Abort, Retry, Fail? on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
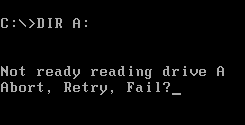 "Abort, Retry, Fail?" (or "Abort, Retry, Ignore?") is an
"Abort, Retry, Fail?" (or "Abort, Retry, Ignore?") is an
error message
An error message is information displayed when an unforeseen occurs, usually on a computer or other device. On modern operating systems with graphical user interfaces, error messages are often displayed using dialog boxes. Error messages are use ...
found in DOS
DOS is shorthand for the MS-DOS and IBM PC DOS family of operating systems.
DOS may also refer to:
Computing
* Data over signalling (DoS), multiplexing data onto a signalling channel
* Denial-of-service attack (DoS), an attack on a communicat ...
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
s, which prompts the end-user
In product development, an end user (sometimes end-user) is a person who ultimately uses or is intended to ultimately use a product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product, such as sysops, system administrato ...
for a course of action to follow. Although welcomed by some, the message also has been cited as an example of poor usability
Usability can be described as the capacity of a system to provide a condition for its users to perform the tasks safely, effectively, and efficiently while enjoying the experience. In software engineering, usability is the degree to which a sof ...
in computer user interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine f ...
s.
Background
InCP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/ 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initi ...
, attempting to read a floppy disk drive
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined w ...
with the door open would hang until a disk was inserted and the disk drive door was closed (very early disk hardware did not send any kind of signal until a disk was spinning, and a timeout to detect the lack of signal required too much code on these tiny systems). Many users of CP/M became accustomed to this as a method of managing multiple disks, by opening the disk drive to stop a program from reading or writing a file until the correct disk could be inserted.
A primary design consideration for PC DOS was that software written for CP/M be portable
Portable may refer to:
General
* Portable building, a manufactured structure that is built off site and moved in upon completion of site and utility work
* Portable classroom, a temporary building installed on the grounds of a school to provide ...
to DOS without changes. Even the first IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team ...
had hardware that told the operating system that the disk drive door was open, but returning an error to software trying to read the disk would break the ability to manage disks this way without such changes. Still, it was desirable to improve the experience, in particular by giving the user a way to get out of the hang without having to find a disk to insert in the drive. The prompt was invented for this reason.
Description
A missing disk (or disk drive door opened) was defined by DOS as a "critical error" and would call the "critical error handler". The default "critical error handler" was part ofCOMMAND.COM
COMMAND.COM is the default command-line interpreter for MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 and Windows Me. In the case of DOS, it is the default user interface as well. It has an additional role as the usual first program run after boot (init proc ...
and printed the "Abort, Retry, ..." prompt, then waited for user input. Other problems (in particular, a checksum error while reading data from a disk) were also defined as a "critical error", thus causing the prompt to appear for reasons other than a missing disk or opened disk drive. Users could press a key to indicate what they wanted to happen; available options included:
* Abort (A): Terminate the operation or program, and return to the command prompt. In hindsight, this was not a good idea as the program would not do any cleanup (such as completing writing of other files).
* Retry (R): Attempt the operation again. "Retry" was what the user did if they could fix the problem by inserting a disk and closing the disk drive door. On early hardware, retrying a disk read error would sometimes be successful, but as disk drives improved, this became far less likely.
* Ignore (I): Return success status to the calling program or routine, despite the failure of the operation. This could be used for disk read errors, and DOS would return whatever data was in the read buffer (which might contain some of the correct data). "Ignore" did not appear for open drives or missing disks.
* Fail (F): Starting with MS-DOS/PC DOS 3.3, "Fail" returned an error code to the program, similar to a "file not found" error. The program could then gracefully recover, perhaps asking the user for a different file name. This removed the biggest problem with the prompt (which earlier was known as "Abort, Retry, Ignore?") by providing an option that did not crash the program or repeat the prompt.
A program could install its own "critical error handler" while running, and many of the more sophisticated programs (in particular full screen programs) did so in order to avoid the messages disturbing the display. Some programs faked the missing "Fail" response in DOS 2.0 by jumping back to the calling program, skipping the return stack in DOS. This was a risky hack as it relied on the stack layout and skipped cleanup operations in the operating system.
Usability
The error message has been described as being an example of pooruser interface design
User interface (UI) design or user interface engineering is the design of user interfaces for machines and software, such as computers, home appliances, mobile devices, and other electronic devices, with the focus on maximizing usability and the ...
. For most users, if the message appeared, the only choice was to hit 'R'—which repeated the message—or hit another letter, which caused the program to crash and all work to be lost. The scholar Mireille Hildebrandt described it this way:
MS-DOS 6.22 contained a singular case where the only option was "(R) Retry": when flushing the hard disk write-behind cache could not be completed. The user may attempt to repeat the write until successful or power off the system.
Modern systems
Hard disks and larger removable media such as Zip drives made the need to manage multiple disks per drive obsolete, and thus made the prompt useless. It was gradually replaced with code that acted like "Fail" immediately. DOS 3.3 COMMAND.COM provided the startup option/F to force the default critical error handler to return "Fail" on all errors. Starting with version 4.0, the alternative command line processors 4DOS
4DOS is a command-line interpreter by JP Software, designed to replace the default command interpreter COMMAND.COM in Microsoft DOS and Windows. It was written by Rex C. Conn and Tom Rawson and first released in 1989. Compared to the default, ...
and NDOS supported /F and the corresponding CritFail=Yes directive in 4DOS.INI/NDOS.INI as well. The option was also supported by the COMMAND.COM of PTS-DOS 6.51 and S/DOS 1.0, as well as by DR-DOS 7.02 and higher. In OpenDOS 7.01, COMMAND.COM provides a similar feature with /N (described as "do not install a critical error handler") which is still supported in newer versions. Most other operating systems, such as Linux, always act like "Fail" in all cases.
Windows can still generate a similar prompt, although in a dialog box
The dialog box (also called dialogue box (non-U.S. English), message box or simply dialog) is a graphical control element in the form of a small window that communicates information to the user and prompts them for a response.
Dialog boxes ar ...
and with a more comprehensive error message. The choices are similar but renamed: "Cancel" (to the user this is similar to "Abort" but technically it is a "Fail" with a different error code), "Try Again" (instead of "Retry") and "Continue" (instead of "Fail"). This may be supported by the drivers for some removable media when a file is opened with a full volume name or the disk is removed while the file is open. However for mundane actions similar to what triggered the prompt in DOS, such as attempting to read "E:" when there is no disk in the CD drive, Windows produces an immediate "Fail".
In popular culture
Humorous variations of Edgar Allen Poe's ''The Raven
"The Raven" is a narrative poem by American writer Edgar Allan Poe. First published in January 1845, the poem is often noted for its musicality, stylized language, and supernatural atmosphere. It tells of a distraught lover who is paid a myst ...
'' using "Abort, Retry, Ignore?" in place of "nevermore" were written in the 1980s and 1990s and were quite popular, distributed by bulletin board and email. The original and best known version has been credited to Cleveland poet Marcus Bales Marcus, Markus, Márkus or Mărcuș may refer to:
* Marcus (name), a masculine given name
* Marcus (praenomen), a Roman personal name
Places
* Marcus, a main belt asteroid, also known as (369088) Marcus 2008 GG44
* Mărcuş, a village in Dobâr ...
.
In 1993, Neil Howe
Neil Howe (born October 21, 1951) is an American author and consultant. He is best known for his work with William Strauss on social generations regarding a theorized generational cycle in American history. Howe is currently the managing direct ...
published ''13th Gen: Abort, Retry, Ignore, Fail?'', a sympathetic book about the culture of Generation X
Generation X (or Gen X for short) is the Western demographic cohort following the baby boomers and preceding the millennials. Researchers and popular media use the mid-to-late 1960s as starting birth years and the late 1970s to early 1980s ...
.
In 1996, White Town
Jyoti Prakash Mishra (born 30 July 1966), better known by his stage name White Town, is a British-Indian singer and musician. He is best known for his 1997 hit song " Your Woman".
Early life
Jyoti Prakash Mishra was born in Rourkela on 30 July ...
released an EP entitled '' >Abort, Retry, Fail?_''.
''PC Magazine
''PC Magazine'' (shortened as ''PCMag'') is an American computer magazine published by Ziff Davis. A print edition was published from 1982 to January 2009. Publication of online editions started in late 1994 and have continued to the presen ...
'' has used the term as the title of its column highlighting humorous computer-related errors.
In the 1999 video game Sid Meier's Alpha Centauri
''Sid Meier's Alpha Centauri'' is a 4X video game, considered a spiritual sequel to the ''Civilization'' series. Set in a science fiction depiction of the 22nd century, the game begins as seven competing ideological factions land on the planet ...
"Abort, Retry, Fail?" was graffiti
Graffiti (plural; singular ''graffiti'' or ''graffito'', the latter rarely used except in archeology) is art that is written, painted or drawn on a wall or other surface, usually without permission and within public view. Graffiti ranges from s ...
next to the door of the "Edit Universe project," implied to be a research and development undertaking with an ominous potential. The phrase is introduced as an audio quote when the player achieves the technological advance of "Nanomatter Editation," and ends with the warning, "...if you see this message, ''always'' choose 'Retry'."
See also
*Bad command or file name
"Bad command or file name" is a common and ambiguous error message in MS-DOS and some other operating systems.
COMMAND.COM, the primary user interface of MS-DOS, produces this error message when the first word of a command could not be interpreted ...
* Error message
An error message is information displayed when an unforeseen occurs, usually on a computer or other device. On modern operating systems with graphical user interfaces, error messages are often displayed using dialog boxes. Error messages are use ...
* PC LOAD LETTER
References
{{Error messages DOS technology Computer error messages English phrases