1990 IIHF Women's World Championship on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 1990 IIHF Women's World Championships was an international
Women's Hockey Net page on the IIHF World Women's Championships
accessed July 16, 2006. The 1989 European Women's Ice Hockey Championship served as the qualification tournament for this championship. The top five finishers in the top pool qualified. They were
Source
whockey.com
/small>
 This is the only major international tournament in women's ice hockey to allow bodychecking.Kelly, p. 89. Bodychecking rules allowed for full-contact checking, with certain limitations along the boards.
Before the tournament, bodychecking had been allowed in women's ice hockey in Europe and North America though Canada had begun to gradually eliminate the tactic from their women's ice hockey programs in the mid-1980's, with contact having already been banned at all national women's ice hockey tournaments in Canada in 1983 due to the efforts of
This is the only major international tournament in women's ice hockey to allow bodychecking.Kelly, p. 89. Bodychecking rules allowed for full-contact checking, with certain limitations along the boards.
Before the tournament, bodychecking had been allowed in women's ice hockey in Europe and North America though Canada had begun to gradually eliminate the tactic from their women's ice hockey programs in the mid-1980's, with contact having already been banned at all national women's ice hockey tournaments in Canada in 1983 due to the efforts of
p. 84 accessed July 16, 2006.
Summary from the Women's Hockey Net
{{Women's ice hockey tournaments IIHF Women's World Ice Hockey Championships Ice hockey in Ottawa
women's ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hoc ...
competition held at the Civic Centre
A civic center or civic centre is a prominent land area within a community that is constructed to be its focal point or center. It usually contains one or more dominant public buildings, which may also include a government building. Recently, the ...
in Ottawa, Ontario
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
(now renamed the TD Place Arena) from March 19 to 25, in 1990. This was the first IIHF
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: Fédération internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-Föderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 m ...
-sanctioned international tournament in women's ice hockey and is the only major international tournament in women's ice hockey to allow bodychecking.Kelly, p. 89. Full contact bodychecking was allowed with certain restrictions near the boards. The intermissions between periods were twenty minutes instead of fifteen. This has since been changed to the usual fifteen minutes.
The Canadian team won the gold medal, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
won silver, and Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
won bronze. Team Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
had won the first IIHF European Women’s Championship the previous year (1989), in Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf ( , , ; often in English sources; Low Franconian and Ripuarian language, Ripuarian: ''Düsseldörp'' ; archaic nl, Dusseldorp ) is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second- ...
and Ratingen, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
.
Canada's Fran Rider helped to organize the championships without the financial support from the Canadian Amateur Hockey Association (now known as Hockey Canada).
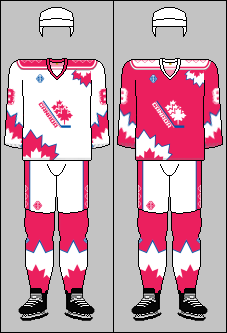
The tournament drew strong international attention. The gold medal game packed 9,000 people into the arena and drew over a million viewers on television. For marketing purposes, the Canadian Amateur Hockey Association decided the Canadian national team should wear pink and white uniforms instead of the expected red and whiteKelly p. 88. and released a related film called, "Pretty in Pink". While the experiment only lasted for this tournament, Ottawa was taken over by a "pink craze" during the championships. Restaurants had pink-coloured food on special, and pink became a popular colour for flowers and bow ties.
Qualification Tournament
TheUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
and Asian representative Japan, qualified automatically.Andria HunteWomen's Hockey Net page on the IIHF World Women's Championships
accessed July 16, 2006. The 1989 European Women's Ice Hockey Championship served as the qualification tournament for this championship. The top five finishers in the top pool qualified. They were
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
, Sweden, Switzerland, and West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
.
U.S. team members ranged in age from 17 to 30 and included high school and college players, a law student and a construction worker.
Venue
The tournament took place in Canada at the Civic Centre in Ottawa, now renamed,TD Place Arena
TD Place Arena, originally the Ottawa Civic Centre, is an indoor arena located in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, seating 9,500. With temporary seating and standing room it can hold 10,585. Opened in December 1967, it is used primarily for sports, inc ...
.
Final tournament
Group stage
Group A
Group B
Consolation round
5–8 place
7–8 place
5–6 place
Final round
Semifinals
3–4 place
Final
Rankings and statistics
Final rankings
# # # # # # # #Scoring leaders
List shows the top ten skaters sorted by points, then goals. Canada's Dawn McGuire was namedMVP
In team sports, a most valuable player award, abbreviated 'MVP award', is an honor typically bestowed upon an individual (or individuals, in the instance of a tie) whose individual performance is the greatest in an entire league, for a particu ...
of the gold medal game.
Leading goaltenders
Only the top five goaltenders, based on save percentage, who have played 40% of their team's minutes are included in this list. ''TOI = Time On Ice (minutes:seconds); SA = Shots against; GA = Goals against; GAA = Goals against average; Sv% = Save percentage; SO =Shutout
In team sports, a shutout ( US) or clean sheet ( UK) is a game in which one team prevents the other from scoring any points. While possible in most major sports, they are highly improbable in some sports, such as basketball.
Shutouts are usuall ...
s''Source
whockey.com
/small>
Bodychecking
 This is the only major international tournament in women's ice hockey to allow bodychecking.Kelly, p. 89. Bodychecking rules allowed for full-contact checking, with certain limitations along the boards.
Before the tournament, bodychecking had been allowed in women's ice hockey in Europe and North America though Canada had begun to gradually eliminate the tactic from their women's ice hockey programs in the mid-1980's, with contact having already been banned at all national women's ice hockey tournaments in Canada in 1983 due to the efforts of
This is the only major international tournament in women's ice hockey to allow bodychecking.Kelly, p. 89. Bodychecking rules allowed for full-contact checking, with certain limitations along the boards.
Before the tournament, bodychecking had been allowed in women's ice hockey in Europe and North America though Canada had begun to gradually eliminate the tactic from their women's ice hockey programs in the mid-1980's, with contact having already been banned at all national women's ice hockey tournaments in Canada in 1983 due to the efforts of Rhonda Leeman Taylor
Rhonda Leeman Taylor (born 1953 in Kingston, Ontario) is a former women's ice hockey player and ice hockey administrator from Canada. In 1980, Leeman Taylor became the first salaried female employee of the Ontario Women's Hockey Association (OWHA). ...
. However, the European teams had asked for bodychecking to be included in the 1990 international tournament.
After this tournament, the International Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: Fédération internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-Föderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
disallowed bodychecking in women's ice hockey. It is currently an infraction punished with a minor or major and game misconduct penalty
Penalty or The Penalty may refer to:
Sports
* Penalty (golf)
* Penalty (gridiron football)
* Penalty (ice hockey)
* Penalty (rugby)
* Penalty (rugby union)
* Penalty kick (association football)
* Penalty shoot-out (association football)
A p ...
.International Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: Fédération internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-Föderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
br>Section 5, Rule 441 of Official Ice Hockey rulesp. 84 accessed July 16, 2006.
Injuries
A number of players sufferedhead injuries
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
from the beginning of the tournament. Finland's Kirsi Hirvonen was "carried away with a neck injury after being cross-checked." U.S. team captain Tina Cardinale-Beauchemin's right forearm and elbow, "were a mass of purple-and-blue welts, courtesy of a slash early in the tournament." Canada's France Saint-Louis, "spent three days in a hospital after taking a stick across the throat".
See also
*IIHF World Women's Championships
The IIHF World Women's Championship (WW or WWC), officially the IIHF Ice Hockey Women's World Championship, is the premier international tournament in women's ice hockey. It is governed by the International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF).
The offi ...
Notes
References
* Malcolm G. Kelly, "The Complete Idiot's Guide to Canadian Sports History and Trivia", Alpha Books, . * *External links
Summary from the Women's Hockey Net
{{Women's ice hockey tournaments IIHF Women's World Ice Hockey Championships Ice hockey in Ottawa
World
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the worl ...
World
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the worl ...
1990
File:1990 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1990 FIFA World Cup is played in Italy; The Human Genome Project is launched; Voyager I takes the famous Pale Blue Dot image- speaking on the fragility of humanity on Earth, astrophysicist ...
March 1990 sports events in Canada
1990s in Ottawa
1990 in Ontario
Women's ice hockey competitions in Canada
Sports competitions in Ottawa