46th (South Devonshire) Regiment of Foot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 46th (South Devonshire) Regiment of Foot was an infantry

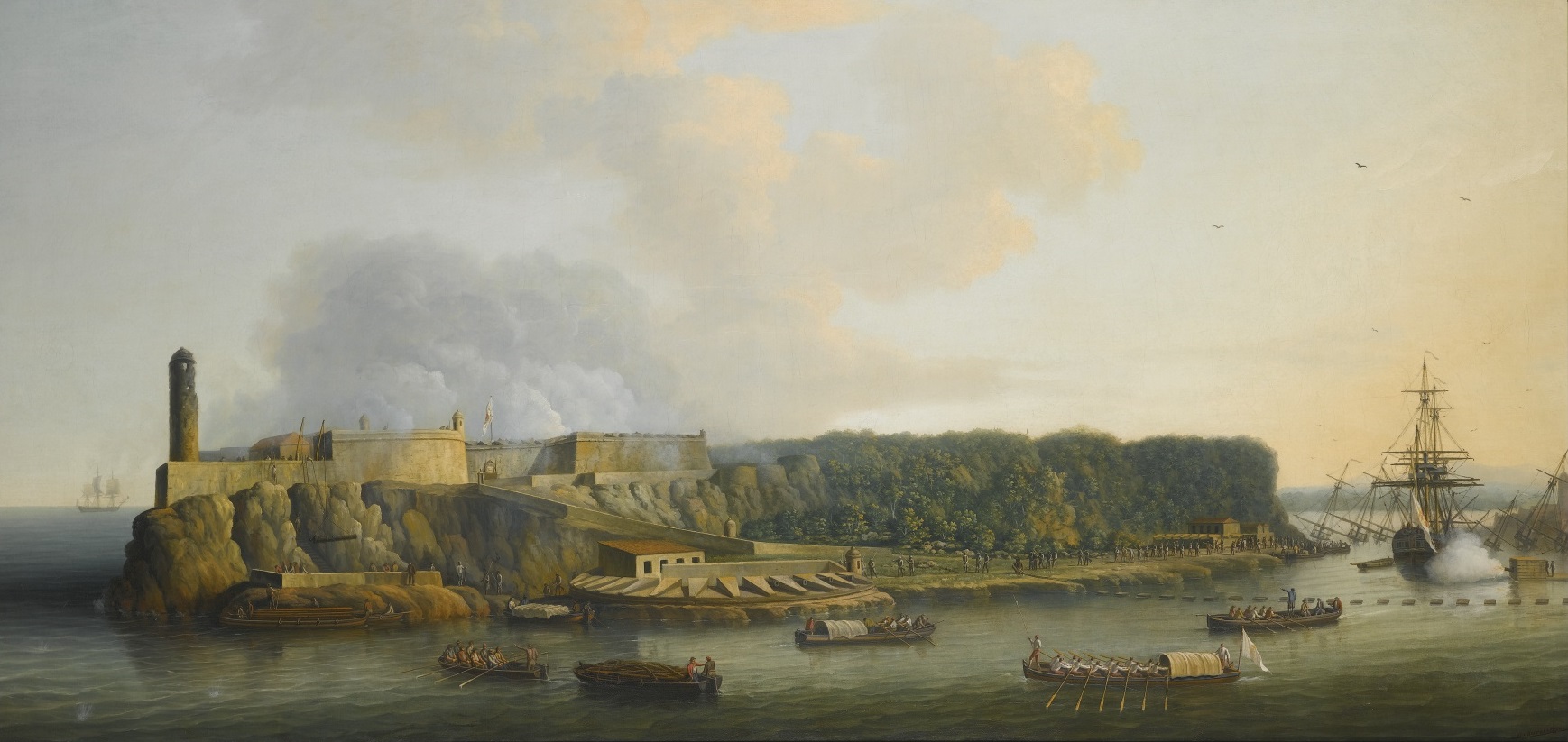 The regiment was raised in
The regiment was raised in  The regiment arrived at in
The regiment arrived at in
 The regiment embarked for the West Indies in November 1794 and helped suppress an insurrection by caribs on Saint Vincent before returning home in November 1796. It returned to the West Indies in April 1804 and, fighting alongside the 1st West India Regiment in February 1805, defended
The regiment embarked for the West Indies in November 1794 and helped suppress an insurrection by caribs on Saint Vincent before returning home in November 1796. It returned to the West Indies in April 1804 and, fighting alongside the 1st West India Regiment in February 1805, defended
regiment
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, service and/or a specialisation.
In Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of front-line soldiers, recruited or conscript ...
of the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkha ...
, raised in 1741. Under the Childers Reforms
The Childers Reforms of 1881 reorganised the infantry regiments of the British Army. The reforms were done by Secretary of State for War Hugh Childers during 1881, and were a continuation of the earlier Cardwell Reforms.
The reorganisation wa ...
it amalgamated with the 32nd (Cornwall) Regiment of Foot
The 32nd Regiment of Foot was an infantry regiment of the British Army, raised in 1702. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 46th (South Devonshire) Regiment of Foot to form the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry in 1881.
History ...
to form the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry
The Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry (DCLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1881 to 1959.
The regiment was created on 1 July 1881 as part of the Childers Reforms, by the merger of the 32nd (Cornwall Ligh ...
in 1881, becoming the 2nd Battalion of the new regiment.
History
Early wars

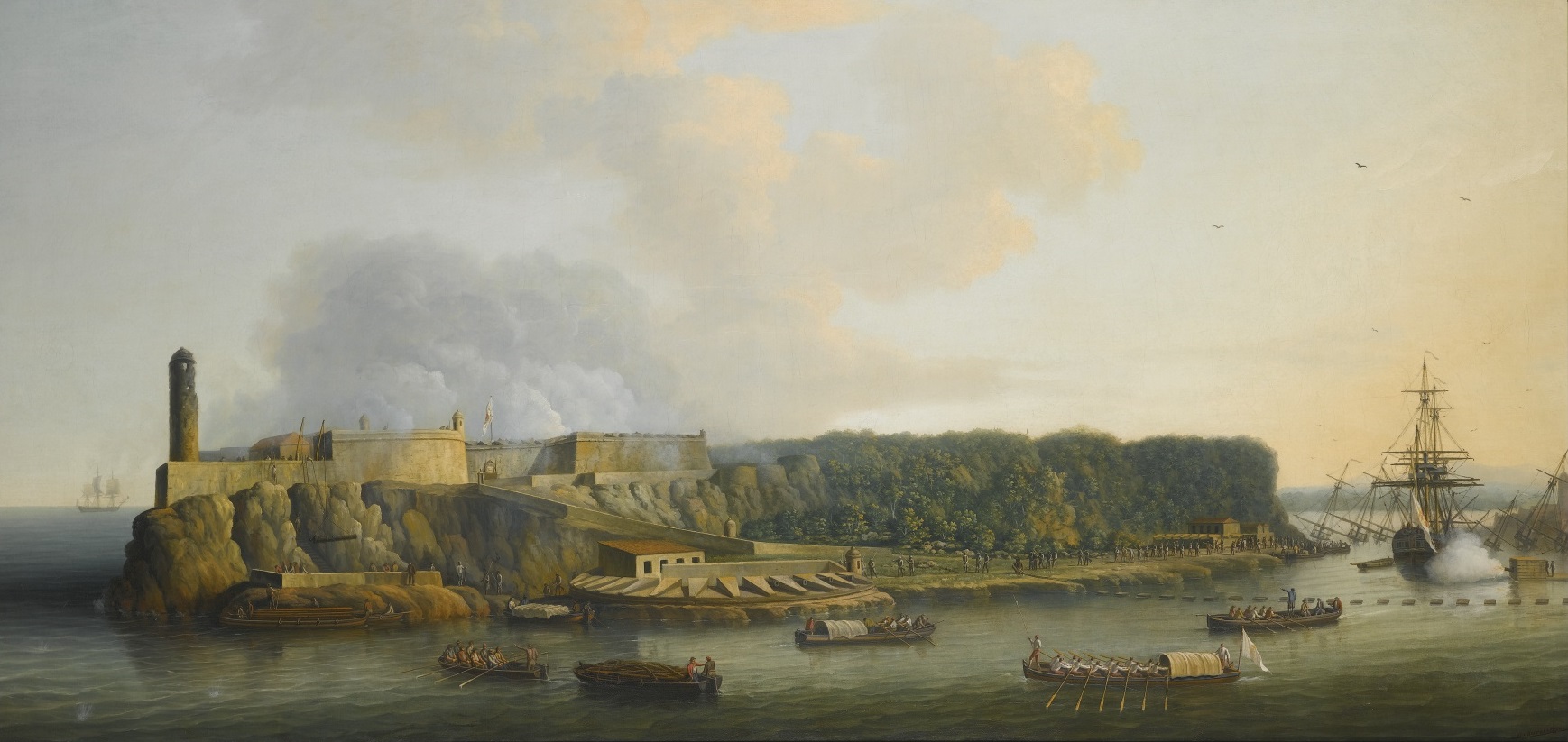 The regiment was raised in
The regiment was raised in Newcastle upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne ( RP: , ), or simply Newcastle, is a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. The city is located on the River Tyne's northern bank and forms the largest part of the Tyneside built-up area. Newcastle is ...
by John Price as John Price's Regiment of Foot in 1741. The regiment proceeded to Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
and took part in the Battle of Prestonpans
The Battle of Prestonpans, also known as the Battle of Gladsmuir, was fought on 21 September 1745, near Prestonpans, in East Lothian, the first significant engagement of the Jacobite rising of 1745.
Jacobite forces, led by the Stuart exile C ...
in September 1745 during the Jacobite rising
Jacobitism (; gd, Seumasachas, ; ga, Seacaibíteachas, ) was a political movement that supported the restoration of the senior line of the House of Stuart to the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British throne. The name derives from the first name ...
. It was ranked as the 57th Regiment of Foot in 1747 but re-ranked as the 46th Regiment of Foot in 1751. After eight years' service in Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
, the regiment embarked for Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
in May 1757 for service in the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the st ...
.Cannon, p. 11 The regiment saw action at the assault on Fort Ticonderoga in July 1758 the assault and capture of Fort Niagara in July 1759Cannon, p. 13 and the Montreal Campaign in August to September 1760.
The regiment then moved to the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
in October 1761 and took part in the capture of Martinique in January 1762, the storming of Morro Castle in July 1762 and the capture of Havana in August 1762. The regiment returned home in 1767.
 The regiment arrived at in
The regiment arrived at in North Carolina
North Carolina () is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 28th largest and List of states and territories of the United ...
in April 1776 for service in the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
.Cannon, p. 21 It fought at the Battle of Sullivan's Island
The Battle of Sullivan's Island or the Battle of Fort Sullivan was fought on June 28, 1776, during the American Revolutionary War. It took place near Charleston, South Carolina, during the first British attempt to capture the city from American ...
in June 1776, Battle of Long Island
The Battle of Long Island, also known as the Battle of Brooklyn and the Battle of Brooklyn Heights, was an action of the American Revolutionary War fought on August 27, 1776, at the western edge of Long Island in present-day Brooklyn, New Yor ...
in August 1776, the Battle of White Plains
The Battle of White Plains was a battle in the New York and New Jersey campaign of the American Revolutionary War, fought on October 28, 1776 near White Plains, New York. Following the retreat of George Washington's Continental Army northward f ...
in October 1776Cannon, p. 22 and the Battle of Fort Washington
The Battle of Fort Washington was fought in New York on November 16, 1776, during the American Revolutionary War between the United States and Great Britain. It was a British victory that gained the surrender of the remnant of the garrison of ...
in November 1776. It saw further action during the Philadelphia campaign
The Philadelphia campaign (1777–1778) was a British effort in the American Revolutionary War to gain control of Philadelphia, which was then the seat of the Second Continental Congress. British General William Howe, after failing to dra ...
at the Battle of Brandywine
The Battle of Brandywine, also known as the Battle of Brandywine Creek, was fought between the American Continental Army of General George Washington and the British Army of General William Howe, 5th Viscount Howe, Sir William Howe on September& ...
in September 1777 the Battle of Paoli also in September 1777Cannon, p. 24 and the Battle of Germantown
The Battle of Germantown was a major engagement in the Philadelphia campaign of the American Revolutionary War. It was fought on October 4, 1777, at Germantown, Pennsylvania, between the British Army led by Sir William Howe, and the American Con ...
in October 1777. It was following the British attack on the Americans at Paoli, where the light company of the regiment took no prisoners and the Americans demanded vengeance, that the regiment decided to insert identifying red feathers in their shako
A shako (, , or ) is a tall, cylindrical military cap, usually with a visor, and sometimes tapered at the top. It is usually adorned with an ornamental plate or badge on the front, metallic or otherwise; and often has a feather, plume (see hackle) ...
helmets to prevent anyone else suffering on their account: hence the nickname ''the Red Feathers''.Cannon, p. 25 The regiment went on to fight at the Battle of Monmouth
The Battle of Monmouth, also known as the Battle of Monmouth Court House, was fought near Monmouth Court House in modern-day Freehold Borough, New Jersey on June 28, 1778, during the American Revolutionary War. It pitted the Continental Army, co ...
in June 1778 and operations against New Bedford and Martha's Vineyard in September 1778. It sailed for the West Indies in November 1778 and took part in the attack on Saint Lucia and the Battle of Vigie in December 1778. The regiment returned to England and was renamed the 46th (South Devonshire) Regiment of Foot in 1782.
Napoleonic Wars
 The regiment embarked for the West Indies in November 1794 and helped suppress an insurrection by caribs on Saint Vincent before returning home in November 1796. It returned to the West Indies in April 1804 and, fighting alongside the 1st West India Regiment in February 1805, defended
The regiment embarked for the West Indies in November 1794 and helped suppress an insurrection by caribs on Saint Vincent before returning home in November 1796. It returned to the West Indies in April 1804 and, fighting alongside the 1st West India Regiment in February 1805, defended Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographical ...
against a French force for over a week until the French abandoned the attack; hence the regiment's first battle honour "Dominica". The regiment took part in another action when in May 1806 when 40 of its soldiers boarded the packet boat
Packet boats were medium-sized boats designed for domestic mail, passenger, and freight transportation in European countries and in North American rivers and canals, some of them steam driven. They were used extensively during the 18th and 19th ...
''Duke of Montrose'' and set out in pursuit of the French privateers ''Napoleon'' and ''Impériale'': they captured the ''Impériale'' and its crew. The regiment took part in the invasion of Martinique in February 1809 and then returned to England in December 1811.
Colonial Australia
The regiment embarked forNew South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
in August 1813: they were stationed at Hobart
Hobart ( ; Nuennonne/ Palawa kani: ''nipaluna'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian island state of Tasmania. Home to almost half of all Tasmanians, it is the least-populated Australian state capital city, and second-small ...
on Van Diemens Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a sepa ...
with orders to suppress a gang of bushranger
Bushrangers were originally escaped convicts in the early years of the British settlement of Australia who used the bush as a refuge to hide from the authorities. By the 1820s, the term had evolved to refer to those who took up " robbery unde ...
s. In April 1816, Governor Lachlan Macquarie
Major General Lachlan Macquarie, CB (; gd, Lachann MacGuaire; 31 January 1762 – 1 July 1824) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator from Scotland. Macquarie served as the fifth Governor of New South Wales from 1810 to 1821, an ...
issued orders for the regiment to undertake punitive expedition
A punitive expedition is a military journey undertaken to punish a political entity or any group of people outside the borders of the punishing state or union. It is usually undertaken in response to perceived disobedient or morally wrong beh ...
s against Aboriginal groups in the Nepean, Hawkesbury and Grose River valleys in New South Wales. The regiment was to take as many prisoners as they could; if anyone refused to surrender, the soldiers were to "fire upon and compel them to surrender, breaking and destroying the spears, clubs and waddies of all those you take prisoners". Furthermore, if the soldiers did kill anyone, Macquarie ordered their bodies to be "hanged up on trees in conspicuous situations, to strike the survivors with greater terror". The orders issued by Macquarie would then be replicated by other colonial officials in Australia during the Australian frontier wars of the 19th and early 20th centuries. The regiment then sailed for Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
in September 1817 and, after a tour on the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, returned to England in March 1833.
The Victorian era
The regiment was sent to theCrimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
in summer 1854 and saw action at the Battle of Alma
The Battle of the Alma (short for Battle of the Alma River) was a battle in the Crimean War between an allied expeditionary force (made up of French, British, and Ottoman forces) and Russian forces defending the Crimean Peninsula on 20Septem ...
in September 1854, the Battle of Balaclava
The Battle of Balaclava, fought on 25 October 1854 during the Crimean War, was part of the Siege of Sevastopol (1854–55), an Allied attempt to capture the port and fortress of Sevastopol, Russia's principal naval base on the Black Sea. The en ...
in October 1854 and the Battle of Inkerman
The Battle of Inkerman was fought during the Crimean War on 5 November 1854 between the allied armies of Britain and France against the Imperial Russian Army. The battle broke the will of the Russian Army to defeat the allies in the field, an ...
in November 1854 as well as the Siege of Sebastopol
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteri ...
in winter 1854.
As part of the Cardwell Reforms
The Cardwell Reforms were a series of reforms of the British Army undertaken by Secretary of State for War Edward Cardwell between 1868 and 1874 with the support of Liberal prime minister William Ewart Gladstone. Gladstone paid little attention ...
of the 1870s, where single-battalion regiments were linked together to share a single depot and recruiting district in the United Kingdom, the 46th was linked with the 32nd (Cornwall) Regiment of Foot
The 32nd Regiment of Foot was an infantry regiment of the British Army, raised in 1702. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 46th (South Devonshire) Regiment of Foot to form the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry in 1881.
History ...
, and assigned to district no. 35 at Victoria Barracks, Bodmin
Victoria Barracks was a military installation in Bodmin, Cornwall.
History
The barracks originally comprised a keep, adjoining stables and a parade ground completed in 1859. In 1873 a system of recruiting areas based on counties was instituted ...
. On 1 July 1881 the Childers Reforms
The Childers Reforms of 1881 reorganised the infantry regiments of the British Army. The reforms were done by Secretary of State for War Hugh Childers during 1881, and were a continuation of the earlier Cardwell Reforms.
The reorganisation wa ...
came into effect and the regiment amalgamated with the 32nd (Cornwall) Regiment of Foot to form the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry
The Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry (DCLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1881 to 1959.
The regiment was created on 1 July 1881 as part of the Childers Reforms, by the merger of the 32nd (Cornwall Ligh ...
, becoming the 2nd Battalion (with the 32nd (Cornwall) Regiment of Foot becoming the 1st Battalion).
Battle Honours
Battle honours were:Chant, p. 144 *Dominica (1805) *Crimean War:Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
Colonels
Colonels of the regiment were: *1741–1743: Brig-Gen. John Price *1743–1764: Lt-Gen. Hon. Thomas MurrayThe 46th Regiment of Foot - (1748)
*1764–1775: Gen. Sir William (Howe), 5th Viscount Howe, KB *1775–1795: Lt-Gen. Hon. Sir John Vaughan, KBThe 46th (South Devon) Regiment - (1782)
*1795–1804: Gen. Sir James Henry Craig, KB *1804–1816: Gen. John Whyte *1816–1838: Gen. Henry Wynyard *1838–1839: Lt-Gen. Sir John Keane, 1st Baron Keane, GCB, GCH *1839–1843: Lt-Gen. John Ross, CB *1843–1853: Gen. Sir John Hamilton Dalrymple, Bt., later 8thEarl of Stair
Earl of Stair is a title in the Peerage of Scotland. It was created in 1703 for the lawyer and statesman John Dalrymple, 2nd Viscount of Stair.
Dalrymple's father, James Dalrymple, had been a prominent lawyer; having served as Lord President ...
, KT
*1853–1854: Lt-Gen. Richard Egerton, CB
*1854–1860: Gen. Sir John Pennefather, GCB
*1860: Lt-Gen. John Geddes, KH
*1860–1861: Gen. Thomas Gerrard Ball
*1861–1870: Lt-Gen. Sir Charles Ash Windham, KCB
*1870:Lt-Gen. Edward Hungerford Delaval Elers Napier
*1870–1881: Gen. Charles Stuart
References
Sources
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:46th (South Devonshire) Regiment Of Foot Military units and formations established in 1741 Military units and formations in Devon Regiments of the British Army in the Crimean War Regiments of the British Army in the American Revolutionary War Military units and formations disestablished in 1881 Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry