AT (form factor) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In the era of IBM compatible
In the era of IBM compatible
 The original AT
The original AT
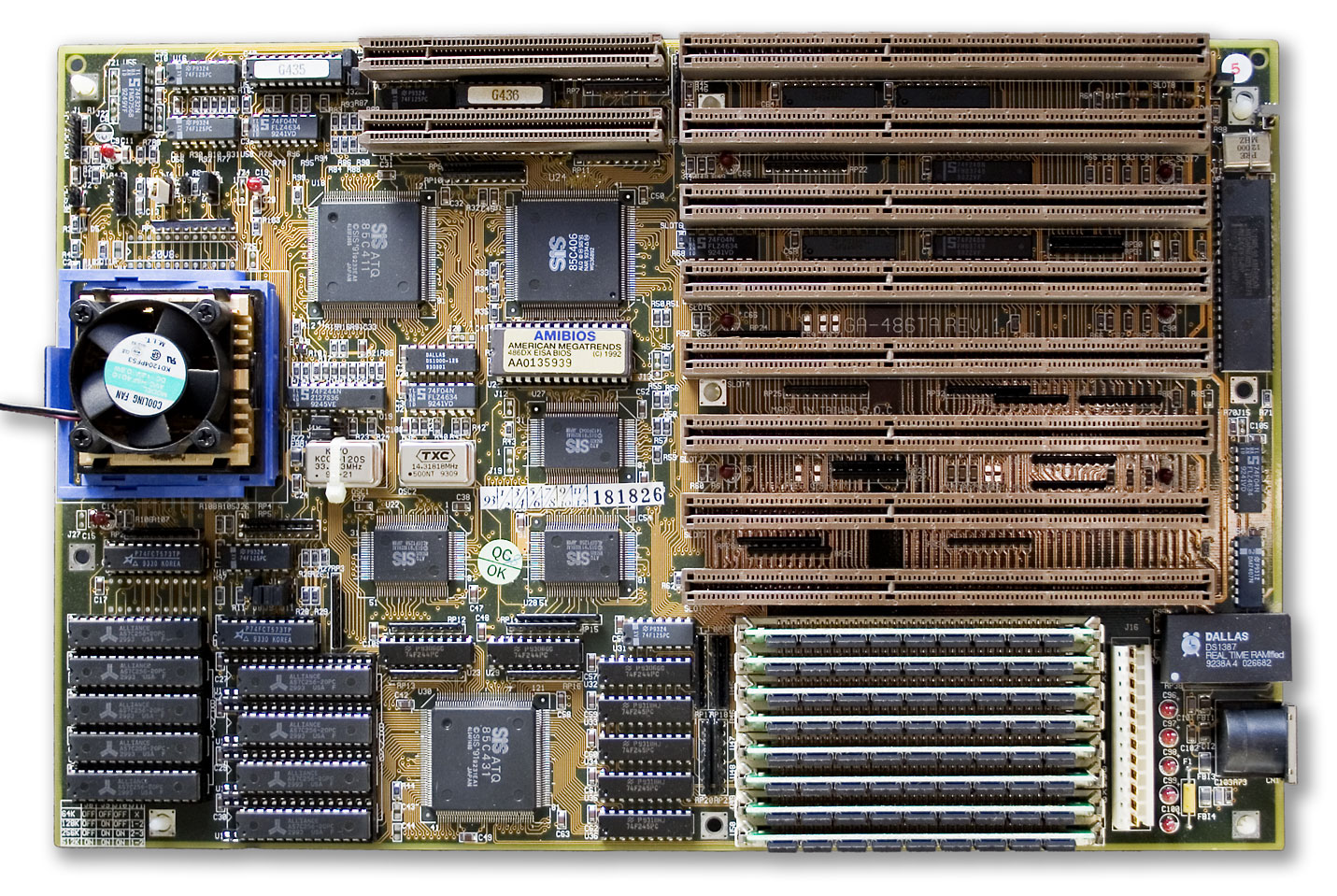
 In 1987, the Baby AT form factor was introduced, based on the motherboard found in the IBM PC/XT 286 (5162) and soon after all computer makers abandoned AT for the cheaper and smaller Baby AT form factor, using it for computers that spanned several generations, from those that used 286 processors to the P5
In 1987, the Baby AT form factor was introduced, based on the motherboard found in the IBM PC/XT 286 (5162) and soon after all computer makers abandoned AT for the cheaper and smaller Baby AT form factor, using it for computers that spanned several generations, from those that used 286 processors to the P5
PC Power Supply LinksAT power supply connectors with pinoutsPC Magazine
{{Computer form factors
personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or te ...
s, the AT form factor comprises the dimensions and layout ( form factor) of the motherboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
for the IBM AT
The IBM Personal Computer/AT (model 5170, abbreviated as IBM AT or PC/AT) was released in 1984 as the fourth model in the IBM Personal Computer line, following the IBM PC/XT and its IBM Portable PC variant. It was designed around the Intel 802 ...
. Baby AT motherboards are a little smaller, measuring 8.5" by 13". Like the IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team ...
and IBM XT models before it, many third-party manufacturers produced motherboards compatible with the IBM AT form factor, allowing end users to upgrade
Upgrading is the process of replacing a product with a newer version of the same product. In computing and consumer electronics an upgrade is generally a replacement of hardware, software or firmware with a newer or better version, in order to ...
their computers for faster processor
Processor may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Processor (computing)
**Central processing unit (CPU), the hardware within a computer that executes a program
*** Microprocessor, a central processing unit contained on a single integrated circuit (I ...
s. The IBM AT became a widely copied design in the booming home computer market of the 1980s. IBM clones made at the time began using AT compatible designs, contributing to its popularity. In the 1990s many computers still used AT and its variants. Since 1997, the AT form factor has been largely supplanted by ATX
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) is a motherboard and power supply configuration specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT design. It was the first major change in desktop computer enclo ...
.
Design
 The original AT
The original AT motherboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
, later known as "Full AT", is , which means it will not fit in "mini desktop" or "minitower cases". The board's size also means that it takes up space behind the drive bay
A drive bay is a standard-sized area for adding hardware to a computer. Most drive bays are fixed to the inside of a case, but some can be removed.
Over the years since the introduction of the IBM PC, it and its compatibles have had many form f ...
s, making installation of new drives more difficult. (In IBM's original heavy-gauge steel case, the two " full-height drive bays overhang the front of the motherboard. More precisely, the left bay overhangs the motherboard, while the right bay is subdivided into two half-height bays and additionally extends downward toward the bottom of the chassis, allowing a second full-height fixed disk to be installed below a single half-height drive.)
The power connectors for AT motherboards are two nearly identical 6-pin plugs and sockets. As designed by IBM, the connectors are mechanically keyed so that each can only be inserted in its correct position, but some clone manufacturers cut costs and used unkeyed (interchangeable) connectors. Unfortunately, the two power connectors it requires are not easily distinguishable, leading many people to damage their boards when they were improperly connected; when plugged in, the two black wires on each connector must be adjacent to each other, making a row of four consecutive black wires (out of the total 12). Technicians developed mnemonic device
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding.
Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imagery ...
s to help assure proper installation, including "black wires together in the middle" and "red and red and you are dead".
Variants

 In 1987, the Baby AT form factor was introduced, based on the motherboard found in the IBM PC/XT 286 (5162) and soon after all computer makers abandoned AT for the cheaper and smaller Baby AT form factor, using it for computers that spanned several generations, from those that used 286 processors to the P5
In 1987, the Baby AT form factor was introduced, based on the motherboard found in the IBM PC/XT 286 (5162) and soon after all computer makers abandoned AT for the cheaper and smaller Baby AT form factor, using it for computers that spanned several generations, from those that used 286 processors to the P5 Pentium
Pentium is a brand used for a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel. The original Pentium processor from which the brand took its name was first released on March 22, 1993. After that, the Pentium II and P ...
and a limited number of Pentium II
The Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture (" P6") and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors (27.4 million in the case of the mobile Dixon with 256 K ...
systems. These motherboards have similar mounting hole positions and the same eight card slot locations as those with the AT form factor, but are wide and marginally shorter than full-size AT boards, with a maximum length of . However, Baby AT boards were mostly shorter than this, typically . The size and flexibility of this kind of motherboard were the key to success of this format. The development of bigger CPU coolers—and the fact that they blocked full-length PCI and ISA cards—spelled the end of Baby AT and was the main impetus for its successor ATX
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) is a motherboard and power supply configuration specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT design. It was the first major change in desktop computer enclo ...
. While the AT standard is now considered to be mostly obsolete, some industrial computers still use it.
In 1995, Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 ser ...
introduced ATX
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) is a motherboard and power supply configuration specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT design. It was the first major change in desktop computer enclo ...
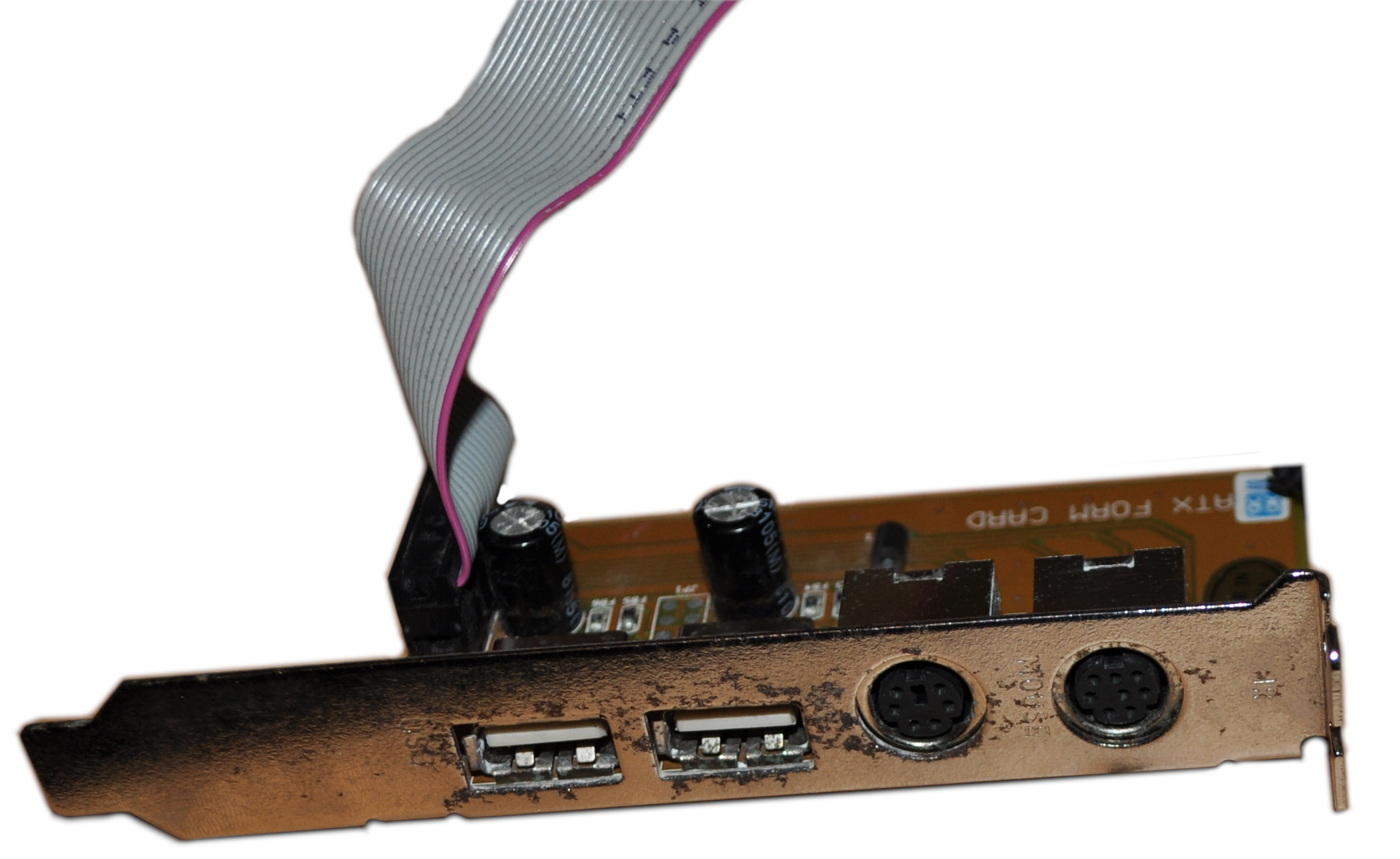
, a form factor which gradually replaced older Baby AT motherboards. During the late 1990s, a great majority of boards were either Baby AT or ATX. Many motherboard manufacturers favored Baby AT over ATX as many computer cases and power supplies in the industry were still designed for AT boards and not ATX boards. Also, the lack of an eighth slot on ATX motherboards kept it from being used in some servers. Later Baby AT boards supported both AT and ATX power connectors in addition to ATX features such as standby power (allowing for a low voltage power switch, as well as Wake-on-LAN/Wake-on-Modem Ring) and USB by use of an ATX Form Card. After the industry shifted to ATX motherboard configurations, it became common to design cases and power supplies to support both Baby AT and ATX motherboards.
Power connector
The connector at the board is two Molex 15-48-0106 connectors. This mates with a Molex 90331.References
External links
PC Power Supply Links
{{Computer form factors
At form factor
In the era of IBM compatible personal computers, the AT form factor comprises the dimensions and layout ( form factor) of the motherboard for the IBM AT. Baby AT motherboards are a little smaller, measuring 8.5" by 13". Like the IBM PC and IBM ...
Motherboard form factors