450 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
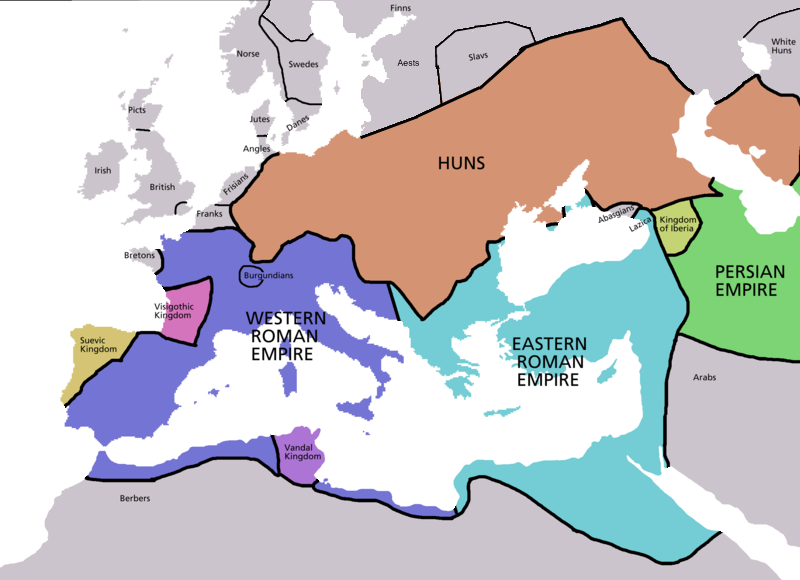 __NOTOC__
Year 450 ( CDL) was a
__NOTOC__
Year 450 ( CDL) was a
common year starting on Sunday
A common year starting on Sunday is any non-leap year (i.e. a year with 365 days) that begins on Sunday, January 1, 1 January, and ends on Sunday, December 31, 31 December. Its dominical letter hence is A. The most recent year was 2017 and the next ...
(link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
, the 450th Year of the Common Era ( CE) and Anno Domini ( AD designations, the 450th year of the 1st millennium
File:1st millennium montage.png, From top left, clockwise: Depiction of Jesus, the central figure in Christianity; The Colosseum, a landmark of the once-mighty Roman Empire; Kaaba, the Great Mosque of Mecca, the holiest site of Islam; Chess, a new ...
, the 50th year of the half of 5th century
The 5th century is the time period from 401 ( CDI) through 500 ( D) ''Anno Domini'' (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia.
It saw the ...
, and the 1st year of the 450s decade. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Valentinianus and Avienus (or, less frequently, year 1203 ''Ab urbe condita
''Ab urbe condita'' ( 'from the founding of the City'), or ''anno urbis conditae'' (; 'in the year since the city's founding'), abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is an exp ...
''). The denomination 450 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", ...
calendar era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one ''epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, it is the year as per the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era (the Coptic ...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Byzantium
*July 28
Events Pre-1600
* 1364 – Troops of the Republic of Pisa and the Republic of Florence clash in the Battle of Cascina.
* 1540 – Henry VIII of England marries his fifth wife, Catherine Howard, on the same day his former Chancellor, T ...
– Emperor Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος, Theodosios; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450) was Roman emperor for most of his life, proclaimed ''Augustus (title), augustus'' as an infant in 402 and ruling as the eastern Empire's sole emperor after ...
, age 49, falls from his horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...
while hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
at Constantinople and dies soon afterward. He has reigned since 408
__NOTOC__
Year 408 (Roman numerals, CDVIII) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Bassus and Philippus (or, less frequentl ...
, mostly under the domination of his Christian sister Pulcheria
Aelia Pulcheria (; grc-gre, Πουλχερία; 19 January 398 or 399 – July 453) was an Eastern Roman empress who advised her brother emperor Theodosius II during his minority and then became wife to emperor Marcian from November 450 to he ...
, who has been allowed to return to court (see 441).
* August 25
Events Pre-1600
* 19 – The Roman general Germanicus dies near Antioch. He was convinced that the mysterious illness that ended in his death was a result of poisoning by the Syrian governor Gnaeus Calpurnius Piso, whom he had ordered to ...
– Pulcheria is forced to marry and co-rule the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. She gives the imperial diadem
A diadem is a type of crown, specifically an ornamental headband worn by monarchs and others as a badge of royalty.
Overview
The word derives from the Greek διάδημα ''diádēma'', "band" or "fillet", from διαδέω ''diadéō'', "I ...
to the Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
n (or Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
) officer and senator Marcian
Marcian (; la, Marcianus, link=no; grc-gre, Μαρκιανός, link=no ; 392 – 27 January 457) was Roman emperor of the East from 450 to 457. Very little of his life before becoming emperor is known, other than that he was a (personal as ...
, age 58, and is crowned as empress in the Hippodrome
The hippodrome ( el, ἱππόδρομος) was an ancient Greek stadium for horse racing and chariot racing. The name is derived from the Greek words ''hippos'' (ἵππος; "horse") and ''dromos'' (δρόμος; "course"). The term is used i ...
at Constantinople, in the first religious
Religion is usually defined as a social system, social-cultural system of designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morality, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sacred site, sanctified places, prophecy, prophecie ...
coronation ceremony.
* Marcian orders the execution (or assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
) of the unpopular court eunuch Chrysaphius Chrysaphius ( el, Χρυσάφιος) was a eunuch in the Eastern Roman court who became the chief minister of Theodosius II (r. 402–450). Having a great influence on the rule of the empire during his ascendancy, he pursued a policy of appeasement ...
. He discontinues the tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conqu ...
payments to Attila.
* All the Temples of Aphrodisias
Aphrodisias (; grc, Ἀφροδισιάς, Aphrodisiás) was a small Ancient Greece, ancient Greek Hellenistic_period, Hellenistic city in the historic Caria cultural region of western Anatolia, Turkey. It is located near the modern village of ...
(City of Goddess Aphrodite) are demolished and its libraries burned down. The city is renamed Stauroupolis (City of the Cross).
Europe
* Spring –Justa Grata Honoria
Justa Grata Honoria, commonly referred to during her lifetime as Honoria, (born ''c.'' 418 – died ''c.'' 455) was the older sister of the Western Roman Emperor Valentinian III. She is famous for her plea of love and help to Attila the Hun, whi ...
, eldest sister of emperor Valentinian III
Valentinian III ( la, Placidus Valentinianus; 2 July 41916 March 455) was Roman emperor in the West from 425 to 455. Made emperor in childhood, his reign over the Roman Empire was one of the longest, but was dominated by powerful generals vying ...
, sends her ring to Attila the Hun
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in March 453. He was also the leader of a tribal empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Bulgars, among others, in Central and Ea ...
in an effort to escape a marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between ...
being forced upon her by her brother. Now about 34, she has had an affair with an officer in her household and has allegedly plotted to overthrow Valentinian, who has sent her to a convent
A convent is a community of monks, nuns, religious brothers or, sisters or priests. Alternatively, ''convent'' means the building used by the community. The word is particularly used in the Catholic Church, Lutheran churches, and the Anglican ...
at Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
. Attila announces his intention to marry her, says he expects to be given half the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
as her dowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment b ...
, and gathers a large Hun invasion force. Flavius Aetius
Aetius (also spelled Aëtius; ; 390 – 454) was a Roman general and statesman of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most influential man in the Empire for two decades (433454). He managed pol ...
, Roman general (''magister militum
(Latin for "master of soldiers", plural ) was a top-level military command used in the later Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, ...
''), musters an army in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
of Burgundians
The Burgundians ( la, Burgundes, Burgundiōnes, Burgundī; on, Burgundar; ang, Burgendas; grc-gre, Βούργουνδοι) were an early Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared in the middle Rhine region, near the Roman Empire, and ...
, Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
, Ripuarians
Ripuarian or Rhineland Franks (Latin: ''Ripuarii'' or ''Ribuarii'') were one of the two main groupings of early Frankish people, and specifically it was the name eventually applied to the tribes who settled in the old Roman territory of the Ubii, ...
, Salian Franks
The Salian Franks, also called the Salians (Latin: ''Salii''; Greek: Σάλιοι, ''Salioi''), were a northwestern subgroup of the early Franks who appear in the historical record in the fourth and fifth centuries. They lived west of the Lowe ...
and Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
under the command of the Visigoth king Theodoric I
Theodoric I ( got, Þiudarīks; la, Theodericus; 390 or 393 – 20 or 24 June 451) was the King of the Visigoths from 418 to 451. Theodoric is famous for his part in stopping Attila (the Hun) at the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains in 451, wher ...
.
* Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ' ...
, Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
and Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nations ...
invade Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, marking the beginning of the Old English period (approximate date).
* Remodelling of the Dome of Baptistry of Neon, Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the cap ...
(Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
) begins (approximate date).
Persia
* KingYazdegerd II
Yazdegerd II (also spelled Yazdgerd and Yazdgird; pal, 𐭩𐭦𐭣𐭪𐭥𐭲𐭩), was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 438 to 457. He was the successor and son of Bahram V ().
His reign was marked by wars against the Eastern Roman ...
summons the leading Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
nobles to the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
capital Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ...
, pressuring them to cut their ties with the Western Church
Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic C ...
.Ronald Grigor Suny, ''The Making of the Georgian Nation'', (Indiana University Press, 1994), 23.
Asia
* Nalanda University (India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
) is founded (approximate date).
By topic
Agriculture
* Metalhorseshoe
A horseshoe is a fabricated product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human toen ...
s come into more common use in the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
and in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, increasing the efficiency of horsepower in agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
and transportation.
Births
*February 2
Events Pre-1600
* 506 – Alaric II, eighth king of the Visigoths, promulgates the Breviary of Alaric (''Breviarium Alaricianum'' or ''Lex Romana Visigothorum''), a collection of "Roman law".
* 880 – Battle of Lüneburg Heath: King ...
– Justin I
Justin I ( la, Iustinus; grc-gre, Ἰουστῖνος, ''Ioustînos''; 450 – 1 August 527) was the Eastern Roman emperor from 518 to 527. Born to a peasant family, he rose through the ranks of the army to become commander of the imperial ...
, Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
(d. 527
__NOTOC__
Year 527 ( DXXVII) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Mavortius without colleague (or, less frequently, year ...
)
* Ariadne
Ariadne (; grc-gre, Ἀριάδνη; la, Ariadne) was a Cretan princess in Greek mythology. She was mostly associated with mazes and labyrinths because of her involvement in the myths of the Minotaur and Theseus. She is best known for having ...
, Byzantine Empress
This is a list of Roman and Byzantine empresses. A Roman empress was a woman who was the wife of a Roman emperor, the ruler of the Roman Empire.
The Romans had no single term for the position: Latin and Greek titles such as '' augusta'' (Greek ...
(approximate date)
*Avitus
Eparchius Avitus (c. 390 – 457) was Roman emperor of the West from July 455 to October 456. He was a senator of Gallic extraction and a high-ranking officer both in the civil and military administration, as well as Bishop of Piacenza.
He o ...
, archbishop of Vienne
The Archbishopric of Vienne, named after its episcopal seat in Vienne in the Isère département of southern France, was a metropolitan Roman Catholic archdiocese. It is now part of the Archdiocese of Lyon.
History
The legend according to whic ...
(approximate date) (d. 518)
* Chilperic II
Chilperic II (c. 672 – 13 February 721), known as Daniel prior to his coronation, was the youngest son of Childeric II and his half-cousin wife, Bilichild. He reigned as king of Neustria from 715 and sole king of the Franks from 718 until hi ...
, king of Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
(approximate date)
* Gunthamund
Gunthamund (c. 450–496), King of the Vandals and Alans (484-496) was the third king of the north African Vandal Kingdom. He succeeded his unpopular uncle Huneric, and for that reason alone, enjoyed a rather successful reign.
Gunthamund was the ...
, king of the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal Kingdom, Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The ...
(d. 496
__NOTOC__
Year 496 ( CDXCVI) was a leap year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Paulus without colleague (or, less frequently, ye ...
)
* Isidore
Isidore ( ; also spelled Isador, Isadore and Isidor) is an English and French masculine given name. The name is derived from the Greek name ''Isídōros'' (Ἰσίδωρος) and can literally be translated to "gift of Isis." The name has survived ...
, Neoplatonist
Neoplatonism is a strand of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a chain of thinkers. But there are some ide ...
philosopher (approximate date)
* Pope Hormisdas
Pope Hormisdas (450 – 6 August 523) was the bishop of Rome from 20 July 514 to his death. His papacy was dominated by the Acacian schism, started in 484 by Acacius of Constantinople's efforts to placate the Monophysites. His efforts to resolve ...
(approximate date)
* Thrasamund
Thrasamund (450–523), King of the Vandals and Alans (496–523), was the fourth king of the North African Kingdom of the Vandals. He reigned longer than any other Vandal king in Africa other than his grandfather Genseric.
Thrasamund was the t ...
, king of the Vandals (d. 523)
Deaths
*July 28
Events Pre-1600
* 1364 – Troops of the Republic of Pisa and the Republic of Florence clash in the Battle of Cascina.
* 1540 – Henry VIII of England marries his fifth wife, Catherine Howard, on the same day his former Chancellor, T ...
– Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος, Theodosios; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450) was Roman emperor for most of his life, proclaimed ''Augustus (title), augustus'' as an infant in 402 and ruling as the eastern Empire's sole emperor after ...
, Roman Emperor (b. 401)
* July 31
Events Pre-1600
*30 BC – Battle of Alexandria: Mark Antony achieves a minor victory over Octavian's forces, but most of his army subsequently deserts, leading to his suicide.
* 781 – The oldest recorded eruption of Mount Fuji (Tr ...
– Peter Chrysologus
Peter Chrysologus ( el, Ἅγιος Πέτρος ὁ Χρυσολόγος, ''Petros Chrysologos'', "Peter the Golden-worded"; c. 380 – c. 450) was Bishop of Ravenna from about 433 until his death. He is known as the “Doctor of Homilies” for ...
, bishop of Ravenna
This page is a list of Roman Catholic bishops and archbishops of Ravenna and, from 1985, of the Archdiocese of Ravenna-Cervia.November 27
Events Pre-1600
*AD 25 – Luoyang is declared capital of the Eastern Han dynasty by Emperor Guangwu of Han.
* 176 – Emperor Marcus Aurelius grants his son Commodus the rank of " Imperator" and makes him Supreme Commander of the ...
– Galla Placidia
Galla Placidia (388–89/392–93 – 27 November 450), daughter of the Roman emperor Theodosius I, was a mother, tutor, and advisor to emperor Valentinian III, and a major force in Roman politics for most of her life. She was List of Visigothi ...
, Roman Empress
This is a list of Roman and Byzantine empresses. A Roman empress was a woman who was the wife of a Roman emperor, the ruler of the Roman Empire.
The Romans had no single term for the position: Latin and Greek titles such as '' augusta'' (Greek ...
(b. 392
__NOTOC__
Year 392 ( CCCXCII) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Rufinus (or, less frequently, year 1145 ''A ...
)
* Chrysaphius Chrysaphius ( el, Χρυσάφιος) was a eunuch in the Eastern Roman court who became the chief minister of Theodosius II (r. 402–450). Having a great influence on the rule of the empire during his ascendancy, he pursued a policy of appeasement ...
, eunuch
A eunuch ( ) is a male who has been castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function.
The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2nd millennium ...
and chief minister
A chief minister is an elected or appointed head of government of – in most instances – a sub-national entity, for instance an administrative subdivision or federal constituent entity. Examples include a state (and sometimes a union terri ...
* Cui Hao
Cui Hao () (died 450 CE), courtesy name Boyuan (伯淵), was a ''shangshu'' of the Xianbei-led Northern Wei dynasty of China. Largely because of Cui's counsel, Emperor Taiwu of Northern Wei was able to unify northern China, ending the Sixteen Kin ...
, prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
of Northern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Northern dynasties, Northern dynasties ...
* Chlodio
Chlodio (probably died after 450), also Clodio, Clodius, Clodion, Cloio or Chlogio, was a Frankish king who attacked and then apparently ruled Roman-inhabited lands around Cambrai and Tournai, near the modern border of Belgium and France. He is k ...
, semi legendary Frankish king and supposed great-grandfather of Clovis I
Clovis ( la, Chlodovechus; reconstructed Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single kin ...
(approximate date) (b.390
__NOTOC__
Year 390 (Roman numerals, CCCXC) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Neoterius (or, less frequen ...
)
* Kālidāsa
Kālidāsa (''fl.'' 4th–5th century CE) was a Classical Sanskrit author who is often considered ancient India's greatest poet and playwright. His plays and poetry are primarily based on the Vedas, the Rāmāyaṇa, the Mahābhārata and t ...
, Classical Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
writer (approximate date)
* Quodvultdeus
Quodvultdeus (Latin for "what God wills", died 450 AD) was a fifth-century Church Father and Bishop of Carthage who was exiled to Naples. He was known to have been living in Carthage around 407 and became a deacon in 421 AD. He corresponded wi ...
, bishop of Carthage
The Archdiocese of Carthage, also known as the Church of Carthage, was a Latin Catholic diocese established in Carthage, Roman Empire, in the 2nd century. Agrippin was the first named bishop, around 230 AD. The temporal importance of the city of ...
(approximate date)
* Socrates Scholasticus
Socrates of Constantinople ( 380 – after 439), also known as Socrates Scholasticus ( grc-gre, Σωκράτης ὁ Σχολαστικός), was a 5th-century Greeks, Greek Christians, Christian church historian, a contemporary of Sozomen and Th ...
, church historian
Church Historian and Recorder (usually shortened to Church Historian) is a priesthood calling in the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. The role of the Church Historian and Recorder is to keep an accurate and comprehensive record of th ...
(approximate date)
* Sozomen
Salamanes Hermias Sozomenos ( grc-gre, Σαλαμάνης Ἑρμείας Σωζομενός; la, Sozomenus; c. 400 – c. 450 AD), also known as Sozomen, was a Roman lawyer and historian of the Christian Church.
Family and home
He was born arou ...
, church historian (approximate date)
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:450