Aden Protectorate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Aden Protectorate ( ar, محمية عدن ') was a British protectorate in
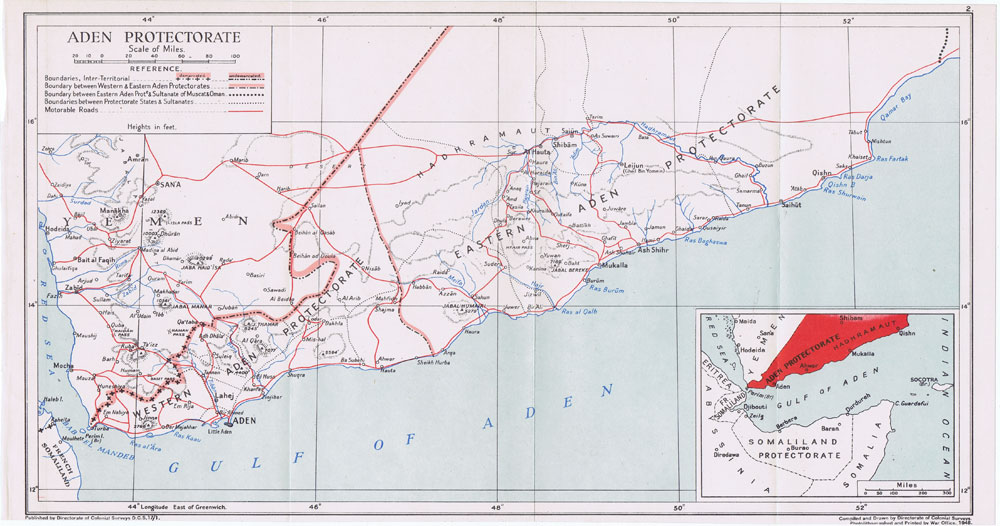 Beginning with a formal treaty of protection with the Mahra Sultanate of Qishn and Socotra in 1886, Britain embarked on a slow formalisation of protection arrangements that included over 30 major treaties of protection with the last signed only in 1954. These treaties, together with a number of other minor agreements, created the Aden Protectorate that extended well east of Aden to Hadhramaut and included all of the territory that would become
Beginning with a formal treaty of protection with the Mahra Sultanate of Qishn and Socotra in 1886, Britain embarked on a slow formalisation of protection arrangements that included over 30 major treaties of protection with the last signed only in 1954. These treaties, together with a number of other minor agreements, created the Aden Protectorate that extended well east of Aden to Hadhramaut and included all of the territory that would become

 The Eastern Protectorate (c. 230,000 km2) came to include the following entities (mostly in Hadhramaut):
*
The Eastern Protectorate (c. 230,000 km2) came to include the following entities (mostly in Hadhramaut):
*
 In 1938, Britain signed an advisory treaty with the Qu'aiti sultan and, throughout the 1940s and 1950s, signed similar treaties with twelve other protectorate states. The following were the states with advisory treaties:
; Eastern Protectorate States
* Kathiri
* Mahra
* Qu'aiti
* Wahidi Balhaf
; Western Protectorate States
* Audhali
* Beihan
* Dhala
* Haushabi
* Fadhli
* Lahej
* Lower Aulaqi
* Lower Yafa
* Upper Aulaqi Sheikhdom
These agreements allowed for the stationing of a
In 1938, Britain signed an advisory treaty with the Qu'aiti sultan and, throughout the 1940s and 1950s, signed similar treaties with twelve other protectorate states. The following were the states with advisory treaties:
; Eastern Protectorate States
* Kathiri
* Mahra
* Qu'aiti
* Wahidi Balhaf
; Western Protectorate States
* Audhali
* Beihan
* Dhala
* Haushabi
* Fadhli
* Lahej
* Lower Aulaqi
* Lower Yafa
* Upper Aulaqi Sheikhdom
These agreements allowed for the stationing of a
 By 1965, the RAF station (
By 1965, the RAF station (
Official website of the Al-Quaiti Royal Family of Hadhramaut
Map of Arabia (1905–1923) including the states of Aden Protectorate
British-Yemeni Society
Aden Veterans Association
{{South Arabia 1886 establishments in Asia 1886 establishments in the British Empire 1963 disestablishments in Asia 1963 disestablishments in the British Empire 19th century in Yemen 19th-century establishments in Yemen 20th century in Yemen Aden in World War II Aden Former countries in the Middle East States and territories disestablished in 1963 States and territories established in 1872 United Kingdom–Yemen relations Former countries South Arabia Former monarchies of Asia Former British protectorates
South Arabia
South Arabia () is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jizan, Al-Bahah, and 'As ...
which evolved in the hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning "the land behind" (a city, a port, or similar). Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associate ...
of the port of Aden
Aden ( ar, عدن ' Yemeni: ) is a city, and since 2015, the temporary capital of Yemen, near the eastern approach to the Red Sea (the Gulf of Aden), some east of the strait Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000 peopl ...
and in the Hadhramaut following the conquest of Aden by the Bombay Presidency
The Bombay Presidency or Bombay Province, also called Bombay and Sind (1843–1936), was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India, with its capital in the city that came up over the seven islands of Bombay. The first mainl ...
of British India in 1839, and it continued until the 1960s. In 1940 it was divided for administrative purposes into the Western Protectorate and the Eastern Protectorate. Today the territory forms part of the Republic of Yemen.
The rulers of the Aden Protectorate, as generally with the other British protectorates and protected states, remained sovereign: their flags still flew over their government buildings, government was still carried out by them or in their names, and their states maintained a distinct 'international personality' in the eyes of international law, in contrast to states forming part of the British Empire, such as Aden Colony, where the British monarch was the head of every state.
History
Informal beginnings
What became known as the Aden Protectorate was initially informal arrangements of protection with ninetribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confli ...
in the immediate hinterland of the port city of Aden
Aden ( ar, عدن ' Yemeni: ) is a city, and since 2015, the temporary capital of Yemen, near the eastern approach to the Red Sea (the Gulf of Aden), some east of the strait Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000 peopl ...
:
* Abdali Abdali may refer to:
* An alternate name for the Durrani, one of the largest Pashtun tribes of Afghanistan and western Pakistan
** Ahmed Shah Durrani, also known as Ahmad Shah Abdali, founder of the Durrani Empire in Afghanistan
* Al-Abdali, a dist ...
(Lahej)
* Alawi
* Amiri (Dhala)
* Aqrabi
* Aulaqi
* Fadhli
Fadhli ( ar, فضلي '), or the Fadhli Sultanate ( ar, السلطنة الفضلية '), was an independent sultanate on the southern coast of the Arabian Peninsula from the 17th century until 1967.
* Haushabi
* Subeihi
* Yafa
Yafa () is an Arab tribe, geographical area, and district inhabited by the Yafa'i tribe in South Arabia, located in Lahij Governorate. It is one of the biggest tribes that descended from the ancient Himyarites. Today, most members of the tribe ...
British expansion into the area was designed to secure the important port that was, at the time, governed from British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
. From 1874, these protection arrangements existed with the tacit acceptance of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
that maintained suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is ca ...
over Yemen to the north and the polities became known collectively as the "Nine Tribes" or the "Nine Cantons."
Formal treaties of protection
 Beginning with a formal treaty of protection with the Mahra Sultanate of Qishn and Socotra in 1886, Britain embarked on a slow formalisation of protection arrangements that included over 30 major treaties of protection with the last signed only in 1954. These treaties, together with a number of other minor agreements, created the Aden Protectorate that extended well east of Aden to Hadhramaut and included all of the territory that would become
Beginning with a formal treaty of protection with the Mahra Sultanate of Qishn and Socotra in 1886, Britain embarked on a slow formalisation of protection arrangements that included over 30 major treaties of protection with the last signed only in 1954. These treaties, together with a number of other minor agreements, created the Aden Protectorate that extended well east of Aden to Hadhramaut and included all of the territory that would become South Yemen
South Yemen ( ar, اليمن الجنوبي, al-Yaman al-Janubiyy), officially the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (, ), also referred to as Democratic Yemen (, ) or Yemen (Aden) (, ), was a communist state that existed from 1967 to 19 ...
except for the immediate environs and port of the colonial capital, Aden.
Aden with its harbour was the only area under full British sovereignty and, together with some offshore islands, was known as Aden Settlement (1839–1932), Aden Province
The Chief Commissioner's Province of Aden was the administrative status under which the former Aden Settlement (1839–1932) was placed from 1932 to 1937. Under that new status, the Viceroy of India assumed direct control over Aden, which had h ...
(1932–1937), Aden Colony (1937–1963) and finally State of Aden (1963–1967).
In exchange for British protection, the rulers of the constituent territories of the Protectorate agreed not to enter into treaties with or cede territory to any other foreign power.
In 1917, control of Aden Protectorate was transferred from the Government of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
, which had inherited the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
's interests in various princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
s on the strategically important naval route from Europe to India, to the British Foreign Office
Foreign may refer to:
Government
* Foreign policy, how a country interacts with other countries
* Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in many countries
** Foreign Office, a department of the UK government
** Foreign office and foreign minister
* Unit ...
. For administrative purposes, the protectorate was informally divided into the Eastern Protectorate (with its own Political Officer, a British advisor, stationed at Mukalla
Mukalla ( ar, ٱلْمُكَلَّا, ') is a seaport and the capital city of Yemen's largest governorate, Hadhramaut. The city is in the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula on the Gulf of Aden, on the shores of the Arabian Sea, about east of ...
in Qu'aiti from 1937 to ca. 1967) and the Western Protectorate (with its own Political Officer, stationed at Lahej from 1 April 1937 to 1967), for some separation of administration.
In 1928, the British established Aden Command, under Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
leadership, to preserve the security of the Protectorate. It was renamed British Forces Aden
British Forces Aden was the name given to the British Armed Forces stationed in the Aden Protectorate during part of the 20th century. Their purpose was to preserve the security of the Protectorate from both internal threats and external aggressi ...
in 1936 and was later known as British Forces Arabian Peninsula and then Middle East Command (Aden).
Polities
The boundaries between the polities and even their number fluctuated over time. Some such as the Mahra Sultanate barely had any functioning administration. Not included in the protectorate were Aden Colony and the insular areas ofPerim
Perim ( ar, بريم 'Barīm'', also called Mayyun in Arabic, is a volcanic island in the Strait of Mandeb at the south entrance into the Red Sea, off the south-west coast of Yemen and belonging to Yemen. It administratively belongs to Dh ...
, Kamaran
Kamaran Island ( ar, كمران ''Kamarān'') is the largest Yemeni island in the Red Sea. The island is long and wide and is strategically located at the southern end of the Red Sea. It is a "shelf island" located in the shallow waters of the ...
, and Khuriya Muriya that accrued to it.
Eastern Protectorate

 The Eastern Protectorate (c. 230,000 km2) came to include the following entities (mostly in Hadhramaut):
*
The Eastern Protectorate (c. 230,000 km2) came to include the following entities (mostly in Hadhramaut):
* Kathiri
Kathiri ( ar, ٱلْكَثِيْرِي, al-Kathīrī), officially the Kathiri State of Seiyun ( ar, ٱلسَّلْطَنَة ٱلْكَثِيْرِيَّة - سَيْؤُوْن, al-Salṭanah al-Kathīrīyah - Sayʾūn), was a sultanate in the ...
* Mahra
* Qu'aiti
* Wahidi Balhaf
Wahidi Balhaf ( '), or the Wahidi Sultanate of Balhaf in Hadhramaut ( ar, سلطنة الواحدي في بالحاف '), was one of several Wahidi states in the British Aden Protectorate. It was previously part of the Federation of Arab Emirat ...
* Wahidi Bir Ali
Wahidi Bir Ali ( '), or the Wahidi Sultanate of Bir Ali ( ar, سلطنة واحدي بير علي '), was one of several Wahidi states in the British Aden Protectorate and the Protectorate of South Arabia. Its capital was Bi'r `Ali on the Gu ...
* Wahidi Haban
Wahidi Habban ( '), or the Wahidi Sultanate of Habban in Hadhramaut ( ar, سلطنة الواحدي حبان حضرموت '), was one of several Wahidi states in the British Aden Protectorate. Its capital was Habban. The last sultan, Husayn ibn ...
Western Protectorate
The Western Protectorate (c. 55,000 km2) included: * Alawi * Aqrabi *Audhali
Audhali ( ' or '), or the Audhali Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة العوذلي '), was a state in the British Aden Protectorate. It was a founding member of the Federation of Arab Emirates of the South in 1959 and its successor, the Federation of Sou ...
* Beihan
* Dathina
* Dhala
Dhale or Dhala, also spelled Dali and Dhalea and sometimes prefixed with Al or Ad ( ar, الضالع, Aḍ-Ḍāliʿ), is the capital town of Dhale Governorate in south-western Yemen. It is located at around , in the elevation of around 1500 metr ...
** Qutaibi Dependence of Dhala
* Fadhli
Fadhli ( ar, فضلي '), or the Fadhli Sultanate ( ar, السلطنة الفضلية '), was an independent sultanate on the southern coast of the Arabian Peninsula from the 17th century until 1967.
* Haushabi
* Lahej
* Lower Aulaqi
Lower Aulaqi ( '), or the Lower Aulaqi Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة العوالق السفلى '), was a state in the Aden Protectorate, the Federation of Arab Emirates of the South, and its successor, the Federation of South Arabia. Its capital w ...
* Lower Yafa
* Shaib
Shaib or Sha‘ib ( ar, شعيب '), or the Sheikhdom of Shaib ( ar, مشيخة الشعيب '), was a state in the Aden Protectorate, South Arabia. The area is now part of the Republic of Yemen.
History
The Sha`ib Sheikhdom was established at an ...
* Upper Aulaqi Sheikhdom
The Upper Aulaqi Sheikhdom ( ') was a state in the British Aden Protectorate, the Federation of Arab Emirates of the South, and its successor, the Federation of South Arabia. Its capital was Sa'id. The area of the former state is now central part ...
* Upper Aulaqi Sultanate
The Upper Aulaqi Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة العوالق العليا ') was a state in the British Aden Protectorate and the Federation of South Arabia. Its capital was Nisab.
History
The Lower Aulaqi sultans separated from the Upper Aulaq ...
* Upper Yafa Sultanate and the five Upper Yafa sheikhdoms of:
** Al-Busi
Al-Bu`si, Busi, Bo'sī, ( ''Bu`sī''), or the Bu`si Sheikhdom ( ''Mashyakhat al-Bu`sī''), was a small state in the British Aden Protectorate. It was one of the states of Upper Yafa.
History
Busi was established around the 18th century.
Protector ...
** Al-Dhubi
Al-Dhubi, Al-Dubi ( ''Dhubī''), or the Dhubi Sheikhdom ( ''Mashyakhat ad-Dhubī''), was a small state in the British Aden Protectorate. Dhubi was located between Mawsata in the southwest, Hadrami in the northeast, Lower Yafa in the south and U ...
** Hadrami
** Maflahi
Muflihi, Muflahi ( '), Muflihi or the Muflahi Sheikhdom ( '), was a state in the British Aden Protectorate.
Its last sheikh, Kassim Abdulrahaman Al-Muflihi, was deposed in 1967 upon the founding of the People's Republic of South Yemen and the area ...
** Mawsata
Mawsata, Mausata (), or the Mawsata State ( '), was a state in the British Aden Protectorate. Mawsata was located in the western and southwestern part of Upper Yafa. The main mountain in the area is Jabal Darfan.
Mawsata was the most populated of ...
Advisory treaties
 In 1938, Britain signed an advisory treaty with the Qu'aiti sultan and, throughout the 1940s and 1950s, signed similar treaties with twelve other protectorate states. The following were the states with advisory treaties:
; Eastern Protectorate States
* Kathiri
* Mahra
* Qu'aiti
* Wahidi Balhaf
; Western Protectorate States
* Audhali
* Beihan
* Dhala
* Haushabi
* Fadhli
* Lahej
* Lower Aulaqi
* Lower Yafa
* Upper Aulaqi Sheikhdom
These agreements allowed for the stationing of a
In 1938, Britain signed an advisory treaty with the Qu'aiti sultan and, throughout the 1940s and 1950s, signed similar treaties with twelve other protectorate states. The following were the states with advisory treaties:
; Eastern Protectorate States
* Kathiri
* Mahra
* Qu'aiti
* Wahidi Balhaf
; Western Protectorate States
* Audhali
* Beihan
* Dhala
* Haushabi
* Fadhli
* Lahej
* Lower Aulaqi
* Lower Yafa
* Upper Aulaqi Sheikhdom
These agreements allowed for the stationing of a Resident Advisor
''Resident Advisor'' (also known as ''RA'') is an online music magazine and community platform dedicated to showcasing electronic music, artists and events across the globe. It was established in 2001. ''RA''s editorial team provides news, musi ...
in the signatory states which gave the British a greater degree of control over their domestic affairs. This rationalised and stabilised the rulers' status and laws of succession but had the effect of ossifying the leadership and encouraging official corruption. Aerial bombardment
A bombardment is an attack by artillery fire or by dropping bombs from aircraft on fortifications, combatants, or towns and buildings.
Prior to World War I, the term was only applied to the bombardment of defenseless or undefended objects, ...
and collective punishment
Collective punishment is a punishment or sanction imposed on a group for acts allegedly perpetrated by a member of that group, which could be an ethnic or political group, or just the family, friends and neighbors of the perpetrator. Because ind ...
were sometimes used against wayward tribes to enforce the rule of Britain's clients. British protection came to be seen as an impediment to progress, a view reinforced by the arrival of news of Arab nationalism
Arab nationalism ( ar, القومية العربية, al-Qawmīya al-ʿArabīya) is a nationalist ideology that asserts the Arabs are a nation and promotes the unity of Arab people, celebrating the glories of Arab civilization, the language ...
from the outside world on newly available transistor radio
A transistor radio is a small portable radio receiver that uses transistor-based circuitry. Following the invention of the transistor in 1947—which revolutionized the field of consumer electronics by introducing small but powerful, convenient ...
s.
Challenges to the status quo
British control was also challenged byKing
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen regnant, queen, which title is also given to the queen consort, consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contempora ...
Ahmad bin Yahya
, succession = King and Imam of Yemen
, image = YemenAhmad.jpg
, image_size =
, caption =
, reign = 17 February 1948 – 19 September 1962
, predecessor = Yahya Muhammad Hamid ed-Din
, successor = M ...
of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen
The Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen ( ar, المملكة المتوكلية اليمنية '), also known as the Kingdom of Yemen or simply as Yemen, or, retrospectively, as North Yemen, was a state that existed between 1918 and 1962 in the nor ...
to the north who did not recognise British suzerainty in South Arabia and had ambitions of creating a unified Greater Yemen. In the late 1940s and the early 1950s, Yemen was involved in a series of border skirmishes along the disputed Violet Line, a 1914 Anglo-Ottoman demarcation that served to separate Yemen from the Aden Protectorate.
In 1950, Kennedy Trevaskis, the Advisor for the Western Protectorate drew up a plan for the protectorate states to form two federations, corresponding to the two-halves of the protectorate. Although little progress was made in bringing the plan to fruition, it was considered a provocation by Ahmad bin Yahya. In addition to his role as king, he also served as the imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, serve ...
of the ruling Zaidi branch of Shi'a Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most ...
. He feared that a successful federation in the Shafi'i
The Shafii ( ar, شَافِعِي, translit=Shāfiʿī, also spelled Shafei) school, also known as Madhhab al-Shāfiʿī, is one of the four major traditional schools of religious law (madhhab) in the Sunnī branch of Islam. It was founded by ...
Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a dis ...
te protectorates would serve as a beacon for discontented Shafi'ites who inhabited the coastal regions of Yemen. To counter the threat, Ahmad stepped up Yemeni efforts to undermine British control and, in the mid-1950s, Yemen supported a number of revolts by disgruntled tribes against protectorate states. The appeal of Yemen was limited initially in the protectorate but a growing intimacy between Yemen and the popular Arab nationalist president of Egypt Gamal Abdel Nasser
Gamal Abdel Nasser Hussein, . (15 January 1918 – 28 September 1970) was an Egyptian politician who served as the second president of Egypt from 1954 until his death in 1970. Nasser led the Egyptian revolution of 1952 and introduced far-r ...
and the formation of United Arab States increased its attraction.
Federation and the end of the Protectorate
Aden had been of interest to Britain as a link toBritish India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
and then, after the loss of most of Britain's colonies from 1945 and the disastrous Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 Wa ...
in 1956, as a valuable port for accessing crucial Middle Eastern oil. It had also been chosen as the new location for Middle East Command
Middle East Command, later Middle East Land Forces, was a British Army Command established prior to the Second World War in Egypt. Its primary role was to command British land forces and co-ordinate with the relevant naval and air commands to ...
.
Nationalist pressure prodded the threatened rulers of the Aden Protectorate states to revive efforts at forming a federation and, on 11 February 1959, six of them signed an accord forming the ''Federation of Arab Emirates of the South
__NOTOC__
The Federation of the Emirates of the South ( ar, اتحاد إمارات الجنوب العربي ''Ittiḥād ʾImārāt al-Janūb al-ʿArabiyy'') was an organization of states within the British Aden Protectorate in what would be ...
''. In the next three years, they were joined by nine others and, on 18 January 1963, Aden Colony was merged with the federation creating the new ''Federation of South Arabia
The Federation of South Arabia ( ar, اتحاد الجنوب العربي ') was a federal state under British protection in what would become South Yemen. Its capital was Aden.
It was formed on 4 April 1962 from the 15 protected states of ...
''. At the same time, the (mostly eastern) states that had not joined the federation became the ''Protectorate of South Arabia
The Protectorate of South Arabia consisted of various states located at the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula under treaties of protection with Britain. The area of the former protectorate became part of South Yemen after the Radfan upri ...
'', thus ending the existence of the Aden Protectorate.
Aden Emergency
On 10 December 1963, astate of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to be able to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state du ...
was declared in the former protectorate and the newly created State of Aden.
The Emergency was precipitated in large part by a wave of Arab nationalism
Arab nationalism ( ar, القومية العربية, al-Qawmīya al-ʿArabīya) is a nationalist ideology that asserts the Arabs are a nation and promotes the unity of Arab people, celebrating the glories of Arab civilization, the language ...
spreading to the Arabian Peninsula and stemming largely from the Socialist and pan-Arabist doctrines of the Egyptian leader Gamel Abdel Nasser. The British, French, and Israeli invasion forces that had invaded Egypt following Nasser's nationalisation
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to p ...
of the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popula ...
in 1956 had been forced to withdraw following intervention from both the United States and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
.
Nasser had only limited success in spreading his pan-Arabist doctrines through the Arab world, with his 1958 attempt to unify Egypt and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
as the United Arab Republic
The United Arab Republic (UAR; ar, الجمهورية العربية المتحدة, al-Jumhūrīyah al-'Arabīyah al-Muttaḥidah) was a sovereign state in the Middle East from 1958 until 1971. It was initially a political union between Eg ...
collapsing in failure only 3 years later. An anti-colonial uprising in Aden in 1963 provided another potential opportunity for his doctrines, though it is not clear whether the revolt among the Arabs in Aden had the Yemeni guerrilla groups drawing inspiration from Nasser's pan-Arabist ideas or acting independently themselves.
By 1963 and in the ensuing years, anti-British guerrilla groups with varying political objectives began to coalesce into two larger, rival organisations: first the Egyptian-supported National Liberation Front (NLF) and then the Front for the Liberation of Occupied South Yemen (FLOSY), who attacked each other as well as the British.
 By 1965, the RAF station (
By 1965, the RAF station (RAF Khormaksar
Royal Air Force Khormaksar or more simply RAF Khormaksar was a Royal Air Force (RAF) station in Aden, Yemen. Its motto was "Into the Remote Places". During the 1960s, it was the base for nine squadrons and became the RAF's busiest-ever station ...
) was operating nine squadrons. These included transport units with helicopters and a number of Hawker Hunter
The Hawker Hunter is a transonic British jet-powered fighter aircraft that was developed by Hawker Aircraft for the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It was designed to take advantage of the newly developed Rolls-Ro ...
ground attack aircraft. They were called in by the army for strikes against positions using "60 lb" high explosive rockets and 30 mm Aden
The Royal Small Arms Factory ADEN cannon (ADEN being an acronym for "Armament Development, Enfield") is a 30 mm revolver cannon used on many military aircraft, particularly those of the British Royal Air Force and Fleet Air Arm. Developed ...
cannon.
The Battle of Crater brought Lt-Col Colin Campbell Mitchell (AKA "Mad Mitch") to prominence. On 20 June 1967 there was a mutiny in the South Arabian Federation Army, which spread to the police. Order was restored by the British, mainly due to the efforts of the 1st Battalion Argyll and Sutherland Highlanders
Argyll (; archaically Argyle, in modern Gaelic, ), sometimes called Argyllshire, is a historic county and registration county of western Scotland.
Argyll is of ancient origin, and corresponds to most of the part of the ancient kingdom of ...
, under the command of Lt-Col Mitchell.
Nevertheless, deadly guerrilla attacks particularly by the NLF soon resumed against British forces, with the British leaving Aden by the end of November 1967, earlier than had been planned by British Prime Minister Harold Wilson
James Harold Wilson, Baron Wilson of Rievaulx, (11 March 1916 – 24 May 1995) was a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from October 1964 to June 1970, and again from March 1974 to April 1976. He ...
and without an agreement on the succeeding governance. The NLF then seized power.
References
Further reading
* Paul Dresch. ''A History of Modern Yemen''.Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2000. * R. J. Gavin. ''Aden Under British Rule: 1839–1967''. London: C. Hurst & Company, 1975. * Tom Little. ''South Arabia: Arena of Conflict''. London: Pall Mall Press, 1968.External links
Official website of the Al-Quaiti Royal Family of Hadhramaut
Map of Arabia (1905–1923) including the states of Aden Protectorate
British-Yemeni Society
Aden Veterans Association
{{South Arabia 1886 establishments in Asia 1886 establishments in the British Empire 1963 disestablishments in Asia 1963 disestablishments in the British Empire 19th century in Yemen 19th-century establishments in Yemen 20th century in Yemen Aden in World War II Aden Former countries in the Middle East States and territories disestablished in 1963 States and territories established in 1872 United Kingdom–Yemen relations Former countries South Arabia Former monarchies of Asia Former British protectorates