AV-8B on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing) AV-8B Harrier II is a single-engine
 Between 1978 and 1980, the DoD and USN repeatedly attempted to terminate the AV-8B program. There had previously been conflict between the USMC and USN over budgetary issues. At the time, the USN wanted to procure A-18s for its ground attack force and, to cut costs, pressured the USMC to adopt the similarly designed F-18 fighter instead of the AV-8B to fulfill the role of close air support (both designs were eventually amalgamated to create the multirole
Between 1978 and 1980, the DoD and USN repeatedly attempted to terminate the AV-8B program. There had previously been conflict between the USMC and USN over budgetary issues. At the time, the USN wanted to procure A-18s for its ground attack force and, to cut costs, pressured the USMC to adopt the similarly designed F-18 fighter instead of the AV-8B to fulfill the role of close air support (both designs were eventually amalgamated to create the multirole
 Production was authorized on 3 June 1992. The maiden flight of the prototype took place on 22 September, marking the start of a successful flight-test program. The first production aircraft made its initial flight on 17 March 1993. Deliveries of new aircraft took place from April 1993 to 1995. At the same time, the plan to remanufacture existing AV-8Bs to the Plus standard proceeded. On 11 March 1994, the Defense Acquisition Board approved the program,Nordeen 2006, p. 103. which initially involved 70 aircraft, with four converted in
Production was authorized on 3 June 1992. The maiden flight of the prototype took place on 22 September, marking the start of a successful flight-test program. The first production aircraft made its initial flight on 17 March 1993. Deliveries of new aircraft took place from April 1993 to 1995. At the same time, the plan to remanufacture existing AV-8Bs to the Plus standard proceeded. On 11 March 1994, the Defense Acquisition Board approved the program,Nordeen 2006, p. 103. which initially involved 70 aircraft, with four converted in
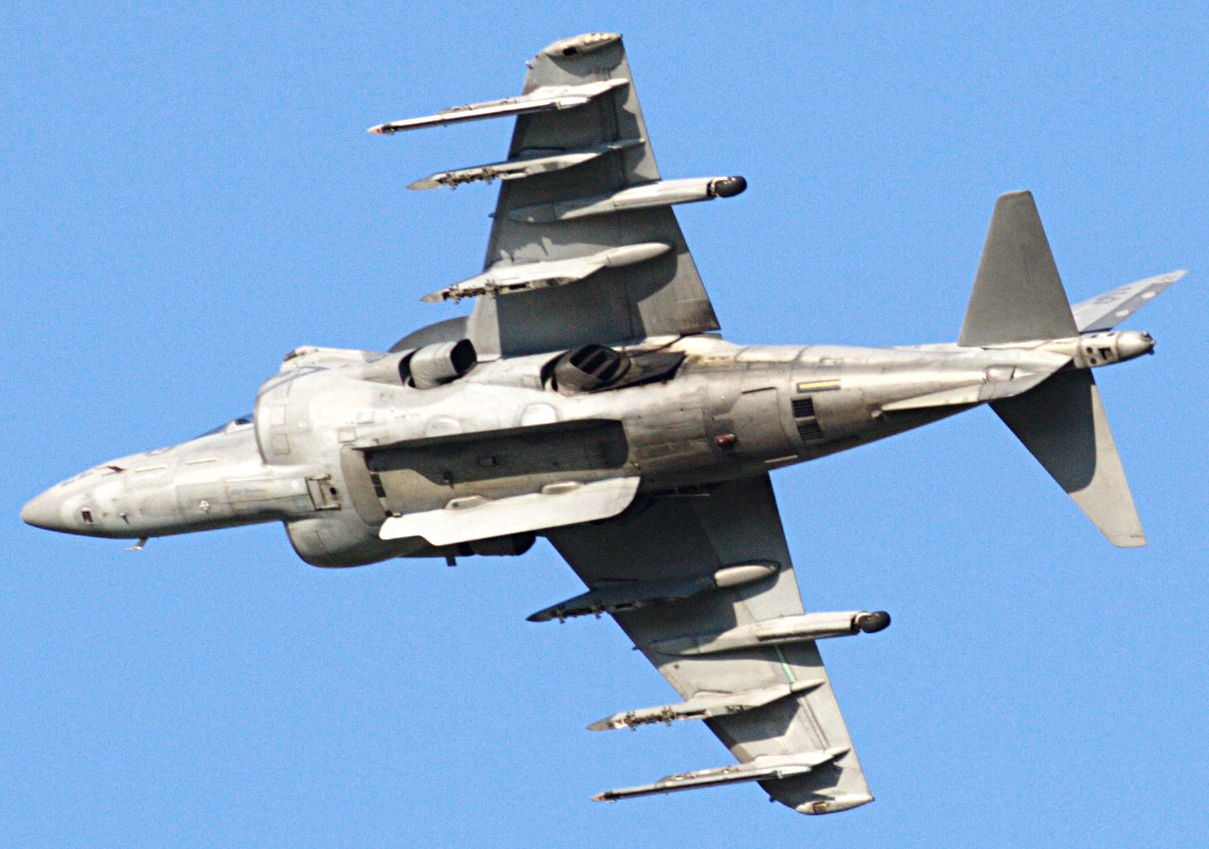 The AV-8B Harrier II is a subsonic attack aircraft of metal and composite construction that retains the basic layout of the Hawker Siddeley Harrier, with horizontal stabilizers and shoulder-mounted wings featuring prominent anhedral (downward slope). The aircraft is powered by a single
The AV-8B Harrier II is a subsonic attack aircraft of metal and composite construction that retains the basic layout of the Hawker Siddeley Harrier, with horizontal stabilizers and shoulder-mounted wings featuring prominent anhedral (downward slope). The aircraft is powered by a single
 The AV-8B saw extensive action in the Gulf War of 1990–91. Aircraft based on and , and at on-shore bases, initially flew training and support
The AV-8B saw extensive action in the Gulf War of 1990–91. Aircraft based on and , and at on-shore bases, initially flew training and support
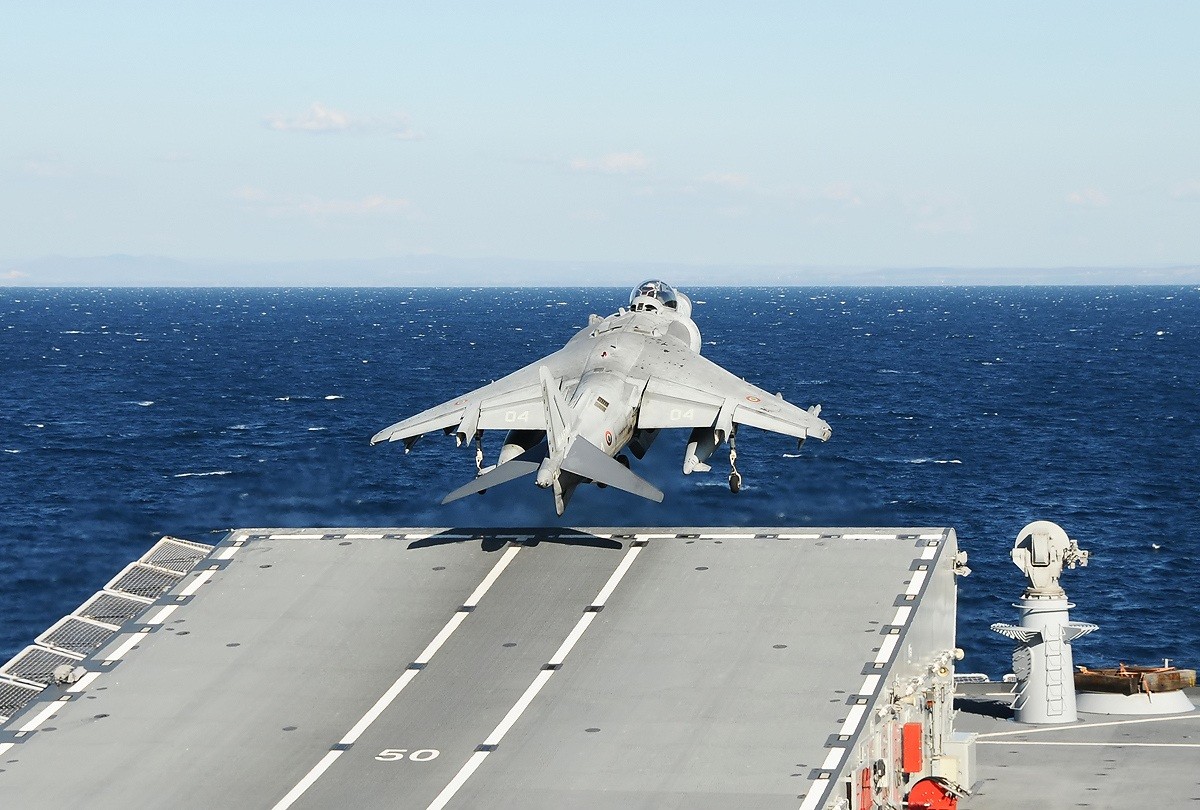 In 1999, Italian AV-8Bs were used for the first time in combat missions when they were deployed aboard ''Giuseppe Garibaldi'', which was participating in Operation Allied Force in
In 1999, Italian AV-8Bs were used for the first time in combat missions when they were deployed aboard ''Giuseppe Garibaldi'', which was participating in Operation Allied Force in
 Spain, already using the AV-8S Matador, became the first international operator of the AV-8B by signing an order for 12 aircraft in March 1983. Designated VA-2 Matador II by the
Spain, already using the AV-8S Matador, became the first international operator of the AV-8B by signing an order for 12 aircraft in March 1983. Designated VA-2 Matador II by the
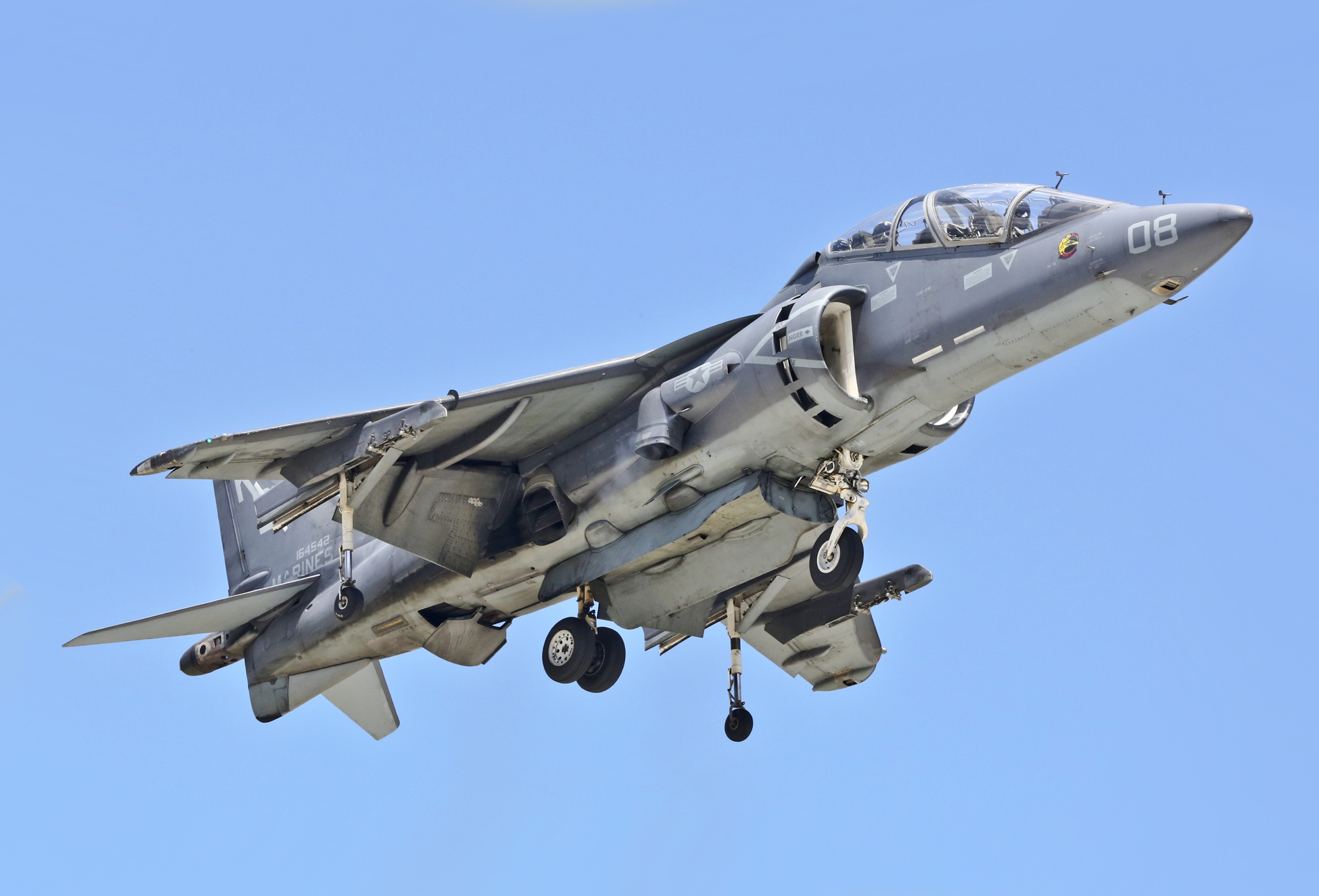 ;AV-8B Harrier II Night Attack: Improved version with FLIR, an upgraded cockpit with night-vision goggle compatibility, and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Pegasus 11 engine.
;AV-8B Harrier II Plus: Similar to the Night Attack variant, with the addition of an APG-65 radar and separate targeting pod. It is used by the USMC, Spanish Navy, and Italian Navy. Forty-six were built.Wilson 2000, p. 48.
;TAV-8B Harrier II: Two-seat trainer version.
;EAV-8B Matador II: Company designation for the Spanish Navy version.
;EAV-8B Matador II Plus: The AV-8B Harrier II Plus, ordered for the Spanish Navy.
;Harrier GR5, GR7, GR9: See ''
;AV-8B Harrier II Night Attack: Improved version with FLIR, an upgraded cockpit with night-vision goggle compatibility, and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Pegasus 11 engine.
;AV-8B Harrier II Plus: Similar to the Night Attack variant, with the addition of an APG-65 radar and separate targeting pod. It is used by the USMC, Spanish Navy, and Italian Navy. Forty-six were built.Wilson 2000, p. 48.
;TAV-8B Harrier II: Two-seat trainer version.
;EAV-8B Matador II: Company designation for the Spanish Navy version.
;EAV-8B Matador II Plus: The AV-8B Harrier II Plus, ordered for the Spanish Navy.
;Harrier GR5, GR7, GR9: See ''

AV-8B Plus product page
at Boeing.com
AV-8B Harrier II page
at Navy.mil
at Globalsecurity.org
McDonnell Douglas/British Aerospace AV-8B Harrier II Attack Fighter page
on Aerospaceweb.org
3D view of Harrier AV-8B
at the National Museum of the Marines Corps site {{DEFAULTSORT:Mcdonnell Douglas AV-8B Harrier II Carrier-based aircraft
ground-attack aircraft
An attack aircraft, strike aircraft, or attack bomber is a tactical military aircraft that has a primary role of carrying out airstrikes with greater precision than bombers, and is prepared to encounter strong low-level air defenses while pres ...
that constitutes the second generation of the Harrier family, capable of vertical or short takeoff and landing (V/STOL). The aircraft is primarily employed on light attack or multi-role missions, ranging from close air support
In military tactics, close air support (CAS) is defined as air action such as air strikes by fixed or rotary-winged aircraft against hostile targets near friendly forces and require detailed integration of each air mission with fire and movemen ...
of ground troops to armed reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops ( skirmishe ...
. The AV-8B is used by the United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through c ...
(USMC), the Spanish Navy
The Spanish Navy or officially, the Armada, is the maritime branch of the Spanish Armed Forces and one of the oldest active naval forces in the world. The Spanish Navy was responsible for a number of major historic achievements in navigation, ...
, and the Italian Navy
"Fatherland and Honour"
, patron =
, colors =
, colors_label =
, march = ( is the return of soldiers to their barrack, or sailors to their ship after a ...
. A variant of the AV-8B, the British Aerospace Harrier II
The British Aerospace Harrier II is a second-generation vertical/short takeoff and landing (V/STOL) jet aircraft used previously by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and, between 2006 and 2010, the Royal Navy (RN). The aircraft was the latest develop ...
, was developed for the British military, while another, the TAV-8B, is a dedicated two-seat trainer.
The project that eventually led to the AV-8B's creation started in the early 1970s as a cooperative effort between the United States and United Kingdom, aimed at addressing the operational inadequacies of the first-generation Hawker Siddeley Harrier
The Hawker Siddeley Harrier is a British military aircraft. It was the first of the Harrier series of aircraft and was developed in the 1960s as the first operational ground attack and reconnaissance aircraft with vertical/short takeoff an ...
. Early efforts centered on a larger, more powerful Pegasus engine to dramatically improve the capabilities of the Harrier. Because of budgetary constraints, the UK abandoned the project in 1975. Following the UK's withdrawal, McDonnell Douglas
McDonnell Douglas was a major American aerospace manufacturing corporation and defense contractor, formed by the merger of McDonnell Aircraft and the Douglas Aircraft Company in 1967. Between then and its own merger with Boeing in 1997, it ...
extensively redesigned the earlier AV-8A Harrier to create the AV-8B. While retaining the general layout of its predecessor, the aircraft incorporates a new, larger composite
Composite or compositing may refer to:
Materials
* Composite material, a material that is made from several different substances
** Metal matrix composite, composed of metal and other parts
** Cermet, a composite of ceramic and metallic materials ...
wing with an additional hardpoint
A hardpoint is an attachment location on a structural frame designed to transfer force and carry an external or internal structural load, load. The term is usually used to refer to the mounting points (more formally known as a weapon station or ...
on each side, an elevated cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, usually near the front of an aircraft or spacecraft, from which a pilot controls the aircraft.
The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the controls that e ...
, a redesigned fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft t ...
and other structural and aerodynamic
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dyn ...
refinements. The aircraft is powered by an upgraded version of the Pegasus. The AV-8B made its maiden flight
The maiden flight, also known as first flight, of an aircraft is the first occasion on which it leaves the ground under its own power. The same term is also used for the first launch of rockets.
The maiden flight of a new aircraft type is alw ...
in November 1981 and entered service with the USMC in January 1985. Later upgrades added a night-attack capability and radar, resulting in the AV-8B(NA) and AV-8B Harrier II Plus versions, respectively. An enlarged version named Harrier III was also studied but not pursued. The UK, through British Aerospace
British Aerospace plc (BAe) was a British aircraft, munitions and defence-systems manufacturer. Its head office was at Warwick House in the Farnborough Aerospace Centre in Farnborough, Hampshire. Formed in 1977, in 1999 it purchased Marconi ...
, re-joined the improved Harrier project as a partner in 1981, giving it a significant work-share in the project. Following corporate mergers in the 1990s, Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and ...
and BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh-largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenue ...
have jointly supported the program. Approximately 340 aircraft were produced in a 22-year production program that ended in 2003.
Typically operated from small aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a ...
s, large amphibious assault ship
An amphibious assault ship is a type of amphibious warfare ship employed to land and support ground forces on enemy territory by an amphibious assault. The design evolved from aircraft carriers converted for use as helicopter carriers (and, a ...
s and simple forward operating base
A forward operating base (FOB) is any secured forward operational level military position, commonly a military base, that is used to support strategic goals and tactical objectives. A FOB may or may not contain an airfield, hospital, machine ...
s, AV-8Bs have participated in numerous military and humanitarian operations, proving themselves versatile assets. U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
General Norman Schwarzkopf
Herbert Norman Schwarzkopf Jr. (; August 22, 1934 – December 27, 2012) was a United States Army general. While serving as the commander of United States Central Command, he led all coalition forces in the Gulf War.
Born in Trenton, N ...
named the USMC Harrier II as one of several important weapons in the Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Iraq were carried out in two key phases: ...
. It has also served in Operation Enduring Freedom
Operation Enduring Freedom (OEF) was the official name used synonymously by the U.S. government for both the War in Afghanistan (2001–2014) and the larger-scale Global War on Terrorism. On 7 October 2001, in response to the September 11 a ...
in Afghanistan since 2001, the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003–present), I ...
since 2003, and was used in Operation Odyssey Dawn
Operation Odyssey Dawn was the U.S. code name for the American role in the international military operation in Libya to enforce United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973 during the initial period of 19–31 March 2011, which continued af ...
in Libya in 2011. Italian and Spanish Harrier IIs have taken part in overseas conflicts in conjunction with NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
coalitions. During its service history, the AV-8B has had a high accident rate, related to the percentage of time spent in critical take-off and landing phases. USMC and Italian Navy AV-8Bs are being replaced by the Lockheed Martin F-35B Lightning II
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is an American family of single-seat, single-engine, all-weather stealth multirole combat aircraft that is intended to perform both air superiority and strike missions. It is also able to provide elect ...
, with the former expected to operate its Harriers until 2025.
Development
Origins
In the late 1960s and early 1970s, the first-generation Harriers entered service with theRoyal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
(RAF) and USMC but were handicapped in range and payload
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of ...
. In short takeoff and landing configuration, the AV-8A (American designation for the Harrier) carried less than half the 4,000 lb (1,800 kg) payload of the smaller A-4 Skyhawk
The Douglas A-4 Skyhawk is a single-seat subsonic carrier-capable light attack aircraft developed for the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps in the early 1950s. The delta-winged, single turbojet engined Skyhawk was designed ...
, over a more limited radius. To address this, Hawker Siddeley and McDonnell Douglas began joint development of a more capable version of the Harrier in 1973. Early efforts concentrated on an improved Pegasus engine, designated the Pegasus 15, which was being tested by Bristol Siddeley
Bristol Siddeley Engines Ltd (BSEL) was a British aero engine manufacturer. The company was formed in 1959 by a merger of Bristol Aero-Engines Limited and Armstrong Siddeley Motors Limited. In 1961 the company was expanded by the purchase of t ...
.Wilson 2000, p. 26. Although more powerful, the engine's diameter was too large by to fit into the Harrier easily.Jenkins 1998, pp. 69–70.
In December 1973, a joint American and British team completed a project document defining an advanced Harrier powered by the Pegasus 15 engine. The advanced Harrier was intended to replace the original RAF and USMC Harriers, as well as the USMC's A-4 Skyhawk.Nordeen 2006, p. 41. The aim of the advanced Harrier was to double the AV-8's payload and range and was therefore unofficially named AV-16. The British government pulled out of the project in March 1975 owing to decreased defense funding, rising costs, and the RAF's insufficient 60-aircraft requirement. With development costs estimated to be around £180–200 million (1974 British pounds), the United States was unwilling to fund development by itself and ended the project later that year.
Despite the project's termination, the two companies continued to take different paths toward an enhanced Harrier. Hawker Siddeley focused on a new larger wing that could be retrofitted to existing operational aircraft, while McDonnell Douglas independently pursued a less ambitious, though still expensive, project catering to the needs of the U.S. military. Using knowledge gleaned from the AV-16 effort, though dropping some items—such as the larger Pegasus engine—McDonnell Douglas kept the basic structure and engine for an aircraft tailored for the USMC.
Designing and testing
As the USMC wanted a substantially improved Harrier without the development of a new engine, the plan for Harrier II development was authorized by theUnited States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national sec ...
(DoD) in 1976.Nordeen 2006, pp. 42–44, 48–49. The United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
(USN), which had traditionally procured military aircraft for the USMC, insisted that the new design be verified with flight testing. McDonnell Douglas modified two AV-8As with new wings, revised intakes, redesigned exhaust nozzles, and other aerodynamic changes; the modified forward fuselage and cockpit found on all subsequent aircraft were not incorporated on these prototypes.Wilson 2000, p. 28. Designated YAV-8B, the first converted aircraft flew on 9 November 1978. The aircraft performed three vertical take-offs and hovered for seven minutes at Lambert–St. Louis International Airport. The second aircraft followed on 19 February 1979 but crashed that November because of an engine flameout
In aviation, a flameout (or flame-out) is the run-down of a jet engine or other turbine engine due to the extinction of the flame in its combustor. The loss of flame can have a variety of causes, such as fuel starvation, excessive altitude, com ...
; the pilot ejected safely. Flight testing of these modified AV-8s continued into 1979. The results showed greater than expected drag, hampering the aircraft's maximum speed. Further refinements to the aerodynamic profile yielded little improvement. Positive test results in other areas, including payload, range, and V/STOL performance, led to the award of a development contract in 1979. The contract stipulated a procurement of 12 aircraft initially, followed by a further 324.Wilson 2000, p. 29.
 Between 1978 and 1980, the DoD and USN repeatedly attempted to terminate the AV-8B program. There had previously been conflict between the USMC and USN over budgetary issues. At the time, the USN wanted to procure A-18s for its ground attack force and, to cut costs, pressured the USMC to adopt the similarly designed F-18 fighter instead of the AV-8B to fulfill the role of close air support (both designs were eventually amalgamated to create the multirole
Between 1978 and 1980, the DoD and USN repeatedly attempted to terminate the AV-8B program. There had previously been conflict between the USMC and USN over budgetary issues. At the time, the USN wanted to procure A-18s for its ground attack force and, to cut costs, pressured the USMC to adopt the similarly designed F-18 fighter instead of the AV-8B to fulfill the role of close air support (both designs were eventually amalgamated to create the multirole F/A-18 Hornet
The McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet is an all-weather, twin-engine, supersonic, carrier-capable, multirole combat aircraft, designed as both a fighter and attack aircraft (hence the F/A designation). Designed by McDonnell Douglas (now pa ...
). Despite these bureaucratic obstacles, in 1981 the DoD included the Harrier II in its annual budget and five-year defense plan. The USN declined to participate in the procurement, citing the limited range and payload compared with conventional aircraft.
In August 1981, the program received a boost when British Aerospace (BAe) and McDonnell Douglas signed a memorandum of understanding, marking the UK's re-entry into the program. The British government was enticed by the lower cost of acquiring Harriers promised by a large production run, and the fact that the U.S. was shouldering the expense of development. Under the agreement, BAe was relegated to the position of a subcontractor, instead of the full partner status that would have been the case had the UK not left the program. Consequently, the company received, in man-hours, 40% of the airframe work-share. Aircraft production took place at McDonnell Douglas' facilities in suburban St. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
, Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
, and manufacturing by BAe at its Kingston and Dunsfold facilities in Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant ur ...
, England. Meanwhile, 75% work-share for the engine went to Rolls-Royce
Rolls-Royce (always hyphenated) may refer to:
* Rolls-Royce Limited, a British manufacturer of cars and later aero engines, founded in 1906, now defunct
Automobiles
* Rolls-Royce Motor Cars, the current car manufacturing company incorporated in ...
, which had absorbed Bristol Siddeley, with the remaining 25% assigned to Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney is an American aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of Raytheon Technologies. Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation (especially airlines) and military av ...
. The two companies planned to manufacture 400 Harrier IIs, with the USMC expected to procure 336 aircraft and the RAF to procure 60.
Four full-scale development (FSD) aircraft were constructed. The first of these, used mainly for testing performance and handling qualities, made its maiden flight on 5 November 1981. The second and third FSD aircraft, which introduced wing leading-edge root extensions and revised engine intakes, first flew in April the following year; the fourth followed in January 1984. The first production AV-8B was delivered to the Marine Attack Training Squadron 203 (VMAT-203) at Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point
Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point or MCAS Cherry Point (*) is a United States Marine Corps airfield located in Havelock, North Carolina, United States, in the eastern part of the state. It was built in 1941, and was commissioned in 1942 and ...
on 12 December 1983,Nordeen 2006, p. 59. and officially handed over one month later. The last of the initial batch of 12 was delivered in January 1985 to the front-line Marine Attack Squadron 331.Nordeen 2006, p. 61. These aircraft had F402-RR-404A engines, with 21,450 lb (95.4 kN) of thrust; aircraft from 1990 onwards received upgraded engines.
Upgrades
During the initial pilot conversion course, it became apparent that the AV-8B exhibited flight characteristics different from the AV-8A. These differences, as well as thedigital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
** Digital camera, which captures and stores digital ...
cockpit fitted instead of the analog cockpit of the TAV-8A, necessitated additional pilot training.Jenkins 1998, pp. 76–77. In 1984, funding for eight AV-8Bs was diverted to the development of a two-seat TAV-8B trainer. The first of the 28 TAV-8Bs eventually procured had its maiden flight on 21 October 1986. This aircraft was delivered to VMAT-203 on 24 July 1987; the TAV-8B was also ordered by Italy and Spain.Wilson 2000, p. 39.
With export interest from Brazil, Japan, and Italy serving as a source of encouragement to continue development of the Harrier II, McDonnell Douglas commenced work on a night-attack variant in 1985. With the addition of an infrared sensor and cockpit interface enhancements,Elliot 1990, p. 56. the 87th production single-seat AV-8B became the first Harrier II to be modified for night attacks, leaving the McDonnell Douglas production line in June 1987. Flight tests proved successful and the night attack capability was validated. The first of 66 AV-8B(NA)s was delivered to the USMC in September 1989. An equivalent version of the AV-8B(NA) also served with the RAF under the designation GR7; earlier GR5 aircraft were subsequently upgraded to GR7 standards.Nordeen 2006, p. 92.Jenkins 1998, p. 81.
In June 1987, as a private venture, BAe, McDonnell Douglas, and Smiths Industries Smiths or Smith's may refer to:
Companies
*Smith Electric Vehicles, or Smith's, a manufacturer of electric trucks
*Smith's Food and Drug, or Smith's, an American supermarket chain
** Smith's Ballpark, a baseball stadium in Salt Lake City, Utah, U.S ...
agreed on the development of what was to become the AV-8B Plus with the addition of radar and increased missile compatibility. The agreement was endorsed by the USMC and, after much consideration, the Spanish and Italian navies developed a joint requirement for a fleet of air-defense Harriers. The United States, Spain, and Italy signed an MoU in September 1990 to define the responsibilities of the three countries and establish a Joint Program Office to manage the program. On 30 November 1990, the USN, acting as an agent for the three participating countries, awarded McDonnell Douglas the contract to develop the improved Harrier.Nordeen 2006, p. 99. The award was followed by an order from the USMC in December 1990 for 30 new aircraft, and 72 rebuilt from older aircraft.Wilson 2000, pp. 30–31. Italy ordered 16 Harrier II Plus and two twin-seat TAV-8B aircraft, while Spain signed a contract for eight aircraft. Production of the AV-8B Harrier II Plus was conducted, in addition to McDonnell Douglas' plant, at CASA's facility in Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
, Spain, and Alenia Aeronautica
Alenia Aeronautica was an Italian aerospace company. Its subsidiaries included Alenia Aermacchi and Alenia Aeronavali.
Alenia Aeronautica was also the part-owner of ATR, a joint venture with European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company (EADS). ...
's facility in Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
, Italy. The UK also participated in the program by manufacturing components for the AV-8B.Nordeen 2006, p. 100.
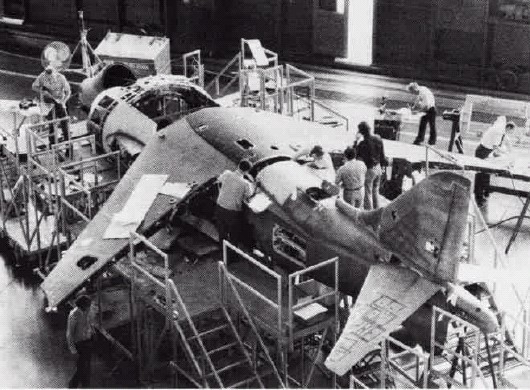
 Production was authorized on 3 June 1992. The maiden flight of the prototype took place on 22 September, marking the start of a successful flight-test program. The first production aircraft made its initial flight on 17 March 1993. Deliveries of new aircraft took place from April 1993 to 1995. At the same time, the plan to remanufacture existing AV-8Bs to the Plus standard proceeded. On 11 March 1994, the Defense Acquisition Board approved the program,Nordeen 2006, p. 103. which initially involved 70 aircraft, with four converted in
Production was authorized on 3 June 1992. The maiden flight of the prototype took place on 22 September, marking the start of a successful flight-test program. The first production aircraft made its initial flight on 17 March 1993. Deliveries of new aircraft took place from April 1993 to 1995. At the same time, the plan to remanufacture existing AV-8Bs to the Plus standard proceeded. On 11 March 1994, the Defense Acquisition Board approved the program,Nordeen 2006, p. 103. which initially involved 70 aircraft, with four converted in fiscal year
A fiscal year (or financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. Laws in many ...
1994. The program planned to use new and refurbished components to rebuild aircraft at a lower cost than manufacturing new ones.Lopez 1993, p. 17. Conversion began in April 1994, and the first aircraft was delivered to the USMC in January 1996.Lopez 1996, p. 19.
End of production and further improvements
In March 1996, the U.S.General Accounting Office
The U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) is a legislative branch government agency that provides auditing, evaluative, and investigative services for the United States Congress. It is the supreme audit institution of the federal gover ...
(GAO) stated that it was less expensive to buy Harrier II Plus aircraft outright than to remanufacture existing AV-8Bs. The USN estimated the cost for remanufacture of each aircraft to be US$23–30 million, instead of $30 million for each new-built aircraft, while the GAO estimated the cost per new aircraft at $24 million. Nevertheless, the program continued and, in 2003, the 72nd and last AV-8B to be remanufactured for the USMC was delivered. Spain also participated in the program, the delivery of its last refurbished aircraft occurring in December 2003, which marked the end of the AV-8B's production; the final new AV-8B had been delivered in 1997.
In the 1990s, Boeing and BAE Systems assumed management of the Harrier family following corporate mergers that saw Boeing acquire McDonnell Douglas and BAe acquire Marconi Electronic Systems to form BAE Systems. Between 1969 and 2003, 824 Harriers of all models were delivered. In 2001, ''Flight International
''Flight International'' is a monthly magazine focused on aerospace. Published in the United Kingdom and founded in 1909 as "A Journal devoted to the Interests, Practice, and Progress of Aerial Locomotion and Transport", it is the world's olde ...
'' reported that Taiwan might meet its requirement for a V/STOL aircraft by purchasing AV-8Bs outfitted with the F-16 Fighting Falcon
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successf ...
's APG-66 radar. A Taiwanese purchase would have allowed the production line to stay open beyond 2005. Despite the possibility of leasing AV-8Bs, interest in the aircraft waned as the country switched its intentions to procuring the F-35 and upgrading its fleet of F-16s.
Although there have been no new AV-8B variants, in 1990 McDonnell Douglas and British Aerospace began discussions on an interim aircraft between the AV-8B and the next generation of advanced V/STOL aircraft. The Harrier III would have presented an "evolutionary approach to get the most from the existing aircraft", as many of the structures employed on the Sea Harrier
The British Aerospace Sea Harrier is a naval short take-off and vertical landing/ vertical take-off and landing jet fighter, reconnaissance and attack aircraft. It is the second member of the Harrier family developed. It first entered servic ...
and AV-8B would be used.''Flight International'' 1990, p. 12. The wing and the torsion box
A torsion box consists of two thin layers of material (skins) on either side of a lightweight core, usually a grid of beams. It is designed to resist torsion under an applied load. A hollow core door is probably the most common example of a torsi ...
were to be enlarged to accommodate extra fuel and hardpoint
A hardpoint is an attachment location on a structural frame designed to transfer force and carry an external or internal structural load, load. The term is usually used to refer to the mounting points (more formally known as a weapon station or ...
s to improve the aircraft's endurance. Because of the increase in size, the wing would have had folding wing
A folding wing is a wing configuration design feature of aircraft to save space and is typical of carrier-based aircraft that operate from the limited deck space of aircraft carriers. The folding allows the aircraft to occupy less space in a con ...
tips. To meet the heavier weight of the aircraft, Rolls-Royce was expected to design a Pegasus engine variant that would have produced more thrust than the latest production variant at the time. The Harrier III would have carried weapons such as AIM-120 AMRAAM
The AIM-120 Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile, or AMRAAM (pronounced ), is an American beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) capable of all-weather day-and-night operations. It is 7 inches (18 cm) in diameter, and employ ...
and AIM-132 ASRAAM
The Advanced Short Range Air-to-Air Missile (ASRAAM), also known by its United States designation AIM-132, is an imaging infrared homing (heat seeking) air-to-air missile, produced by MBDA UK, that is designed for close-range combat. It is in s ...
missiles. Boeing and BAE Systems continued studying the design until the early 2000s, when the project was abandoned.Nativi 2000, p. 26.
In 2013, the USMC was studying potential enhancements to keep the AV-8B Harrier IIs up to date until its planned retirement, such as a helmet-mounted cueing system. It is also predicted that additional work on the aircraft's radars and sensor systems may take place. The USMC's Harrier II fleet was planned to remain in service until 2030, owing to delays with the F-35B and the fact that the Harriers have more service life
A product's service life is its period of use in service. Several related terms describe more precisely a product's life, from the point of manufacture, storage, and distribution, and eventual use.
Service life has been defined as "a product's ...
left than USMC F/A-18 Hornets. However, by 2014 the USMC had decided to retire the AV-8B sooner because changing the transition orders of Harrier II and Hornet fleets to the Lightning II would save $1 billion. The F-35B began replacing the AV-8B in 2016, with the AV-8B expected to continue service until 2025. Meanwhile, the AV-8B is to receive revamped defensive measures, updated data-link capability and targeting sensors, and improved missiles and rockets, among other enhancements.
Design
Overview
 The AV-8B Harrier II is a subsonic attack aircraft of metal and composite construction that retains the basic layout of the Hawker Siddeley Harrier, with horizontal stabilizers and shoulder-mounted wings featuring prominent anhedral (downward slope). The aircraft is powered by a single
The AV-8B Harrier II is a subsonic attack aircraft of metal and composite construction that retains the basic layout of the Hawker Siddeley Harrier, with horizontal stabilizers and shoulder-mounted wings featuring prominent anhedral (downward slope). The aircraft is powered by a single Rolls-Royce Pegasus
The Rolls-Royce Pegasus, formerly the Bristol Siddeley Pegasus, is a British turbofan engine originally designed by Bristol Siddeley. It was manufactured by Rolls-Royce plc. The engine is not only able to power a jet aircraft forward, but also ...
turbofan
The turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft engine, aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a portmanteau of "turbine" and "fan": the ''turbo'' portion refers to a gas turbine engine which ac ...
engine, which has two intakes and four synchronized vectorable nozzles close to its turbine. Two of these nozzles are located near the forward, cold end of the engine and two are near the rear, hot end of the engine. This arrangement contrasts with most fixed-wing aircraft, which have engine nozzles only at the rear. The Harrier II also has smaller valve-controlled nozzles in the nose, tail, and wingtips to provide control at low airspeeds.
The AV-8B is equipped with one centerline fuselage and six wing hardpoints (compared to four wing hardpoints on the original Harrier), along with two fuselage stations for a 25 mm GAU-12
The General Dynamics GAU-12/U Equalizer is a five-barrel 25 mm Gatling-type rotary cannon. The GAU-12/U is used by the United States, Italy and Spain, which mount the weapon in their attack jets such as the AV-8B Harrier II, airborne gunships ...
cannon and ammunition pack.Lambert 1993, p. 166. These hardpoints give it the ability to carry a total of of weapons, including air-to-air, air-to-surface
An air-to-surface missile (ASM) or air-to-ground missile (AGM) is a missile designed to be launched from military aircraft at targets on land or sea. There are also unpowered guided glide bombs not considered missiles. The two most common prop ...
, and anti-ship missile
An anti-ship missile (AShM) is a guided missile that is designed for use against ships and large boats. Most anti-ship missiles are of the sea skimming variety, and many use a combination of inertial guidance and active radar homing. A goo ...
s, as well as unguided and guided bomb
A guided bomb (also known as a smart bomb, guided bomb unit, or GBU) is a precision-guided munition designed to achieve a smaller circular error probable (CEP).
The creation of precision-guided munitions resulted in the retroactive renaming of ...
s.Warwick 1979, p. 2132. The aircraft's internal fuel capacity is , up 50% compared to its predecessor. Fuel capacity can be carried in hardpoint-compatible external drop tank
In aviation, a drop tank (external tank, wing tank or belly tank) is used to describe auxiliary fuel tanks externally carried by aircraft. A drop tank is expendable and often capable of being jettisoned. External tanks are commonplace on modern ...
s, which give the aircraft a maximum ferry range
The maximal total range is the maximum distance an aircraft can fly between takeoff and landing. Powered aircraft range is limited by the aviation fuel energy storage capacity (chemical or electrical) considering both weight and volume limits. U ...
of 2,100 mi (3,300 km) and a combat radius
Radius of action, combat radius, or combat range in military terms, refers to the maximum distance a ship, aircraft, or vehicle can travel away from its base along a given course with normal load and return without refueling, allowing for all safet ...
of 300 mi (556 km). The AV-8B can also receive additional fuel via aerial refueling
Aerial refueling, also referred to as air refueling, in-flight refueling (IFR), air-to-air refueling (AAR), and tanking, is the process of transferring aviation fuel from one aircraft (the tanker) to another (the receiver) while both aircraft a ...
using the probe-and-drogue system. The British Aerospace Harrier II, a variant tailored to the RAF, uses different avionics and has one additional missile pylon on each wing.Jenkins 1998, pp. 88–89.
The Harrier II retains the tandem landing gear
Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for takeoff or landing. For aircraft it is generally needed for both. It was also formerly called ''alighting gear'' by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Mart ...
layout of the first-generation Harriers, although each outrigger
An outrigger is a projecting structure on a boat, with specific meaning depending on types of vessel. Outriggers may also refer to legs on a wheeled vehicle that are folded out when it needs stabilization, for example on a crane that lifts ...
landing gear leg was moved from the wingtip to mid-span for a tighter turning radius when taxiing
Taxiing (rarely spelled taxying) is the movement of an aircraft on the ground, under its own power, in contrast to towing or pushback where the aircraft is moved by a tug. The aircraft usually moves on wheels, but the term also includes aircr ...
.Wilson 2000, p. 27. The engine intakes are larger than those of the first-generation Harrier and have a revised inlet. On the underside of the fuselage, McDonnell Douglas added lift-improvement devices, which capture the reflected engine exhaust when close to the ground, giving the equivalent of up to 1,200 lb (544 kg) of extra lift.Walker 1986, p. 25.
The technological advances incorporated into the Harrier II, compared with the original Harrier, significantly reduce the workload on the pilot. The supercritical wing, hands-on-throttle-and-stick
HOTAS, an acronym of hands on throttle-and-stick, is the concept of placing buttons and switches on the throttle lever and flight control stick in an aircraft's cockpit. By adopting such an arrangement, pilots are capable of performing all vit ...
(HOTAS) control principle, and increased engineered lateral stability make the aircraft fundamentally easier to fly.Walker 1986, p. 24. Ed Harper, general manager for the McDonnell Douglas Harrier II development program, summarizes: "The AV-8B looks a lot like the original Harrier and it uses the same operating fundamentals. It just uses them a lot better". A large cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a Phosphorescence, phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms (osci ...
multi-purpose display, taken from the F/A-18, makes up much of the instrument panel in the cockpit. It has a wide range of functions, including radar warning information and weapon delivery checklist. The pilots sit on UPC/Stencel 10B zero-zero ejection seats, meaning that they are able to eject from a stationary aircraft at zero altitude.Evans 1998, p. 92.Spick 2000, pp. 402–409.
Airframe
For the AV-8B, McDonnell Douglas redesigned the entire airframe of the Harrier, incorporating numerous structural and aerodynamic changes. To improve visibility and better accommodate the crew and avionics hardware, McDonnell Douglas elevated the cockpit by and redesigned the canopy. This improved the forward (17° down), side (60°), and rear visibility.Warwick 1979, p. 2128. The front fuselage is composed of a molded skin with an epoxy-based core sandwiched between two carbon-fiber sheets. To compensate for the changes in the front fuselage, the rear fuselage was extended by , and the taller vertical stabilizer of the Sea Harrier was used. The tail assembly is made up of composites to reduce weight.Walker 1986, pp. 23–25. Perhaps the most thorough redesign was of the wing, the objective being to match the performance of the cancelled AV-16 while retaining the Pegasus engine of the AV-8A.Warwick 1979, p. 2127. Engineers designed a new, one-piece supercritical wing, which improves cruise performance by delaying the rise in drag and increasing lift-to-drag ratio. Made of composites, the wing is thicker and has a longer span than that of the AV-8A. Compared to the AV-8A's wing, it has a higher aspect ratio, reducedsweep
Sweep or swept may refer to:
Cleaning
* Sweep, the action of using a brush to clean
* Chimney sweep, a worker who clears ash and soot from chimneys
* Street sweeper, a person's occupation, or a machine that cleans streets
* Swept quartz, a cleani ...
(from 40° to 37°), and an area increased from to . The wing has a high-lift configuration, employing flaps that deploy automatically when maneuvering, and drooped aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around ...
s. Using the leading edge root extensions, the wing allows for a 6,700 lb (3,035 kg) increase in payload compared with the first-generation Harriers after a 1,000 ft (300 m) takeoff roll. Because the wing is almost exclusively composite, it is lighter than the AV-8A's smaller wing.
The Harrier II was the first combat aircraft to extensively employ carbon-fiber composite materials, exploiting their light weight and high strength;Wilson 2000, pp. 26–27. they are used in the wings, rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally air or water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adve ...
, flaps, nose, forward fuselage, and tail. Twenty-six percent of the aircraft's structure is made of composites, reducing its weight by 480 lb (217 kg) compared to a conventional metal structure.
Differences between versions
Most of the first "day attack" AV-8B Harrier IIs were upgraded to Night Attack Harrier or Harrier II Plus standards, with the remainder being withdrawn from service. The AV-8B cockpit was also used for the early trialing ofdirect voice input Direct voice input (DVI), sometimes called voice input control (VIC), is a style of human–machine interaction "HMI" in which the user makes voice commands to issue instructions to the machine through speech recognition.
In the field of milita ...
which allows the pilot to use voice commands to issue instructions to the aircraft, using a system developed by Smiths Industries. The main attack avionics
Avionics (a blend of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, and the hundreds of systems that are fit ...
system in original aircraft was the nose-mounted Hughes AN/ASB-19 angle-rate bombing system. The system combined a TV imager and laser tracker to provide a highly accurate targeting capability. Defensive equipment include several AN/ALE-39 chaff
Chaff (; ) is the dry, scaly protective casing of the seeds of cereal grains or similar fine, dry, scaly plant material (such as scaly parts of flowers or finely chopped straw). Chaff is indigestible by humans, but livestock can eat it. In agri ...
-flare
A flare, also sometimes called a fusée, fusee, or bengala in some Latin-speaking countries, is a type of pyrotechnic that produces a bright light or intense heat without an explosion. Flares are used for distress signaling, illumination, ...
dispensers, an AN/ALR-67 radar warning receiver
Radar warning receiver (RWR) systems detect the radio emissions of radar systems. Their primary purpose is to issue a warning when a radar signal that might be a threat is detected, like a fighter aircraft's fire control radar. The warning can ...
, and an AN/ALQ-126C jammer pod.
The trainer version of the AV-8B is the TAV-8B, seating two pilots in tandem. Among other changes, the forward fuselage features a 3 ft 11 in (1.19 m) extension to accommodate the second cockpit. To compensate for the slight loss of directional stability, the vertical stabilizer's area was enlarged through increases in chord (length of the stabilizer's root) and height. USMC TAV-8Bs feature the AV-8B's digital cockpit and new systems but have only two hardpoints and are not combat capable. Initial TAV-8Bs were powered by a 21,450 lbf (95.4 kN) F402-RR-406A engine, while later examples were fitted with the 23,000 lbf (105.8 kN) F402-RR-408A. In the early 2000s, 17 TAV-8Bs were upgraded to include a night-attack capability, the F402-RR-408 engine, and software and structural changes.
Fielded in 1991, the Night Attack Harrier was the first upgrade of the AV-8B. It differed from the original aircraft in having a forward-looking infrared
Forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras, typically used on military and civilian aircraft, use a thermographic camera that senses infrared radiation.
The sensors installed in forward-looking infrared cameras, as well as those of other therma ...
(FLIR) camera added to the top of the nose cone, a wide Smiths Industries head-up display
A head-up display, or heads-up display, also known as a HUD (), is any transparent display that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints. The origin of the name stems from a pilot being able to view informa ...
(HUD), provisions for night vision goggles
A night-vision device (NVD), also known as a night optical/observation device (NOD), night-vision goggle (NVG), is an optoelectronic device that allows visualization of images in low levels of light, improving the user's night vision. The dev ...
, and a Honeywell digital moving map system. The FLIR uses thermal imaging to identify objects by their heat signatures. The variant was powered by the F402-RR-408 engine, which featured an electronic control system and was more powerful and reliable. The flare and chaff dispensers were moved, and the ram-air intake was lengthened at the fin's base. Initially known as the AV-8D, the night-attack variant was designated the AV-8B(NA).Wilson 2000, pp. 29–30.
The Harrier II Plus is very similar to the Night Attack variant, with the addition of an APG-65 The AN/APG-65 and AN/APG-73 are designations for a family of all-weather multimode airborne radar systems designed by Hughes Aircraft (now Raytheon) for the F/A-18 Hornet, and used on a variety of fighter aircraft types. The APG-79 is an upgraded A ...
multi-mode pulse-Doppler radar
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and ...
in an extended nose, allowing it to launch advanced beyond-visual-range missile
A beyond-visual-range missile (BVR) is an air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) that is capable of engaging at ranges of or beyond. This range has been achieved using dual pulse rocket motors or booster rocket motor and ramjet sustainer motor.
In additi ...
s such as the AIM-120 AMRAAM. To make additional space for the radar, the angle-rate bombing system was removed. The radars used were taken from early F/A-18
The McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet is an all-weather, twin-engine, supersonic, carrier-capable, multirole combat aircraft, designed as both a fighter and attack aircraft (hence the F/A designation). Designed by McDonnell Douglas (now part ...
aircraft, which had been upgraded with the related APG-73. According to aviation author Lon Nordeen, the changes "had a slight increase in drag and a bit of additional weight, but there really was not much difference in performance between the ��408-poweredNight Attack and radar Harrier II Plus aircraft".
Operational history
United States Marine Corps
The AV-8B underwent standard evaluation to prepare for its USMC service. In the operational evaluation (OPEVAL), lasting from 31 August 1984 to 30 March 1985, four pilots and a group of maintenance and support personnel tested the aircraft under combat conditions. The aircraft was graded for its ability to meet its mission requirements for navigating, acquiring targets, delivering weapons, and evading and surviving enemy actions, all at the specified range and payload limits. The first phase of OPEVAL, running until 1 February 1985, required the AV-8B to fly both deep andclose air support
In military tactics, close air support (CAS) is defined as air action such as air strikes by fixed or rotary-winged aircraft against hostile targets near friendly forces and require detailed integration of each air mission with fire and movemen ...
missions (deep air support missions do not require coordination with friendly ground forces) in concert with other close-support aircraft, as well as flying battlefield interdiction and armed reconnaissance missions. The aircraft flew from military installations at Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton
Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton is the major West Coast base of the United States Marine Corps and is one of the largest Marine Corps bases in the United States. It is on the Southern California coast in San Diego County and is bordered by O ...
and Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake
Naval Air Weapons Station (NAWS) China Lake is a large military installation in California that supports the research, testing and evaluation programs of the United States Navy. It is part of Navy Region Southwest under Commander, Navy Installa ...
in California; Canadian Forces Base Cold Lake
Canadian Forces Base Cold Lake , abbreviated as CFB Cold Lake, is a Canadian Forces Base in the City of Cold Lake, Alberta.
The facility is operated as an air force base by the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and is approximately south of the ...
in Canada; and Marine Corps Air Station Yuma
Marine Corps Air Station Yuma or MCAS Yuma is a United States Marine Corps air station. It is the home of multiple squadrons of F-35B Lightning IIs of the 3rd Marine Aircraft Wing, Marine Aviation Weapons and Tactics Squadron 1 (MAWTS-1), Mar ...
in Arizona.Nordeen 2006, pp. 57–59.
The second phase of OPEVAL, which took place at MCAS Yuma from 25 February to 8 March, required the AV-8B to perform fighter escort, combat air patrol
Combat air patrol (CAP) is a type of flying mission for fighter aircraft. A combat air patrol is an aircraft patrol provided over an objective area, over the force protected, over the critical area of a combat zone, or over an air defense area, ...
, and deck-launched intercept missions. Although the evaluation identified shortfalls in the design (subsequently rectified), OPEVAL was deemed successful.Nordeen 2006, p 58. The AV-8B Harrier II reached initial operating capability
Initial operating capability or initial operational capability (IOC) is the state achieved when a capability is available in its minimum usefully deployable form. The term is often used in government or military procurement.
The United States D ...
(IOC) in January 1985 with USMC squadron VMA-331.
 The AV-8B saw extensive action in the Gulf War of 1990–91. Aircraft based on and , and at on-shore bases, initially flew training and support
The AV-8B saw extensive action in the Gulf War of 1990–91. Aircraft based on and , and at on-shore bases, initially flew training and support sortie
A sortie (from the French word meaning ''exit'' or from Latin root ''surgere'' meaning to "rise up") is a deployment or dispatch of one military unit, be it an aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining supp ...
s, as well as practicing with coalition forces. The AV-8Bs were to be held in reserve during the initial phase of the preparatory air assault of Operation Desert Storm. The AV-8B was first used in the war on the morning of 17 January 1991, when a call for air support from an OV-10 Bronco
The North American Rockwell OV-10 Bronco is an American twin- turboprop light attack and observation aircraft. It was developed in the 1960s as a special aircraft for counter-insurgency (COIN) combat, and one of its primary missions was as a for ...
forward air control
Forward air control is the provision of guidance to close air support (CAS) aircraft intended to ensure that their attack hits the intended target and does not injure friendly troops. This task is carried out by a forward air controller (FAC).
...
ler against Iraqi artillery that was shelling Khafji and an adjacent oil refinery, brought the AV-8B into combat.Nordeen 2006, p. 81. The following day, USMC AV-8Bs attacked Iraqi positions in southern Kuwait. Throughout the war, AV-8Bs performed armed reconnaissance and worked in concert with coalition forces to destroy targets.
During Operations Desert Shield and Desert Storm, 86 AV-8Bs amassed 3,380 flights and about 4,100 flight hours,Nordeen 2006, p. 87. with a mission availability rate of over 90%. Five AV-8Bs were lost to enemy surface-to-air missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft syst ...
s, and two USMC pilots were killed. The AV-8B had an attrition rate of 1.5 aircraft for every 1,000 sorties flown. U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
General Norman Schwarzkopf
Herbert Norman Schwarzkopf Jr. (; August 22, 1934 – December 27, 2012) was a United States Army general. While serving as the commander of United States Central Command, he led all coalition forces in the Gulf War.
Born in Trenton, N ...
later named the AV-8B among the seven weapons—along with the F-117 Nighthawk
The Lockheed F-117 Nighthawk is a retired American single-seat, twin-engine stealth attack aircraft developed by Lockheed's secretive Skunk Works division and operated by the United States Air Force (USAF). It was the first operational aircr ...
and AH-64 Apache
The Boeing AH-64 Apache () is an American twin- turboshaft attack helicopter with a tailwheel-type landing gear arrangement and a tandem cockpit for a crew of two. It features a nose-mounted sensor suite for target acquisition and night v ...
—that played a crucial role in the war.Wilson 2000, p. 43. In the aftermath of the war, from 27 August 1992 until 2003, USMC AV-8Bs and other aircraft patrolled Iraqi skies in support of Operation Southern Watch
Operation Southern Watch was an air-centric military operation conducted by the United States Department of Defense from Summer 1992 to Spring 2003.
United States Central Command's Joint Task Force Southwest Asia (JTF-SWA) had the mission of mon ...
. The AV-8Bs launched from amphibious assault ship
An amphibious assault ship is a type of amphibious warfare ship employed to land and support ground forces on enemy territory by an amphibious assault. The design evolved from aircraft carriers converted for use as helicopter carriers (and, a ...
s in the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
and from forward operating bases such as Ali Al Salem Air Base
Ali Al Salem Air Base is a military air base situated in Kuwait, approximately 23 miles (37 km) from the Iraqi border, and roughly 15 km west of Al Jahra. The airfield is owned by the Government of Kuwait, and during Operation Southe ...
, Kuwait.
In 1999, the AV-8B participated in NATO's bombing of Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
during Operation Allied Force
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) carried out an aerial bombing campaign against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia during the Kosovo War. The air strikes lasted from 24 March 1999 to 10 June 1999. The bombings continued until an a ...
. Twelve Harriers were split evenly between the 24th and 26th Marine Expeditionary Unit
The 26th Marine Expeditionary Unit (26th MEU) is one of seven such units currently in existence in the United States Marine Corps. It is an air-ground task force with a strength of about 2,400 personnel when at full strength during a deployment. ...
s (MEU). AV-8Bs of the 24th MEU were introduced into combat on 14 April and over the next 14 days flew 34 combat air support missions over Kosovo. During their six-month deployment aboard USS ''Nassau'', 24th MEU Harriers averaged a high mission-capable rate of 91.8%. On 28 April, the 24th MEU was relieved by the 26th MEU, based on . The first combat sorties of the unit's AV-8Bs occurred two days later, one aircraft being lost. The 26th MEU remained in the theater of operations until 28 May, when it was relocated to Brindisi
Brindisi ( , ) ; la, Brundisium; grc, Βρεντέσιον, translit=Brentésion; cms, Brunda), group=pron is a city in the region of Apulia in southern Italy, the capital of the province of Brindisi, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea.
Histo ...
, Italy.Nordeen 2006, p. 111.
USMC AV-8Bs took part in Operation Enduring Freedom
Operation Enduring Freedom (OEF) was the official name used synonymously by the U.S. government for both the War in Afghanistan (2001–2014) and the larger-scale Global War on Terrorism. On 7 October 2001, in response to the September 11 a ...
in Afghanistan from 2001. The USMC 15th MEU
The 15th Marine Expeditionary Unit (15th MEU) is one of seven Marine expeditionary unit, such units currently in existence in the United States Marine Corps. The Marine Expeditionary Unit (MEU) is a Marine Air Ground Task Force (MAGTF) with a s ...
arrived off the coast of Pakistan in October 2001. Operating from the unit's ships, four AV-8Bs began attack missions into Afghanistan on 3 November 2001. The 26th MEU and its AV-8Bs joined 15th MEU later that month. In December 2001, two AV-8Bs first deployed to a forward base at Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the c ...
in Afghanistan. More AV-8Bs were deployed with other USMC units to the region in 2002. The VMA-513 squadron deployed six Night Attack AV-8Bs to Bagram
Bagram (; Pashto/ fa, بگرام) is a town and seat in Bagram District in Parwan Province of Afghanistan, about 60 kilometers north of the capital Kabul. It is the site of an ancient city located at the junction of the Ghorband and Panjshir ...
in October 2002. These aircraft each carried a LITENING targeting pod to perform reconnaissance missions along with attack and other missions, primarily at night.Nordeen 2006, pp. 144–151.
The aircraft participated in the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003–present), I ...
in 2003, acting primarily in support of USMC ground units. During the initial action, 60 AV-8Bs were deployed on ships such as and , from which over 1,000 sorties were flown throughout the war. When possible, land-based forward arming and refuelling points were set up to enable prompt operations. USMC commander Lieutenant General Earl B. Hailston said that the Harriers were able to provide 24-hour support for ground forces, and noted that "The airplane ... became the envy of pilots even from my background ... there's an awful lot of things on the Harrier that I've found the Hornet pilots asking me ornbsp;... We couldn't have asked for a better record".Cordesman 2003, p. 333.
USMC sources documented the Harrier as holding an 85% aircraft availability
In reliability engineering, the term availability has the following meanings:
* The degree to which a system, subsystem or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at ...
record in the Iraq War; in just under a month of combat, the aircraft flew over 2,000 sorties. When used, the LITENING II targeting pod achieved greater than 75% kill effectiveness on targets. In a single sortie from USS ''Bonhomme Richard'', a wave of Harriers inflicted heavy damage on a Republican Guard
A republican guard, sometimes called a national guard, is a state organization of a country (often a republic, hence the name ''Republican'') which typically serves to protect the head of state and the government, and thus is often synonymous wi ...
tank battalion in advance of a major ground assault on Al Kut
Kūt ( ar, ٱلْكُوت, al-Kūt), officially Al-Kut, also spelled Kutulamare or Kut al-Imara, is a city in eastern Iraq, on the left bank of the Tigris River, about south east of Baghdad. the estimated population is about 389,400 people.
It ...
.Cordesman 2003, p. 334. Harriers regularly operated in close support roles for friendly tanks, one of the aircraft generally carrying a LITENING pod. Despite the Harrier's high marks, the limited amount of time that each aircraft could remain on station, around 15–20 minutes, led to some calls from within the USMC for the procurement of AC-130
The Lockheed AC-130 gunship is a heavily armed, long-endurance, ground-attack variant of the C-130 Hercules transport, fixed-wing aircraft. It carries a wide array of ground-attack weapons that are integrated with sophisticated sensors, naviga ...
gunships, which could loiter for six hours and had a heavier close air support capability than the AV-8B. AV-8Bs were later used in combination with artillery to provide constant fire support for ground forces during heavy fighting in 2004 around the insurgent stronghold of Fallujah
Fallujah ( ar, ٱلْفَلُّوجَة, al-Fallūjah, Iraqi pronunciation: ) is a city in the Iraqi province of Al Anbar, located roughly west of Baghdad on the Euphrates. Fallujah dates from Babylonian times and was host to important Je ...
. The urban environment there required extreme precision for airstrikes.
On 20 March 2011, USMC AV-8Bs were launched from USS ''Kearsarge'' in support of Operation Odyssey Dawn
Operation Odyssey Dawn was the U.S. code name for the American role in the international military operation in Libya to enforce United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973 during the initial period of 19–31 March 2011, which continued af ...
, enforcing the UN no-fly zone
A no-fly zone, also known as a no-flight zone (NFZ), or air exclusion zone (AEZ), is a territory or area established by a military power over which certain aircraft are not permitted to fly. Such zones are usually set up in an enemy power's te ...
over Libya. They carried out airstrikes on Sirte
Sirte (; ar, سِرْت, ), also spelled Sirt, Surt, Sert or Syrte, is a city in Libya. It is located south of the Gulf of Sirte, between Tripoli and Benghazi. It is famously known for its battles, ethnic groups, and loyalty to Muammar ...
on 5 April 2011. Multiple AV-8Bs were involved in the defense of a downed F-15E
The McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing) F-15E Strike Eagle is an American all-weather multirole strike fighter derived from the McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle. The F-15E was designed in the 1980s for long-range, high-speed interdiction without relyin ...
pilot, attacking approaching Libyans prior to the pilot's extraction by a MV-22 Osprey
The Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey is an American multi-mission, tiltrotor military aircraft with both vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) and short takeoff and landing (STOL) capabilities. It is designed to combine the functionality of a convention ...
. In addition to major conflicts, USMC AV-8Bs have been deployed in support of contingency and humanitarian operations, providing fixed-wing air cover and armed reconnaissance. The aircraft served in Somalia throughout the 1990s, Liberia (1990, 1996, and 2003), Rwanda (1994), Central African Republic (1996), Albania (1997), Zaire
Zaire (, ), officially the Republic of Zaire (french: République du Zaïre, link=no, ), was a Congolese state from 1971 to 1997 in Central Africa that was previously and is now again known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Zaire was, ...
(1997), and Sierra Leone (1997).
The AV-8B is to be replaced by the F-35B version of the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is an American family of single-seat, single-engine, all-weather stealth multirole combat aircraft that is intended to perform both air superiority and strike missions. It is also able to provide el ...
, which was planned to enter service in 2012. The USMC had sought a replacement since the 1980s and has argued strongly in favor of the development of the F-35B. The Harrier's performance in Iraq, including its ability to use forward operating bases, reinforced the need for a V/STOL aircraft in the USMC arsenal. In November 2011, the USN purchased the UK's fleet of 72 retired BAe Harrier IIs (63 single-seat GR.7/9/9As plus 9 twin-seat T.12/12As) and replacement engines to provide spares for the existing USMC Harrier II fleet. Although the March 2012 issue of the magazine ''AirForces Monthly
''Air Forces Monthly'' is a military aviation magazine published by Key Publishing, and based in Stamford, Lincolnshire, United Kingdom. It was established in 1988. It provides news and analysis on military aviation, technology and related topic ...
'' states that the USMC intended to fly some of the ex-British Harrier IIs, instead of using them just for spare parts,Parsons 2012, p. 5. the Naval Air Systems Command
The Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR) provides materiel support for aircraft and airborne weapon systems for the United States Navy. It is one of the Echelon II Navy systems commands (SYSCOM), and was established in 1966 as the successor to the ...
(NAVAIR) has since stated that the USMC has never had any plans to operate those Harriers.
On 14 September 2012, a Taliban raid destroyed six AV-8Bs and severely damaged two others while they were parked on the ramp at Camp Bastion
Camp Shorabak (formerly Camp Bastion) is a former British Army airbase, located northwest of the city of Lashkargah in Helmand Province, Afghanistan. The camp was situated in a remote desert area, far from population centres.
The camp was built ...
in Afghanistan's Helmand Province
Helmand (Pashto/Dari: ; ), also known as Hillmand, in ancient times, as Hermand and Hethumand, is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, in the south of the country. It is the largest province by area, covering area. The province contains 13 ...
. All of the aircraft belonged to VMFA-211
Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 211 (VMFA-211) is a United States Marine Corps fighter attack squadron, currently consisting of F-35B Lightning II stealth STOVL strike fighter jets. Known as the "Wake Island Avengers" and the "Bastion Defenders", ...
. The two damaged AV-8Bs were flown out of Afghanistan in the hours after the attack. The attack was described as "the worst loss of U.S. airpower in a single incident since the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
." The lost aircraft were quickly replaced by those from VMA-231
Marine Attack Squadron 231 (VMA-231) is a United States Marine Corps fixed wing attack squadron that consists of AV-8B Harrier ( V/STOL) jets. The squadron, known as the "Ace of Spades", is based at Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point, North ...
.
On 27 July 2014, USS ''Bataan'' began deploying USMC AV-8Bs over Iraq to provide surveillance of Islamic State
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic ter ...
(IS) forces. Surveillance operations continued after the start of Operation Inherent Resolve
Operation Inherent Resolve (OIR) is the U.S. military's operational name for the International military intervention against IS, including both a campaign in Iraq and a campaign in Syria, with a closely-related campaign in Libya. Throu ...
against IS militants. In early September 2014, a USMC Harrier from the 22nd MEU
The 22nd Marine Expeditionary Unit (22nd MEU) is one of seven Marine expeditionary unit, such units currently in existence in the United States Marine Corps. It is a Marine Air Ground Task Force with a strength of about 2,200 personnel. They are ...
struck an IS target near the Haditha Dam
The Haditha Dam ( ar, سد حديثة, Sadd Ḥadītha) or Qadisiya Dam is an earth-fill dam on the Euphrates, north of Haditha (Iraq), creating Lake Qadisiyah ( ar, script=Latn, Buhayrat al-Qadisiyyah). The dam is just over long and high. The ...
in Iraq, marking the first time a USMC unit dropped ordnance in the operation. On 1 August 2016, USMC Harriers from began strikes against ISIL in Libya as part of manned and unmanned airstrikes on targets near Sirte
Sirte (; ar, سِرْت, ), also spelled Sirt, Surt, Sert or Syrte, is a city in Libya. It is located south of the Gulf of Sirte, between Tripoli and Benghazi. It is famously known for its battles, ethnic groups, and loyalty to Muammar ...
, launching at least five times within two days.
Italian Navy
In the late 1960s, following a demonstration of the Hawker Siddeley Harrier on theItalian Navy
"Fatherland and Honour"
, patron =
, colors =
, colors_label =
, march = ( is the return of soldiers to their barrack, or sailors to their ship after a ...
(''Marina Militare'') helicopter carrier , the country began investigating the possibility of acquiring the Harrier.Eden 2004, p. 295. Early efforts were hindered by a 1937 Italian law that prohibited the navy from operating fixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are dist ...
because they were the domain of the air force. In early 1989, the law was changed to allow the navy to operate any fixed-wing aircraft with a maximum weight of over 3,300 lb (1,500 kg).Wilson 2000, p. 44. Following a lengthy evaluation of the Sea Harrier and AV-8B, an order was placed for two TAV-8Bs in May 1989. Soon, a contract for a further 16 AV-8B Plus aircraft was signed. After the TAV-8Bs and the first three AV-8Bs, all subsequent Italian Navy Harriers were locally assembled by Alenia Aeronautica
Alenia Aeronautica was an Italian aerospace company. Its subsidiaries included Alenia Aermacchi and Alenia Aeronavali.
Alenia Aeronautica was also the part-owner of ATR, a joint venture with European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company (EADS). ...
from kits delivered from the U.S.Wilson 2000, p. 45. The two-seaters, the first to be delivered, arrived at Grottaglie in August 1991. They were used for proving flights with the navy's helicopter carriers and on the light aircraft carrier .
In early 1994, the initial batch of U.S.-built aircraft arrived at MCAS Cherry Point for pilot conversion training. The first Italian-assembled Harrier was rolled out the following year. In mid-January 1995, ''Giuseppe Garibaldi'' set off from Taranto
Taranto (, also ; ; nap, label=Tarantino, Tarde; Latin: Tarentum; Old Italian: ''Tarento''; Ancient Greek: Τάρᾱς) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Taranto, serving as an important comme ...
to Somalia with three Harriers on board to maintain stability following the withdrawal of UN forces. The Harriers, flown by five Italian pilots, accumulated more than 100 flight hours and achieved 100% availability during the three-month deployment, performing reconnaissance and other missions. The squadron returned to port on 22 March.
 In 1999, Italian AV-8Bs were used for the first time in combat missions when they were deployed aboard ''Giuseppe Garibaldi'', which was participating in Operation Allied Force in
In 1999, Italian AV-8Bs were used for the first time in combat missions when they were deployed aboard ''Giuseppe Garibaldi'', which was participating in Operation Allied Force in Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a international recognition of Kosovo, partiall ...
. Italian pilots conducted more than 60 sorties alongside other NATO aircraft, attacking the Yugoslav army and paramilitary forces and bombing the country's infrastructure with conventional and laser-guided bomb
A laser-guided bomb (LGB) is a guided bomb that uses semi-active laser guidance to strike a designated target with greater accuracy than an unguided bomb. First developed by the United States during the Vietnam War, laser-guided bombs quickly pr ...
s.
In 2000, the Italian Navy was looking to acquire 7 additional remanufactured aircraft to equip ''Giuseppe Garibaldi'' and a new carrier, . Existing aircraft, meanwhile, were updated to allow them to carry AIM-120 AMRAAMs and Joint Direct Attack Munition
The Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) is a guidance kit that converts unguided bombs, or "dumb bombs", into all-weather precision-guided munitions. JDAM-equipped bombs are guided by an integrated inertial guidance system coupled to a Global Po ...
guided bombs. From November 2001 to March 2002, eight AV-8Bs were embarked aboard ''Giuseppe Garibaldi'' and were deployed to the Indian Ocean in support of Operation Enduring Freedom. The aircraft, equipped with LGBs, operated throughout January and February 2002, during which 131 missions were logged for a total of 647 flight hours.
In 2011, Italian Harriers, operating from ''Giuseppe Garibaldi'', worked alongside Italian Typhoons
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for a ...
and aircraft of other nations during Operation Unified Protector
Operation Unified Protector was a NATO operation in 2011 enforcing United Nations Security Council resolutions 1970 and 1973 concerning the Libyan Civil War and adopted on 26 February and 17 March 2011, respectively. These resolutions imposed ...
, part of the 2011 military intervention in Libya
On 19 March 2011, a multi-state NATO-led coalition began a military intervention in Libya, to implement United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973, in response to events during the First Libyan Civil War. With ten votes in favour and ...
. They conducted airstrikes as well as intelligence and reconnaissance sorties over Libya, using the Litening targeting pods while armed with AIM-120 AMRAAMs and AIM-9 Sidewinder
The AIM-9 Sidewinder (where "AIM" stands for "Air Intercept Missile") is a short-range air-to-air missile which entered service with the US Navy in 1956 and subsequently was adopted by the US Air Force in 1964. Since then the Sidewinder has prove ...
s. In total, Italian military aircraft delivered 710 guided bombs and missiles during sorties: Italian Air Force Tornados and AMX fighter bombers delivered 550 bombs and missiles, while the eight Italian Navy AV-8Bs flying from ''Giuseppe Garibaldi'' dropped 160 guided bombs during 1,221 flight hours.
Italian Navy AV-8Bs are slated to be replaced by 15 (originally 22) F-35Bs, which will form the air wing of ''Cavour''.
Spanish Navy
 Spain, already using the AV-8S Matador, became the first international operator of the AV-8B by signing an order for 12 aircraft in March 1983. Designated VA-2 Matador II by the
Spain, already using the AV-8S Matador, became the first international operator of the AV-8B by signing an order for 12 aircraft in March 1983. Designated VA-2 Matador II by the Spanish Navy
The Spanish Navy or officially, the Armada, is the maritime branch of the Spanish Armed Forces and one of the oldest active naval forces in the world. The Spanish Navy was responsible for a number of major historic achievements in navigation, ...
(''Armada Española''), this variant is known as EAV-8B by McDonnell Douglas.Eden 2004, p. 294. Pilot conversion took place in the U.S. On 6 October 1987, the first three Matador IIs were delivered to Naval Station Rota
Naval Station Rota, also known as NAVSTA Rota ( es, Base Naval de Rota, links=no), is a Spanish-American naval base commanded by a Spanish Rear Admiral. Located in Rota in the Province of Cádiz, NAVSTA Rota is the largest American military com ...
. The new aircraft were painted in a two-tone matte grey finish, similar to U.S. Navy aircraft, and deliveries were complete by 1988.
BAe test pilots cleared the aircraft carrier for Harrier operations in July 1989. The carrier, which replaced the World War II-era , has a 12° ski-jump ramp
In aviation, a ski-jump is an upward-curved ramp that allows aircraft to take off from a runway that is shorter than the aircraft's required takeoff roll. By forcing the aircraft upwards, lift-off can be achieved at a lower airspeed than that req ...
.Wilson 2000, p. 46. It was originally planned that the first unit to operate the aircraft would be the ''8a Escuadrilla''. This unit was disbanded on 24 October 1986, following the sales of AV-8S Matadors to Thailand. Instead, ''9a Escuadrilla'' was formed on 29 September 1987, to become part of the Alpha Carrier Air Group and operate the EAV-8B.
In March 1993, under the September 1990 Tripartite MoU between the U.S., Italy, and Spain, eight EAV-8B Plus Matadors were ordered, along with a twin-seat TAV-8B. Deliveries of the Plus-standard aircraft started in 1996. On 11 May 2000, Boeing and the NAVAIR finalized a contract to remanufacture Spanish EAV-8Bs to bring them up to Plus standard. Boeing said the deal required it to remanufacture two EAV-8Bs, with an option for another seven aircraft; other sources say the total was 11 aircraft. The remanufacture allowed the aircraft to carry four AIM-120 AMRAAMs, enhanced the pilot's situational awareness through the installation of new radar and avionics, and provided a new engine. Eventually, 5 aircraft were modified, the last having been delivered on 5 December 2003.
Spanish EAV-8Bs joined Operation Deny Flight
Operation Deny Flight was a North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) operation that began on 12 April 1993 as the enforcement of a United Nations (UN) no-fly zone over Bosnia and Herzegovina. The United Nations and NATO later expanded the mis ...
, enforcing the UN's no-fly zone over Bosnia and Herzegovina. Spain did not send its aircraft carrier to participate in the Iraq War in 2003, instead deploying F/A-18s and other aircraft to Turkey to defend that country against potential Iraqi attacks. Starting in 2007, Spain was looking to replace its Harrier IIs—with the likely option being the F-35B. The Spanish government, in May 2014 however, announced that it had decided to extend the aircraft's service life to beyond 2025 due to a lack of funds for a replacement aircraft.
Following the decommissioning of ''Príncipe de Asturias'' in February 2013, the sole naval platform from which Spanish Harrier IIs can operate is the amphibious assault ship .
Variants
;YAV-8B: Two prototypes converted in 1978 from existing AV-8A airframes (BuNo
In the United States, all military aircraft display a serial number to identify individual aircraft. These numbers are located on the aircraft tail, so they are sometimes referred to unofficially as "tail numbers". On the Northrop Grumman B-2 Spi ...
158394 and 158395).
;AV-8B Harrier II: The initial "day attack" variant.
 ;AV-8B Harrier II Night Attack: Improved version with FLIR, an upgraded cockpit with night-vision goggle compatibility, and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Pegasus 11 engine.
;AV-8B Harrier II Plus: Similar to the Night Attack variant, with the addition of an APG-65 radar and separate targeting pod. It is used by the USMC, Spanish Navy, and Italian Navy. Forty-six were built.Wilson 2000, p. 48.
;TAV-8B Harrier II: Two-seat trainer version.
;EAV-8B Matador II: Company designation for the Spanish Navy version.
;EAV-8B Matador II Plus: The AV-8B Harrier II Plus, ordered for the Spanish Navy.
;Harrier GR5, GR7, GR9: See ''
;AV-8B Harrier II Night Attack: Improved version with FLIR, an upgraded cockpit with night-vision goggle compatibility, and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Pegasus 11 engine.
;AV-8B Harrier II Plus: Similar to the Night Attack variant, with the addition of an APG-65 radar and separate targeting pod. It is used by the USMC, Spanish Navy, and Italian Navy. Forty-six were built.Wilson 2000, p. 48.
;TAV-8B Harrier II: Two-seat trainer version.
;EAV-8B Matador II: Company designation for the Spanish Navy version.
;EAV-8B Matador II Plus: The AV-8B Harrier II Plus, ordered for the Spanish Navy.
;Harrier GR5, GR7, GR9: See ''British Aerospace Harrier II
The British Aerospace Harrier II is a second-generation vertical/short takeoff and landing (V/STOL) jet aircraft used previously by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and, between 2006 and 2010, the Royal Navy (RN). The aircraft was the latest develop ...
''.
Operators
; *Italian Navy
"Fatherland and Honour"
, patron =
, colors =
, colors_label =
, march = ( is the return of soldiers to their barrack, or sailors to their ship after a ...
:* ''Gruppo Aerei Imbarcati'' (1991–present)
;
* Spanish Navy
The Spanish Navy or officially, the Armada, is the maritime branch of the Spanish Armed Forces and one of the oldest active naval forces in the world. The Spanish Navy was responsible for a number of major historic achievements in navigation, ...
:* ''9a Escuadrilla Aeronaves'' (1987–present)
;
* United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through c ...
** VMA-211
Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 211 (VMFA-211) is a United States Marine Corps fighter attack squadron, currently consisting of F-35B Lightning II stealth STOVL strike fighter jets. Known as the "Wake Island Avengers" and the "Bastion Defenders", ...
"Wake Island Avengers" (1990–2016)
** VMA-214
Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 214 (VMFA-214) is a United States Marine Corps attack squadron consisting of Lockheed Martin F-35B STOVL jets. It is currently in the process of transitioning from its fleet of AV-8B Harrier ( V/STOL) jets. The ...
"The Black Sheep" (1989–2022)
** VMA-223 "Bulldogs" (1987–present)
** VMA-231
Marine Attack Squadron 231 (VMA-231) is a United States Marine Corps fixed wing attack squadron that consists of AV-8B Harrier ( V/STOL) jets. The squadron, known as the "Ace of Spades", is based at Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point, North ...
"Ace of Spades" (1985–present)
** VMA-311
Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 311 (VMFA-311) is a United States Marine Corps fighter attack squadron consisting of F-35C Lightning II. Known as the "Tomcats", the squadron is based at Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, California and falls under ...
"Tomcats" (1988–2020)
** VMA-331 "Bumblebees" (1985–1992)
** VMA-513 "Flying Nightmares" (1987–2013)
** VMA-542
Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 542 (VMFA-542) is a United States Marine Corps Aviation fighter attack squadron transitioning to the F-35B Lightning II. VMFA-542 is based at Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point, North Carolina and falls under t ...
"Tigers" (1986–present)
** VMAT-203 "Hawks" (1983–2021)
* United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
** VX-9
Air Test and Evaluation Squadron Nine (''AIRTEVRON NINE'', VX-9, nicknamed ''The Vampires'') is a United States Navy air test and evaluation squadron based at Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake, California. Using the tail code ''XE'', the squad ...
"The Vampires" (unknown)
** VX-31
Air Test and Evaluation Squadron 31 (VX-31 or AIRTEVRON THREE ONE, commonly referred to by its nickname, "The Dust Devils" ) is a United States Navy air test and evaluation squadron based at Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake
Naval Air Weapo ...
"Dust Devils" (unknown–present)
Accidents
During its service with the USMC, the Harrier has had an accident rate three times that of the Corps' F/A-18s. , approximately 110 aircraft have been damaged beyond repair since the type entered service in 1985, the first accident occurring in March 1985. The ''Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' (abbreviated as ''LA Times'') is a daily newspaper that started publishing in Los Angeles in 1881. Based in the LA-adjacent suburb of El Segundo since 2018, it is the sixth-largest newspaper by circulation in the ...
'' reported in 2003 that the Harrier family had the highest rate of major accidents among military aircraft in service at that time, with 148 accidents and 45 people killed. Author Lon Nordeen notes that several other USMC single-engine strike aircraft, like the A-4 Skyhawk
The Douglas A-4 Skyhawk is a single-seat subsonic carrier-capable light attack aircraft developed for the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps in the early 1950s. The delta-winged, single turbojet engined Skyhawk was designed ...
and A-7 Corsair II
The LTV A-7 Corsair II is an American carrier-capable subsonic light attack aircraft designed and manufactured by Ling-Temco-Vought (LTV).
The A-7 was developed during the early 1960s as replacement for the Douglas A-4 Skyhawk. Its design w ...
, had higher accident rates.Nordeen 2006, p. 155.
Accidents have in particular been connected to the proportionate amount of time the aircraft spends taking off and landing, which are the most critical phases in flight.Jenkins 1998, p. 4. The AV-8 was dubbed a " widow maker" by some in the military. Further analysis shows that U.S. Marine senior officers never understood the uniqueness of the aircraft. Cutbacks in senior maintenance personnel and pilot mistakes had a disastrous effect on the safety of the American-operated AV-8B and unfairly gained it a negative reputation in the U.S. press.
Aircraft on display
;AV-8B * BuNo 161396 –National Museum of the Marine Corps
The National Museum of the Marine Corps is the historical museum of the United States Marine Corps. Located in Triangle, Virginia near MCB Quantico, the museum opened on November 10, 2006, and is now one of the top tourist attractions in the st ...
, Triangle, Virginia
Triangle is a census-designated place (CDP) in Prince William County, Virginia, United States. The population was 8,188 at the 2010 census. It is bounded to the south by the Marine Corps Base Quantico, which surrounds the town of Quantico.
Geogr ...
.
* BuNo 161397 – Carolinas Aviation Museum
The Carolinas Aviation Museum is an aviation museum on the grounds of Charlotte Douglas International Airport in Charlotte, North Carolina.
It is one of a few aviation museums located at an airport which serves as a major hub (Charlotte is the ...
, Charlotte, North Carolina
Charlotte ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of North Carolina. Located in the Piedmont region, it is the county seat of Mecklenburg County. The population was 874,579 at the 2020 census, making Charlotte the 16th-most popu ...
.
Specifications (AV-8B Harrier II Plus)

Popular culture
As part of its 1996Pepsi Stuff
Pepsi Stuff was a major loyalty program launched by PepsiCo, first in North America on March 28, 1996 and then around the world, featuring premiums — such as T-shirts, hats, denim and leather jackets, bags, and mountain bikes — that could b ...
marketing campaign, Pepsi ran an advertisement promising a Harrier jet to anyone who collected 7 million Pepsi Points, a gag that backfired when a participant attempted to take advantage of the ability to buy additional points for 10 cents each to claim a jet for US$700,000. When Pepsi turned him down, a lawsuit ensued, in which the judge ruled that any reasonable person would conclude that the advertisement was a joke.Epstein 2006, p. 55.
See also
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
AV-8B Plus product page
at Boeing.com
AV-8B Harrier II page
at Navy.mil
at Globalsecurity.org
McDonnell Douglas/British Aerospace AV-8B Harrier II Attack Fighter page
on Aerospaceweb.org
3D view of Harrier AV-8B
at the National Museum of the Marines Corps site {{DEFAULTSORT:Mcdonnell Douglas AV-8B Harrier II Carrier-based aircraft
AV-8B Harrier II
The McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing) AV-8B Harrier II is a single-engine ground-attack aircraft that constitutes the second generation of the Harrier family, capable of vertical or short takeoff and landing (V/STOL). The aircraft is primari ...
1970s United States attack aircraft
V/STOL aircraft by thrust vectoring
Single-engined jet aircraft
High-wing aircraft
Harrier Jump Jet
Articles containing video clips
Aircraft first flown in 1978