290 BC on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 __NOTOC__
Year 290 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Rufinus and Dentatus (or, less frequently, year 464 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 290 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the
__NOTOC__
Year 290 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Rufinus and Dentatus (or, less frequently, year 464 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 290 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the
Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", ...
calendar era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one '' epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, it is the year as per the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era (the Copti ...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Roman Republic
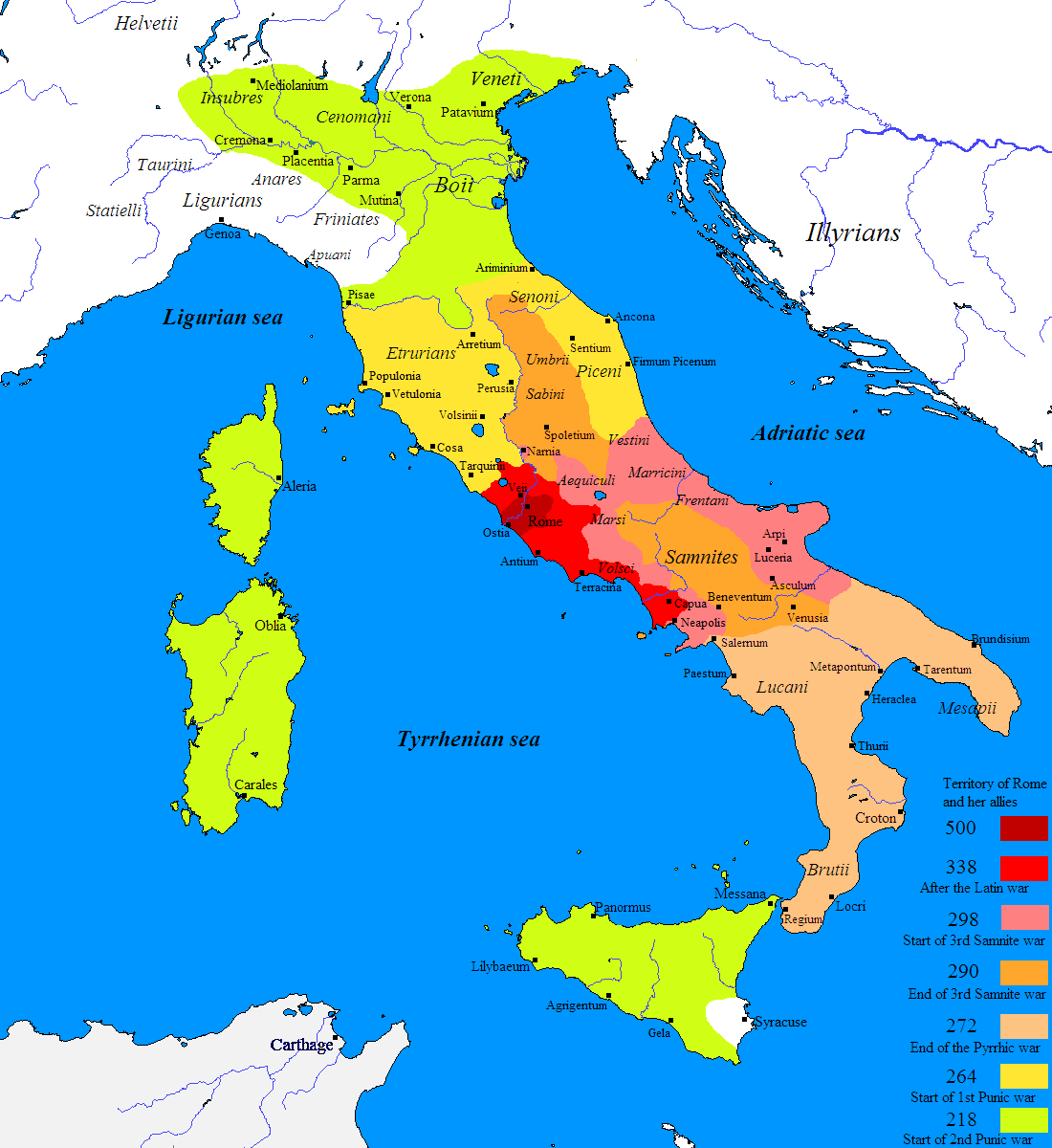
*Third Samnite War
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars (343–341 BC, 326–304 BC, and 298–290 BC) were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe.
...
:
:* Lucius Postumius Megellus, a consul from the previous year, is publicly tried for having used his office to have 2000 of his soldiers work on his farm. He is condemned by all the tribes and fined 50,000 denarii.
:* The consuls Manius Curius Dentatus
Manius Curius Dentatus (died 270 BC) was a Roman general and statesman noted for ending the Samnite War and for his military exploits during the Pyrrhic War. According to Pliny, he was born with teeth, thus earning the surname Dentatus, "toothed ...
and Publius Cornelius Rufinus
Publius Cornelius Rufinus was a dictator during the Roman Republic.
Rufinus belonged to the famous patrician gens Cornelia, as well as being the earliest recorded member of the branch of the family, the gens Cornelii Rufinii et Sullae.
He was a ...
invade Samnium
Samnium ( it, Sannio) is a Latin exonym for a region of Southern Italy anciently inhabited by the Samnites. Their own endonyms were ''Safinim'' for the country (attested in one inscription and one coin legend) and ''Safineis'' for the The ...
and defeat the Samnites in several engagements. The Samnites sue for peace, thus ending the Third Samnite War. The Samnites are recognised by the Romans as autonomous allies but are subordinate to Rome and must give up land as compensation.
:* Curius subjugates the Sabines, possibly for their actions or inaction during the Third Samnite War. Their territory is annexed, securing direct Roman access to the Adriatic. The Sabines are granted civitas sine suffragio ("citizenship without the right to vote").
:* Rome founds the colonies of Castrum, Sena and Adria.
Egypt
* Berenice, wife ofPtolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
, is proclaimed queen of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
. Ptolemy has the city of Berenice built on the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
in her honour. It becomes a great emporium for Egyptian trade with the East.
China
* The city of Yuan is returned by the State of Qin to theState of Wei
Wei (; ; Old Chinese: *') was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It was created from the three-way Partition of Jin, together with Han and Zhao. Its territory lay between the states of Qin and ...
in exchange for the cities of Puban and Pishi.
Births
* Lucius Caecilius Metellus, Roman consul and Pontifex Maximus (approximate date) (d.221 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 221 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Asina and Rufus/Lepidus (or, less frequently, year 533 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 221 BC for this year has ...
)
Deaths
*Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; grc, Μεγασθένης, c. 350 BCE– c. 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, diplomat and Indian ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but ha ...
, Greek historian, diplomat and Indian ethnographer
Ethnography (from Greek ''ethnos'' "folk, people, nation" and ''grapho'' "I write") is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject o ...
(approximate date) (b. c. 350 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 350 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Laenas and Scipio (or, less frequently, year 404 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 350 BC for this year has been ...
)
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:290 Bc