its place. The Kingdom of Italy expanded in 1866: it Third Italian War of Independence, annexed Venetia, but Regia Marina, its navy was defeated in the Adriatic near Battle of Lissa (1866), Vis. Following the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 and the Croatian–Hungarian Settlement of 1868, the control of much of the eastern Adriatic coast was redefined. The cisleithanian (Austrian) part of Austria-Hungary spanned from the Austrian Littoral to the Bay of Kotor, with the exception of the Croatian Littoral mainland. In the territory outside the Austrian Littoral, Corpus separatum (Fiume), special status was given to Fiume (modern-day Rijeka) as a separate part of the Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen, Kingdom of Hungary. The rest of the territory was made a part of the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia, which in turn was also in the Transleithanian part of the dual monarchy. The Adriatic coastline controlled by the Ottoman Empire was reduced by the Congress of Berlin in 1878, through recognition of the independence of the Principality of Montenegro, which controlled the coast south of the Bay of Kotor to the Bojana River. The Ottoman Empire lost all territories along the Adriatic following the First Balkan War and consequent Treaty of London (1913), 1913 Treaty of London that established an independent Albania.
 The
The
 During World War II, the Adriatic saw only Adriatic Campaign of World War II, limited naval action, starting with the Italian invasion of Albania and the joint Axis invasion of Yugoslavia. The latter led to the annexation of a large part of Dalmatia and nearly all the eastern Adriatic islands by Italy and the establishment of two puppet states, the Independent State of Croatia and the Kingdom of Montenegro (1941–1944), Kingdom of Montenegro, which controlled the remainder of the former Yugoslav Adriatic coast. In 1947, after the Armistice between Italy and Allied armed forces and the war's end, Italy (now a 1946 Italian constitutional referendum, republic) and the Allies of World War II, Allies signed the Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947, Treaty of Peace with Italy. The treaty reversed all wartime annexations, guaranteed the independence of Albania, created the Free Territory of Trieste (FTT) as a city-state, and gave Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, communist Yugoslavia most of the Slovenian Littoral, as well as Istria, the islands of Cres, Lastovo and Palagruža, and the cities of Zadar and Rijeka. The FTT was partitioned in 1954: Trieste itself and the area to the North of it were placed under Italian control, while the rest came under Yugoslav control. This arrangement was made permanent in the 1975 Treaty of Osimo.
During the Cold War, the Adriatic Sea became the southernmost flank of the Iron Curtain as Italy joined NATO, while the Warsaw Pact established bases in Albania. After the fall of communism, Breakup of Yugoslavia#Secession and War (1991–1992), Yugoslavia broke apart: Ten-Day War, Slovenia and 1991 Croatian independence referendum, Croatia declared independence in 1991, and Bosnia–Herzegovina followed in 1992, while Montenegro remained in a federation with Serbia, officially called Serbia and Montenegro. The ensuing Croatian War of Independence included limited naval engagements and a blockade of Croatia's coast by the Yugoslav Navy, leading to the Battle of the Dalmatian channels and a later withdrawal of Yugoslav vessels. Montenegro declared itself independent in 2006, effectively land-locking Serbia. The period also saw the Adriatic Sea as the theatre of several NATO operations, including the Operation Maritime Guard, blockade of Yugoslavia, NATO intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina, intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the 1999 NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, 1999 bombing of Yugoslavia.
During World War II, the Adriatic saw only Adriatic Campaign of World War II, limited naval action, starting with the Italian invasion of Albania and the joint Axis invasion of Yugoslavia. The latter led to the annexation of a large part of Dalmatia and nearly all the eastern Adriatic islands by Italy and the establishment of two puppet states, the Independent State of Croatia and the Kingdom of Montenegro (1941–1944), Kingdom of Montenegro, which controlled the remainder of the former Yugoslav Adriatic coast. In 1947, after the Armistice between Italy and Allied armed forces and the war's end, Italy (now a 1946 Italian constitutional referendum, republic) and the Allies of World War II, Allies signed the Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947, Treaty of Peace with Italy. The treaty reversed all wartime annexations, guaranteed the independence of Albania, created the Free Territory of Trieste (FTT) as a city-state, and gave Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, communist Yugoslavia most of the Slovenian Littoral, as well as Istria, the islands of Cres, Lastovo and Palagruža, and the cities of Zadar and Rijeka. The FTT was partitioned in 1954: Trieste itself and the area to the North of it were placed under Italian control, while the rest came under Yugoslav control. This arrangement was made permanent in the 1975 Treaty of Osimo.
During the Cold War, the Adriatic Sea became the southernmost flank of the Iron Curtain as Italy joined NATO, while the Warsaw Pact established bases in Albania. After the fall of communism, Breakup of Yugoslavia#Secession and War (1991–1992), Yugoslavia broke apart: Ten-Day War, Slovenia and 1991 Croatian independence referendum, Croatia declared independence in 1991, and Bosnia–Herzegovina followed in 1992, while Montenegro remained in a federation with Serbia, officially called Serbia and Montenegro. The ensuing Croatian War of Independence included limited naval engagements and a blockade of Croatia's coast by the Yugoslav Navy, leading to the Battle of the Dalmatian channels and a later withdrawal of Yugoslav vessels. Montenegro declared itself independent in 2006, effectively land-locking Serbia. The period also saw the Adriatic Sea as the theatre of several NATO operations, including the Operation Maritime Guard, blockade of Yugoslavia, NATO intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina, intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the 1999 NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, 1999 bombing of Yugoslavia.
 The Adriatic Euroregion was established in Pula in 2006 to promote trans-regional and trans-national cooperation in the Adriatic Sea area and serve as an Adriatic framework to help resolve issues of regional importance. The Adriatic Euroregion consists of 23 members: the Apulia, Molise, Abruzzo, the Marches, Emilia-Romagna, Veneto and Friuli-Venezia Giulia regions of Italy; the municipality of Izola in Slovenia; the Istria County, Istria, Primorje-Gorski Kotar County, Primorje-Gorski Kotar, Lika-Senj County, Lika-Senj, Zadar County, Zadar, Šibenik-Knin County, Šibenik-Knin, Split-Dalmatia County, Split-Dalmatia and Dubrovnik-Neretva County, Dubrovnik-Neretva counties of Croatia; the Herzegovina-Neretva Canton of Bosnia–Herzegovina; the municipalities of Kotor and Tivat in Montenegro; the Fier County, Fier, Vlorë County, Vlorë, Tirana County, Tirana, Shkodër County, Shkodër, Durrës County, Durrës and Lezhë County, Lezhë counties of Albania; and the Greek prefectures of Thesprotia and Corfu (regional unit), Corfu.
The Adriatic Euroregion was established in Pula in 2006 to promote trans-regional and trans-national cooperation in the Adriatic Sea area and serve as an Adriatic framework to help resolve issues of regional importance. The Adriatic Euroregion consists of 23 members: the Apulia, Molise, Abruzzo, the Marches, Emilia-Romagna, Veneto and Friuli-Venezia Giulia regions of Italy; the municipality of Izola in Slovenia; the Istria County, Istria, Primorje-Gorski Kotar County, Primorje-Gorski Kotar, Lika-Senj County, Lika-Senj, Zadar County, Zadar, Šibenik-Knin County, Šibenik-Knin, Split-Dalmatia County, Split-Dalmatia and Dubrovnik-Neretva County, Dubrovnik-Neretva counties of Croatia; the Herzegovina-Neretva Canton of Bosnia–Herzegovina; the municipalities of Kotor and Tivat in Montenegro; the Fier County, Fier, Vlorë County, Vlorë, Tirana County, Tirana, Shkodër County, Shkodër, Durrës County, Durrës and Lezhë County, Lezhë counties of Albania; and the Greek prefectures of Thesprotia and Corfu (regional unit), Corfu.
 The Adriatic Sea fishery's production is distributed among countries in the basin. In 2000, the nominal—on a live weight basis—total landings of all Adriatic fisheries reached . Overfishing is a recognised problem—450 species of fish live in the Adriatic Sea, including 120 species threatened by excessive commercial fishing, a problem exacerbated by pollution and global warming. Overexploited species include common dentex, Scorpaena scrofa, red scorpionfish, Lophius piscatorius, monkfish, John Dory, blue shark, spiny dogfish, Mullet (fish), mullet, Mullus barbatus, red mullet, Nephrops norvegicus, Norway lobster, as well as Merluccius merluccius, European hake, and sardines. Turtles and
The Adriatic Sea fishery's production is distributed among countries in the basin. In 2000, the nominal—on a live weight basis—total landings of all Adriatic fisheries reached . Overfishing is a recognised problem—450 species of fish live in the Adriatic Sea, including 120 species threatened by excessive commercial fishing, a problem exacerbated by pollution and global warming. Overexploited species include common dentex, Scorpaena scrofa, red scorpionfish, Lophius piscatorius, monkfish, John Dory, blue shark, spiny dogfish, Mullet (fish), mullet, Mullus barbatus, red mullet, Nephrops norvegicus, Norway lobster, as well as Merluccius merluccius, European hake, and sardines. Turtles and  In 2007, Croatia's production in live weight reached . In 2006, the total Croatian fisheries production volume was of catch and from marine aquaculture. Croatian fisheries employed approximately 20,000. The 2006 marine capture catch in Croatian waters consisted of sardines (44.8%), anchovy, anchovies (31.3%), tunas (2.7%), other pelagic fish (4.8%), hake (2.4%), Mullet (fish), mullet (2.1%), other demersal fish (8.3%), crustaceans (largely lobster and ''Nephrops norvegicus'') (0.8%), shellfish (largely oysters and mussels) (0.3%), cuttlefish (0.6%), squids (0.2%) and octopuses and other cephalopods (1.6%). Croatian marine aquaculture production consisted of tuna (47.2%), oysters and mussels (28.2% combined) and Bass (fish), bass and bream (24.6% combined).
In 2007, Albanian fisheries production amounted to , including aquaculture production, which reached in 2006. At the same time, Slovenian fisheries produced a total of with 55% of the production volume originating in aquaculture, representing the highest ratio in the Adriatic. Finally, the Montenegrin fisheries production stood at in 2006, with only 11 tonnes coming from aquaculture. In 2007, the fisheries production in Bosnia–Herzegovina reached volume of and in Slovenia.
In 2007, Croatia's production in live weight reached . In 2006, the total Croatian fisheries production volume was of catch and from marine aquaculture. Croatian fisheries employed approximately 20,000. The 2006 marine capture catch in Croatian waters consisted of sardines (44.8%), anchovy, anchovies (31.3%), tunas (2.7%), other pelagic fish (4.8%), hake (2.4%), Mullet (fish), mullet (2.1%), other demersal fish (8.3%), crustaceans (largely lobster and ''Nephrops norvegicus'') (0.8%), shellfish (largely oysters and mussels) (0.3%), cuttlefish (0.6%), squids (0.2%) and octopuses and other cephalopods (1.6%). Croatian marine aquaculture production consisted of tuna (47.2%), oysters and mussels (28.2% combined) and Bass (fish), bass and bream (24.6% combined).
In 2007, Albanian fisheries production amounted to , including aquaculture production, which reached in 2006. At the same time, Slovenian fisheries produced a total of with 55% of the production volume originating in aquaculture, representing the highest ratio in the Adriatic. Finally, the Montenegrin fisheries production stood at in 2006, with only 11 tonnes coming from aquaculture. In 2007, the fisheries production in Bosnia–Herzegovina reached volume of and in Slovenia.
File:Beach of Rimini (14-07-2012).jpg, Rimini is a major seaside tourist resort in Italy
File:Triestebarcolana.jpg, The Barcolana regatta in Trieste, Italy, was named "the greatest sailing race" by the Guinness World Record for its 2,689 boats and over 16,000 sailors on the starting line.
File:Ulcinj, Montenegro - Sept. 2010.jpg, View of Ulcinj, Montenegro
File:Golden Cape.jpg, The Zlatni Rat (Golden Cape) on the island of Brač
File:Split center from the air 1.jpg, The Palace of the Emperor Diocletian in
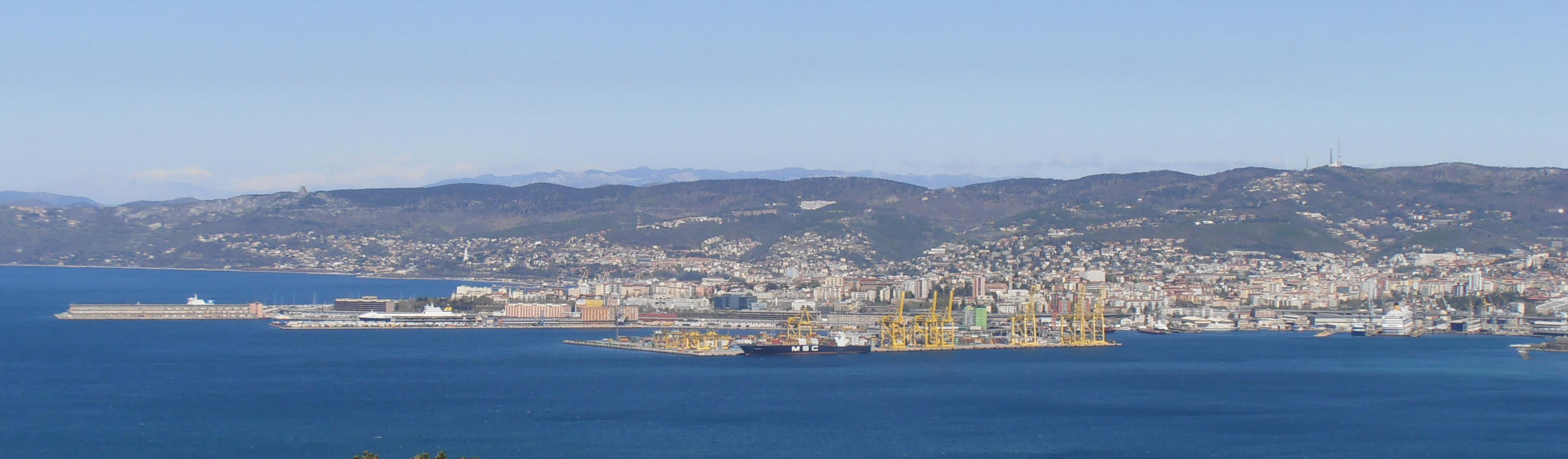 The largest passenger ports in the Adriatic are the Port of Split (the largest Croatian passenger port) and ports in Ancona#Transportation, Ancona (the largest Italian passenger seaport in the Adriatic). The largest seaport in Montenegro is the Port of Bar. In 2010, the Northern Adriatic seaports of Trieste, Venice, Ravenna, Koper and Rijeka founded the North Adriatic Ports Association to position themselves more favourably in the EU's transport systems.
The port of Trieste is of particular importance for Central Europe because this is where the Transalpine Pipeline begins, supplying 100 percent of southern Germany, 90 percent of Austria and 50 percent of the Czech Republic with crude oil.
The largest passenger ports in the Adriatic are the Port of Split (the largest Croatian passenger port) and ports in Ancona#Transportation, Ancona (the largest Italian passenger seaport in the Adriatic). The largest seaport in Montenegro is the Port of Bar. In 2010, the Northern Adriatic seaports of Trieste, Venice, Ravenna, Koper and Rijeka founded the North Adriatic Ports Association to position themselves more favourably in the EU's transport systems.
The port of Trieste is of particular importance for Central Europe because this is where the Transalpine Pipeline begins, supplying 100 percent of southern Germany, 90 percent of Austria and 50 percent of the Czech Republic with crude oil.
File:Durres harbor from the sea.jpg, Port of Durrës, the largest port in Albania
File:Luka brajdica 040408.jpg, Port of Rijeka, the largest cargo port in Croatia
File:Koper (39).jpg, Port of Koper, the largest port in
Region 5 – Western Africa, Mediterranean, Black Sea Nautical Charts
from the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency
Nautical Chart 54131 (Adriatic Sea)
from the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency
the seashore of our posterity
nbsp;– video recording of Albanian, Croatian, and Montenegrin coasts {{good article Adriatic Sea, European seas Marginal seas of the Mediterranean Seas of Italy Bodies of water of Croatia Seas of Albania Bodies of water of Montenegro Bodies of water of Slovenia Bodies of water of Bosnia and Herzegovina Bodies of water of the Slovene Littoral Geography of Southern Europe Geography of Central Europe
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the northwest and the Po Valley. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Montenegro, and Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
.
The Adriatic contains more than 1,300 islands, mostly located along the Croatian part of its eastern coast. It is divided into three basins, the northern being the shallowest and the southern being the deepest, with a maximum depth of . The Otranto Sill, an underwater ridge, is located at the border between the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. The prevailing currents flow counterclockwise from the Strait of Otranto, along the eastern coast and back to the strait along the western (Italian) coast. Tidal movements in the Adriatic are slight, although larger amplitudes are known to occur occasionally. The Adriatic's salinity is lower than the Mediterranean's because the Adriatic collects a third of the fresh water flowing into the Mediterranean, acting as a dilution basin. The surface water temperatures generally range from in summer to in winter, significantly moderating the Adriatic Basin
The Adriatic Abyssal Plain, more commonly referred to as the Adriatic Basin, is an oceanic basin under the Adriatic Sea. The Adriatic Sea's average depth is , and its maximum depth is ; however, the North Adriatic basin rarely exceeds a depth of ...
's climate.
The Adriatic Sea sits on the Apulian or Adriatic Microplate, which separated from the African Plate
The African Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes much of the continent of Africa (except for its easternmost part) and the adjacent oceanic crust to the west and south. It is bounded by the North American Plate and South American Plate ...
in the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
era. The plate's movement contributed to the formation of the surrounding mountain chains and Apennine tectonic uplift after its collision
In physics, a collision is any event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in a relatively short time. Although the most common use of the word ''collision'' refers to incidents in which two or more objects collide with great fo ...
with the Eurasian plate. In the Late Oligocene
The Chattian is, in the geologic timescale, the younger of two ages or upper of two stages of the Oligocene Epoch/ Series. It spans the time between . The Chattian is preceded by the Rupelian and is followed by the Aquitanian (the lowest stage ...
, the Italian Peninsula first formed, separating the Adriatic Basin from the rest of the Mediterranean. All types of sediment are found in the Adriatic, with the bulk of the material transported by the Po and other rivers on the western coast. The western coast is alluvial or terraced
In agriculture, a terrace is a piece of sloped plane that has been cut into a series of successively receding flat surfaces or platforms, which resemble steps, for the purposes of more effective farming. This type of landscaping is therefore ...
, while the eastern coast is highly indented with pronounced karstification. There are dozens of marine protected areas in the Adriatic, designed to protect the sea's karst habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
s and biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
. The sea is abundant in flora and fauna—more than 7,000 species are identified as native to the Adriatic, many of them endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
, rare and threatened ones.
The Adriatic's shores are populated by more than 3.5 million people; the largest cities are Bari, Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
, Trieste and Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertai ...
. The earliest settlements on the Adriatic shores were Etruscan, Illyrian, and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
. By the 2nd century BC, the shores were under Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
's control. In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the Adriatic shores and the sea itself were controlled, to a varying extent, by a series of states—most notably the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, the Croatian Kingdom, the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
, the Habsburg monarchy and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. The Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
resulted in the First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental E ...
gaining coastal control and the British effort to counter the French in the area, ultimately securing most of the eastern Adriatic shore and the Po Valley for Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. Following Italian unification, the Kingdom of Italy started an eastward expansion that lasted until the 20th century. Following World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and the collapse of Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire, the entire eastern coast's control passed to Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
and Albania, except for Trieste and surrounding area which remained under Italian control. The former disintegrated during the 1990s, resulting in four new states on the Adriatic coast. Italy and Yugoslavia agreed on their maritime boundaries by 1975 and this boundary is recognised by Yugoslavia's successor states, but the maritime boundaries between Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro are still disputed. Italy and Albania agreed on their maritime boundary in 1992.
Fisheries and tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
are significant sources of income all along the Adriatic coast. Adriatic Croatia's tourism industry has grown faster economically than the rest of the Adriatic Basin
The Adriatic Abyssal Plain, more commonly referred to as the Adriatic Basin, is an oceanic basin under the Adriatic Sea. The Adriatic Sea's average depth is , and its maximum depth is ; however, the North Adriatic basin rarely exceeds a depth of ...
's. Maritime transport
Maritime transport (or ocean transport) and hydraulic effluvial transport, or more generally waterborne transport, is the transport of people ( passengers) or goods (cargo) via waterways. Freight transport by sea has been widely used throu ...
is also a significant branch of the area's economy—there are 19 seaports in the Adriatic that each handle more than a million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s of cargo per year. The largest Adriatic seaport by annual cargo turnover is the Port of Trieste, while the Port of Split is the largest Adriatic seaport by passengers served per year.
Name
The origins of the name ''Adriatic'' are linked to the Etruscan settlement of Adria, which probably derives its name from Illyrian ''adur'' 'water, sea'. Inclassical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, the sea was known as ''Mare Adriaticum'' (''Mare Hadriaticum'', also sometimes simplified to ''Adria'') or, less frequently, as ''Mare Superum'' ' heupper sea'. The two terms were not synonymous, however. ''Mare Adriaticum'' generally corresponds to the Adriatic Sea's extent, spanning from the Gulf of Venice to the Strait of Otranto. That boundary became more consistently defined by Roman authors – early Greek sources place the boundary between the Adriatic and Ionian seas at various places ranging from adjacent to the Gulf of Venice to the southern tip of the Peloponnese, eastern shores of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
and western shores of Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
. ''Mare Superum'' on the other hand normally encompassed both the modern Adriatic Sea and the sea off the Apennine peninsula's southern coast, as far as the Strait of Sicily. Another name used in the period was ''Mare Dalmaticum'', applied to waters off the coast of Dalmatia or Illyricum.
The names for the sea in the languages of the surrounding countries include sq, Deti Adriatik; egl, Mèr Adriatic; fur, Mâr Adriatic; gr, Αδριατική θάλασσα – ''Adriatikí thálassa''; ruo, Marea Adriatică; it, Mare Adriatico; sh, Jadransko more, Јадранско море; sl, Jadransko morje; vec, Mar Adriàtico. In Serbo-Croatian and Slovene, the sea is often referred to as simply ''Jadran''.
Geography
The Adriatic Sea is a semi-enclosed sea, bordered in the southwest by the Apennine or Italian Peninsula, in the northwest by the Italian regions of Veneto and Friuli-Venezia Giulia, and in the northeast bySlovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
, Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and Albania—the Balkan peninsula. In the southeast, the Adriatic Sea connects to the Ionian Sea at the wide Strait of Otranto. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) defines the boundary between the Adriatic and the Ionian seas as a line running from the Butrinto River's mouth (latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
39°44'N) in Albania to the Karagol Cape in Corfu, through this island to the Kephali Cape (these two capes are in latitude 39°45'N), and on to the Santa Maria di Leuca Cape (latitude 39°48'N). It extends from the northwest to the southeast and is wide. It covers and has a volume of . The Adriatic extends northwest from 40° to 45°47' north, representing the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
's northernmost portion. The sea is geographically divided into the Northern Adriatic, Central (or Middle) Adriatic, and Southern Adriatic.
The Adriatic Sea drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
encompasses , yielding a land–sea ratio of 1.8. The drainage basin's mean elevation is above sea level, with a mean slope of 12.1°. Major rivers discharging into the Adriatic include the Po, Soča
The Soča ( in Slovene) or Isonzo ( in Italian; other names fur, Lusinç, german: Sontig, la, Aesontius or ') is a long river that flows through western Slovenia () and northeastern Italy ().
An Alpine river in character, its source lies i ...
, Krka, Neretva, Drin, Bojana, and Vjosë. In the late 19th century, Austria-Hungary established a geodetic
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivale ...
network with an elevation benchmark using the average Adriatic Sea level at the Sartorio pier in Trieste, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. The benchmark was subsequently retained by Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, adopted by Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, and retained by the states that emerged after its dissolution. In 2016, Slovenia adopted a new elevation benchmark referring to the upgraded tide gauge
A tide gauge is a device for measuring the change in sea level relative to a vertical datum.
It its also known as mareograph, marigraph, sea-level recorder and limnimeter.
When applied to freshwater continental water bodies, the instrument ma ...
station in the coastal town of Koper.
The Alps, which also have a large meteorological impact on the Mediterranean, touch the Adriatic in the area around Trieste towards Duino and Barcola
Barcola is a maritime neighbourhood of Trieste, Italy. It is a popular tourist place with beaches and long promenades, near the Habsburg-established Miramare Castle.
Barcola is highly valued for the high quality of life and the free access to the ...
.

Šibenik
Šibenik () is a historic city in Croatia, located in central Dalmatia, where the river Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea. Šibenik is a political, educational, transport, industrial and tourist center of Šibenik-Knin County, and is also the ...
as well.
 It is estimated that the Adriatic's entire volume is exchanged through the Strait of Otranto in 3.4±0.4 years, a comparatively short period. (For instance, approximately 500 years are necessary to exchange all the
It is estimated that the Adriatic's entire volume is exchanged through the Strait of Otranto in 3.4±0.4 years, a comparatively short period. (For instance, approximately 500 years are necessary to exchange all the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
's water.) This short period is particularly important as the rivers flowing into the Adriatic discharge up to . This rate of discharge amounts to 0.5% of the total Adriatic Sea volume, or a layer of water each year. The greatest portion of the discharge from any single river comes from the Po (28%), with an average discharge from it alone of . In terms of the annual total discharge into the entire Mediterranean Sea, the Po is ranked second, followed by the Neretva and Drin, which rank as third and fourth. Another significant contributor of freshwater to the Adriatic is the submarine groundwater discharge through submarine springs ( hr, vrulja); it is estimated to comprise 29% of the total water flux into the Adriatic. The submarine springs include thermal springs, discovered offshore near the town of Izola. The thermal spring water is rich with hydrogen sulfide, has a temperature of , and has enabled the development of specific ecosystems. The inflow of freshwater, representing a third of the freshwater volume flowing into the Mediterranean, makes the Adriatic a dilution basin for the Mediterranean Sea. The Middle and South Adriatic Gyres (SAG), are significant cyclonic circulation features, with the former being intermittent and the latter permanent. The SAG measures in diameter. It contributes to the flow of bottom water
Bottom water is the lowermost water mass in a water body, by its bottom, with distinct characteristics, in terms of physics, chemistry, and ecology.
Oceanography
Bottom water consists of cold, dense water near the ocean floor. This water is char ...
from the Adriatic to the Levantine Basin through the Ionian Sea. Through that process, the Adriatic Sea produces most of the East Mediterranean deep water.
Temperature and salinity
The Adriatic's surface temperature usually ranges from in the summer, or in the winter, except along the western Adriatic coast's northern part, where it drops to in the winter. The distinct seasonal temperature variations, with a longitudinal gradient in the Northern and transversal gradient in the Middle and Southern Adriatic, are attributed to the continental characteristics of the Adriatic Sea: it is shallower and closer to land than are oceans. During particularly cold winters, sea ice may appear in the Adriatic's shallow coastal areas, especially in the Venetian Lagoon but also in isolated shallows as far south asTisno
Tisno is a town and municipality in Šibenik-Knin County, Croatia.
Etymology
Tisno was named after the Croatian ikavian word ''tisno'' which means strait, which describes its location at the narrow strait separating the island of Murter from th ...
(south of Zadar). The Southern Adriatic is about 8 to 10 °C (14 to 18 °F) warmer during the winter than the more northerly regions. The Adriatic's salinity variation over the year is likewise distinct: it ranges between 38 and 39 PSUs. The southern Adriatic is subjected to saltier water from the Levantine Basin.
Climate
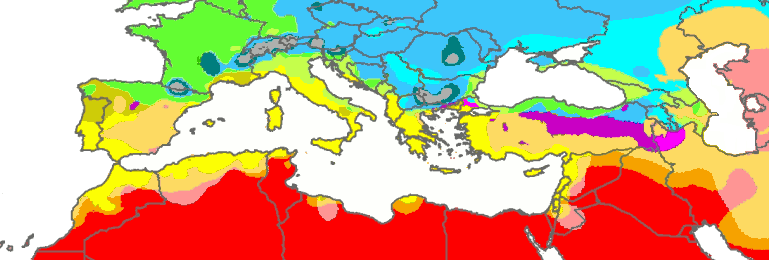
 According to the
According to the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
, the upper half of the Adriatic is classified as humid subtropical climate (''Cfa''), with wetter summers and colder and drier winters, and the southern Adriatic are classified as hot-summer Mediterranean climate (''Csa''). The air temperature can fluctuate by about during a season.
The predominant winter winds are the bora and sirocco
Sirocco ( ), scirocco, or, rarely, siroc (see below) is a Mediterranean wind that comes from the Sahara and can reach hurricane speeds in North Africa and Southern Europe, especially during the summer season.
Names
''Sirocco'' derives from ...
(called ''jugo'' along the eastern coast). The bora is significantly conditioned by wind gaps in the Dinaric Alps bringing cold and dry continental air; it reaches peak speeds in the areas of Trieste, Senj
Senj (; it, Segna, la, Senia, Hungarian and german: Zengg) is a town on the upper Adriatic coast in Croatia, in the foothills of the Mala Kapela and Velebit mountains.
The symbol of the town is the Nehaj Fortress ( hr, Tvrđava Nehaj) whic ...
, and Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertai ...
, with gusts of up to . The sirocco brings humid and warm air, often carrying Saharan sand causing rain dust.
Population
On the Adriatic Sea's coasts and islands, there are numerous small settlements and a number of larger cities. Among the largest are (counterclockwise) Trieste, Venice, Rimini, Ancona, Pescara and Bari in Italy; Vlorë and Durrës in Albania; Split, Zadar and Rijeka in Croatia; Koper in Slovenia. In total, more than 3.5 million people live on the Adriatic coasts. There are also some larger cities that are located very near the coast, such as the Italian cities of Ravenna and Lecce.Coastal management

Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
, which was originally built on islands off the coast, is most at risk due to subsidence, but the threat is present in the Po delta as well. The causes are a decrease in sedimentation
Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to the ...
rate due to loss of sediment behind dams, the deliberate excavation of sand for industrial purposes, agricultural use of water, and removal of ground water.
The sinking of Venice slowed after artesian wells
An artesian aquifer is a confined aquifer containing groundwater under positive pressure. An artesian aquifer has trapped water, surrounded by layers of impermeable rock or clay, which apply positive pressure to the water contained within th ...
were banned in the 1960s, but the city remains threatened by the ''acqua alta'' floods. Recent studies have suggested that the city is no longer sinking, but a state of alert remains in place. In May 2003, then-Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi inaugurated the MOSE project Mose, Mosè, or Mosé is a given name which may refer to:
People In religion
* Mose Durst, former president of the Unification Church of the United States
* Mosé Higuera, Colombian Catholic bishop
* Mosè Tovini, Italian Roman Catholic priest
I ...
( it, Modulo Sperimentale Elettromeccanico), an experimental model for evaluating the performance of inflatable gates. The project proposes laying a series of 79 inflatable pontoons across the sea bed at the three entrances to the Venetian Lagoon. When tides are predicted to rise above , the pontoons will be filled with air and block the incoming water from the Adriatic Sea. This engineering work was due to be completed by 2014, but as of November 2020 is expected to be completed in 2021.
Implemented for the first time on October 3, 2020, the barriers are made to seal off three inlets that lead to the Venetian Lagoon and counteract floods of up to ten feet; in addition to protecting the city from flooding, the barrier system is also intended to stabilize Venice's water levels so as to minimize erosion of the brick walls and, subsequently, the foundations of various buildings in the city. However, concern has been raised regarding the frequency of its use - while only necessary a few days a year, the worst-case sea level rise scenario between 2050 and 2100 would prompt deployment up to 187 days a year, essentially cutting off the Venetian Lagoon from the Adriatic Sea. Among other possible adverse effects, this can be expected to lower the lagoon's oxygen levels and trap pollution inside of the city.
Geology
 Geophysical and geological information indicate that the Adriatic Sea and the Po Valley are associated with a tectonic
Geophysical and geological information indicate that the Adriatic Sea and the Po Valley are associated with a tectonic microplate
A microplate, also known as a microtiter plate (''Microtiter'' is a registered trademark in the United States, therefore it should not be used generically without attribution), microwell plate or multiwell, is a flat plate with multiple "wells" ...
—identified as the Apulian or Adriatic Plate—that separated from the African Plate
The African Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes much of the continent of Africa (except for its easternmost part) and the adjacent oceanic crust to the west and south. It is bounded by the North American Plate and South American Plate ...
during the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
era. This separation began in the Middle and Late Triassic, when limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
began to be deposited in the area. Between the Norian and Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
, the Adriatic and Apulia Carbonate Platforms formed as a thick series of carbonate sediments ( dolomites and limestones), up to deep. Remnants of the former are found in the Adriatic Sea, as well as in the southern Alps and the Dinaric Alps
The Dinaric Alps (), also Dinarides, are a mountain range in Southern and Southcentral Europe, separating the continental Balkan Peninsula from the Adriatic Sea. They stretch from Italy in the northwest through Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herz ...
, and remnants of the latter are seen as the Gargano Promontory and the Maiella
The Maiella (or Majella) is a massif in the Central Apennines, in Abruzzo, central Italy.
Geography
The mountain is located at the boundary between the provinces of Chieti, Pescara and L'Aquila.
The highest peak is Monte Amaro at 2,793&n ...
mountain. In the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
and early Oligocene, the plate moved north and north-east, contributing to the Alpine orogeny (along with the African and Eurasian Plates' movements) via the tectonic uplift
Tectonic uplift is the geologic uplift of Earth's surface that is attributed to plate tectonics. While isostatic response is important, an increase in the mean elevation of a region can only occur in response to tectonic processes of crustal th ...
of the Dinarides and Alps. In the Late Oligocene
The Chattian is, in the geologic timescale, the younger of two ages or upper of two stages of the Oligocene Epoch/ Series. It spans the time between . The Chattian is preceded by the Rupelian and is followed by the Aquitanian (the lowest stage ...
, the motion was reversed and the Apennine Mountains' orogeny took place. An unbroken zone of increased seismic activity borders the Adriatic Sea, with a belt of thrust faults generally oriented in the northeast–southwest direction on the east coast and the northeast–southwest normal faults in the Apennines, indicating an Adriatic counterclockwise rotation.
An active fault has been identified to the northwest of Dubrovnik, adding to the Dalmatian islands as the Eurasian Plate slides over the Adriatic microplate. Furthermore, the fault causes the Apennine peninsula's southern tip to move towards the opposite shore by about per year. If this movement continues, the seafloor will be completely consumed and the Adriatic Sea closed off in 50–70 million years. In the Northern Adriatic, the coast of the Gulf of Trieste
The Gulf of Trieste ( it, Golfo di Trieste, sl, Tržaški zaliv, hr, Tršćanski zaljev, german: Golf von Triest) is a very shallow bay of the Adriatic Sea, in the extreme northern part of the Adriatic Sea. It is part of the Gulf of Venice an ...
and western Istria is gradually subsiding, having sunk about in the past two thousand years. In the Middle Adriatic Basin, there is evidence of Permian volcanism in the area of Komiža
Komiža (; it, Comisa) is a Croatian coastal town lying on the western coast of the island of Vis in the central part of the Adriatic Sea. As of 2011 Komiža proper has a population of 1,397 while the entire municipality has 1,526 residents.
Ko ...
on the island of Vis and the volcanic islands of Jabuka and Brusnik. Earthquakes have been observed in the region since the earliest historical records. A recent strong earthquake in the region was the 1979 Montenegro earthquake
The 1979 Montenegro earthquake occurred on 15 April at 06:19 UTC with a moment magnitude of 6.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). It was the most devastating earthquake in SR Montenegro, then part of Yugoslavia,(Montenegrin)Crn ...
, measuring 7.0 on the Richter scale. Historical earthquakes in the area include the 1627 Gargano peninsula and the 1667 Dubrovnik earthquakes, both followed by strong tsunamis. In the last 600 years, fifteen tsunamis have occurred in the Adriatic Sea.
Seafloor sediment
 All types of
All types of seafloor sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, main ...
s are found in the Adriatic Sea. The Northern Adriatic's comparatively shallow seabed is characterised by relict sand (from times when the water level was lower and the area was a sandy beach), while a muddy bed is typical at depths below . There are five geomorphological units in the Adriatic: the Northern Adriatic (up to deep); the North Adriatic islands area protected against sediments filling it in by outer islands (pre-Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
karst relief); the Middle Adriatic islands area (large Dalmatian islands); the Middle Adriatic (characterized by the Middle Adriatic Depression); and the Southern Adriatic consisting of a coastal shelf and the Southern Adriatic Depression. Sediments deposited in the Adriatic Sea today generally come from the northwest coast, being carried by the Po, Reno, Adige
The Adige (; german: Etsch ; vec, Àdexe ; rm, Adisch ; lld, Adesc; la, Athesis; grc, Ἄθεσις, Áthesis, or , ''Átagis'') is the second-longest river in Italy, after the Po. It rises near the Reschen Pass in the Vinschgau in the pro ...
, Brenta, Tagliamento
The Tagliamento () is a braided river in north-east Italy, flowing from the Alps to the Adriatic Sea at a point between Trieste and Venice.
The Tagliamento river is considered as the last morphologically intact river in the Alps. (Its c ...
, Piave and Soča rivers. The volume of sediments carried from the eastern shore by the Rječina, Zrmanja
Zrmanja (, it, Zermagna) is a river in southern Lika and northern Dalmatia, Croatia. It is long and its basin covers an area of .
It was known to the ancient Romans as ''Tedanius''. The spring of Zrmanja is located in southern part of Lika unde ...
, Krka, Cetina
Cetina () is a river in southern Croatia. It has a length of and its basin covers an area of . From its source, Cetina descends from an elevation of above sea level to the Adriatic Sea. It is the most water-rich river in Dalmatia.Naklada Naprijed ...
, Ombla, Dragonja
The Dragonja (; it, Dragogna) is a long river in the northern part of the Istrian peninsula. It is a meandering river with a very branched basin and a small quantity of water. It has a pluvial regime and often dries up in summer. It features ...
, Mirna
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miR ...
, Raša and Neretva rivers is negligible, because these sediments are mostly deposited at the river mouths. The Adriatic's western shores are largely either alluvial or terraced
In agriculture, a terrace is a piece of sloped plane that has been cut into a series of successively receding flat surfaces or platforms, which resemble steps, for the purposes of more effective farming. This type of landscaping is therefore ...
, whereas the eastern shores are predominantly rocky, except for the southernmost part of the shore located in Albania that consists of sandy coves and rocky capes.
Coasts
 The eastern Adriatic shore's Croatian part is the most indented Mediterranean coastline. Most of the eastern coast is characterised by a karst topography, developed from the Adriatic Carbonate Platform's exposure to weathering. Karstification there largely began after the Dinarides' final uplift in the Oligocene and the
The eastern Adriatic shore's Croatian part is the most indented Mediterranean coastline. Most of the eastern coast is characterised by a karst topography, developed from the Adriatic Carbonate Platform's exposure to weathering. Karstification there largely began after the Dinarides' final uplift in the Oligocene and the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
, when carbonate deposits were exposed to atmospheric effects; this extended to the level of below the present sea level, exposed during the Last Glacial Maximum. It is estimated that some karst formations are from earlier sea level drops, most notably the Messinian salinity crisis
The Messinian salinity crisis (MSC), also referred to as the Messinian event, and in its latest stage as the Lago Mare event, was a geological event during which the Mediterranean Sea went into a cycle of partial or nearly complete desiccation (d ...
. Similarly, karst developed in Apulia from the Apulian Carbonate Platform.
The largest part of the eastern coast consists of carbonate rocks, while flysch
Flysch () is a sequence of sedimentary rock layers that progress from deep-water and turbidity flow deposits to shallow-water shales and sandstones. It is deposited when a deep basin forms rapidly on the continental side of a mountain building epi ...
(a particular type of sedimentary rock) is significantly represented in the Gulf of Trieste coast, especially along Slovenia's coast where the Strunjan cliff—the highest cliff on the entire Adriatic and the only one of its type on the eastern Adriatic coast—is located, on the Kvarner Gulf coast opposite Krk, and in Dalmatia north of Split. Rocks of the same type are found in Albania and on the western Adriatic coast.
There are alternations of maritime and alluvial sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
s occurring in the Po Valley, at the Adriatic's north-west coast, and as far west as Piacenza
Piacenza (; egl, label= Piacentino, Piaṡëinsa ; ) is a city and in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy, and the capital of the eponymous province. As of 2022, Piacenza is the ninth largest city in the region by population, with over ...
, dating to the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
as the sea advanced and receded over the valley. An advance began after the Last Glacial Maximum, which brought the Adriatic to a high point at about 5,500 years ago. Since then, the Po delta has been prograding (expanding/extending). The rate of coastal zone progradation between 1000 BC and 1200 AD was per year. In the 12th century, the delta advanced at a rate of per year. In the 17th century, the delta began to become a human-controlled environment, as the excavation of artificial channels started; the channels and new distributaries of the Po have been prograding at rates of per year or more since then. There are more than 20 other rivers flowing into the Adriatic Sea in Italy alone, also forming alluvial coastlines, including the lagoons of Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
, Grado and Caorle. There are smaller eastern Adriatic alluvial coasts—in the deltas of the Dragonja, Bojana and Neretva rivers.
Biogeography and ecology
The Adriatic Sea is a unique water body in respect of its overallbiogeochemical
Biogeochemistry is the scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natural environment (including the biosphere, the cryosphere, th ...
physiognomy. It exports inorganic nutrients and imports particulate organic carbon and nitrogen through the Strait of Otranto—acting as a mineralization site. The exchange of the substances is made more complex by bathymetry of the Adriatic Sea—75% of water flowing north through the strait recirculates at the Palagruža Sill and North Adriatic adds no more than 3 – 4% of water to the South Adriatic. This is reflected in its biogeography and ecology, and particularly in the composition and properties of its ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
s. Its main biogeographic units are the Northern Adriatic, the Central Adriatic, and the Southern Adriatic.
Flora and fauna
The unique nature of the Adriatic gives rise to an abundance ofendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
flora and fauna. The Croatian National Biodiversity Strategy Action Plan identified more than 7,000 animal and plant species in the Adriatic Sea. The Central Adriatic is especially abundant in endemic plant species, with 535 identified species of green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combi ...
, brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
and red algae. Four out of five Mediterranean seagrass species are found in the Adriatic Sea. The most common species are '' Cymodocea nodosa'' and '' Zostera noltii'', while '' Zostera marina'' and ''Posidonia oceanica
''Posidonia oceanica'', commonly known as Neptune grass or Mediterranean tapeweed, is a seagrass species that is endemic to the Mediterranean Sea. It forms large underwater meadows that are an important part of the ecosystem. The fruit is free f ...
'' are comparatively rare.
A number of rare and threatened species are also found along the Adriatic's eastern coast; it is relatively clearer and less polluted than the western Adriatic coast—in part because the sea currents flow through the Adriatic in a counterclockwise direction, thus bringing clearer waters up the eastern coast and returning increasingly polluted water down the western coast. This circulation has significantly contributed to the biodiversity of the countries along the eastern Adriatic coast; the common bottlenose dolphin
The common bottlenose dolphin or Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatus'') is a wide-ranging marine mammal of the family Delphinidae. The common bottlenose dolphin is a very familiar dolphin due to the wide exposure it gets in captiv ...
is frequent in the eastern coast's waters only, and the Croatian coast provides refuge for the critically endangered monk seal and sea turtles. Recent studies revealed that cetaceans and other marine megafaunas, that were once thought to be vagrants to Adriatic Sea, migrate and live in the semi-closed sea on larger scales.D.
Holcer D.. Fortuna M.C.. Mackelworth C. P.. 2014Status and Conservation of Cetaceans in the Adriatic Sea
(pdf). United Nations Environment Programme. Mediterranean Action Plan. Regional Activity Centre for Specially Protected Areas. Retrieved on 4 September 2017 Largest of these live normally is the fin whale, and sperm whale, the largest of toothed whales also migrate but less common than fin whales, followed by Cuvier's beaked whales.
Basking shark
The basking shark (''Cetorhinus maximus'') is the second-largest living shark and fish, after the whale shark, and one of three plankton-eating shark species, along with the whale shark and megamouth shark. Adults typically reach in leng ...
s and manta rays are some of migrant species to the sea. Historical presences of depleted or extinct species such as North Atlantic right whale
The North Atlantic right whale (''Eubalaena glacialis'') is a baleen whale, one of three right whale species belonging to the genus '' Eubalaena'', all of which were formerly classified as a single species. Because of their docile nature, their s ...
s (extinct or functionally extinct), Atlantic gray whales (extinct), and humpback whales have been speculated as well.
Tuna has been caught by the locals in the upper Adriatic for thousands of years. The very large schools consisted mainly of little tunny and moved as far as the Gulf of Trieste
The Gulf of Trieste ( it, Golfo di Trieste, sl, Tržaški zaliv, hr, Tršćanski zaljev, german: Golf von Triest) is a very shallow bay of the Adriatic Sea, in the extreme northern part of the Adriatic Sea. It is part of the Gulf of Venice an ...
. However, increasing fishing prevented the migration of large schools of fish to the north. The last major tuna catch was made there in 1954 by the fishermen from Santa Croce, Contovello and Barcola
Barcola is a maritime neighbourhood of Trieste, Italy. It is a popular tourist place with beaches and long promenades, near the Habsburg-established Miramare Castle.
Barcola is highly valued for the high quality of life and the free access to the ...
.
The Northern Adriatic in particular is rich in endemic fish fauna. Around thirty species of fish are found in only one or two countries bordering the Adriatic Sea. These are particularly due to or dependent upon the karst morphology of the coastal or submarine topography; this includes inhabiting subterranean habitats, karst rivers, and areas around freshwater springs. There are 45 known subspecies endemic to the Adriatic's coasts and islands. In the Adriatic, there are at least 410 species and subspecies of fish, representing approximately 70% of Mediterranean taxa, with at least 7 species endemic to the Adriatic. Sixty-four known species are threatened with extinction, largely because of overfishing. Only a small fraction of the fish found in the Adriatic are attributed to recent processes such as Lessepsian migration
The Lessepsian migration (also called Erythrean invasion) is the migration of marine species across the Suez Canal, usually from the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea, and more rarely in the opposite direction. When the canal was completed in 18 ...
, and escape from mariculture.
Protected areas
 The biodiversity of the Adriatic is relatively high, and several marine protected areas have been established by countries along its coasts. In Italy, these are Miramare in the Gulf of Trieste (in the Northern Adriatic), Torre del Cerrano and Isole Tremiti in the Middle Adriatic basin and Torre Guaceto in southern Apulia. The Miramare protected area was established in 1986 and covers of coast and of sea. The area encompasses of coastline near the Miramare promontory in the Gulf of Trieste. The Torre del Cerrano protected area was created in 2009, extending into the sea and along of coastline. Various zones of the protected area cover of sea surface. The Isole Tremiti reserve has been protected since 1989, while the Tremiti islands themselves are part of the
The biodiversity of the Adriatic is relatively high, and several marine protected areas have been established by countries along its coasts. In Italy, these are Miramare in the Gulf of Trieste (in the Northern Adriatic), Torre del Cerrano and Isole Tremiti in the Middle Adriatic basin and Torre Guaceto in southern Apulia. The Miramare protected area was established in 1986 and covers of coast and of sea. The area encompasses of coastline near the Miramare promontory in the Gulf of Trieste. The Torre del Cerrano protected area was created in 2009, extending into the sea and along of coastline. Various zones of the protected area cover of sea surface. The Isole Tremiti reserve has been protected since 1989, while the Tremiti islands themselves are part of the Gargano National Park
The Gargano National Park () is a national park in the province of Foggia in southern Italy. Aside from the Gargano promontory (encompassing the ancient woodlands of the Foresta Umbra) from which it takes its name, it includes also the Tremiti Is ...
. The Torre Guaceto protected area, located near Brindisi and Carovigno, covers a sea surface of and is adjacent to the Torre Guaceto State Reserve covering of coast and sharing an coastline with the marine protected area. Furthermore, there are 10 internationally important (Ramsar) wetland reserves in Italy located along the Adriatic coast.
 There are seven marine protected areas in Croatia:
There are seven marine protected areas in Croatia: Brijuni
The Brijuni () or the Brijuni Islands (also known as the Brionian Islands; same as it, Brioni) are a group of fourteen small islands in the Croatian part of the northern Adriatic Sea, separated from the west coast of the Istrian peninsula by ...
and the Lim Canal off the Istria peninsula's coast, near Pula and Rovinj
Rovinj (; it, Rovigno; Istriot: or ; grc, Ρυγίνιον, Rygínion; la, Ruginium) is a city in Croatia situated on the north Adriatic Sea with a population of 14,294 (2011). Located on the western coast of the Istrian peninsula, it is a p ...
respectively; Kornati
The Kornati archipelago (; it, Isole Incoronate) of Croatia, also known as the Stomorski islands, is located in the northern part of Dalmatia, south from Zadar and west from Šibenik, in the Šibenik-Knin County. With length and 89 islands, som ...
and Telašćica
Telašćica () is a bay in the southeastern part of the island of Dugi Otok, Croatia, in the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost ar ...
in the Middle Adriatic basin, near Zadar; and Lastovo, Bay of Mali Ston ( hr, Malostonski zaljev) and Mljet
Mljet (; la, Melita, it, Meleda) is the southernmost and easternmost of the larger Adriatic islands of the Dalmatia region of Croatia. The National Park includes the western part of the island, Veliko jezero, Malo jezero, Soline Bay and a sea be ...
in southern Dalmatia. The Brijuni national park encompasses the archipelago itself and of surrounding sea; it became a national park in 1999. The Lim Canal is a ria
A ria (; gl, ría) is a coastal inlet formed by the partial submergence of an unglaciated river valley. It is a drowned river valley that remains open to the sea.
Definitions
Typically rias have a dendritic, treelike outline although they ca ...
of the Pazinčica river. The Kornati national park was established in 1980; it covers approximately , including 89 islands and islets. The marine environment encompasses three-quarters of the total area, while the island shores' combined length equals . Telašćica is a nature park established on Dugi Otok in 1988. The park covers of coastline, of land and of sea. The Bay of Mali Ston is located at the border of Croatia and Bosnia–Herzegovina, north of the Pelješac peninsula. The marine protected area covers . The Lastovo nature park was established in 2006, and it includes 44 islands and islets, of land and of sea surface. The Mljet national park was established in 1960, covering a marine protection area. In addition, there is a Ramsar wetland reserve in Croatia—the Neretva river's delta.
 In Slovenia, the marine and coastal protected nature areas are the Sečovlje Salina Landscape Park, Strunjan Landscape Park, Škocjan Inlet Nature Reserve, and the Debeli Rtič, Cape Madona and Lakes in Fiesa natural monuments. The Sečovlje Salina Landscape Park was established in 1990, covers , and includes four nature reserves. In 1993, the area was designated a Ramsar site; it is also a site of international importance for waterbird species. The Strunjan Landscape Park was established in 2004 and comprises two nature reserves. It includes a long cliff, the northernmost Mediterranean salt field and the only Slovenian
In Slovenia, the marine and coastal protected nature areas are the Sečovlje Salina Landscape Park, Strunjan Landscape Park, Škocjan Inlet Nature Reserve, and the Debeli Rtič, Cape Madona and Lakes in Fiesa natural monuments. The Sečovlje Salina Landscape Park was established in 1990, covers , and includes four nature reserves. In 1993, the area was designated a Ramsar site; it is also a site of international importance for waterbird species. The Strunjan Landscape Park was established in 2004 and comprises two nature reserves. It includes a long cliff, the northernmost Mediterranean salt field and the only Slovenian lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') ...
system. It is also the northernmost point of growth of some Mediterranean plant species. The Škocjan Inlet Nature Reserve was established in 1998 and covers . The Debeli Rtič natural monument covers , the Cape Madona natural monument covers , and the Lakes in Fiesa natural monument, with the coastal lake as the only brackish lake in Slovenia, covers .
In 2010, Albania established its first marine protection area, the Karaburun-Sazan National Marine Park
The Karaburun-Sazan Marine Park ( sq, Parku Detar Karaburun-Sazan) is a marine park in the Vlorë County of southwestern Albania. The marine park encompasses over and comprises the boundaries of both the Peninsula of Karaburun and the Island ...
at the Karaburun Peninsula where the Adriatic and Ionian Seas meet. The park covers a total of . Two additional marine protection areas are planned in Albania: the Cape of Rodon
The Cape of Rodon or Cape of Skanderbeg ( sq, Kepi i Rodonit or ''Kepi i Skenderbeut'') is a rocky cape on the Adriatic Sea north of Durrës, Albania. On the Cape is the Rodoni Castle, built by Skanderbeg in 1463. and a Saint Anthony Church. Fu ...
( sq, Kepi i Rodonit) and Porto Palermo. In addition, Albania is home to two Ramsar wetland reserves: Karavasta Lagoon, and Butrint
Butrint ( el, Βουθρωτόν and Βουθρωτός, ''Bouthrōtón'', la, Buthrōtum) was an ancient Greek and later Roman city and bishopric in Epirus. "Speakers of these various Greek dialects settled different parts of Greece at differe ...
. Neither Bosnia–Herzegovina nor Montenegro have or plan to establish any marine protection areas.
Pollution
The Adriatic Sea ecosystem is threatened by excessive input of nutrients through drainage from agricultural land and wastewater flowing from cities; this includes both along its coast and from rivers draining into the sea—especially from the Po River. Venice is often cited as an example of polluted coastal waters where shipping, transportation, farming, manufacturing and wastewater disposal contribute to polluting the sea. A further risk is presented by ballast water discharge by ships, especially tankers. Still, since most of the cargo handled by the Adriatic ports, and virtually all liquid (tanker) cargo handled by the ports, is coming to—not coming from—the Adriatic Basin, the risk from ballast water (from tankers expelling ballast water then loading in the Adriatic) remains minimal. However, proposed export oil pipelines were objected to specifically because of this issue. Oil spills are a major concern in terms of potential environmental impact and damage to tourism and fisheries. It is estimated that if a major oil spill happened, a million people would lose their livelihoods in Croatia alone. An additional risk is presented by oil refineries in the Po River basin where oil spills have occurred before, in addition to accidents occurring in the Adriatic already, so far with no significant environmental consequences. Since 2006, Italy has been considering the construction of an offshore and an onshore LNG terminal in theGulf of Trieste
The Gulf of Trieste ( it, Golfo di Trieste, sl, Tržaški zaliv, hr, Tršćanski zaljev, german: Golf von Triest) is a very shallow bay of the Adriatic Sea, in the extreme northern part of the Adriatic Sea. It is part of the Gulf of Venice an ...
, as well as a pipeline, in the immediate vicinity of the Slovenian–Italian border. The Slovenian government and municipalities, the municipal council of Trieste, and non-governmental organisations have voiced concern over their environmental hazards, effect on transport and effect on tourism.
Another source of pollution of the Adriatic is solid waste. Drifting waste—occasionally relatively large quantities of material, especially waste plastic—is transported northwest by the sirocco. Air pollution in the Adriatic Basin
The Adriatic Abyssal Plain, more commonly referred to as the Adriatic Basin, is an oceanic basin under the Adriatic Sea. The Adriatic Sea's average depth is , and its maximum depth is ; however, the North Adriatic basin rarely exceeds a depth of ...
is associated with the large industrial centres in the Po River valley and the large industrial cities along the coast.
Italy and Yugoslavia established a joint commission to protect the Adriatic Sea from pollution in 1977; the organization later changed with Slovenia, Croatia and Montenegro replacing Yugoslavia. Future pollution hazards are addressed and pollution hotspots are assessed not only by nations in the basin but also through regional projects with World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
support. 27 such hotspots have been determined as of 2011, 6 warranting an urgent response.
History
 Settlements along the Adriatic dating to between 6100 and 5900 BC appear in Albania and Dalmatia on the eastern coast, related to the Cardium pottery culture. During classical antiquity, Illyrians inhabited the eastern Adriatic coast, and the western coast was inhabited by the peoples of Ancient Italy, mainly Etruscans, before the
Settlements along the Adriatic dating to between 6100 and 5900 BC appear in Albania and Dalmatia on the eastern coast, related to the Cardium pottery culture. During classical antiquity, Illyrians inhabited the eastern Adriatic coast, and the western coast was inhabited by the peoples of Ancient Italy, mainly Etruscans, before the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
's rise. Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
colonisation of the Adriatic dates back to the 7th and 6th centuries BC when Epidamnos and Apollonia were founded. The Greeks soon expanded further north establishing several cities, including Ancona, Black Corcyra, Epidaurus, Issa, with trade established as far north as the Po River delta, where the emporion (trading station) of Adria was founded.
Roman era
Roman economic and military influence in the region began to grow with the creation by 246 BC of a major naval base at Brundisium (now Brindisi), which was established to bar Carthaginian ships from the Adriatic during the Punic Wars. This led to conflict with the Illyrians, who lived in a collection of semi- Hellenized kingdoms that covered much of the Balkans and controlled the eastern shore of the sea, resulting in the Illyrian Wars from 229–168 BC. The initial Roman intervention in 229 BC, motivated in part by a desire to suppress Illyrian piracy in the Adriatic, marked the first time that the Roman navy crossed that sea to launch a military campaign. Those wars ended with the eastern shore becoming a province of the Roman Republic. However, resistance to Roman rule continued sporadically and Rome did not completely consolidate control of the region untilAugustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
's general Tiberius put down the Great Illyrian Revolt
The (Latin for 'War of the Batos') was a military conflict fought in the Roman province of Illyricum in the 1st century AD, in which an alliance of native peoples of the two regions of Illyricum, Dalmatia and Pannonia, revolted against the Roma ...
, a bitter struggle waged from 6 to 9 AD. Following the repression of the revolt the Roman province of Illyricum was split into Dalmatia and Pannonia. Most of the eastern shore of the Adriatic was part of Dalmatia, except for the southernmost portion, part of the province of Macedonia, and the peninsula of Istria on the northern part of the eastern shore; Istria contained the important Roman colony at Pula and was incorporated into the province of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
.
During the Roman period, Brundisium, on the western shore, and Apollonia and Dyrrachium (originally called Epidamnos, now Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of ...
in Albania) on the eastern shore became important ports. Brundisium was linked by the Via Appia road to the city of Rome, and Dyrrachium and Apollonia were both on the Via Egnatia, a road that by about 130 BC the Romans had extended eastward across the Balkans to Byzantium (later Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
, now Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
). This made the sea passage across the Adriatic between Brundisium and Dyrrachium (or Apollonia) a link in the primary route for travelers, trade, and troop movements, between Rome and the East. This route played a major role in some of the military operations that marked the end of the Roman Republic and the start of the imperial period. Sulla used it during the First Mithridatic War. During Caesar's Civil War, there was a three-month delay in Caesar's
Caesar's is a restaurant on Avenida Revolución in Tijuana, Mexico, famous as the home of the Caesar salad. Restaurateur Caesar Cardini, an Italian immigrant, opened the restaurant in 1923,
and it is now under chef Javier Plascencia, leading ...
Balkan campaign against Pompey caused when winter storms on the Adriatic and a naval blockade held up Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
from reaching him from Brundisium with reinforcements; after the reinforcements finally arrived Caesar made an unsuccessful attempt to capture Dyrrachium before the campaign moved inland. Marc Antony and Octavian (later Augustus) crossed the Adriatic to Dyrrachium with their armies in their campaign against two of Caesar's assassins, Brutus
Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC), often referred to simply as Brutus, was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Serv ...
and Cassius, that culminated in the Battle of Philippi
The Battle of Philippi was the final battle in the Wars of the Second Triumvirate between the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian (of the Second Triumvirate) and the leaders of Julius Caesar's assassination, Brutus and Cassius in 42 BC, at ...
. Brundisium and Dyrrachium remained important ports well after the Roman period, but an earthquake in the 3rd century AD changed the path of a river causing Apollonia's harbor to silt up, and the city to decline.
Another city on the Italian coast of the Adriatic that increased in importance during the Roman era was Ravenna. During the reign of Augustus, it became a major naval base as part of his program to re-organize the Roman navy to better protect commerce in the Mediterranean. During the 4th century AD the emperors of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
had moved their official residence north from Rome to Mediolanum
Mediolanum, the ancient city where Milan now stands, was originally an Insubrian city, but afterwards became an important Roman city in northern Italy. The city was settled by the Insubres around 600 BC, conquered by the Romans in 222 BC, and ...
(now Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
) in order to be better able to control the military frontier with the Germanic tribes. In 402 AD, during a period of repeated Germanic invasions of Italy, the capital was shifted to Ravenna because nearby marshes made it more defensible, and the Adriatic provided an easy escape path by sea. When the Western Empire fell in 476 AD Ravenna became the capital of the Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), existed under the control of the Germanic Ostrogoths in Italy and neighbouring areas from 493 to 553.
In Italy, the Ostrogoths led by Theodoric the Great killed and replaced Odoacer, ...
of Italy.
Middle Ages
 In the Early Middle Ages, after the Roman Empire's decline, the Adriatic's coasts were ruled by Ostrogoths, Lombards and the
In the Early Middle Ages, after the Roman Empire's decline, the Adriatic's coasts were ruled by Ostrogoths, Lombards and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. The Ostrogothic Kingdom ruled Italy following the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD. However, during the reign of Justinian the Byzantine Empire sent an army under the general Belisarius
Belisarius (; el, Βελισάριος; The exact date of his birth is unknown. – 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean terr ...
to regain control of Italy, resulting in the Gothic War (535–554). The Byzantines established the Exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna ( la, Exarchatus Ravennatis; el, Εξαρχάτο της Ραβέννας) or of Italy was a lordship of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) in Italy, from 584 to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the ...
and by 553 AD their viceroy (Exarch) ruled almost the entire Italian peninsula from that city. In 568 AD the Lombards invaded northern Italy, and over the course of the next century or so the importance of the Exarchate declined as the territory under Lombard control expanded and as the Byzantine outpost of Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
became increasingly independent. In 752 AD the Lombards overthrew the Exarchate, ending the influence of the Byzantine Empire on the western shore of the Adriatic for a few centuries.
The last part of the period saw the rise of the Carolingian Empire and then the Frankish Kingdom of Italy, which controlled the Adriatic Sea's western coast, while Byzantine Dalmatia on the east coast gradually shrunk following the Avar and Croatian invasions starting in the 7th century. The Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
was founded during this period and went on to become a significant maritime power after receiving a Byzantine tax exemption in 1082. The end of the period brought about the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
's control over the Kingdom of Italy (which would last until the Peace of Westphalia in 1648), the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Croatia and the Byzantine Empire's return to the southern Apennine peninsula. In addition, the Papal States were carved out in the area around Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and central Italy in the 8th century.
 The
The High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 150 ...
in the Adriatic Sea basin saw further territorial changes, including the Norman conquest of southern Italy
The Norman conquest of southern Italy lasted from 999 to 1139, involving many battles and independent conquerors.
In 1130, the territories in southern Italy united as the Kingdom of Sicily, which included the island of Sicily, the southern ...
ending the Byzantine presence on the Apennine peninsula in the 11th and 12th centuries (the territory would become the Kingdom of Naples in 1282) and the control of a substantial part of the eastern Adriatic coast by the Kingdom of Hungary after a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
was established between Croatia and Hungary in 1102. In this period, the Republic of Venice began to expand its territory and influence. In 1202, the Fourth Crusade was diverted to conquer Siege of Zara, Zadar at the behest of the Venetians—the first instance of a Crusades, Crusader force attacking a Catholic city—before proceeding to sack Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
. In the 13th century, Venice established itself as a leading Economic history of Venice, maritime nation. During much of the 12th and 13th centuries, Venice and the Republic of Genoa were Venetian–Genoese Wars, engaged in warfare culminating in the War of Chioggia, ousting the Genoese from the Adriatic. Still, the 1381 Treaty of Turin that ended the war required Venice to renounce claims to Dalmatia, after losing the territory to Hungary in 1358. In the same year, the Republic of Ragusa was established in Dubrovnik as a city-state after it was freed from Venetian suzerainty.
Venice regained Dalmatia in 1409 and held it for nearly four hundred years, with the republic's apex of trading and military power in the first half of the 15th century. The 15th and the 16th centuries brought about the Byzantine Empire's destruction in 1453 and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
's expansion that reached Adriatic shores in present-day Albania and Montenegro as well as the immediate hinterland of the Dalmatian coast, defeating the Hungarian and Croatian armies at Battle of Krbava field, Krbava in 1493 and Battle of Mohács, Mohács in 1526. These defeats spelled the end of an independent Hungarian kingdom, and both Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatian and Kingdom of Hungary (1538–1867), Hungarian nobility chose Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I of the House of Habsburg as their new ruler, bringing the Habsburg monarchy to the shore of the Adriatic Sea, where it would remain for nearly four hundred years. The Ottomans and Venetians fought a Ottoman–Venetian War, series of wars, but until the 17th century these were not fought in the Adriatic area. Ottoman raids on the Adriatic coasts effectively ceased after the massive setback in the Battle of Lepanto in October 1571.
Early modern period
 In 1648, the Holy Roman Empire lost its claim on its former Italian lands, formally ending the Kingdom of Italy; however, its only outlet on the Adriatic Sea, the Duchy of Ferrara, was already lost to the Papal States. The 17th century's final territorial changes were caused by the Morean War, Morean or Sixth Ottoman–Venetian War, when in 1699 Venice slightly enlarged its possessions in Dalmatia. In 1797, the Republic of Venice was abolished after the Napoleonic Wars, French conquest. The Venetian territory was then handed over to Venetian Province, Austria and briefly ruled as part of the Archduchy of Austria. The territory was turned back over to France after the Peace of Pressburg (1805), Peace of Pressburg in 1805 when the territory in the Po Valley#Early modern, Po valley became an integral part of the new Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy. The new kingdom included the province of Romagna, thus removing the Papal State from the Adriatic coast; however, Trieste, Istria and Dalmatia were joined into a set of separate provinces of the First French Empire, French Empire: the Illyrian Provinces. These were created in 1809 through the Treaty of Schönbrunn; they represented the end of Venetian rule on the eastern Adriatic coast, as well as the end of the Republic of Ragusa. The Adriatic Sea was a minor Theater (warfare), theatre in the Napoleonic Wars; the Adriatic campaign of 1807–1814 involved the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British Royal Navy contesting the Adriatic's control by the combined navies of France, Italy and the Kingdom of Naples. During the campaign, the Royal Navy occupied Vis and established its base there in Vis (town), Port St. George. The campaign reached its climax in the 1811 Battle of Lissa (1811), Battle of Lissa, and ended with British and Austrian Empire, Austrian troops seizing the coastal cities on the eastern Adriatic coast from the French. Days before the Battle of Waterloo, the Congress of Vienna awarded the Illyrian Provinces (spanning from the Gulf of Trieste#History, Trieste to the Bay of Kotor) to Austria. The Congress of Vienna also created the Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia which encompassed the city of Venice, the surrounding coast and a substantial hinterland, and was controlled by Austria. In the Apennine peninsula's south, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was formed in 1816 by unifying the kingdoms of Naples and Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily.
In 1648, the Holy Roman Empire lost its claim on its former Italian lands, formally ending the Kingdom of Italy; however, its only outlet on the Adriatic Sea, the Duchy of Ferrara, was already lost to the Papal States. The 17th century's final territorial changes were caused by the Morean War, Morean or Sixth Ottoman–Venetian War, when in 1699 Venice slightly enlarged its possessions in Dalmatia. In 1797, the Republic of Venice was abolished after the Napoleonic Wars, French conquest. The Venetian territory was then handed over to Venetian Province, Austria and briefly ruled as part of the Archduchy of Austria. The territory was turned back over to France after the Peace of Pressburg (1805), Peace of Pressburg in 1805 when the territory in the Po Valley#Early modern, Po valley became an integral part of the new Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy. The new kingdom included the province of Romagna, thus removing the Papal State from the Adriatic coast; however, Trieste, Istria and Dalmatia were joined into a set of separate provinces of the First French Empire, French Empire: the Illyrian Provinces. These were created in 1809 through the Treaty of Schönbrunn; they represented the end of Venetian rule on the eastern Adriatic coast, as well as the end of the Republic of Ragusa. The Adriatic Sea was a minor Theater (warfare), theatre in the Napoleonic Wars; the Adriatic campaign of 1807–1814 involved the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British Royal Navy contesting the Adriatic's control by the combined navies of France, Italy and the Kingdom of Naples. During the campaign, the Royal Navy occupied Vis and established its base there in Vis (town), Port St. George. The campaign reached its climax in the 1811 Battle of Lissa (1811), Battle of Lissa, and ended with British and Austrian Empire, Austrian troops seizing the coastal cities on the eastern Adriatic coast from the French. Days before the Battle of Waterloo, the Congress of Vienna awarded the Illyrian Provinces (spanning from the Gulf of Trieste#History, Trieste to the Bay of Kotor) to Austria. The Congress of Vienna also created the Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia which encompassed the city of Venice, the surrounding coast and a substantial hinterland, and was controlled by Austria. In the Apennine peninsula's south, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was formed in 1816 by unifying the kingdoms of Naples and Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily.
Modern period
 The process of Italian unification culminated in the Second Italian War of Independence, resulting in the Kingdom of Sardinia annexing all territories along the western Adriatic coast south of Venetia (region), Venetia in 1860, and the 1861 establishment of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946), Kingdom of Italy in its place. The Kingdom of Italy expanded in 1866: it Third Italian War of Independence, annexed Venetia, but Regia Marina, its navy was defeated in the Adriatic near Battle of Lissa (1866), Vis. Following the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 and the Croatian–Hungarian Settlement of 1868, the control of much of the eastern Adriatic coast was redefined. The cisleithanian (Austrian) part of Austria-Hungary spanned from the Austrian Littoral to the Bay of Kotor, with the exception of the Croatian Littoral mainland. In the territory outside the Austrian Littoral, Corpus separatum (Fiume), special status was given to Fiume (modern-day Rijeka) as a separate part of the Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen, Kingdom of Hungary. The rest of the territory was made a part of the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia, which in turn was also in the Transleithanian part of the dual monarchy. The Adriatic coastline controlled by the Ottoman Empire was reduced by the Congress of Berlin in 1878, through recognition of the independence of the Principality of Montenegro, which controlled the coast south of the Bay of Kotor to the Bojana River. The Ottoman Empire lost all territories along the Adriatic following the First Balkan War and consequent Treaty of London (1913), 1913 Treaty of London that established an independent Albania.
The process of Italian unification culminated in the Second Italian War of Independence, resulting in the Kingdom of Sardinia annexing all territories along the western Adriatic coast south of Venetia (region), Venetia in 1860, and the 1861 establishment of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946), Kingdom of Italy in its place. The Kingdom of Italy expanded in 1866: it Third Italian War of Independence, annexed Venetia, but Regia Marina, its navy was defeated in the Adriatic near Battle of Lissa (1866), Vis. Following the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 and the Croatian–Hungarian Settlement of 1868, the control of much of the eastern Adriatic coast was redefined. The cisleithanian (Austrian) part of Austria-Hungary spanned from the Austrian Littoral to the Bay of Kotor, with the exception of the Croatian Littoral mainland. In the territory outside the Austrian Littoral, Corpus separatum (Fiume), special status was given to Fiume (modern-day Rijeka) as a separate part of the Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen, Kingdom of Hungary. The rest of the territory was made a part of the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia, which in turn was also in the Transleithanian part of the dual monarchy. The Adriatic coastline controlled by the Ottoman Empire was reduced by the Congress of Berlin in 1878, through recognition of the independence of the Principality of Montenegro, which controlled the coast south of the Bay of Kotor to the Bojana River. The Ottoman Empire lost all territories along the Adriatic following the First Balkan War and consequent Treaty of London (1913), 1913 Treaty of London that established an independent Albania.
 The
The World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
Adriatic Campaign of World War I, Adriatic Campaign was largely limited to blockade attempts by the Allies of World War I, Allies and the Battle of the Strait of Otranto (1917), effort of the Central Powers to thwart the British, French and Italian moves. Italy joined the Allies in April 1915 with the Treaty of London (1915), Treaty of London, which promised Italy the Austrian Littoral, northern Dalmatia, the port of Vlorë, most of the eastern Adriatic islands and Albania as a protectorate. The treaty provided the basis for all the following divisions between Italy and Yugoslavia. In 1918, the Montenegrin national assembly voted to unite with the Kingdom of Serbia, giving the latter access to the Adriatic. Another short-lived, unrecognised state established in 1918 was the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, formed from parts of Austria-Hungary, comprising most of the former monarchy's Adriatic coastline. Later that year, the Kingdom of Serbia and the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs formed the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes—subsequently renamed Yugoslavia. The proponents of the new union in the Croatian parliament saw the move as a safeguard against Italian expansionism as stipulated in the Treaty of London. The treaty was largely disregarded by Britain and French Third Republic, France because of conflicting promises made to Serbia and a perceived lack of Italian contribution to the war effort outside Italy itself. The 1919 Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919), Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye did transfer the Austrian Littoral and Istria to Italy but awarded Dalmatia to Yugoslavia. Following the war, a Gabriele d'Annunzio, private force of demobilized Italian soldiers seized Rijeka and set up the Italian Regency of Carnaro—seen as a harbinger of Fascism—in order to force the recognition of Italian claims to the city. After sixteen months of the Regency's existence, the Treaty of Rapallo (1920), 1920 Treaty of Rapallo redefined the Italian–Yugoslav borders, among other things transferring Zadar and the islands of Cres, Lastovo and Palagruža to Italy, securing the island of Krk for Yugoslavia and establishing the Free State of Fiume; this new state was abolished in 1924 by the Treaty of Rome (1924), Treaty of Rome that awarded Fiume (modern Rijeka) to Italy and Sušak, Rijeka, Sušak to Yugoslavia.
Late 20th century
 During World War II, the Adriatic saw only Adriatic Campaign of World War II, limited naval action, starting with the Italian invasion of Albania and the joint Axis invasion of Yugoslavia. The latter led to the annexation of a large part of Dalmatia and nearly all the eastern Adriatic islands by Italy and the establishment of two puppet states, the Independent State of Croatia and the Kingdom of Montenegro (1941–1944), Kingdom of Montenegro, which controlled the remainder of the former Yugoslav Adriatic coast. In 1947, after the Armistice between Italy and Allied armed forces and the war's end, Italy (now a 1946 Italian constitutional referendum, republic) and the Allies of World War II, Allies signed the Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947, Treaty of Peace with Italy. The treaty reversed all wartime annexations, guaranteed the independence of Albania, created the Free Territory of Trieste (FTT) as a city-state, and gave Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, communist Yugoslavia most of the Slovenian Littoral, as well as Istria, the islands of Cres, Lastovo and Palagruža, and the cities of Zadar and Rijeka. The FTT was partitioned in 1954: Trieste itself and the area to the North of it were placed under Italian control, while the rest came under Yugoslav control. This arrangement was made permanent in the 1975 Treaty of Osimo.
During the Cold War, the Adriatic Sea became the southernmost flank of the Iron Curtain as Italy joined NATO, while the Warsaw Pact established bases in Albania. After the fall of communism, Breakup of Yugoslavia#Secession and War (1991–1992), Yugoslavia broke apart: Ten-Day War, Slovenia and 1991 Croatian independence referendum, Croatia declared independence in 1991, and Bosnia–Herzegovina followed in 1992, while Montenegro remained in a federation with Serbia, officially called Serbia and Montenegro. The ensuing Croatian War of Independence included limited naval engagements and a blockade of Croatia's coast by the Yugoslav Navy, leading to the Battle of the Dalmatian channels and a later withdrawal of Yugoslav vessels. Montenegro declared itself independent in 2006, effectively land-locking Serbia. The period also saw the Adriatic Sea as the theatre of several NATO operations, including the Operation Maritime Guard, blockade of Yugoslavia, NATO intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina, intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the 1999 NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, 1999 bombing of Yugoslavia.
During World War II, the Adriatic saw only Adriatic Campaign of World War II, limited naval action, starting with the Italian invasion of Albania and the joint Axis invasion of Yugoslavia. The latter led to the annexation of a large part of Dalmatia and nearly all the eastern Adriatic islands by Italy and the establishment of two puppet states, the Independent State of Croatia and the Kingdom of Montenegro (1941–1944), Kingdom of Montenegro, which controlled the remainder of the former Yugoslav Adriatic coast. In 1947, after the Armistice between Italy and Allied armed forces and the war's end, Italy (now a 1946 Italian constitutional referendum, republic) and the Allies of World War II, Allies signed the Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947, Treaty of Peace with Italy. The treaty reversed all wartime annexations, guaranteed the independence of Albania, created the Free Territory of Trieste (FTT) as a city-state, and gave Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, communist Yugoslavia most of the Slovenian Littoral, as well as Istria, the islands of Cres, Lastovo and Palagruža, and the cities of Zadar and Rijeka. The FTT was partitioned in 1954: Trieste itself and the area to the North of it were placed under Italian control, while the rest came under Yugoslav control. This arrangement was made permanent in the 1975 Treaty of Osimo.
During the Cold War, the Adriatic Sea became the southernmost flank of the Iron Curtain as Italy joined NATO, while the Warsaw Pact established bases in Albania. After the fall of communism, Breakup of Yugoslavia#Secession and War (1991–1992), Yugoslavia broke apart: Ten-Day War, Slovenia and 1991 Croatian independence referendum, Croatia declared independence in 1991, and Bosnia–Herzegovina followed in 1992, while Montenegro remained in a federation with Serbia, officially called Serbia and Montenegro. The ensuing Croatian War of Independence included limited naval engagements and a blockade of Croatia's coast by the Yugoslav Navy, leading to the Battle of the Dalmatian channels and a later withdrawal of Yugoslav vessels. Montenegro declared itself independent in 2006, effectively land-locking Serbia. The period also saw the Adriatic Sea as the theatre of several NATO operations, including the Operation Maritime Guard, blockade of Yugoslavia, NATO intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina, intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the 1999 NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, 1999 bombing of Yugoslavia.
Boundaries
Italy and Yugoslavia defined their Adriatic continental shelf delimitation in 1968, with an additional agreement signed in 1975 on the Gulf of Trieste boundary, following the Treaty of Osimo. The boundary agreed in 1968 extends and consists of 43 points connected by straight lines or circular Arc (geometry), arc segments. The additional boundary agreed upon in 1975 consists of 5 points, extending from an end point of the 1968 line. All successor states of former Yugoslavia accepted the agreements. In the Adriatic's southernmost areas the border was not determined in order to avoid prejudicing the location of the tripoint with the Albanian continental shelf border, which remains undefined. Before the breakup of Yugoslavia, Albania, Italy and Yugoslavia initially proclaimed territorial waters, subsequently reduced to international-standard and all sides adopted Baseline (sea), baseline systems (mostly in the 1970s). Albania and Italy determined their sea border in 1992 according to the equidistance principle. Following Accession of Croatia to the European Union, Croatian EU membership, the Adriatic became an internal waters, internal sea of the EU. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea defines the Adriatic Sea as an enclosed or semi-enclosed sea.Adriatic Euroregion
Disputes
The former Yugoslav republics' land borders were decided by demarcation commissions implementing the AVNOJ decisions of 1943 and 1945, but the exact course has not been agreed upon by the successor states, which makes the maritime boundaries' definition difficult; the maritime borders were not defined at all in the time of Yugoslavia. In addition, the maritime boundary between Albania and Montenegro was not defined before the 1990s. Croatia and Slovenia started negotiations to define maritime borders in the Gulf of Piran in 1992 but failed to agree, resulting in a dispute. Both countries also declared their economic zones, which partially overlap. Croatia's application to become an Member state of the European Union, EU member state was initially suspended pending resolution of its Croatia-Slovenia border disputes, border disputes with Slovenia. These disputes with Slovenia were eventually settled with an agreement to accept the decision of an international arbitration commission set up via the United Nations, UN, enabling Croatia to progress towards EU membership. Aside from the EU membership difficulty, even before its settling the dispute has caused no major practical problems. The maritime boundary between Bosnia–Herzegovina and Croatia was formally settled in 1999, but a few issues are still in dispute—the Klek (peninsula), Klek peninsula and two islets in the border area. The Croatia–Montenegro maritime boundary is disputed in the Bay of Kotor, at the Prevlaka peninsula. This dispute was exacerbated by the peninsula's occupation by the Yugoslav People's Army and later by the (Serbian–Montenegrin) Military of Serbia and Montenegro, FR Yugoslav Army, which in turn was replaced by a United Nations Mission of Observers in Prevlaka, United Nations observer mission that lasted until 2002. Croatia took over the area with an agreement that allowed Montenegrin presence in the bay's Croatian waters, and the dispute has become far less contentious since Montenegro's independence in 2006.Economy
Fishing
 The Adriatic Sea fishery's production is distributed among countries in the basin. In 2000, the nominal—on a live weight basis—total landings of all Adriatic fisheries reached . Overfishing is a recognised problem—450 species of fish live in the Adriatic Sea, including 120 species threatened by excessive commercial fishing, a problem exacerbated by pollution and global warming. Overexploited species include common dentex, Scorpaena scrofa, red scorpionfish, Lophius piscatorius, monkfish, John Dory, blue shark, spiny dogfish, Mullet (fish), mullet, Mullus barbatus, red mullet, Nephrops norvegicus, Norway lobster, as well as Merluccius merluccius, European hake, and sardines. Turtles and
The Adriatic Sea fishery's production is distributed among countries in the basin. In 2000, the nominal—on a live weight basis—total landings of all Adriatic fisheries reached . Overfishing is a recognised problem—450 species of fish live in the Adriatic Sea, including 120 species threatened by excessive commercial fishing, a problem exacerbated by pollution and global warming. Overexploited species include common dentex, Scorpaena scrofa, red scorpionfish, Lophius piscatorius, monkfish, John Dory, blue shark, spiny dogfish, Mullet (fish), mullet, Mullus barbatus, red mullet, Nephrops norvegicus, Norway lobster, as well as Merluccius merluccius, European hake, and sardines. Turtles and common bottlenose dolphin
The common bottlenose dolphin or Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatus'') is a wide-ranging marine mammal of the family Delphinidae. The common bottlenose dolphin is a very familiar dolphin due to the wide exposure it gets in captiv ...
s are also being killed by fishing nets. The depleted fish stock, and Croatia's Ecological and Fisheries Protection Zone (ZERP) contributed to accusations of overfishing exchanged between Italian and Croatian fishermen. ZERP was introduced in 2003, but its application to EU member states was suspended in 2004. The depleted stocks of fish are being addressed through a new proposed EU fisheries policy that was scheduled to take effect in 2013, when Accession of Croatia to the European Union, Croatia acceded to the EU, and restore the stocks to sustainable levels by 2015.
The largest volume of fish harvesting was in Italy, where the total production volume in 2007 stood at . In 2003, 28.8% of Italian fisheries production volume was generated in the Northern and central Adriatic, and 24.5% in Apulia (from the Southern Adriatic and Ionian Sea). Italian fisheries, including those operating outside the Adriatic, employed 60,700 in the Primary sector of the economy, primary sector, including aquaculture (which comprises 40% of the total fisheries production). The total fisheries output's gross value in 2002 was $1.9 billion.
 In 2007, Croatia's production in live weight reached . In 2006, the total Croatian fisheries production volume was of catch and from marine aquaculture. Croatian fisheries employed approximately 20,000. The 2006 marine capture catch in Croatian waters consisted of sardines (44.8%), anchovy, anchovies (31.3%), tunas (2.7%), other pelagic fish (4.8%), hake (2.4%), Mullet (fish), mullet (2.1%), other demersal fish (8.3%), crustaceans (largely lobster and ''Nephrops norvegicus'') (0.8%), shellfish (largely oysters and mussels) (0.3%), cuttlefish (0.6%), squids (0.2%) and octopuses and other cephalopods (1.6%). Croatian marine aquaculture production consisted of tuna (47.2%), oysters and mussels (28.2% combined) and Bass (fish), bass and bream (24.6% combined).
In 2007, Albanian fisheries production amounted to , including aquaculture production, which reached in 2006. At the same time, Slovenian fisheries produced a total of with 55% of the production volume originating in aquaculture, representing the highest ratio in the Adriatic. Finally, the Montenegrin fisheries production stood at in 2006, with only 11 tonnes coming from aquaculture. In 2007, the fisheries production in Bosnia–Herzegovina reached volume of and in Slovenia.
In 2007, Croatia's production in live weight reached . In 2006, the total Croatian fisheries production volume was of catch and from marine aquaculture. Croatian fisheries employed approximately 20,000. The 2006 marine capture catch in Croatian waters consisted of sardines (44.8%), anchovy, anchovies (31.3%), tunas (2.7%), other pelagic fish (4.8%), hake (2.4%), Mullet (fish), mullet (2.1%), other demersal fish (8.3%), crustaceans (largely lobster and ''Nephrops norvegicus'') (0.8%), shellfish (largely oysters and mussels) (0.3%), cuttlefish (0.6%), squids (0.2%) and octopuses and other cephalopods (1.6%). Croatian marine aquaculture production consisted of tuna (47.2%), oysters and mussels (28.2% combined) and Bass (fish), bass and bream (24.6% combined).
In 2007, Albanian fisheries production amounted to , including aquaculture production, which reached in 2006. At the same time, Slovenian fisheries produced a total of with 55% of the production volume originating in aquaculture, representing the highest ratio in the Adriatic. Finally, the Montenegrin fisheries production stood at in 2006, with only 11 tonnes coming from aquaculture. In 2007, the fisheries production in Bosnia–Herzegovina reached volume of and in Slovenia.
Tourism
The countries bordering the Adriatic Sea are significant tourist destinations. The largest number of tourist overnight stays and the most numerous tourist accommodation facilities are recorded in Italy, especially in the Veneto region (around Venice). Veneto is followed by the Emilia-Romagna region and by the NUTS of Croatia, Adriatic Croatian Counties of Croatia, counties. The Croatian tourist facilities are further augmented by 21,000 nautical ports and Mooring (watercraft), moorings; nautical tourism, nautical tourists are attracted to various types of marine Protected areas of Croatia, protected areas. All countries along the Adriatic coast, except Albania and Bosnia–Herzegovina, take part in the Blue Flag beach certification programme (of the Foundation for Environmental Education), for beaches and marinas meeting strict quality standards including environmental protection, water quality, safety and services criteria. As of January 2012, the Blue Flag has been awarded to 103 Italian Adriatic beaches and 29 marinas, 116 Croatian beaches and 19 marinas, 7 Slovenian beaches and 2 marinas, and 16 Montenegrin beaches. Adriatic tourism is a significant source of income for these countries, especially in Croatia and Montenegro where the tourism income generated along the Adriatic coast represents the bulk of such income. The direct contribution of travel and tourism to Croatia's GDP stood at 5.1% in 2011, with the total industry contribution estimated at 12.8% of the national GDP. For Montenegro, the direct contribution of tourism to the national GDP is 8.1%, with the total contribution to the economy at 17.2% of Montenegrin GDP. Tourism in Adriatic Croatia has recently exhibited greater growth than in the other regions around the Adriatic.Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertai ...
File:Neum, costa.jpg, The coast of Neum, the only town to be situated along Bosnia and Herzegovina's of coastline
File:Palace Hotel Portoroz.JPG, Portorož is the largest seaside tourist centre in Slovenia
Transport
There are nineteen Adriatic Sea ports (in four different countries) that each handles more than a million tonnes of cargo per year. The largest cargo ports among them are the Port of Trieste (the largest Adriatic cargo port in Italy), the Port of Venice, the Port of Ravenna, the Port of Koper (the largest Slovenian port), the Port of Rijeka (the largest Croatian cargo port), and the Port of Brindisi. The largest passenger ports in the Adriatic are the Port of Split (the largest Croatian passenger port) and ports in Ancona#Transportation, Ancona (the largest Italian passenger seaport in the Adriatic). The largest seaport in Montenegro is the Port of Bar. In 2010, the Northern Adriatic seaports of Trieste, Venice, Ravenna, Koper and Rijeka founded the North Adriatic Ports Association to position themselves more favourably in the EU's transport systems.
The port of Trieste is of particular importance for Central Europe because this is where the Transalpine Pipeline begins, supplying 100 percent of southern Germany, 90 percent of Austria and 50 percent of the Czech Republic with crude oil.
The largest passenger ports in the Adriatic are the Port of Split (the largest Croatian passenger port) and ports in Ancona#Transportation, Ancona (the largest Italian passenger seaport in the Adriatic). The largest seaport in Montenegro is the Port of Bar. In 2010, the Northern Adriatic seaports of Trieste, Venice, Ravenna, Koper and Rijeka founded the North Adriatic Ports Association to position themselves more favourably in the EU's transport systems.
The port of Trieste is of particular importance for Central Europe because this is where the Transalpine Pipeline begins, supplying 100 percent of southern Germany, 90 percent of Austria and 50 percent of the Czech Republic with crude oil.
Oil and gas
Natural gas is produced through several projects, including a joint venture of the Eni and INA (company), INA companies that operates two platforms—one is in Croatian waters and draws gas from six wells, and the other (which started operating in 2010) is located in Italian waters. The Adriatic gas fields were discovered in the 1970s,Ianniello, A., Bolelli, W., and Di Scala, L., 1992, Barbara Field, Adriatic Sea, Offshore Italy, In Giant Oil and Gas Fields of the Decade, 1978–1988, AAPG Memoir 54, Halbouty, M.T., editor, Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, but their development commenced in 1996. In 2008, INA produced 14.58 million Barrel of oil equivalent, BOE per day of gas. About 100 offshore platforms are located in the Emilia-Romagna region, along with 17 in the Northern Adriatic. Eni estimated its Concession (contract), concessions in the Adriatic Sea to hold at least of natural gas, adding that they may even reach . INA estimates, however, are 50% lower than those supplied by Eni. Oil was discovered in the Northern Adriatic at a depth of approximately ; the discovery was assessed as not viable because of its location, depth and quality. These gas and oil reserves are part of the Po basin Province of Northern Italy and the Northern Mediterranean Sea. In the 2000s, investigation works aimed at discovering gas and oil reserves in the Middle and Southern Adriatic basins intensified, and by the decade's end, oil and natural gas reserves were discovered southeast of the Bari, Brindisi—Rovesti and Giove oil discoveries. Surveys indicate reserves of 3 billion Barrel (unit), barrels of oil in place and of gas in place. The discovery was followed by further surveys off the Croatian coast. In January 2012, INA commenced prospecting for oil off Dubrovnik, marking the resumption of oil exploration along the eastern Adriatic coast after surveys commenced in the late 1980s around the island of Brač were cancelled because of Yugoslavia's breakup and Croatian War for Independence, war in Croatia. Montenegro is also expected to look for oil off its coast. As of January 2012, only 200 exploration wells had been sunk off the Croatian coast, with all but 30 in the Northern Adriatic basin.Gallery
Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
File:Triest Port1.JPG, Port of Trieste, the largest cargo port in the Adriatic
File:The port of Bar, view from Vrsuta mnt (39372956332).jpg, Port of Bar, the largest seaport in Montenegro
File:Porto_ancona.jpg, Port of Ancona, a large passenger port
See also
* Geography of Albania * Geography of Bosnia and Herzegovina * Geography of Croatia * Geography of Europe * Geography of Italy * Geography of Montenegro * Geography of SloveniaNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Region 5 – Western Africa, Mediterranean, Black Sea Nautical Charts
from the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency
Nautical Chart 54131 (Adriatic Sea)
from the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency
the seashore of our posterity
nbsp;– video recording of Albanian, Croatian, and Montenegrin coasts {{good article Adriatic Sea, European seas Marginal seas of the Mediterranean Seas of Italy Bodies of water of Croatia Seas of Albania Bodies of water of Montenegro Bodies of water of Slovenia Bodies of water of Bosnia and Herzegovina Bodies of water of the Slovene Littoral Geography of Southern Europe Geography of Central Europe