Adıyaman Province on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Adıyaman Province ( tr, , ku, ) is a
Adıyaman Province ( tr, , ku, ) is a
 Adıyaman Province ( tr, , ku, ) is a
Adıyaman Province ( tr, , ku, ) is a province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''Roman province, provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire ...
in the Southeastern Anatolia Region
The Southeastern Anatolia Region ( tr, Güneydoğu Anadolu Bölgesi) is a geographical region of Turkey. The most populous city in the region is Gaziantep. Other examples of big cities are Şanlıurfa, Diyarbakır, Mardin and Adıyaman.
It ...
of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
. The capital is Adıyaman
Adıyaman ( ku, Semsûr) is a city and district in southeastern Turkey, and the capital of the Adıyaman Province. The inhabitants of the city are mostly Kurdish.
Etymology
An unverified theory is that the former name of the city ''Hisn-Mansur'' ...
. The province is considered part of Turkish Kurdistan
Turkish Kurdistan or Northern Kurdistan () refers to the southeastern part of Turkey, where Kurds form the predominant ethnic group. The Kurdish Institute of Paris estimates that there are 20 million Kurds living in Turkey, the majority of the ...
and has a Kurdish
Kurdish may refer to:
*Kurds or Kurdish people
*Kurdish languages
*Kurdish alphabets
*Kurdistan, the land of the Kurdish people which includes:
**Southern Kurdistan
**Eastern Kurdistan
**Northern Kurdistan
**Western Kurdistan
See also
* Kurd (dis ...
majority.
Adıyaman Province was part of the province of Malatya
Malatya ( hy, Մալաթիա, translit=Malat'ya; Syro-Aramaic ܡܠܝܛܝܢܐ Malīṭīná; ku, Meletî; Ancient Greek: Μελιτηνή) is a large city in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey and the capital of Malatya Province. The city h ...
until 1954, when it was made into a province as a reward for voting for the winning Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
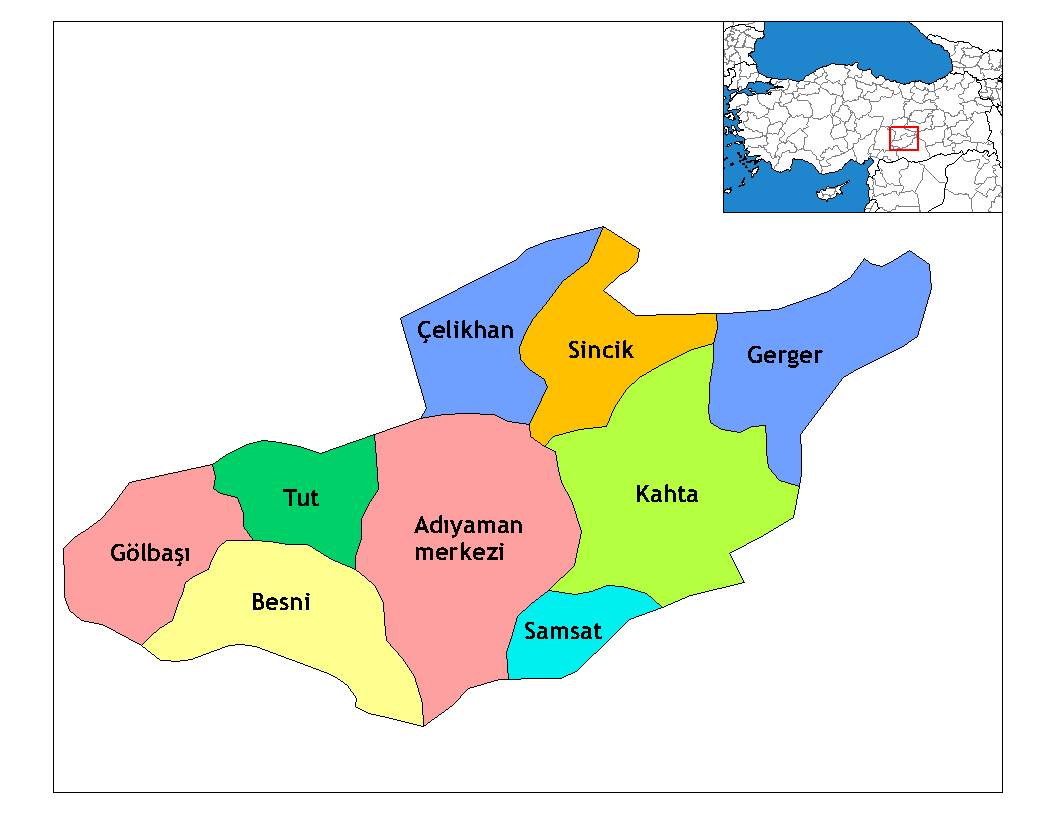
in the 1954 general election. The province consists of the districts Adıyaman
Adıyaman ( ku, Semsûr) is a city and district in southeastern Turkey, and the capital of the Adıyaman Province. The inhabitants of the city are mostly Kurdish.
Etymology
An unverified theory is that the former name of the city ''Hisn-Mansur'' ...
(center district), Besni
Besni ( ku, Bêsnî) is a town and district of Adıyaman Province of Turkey, 44 km west of the city of Adıyaman.
History
The city was historically known as Bahasna. It was controlled by the Byzantines until it was captured by the Umayyad arm ...
, Çelikhan, Gerger
Gerger ( ku, Aldûş) is a town of Adıyaman Province of Turkey. It is the seat of Gerger District.Gölbaşı,
Kâhta
Kâhta ( ku, Kolîk, Ottoman Turkish: کولک / ''Kölük'') is a city in Adıyaman Province of Turkey. It is the seat of Kâhta District.Samsat
Samsat ( ku, Samîsad), formerly Samosata ( grc, Σαμόσατα) is a small town in the Adıyaman Province of Turkey, situated on the upper Euphrates river. It is the seat of Samsat District.Sincik
Sincik ( ku, Sinciq) is a town of Adıyaman Province of Turkey. It is the seat of Sincik District.Tut.
History
Early Armenian rule
Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
existence in Adıyaman dates back to the 4th century, where they were known as 'fire worshippers'. Armenians lived in the area when Arab Muslims captured the area in 639. The Arabs considered the city as part of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
and experienced immigration from Byzantine Armenia
Byzantine Armenia, sometimes known as Western Armenia, is the name given to the parts of Kingdom of Armenia that became part of the Byzantine Empire. The size of the territory varied over time, depending on the degree of control the Byzantine ...
due to Byzantine oppression in 713. The city came under Seljuk rule after the Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and th ...
in 1071 and the local Armenians established principalities
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall under ...
in the area. One of these principalities was founded by Philaretos Brachamios
Philaretos Brachamios ( el, Φιλάρετος Βραχάμιος; Armenian: Փիլարտոս Վարաժնունի, Pilartos Varajnuni; la, Philaretus Brachamius) or Vahram Varajnuni was a distinguished Byzantine general and warlord of Armenia ...
who tried to protect the land between the Seljuk and the Byzantine. The Armenians had good relations with the European Crusader states
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political in ...
, but the Crusader County of Edessa
The County of Edessa (Latin: ''Comitatus Edessanus'') was one of the Crusader states in the 12th century. Ferdinandi, Sergio (2017). La Contea Franca di Edessa. Fondazione e Profilo Storico del Primo Principato Crociato nel Levante (1098-115 ...
would advance against the Armenians in Adıyaman. Political leaders in Adıyaman were also victims of assassinations by Edessa. Wife of Kogh Vasil Kogh Vasil, or Vasil the Robber (; died on 12 October 1112), was the Armenian ruler of Raban and Kaisun at the time of the First Crusade. In the early 12th century, he was the most influential Armenian ruler who adhered to the Armenian Apostolic C ...
founded an army to protect the area from Edessa as well, but Edessa ultimately captured the area. Close relations between the Armenians and the Crusader states, however, continued until Nur ad-Din captured the area in 1150. The area came under the rule of Timurtash of the Artuqids for his support for Nur ad-Din and later the Seljuks from the beginning of the 13th century. The locals failed at removing the rulership of Kilij Arslan II during the late 12th century. In the subsequent period, the area was fought over between the Mamluk Sultanate
The Mamluk Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة المماليك, translit=Salṭanat al-Mamālīk), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz (western Arabia) from the mid-13th to early 16th ...
and the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia (Middle Armenian: , '), also known as Cilician Armenia ( hy, Կիլիկեան Հայաստան, '), Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia ( hy, ...
, changing hands between the two.
Ottoman rule
Ottoman SultanSelim I
Selim I ( ota, سليم الأول; tr, I. Selim; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute ( tr, links=no, Yavuz Sultan Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite las ...
captured the area during the Ottoman–Mamluk War in 1516-1517. In the first defter of the area in 1519, it was mentioned that the Kurdish Reşwan tribe populated the area. Documents from 1524 and 1536 also contain records of the Reşwan tribe living in the area. The tribe was engaged in agriculture after having had a nomadic lifestyle.
Evliya Çelebi
Derviş Mehmed Zillî (25 March 1611 – 1682), known as Evliya Çelebi ( ota, اوليا چلبى), was an Ottoman explorer who travelled through the territory of the Ottoman Empire and neighboring lands over a period of forty years, recording ...
visited the city in the 17th century and described the agricultural life.
At the beginning of the 19th century, most Armenians lived near the castle of Adıyaman city and mostly made their living through shop keeping and trading. In the villages, they were involved in agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
and animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, starti ...
. The local Armenians welcomed American missionaries approaching them during the 19th century at first, but prevented them from converted them later on. Some of the Gregorian Armenians did however convert to Protestantism and the missionaries ultimately divided the local Armenian community. Ainsworth
Ainsworth may refer to:
Places
;Canada
*Ainsworth Hot Springs, British Columbia
;United Kingdom
*Ainsworth, Greater Manchester, England
;United States
* Ainsworth, Indiana
*Ainsworth, Iowa
*Ainsworth, Nebraska
*Ainsworth, Wisconsin
*Ainsworth, Wa ...
visited the town of Adıyaman in the 1842 and mentioned that the town contained 800 Muslim households and 300 Armenian households and that it had several mosques
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, i ...
but no churches. After his visit to the town, he visited the Kurdish village of Kerkunah in the outskirts and afterwards Kâhta
Kâhta ( ku, Kolîk, Ottoman Turkish: کولک / ''Kölük'') is a city in Adıyaman Province of Turkey. It is the seat of Kâhta District.Kurdish
Kurdish may refer to:
*Kurds or Kurdish people
*Kurdish languages
*Kurdish alphabets
*Kurdistan, the land of the Kurdish people which includes:
**Southern Kurdistan
**Eastern Kurdistan
**Northern Kurdistan
**Western Kurdistan
See also
* Kurd (dis ...
in 1882, while Turkish was prevalent in Adıyaman town.
Armenian nationalism
Armenian nationalism in the modern period has its roots in the romantic nationalism of Mikayel Chamchian (1738–1823) and generally defined as the creation of a free, independent and united Armenia formulated as the Armenian Cause ( hy, Հայ ...
increased among the Armenians by the end of the century and most of the Armenian population fell victim to the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was ...
in 1915. There are, however, still some Armenians around Kâhta
Kâhta ( ku, Kolîk, Ottoman Turkish: کولک / ''Kölük'') is a city in Adıyaman Province of Turkey. It is the seat of Kâhta District.
The area was part of
Mamuret-ul-Aziz Vilayet
The Vilayet of Mamuret-ul-Aziz,Vilayet of Ma'muretül'aziz, ''Redhouse Yeni Türkçe-İngilizce Sözlük'', On İkinci Basım, Redhouse Yayınevi, 1991, , p. 729, Ma'mûretü'l-Azîz, Ma'muretül Aziz or Mamûretü'l-Azîz ( Ottoman: ''Vilâyet- ...
as Behisni, Hasanmansur and Kahta districts. These three districts had a total population of 99,439 in 1914 of which was Muslim and Christian.
Republican era
The names of 224 villages in Adiyaman Province was Turkified as part of the campaign to remove any mention of Kurdishness in the country. In 1932, the whole region was chiefly populated by Kurds. The province had a population of 208,755 in 1955 of which adhered toIslam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
and to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
. In 1960, the province had a population of 233,717 of which was Muslim and Christian. In 1965, the population increased to 267,277 of which was Muslim and Christian. The Turkish authorities put the province under State of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to be able to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state du ...
(OHAL
The OHAL region ( tr, Olağanüstü Hâl Bölge Valiliği, lit=Governorship of Region in State of Emergency) was a "super-region" created in Turkey under state of emergency legislation, as part of its approach to the Kurdish–Turkish conflict. Fr ...
) in the early 1990s as part of the Kurdish–Turkish conflict
Kurdish nationalist uprisings have periodically occurred in Turkey, beginning with the Turkish War of Independence and the consequent transition from the Ottoman Empire to the modern Turkish state and continuing to the present day with the curr ...
.
Demographics
Out of the 339 villages in the province, 296 are populated by Kurds while the remaining 43 are populated by Turks. In terms of religious affiliation, 293 of the villages have an Hanafi population, 80 villages with an Alevi population and two villages are reported to having aShafi'i
The Shafii ( ar, شَافِعِي, translit=Shāfiʿī, also spelled Shafei) school, also known as Madhhab al-Shāfiʿī, is one of the four major traditional schools of religious law (madhhab) in the Sunnī branch of Islam. It was founded by ...
population.
The majority of the population is Hanafi
The Hanafi school ( ar, حَنَفِية, translit=Ḥanafiyah; also called Hanafite in English), Hanafism, or the Hanafi fiqh, is the oldest and one of the four traditional major Sunni schools ( maddhab) of Islamic Law (Fiqh). It is named aft ...
Kurdish
Kurdish may refer to:
*Kurds or Kurdish people
*Kurdish languages
*Kurdish alphabets
*Kurdistan, the land of the Kurdish people which includes:
**Southern Kurdistan
**Eastern Kurdistan
**Northern Kurdistan
**Western Kurdistan
See also
* Kurd (dis ...
, with a significant Kurdish Alevi population. One estimate from 2014 places the Alevi population at 11%. The province is generally more pious than other Kurdish areas in Turkey and has been a hotspot for radicalization and Islamism
Islamism (also often called political Islam or Islamic fundamentalism) is a political ideology which posits that modern states and regions should be reconstituted in constitutional, economic and judicial terms, in accordance with what is ...
in recent years (see Dokumacılar
The Dokumacılar (English: ''Weavers'') was a Turkish organisation linked to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) that specifically targeted the Kurdish People's Protection Units (YPG) that were fighting against ISIL in the Syrian Civ ...
). Historian Şahidin Şimşek argued that Hanafi adherents in the province had been manipulated by the state to believe that Kurdish nationalism
Kurdish nationalism (, ) is a nationalist political movement which asserts that Kurds are a nation and espouses the creation of an independent Kurdistan from Iran, Iraq, Syria and Turkey.
Early Kurdish nationalism had its roots in the Ottoman ...
equated to Alevism. Another theory points at the poverty in the province.
The Kurdish tribes in the province include the Alikan, Atman, Balyan, Belikan tribe, Bêzikan, Birîmşa, Bîstikan, Canbegan, Celikan, Dêrsimî, Dirêjan, Gewozî, Hevêdan, Heyderan, Hûriyan, Izol, Kawan, Kerdizan, Kîkan, Kirvar, Mirdesan, Molikan, Mukriyan, Pîrvan, Reşwan, Şavak, Sinemilli, Sînanka, Şêxbizin and the Teşikan tribe.
The Alevis of the western districts of Besni
Besni ( ku, Bêsnî) is a town and district of Adıyaman Province of Turkey, 44 km west of the city of Adıyaman.
History
The city was historically known as Bahasna. It was controlled by the Byzantines until it was captured by the Umayyad arm ...
, Gölbaşı and Tut are Turkmen and Kurdish.
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Adiyaman Province Provinces of Turkey Turkish Kurdistan