1983 invasion of Grenada on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The United States invasion of Grenada began at dawn on 25 October 1983. The
 Sir
Sir
 In 1983, Representative Ron Dellums ( D,
In 1983, Representative Ron Dellums ( D,
 The
The
 H-hour for the invasion was set for 05:00 on 25 October 1983. U.S. troops deployed for Grenada by helicopter from
H-hour for the invasion was set for 05:00 on 25 October 1983. U.S. troops deployed for Grenada by helicopter from
 U.S. Special Operations Forces were deployed to Grenada beginning on 23 October, before 25 October invasion. Navy SEALs from
U.S. Special Operations Forces were deployed to Grenada beginning on 23 October, before 25 October invasion. Navy SEALs from
 The last major special operation was a mission to rescue Governor-General Scoon from his mansion in Saint George, Grenada. The mission departed late at 05:30 on 25 October from Barbados, resulting in the Grenadian forces being already aware of the invasion and they guarded Scoon closely. The SEAL team entered the mansion without opposition, but
The last major special operation was a mission to rescue Governor-General Scoon from his mansion in Saint George, Grenada. The mission departed late at 05:30 on 25 October from Barbados, resulting in the Grenadian forces being already aware of the invasion and they guarded Scoon closely. The SEAL team entered the mansion without opposition, but
 General Trobaugh of the 82nd Airborne Division had two goals on the second day: securing the perimeter around Salines Airport, and rescuing American students held in Grand Anse. The Army lacked undamaged helicopters after the losses on the first day and consequently had to delay the student rescue until they made contact with Marine forces.
General Trobaugh of the 82nd Airborne Division had two goals on the second day: securing the perimeter around Salines Airport, and rescuing American students held in Grand Anse. The Army lacked undamaged helicopters after the losses on the first day and consequently had to delay the student rescue until they made contact with Marine forces.
 By 27 October, organized resistance was rapidly diminishing, but the American forces did not yet realize this. The 2nd Battalion, 8th Marines continued advancing along the coast and capturing additional towns, meeting little resistance, although one patrol did encounter a single
By 27 October, organized resistance was rapidly diminishing, but the American forces did not yet realize this. The 2nd Battalion, 8th Marines continued advancing along the coast and capturing additional towns, meeting little resistance, although one patrol did encounter a single
 Official U.S. sources state that some of the opponents were well-prepared and well-positioned and put up stubborn resistance, to the extent that the Americans called in two battalions of reinforcements on the evening of 26 October. The total naval and air superiority of the American forces had overwhelmed the defenders. Nearly 8,000 soldiers, sailors, airmen, and Marines had participated in Operation Urgent Fury, along with 353 Caribbean allies from the Caribbean Peace Forces. American forces sustained 19 killed and 116 wounded; Cuban forces sustained 25 killed, 59 wounded, and 638 combatants captured. Grenadian forces suffered 45 dead and 358 wounded; at least 24 civilians were also killed, 18 of whom died in the accidental bombing of a Grenadian mental hospital. The US troops also destroyed a significant amount of Grenada's military hardware, including six BTR-60 APCs and a BRDM-2 armored car. A second BRDM-2 armored car was impounded and shipped back to
Official U.S. sources state that some of the opponents were well-prepared and well-positioned and put up stubborn resistance, to the extent that the Americans called in two battalions of reinforcements on the evening of 26 October. The total naval and air superiority of the American forces had overwhelmed the defenders. Nearly 8,000 soldiers, sailors, airmen, and Marines had participated in Operation Urgent Fury, along with 353 Caribbean allies from the Caribbean Peace Forces. American forces sustained 19 killed and 116 wounded; Cuban forces sustained 25 killed, 59 wounded, and 638 combatants captured. Grenadian forces suffered 45 dead and 358 wounded; at least 24 civilians were also killed, 18 of whom died in the accidental bombing of a Grenadian mental hospital. The US troops also destroyed a significant amount of Grenada's military hardware, including six BTR-60 APCs and a BRDM-2 armored car. A second BRDM-2 armored car was impounded and shipped back to
Fortitudine: Newsletter of the Marine Corps Historical Program, Volumes 15–18
'. Tommell, Anthony Wayne. History and Museums Division, U.S. Marine Corps, 1985.
 ''
'' However, some members of the study group dissented from its findings. Congressman
However, some members of the study group dissented from its findings. Congressman
 The American and Caribbean governments quickly reaffirmed Scoon as Queen Elizabeth's sole legitimate representative in Grenada, and hence was thus the only lawful authority on the island. In accordance with Commonwealth constitutional practice, Scoon assumed power as interim head of government and formed an advisory council which named
The American and Caribbean governments quickly reaffirmed Scoon as Queen Elizabeth's sole legitimate representative in Grenada, and hence was thus the only lawful authority on the island. In accordance with Commonwealth constitutional practice, Scoon assumed power as interim head of government and formed an advisory council which named  American forces remained in Grenada after combat operations finished in December as part of Operation Island Breeze. Elements remaining performed security missions and assisted members of the Caribbean Peacekeeping Force and the Royal Grenadian Police Force, including military police, special forces, and a specialized intelligence detachment. The Point Salines International Airport was renamed in honor of Prime Minister Maurice Bishop on 29 May 2009, his 65th birthday. Hundreds of Grenadians turned out to commemorate the honoring of the event. Prime Minister gave the keynote speech and referred to the renaming as an act of the Grenadian people coming home to themselves. He also hoped that it would help bring closure to a chapter of denial in Grenada's history.
American forces remained in Grenada after combat operations finished in December as part of Operation Island Breeze. Elements remaining performed security missions and assisted members of the Caribbean Peacekeeping Force and the Royal Grenadian Police Force, including military police, special forces, and a specialized intelligence detachment. The Point Salines International Airport was renamed in honor of Prime Minister Maurice Bishop on 29 May 2009, his 65th birthday. Hundreds of Grenadians turned out to commemorate the honoring of the event. Prime Minister gave the keynote speech and referred to the renaming as an act of the Grenadian people coming home to themselves. He also hoped that it would help bring closure to a chapter of denial in Grenada's history.
 The
The
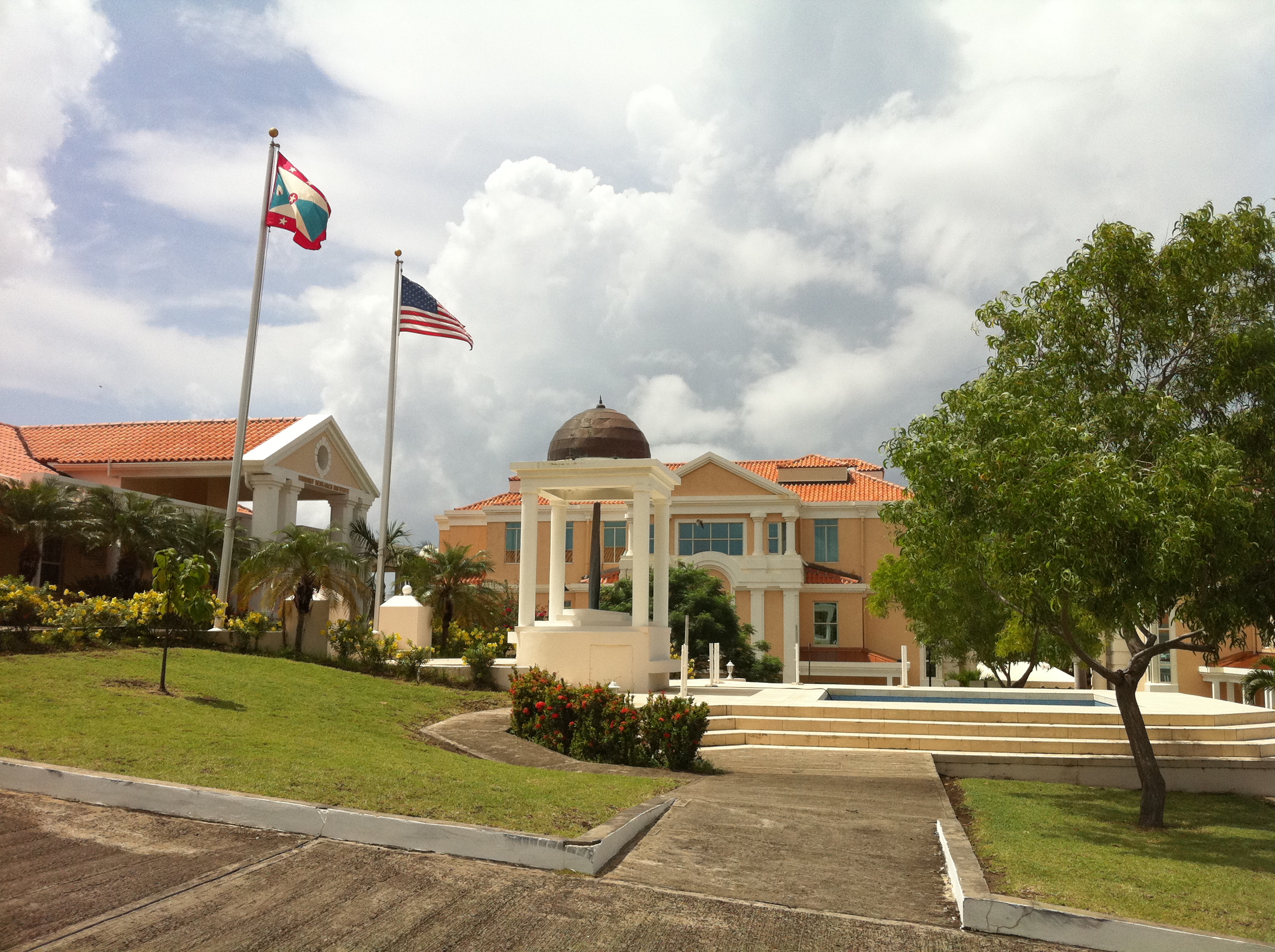 25 October is a national holiday in Grenada, called Thanksgiving Day, to commemorate the invasion. St. George's University (SGU) built a monument on its True Blue campus to honor the American servicemen killed during the invasion, and marks the day with an annual memorial ceremony.
On 29 May 2009, the Grenadian government changed the name of Point Salines International Airport to
25 October is a national holiday in Grenada, called Thanksgiving Day, to commemorate the invasion. St. George's University (SGU) built a monument on its True Blue campus to honor the American servicemen killed during the invasion, and marks the day with an annual memorial ceremony.
On 29 May 2009, the Grenadian government changed the name of Point Salines International Airport to
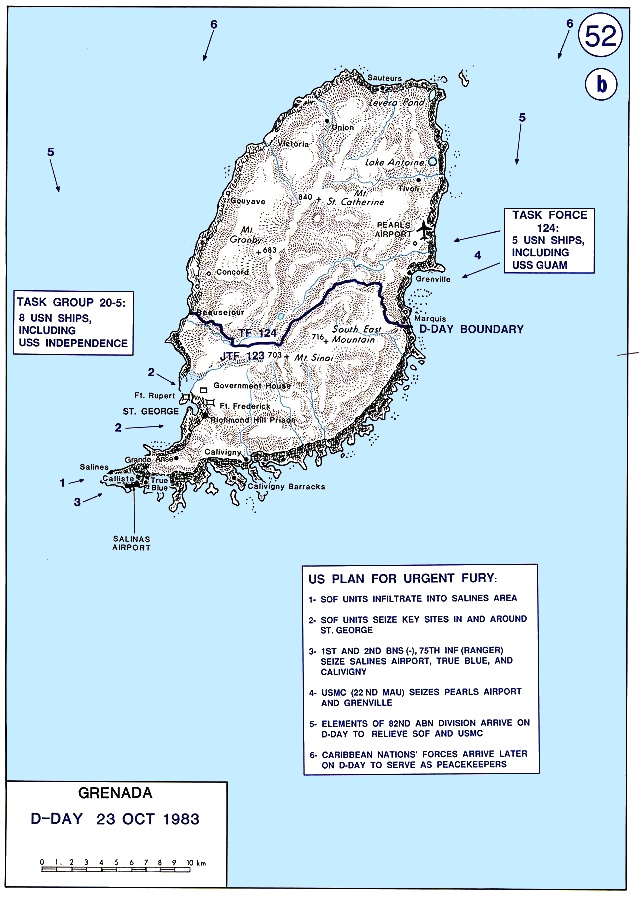
 Vice Admiral Joseph Metcalf, III, COMSECONDFLT, became Commander of Joint Task Force 120 (CJTF 120) and commanded units from the Air Force, Army, Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard from the MARG flagship USS ''Guam''. Rear Admiral Richard C. Berry (COMCRUDESGRU Eight) (Commander Task Group 20) supported the task force on the aircraft carrier USS ''Independence''. Commanding Officer USS Guam (Task Force 124) was assigned the mission of seizing Pearls Airport and the port of Grenville, and of neutralizing any opposing forces in the area. Simultaneously, Army Rangers in Task Force 123 would secure points at the southern end of the island, including the airfield under construction near Point Salines. The 82d Airborne Division (Task Force 121) were designated to follow and assume the security at Point Salines once it was seized by Task Force 123. Task Group 20.5, a carrier battle group built around USS ''Independence'', and Air Force elements would support the ground forces.
Vice Admiral Joseph Metcalf, III, COMSECONDFLT, became Commander of Joint Task Force 120 (CJTF 120) and commanded units from the Air Force, Army, Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard from the MARG flagship USS ''Guam''. Rear Admiral Richard C. Berry (COMCRUDESGRU Eight) (Commander Task Group 20) supported the task force on the aircraft carrier USS ''Independence''. Commanding Officer USS Guam (Task Force 124) was assigned the mission of seizing Pearls Airport and the port of Grenville, and of neutralizing any opposing forces in the area. Simultaneously, Army Rangers in Task Force 123 would secure points at the southern end of the island, including the airfield under construction near Point Salines. The 82d Airborne Division (Task Force 121) were designated to follow and assume the security at Point Salines once it was seized by Task Force 123. Task Group 20.5, a carrier battle group built around USS ''Independence'', and Air Force elements would support the ground forces.
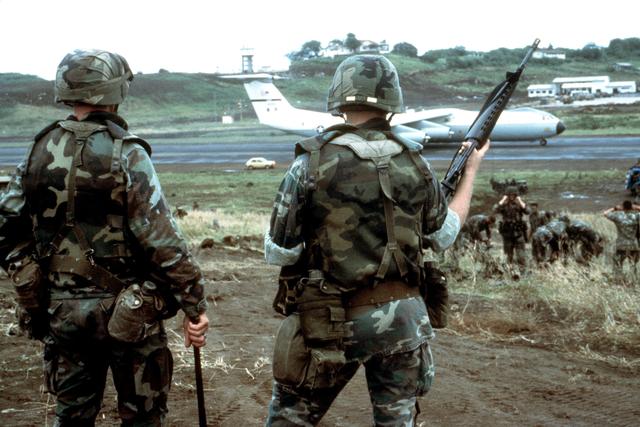


 * 1st and 2nd Ranger Battalions 75th Ranger Regiment conducted a low-level parachute assault to secure Point Salines Airport. Hunter Army Airfield, GA and Ft. Lewis, WA
* 82nd Airborne Division – 2nd Brigade Task Force ( 325th Airborne Infantry Regiment 2nd & 3rd Battalions plus supporting units) and 3rd Brigade Task Force (1st and 2nd Battalions of the
* 1st and 2nd Ranger Battalions 75th Ranger Regiment conducted a low-level parachute assault to secure Point Salines Airport. Hunter Army Airfield, GA and Ft. Lewis, WA
* 82nd Airborne Division – 2nd Brigade Task Force ( 325th Airborne Infantry Regiment 2nd & 3rd Battalions plus supporting units) and 3rd Brigade Task Force (1st and 2nd Battalions of the
Grenada Documents, an Overview & Selection
DOD & State Dept, Sept 1984, 813 pages.
Grenada, A Preliminary Report
DOD & State
Joint Overview, Operation Urgent Fury
1 May 1985, 87 pages
online
* , A military history. * Williams, Gary. ''US–Grenada Relations: Revolution and Intervention in the Backyard'' (Macmillan, 2007).
Invasion of Grenada and Its Political Repercussions
from th
Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
��
Grenadian Revolution Archive
at marxists.org
The dream of a Black utopia
podcast from
''Grenada''
— a 1984 comic book about the invasion written by the CIA. {{Authority control 1983 in Grenada 1983 in the United States Airborne operations Cold War conflicts Communism in Grenada Conflicts in 1983 Cuba–United States relations Grenada–United States military relations Invasions by the United States Invasions of Grenada Military expeditions of the United States Operations involving American special forces Reagan administration controversies United States Army Rangers United States Marine Corps in the 20th century United States–Caribbean relations Grenada Grenada Grenada Grenada Grenada Grenada Grenada Grenada Invasions Proxy wars October 1983 events in North America November 1983 events in North America December 1983 events in North America United States involvement in regime change
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
and a coalition of six Caribbean nations invaded the island nation of Grenada, north of Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
. Codenamed Operation Urgent Fury by the U.S. military, it resulted in military occupation within a few days. It was triggered by the strife within the People's Revolutionary Government
The People's Revolutionary Government (PRG) was proclaimed on 13 March 1979 after the Marxist–Leninist New Jewel Movement overthrew the government of Grenada in a revolution, making Grenada the only socialist state within the Commonwealth. ...
which resulted in the house arrest and execution of the previous leader and second Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
of Grenada Maurice Bishop
Maurice Rupert Bishop (29 May 1944 – 19 October 1983) was a Grenadian revolutionary and the leader of New Jewel Movement – a Marxist–Leninist party which sought to prioritise socio-economic development, education, and black liberation � ...
, and the establishment of the Revolutionary Military Council with Hudson Austin as Chairman. The invasion resulted in the appointment of an interim government, followed by elections in 1984.
Grenada had gained independence from the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
in 1974. The allegedly communist New Jewel Movement
The New Joint Endeavor for Welfare, Education, and Liberation, or New JEWEL Movement (NJM), was a Marxist–Leninist vanguard party in the Caribbean island nation of Grenada that was led by Maurice Bishop.
Established in 1973, the NJM issued i ...
seized power in a coup in 1979 under Maurice Bishop, suspending the constitution and detaining several political prisoners. In September 1983, an internal power struggle began over Bishop's leadership performance. Bishop was pressured at a party meeting to share power with Deputy Prime Minister Bernard Coard
Winston Bernard Coard (born 10 August 1945) is a Grenadian politician who was Deputy Prime Minister in the People's Revolutionary Government of the New Jewel Movement. Coard launched a coup within the revolutionary government and took power f ...
. Bishop initially agreed, but later balked. He was put under house arrest by his own party's Central Committee until he relented. When his secret detention became widely known, Bishop was freed by an aroused crowd of his supporters. A confrontation then ensued at military headquarters between Grenadian soldiers loyal to Coard and civilians supporting Bishop. Shooting started under still-disputed circumstances. At least 19 soldiers and civilians were killed on 19 October 1983 including Bishop, his partner Jacqueline Creft, two other cabinet ministers and two union leaders.
The Reagan administration
Ronald Reagan's tenure as the 40th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1981, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Republican from California, took office following a landslide victory over ...
in the U.S. launched a military intervention following receipt of a formal appeal for help from the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States
The Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS; French: ''Organisation des États de la Caraïbe orientale'', OECO) is an inter-governmental organisation dedicated to economic harmonisation and integration, protection of human and legal ri ...
. In addition, the Governor-General of Grenada
The governor-general of Grenada is the vice-regal representative of the Grenadian monarch, currently King Charles III, in Grenada. The governor-general is appointed by the monarch on the recommendation of the prime minister of Grenada. The fun ...
Paul Scoon
Sir Paul Godwin Scoon (4 July 1935 – 2 September 2013) was a Grenadian politician who served as Governor-General of Grenada from 1978 to 1992. His tenure is notable for its hectic events related to the rise and fall of the People's Revolutiona ...
secretly signaled he would also support outside intervention, but he put off signing a letter of invitation until 26 October. Reagan also acted due to "concerns over the 600 U.S. medical students on the island" and fears of a repeat of the Iran hostage crisis
On November 4, 1979, 52 United States diplomats and citizens were held hostage after a group of militarized Iranian college students belonging to the Muslim Student Followers of the Imam's Line, who supported the Iranian Revolution, took over ...
.
The invasion began on the morning of 25 October 1983, just two days after the bombing of the U.S. Marine barracks in Beirut. The invading force consisted of the 1st and 2nd battalions of the US Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
's 75th Ranger Regiment, the 82nd Airborne and the Army's rapid deployment force
A rapid deployment force is a military formation that is capable of fast deployment. Such forces typically consist of elite military units ( special forces, paratroopers, marines, etc.) and are usually trained at a higher intensity than the rest ...
, U.S. Marines
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combi ...
, Army Delta Force
The 1st Special Forces Operational Detachment–Delta (1st SFOD-D), referred to variously as Delta Force, Combat Applications Group (CAG), Army Compartmented Elements (ACE), "The Unit", or within Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC), Task Fo ...
, Navy SEAL
The United States Navy Sea, Air, and Land (SEAL) Teams, commonly known as Navy SEALs, are the U.S. Navy's primary special operations force and a component of the Naval Special Warfare Command. Among the SEALs' main functions are conducting s ...
s, and ancillary forces totaling 7,600 troops, together with Jamaican forces and troops of the Regional Security System
The Regional Security System (RSS) is an international agreement for the defence and security of the eastern Caribbean region with future expansion planned with South America.
History
The Regional Security System was created in 1982 to counter ...
(RSS). The force defeated Grenadian resistance after a low-altitude airborne assault by Rangers and the 82nd Airborne on Point Salines Airport at the south end of the island, and a Marine helicopter and amphibious landing on the north end at Pearls Airport. Austin's military government was deposed and replaced, with Scoon as Governor-General, by an interim advisory council until the 1984 elections.
The invasion was criticized by many countries. British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1975 to 1990. She was the first female British prime ...
privately disapproved of the mission and the lack of notice that she received, but she publicly supported it. The United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Curr ...
condemned it as "a flagrant violation of international law" on 2 November 1983 by a vote of 108 to 9.
The date of the invasion is now a national holiday in Grenada called Thanksgiving Day
Thanksgiving is a national holiday celebrated on various dates in the United States, Canada, Grenada, Saint Lucia, Liberia, and unofficially in countries like Brazil and Philippines. It is also observed in the Netherlander town of Leiden and ...
, commemorating the freeing of several political prisoners who were subsequently elected to office. A truth and reconciliation commission
A truth commission, also known as a truth and reconciliation commission or truth and justice commission, is an official body tasked with discovering and revealing past wrongdoing by a government (or, depending on the circumstances, non-state act ...
was launched in 2000 to re-examine some of the controversies of the era; in particular, the commission made an unsuccessful attempt to find Bishop's body, which had been disposed of at Austin's order and never found. The invasion also highlighted issues with communication and coordination between the different branches of the American military when operating together as a joint force, contributing to investigations and sweeping changes in the form of the Goldwater-Nichols Act and other reorganizations.
Background
 Sir
Sir Eric Gairy
Sir Eric Matthew Gairy PC (18 February 192223 August 1997) was the first Prime Minister of Grenada, serving from his country's independence in 1974 until his overthrow in a coup by Maurice Bishop in 1979. Gairy also served as head of governme ...
had led Grenada to independence from the United Kingdom in 1974, but his term in office coincided with civil strife in Grenada. He was head of the Grenada United Labour Party
The Grenada United Labour Party (GULP) is a political party in Grenada.
History
The party was founded by Eric Gairy in 1950. It contested the first elections held under universal suffrage in 1951, and won six of the eight seats. Nohlen, D (2005) ...
and claimed victory in the general election of 1976, but the opposition did not accept the result as legitimate. The civil strife took the form of street violence between Gairy's private army the Mongoose Gang The Mongoose Gang was a private army or militia which operated from 1967 to 1979 under the control of Sir Eric Gairy, the Premier and later Prime Minister of Grenada, and head of the Grenada United Labour Party. Officially, Mongoose Gang members we ...
, and gangs organized by the New Jewel Movement
The New Joint Endeavor for Welfare, Education, and Liberation, or New JEWEL Movement (NJM), was a Marxist–Leninist vanguard party in the Caribbean island nation of Grenada that was led by Maurice Bishop.
Established in 1973, the NJM issued i ...
(NJM). Maurice Bishop
Maurice Rupert Bishop (29 May 1944 – 19 October 1983) was a Grenadian revolutionary and the leader of New Jewel Movement – a Marxist–Leninist party which sought to prioritise socio-economic development, education, and black liberation � ...
led the NJM in an armed revolution and overthrew the government on 13 March 1979, while Gairy was out of the country, establishing the People's Revolutionary Government
The People's Revolutionary Government (PRG) was proclaimed on 13 March 1979 after the Marxist–Leninist New Jewel Movement overthrew the government of Grenada in a revolution, making Grenada the only socialist state within the Commonwealth. ...
.
Airport
The Bishop government began constructing the Point Salines International Airport with the help of the United Kingdom,Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, and other nations. The British government proposed the airport in 1954 when Grenada was still a British colony. Canadians
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
designed it, the British government underwrote it, and a London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
firm built it. The American government accused Grenada of constructing facilities to aid a Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
-Cuban military buildup in the Caribbean based on the runway which could accommodate the largest Soviet aircraft, such as the An-12
The Antonov An-12 ( Russian: Антонов Ан-12; NATO reporting name: Cub) is a four-engined turboprop transport aircraft designed in the Soviet Union. It is the military version of the Antonov An-10 and has many variants. For more than th ...
, An-22
The Antonov An-22 "Antei" (, ''An-22 Antej''; English ''Antaeus'') (NATO reporting name "Cock") is a heavy military transport aircraft designed by the Antonov Design Bureau in the Soviet Union. Powered by four turboprop engines each driving a pa ...
, and the An-124
The Antonov An-124 Ruslan (; russian: Антонов Ан-124 Руслан, , Ruslan; NATO reporting name: Condor) is a large, strategic airlift, four-engined aircraft that was designed in the 1980s by the Antonov design bureau in the Ukrain ...
. Such a facility would enhance the Soviet and Cuban transportation of weapons to Central American insurgents and expand Soviet regional influence. Bishop's government claimed that the airport was built to accommodate commercial aircraft carrying tourists, pointing out that such jets could not land at Pearls Airport with its runway on the island's north end, and that Pearls could not be expanded because its runway abutted a mountain at one end and the ocean at the other.
 In 1983, Representative Ron Dellums ( D,
In 1983, Representative Ron Dellums ( D, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
) traveled to Grenada on a fact-finding mission, having been invited by the country's prime minister. He described his findings before Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
:
Based on my personal observations, discussion, and analysis of the new international airport under construction in Grenada, it is my conclusion that this project is specifically now and has always been for the purpose of economic development and is not for military use.... It is my thought that it is absurd, patronizing, and totally unwarranted for the United States government to charge that this airport poses a military threat to the United States' national security.In March 1983, President Reagan began issuing warnings about the threat posed to the United States and the Caribbean by the Soviet-Cuban militarization of the Caribbean, evident from the excessively long airplane runway being built and intelligence indicating increased Soviet interest in the island. He said that the runway and the numerous fuel storage tanks were unnecessary for commercial flights, and that evidence indicated that the airport was to become a Cuban-Soviet forward military airbase.
October 1983
On 16 October 1983, Deputy Prime MinisterBernard Coard
Winston Bernard Coard (born 10 August 1945) is a Grenadian politician who was Deputy Prime Minister in the People's Revolutionary Government of the New Jewel Movement. Coard launched a coup within the revolutionary government and took power f ...
seized power and placed Bishop under house arrest. Mass protests against the coup led to Bishop escaping detention and reasserting his authority as the head of the government. He was eventually captured and murdered by a firing squad of soldiers, along with his partner and several government officials and union leaders loyal to him. The army under Hudson Austin then stepped in and formed a military council to rule the country, placing Governor-General Paul Scoon
Sir Paul Godwin Scoon (4 July 1935 – 2 September 2013) was a Grenadian politician who served as Governor-General of Grenada from 1978 to 1992. His tenure is notable for its hectic events related to the rise and fall of the People's Revolutiona ...
under house arrest. The army announced a four-day total curfew during which anyone seen on the streets would be summarily executed.
 The
The Organization of Eastern Caribbean States
The Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS; French: ''Organisation des États de la Caraïbe orientale'', OECO) is an inter-governmental organisation dedicated to economic harmonisation and integration, protection of human and legal ri ...
(OECS), Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
, and Jamaica all appealed to the United States for assistance. Scoon had requested the invasion through secret diplomatic channels, but it was not made public for his safety. He was well within his rights to take this action under the reserve power
In a parliamentary or semi-presidential system of government, a reserve power, also known as discretionary power, is a power that may be exercised by the head of state without the approval of another branch or part of the government. Unlike in ...
s vested in the Crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
. On Saturday, 22 October 1983, the Deputy High Commissioner in Bridgetown
Bridgetown (UN/LOCODE: BB BGI) is the capital and largest city of Barbados. Formerly The Town of Saint Michael, the Greater Bridgetown area is located within the parish of Saint Michael. Bridgetown is sometimes locally referred to as "The Ci ...
, Barbados visited Grenada and reported that Scoon was well and "did not request military intervention, either directly or indirectly", but in his 2003 autobiography, ''Survival for Service'', Scoon maintains he asked the visiting British diplomat to pass along "an oral request" for outside military intervention at this meeting.
On 25 October, the combined forces of the United States and the Regional Security System (RSS) based in Barbados invaded Grenada in an operation code named ''Operation Urgent Fury''. The United States stated that this was done at the request of Barbados' Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
Tom Adams and Dominica's Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
Eugenia Charles. The invasion was highly criticized by the governments in Canada, Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
, and the United Kingdom. The United Nations General Assembly condemned it as "a flagrant violation of international law" by a vote of 108 to 9, with 27 abstentions.
First day of the invasion
 H-hour for the invasion was set for 05:00 on 25 October 1983. U.S. troops deployed for Grenada by helicopter from
H-hour for the invasion was set for 05:00 on 25 October 1983. U.S. troops deployed for Grenada by helicopter from Grantley Adams International Airport
Grantley Adams International Airport (GAIA) is the international airport of Barbados, located in Seawell, Christ Church. It is the only designated port of entry for persons arriving and departing by air in Barbados and operates as one of th ...
on Barbados before daybreak. Nearly simultaneously, American paratroopers arrived directly by transport aircraft from bases in the eastern United States and U.S. Marines were airlifted to the island from the USS ''Guam'' offshore. It was the first major operation conducted by the American military since the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
. Vice Admiral Joseph Metcalf III
Joseph Metcalf III (20 December 1927 – 2 March 2007) was a United States Navy vice admiral. He graduated from Vermont Academy in 1946 and then from the Naval Academy in 1951 and retired from active duty in 1987.
Experience
Vice Admiral M ...
, Commander of the Second Fleet, was the overall commander of American forces, designated Joint Task Force 120, which included elements of each military service and multiple special operations units. Fighting continued for several days and the total number of American troops reached some 7,000 along with 300 troops from the Organization of American States, commanded by Brigadier Rudyard Lewis of Barbados.
The main objectives on the first day were for the 75th Ranger Regiment to capture the Point Salines International Airport in order for the 82nd Airborne Division to land reinforcements on the island; the 2nd Battalion, 8th Marine Regiment to capture Pearls Airport; and other forces to rescue the American students at the True Blue Campus of St. George's University. In addition, a number of special operations missions were undertaken by Army Delta Force operatives and Navy SEALs to obtain intelligence and secure key individuals and equipment. Many of these missions were plagued by inadequate intelligence, planning, and accurate maps of any kind, and the American forces mostly relied upon tourist maps.
Defending forces
People's Revolutionary Army
The invading forces encountered about 1,500 Grenadian soldiers of the People's Revolutionary Army (PRA) manning defensive positions. The PRA troops were for the most part equipped with light weapons, mostly Kalashnikov-pattern automatic rifles of Soviet bloc origin, and smaller numbers of obsolete SKS carbines and PPSh-41 submachine guns. They had few heavy weapons and no modern air defense systems. The PRA was not regarded as a serious military threat by the US, which was more concerned by the possibility that Cuba would send a large expeditionary force to intervene on behalf of its erstwhile ally. The PRA did possess eightBTR-60PB
The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers (APCs). It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen in public for the first time in 1961. BTR stands for ''Brone ...
armored personnel carriers and two BRDM-2
The BRDM-2 (''Boyevaya Razvedyvatelnaya Dozornaya Mashina'', Боевая Разведывательная Дозорная Машина, literally "Combat Reconnaissance/Patrol Vehicle") is an amphibious armoured scout car used by states that we ...
armored cars delivered as military aid from the Soviet Union in February 1981, but no tanks.''Grenada 1983'' by Lee E. Russell and M. Albert Mendez, 1985 Osprey Publishing Ltd., pp. 28–48.
Cuban forces in Grenada
The Cuban military presence in Grenada was more complex than initially thought. Most of the Cuban civilian expatriates present were also military reservists. Fidel Castro described the Cuban construction crews in Grenada as "workers and soldiers at the same time", claiming the dual nature of their role was consistent with Cuba's "citizen soldier" tradition. At the time of the invasion, there were an estimated 784 Cuban nationals on the island.Domínguez, Jorge I. (1989). ''To Make a World Safe for Revolution: Cuba's Foreign Policy''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. . pp. 168–169 About 630 of the Cuban nationals listed their occupations as construction workers, another 64 as military personnel, and 18 as dependents. The remainder were medical staff or teachers. Colonel Pedro Tortoló Comas was the highest-ranking Cuban military officer in Grenada in 1983, and he later stated that he issued small arms and ammunition to the construction workers for the purpose of self-defense during the invasion, which may have further blurred the line between their status as civilians and combatants. They were also expressly forbidden to surrender to US military forces if approached. The regular Cuban military personnel on the island were serving as advisers to the PRA at the time. Cuban advisers and instructors deployed with overseas military missions were not confined to non-combat and technical support roles; if the units to which they were attached participated in an engagement, they were expected to fight alongside their foreign counterparts.Bob Woodward
Robert Upshur Woodward (born March 26, 1943) is an American investigative journalist. He started working for '' The Washington Post'' as a reporter in 1971 and now holds the title of associate editor.
While a young reporter for ''The Washingt ...
wrote in ''Veil'' that captured "military advisors" from socialist countries, including Cuba, were actually accredited diplomats and their dependents. He claimed that none of them took any actual part in the fighting. The US government asserted that most of the supposed Cuban civilian technicians on Grenada were in fact military personnel, including special forces and combat engineers. A summary of the Cuban presence in ''The Engineer'', the official periodical of the US Army Engineer School, noted that "resistance from these well-armed military and paramilitary forces belied claims that they were simply construction crews."
Navy SEAL reconnaissance missions
 U.S. Special Operations Forces were deployed to Grenada beginning on 23 October, before 25 October invasion. Navy SEALs from
U.S. Special Operations Forces were deployed to Grenada beginning on 23 October, before 25 October invasion. Navy SEALs from SEAL Team 6
The Naval Special Warfare Development Group (NSWDG), abbreviated as DEVGRU ("Development Group") and commonly known as SEAL Team Six, is the United States Navy component of the Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC). The unit is often referre ...
and Air Force combat controllers were air-dropped at sea to perform a reconnaissance mission on Point Salines. The helicopter drop went wrong; four SEALs were lost at sea and their bodies never recovered, causing most people to suspect they had drowned. The four SEALs were Machinist Mate 1st Class Kenneth J. Butcher, Quartermaster 1st Class Kevin E. Lundberg, Hull Technician 1st Class Stephen L. Morris, and Senior Chief Engineman Robert R. Schamberger. In an interview conducted by Bill Salisbury and published on 4 October 1990, Kenneth Butcher's widow claimed that she had gone to Grenada hoping that her husband had survived. She said, "There was this fisherman who said he saw four guys in wetsuits come out of the water, and then two days later he saw four bodies being thrown into the water. So we would like to think they made it, 'cause there was a boat smashed up on the beach. We would like to think the four of them got in that boat, made it to shore, got someplace, and were captured. And they're, you know, gonna come back." The SEAL and Air Force survivors continued their mission, but their boats flooded while evading a patrol boat, causing the mission to be aborted. Another SEAL mission on 24 October was also unsuccessful, due to harsh weather, resulting in little intelligence being gathered in advance of the impending intervention.
Air assault on Point Salines
Alpha and Bravo companies of the 1st Battalion of the 75th Ranger Regiment embarked onC-130
The Lockheed C-130 Hercules is an American four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft designed and built by Lockheed Corporation, Lockheed (now Lockheed Martin). Capable of using unprepared runways for takeoffs and landings, the C-130 ...
s at Hunter Army Airfield
Hunter Army Airfield , located in Savannah, Georgia, United States, is a military airfield and subordinate installation to Fort Stewart located in Hinesville, Georgia.
Hunter features a runway that is 11,375 feet (3,468 m) long and an aircr ...
at midnight on 24 October to perform an air assault landing on Point Salines International Airport, intending to land at the airport and then disembark. The Rangers had to switch abruptly to a parachute landing when they learned mid-flight that the runway was obstructed. The air drop began at 05:30 on 25 October in the face of moderate resistance from ZU-23
The ZU-23-2, also known as ZU-23, is a Soviet towed 23×152mm anti-aircraft twin-barreled autocannon. ZU stands for ''Zenitnaya Ustanovka'' (Russian: Зенитная Установка) – anti-aircraft mount. The GRAU index is 2A13.
Developm ...
anti-aircraft guns and several BTR-60 armored personnel carriers (APCs), which were knocked out by M67 recoilless rifle
The M67 recoilless rifle is a 90 mm (3.55 inch) anti-tank recoilless rifle made in the United States and later in South Korea. It could also be employed in an anti-personnel role with the use of the M590 antipersonnel round. It was designed ...
fire. AC-130
The Lockheed AC-130 gunship is a heavily armed, long-endurance, ground-attack variant of the C-130 Hercules transport, fixed-wing aircraft. It carries a wide array of ground-attack weapons that are integrated with sophisticated sensors, naviga ...
gunships provided support for the landing. Cuban construction vehicles were commandeered to help clear the airfield, and one even used to provide mobile cover for the Rangers as they moved to seize the heights surrounding the airfield.
The Rangers cleared the airstrip of obstructions by 10:00 AM, and transport planes were able to land and unload additional reinforcements, including M151 Jeeps and members of the Caribbean Peace Force assigned to guard the perimeter and detainees. Starting at 14:00, units began landing at Point Salines from the 82nd Airborne Division under Edward Trobaugh, including battalions of the 325th Infantry Regiment
The 325th Airborne Infantry Regiment is a light infantry parachute insertion fighting force of the United States Army. The subordinate units of the regiment constitute the bulk of the infantry elements assigned to the 2nd Infantry Brigade Com ...
. At 15:30, three BTR-60s of the Grenadian Army Motorized Company counter-attacked, but the Americans repelled them with recoilless rifles and an AC-130.
The Rangers fanned out and secured the surrounding area, negotiating the surrender of over 100 Cubans in an aviation hangar. However, a Jeep-mounted Ranger patrol became lost searching for True Blue Campus and was ambushed, with four killed. The Rangers eventually secured True Blue campus and its students, where they found only 140 students and were told that more were at another campus in Grand Anse. In all, the Rangers lost five men on the first day, but succeeded in securing Point Salines and the surrounding area.
Capture of Pearls Airport
A platoon of Navy SEALs fromSEAL Team 4
The United States Navy Sea, Air, and Land (SEAL) Teams, commonly known as Navy SEALs, are the U.S. Navy's primary special operations force and a component of the Naval Special Warfare Command. Among the SEALs' main functions are conducting sm ...
under Lieutenant Mike Walsh approached the beach near Pearls Airport around midnight on 24 October after evading patrol boats and overcoming stormy weather. They found that the beach was lightly defended but unsuitable for an amphibious landing. The 2nd Battalion of the 8th Marine Regiment
The 8th Marine Regiment was an infantry regiment of the United States Marine Corps. When last active, it was based at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune, North Carolina, and fell under the command of the 2nd Marine Division and the II Marine Exped ...
then landed south of Pearls Airport using CH-46 Sea Knight
The Boeing Vertol CH-46 Sea Knight is a medium-lift tandem-rotor transport helicopter powered by twin turboshaft engines. It was designed by Vertol and manufactured by Boeing Vertol following Vertol's acquisition by Boeing.
Development of ...
and CH-53 Sea Stallion
The CH-53 Sea Stallion (Sikorsky S-65) is an American family of heavy-lift transport helicopters designed and built by the American manufacturer Sikorsky Aircraft.
It was originally developed in response to a request from the United States N ...
helicopters at 05:30 on 25 October; they captured Pearls Airport, encountering only light resistance, including a DShK
The DShK 1938 ( Cyrillic: ДШК, for russian: Дегтярёва-Шпагина Крупнокалиберный, Degtyaryova-Shpagina Krupnokaliberny, links=no, "Degtyaryov-Shpagin large-calibre") is a Soviet heavy machine gun with a V-shaped bu ...
machine gun which a Marine AH-1 Cobra
The Bell AH-1 Cobra is a single-engined attack helicopter developed and manufactured by the American rotorcraft manufacturer Bell Helicopter. A member of the prolific Huey family, the AH-1 is also referred to as the HueyCobra or Snake.
The AH ...
destroyed.
Raid on Radio Free Grenada
UH-60 Blackhawk
The Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk is a four-blade, twin-engine, medium-lift utility military helicopter manufactured by Sikorsky Aircraft. Sikorsky submitted the S-70 design for the United States Army's Utility Tactical Transport Aircraft System ( ...
helicopters delivered SEAL Team 6
The Naval Special Warfare Development Group (NSWDG), abbreviated as DEVGRU ("Development Group") and commonly known as SEAL Team Six, is the United States Navy component of the Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC). The unit is often referre ...
operators in the early morning of 25 October to Radio Free Grenada with the purpose of using the radio station for psychological operations
Psychological warfare (PSYWAR), or the basic aspects of modern psychological operations (PsyOp), have been known by many other names or terms, including Military Information Support Operations (MISO), Psy Ops, political warfare, "Hearts and M ...
. They captured the station unopposed and destroyed the radio transmitter. AO2 Robert Wilczynski witnessed the radio station being taken out by the SEALS while using an AM/FM radio and a spool of wire onboard the USS Independence (CV-62) flight deck. However, they were attacked by Grenadian forces in cars and an armored personnel carrier (APC), which forced the lightly armed SEALs to cut open a fence, fight their way to the water and retreat into the ocean while receiving fire from the APC. The SEALs bleeding profusely, one from the calf and one from the shoulder swam toward the open sea for three miles to the USS Guam (LPH-9), and were picked up by a helicopter several hours later after being spotted by a reconnaissance plane. The SEALS were transported from the USS Guam (LPH-9) to the USS Independence (CV-62) for medical treatment. One of two injured SEALS were carried from the USS Independence (CV-62) flight deck to sick bay by AO2 Robert Wilczynski Personal accounts of what took place onboard USS Independence (CV-62) by AO2 Robert Wilczynski.
Raids on Fort Rupert and Richmond Hill Prison
On 25 October,Delta Force
The 1st Special Forces Operational Detachment–Delta (1st SFOD-D), referred to variously as Delta Force, Combat Applications Group (CAG), Army Compartmented Elements (ACE), "The Unit", or within Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC), Task Fo ...
and C Company of the 75th Ranger Regiment embarked in MH-60 and MH-6 Little Bird
The Boeing MH-6M Little Bird (nicknamed the Killer Egg) and its attack variant, the AH-6, are light helicopters used for special operations in the United States Army. Originally based on a modified OH-6A, it was later based on the MD 500E, w ...
helicopters of Task Force 160
The 160th Special Operations Aviation Regiment (Airborne), abbreviated as 160th SOAR (A), is a special operations force of the United States Army that provides helicopter aviation support for special operations forces. Its missions have include ...
to capture Fort Rupert
Fort Rupert is the site of a former Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) fort on the east coast near the northern tip of Vancouver Island, British Columbia. The unincorporated community on Beaver Harbour is about by road southeast of Port Hardy.
Coal & fo ...
, where they believed the Revolutionary Council leaders lived, and Richmond Hill Prison
Richmond Hill Prison is a prison in Saint George's, the capital of Grenada. Known officially as His Majesty's Prison, it is run by the Ministry of National Security. The prison governor is Dr John Mitchell, the Commissioner of Prisons in Grenad ...
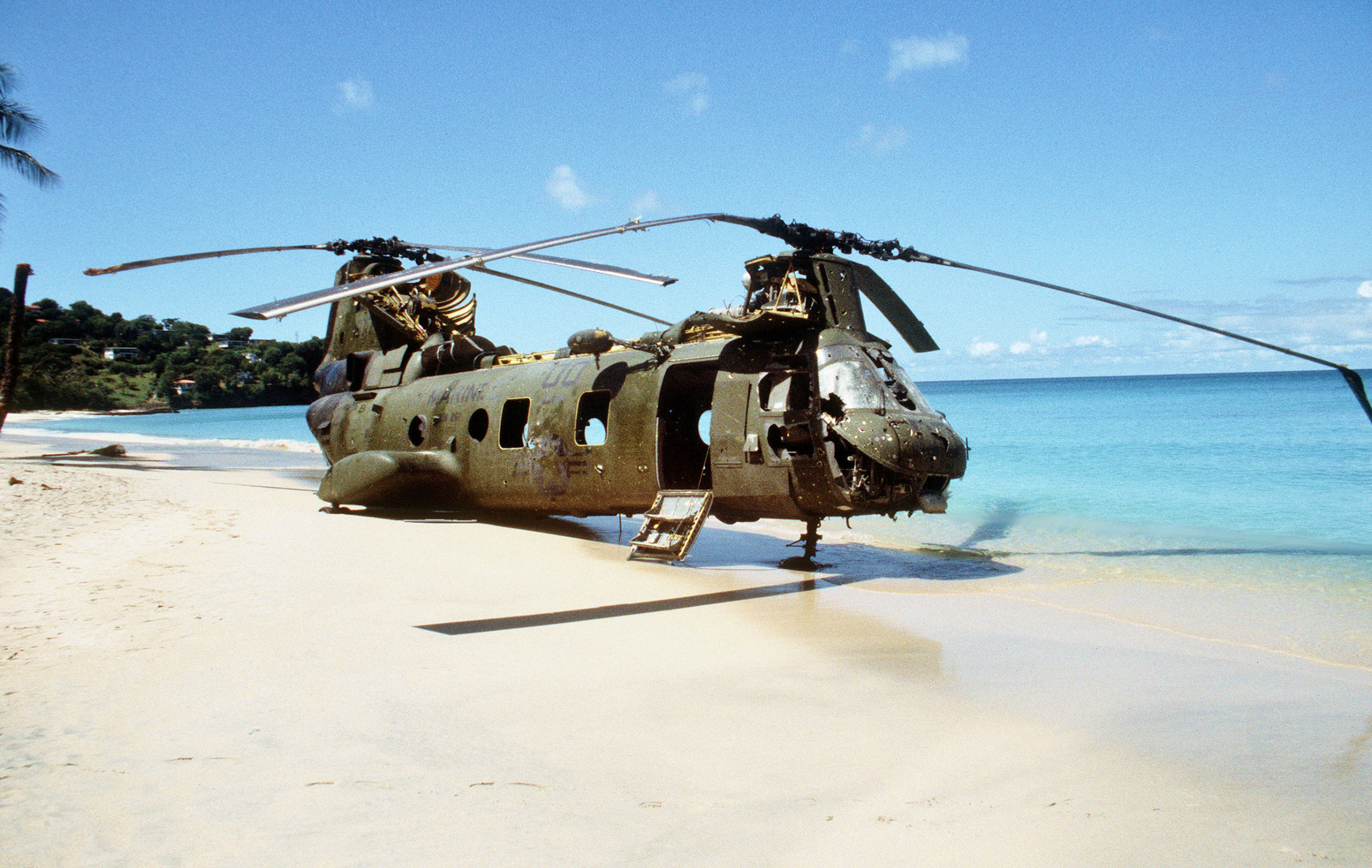
, where political prisoners were being held. The raid on Richmond Hill Prison lacked vital intelligence, leaving the attackers unaware of the presence of several anti-aircraft guns and steep hilly terrain that left no room for helicopter landings. Anti-aircraft fire wounded passengers and crew and forced one MH-60 helicopter to crash land, causing another helicopter to land next to it to protect the survivors. One pilot was killed, and the Delta Force operators had to be relieved by a Navy Sea King helicopter. The raid on Fort Rupert, however, was successful in capturing several leaders of the People's Revolutionary Government.
Mission to rescue Governor-General Scoon
BTR-60
The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers (APCs). It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen in public for the first time in 1961. BTR stands for ''Brone ...
armored personnel carriers counter-attacked and trapped the SEALs and governor inside. AC-130
The Lockheed AC-130 gunship is a heavily armed, long-endurance, ground-attack variant of the C-130 Hercules transport, fixed-wing aircraft. It carries a wide array of ground-attack weapons that are integrated with sophisticated sensors, naviga ...
gunships, A-7 Corsair strike planes, and AH-1 Cobra
The Bell AH-1 Cobra is a single-engined attack helicopter developed and manufactured by the American rotorcraft manufacturer Bell Helicopter. A member of the prolific Huey family, the AH-1 is also referred to as the HueyCobra or Snake.
The AH ...
attack helicopters were called in to support the besieged SEALs, but they remained trapped for the next 24 hours.
At 19:00 on 25 October, 250 Marines from G Company of the 2nd Battalion, 8th Marine Regiment landed at Grand Mal Bay equipped with amphibious assault vehicles and four M60 Patton
The M60 is an American second-generation main battle tank (MBT). It was officially standardized as the Tank, Combat, Full Tracked: 105-mm Gun, M60 in March 1959. Although developed from the M48 Patton, the M60 tank series was never officially ...
tanks; they relieved the Navy SEALs the following morning, allowing Governor Scoon, his wife, and nine aides to be safely evacuated at 10:00 that day. The Marine tank crews continued advancing in the face of sporadic resistance, knocking out a BRDM-2 armored car. G Company subsequently defeated and overwhelmed the Grenadian defenders at Fort Frederick.
Airstrikes
Navy A-7 Corsairs and MarineAH-1 Cobra
The Bell AH-1 Cobra is a single-engined attack helicopter developed and manufactured by the American rotorcraft manufacturer Bell Helicopter. A member of the prolific Huey family, the AH-1 is also referred to as the HueyCobra or Snake.
The AH ...
attack helicopters made airstrikes against Fort Rupert and Fort Frederick. An A-7 raid on Fort Frederick targeting anti-aircraft guns hit a nearby mental hospital, killing 18 civilians. Two Marine AH-1T Cobras and a UH-60 Blackhawk were shot down in a raid against Fort Frederick, resulting in five casualties.
Second day of the invasion
 General Trobaugh of the 82nd Airborne Division had two goals on the second day: securing the perimeter around Salines Airport, and rescuing American students held in Grand Anse. The Army lacked undamaged helicopters after the losses on the first day and consequently had to delay the student rescue until they made contact with Marine forces.
General Trobaugh of the 82nd Airborne Division had two goals on the second day: securing the perimeter around Salines Airport, and rescuing American students held in Grand Anse. The Army lacked undamaged helicopters after the losses on the first day and consequently had to delay the student rescue until they made contact with Marine forces.
Morning ambushes
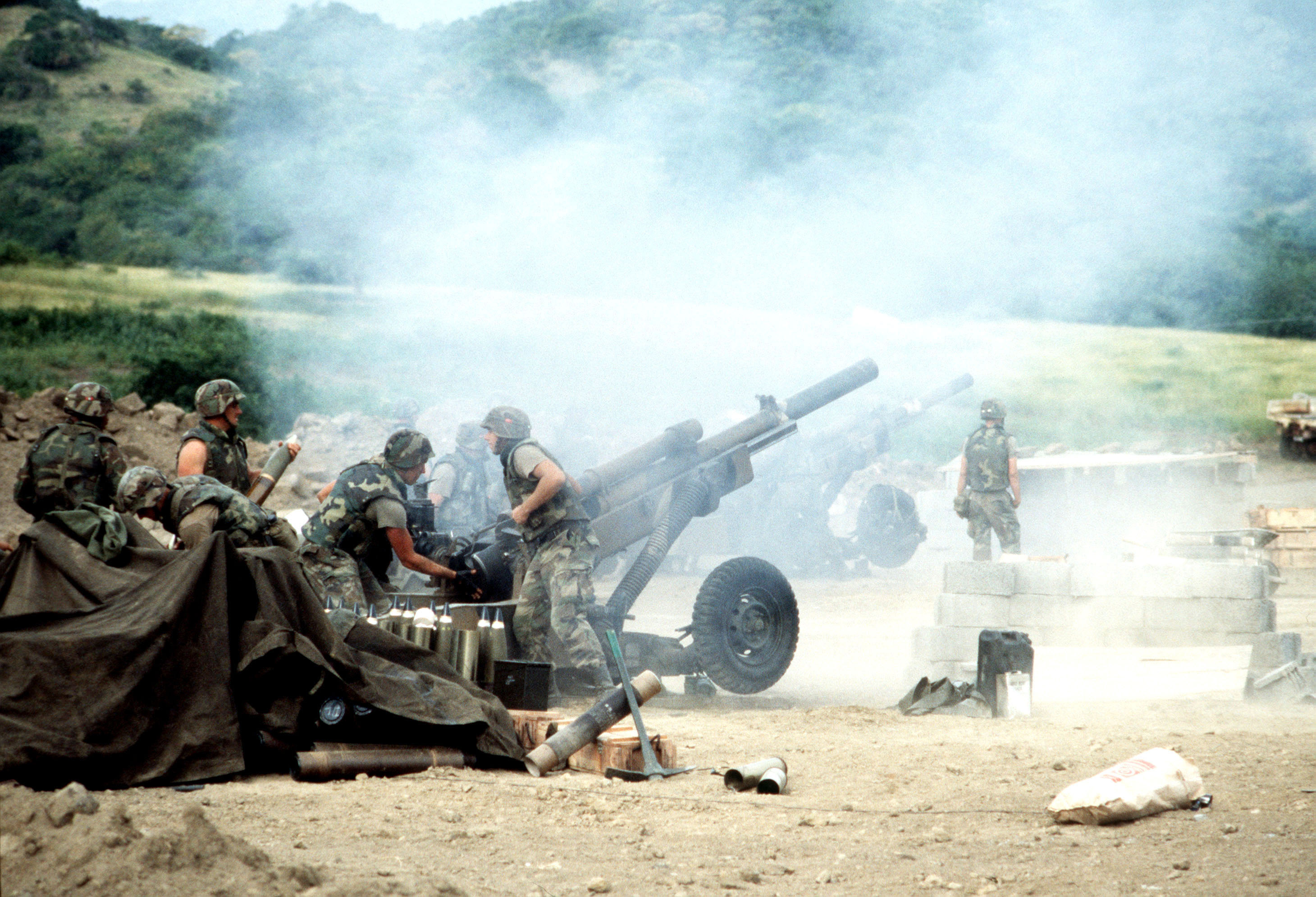
Early on the morning of 26 October, Cuban forces ambushed a patrol from the 2nd Battalion of the 325th Infantry Regiment near the village of Calliste. The American patrol suffered six wounded and two killed, including the commander of Company B. Navy airstrikes and an artillery bombardment by 105mm howitzers targeting the main Cuban encampment eventually led to their surrender at 08:30. American forces pushed on to the village of Frequente, where they discovered a Cuban weapons cache reportedly sufficient to equip six battalions. Cuban forces ambushed a reconnaissance platoon mounted on gun-jeeps, but the jeeps returned fire, and a nearby infantry unit added mortar fire; the Cubans suffered four casualties with no American losses. Cuban resistance largely ended after these engagements.Rescue at Grand Anse
On the afternoon of 26 October, Rangers of the 2nd Battalion of the 75th Ranger Regiment mounted MarineCH-46 Sea Knight
The Boeing Vertol CH-46 Sea Knight is a medium-lift tandem-rotor transport helicopter powered by twin turboshaft engines. It was designed by Vertol and manufactured by Boeing Vertol following Vertol's acquisition by Boeing.
Development of ...
helicopters to launch an air assault on the Grand Anse campus. The campus police offered light resistance before fleeing, wounding one Ranger, and one of the helicopters crashed on approach after its blade hit a palm tree. The Rangers evacuated the 233 American students by CH-53 Sea Stallion
The CH-53 Sea Stallion (Sikorsky S-65) is an American family of heavy-lift transport helicopters designed and built by the American manufacturer Sikorsky Aircraft.
It was originally developed in response to a request from the United States N ...
helicopters, but the students informed them that there was a third campus with Americans at Prickly Bay. A squad of 11 Rangers was accidentally left behind; they departed on a rubber raft which was picked up by at 23:00.
Third day of the invasion and after
BTR-60
The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers (APCs). It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen in public for the first time in 1961. BTR stands for ''Brone ...
during the night, dispatching it with a M72 LAW. The 325th Infantry Regiment advanced toward the capital of Saint George, capturing Grand Anse and discovering 200 American students whom they had missed the first day. They continued to the town of Ruth Howard and Saint George, meeting only scattered resistance. An air-naval gunfire liaison team called in an A-7 airstrike and accidentally hit the command post of the 2nd Brigade, wounding 17 troops, one of whom died.
The Army had reports that PRA forces were amassing at the Calivigny Barracks, only five kilometers from the Point Salines airfield. They organized an air assault by the 2nd Battalion of the 75th Ranger Regiment preceded by a preparatory bombardment by field howitzers (which mostly missed, their shells falling into the ocean), A-7s, AC-130
The Lockheed AC-130 gunship is a heavily armed, long-endurance, ground-attack variant of the C-130 Hercules transport, fixed-wing aircraft. It carries a wide array of ground-attack weapons that are integrated with sophisticated sensors, naviga ...
s, and USS ''Caron''. However, the Blackhawk Black Hawk and Blackhawk may refer to:
Animals
* Black Hawk (horse), a Morgan horse that lived from 1833 to 1856
* Common black hawk, ''Buteogallus anthracinus''
* Cuban black hawk, ''Buteogallus gundlachii''
* Great black hawk, ''Buteogallus uru ...
helicopters began dropping off troops near the barracks but they approached too fast. One of them crash landed and the two behind it collided with it, killing three and wounding four. The barracks were deserted.
In the following days, resistance ended entirely and the Army and Marines spread across the island, arresting PRA officials, seizing caches of weapons, and seeing to the repatriation of Cuban engineers. On 1 November, two companies from the 2/8 Marines made a combined sea and helicopter landing on the island of Carriacou
Carriacou is an island of the Grenadine Islands. It is a dependency of Grenada, and is located in the south-eastern Caribbean Sea, northeast of the island Grenada and the north coast of South America. The name is derived from the Carib lang ...
northeast of Grenada. The 19 Grenadian soldiers defending the island surrendered without a fight. This was the last military action of the campaign.
Outcome
Marine Corps Base Quantico
Marine Corps Base Quantico (commonly abbreviated MCB Quantico) is a United States Marine Corps installation located near Triangle, Virginia, covering nearly of southern Prince William County, Virginia, northern Stafford County, and southeas ...
for inspection.Fortitudine: Newsletter of the Marine Corps Historical Program, Volumes 15–18
'. Tommell, Anthony Wayne. History and Museums Division, U.S. Marine Corps, 1985.
Legality of the invasion
The US government defended its invasion of Grenada as an action to protect American citizens living on the island, including medical students. Deputy Secretary of State Kenneth W. Dam said that action was necessary to "resolve" what Article 28 of the charter of the Organization of American States (O.A.S.) refers to as "a situation that might endanger the peace". He added that the OAS charter and the UN charter both "recognize the competence of regional security bodies in ensuring regional peace and stability," referring to the decision by theOrganisation of Eastern Caribbean States
The Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS; French: ''Organisation des États de la Caraïbe orientale'', OECO) is an inter-governmental organisation dedicated to economic harmonisation and integration, protection of human and legal ri ...
to approve the invasion.
The UN Charter
The Charter of the United Nations (UN) is the foundational treaty of the UN, an intergovernmental organization. It establishes the purposes, governing structure, and overall framework of the UN system, including its six principal organs: th ...
prohibits the use of force by member states except in cases of self-defense or when specifically authorized by the UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the Organs of the United Nations, six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international security, international peace and security, recommending the admi ...
. The UN Security Council had not authorized invasion. Similarly, the United Nations General Assembly adopted General Assembly Resolution 38/7 by a vote of 108 to 9 with 27 abstentions, which "deeply deplores the armed intervention in Grenada, which constitutes a flagrant violation of international law." A similar resolution in the United Nations Security Council received widespread support but was vetoed by the United States.
Reaction in the United States
 ''
''Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, ...
'' magazine described the invasion as having "broad popular support." A congressional study group concluded that the invasion had been justified, as most members felt that American students at the university near a contested runway could have been taken hostage as American diplomats in Iran had been four years previously. The group's report caused House Speaker Tip O'Neill
Thomas Phillip "Tip" O'Neill Jr. (December 9, 1912 – January 5, 1994) was an American politician who served as the 47th speaker of the United States House of Representatives from 1977 to 1987, representing northern Boston, Massachusetts, as ...
to change his position on the issue from opposition to support.
 However, some members of the study group dissented from its findings. Congressman
However, some members of the study group dissented from its findings. Congressman Louis Stokes
Louis Stokes (February 23, 1925 – August 18, 2015) was an American attorney, civil rights pioneer and politician. He served 15 terms in the United States House of Representatives – representing the east side of Cleveland – and was the firs ...
(D, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
) stated: "Not a single American child nor single American national was in any way placed in danger or placed in a hostage situation prior to the invasion." The Congressional Black Caucus
The Congressional Black Caucus (CBC) is a caucus made up of most African-American members of the United States Congress. Representative Karen Bass from California chaired the caucus from 2019 to 2021; she was succeeded by Representative Joyce B ...
denounced the invasion, and seven Democratic congressmen introduced an unsuccessful resolution to impeach President Reagan, led by Ted Weiss.
Medical students in Grenada speaking to Ted Koppel
Edward James Martin Koppel (born February 8, 1940) is a British-born American broadcast journalist, best known as the anchor for ''Nightline'', from the program's inception in 1980 until 2005.
Before ''Nightline'', he spent 20 years as a broadc ...
on 25 October 1983 edition of his newscast '' Nightline'' stated that they were safe and did not feel that their lives were in danger. Medical students told Koppel the next evening how grateful they were for the invasion and the Army Rangers, which probably saved their lives. State Department officials had assured the medical students that they would be able to complete their medical school education in the United States.
An anti-war march attended by over 50,000 people, including Burlington, Vermont Mayor Bernie Sanders, was held in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
The march received support from presidential candidate Jesse Jackson.
International reaction
The United Nations General Assembly adopted General Assembly Resolution 38/7 on 2 November 1983 by a vote of 108 to 9 which "deeply deplores the armed intervention in Grenada, which constitutes a flagrant violation of international law and of the independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity of that State." It went on to deplore "the death of innocent civilians" and the "killing of the Prime Minister and other prominent Grenadians", and it called for an "immediate cessation of the armed intervention" and demanded, "that free elections be organized". This was the first overthrow of a Communist government by armed means since the end ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. The Soviet Union said that Grenada had been the object of United States threats, that the invasion violated international law, and that no small nation would find itself safe if the aggression were not rebuffed. The governments of some countries stated that the United States intervention was a return to the era of barbarism. The governments of other countries said the United States had violated several treaties and conventions to which it was a party. A similar resolution was discussed in the United Nations Security Council but it was ultimately vetoed by the United States.
President Ronald Reagan was asked if he was concerned by the lopsided 108–9 vote in the UN General Assembly. He said, "it didn't upset my breakfast at all."
Grenada is part of the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the ...
and the intervention was opposed by Commonwealth members including the United Kingdom, Trinidad and Tobago, and Canada. British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher, a close ally of Reagan on other matters, personally opposed it. Reagan told her that it might happen; she did not know for sure that it was coming until three hours before. At 12:30 on the morning of the invasion, Thatcher sent a message to Reagan:
Reagan told Thatcher before anyone else that the invasion would begin in a few hours, but ignored her complaints. She publicly supported the action. Reagan phoned to apologize for the miscommunication, and the long-term friendly relationship endured.
Aftermath and legacy
 The American and Caribbean governments quickly reaffirmed Scoon as Queen Elizabeth's sole legitimate representative in Grenada, and hence was thus the only lawful authority on the island. In accordance with Commonwealth constitutional practice, Scoon assumed power as interim head of government and formed an advisory council which named
The American and Caribbean governments quickly reaffirmed Scoon as Queen Elizabeth's sole legitimate representative in Grenada, and hence was thus the only lawful authority on the island. In accordance with Commonwealth constitutional practice, Scoon assumed power as interim head of government and formed an advisory council which named Nicholas Brathwaite
Sir Nicholas Alexander Brathwaite OBE (8 July 1925 – 28 October 2016) was the head of government of Grenada for two periods, first as Chairman of the Interim Advisory Council (1983 to 1984) established after the United States invasion of Grena ...
as chairman pending new elections. The New National Party won the elections in December 1984 and formed a government led by Prime Minister Herbert Blaize.
 American forces remained in Grenada after combat operations finished in December as part of Operation Island Breeze. Elements remaining performed security missions and assisted members of the Caribbean Peacekeeping Force and the Royal Grenadian Police Force, including military police, special forces, and a specialized intelligence detachment. The Point Salines International Airport was renamed in honor of Prime Minister Maurice Bishop on 29 May 2009, his 65th birthday. Hundreds of Grenadians turned out to commemorate the honoring of the event. Prime Minister gave the keynote speech and referred to the renaming as an act of the Grenadian people coming home to themselves. He also hoped that it would help bring closure to a chapter of denial in Grenada's history.
American forces remained in Grenada after combat operations finished in December as part of Operation Island Breeze. Elements remaining performed security missions and assisted members of the Caribbean Peacekeeping Force and the Royal Grenadian Police Force, including military police, special forces, and a specialized intelligence detachment. The Point Salines International Airport was renamed in honor of Prime Minister Maurice Bishop on 29 May 2009, his 65th birthday. Hundreds of Grenadians turned out to commemorate the honoring of the event. Prime Minister gave the keynote speech and referred to the renaming as an act of the Grenadian people coming home to themselves. He also hoped that it would help bring closure to a chapter of denial in Grenada's history.
United States
The invasion showed problems with the American "information apparatus," which ''Time'' magazine described as still being in "some disarray" three weeks after the invasion. For example, the State Department falsely claimed that a mass grave had been discovered which held 100 bodies of islanders who had been killed by communist forces. Major GeneralNorman Schwarzkopf
Herbert Norman Schwarzkopf Jr. (; August 22, 1934 – December 27, 2012) was a United States Army general. While serving as the commander of United States Central Command, he led all coalition forces in the Gulf War.
Born in Trenton, N ...
, deputy commander of the invasion force, said that 160 Grenadian soldiers and 71 Cubans had been killed during the invasion; the Pentagon had given a count of 59 Cuban and Grenadian deaths. Ronald H. Cole's report for the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is the body of the most senior uniformed leaders within the United States Department of Defense, that advises the president of the United States, the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council and the ...
showed an even lower count.
Also of concern were the problems that the invasion showed with the military. There was a lack of intelligence about Grenada which exacerbated the difficulties faced by the quickly assembled invasion force. For example, they did not know that the students were actually at two different campuses, and there was a 30-hour delay in reaching students at the second campus. Maps provided to soldiers on the ground were tourist maps on which military grid reference lines were drawn by hand to report locations of units and request artillery and aircraft fire support. They also did not show topography and were not marked with crucial positions. Navy ships providing naval gunfire and Marine, Air Force, and Navy fighter-bomber support aircraft providing close air support mistakenly killed American ground forces due to differences in charts and location coordinates, data, and methods of calling for fire support. Communications between services were also not compatible and hindered the coordination of operations. The landing strip was drawn by hand on the map given to some members of the invasion force.
Reagan attempted to use the invasion of Grenada to end Vietnam Syndrome
Vietnam Syndrome is a term in U.S. politics that refers to public aversion to American overseas military involvements after the domestic controversy over the Vietnam War. In 1973, the U.S. ended combat operations in Vietnam. Since the early 198 ...
, a term used in reference to the American public's aversion to overseas conflicts that resulted from the Vietnam War. After the invasion, on 13 December 1983, Reagan asserted that "our days of weakness are over. Our military forces are back on their feet and standing tall."
Goldwater–Nichols Act
 The
The Department of Defense Department of Defence or Department of Defense may refer to:
Current departments of defence
* Department of Defence (Australia)
* Department of National Defence (Canada)
* Department of Defence (Ireland)
* Department of National Defense (Philipp ...
recognized a need for improved communications and coordination among the branches of the American military. Congress investigated many of the problems and passed the Goldwater-Nichols Act of 1986 (Pub. L.99–433). This act reworked the command structure of the military, making the most sweeping changes to the Department of Defense since the department was established in the National Security Act of 1947. It increased the power of the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff and advanced the concept of unified joint forces organized under one command.
Other
 25 October is a national holiday in Grenada, called Thanksgiving Day, to commemorate the invasion. St. George's University (SGU) built a monument on its True Blue campus to honor the American servicemen killed during the invasion, and marks the day with an annual memorial ceremony.
On 29 May 2009, the Grenadian government changed the name of Point Salines International Airport to
25 October is a national holiday in Grenada, called Thanksgiving Day, to commemorate the invasion. St. George's University (SGU) built a monument on its True Blue campus to honor the American servicemen killed during the invasion, and marks the day with an annual memorial ceremony.
On 29 May 2009, the Grenadian government changed the name of Point Salines International Airport to Maurice Bishop International Airport
Maurice Bishop International Airport , formerly known as Point Salines Airport, is an international airport located in the parish of St. George's. The town of St. George's is about north of the airport and is the capital of the island natio ...
.
Order of battle
Ground forces

 * 1st and 2nd Ranger Battalions 75th Ranger Regiment conducted a low-level parachute assault to secure Point Salines Airport. Hunter Army Airfield, GA and Ft. Lewis, WA
* 82nd Airborne Division – 2nd Brigade Task Force ( 325th Airborne Infantry Regiment 2nd & 3rd Battalions plus supporting units) and 3rd Brigade Task Force (1st and 2nd Battalions of the
* 1st and 2nd Ranger Battalions 75th Ranger Regiment conducted a low-level parachute assault to secure Point Salines Airport. Hunter Army Airfield, GA and Ft. Lewis, WA
* 82nd Airborne Division – 2nd Brigade Task Force ( 325th Airborne Infantry Regiment 2nd & 3rd Battalions plus supporting units) and 3rd Brigade Task Force (1st and 2nd Battalions of the 505th Parachute Infantry Regiment
The 505th Parachute Infantry Regiment (505th PIR), originally the 505th Infantry Regiment, is an airborne infantry regiment of the United States Army, one of four infantry regiments of the 82nd Airborne Division of the United States Army, with ...
, 1st and 2nd Battalions of the 508th Parachute Infantry Regiment, plus supporting units), A Company, 2nd Battalion 504th Parachute Infantry Regiment, 82nd MP General Support Platoon HHC, 313th MI BN (CEWI). Fort Bragg, NC, 1st Battalion of the 319th Field Artillery. 1st Battalion of the 320th Field Artillery.
* 27th Engineer Battalion
The 27th Engineer Battalion (COMBAT)(AIRBORNE) "Tiger Battalion" and its subordinate companies have often used the Fort Bragg/XVIII Airborne Corps standard of "Airborne!" for its motto.
History
The history of the 27th Engineer Battalion (Combat) ...
of the 20th Engineer Brigade (Airborne), Fort Bragg, NC
* 548th Engineer Battalion Ft Bragg, NC
* 160th Aviation Battalion
The 160th Special Operations Aviation Regiment (Airborne), abbreviated as 160th SOAR (A), is a special operations force of the United States Army that provides helicopter aviation support for special operations forces. Its missions have include ...
Ft Campbell, KY
* 18th Aviation Company, 269th Aviation Battalion Ft. Bragg, NC
* 1st and 2nd 82nd Combat Aviation Battalion
The 82d Aviation Regiment, part of the U.S. Army, has three battalions and one separate company under the Combat Aviation Brigade, 82d Airborne Division. The brigade also has the 1st Squadron, 17th Cavalry Regiment and the 122d Aviation Support B ...
, Fort Bragg N.C.
* 1 SQN 17 Air Cavalry Airborne, Fort Bragg N.C.
* 65th MP Company (Airborne), 118th MP Company (Airborne), and HHD, 503rd MP Battalion (Airborne) of the 16th Military Police Brigade (Airborne), XVIII Airborne Corps, Fort Bragg, NC
* 411th MP Company of the 89th Military Police Brigade, III Corps, Ft. Hood, Texas
* 35th Signal Brigade, Ft. Bragg, NC
* 50th Signal Battalion, 35th Signal Brigade, Ft. Bragg, NC
* 203rd Military Intelligence Battalion, Aberdeen Proving Ground, MD
Aberdeen Proving Ground (APG) (sometimes erroneously called Aberdeen Proving ''Grounds'') is a U.S. Army facility located adjacent to Aberdeen, Harford County, Maryland, United States. More than 7,500 civilians and 5,000 military personnel work at ...
* 319th Military Intelligence Battalion and 519th Military Intelligence Battalion, 525th Military Intelligence Brigade, Fort Bragg, NC
* 9th Psychological Operations Battalion (Airborne) of the 4th Psychological Operations Group
The 4th Psychological Operations Group (Airborne) (or 4th POG)(A) is one of the United States Army's active military information support operations units along with the 8th Psychological Operations Group (Airborne), which was activated 26 Augu ...
(Airborne) – provided loudspeaker support and dissemination of informational pamphlets. Fort Bragg, NC
* 1st Corps Support Command COSCOM, 7th Trans Battalion, 546th LMT Fort Bragg, NC
* 44th Medical Brigade – Personnel from the 44th Medical Brigade and operational units including the 5th MASH were deployed. Fort Bragg, NC
* 82nd Finance Company MPT
* 22nd Marine Amphibious Unit Camp Lejeune, NC
* US Navy SEAL Team 4 Little Creek, VA and US Navy SEAL Team 6 Virginia Beach, VA
* Air Force Detachment 1, 507th Tactical Air Control Wing (Fort Bragg, NC) – jump qualified TACPs who were attached to and deployed with the 82d Airborne, Fort Bragg, NC (now the 14th ASOS, part of the 18th Air Support Operations Group)
* 21st Tactical Air Support Squadron
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and reco ...
(Shaw AFB, SC). Jump qualified FACs who were attached to and deployed with Detachment 1, 507th Tactical Air Control Wing and the 82d Airborne, Fort Bragg, NC
* 5th Weather Squadron, 5th Weather Wing (MAC) Fort Bragg, NC. Jump qualified combat weathermen who are attached and deployed with the 82nd, now in AFSOC
Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC), headquartered at Hurlburt Field, Florida, is the special operations component of the United States Air Force. An Air Force major command (MAJCOM), AFSOC is also the U.S. Air Force component command ...
* Det 1 MACOS Combat Controllers
* 1st Special Forces Operational Detachment–Delta
Air Force
* 136th Tactical Airlift Wing,Texas Air National Guard
The Texas Air National Guard (TX ANG) is the aerial militia of the State of Texas, United States of America. It is, along with the Texas Army National Guard, an element of the Texas National Guard. No element of the Texas Air National Guard is ...
– provided C-130 Hercules combat airlift support, cargo, and supplies
* Various Air National Guard tactical fighter wings and squadrons – provided A-7D Corsair II
The LTV A-7 Corsair II is an American carrier-capable subsonic light attack aircraft designed and manufactured by Ling-Temco-Vought (LTV).
The A-7 was developed during the early 1960s as replacement for the Douglas A-4 Skyhawk. Its design was ...
ground-attack aircraft for close air support
* 23rd Tactical Fighter Wing
The 23rd Wing is a front-line United States Air Force Air Combat Command wing currently assigned to Moody Air Force Base, Georgia.
Mission
The mission of the 23rd Wing is to organize, train and employ combat-ready Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunder ...
– provided close air support for allied forces with A-10 Warthog
The Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II is a single-seat, twin-turbofan, straight-wing, subsonic attack aircraft developed by Fairchild Republic for the United States Air Force (USAF). In service since 1976, it is named for the Republic ...
s
* 26th Air Defense Squadron NORAD – provided air support for allied forces with F-15 Eagles
* 33rd Tactical Fighter Wing – provided air superiority cover for allied forces with F-15 Eagles
* 437th Military Airlift Wing
The 437th Airlift Wing (437 AW) is an active unit of the United States Air Force, assigned to 18th Air Force, Air Mobility Command. It is the mission wing at Charleston Air Force Base, Joint Base Charleston, in the City of North Charleston, Sou ...
– provided airlift support with C-141 Starlifter
The Lockheed C-141 Starlifter is a retired military strategic airlifter that served with the Military Air Transport Service (MATS), its successor organization the Military Airlift Command (MAC), and finally the Air Mobility Command (AMC) of the ...
s
* 1st Special Operations Wing
The 1st Special Operations Wing (1 SOW) at Hurlburt Field, Florida is one of three United States Air Force active duty Special Operations wings and falls under the Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC).
The 1st Special Operations Wing is ...
– flew AC-130H Spectre gunships and MC-130E Combat Talons
* 317th Military Airlift Wing – provided airlift support with C-130 Hercules from Pope AFB
Pope Field is a U.S. military facility located 12 miles (19 km) northwest of the central business district of Fayetteville, in Cumberland County, North Carolina, United States.. Federal Aviation Administration. effective 15 November 2012 ...
/ Fort Bragg, NC complex to Grenada
* 63d Military Airlift Wing – Provided airlift support with C-141 Starlifter
The Lockheed C-141 Starlifter is a retired military strategic airlifter that served with the Military Air Transport Service (MATS), its successor organization the Military Airlift Command (MAC), and finally the Air Mobility Command (AMC) of the ...
aircraft in the air landing of Airborne troops, 63rd Security Police Squadron provided airfield security support – (Norton AFB CA)
* 443rd Military Airlift Wing, 443rd Security Police Squadron (Altus AFB
Altus Air Force Base (Altus AFB, AAFB) is a United States Air Force base located approximately east-northeast of Altus, Oklahoma.
The host unit at Altus AFB is the 97th Air Mobility Wing (97 AMW), assigned to the Nineteenth Air Force (19 A ...
, OK) – provided a 44-man Airbase Ground Defense flight (Oct–Nov 1983)
* 19th Air Refueling Wing – provided aerial refueling support for all other aircraft
* 507th Tactical Air Control Wing (elements of the 21st TASS at Shaw AFB, SC and Detachment 1, Fort Bragg, NC) – provided Tactical Air Control Parties ( TACPs) in support of the 82nd Airborne Division
* 552nd Air Control Wing
The 552d Air Control Wing is an operational wing of the United States Air Force. It has been based at Tinker Air Force Base, Oklahoma since July 1976, operating the Boeing E-3 Sentry. It includes the
552d Operations Group, 552d Maintenance Gr ...
, providing air control support with E-3 Sentry AWACS aircraft
* 62nd Security Police Group (Provisional) Multi Squadron Law Enforcement & Security Forces – Prisoner detaining and transport attached to 82nd Airborne
* 60th Military Airlift Wing
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number.
In mathematics
Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second smalles ...
's 60th Security Police Squadron (Travis AFB, CA) provided airfield security in Grenada as well as Barbados. 602nd OMS provided aircraft recovery teams for cargo operations.
Navy
Two formations of U.S. warships took part in the invasion. carrier battle group; and Marine Amphibious Readiness Group, flagship , , , , and . Carrier Group Four was allocated the designation Task Group 20.5 for the operation. In addition, the following ships supported naval operations: , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and .Coast Guard
* *Law Enforcement Detachments
Law Enforcement Detachments or LEDETs are specialized, deployable maritime law enforcement teams of the United States Coast Guard. First established in 1982, their primary mission is to deploy aboard U.S. and allied naval vessels to conduct and ...
* HC-130 aircraft
See also
*United States involvement in regime change
Since the 19th century, the United States government has participated and interfered, both overtly and covertly, in the replacement of several foreign governments. In the latter half of the 19th century, the U.S. government initiated actions for ...
* Foreign interventions by the United States
The United States has been involved in numerous foreign interventions throughout its history. By the broadest definition of military intervention, the US has engaged in nearly 400 military interventions between 1776 and 2019, with half of these ...
* Heartbreak Ridge
''Heartbreak Ridge'' is a 1986 American war film produced and directed by Clint Eastwood, who also starred in the film. The film also co-stars Marsha Mason, Everett McGill, and Mario Van Peebles, and was released in the United States on Decembe ...
- a 1986 Clint Eastwood movie which includes the invasion.
Notes
Primary sources
Grenada Documents, an Overview & Selection
DOD & State Dept, Sept 1984, 813 pages.
Grenada, A Preliminary Report
DOD & State
Joint Overview, Operation Urgent Fury
1 May 1985, 87 pages
Further reading
* * * Official Pentagon study. * * Moore, Charles. ''Margaret Thatcher: At her Zenith in London, Washington and Moscow'' (2016) pp. 117–135. * Payne, Anthony. "The Grenada crisis in British politics." ''The Round Table'' 73.292 (1984): 403–410online
* , A military history. * Williams, Gary. ''US–Grenada Relations: Revolution and Intervention in the Backyard'' (Macmillan, 2007).
External links
Invasion of Grenada and Its Political Repercussions
from th
Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
��
Naval History & Heritage Command
The Naval History and Heritage Command, formerly the Naval Historical Center, is an Echelon II command responsible for the preservation, analysis, and dissemination of U.S. naval history and heritage located at the historic Washington Navy Yard. ...
, U.S. Navy
Grenadian Revolution Archive
at marxists.org
The dream of a Black utopia
podcast from
The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large nati ...
. Includes interview with Dessima Williams, Grenada's former ambassador to the U.S.
''Grenada''
— a 1984 comic book about the invasion written by the CIA. {{Authority control 1983 in Grenada 1983 in the United States Airborne operations Cold War conflicts Communism in Grenada Conflicts in 1983 Cuba–United States relations Grenada–United States military relations Invasions by the United States Invasions of Grenada Military expeditions of the United States Operations involving American special forces Reagan administration controversies United States Army Rangers United States Marine Corps in the 20th century United States–Caribbean relations Grenada Grenada Grenada Grenada Grenada Grenada Grenada Grenada Invasions Proxy wars October 1983 events in North America November 1983 events in North America December 1983 events in North America United States involvement in regime change