786 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 __NOTOC__
Year 786 ( DCCLXXXVI) was a
__NOTOC__
Year 786 ( DCCLXXXVI) was a
 __NOTOC__
Year 786 ( DCCLXXXVI) was a
__NOTOC__
Year 786 ( DCCLXXXVI) was a common year starting on Sunday
A common year starting on Sunday is any non-leap year (i.e. a year with 365 days) that begins on Sunday, January 1, 1 January, and ends on Sunday, December 31, 31 December. Its dominical letter hence is A. The most recent year was 2017 and the next ...
of the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
. The denomination 786 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", ...
calendar era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one ''epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, it is the year as per the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era (the Coptic ...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Europe
* KingCharles the Younger
Charles the Younger or Charles of Ingelheim (c. 772 – 4 December 811) was a member of the Carolingian dynasty, the second son of Charlemagne and the first by his second wife, Hildegard of Swabia and brother of Louis the Pious and Pepin Carloman ...
, son of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
and ruler of Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 January ...
, visits Monte Cassino
Monte Cassino (today usually spelled Montecassino) is a rocky hill about southeast of Rome, in the Latin Valley, Italy, west of Cassino and at an elevation of . Site of the Roman town of Casinum, it is widely known for its abbey, the first h ...
and Capua
Capua ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, situated north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain.
History
Ancient era
The name of Capua comes from the Etrusc ...
, both in Beneventan territory. Prince Arechis II, feeling threatened by the Franks, decides that he needs to stop quarrelling with the Byzantine Duchy of Naples
The Duchy of Naples ( la, Ducatus Neapolitanus, it, Ducato di Napoli) began as a Byzantine province that was constituted in the seventh century, in the reduced coastal lands that the Lombards had not conquered during their invasion of Italy in ...
so he can focus on the Frankish foe. Prince Arechis II therefore signs a peace agreement, or 'pactum', with the Duchy of Naples.
Britain
* Cyneheard, brother of the late king Sigeberht, ambushes and kills his rivalCynewulf of Wessex
Cynewulf was the King of Wessex from 757 until his death in 786. He ruled for about 29 years.
He was a direct male descendant of Cerdic. Cynewulf became king after his predecessor, Sigeberht, was deposed. He may have come to power under the inf ...
, while he is at ''Meretun'' (now called Marten
A marten is a weasel-like mammal in the genus ''Martes'' within the subfamily Guloninae, in the family Mustelidae. They have bushy tails and large paws with partially retractile claws. The fur varies from yellowish to dark brown, depending on t ...
) with his mistress. The Wessex nobles
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristi ...
refuse to recognise Cyneheard as king.
* Cyneheard is executed and succeeded by Beorhtric, through the support of King Offa of Mercia
Offa (died 29 July 796 AD) was List of monarchs of Mercia, King of Mercia, a kingdom of History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon England, from 757 until his death. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa of Mercia, Eowa, Offa came to ...
. His rival claimant to the Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
throne, a distant nephew of the late king Ine
INE, Ine or ine may refer to:
Institutions
* Institut für Nukleare Entsorgung, a German nuclear research center
* Instituto Nacional de Estadística (disambiguation)
* Instituto Nacional de Estatística (disambiguation)
* Instituto Nacional Elec ...
, named Egbert
Egbert is a name that derives from old Germanic words meaning "bright edge", such as that of a blade. Anglo-Saxon variant spellings include Ecgberht () and Ecgbert. German variant spellings include Ekbert and Ecbert.
People with the first name Mid ...
, is driven across the Channel
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Austral ...
.
* Egbert settles at the court of Charlemagne, and learns the arts of government during his time in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
.Kirby, ''Earliest English Kings'', pp. 176-177. During his stay he meets Eadberht, a priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particu ...
, who later becomes king of Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
.
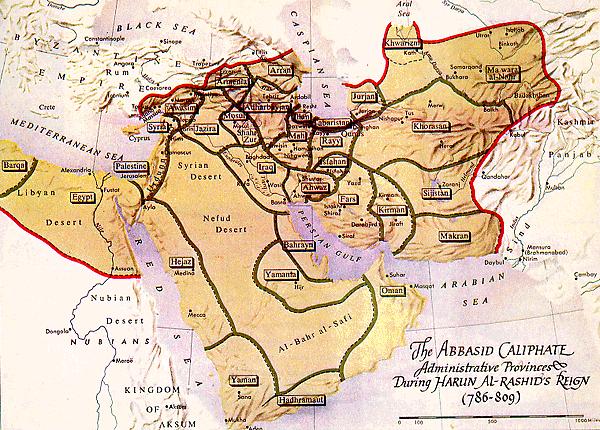
Abbasid Caliphate
*June 11
Events Pre-1600
* 173 – Marcomannic Wars: The Roman army in Moravia is encircled by the Quadi, who have broken the peace treaty (171). In a violent thunderstorm emperor Marcus Aurelius defeats and subdues them in the so-called "miracle ...
– Battle of Fakhkh
The Battle of Fakhkh () was fought on 11 June 786 between the forces of the Abbasid Caliphate and the supporters of a pro-Alid rebellion in Mecca under al-Husayn ibn Ali, a descendant of Hasan ibn Ali.
Husayn and his supporters planned an uprisi ...
: An Alid
The Alids are those who claim descent from the '' rāshidūn'' caliph and Imam ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib (656–661)—cousin, son-in-law, and companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad—through all his wives. The main branches are the (inc ...
uprising in Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the Holiest sites in Islam, second-holiest city in Islam, ...
is crushed by the Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
. One of the Alids, Idris ibn Abdallah
Idris (I) ibn Abd Allah ( ar, إدريس بن عبد الله, translit=Idrīs ibn ʿAbd Allāh), also known as Idris the Elder ( ar, إدريس الأكبر, translit=Idrīs al-Akbar), (d. 791) was an Arab Hasanid Sharif and the founder of the ...
, flees to the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
in western North Africa, where he later founds the Idrisid dynasty
The Idrisid dynasty or Idrisids ( ar, الأدارسة ') were an Arab Muslim dynasty from 788 to 974, ruling most of present-day Morocco and parts of present-day western Algeria. Named after the founder, Idris I, the Idrisids were an Alid an ...
in 788/789.
* September 14
Events Pre-1600
*AD 81 – Domitian becomes Emperor of the Roman Empire upon the death of his brother Titus.
* 629 – Emperor Heraclius enters Constantinople in triumph after his victory over the Persian Empire.
* 786 – "Night o ...
– Harun al-Rashid
Abu Ja'far Harun ibn Muhammad al-Mahdi ( ar
, أبو جعفر هارون ابن محمد المهدي) or Harun ibn al-Mahdi (; or 766 – 24 March 809), famously known as Harun al-Rashid ( ar, هَارُون الرَشِيد, translit=Hārūn ...
becomes the Abbasid caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
, upon the death of his brother Al-Hadi
Abū Muḥammad Mūsā ibn al-Mahdī al-Hādī ( ar, أبو محمد موسى بن المهدي الهادي; 26 April 764 CE 14 September 786 CE) better known by his laqab Al-Hādī (الهادي) was the fourth Arab Abbasid caliph who succee ...
. He appoints Salim Yunisi as governor of Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and the Indus Valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
.
By topic
Religion
*Beatus of Liébana
Saint Beatus of Liébana ( es, Beato; 730 – c. 800) was a monk, theologian, and geographer from the former Duchy of Cantabria and Kingdom of Asturias, in modern Cantabria, northern Spain, who worked and lived in the Picos de Europa mountains ...
, monk and theologian
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
, publishes his ''Commentary on the Apocalypse''.
Births
*October 10
Events Pre-1600
* 680 – The Battle of Karbala marks the Martyrdom of Husayn ibn Ali.
* 732 – Charles Martel's forces defeat an Umayyad army near Tours, France.
*1471 – Sten Sture the Elder, the Regent of Sweden, with the ...
– Saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated on the Game Boy in 1989 as the creation of Akitoshi Kawazu at Square (video game company), Square. It has since continued across multiple platforms, ...
, emperor of Japan (d. 842
__NOTOC__
Year 842 ( DCCCXLII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Byzantine Empire
* January 20 – Emperor Theophilos dies of dysentery at Constantin ...
)
* Adelochus
Adelochus (786–823) or Adeloch was the 27th bishop of Strasbourg, successor of Erlehardus, from 817 to 822. He is buried in a Romanesque carved sarcophagus by the Master of Eschau, supported on couchant lions, and carved with figures in a bli ...
, archbishop of Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label=Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label=Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the Eu ...
(d. 823
__NOTOC__
Year 823 ( DCCCXXIII) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Byzantine Empire
* Emperor Michael II defeats the rebel forces under Thomas the Sla ...
)
* Al-Ḥajjāj ibn Yūsuf ibn Maṭar
(786–833 CE) was a mathematician and translator.
Biography
Almost nothing is known about his life, except that he was active in Baghdad, then the capital of the ʿAbbāsid Empire.
He was the first author who translated Euclid's '' Elements' ...
, Muslim mathematician (d. 833
__NOTOC__
Year 833 ( DCCCXXXIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Byzantine Empire
* Byzantine-Arab War: Emperor Theophilos signs an armistice for p ...
)
* Al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'mu ...
, Muslim caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
(d. 833)
* Sahl ibn Bishr
Sahl ibn Bishr al-Israili (c. 786–c. 845), also known as Rabban al-Tabari and Haya al-Yahudi ("the Jew"), was a Jewish
Syriac Christian astrologer, astronomer and mathematician from Tabaristan. He was the father of Ali ibn Sahl the famous scient ...
, Muslim astrologer
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Dif ...
(approximate date)
* Tachibana no Kachiko
, also known as , was a Japanese empress, the chief consort of Emperor SagaPonsonby-Fane, Richard. (1959). ''The Imperial House of Japan,'' pp. 318-319. and the daughter of .Ponsonby-Fane, p. 319.
The empress was a devout Buddhist. She founded ...
, empress of Japan (d. 850
''For codepage, see CP850.''
__NOTOC__
Year 850 (Roman numerals, DCCCL) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Europe
* February 1 – King Ramiro I of A ...
)
Deaths
*June 11
Events Pre-1600
* 173 – Marcomannic Wars: The Roman army in Moravia is encircled by the Quadi, who have broken the peace treaty (171). In a violent thunderstorm emperor Marcus Aurelius defeats and subdues them in the so-called "miracle ...
– Al-Husayn ibn Ali al-Abid Al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī al-ʿĀbid ( ar, الحسين بن علي العابد) was an Alid who rebelled at Medina against the Abbasid caliph al-Hadi. He was killed with many of his followers at the Battle of Fakhkh outside Mecca on 11 June 786, when ...
, anti-Abbasid rebel leader
* September 14
Events Pre-1600
*AD 81 – Domitian becomes Emperor of the Roman Empire upon the death of his brother Titus.
* 629 – Emperor Heraclius enters Constantinople in triumph after his victory over the Persian Empire.
* 786 – "Night o ...
– Al-Hadi
Abū Muḥammad Mūsā ibn al-Mahdī al-Hādī ( ar, أبو محمد موسى بن المهدي الهادي; 26 April 764 CE 14 September 786 CE) better known by his laqab Al-Hādī (الهادي) was the fourth Arab Abbasid caliph who succee ...
, Muslim caliph (b. 764
__NOTOC__
Year 764 ( DCCLXIV) was a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 764 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era b ...
)
* September – Marajil
Marājil ( ar, مراجل; d. 786) was an umm walad of Caliph Harun al-Rashid and mother of Caliph al-Ma'mun.
Biography
Marajil was a Persian slave concubine of Abbasid prince Harun (future Caliph Harun al-Rashid). According to one account, she ...
, mother of caliph al-Ma'mun.
* October 16
Events Pre-1600
* 456 – Ricimer defeats Avitus at Piacenza and becomes master of the Western Roman Empire.
* 690 – Empress Wu Zetian ascends to the throne of the Tang dynasty and proclaims herself ruler of the Chinese Empire.
* 91 ...
– Lullus
Saint Lullus (Lull or Lul) (born about 710 AD in Wessex, died 16 October 786 in Hersfeld) was the first permanent archbishop of Mainz, succeeding Saint Boniface, and first abbot of the Benedictine Hersfeld Abbey. He is historiographically conside ...
, archbishop of Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main (river), Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-we ...
* Abo of Tiflis
Abo of Tiflis ( ar, أبو التفليسي, translit=Abu al-Tiflisi; ka, აბო თბილელი, tr; c. 756 – 6 January 786) was an early Christian martyr of Arab origin, who went on to practice his faith in what is now Tbilisi, the c ...
, Christian martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
* Al-Rabi' ibn Yunus Al-Rabīʾ ibn Yūnus ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Abī Farwa (; – 785/6) was a freedman who became one of the leading ministers of the early Abbasid Caliphate, serving under the caliphs al-Mansur (), al-Mahdi () and al-Hadi ().
Al-Rabi’ was born to a ...
, Muslim minister (or 785
__NOTOC__
Year 785 ( DCCLXXXV) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The article denomination 785 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent meth ...
)
* Cyneheard the Ætheling
Cyneheard the Atheling (died 786) was the brother of Sigeberht, briefly King of Wessex. Sigeberht was deposed in 757 with the agreement of the Witan. Cynewulf of Wessex succeeded as King.
In 786 Cynewulf "wished to drive out" Cyneheard. Cynewu ...
, nobleman of Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
* Cynewulf
Cynewulf (, ; also spelled Cynwulf or Kynewulf) is one of twelve Old English poets known by name, and one of four whose work is known to survive today. He presumably flourished in the 9th century, with possible dates extending into the late 8th ...
, king of Wessex
* Desiderius
Desiderius, also known as Daufer or Dauferius (born – died ), was king of the Lombards in northern Italy, ruling from 756 to 774. The Frankish king of renown, Charlemagne, married Desiderius's daughter and subsequently conquered his realm. Des ...
, king of the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and ...
(approximate date)
* Diarmait mac Conaing
Diarmait mac Conaing (died 786) was a King of Brega from the Uí Chonaing sept of Cnogba (Knowth) of the Síl nÁedo Sláine branch of the southern Ui Neill. He was the son of Conaing mac Amalgado (died 742) and brother of Congalach mac Conaing ( ...
, king of South Brega
Brega , also known as ''Mersa Brega'' or ''Marsa al-Brega'' ( ar, مرسى البريقة , i.e. "Brega Seaport"), is a complex of several smaller towns, industry installations and education establishments situated in Libya on the Gulf of Sidra, ...
(Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
)
* Sakanoue no Karitamaro
was a samurai commander, and later ''chinjufu-shōgun'' (Commander-in-chief of the defense of the North), during Japan's Nara period.
Karitomo's father was Sakanoue no Inukai.
In 764, Karitamaro aided in the repression of a revolt by Fujiwara ...
, Japanese general (b. 727)
* Tipraiti mac Taidg, king of Connacht
Connacht ( ; ga, Connachta or ), is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, Conmhaícne, and Delbhn ...
(Ireland)
* Empress Wang (Dezong) Empress Wang (王皇后, personal name unknown) (died December 6, 786), formally Empress Zhaode (昭德皇后, "the accomplished and virtuous empress"), was an empress of the Chinese dynasty Tang Dynasty for three days before her death. She was the ...
of China
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:786