756 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 __NOTOC__
Year 756 ( DCCLVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the
__NOTOC__
Year 756 ( DCCLVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the
 __NOTOC__
Year 756 ( DCCLVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the
__NOTOC__
Year 756 ( DCCLVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandri ...
. The denomination 756 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord" ...
calendar era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one '' epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, it is the year as per the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era (the Coptic ...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Byzantine Empire
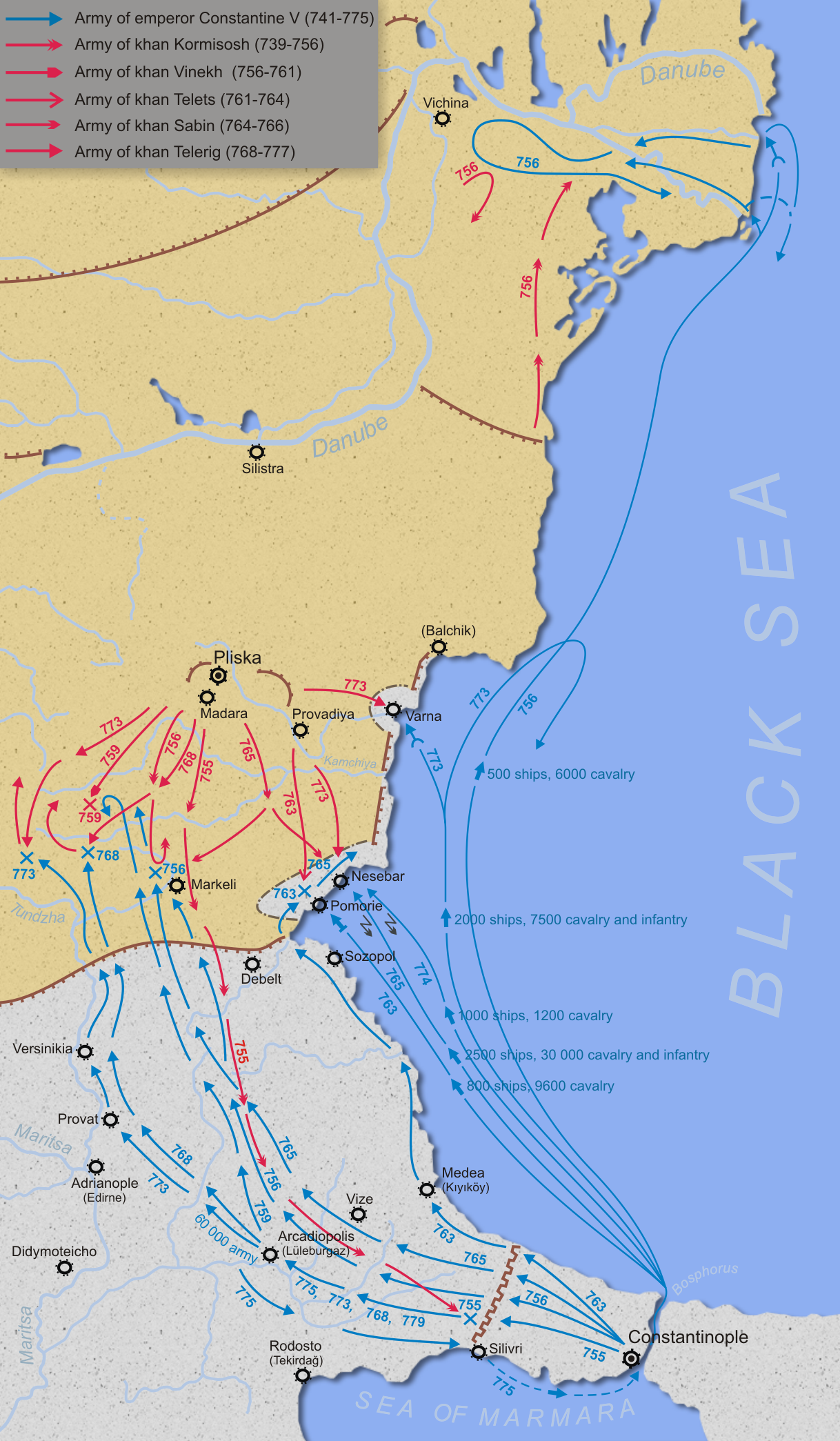
* ByzantineвҖ“Bulgarian War: EmperorConstantine V
Constantine V ( grc-gre, ОҡПүОҪПғП„ОұОҪП„бҝ–ОҪОҝПӮ, KЕҚnstantД«nos; la, Constantinus; July 718 вҖ“ 14 September 775), was Byzantine emperor from 741 to 775. His reign saw a consolidation of Byzantine security from external threats. As an able ...
builds a series of fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere ...
s along the Byzantine frontier on the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
, and starts settling Christian Armenians
Armenians ( hy, Х°ХЎХөХҘЦҖ, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, ШіЩҸЩҲШұЩҗЩҠЩҺШ§ or ШіЩҸЩҲШұЩҗЩҠЩҺШ©, translit=SЕ«riyДҒ), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, Ш§Щ„Ш¬Щ…ЩҮЩҲШұЩҠШ© Ш§Щ„Ш№ШұШЁЩҠШ© Ш§Щ„ШіЩҲШұЩҠШ©, al-JumhЕ«rД«yah al-К»ArabД«yah as-SЕ«rД«yah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
ns in the Thracesian Theme. In response, Kormisosh, ruler (''khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, рҗ°ҙрҗ°Қрҗ°Ј ), or , tr, KaДҹan or ; ug, ЩӮШ§ШәШ§ЩҶ, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, Ш®Ш§ЩӮШ§ЩҶ ''KhДҒqДҒn'', alternatively spelled KaДҹan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
'') of the Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, Р‘СҠлгаСҖСҒРәРҫ СҶР°СҖСҒСӮРІРҫ, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the ...
, demands the payment of tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conq ...
. Constantine refuses, and the Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the PonticвҖ“Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as noma ...
raid into Thrace, reaching the Anastasian Wall
The Anastasian Wall (Greek: , ; tr, Anastasius Suru) or the Long Walls of Thrace (Greek: , ; Turkish: ''Uzun Duvar'') is an ancient stone and turf fortification located west of Istanbul, Turkey, built by the Eastern Roman Empire during the late ...
stretching between the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
and the Sea of Marmara (near the outskirts of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, ЩӮШіШ·ЩҶШ·ЩҠЩҶЩҠЩҮ
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
).
* Battle of Marcellae: Constantine V sends a Byzantine expeditionary force (500 ships and 6,000 cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in ...
) to Thrace
Thrace (; el, ОҳПҒО¬ОәО·, ThrГЎki; bg, РўСҖР°РәРёСҸ, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
, and defeats the Bulgars around the Danube Delta
The Danube Delta ( ro, Delta DunДғrii, ; uk, Р”РөР»СҢСӮР° Р”СғРҪР°СҺ, DeДҫta Dunaju, ) is the second largest river delta in Europe, after the Volga Delta, and is the best preserved on the continent. The greater part of the Danube Delta lies in Ro ...
and near the fortress city of Markeli (modern Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, Р‘СҠлгаСҖРёСҸ, BЗҺlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
). Kormisosh is forced to accept a peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surre ...
, and confirms the existing frontier. Due to the constant political crisis, the Bulgarian Empire is on the verge of destruction. Kormisosh is deposed during a palace coup and succeeded by Vinekh, a member of the Vokil Uokil, or Vokil, was a name of Bulgar dynastic clan listed in the '' Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans''. The first listed in Nominalia was Kormisosh (r. 737вҖ“754) and the last was Umor (r. 766).
Theories regarding origins
Kazakh Turkologist Yur ...
clan.
Europe
* KingAistulf
Aistulf (also Ahistulf, Aistulfus, Haistulfus, Astolf etc.; it, Astolfo; died December 756) was the Duke of Friuli from 744, King of the Lombards from 749, and Duke of Spoleto from 751. His reign was characterized by ruthless and ambitious ...
of the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
again threatens Rome with a view to making it his capital, but the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
under Pepin III ("the Short") arrives with his sons Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was " ...
and Carloman, defeats Aistulf, and confers the Donation of Pepin
The Donation of Pepin in 756 provided a legal basis for the creation of the Papal States, thus extending the temporal rule of the popes beyond the duchy of Rome.
Background
In 751, Aistulf, king of the Lombards, conquered what remained of the ...
, which establishes the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
(including the lands of Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, RavГЁna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the c ...
and the Pentapolis
A pentapolis (from Greek ''penta-'', 'five' and ''polis'', 'city') is a geographic and/or institutional grouping of five cities. Cities in the ancient world probably formed such groups for political, commercial and military reasons, as happene ...
). Pepin has taken territory that legally belongs to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
; he gives it to Pope Stephen II
Pope Stephen II ( la, Stephanus II; 714 вҖ“ 26 April 757) was born a Roman aristocrat and member of the Orsini family. Stephen was the bishop of Rome from 26 March 752 to his death. Stephen II marks the historical delineation between the Byzan ...
.
* Aistulf dies in a hunting accident, and is succeeded by Desiderius
Desiderius, also known as Daufer or Dauferius (born вҖ“ died ), was king of the Lombards in northern Italy, ruling from 756 to 774. The Frankish king of renown, Charlemagne, married Desiderius's daughter and subsequently conquered his realm. Des ...
as king of the Lombards. Ex-king Ratchis
RatchisAlso spelled ''Rachis'', ''Raditschs'', ''Radics'', ''Radiks''. (died after 757) was the Duke of Friuli (739вҖ“744) and then King of the Lombards (744вҖ“749).
Ratchis was the son of Duke Pemmo of Friuli and the nephew of the Lombard ki ...
attempts unsuccessfully to seize the throne, but is opposed by Stephen II.
* Galla Gaulo is deposed, blinded and exiled. He is succeeded by Domenico Monegario
Domenico Monegario was the traditional sixth Doge of Venice (756–764).
History
He was elected with the support of the Lombard king Desiderius. However, in order to maintain necessary good relations with Byzantium and the Franks, two tribu ...
as the sixth doge of Venice
The Doge of Venice ( ; vec, Doxe de Venexia ; it, Doge di Venezia ; all derived from Latin ', "military leader"), sometimes translated as Duke (compare the Italian '), was the chief magistrate and leader of the Republic of Venice between 726 ...
. During his reign Venetian maritime traders become increasingly active.
* May – Prince Abd al-Rahman I and his followers capture the city of Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
without violence. He defeats Yusuf ibn 'Abd al-Rahman al-Fihri in a battle for control of the Muslim-ruled parts of the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: PГ©ninsule IbГ©rique
* mwl, PenГӯnsula EibГ©rica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
(al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-ГҒndalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, вҙ°вөҸвҙ·вҙ°вөҚвө“вөҷ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-ГҖndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al AndalГәs; pt, al-ГӮndalus; es, al-ГҒndalus () was the M ...
). Abd al-Rahman establishes the Emirate of CГіrdoba
The Emirate of CГіrdoba ( ar, ШҘЩ…Ш§ШұШ© ЩӮШұШ·ШЁШ©, ) was a medieval Islamic kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula. Its founding in the mid-eighth century would mark the beginning of seven hundred years of Muslim rule in what is now Spain and Po ...
. During his reign trade and culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
flourish, along with the construction of Islamic architecture
Islamic architecture comprises the architectural styles of buildings associated with Islam. It encompasses both secular and religious styles from the early history of Islam to the present day. The Islamic world encompasses a wide geographic ...
(including the Great Mosque of CГіrdoba).
Britain
* Battle of Newanbirig: Kings Г“engus I of thePicts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
and Eadberht of Northumbria
Eadberht (died 19 or 20 August 768) was king of Northumbria from 737 or 738 to 758. He was the brother of Ecgbert, Archbishop of York. His reign is seen as a return to the imperial ambitions of seventh-century Northumbria and may represent a per ...
attack King Dumnagual III of Strathclyde
Strathclyde ( in Gaelic, meaning "strath (valley) of the River Clyde") was one of nine former local government regions of Scotland created in 1975 by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973 and abolished in 1996 by the Local Government et ...
, at Dumbarton Castle
Dumbarton Castle ( gd, DГ№n Breatainn, ; ) has the longest recorded history of any stronghold in Scotland. It sits on a volcanic plug of basalt known as Dumbarton Rock which is high and overlooks the Scottish town of Dumbarton.
History
Dum ...
(modern Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
). However, Eadberht's entire force is subsequently wiped out, probably by the Britons.
* King Cuthred of Wessex dies after a 16-year reign. He is succeeded by his distant kinsman Sigeberht.
Abbasid Caliphate
*Ibn al-Muqaffa'
AbЕ« Muhammad КҝAbd AllДҒh RЕ«zbih ibn DДҒdЕ«ya ( ar, Ш§ШЁЩҲ Щ…ШӯЩ…ШҜ Ш№ШЁШҜШ§Щ„Щ„ЩҮ ШұЩҲШІШЁЩҮ Ш§ШЁЩҶ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҲЩҠЩҮ), born RЕҚzbih pЕ«r-i DДҒdЕҚД“ ( fa, ШұЩҲШІШЁЩҮ ЩҫЩҲШұ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҲЫҢЩҮ), more commonly known as Ibn al-MuqaffaКҝ ( ar, Ш§ШЁЩҶ Ш§Щ„Щ…Щ ...
, Muslim writer and thinker, is tortured at Basra
Basra ( ar, ЩұЩ„Щ’ШЁЩҺШөЩ’ШұЩҺШ©, al-Baб№Јrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
(modern Iraq
Iraq,; ku, Ш№ЫҺШұШ§ЩӮ, translit=ГҠraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, Ъ©ЫҶЩ…Ш§ШұЫҢ Ш№ЫҺШұШ§ЩӮ, translit=KomarГ® ГҠraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to IraqвҖ“Turkey border, the north, Iran to IranвҖ“Iraq ...
), on orders from Caliph al-Mansur
AbЕ« JaКҝfar КҝAbd AllДҒh ibn MuбёҘammad al-Manб№ЈЕ«r (; ar, ШЈШЁЩҲ Ш¬Ш№ЩҒШұ Ш№ШЁШҜ Ш§Щ„Щ„ЩҮ ШЁЩҶ Щ…ШӯЩ…ШҜ Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҶШөЩҲШұ; 95 AH вҖ“ 158 AH/714 CE вҖ“ 6 October 775 CE) usually known simply as by his laqab Al-Manб№ЈЕ«r (Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҶШөЩҲШұ) ...
. His limbs are severed and he is thrown, still alive, into a burning oven (approximate date).
Chinese Empire
*January 18
Events Pre-1600
* 474 – Seven-year-old Leo II succeeds his maternal grandfather Leo I as Byzantine emperor. He dies ten months later.
* 532 – Nika riots in Constantinople fail.
*1126 – Emperor Huizong abdicates the Chin ...
вҖ“ An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general off ...
: The eastern capital of Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
falls to the 200,000-strong army of the rebel general An Lushan
An Lushan (; 20th day of the 1st month 19 February 703 вҖ“ 29 January 757) was a general in the Tang dynasty and is primarily known for instigating the An Lushan Rebellion.
An Lushan was of Sogdian and Göktürk origin,Yang, Zhijiu, "An Lush ...
, who defeats loyalist forces under Feng Changqing. The rebels cross the Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''HuГЎng hГ©'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
, and march on to capture the cities Chenliu
Chenliu () is a town situated in Kaifeng County, Kaifeng in the province of Henan, China.
See also
*List of township-level divisions of Henan
This is a list of township-level divisions of the province of Henan, People's Republic of China ...
and Yingyang (modern Zhengzhou
Zhengzhou (; ), also spelt Zheng Zhou and alternatively romanized as Chengchow, is the capital and largest city of Henan Province in the central part of the People's Republic of China. Located in north-central Henan, it is one of the Nationa ...
, Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is a ...
).
* Battle of Yongqiu
The siege of Yongqiu (йӣҚдёҳд№ӢжҲ°, pinyin: ''YЕҚngqiЕ« zhД« zhГ n'') was a siege for Yongqiu (current Qi County, Kaifeng) in 756 AD during the An Shi Rebellion, by the An Lushan rebels against the Tang army. The Tang army, led by Zhang Xun, f ...
: A Tang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century вҖ“ 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (е”җ) ...
garrison (2,000 men), under Zhang Xun
Zhang Xun (; September 16, 1854 вҖ“ September 11, 1923), courtesy name Shaoxuan (), art name Songshoulaoren (), nickname Bianshuai (, ), was a Chinese general and Qing loyalist who attempted to restore the abdicated emperor Puyi in the Manchu Re ...
, successfully defend their fortress against the rebel army at Yongqiu. Zhang achieves a victory after a 4-month siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
, and prevents the rebels from capturing the fertile Tang territory south of the Huai River.
* February 5
Events Pre-1600
* 62 – Earthquake in Pompeii, Italy.
* 1576 – Henry of Navarre abjures Catholicism at Tours and rejoins the Protestant forces in the French Wars of Religion.
* 1597 – A group of early Japanese Christians ar ...
вҖ“ An Lushan declares himself emperor at Luoyang, establishing a new empire, called the Great Yan. He pushes on towards the primary Tang capital at Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
(now Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
). An decides to seize southern China, to cut off loyalist reinforcements. Meanwhile, numerous soldiers join the rebellion.
* May – Emperor Xuan Zong hires 4,000 Muslim mercenaries
A mercenary, sometimes Pseudonym, also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a memb ...
to help defend Chang'an against the rebels. Loyalist forces take defensible positions in the mountain passes, but chancellor Yang Guozhong gives orders for them to leave their posts.
* July 7
Events Pre-1600
* 1124 – The city of Tyre falls to the Venetian Crusade after a siege of nineteen weeks.
* 1456 – A retrial verdict acquits Joan of Arc of heresy 25 years after her execution.
* 1520 – Spanish ''conquistad ...
вҖ“ An Lushan crushes the Tang troops at the Tong Pass, leaving the road to the capital wide open.
* July 14
Events Pre-1600
* 982 – King Otto II and his Frankish army are defeated by the Muslim army of al-Qasim at Cape Colonna, Southern Italy.
*1223 – Louis VIII becomes King of France upon the death of his father, Philip II.
*1420 ...
– Xuan Zong flees the capital of Chang'an (along with the imperial court) for Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=SГ¬chuДҒn; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of t ...
, as rebel forces advance through the Tongguan Pass toward the city. Meanwhile, An Lushan is ailing, perhaps with diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
. He is nearly blind and suffers from extreme irascibility.
* July 15 – Xuan Zong is ordered by his Imperial Guards
An imperial guard or palace guard is a special group of troops (or a member thereof) of an empire, typically closely associated directly with the Emperor or Empress. Usually these troops embody a more elite status than other imperial forces, in ...
to execute Yang Guozhong, by forcing him to commit suicide or face a mutiny. He permits his consort Yang Guifei
Yang Yuhuan (; 26 June, 719 вҖ“ 15 July 756Volume 218 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'' recorded that Yang was killed on the ''bingshen'' day of the 6th month of the 1st year of the Zhide era of Tang Suzong's reign. This date corresponds to 15 Jul 756 on t ...
to be strangled by his chief eunuch
A eunuch ( ) is a male who has been castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function.
The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2nd millenni ...
. An Lushan also has other members of the emperor's family killed.
* August 12
Events Pre-1600
*1099 – First Crusade: Battle of Ascalon Crusaders under the command of Godfrey of Bouillon defeat Fatimid forces led by Al-Afdal Shahanshah. This is considered the last engagement of the First Crusade.
* 1121 – B ...
– Xuan Zong abdicates the throne after a 44-year reign. He is succeeded by his son Su Zong, as emperor of the Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690вҖ“705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
. He hires 22,000 Muslim mercenaries to reinforce his decimated army at Lingzhou.
* November 19
Events Pre-1600
* 461 – Libius Severus is declared emperor of the Western Roman Empire. The real power is in the hands of the ''magister militum'' Ricimer.
* 636 – The Rashidun Caliphate defeats the Sasanian Empire at the Battl ...
– Tang General Fang Guan is defeated at Xianyang
Xianyang () is a prefecture-level city in central Shaanxi province, situated on the Wei River a few kilometers upstream (west) from the provincial capital of Xi'an. Once the capital of the Qin dynasty, it is now integrated into the Xi'an m ...
. The imperial forces consisted of two thousand oxcarts with cavalry and foot soldiers on two fronts, but the rebels took advantage of their upwind position and attacked with fire. Imperial forces killed or wounded numbered more than 40,000 men.
Japan
* June 4 –Emperor ShЕҚmu
was the 45th emperor of Japan, Imperial Household Agency (''KunaichЕҚ'') иҒ–жӯҰеӨ©зҡҮ (45)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession. ShЕҚmu's reign spanned the years 724 through 749, during the Nara period.
Traditional narrative ...
(retired since 749
__NOTOC__
Year 749 ( DCCXLIX) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 749 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar ...
) dies at Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an " independent federal agency of the United States government within the executive branch", charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It ...
. His wife KЕҚmyЕҚ dedicates over 600 items to the Great Buddha, and donates large sums of money to the ShЕҚsЕҚ-in treasure ( storehouse) in TЕҚdai-ji
is a Buddhist temple complex that was once one of the powerful Seven Great Temples, located in the city of Nara, Japan. Though it was originally founded in the year 738 CE, TЕҚdai-ji was not opened until the year 752 CE. The temple has undergo ...
.
Births
*Abo of Tiflis
Abo of Tiflis ( ar, ШЈШЁЩҲ Ш§Щ„ШӘЩҒЩ„ЩҠШіЩҠ, translit=Abu al-Tiflisi; ka, бғҗбғ‘бғқ бғ—бғ‘бғҳбғҡбғ”бғҡбғҳ, tr; c. 756 вҖ“ 6 January 786) was an early Christian martyr of Arab origin, who went on to practice his faith in what is now Tbilisi, the c ...
, Christian martyr
A martyr (, ''mГЎrtys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
(approximate date)
* Abu Nuwas, Muslim poet (d. 814)
* Fujiwara no Uchimaro
was a Japanese noble of the Nara period and early Heian period. He was the third son of the '' dainagon'' Fujiwara no Matate and thus a member of the Hokke. He reached the court rank of and the position of '' udaijin'', and posthumously of ...
, Japanese nobleman (d. 812)
* Hisham I, Muslim emir
Emir (; ar, ШЈЩ…ЩҠШұ ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
of CГіrdoba (d. 796)
* Ibrahim I, Muslim emir of the Aghlabids
The Aghlabids ( ar, Ш§Щ„ШЈШәШ§Щ„ШЁШ©) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a ...
(d. 812)
* Ismail ibn Ibrahim
Ismail Ibn Ibrahim ( ar, Ш§ШіЩ…Ш§Ш№ЩҠЩ„ ШЁЩҶ Ш§ШЁШұШ§ЩҮЩҠЩ…) (756 – 810) was most notable for being the father of Imam Bukhari. Ismail ibn Ibrahim died in 810, when Imam Bukhari was only an infant, not yet 1 year old.
Biography Ancestry
Isma ...
, Muslim scholar (d. 810)
* Li Yijian Li Yijian () (756 вҖ“ October 13, 822''Old Book of Tang'', vol. 16.), courtesy name Yizhi (), was an official of the Chinese dynasty Tang Dynasty, serving as a chancellor during the reign of Emperor Xianzong.
Background
Li Yijian was born in 756 ...
, chancellor of the Tang Dynasty
The chancellor () was a semi-formally designated office position for a number of high-level officials at one time during the Tang dynasty of China. This list also includes chancellors of the short-lived Wu Zhou dynasty, which is typically trea ...
(d. 822)
* Nikephoros, son of Constantine V
Constantine V ( grc-gre, ОҡПүОҪПғП„ОұОҪП„бҝ–ОҪОҝПӮ, KЕҚnstantД«nos; la, Constantinus; July 718 вҖ“ 14 September 775), was Byzantine emperor from 741 to 775. His reign saw a consolidation of Byzantine security from external threats. As an able ...
(or 758
__NOTOC__
Year 758 ( DCCLVIII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 758 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar er ...
)
Deaths
* June 4 – ShЕҚmu, emperor ofJapan
Japan ( ja, ж—Ҙжң¬, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
(b. 701)
* July 15 – Yang Guifei
Yang Yuhuan (; 26 June, 719 вҖ“ 15 July 756Volume 218 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'' recorded that Yang was killed on the ''bingshen'' day of the 6th month of the 1st year of the Zhide era of Tang Suzong's reign. This date corresponds to 15 Jul 756 on t ...
, consort of Xuan Zong (b. 719
__NOTOC__
Year 719 ( DCCXIX) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 719 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era ...
)
* Aistulf
Aistulf (also Ahistulf, Aistulfus, Haistulfus, Astolf etc.; it, Astolfo; died December 756) was the Duke of Friuli from 744, King of the Lombards from 749, and Duke of Spoleto from 751. His reign was characterized by ruthless and ambitious ...
, duke of Friuli
Friuli ( fur, FriГ»l, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giuli ...
and king of the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
* Cuthred, king of Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
(approximate date)
* Dantidurga
Dantidurga (reigned 735вҖ“756 CE), also known as Dantivarman II was the founder of the Rashtrakuta Empire of Manyakheta. Reu (1933), p54 His capital was based in Gulbarga region of Karnataka. His successor was his uncle Krishna I who extended his ...
, founder of the Rashtrakuta Empire
Rashtrakuta (IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing th ...
(b. 735)
* Feng Changqing, general of the Tang Dynasty
* Forggus mac Cellaig
Forggus mac Cellaig (or Fergus mac Cellaig) (died 756) was a King of Connacht from the UГӯ BriГәin branch of the Connachta. He was the son of Cellach mac Rogallaig (died 705), a previous king and brother of Domnall mac Cellaig (died 728). The se ...
, king of Connacht
Connacht ( ; ga, Connachta or ), is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms ( UГӯ Fiachrach, UГӯ BriГәin, UГӯ Maine, ConmhaГӯcne, and ...
(Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Гүire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
)
* Gao Xianzhi, general of the Tang Dynasty
* Ibn al-Muqaffa'
AbЕ« Muhammad КҝAbd AllДҒh RЕ«zbih ibn DДҒdЕ«ya ( ar, Ш§ШЁЩҲ Щ…ШӯЩ…ШҜ Ш№ШЁШҜШ§Щ„Щ„ЩҮ ШұЩҲШІШЁЩҮ Ш§ШЁЩҶ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҲЩҠЩҮ), born RЕҚzbih pЕ«r-i DДҒdЕҚД“ ( fa, ШұЩҲШІШЁЩҮ ЩҫЩҲШұ ШҜШ§ШҜЩҲЫҢЩҮ), more commonly known as Ibn al-MuqaffaКҝ ( ar, Ш§ШЁЩҶ Ш§Щ„Щ…Щ ...
, Muslim writer (approximate date)
* Isaac I of Antioch, Syriac Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch.
* Wang Changling
Wang Changling (; 698вҖ“756) was a major Tang dynasty poet. His courtesy name was Shaobo (). He was originally from Taiyuan in present-day Shanxi province, according to the editors of the '' Three Hundred Tang Poems'', although other sources c ...
, Chinese poet and official (b. 698)
* Yang Guozhong, chancellor of the Tang Dynasty
Notes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:756