AS-10 Karen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Kh-25/Kh-25M (russian: Х-25;
The Kh-25/Kh-25M (russian: Х-25;
Zvezda Kh-25 (AS-10 Karen)
FAS
Yak-130
02. August 2013
{{Russian and Soviet military designation sequences Cold War air-to-surface missiles of the Soviet Union Kh-025 Kh-025 Kh-025 Kh-025 Tactical Missiles Corporation products Anti-radiation missiles of the Cold War Military equipment introduced in the 1970s
 The Kh-25/Kh-25M (russian: Х-25;
The Kh-25/Kh-25M (russian: Х-25; NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
: AS-10 'Karen) is a family of Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
lightweight air-to-ground missiles with a modular
Broadly speaking, modularity is the degree to which a system's components may be separated and recombined, often with the benefit of flexibility and variety in use. The concept of modularity is used primarily to reduce complexity by breaking a s ...
range of guidance systems and a range of 10 km. The anti-radar variant (Kh-25MP) is known to NATO as the AS-12 'Kegler
The Kh-25/Kh-25M (russian: Х-25; NATO: AS-10 'Karen) is a family of Soviet lightweight air-to-ground missiles with a modular range of guidance systems and a range of 10 km. The anti-radar variant (Kh-25MP) is known to NATO as the AS-12 ' K ...
and has a range up to 40 km. Designed by Zvezda-Strela, the Kh-25 is derived from the laser-guided version of the Kh-23 Grom
The Zvezda Kh-66 and Kh-23 ''Grom'' (russian: Х-23 Гром 'Thunder'; NATO: AS-7 'Kerry') are a family of early Soviet tactical air-to-surface missiles with a range of 10 km. They were intended for use against small ground or naval targ ...
(AS-7 'Kerry'). The Kh-25 remains in widespread use despite the apparent development of a successor, the Kh-38
The Kh-38/Kh-38M (russian: Х-38) is a family of air-to-surface missiles meant to succeed the Kh-25 and Kh-29 missile families.
Design and development
The basic configuration of the Kh-38M was revealed at the 2007 Moscow Air Show (MAKS). Th ...
.
Development
Based on an air-to-air missile, the beam-riding Kh-66 had been the Soviet Union's first air-to-ground missile for tactical aircraft, entering service in 1968. However it proved difficult to use in practice as the launch aircraft had to dive towards the target. A version with radio-command guidance, theKh-23
The Zvezda Kh-66 and Kh-23 ''Grom'' (russian: Х-23 Гром 'Thunder'; NATO: AS-7 'Kerry') are a family of early Soviet tactical air-to-surface missiles with a range of 10 km. They were intended for use against small ground or naval targ ...
, was first tested in 1968 but problems with the guidance system meant that it would not enter service for another five years. So in 1971 work began on a version with a semi-active laser seeker, which became the Kh-25. This was initially known in the West as the Kh-23L. State testing began on 24 November 1974, and the Kh-25 entered production in 1975.
Work began on an anti-radar missile derived from the Kh-66 in 1972, using a passive radar seeker and SUR-73 autopilot. The long-range Kh-31
The Kh-31 (russian: Х-31; AS-17 'Krypton') is a Russian air-to-surface missile carried by aircraft such as the MiG-29 or Su-27. It is capable of Mach 3.5 and was the first supersonic anti-ship missile that could be launched by tactical aircraf ...
anti-radar missile came out of the same project. The Kh-27 began state testing on a MiG-27 on 8 August 1975 but did not enter service until 2 September 1980. It was assigned the NATO reporting name
NATO reporting names are code names for military equipment from Russia, China, and historically, the Eastern Bloc (Soviet Union and other nations of the Warsaw Pact). They provide unambiguous and easily understood English words in a uniform man ...
AS-12 'Kegler' and in effect it replaced the much heavier Kh-28 (AS-9 'Kyle').
In 1973 Victor Bugaiskii was appointed head engineer of the bureau and he started work on combining the Kh-23M, Kh-25 and Kh-27 into a single modular system to reduce costs and improve tactical flexibility. The Kh-27 missile was chosen as a basis, due to its more powerful rocket engine and new autopilot. This was completed by the end of 1978, resulting in the Kh-25MP (anti-radar), Kh-25ML (laser-guided) and Kh-25MR (radio-guided) family. NATO continued to refer to these as the AS-12 and AS-10 respectively, even though they could now be switched by a simple change of seeker head.
Design
The Kh-25 is very similar to the later version of theKh-23 Grom
The Zvezda Kh-66 and Kh-23 ''Grom'' (russian: Х-23 Гром 'Thunder'; NATO: AS-7 'Kerry') are a family of early Soviet tactical air-to-surface missiles with a range of 10 km. They were intended for use against small ground or naval targ ...
, with cruciform canards and fins.
The Kh-25MP has two versions of its homing head, 1VP and 2VP, sensitive to different frequencies.
Combat history
The original Kh-25 entered service with the Soviet Air Force between 1973-5, equipping the MiG-23, MiG-27 and Su-17M. Since then it has been cleared for use on the MiG-21,MiG-29
The Mikoyan MiG-29 (russian: Микоян МиГ-29; NATO reporting name: Fulcrum) is a twin-engine fighter aircraft designed in the Soviet Union. Developed by the Mikoyan design bureau as an air superiority fighter during the 1970s, the Mi ...
, Sukhoi Su-17/20/22 family, Sukhoi Su-24
The Sukhoi Su-24 (NATO reporting name: Fencer) is a supersonic, all-weather attack aircraft developed in the Soviet Union. The aircraft has a variable-sweep wing, twin-engines and a side-by-side seating arrangement for its crew of two. It was ...
, Su-25
The Sukhoi Su-25 ''Grach'' (russian: Грач ('' rook''); NATO reporting name: Frogfoot) is a subsonic, single-seat, twin-engine jet aircraft developed in the Soviet Union by Sukhoi. It was designed to provide close air support for Soviet ...
and Su-27
The Sukhoi Su-27 (russian: Сухой Су-27; NATO reporting name: Flanker) is a Soviet-origin twin-engine supermaneuverable fighter aircraft designed by Sukhoi. It was intended as a direct competitor for the large US fourth-generation j ...
. It can also be carried by attack helicopters such as the Kamov Ka-50.
The Kh-25MP can be fitted to the MiG-23/27, Su-17/22, Su-24 and Su-25.
Soviet war in Afghanistan
Starting in April 1986, during the second Battle of Zhawar, Kh-25MLs were used by SovietSu-25
The Sukhoi Su-25 ''Grach'' (russian: Грач ('' rook''); NATO reporting name: Frogfoot) is a subsonic, single-seat, twin-engine jet aircraft developed in the Soviet Union by Sukhoi. It was designed to provide close air support for Soviet ...
Frogfoots from the 378th OshAP (Independent Shturmovik Aviation Regiment) to attack Mujahideen
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' ( ar, مُجَاهِدِين, mujāhidīn), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' ( ar, مجاهد, mujāhid, strugglers or strivers or justice, right conduct, Godly rule, etc. doers of jihād), an Arabic term t ...
cave entrances used as shelters and weapons storage facilities. Attacks were carried out from up to 4.5 nm (8 km).
Iraqi invasion of Kuwait
During theIraqi invasion of Kuwait
The Iraqi invasion of Kuwait was an operation conducted by Iraq on 2 August 1990, whereby it invaded the neighboring State of Kuwait, consequently resulting in a seven-month-long Iraqi military occupation of the country. The invasion and Ira ...
, on August 2, 1990 an Iraqi Air Force Sukhoi Su-22 from the No.109 Squadron (based at as-Shoibiyah AB) fired a single Kh-25MP anti-radar variant against a Kuwaiti MIM-23
The Raytheon MIM-23 HAWK ("Homing all the way killer") is an American medium-range surface-to-air missile. It was designed to be a much more mobile counterpart to the MIM-14 Nike Hercules, trading off range and altitude capability for a much sm ...
B I-HAWK SAM site at Bubiyan Island that had earlier downed another Su-22 from the same unit and a MiG-23BN from the 49th Squadron. This forced a radar shutdown on the HAWK. The HAWK battery (which was operated by some American contractors) was later captured by Iraqi special forces and found out to be in automatic mode of operation, after the contractors fled.
Chechen Wars
Russian Air Force Su-25s employed the Kh-25 in its two Chechen campaigns for attacks on fixed positions, such as mortars and bunkers. However, their usage wasn't extensive in relation to those of unguided bombs and rockets. The use of precision-guided munitions allowed air support in areas too dangerous for attack helicopters. Their use was not widespread in the First War as was in the Second, mainly due to differences in weather conditions and, probably, the need to keep a strategic reserve of stockpiles shortly after the fall of the USSR.Russia intervention in Syria
Laser-guided Kh-25s were employed by Su-24 sweep wing strike aircraft against anti-Assad rebels inSyria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
.
Variants
NATO refers to all of the Kh-25 family as AS-10 'Karen' apart from the anti-radar variants. An "M" designation stands for "''Modulnaya''" – modular (seeker head). * Kh-25 (''Izdeliye'' 71, Kh-23L) – original laser-guided variant * Kh-25ML – semi-active laser guidance with tandem warhead that can penetrate of concrete * Kh-25MA – active radar guidance, first offered for export in 1999 * Kh-25MAE – Kh-25MA update announced for export in August 2005 with Ka-band seeker, probably Phazotron's PSM which can detect a tank at and which can also be used on the Kh-25MA * Kh-25MS – satellite navigation ( GPS orGLONASS
GLONASS (russian: ГЛОНАСС, label=none, ; rus, links=no, Глобальная навигационная спутниковая система, r=Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema, t=Global Navigation Satellite System) is ...
)
* Kh-25MSE – export version of Kh-25MS, announced August 2005
* Kh-25MT – TV guidance
* Kh-25MTP – infra-red guidance variant of Kh-25MT
* Kh-25R/Kh-25MR – Radio-command guidance variant, it has a bigger warhead.
* Kh-27 (Kh-27/M, AS-12 'Kegler') – original anti-radiation missile
* Kh-25MP (AS-12 'Kegler') – modular anti-radiation variant
* Kh-25MPU (AS-12 'Kegler') – Updated Kh-25MP
Training rounds have "U" designations, so, e.g., for the Kh-25ML there is:
* Kh-25MUL – combat training Kh-25ML
* Kh-25ML-UD – functional training missile
* Kh-25ML-UR – sectional training missile
Operators

Current operators
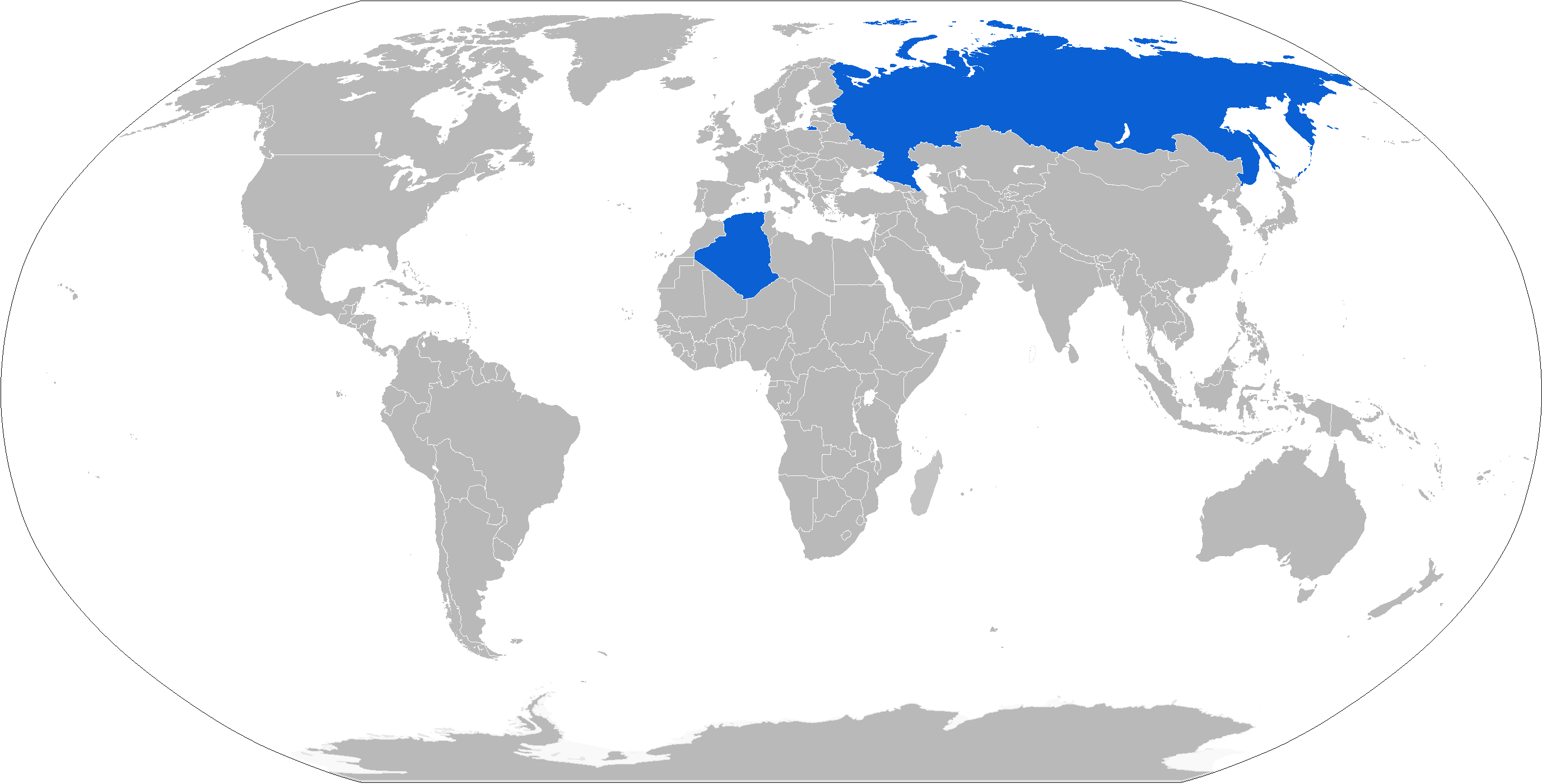
* :Algerian Air Force
The Algerian Air Force (AAF) ( ar, القُوَّاتُ الجَوِّيَّةُ الجَزَائِرِيَّةُ, links=, lit=, translit=al-Quwwāt al-Ǧawwiyyah al-Ǧazāʾiriyyah, french: Forces aériennes algériennes, links=, lit=, translit ...
* : Ethiopian Air Force
The Ethiopian Air Force (ETAF) () is the air service branch of the Ethiopian National Defence Force. The ETAF is tasked with protecting the national air space, providing support to ground forces, as well as assisting civil operations during natio ...
, Kh-25ML on the Su-25
* : unknown status
*
*
* : The Defense Ministry ordered a large-scale upgrade of tactical antiradar air missiles Kh-25MP. They will be able to destroy both radars and armor, aircraft at airfields, bridges and river crossings, surface warships, etc. The missile will be also able to destroy fortified command posts and pillboxes.
*
* : still in use with Sukhoi Su-24
The Sukhoi Su-24 (NATO reporting name: Fencer) is a supersonic, all-weather attack aircraft developed in the Soviet Union. The aircraft has a variable-sweep wing, twin-engines and a side-by-side seating arrangement for its crew of two. It was ...
s.
Former operators
* passed on successor and export countries * * * * SIPRI database * probably some in Serbian / Yugoslavian arsenal *Similar weapons
*Kh-23
The Zvezda Kh-66 and Kh-23 ''Grom'' (russian: Х-23 Гром 'Thunder'; NATO: AS-7 'Kerry') are a family of early Soviet tactical air-to-surface missiles with a range of 10 km. They were intended for use against small ground or naval targ ...
M (AS-7 'Kerry') – predecessor to the Kh-25 had some technology "backported" from the Kh-25
* Kh-29 (AS-14 'Kedge') – 320 kg warhead; semi-active laser, IIR, passive radar and TV guidance with 10–30 km range
* Kh-59 (AS-13 'Kingbolt') – longer range missile with heavier warhead and TV guidance
* Kh-38
The Kh-38/Kh-38M (russian: Х-38) is a family of air-to-surface missiles meant to succeed the Kh-25 and Kh-29 missile families.
Design and development
The basic configuration of the Kh-38M was revealed at the 2007 Moscow Air Show (MAKS). Th ...
– successor to the Kh-25
* AGM-65 Maverick – similar lightweight missile in US service which has seen numerous guidance and warhead variants
* AGM-45 Shrike – US equivalent to the Kh-25MP anti-radar missile
Notes
External links
Zvezda Kh-25 (AS-10 Karen)
FAS
References
*Yak-130
02. August 2013
{{Russian and Soviet military designation sequences Cold War air-to-surface missiles of the Soviet Union Kh-025 Kh-025 Kh-025 Kh-025 Tactical Missiles Corporation products Anti-radiation missiles of the Cold War Military equipment introduced in the 1970s