The 1918–1920 influenza pandemic, commonly known by the
misnomer
A misnomer is a name that is incorrectly or unsuitably applied. Misnomers often arise because something was named long before its correct nature was known, or because an earlier form of something has been replaced by a later form to which the name ...
Spanish flu or as the Great Influenza epidemic, was an exceptionally deadly global
influenza pandemic
An influenza pandemic is an epidemic of an influenza virus that spreads across a large region (either multiple continents or worldwide) and infects a large proportion of the population. There have been six major influenza epidemics in the last ...
caused by the
H1N1 influenza A virus. The earliest documented case was March 1918 in
Kansas
Kansas () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its Capital city, capital is Topeka, Kansas, Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita, Kansas, Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebras ...
, United States, with further cases recorded in France, Germany and the United Kingdom in April. Two years later, nearly a third of the global population, or an estimated 500 million people, had been infected in four successive waves. Estimates of deaths range from 17 million to 50 million, and possibly as high as 100 million, making it
one of the deadliest pandemics in history.
The pandemic broke out near the end of
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, when wartime
censors
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governments ...
suppressed bad news in the
belligerent
A belligerent is an individual, group, country, or other entity that acts in a hostile manner, such as engaging in combat. The term comes from the Latin ''bellum gerere'' ("to wage war"). Unlike the use of ''belligerent'' as an adjective meaning ...
countries to maintain
morale
Morale, also known as esprit de corps (), is the capacity of a group's members to maintain belief in an institution or goal, particularly in the face of opposition or hardship. Morale is often referenced by authority figures as a generic value ...
, but newspapers
freely reported the outbreak in
neutral Spain, creating a false impression of Spain as the epicenter and leading to the "Spanish flu" misnomer.
[ Limited historical ]epidemiological
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evid ...
data make the pandemic's geographic origin indeterminate, with competing hypotheses on the initial spread.
Most influenza outbreaks disproportionately kill the young and old, with a higher survival rate in-between, but this pandemic had unusually high mortality for young adults. Scientists offer several explanations for the high mortality, including a six-year climate anomaly affecting migration of disease vectors with increased likelihood of spread through bodies of water.cytokine storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a physiological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Norma ...
, ravaging the stronger immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
of young adults, although the viral infection
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.
Structural Characteristics
Basic structural characteristics, ...
was apparently no more aggressive than previous influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptom ...
strains. Malnourishment
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
, overcrowded medical camps and hospitals, and poor hygiene
Hygiene is a series of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
, exacerbated by the war, promoted bacterial superinfection
A superinfection is a second infection superimposed on an earlier one, especially by a different microbial agent of exogenous or endogenous origin, that is resistant to the treatment being used against the first infection. Examples of this in bact ...
, killing most of the victims after a typically prolonged death bed.2009 swine flu pandemic
The 2009 swine flu pandemic, caused by the H1N1 influenza virus and declared by the World Health Organization (WHO) from June 2009 to August 2010, is the third recent flu pandemic involving the H1N1 virus (the first being the 1918–1920 Sp ...
.1977 Russian flu
The 1977 Russian flu was an influenza pandemic that was first reported by the Soviet Union in 1977 and lasted until 1979. The outbreak in northern China started in May 1977, slightly earlier than that in the Soviet Union. The pandemic mostly affec ...
was also caused by H1N1 virus.
Etymologies
 This pandemic was known by many different names—some old, some new—depending on place, time, and context. The
This pandemic was known by many different names—some old, some new—depending on place, time, and context. The etymology
Etymology () The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words ...
of alternative names historicises the scourge and its effects on people who would only learn years later
Later may refer to:
* Future, the time after the present
Television
* ''Later'' (talk show), a 1988–2001 American talk show
* '' Later... with Jools Holland'', a British music programme since 1992
* ''The Life and Times of Eddie Roberts'', or ...
that invisible virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
es caused influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptom ...
. This lack of scientific answers led the ''Sierra Leone Weekly News'' (Freetown
Freetown is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educ ...
) to suggest a biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of ...
framing in July 1918, using an interrogative
An interrogative clause is a clause whose form is typically associated with question-like meanings. For instance, the English sentence "Is Hannah sick?" has interrogative syntax which distinguishes it from its declarative counterpart "Hannah is ...
from Exodus 16 in ancient Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
: "One thing is for certain—the doctors are at present flabbergasted; and we suggest that rather than calling the disease influenza they should for the present until they have it in hand, say —'What is it?'"
Descriptive names
Outbreaks of influenza-like illness
Influenza-like illness (ILI), also known as flu-like syndrome or flu-like symptoms, is a medical diagnosis of possible influenza or other illness causing a set of common symptoms. These include fever, shivering, chills, malaise, dry cough, loss ...
were documented in 1916–17 at British military hospitals in Étaples, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, and just across the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Ka ...
at Aldershot
Aldershot () is a town in Hampshire, England. It lies on heathland in the extreme northeast corner of the county, southwest of London. The area is administered by Rushmoor Borough Council. The town has a population of 37,131, while the Alder ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
. Clinical indications in common with the 1918 pandemic included rapid symptom progression to a "dusky" heliotrope cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of body tissue color to a bluish-purple hue as a result of having decreased amounts of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Body tissues that show cyanosis are usually in locations ...
of the face. This characteristic blue-violet cyanosis in expiring patients led to the name 'purple death'.
The Aldershot physicians later wrote in ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823.
The journal publishes original research articles ...
'', "the influenza pneumococcal purulent bronchitis we and others described in 1916 and 1917 is fundamentally the same condition as the influenza of this present pandemic."Purulent
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collect ...
bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
' is not yet linked to the same A/H1N1
In virology, influenza A virus subtype H1N1 (A/H1N1) is a subtype of influenza A virus. Major outbreaks of H1N1 strains in humans include the Spanish flu, the 1977 Russian flu pandemic and the 2009 swine flu pandemic. It is an orthomyxovirus ...
virus,[ but it may be a precursor.][
In 1918, ']epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptom ...
' ( it, influenza, influence),Kansas
Kansas () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its Capital city, capital is Topeka, Kansas, Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita, Kansas, Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebras ...
in the U.S. during late spring, and early reports from Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
began appearing on 21 May. Reports from both places called it 'three-day fever' ().
Associative names
 Many alternative names are
Many alternative names are exonyms
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
in the practice of making new infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
seem foreign.1889–1890 pandemic
The 1889–1890 pandemic, often referred to as the "Asiatic flu" or "Russian flu", was a worldwide respiratory viral pandemic. It was the last great pandemic of the 19th century, and is among the deadliest pandemics in history. The pandemic ...
, also known as the 'Russian flu', when the Russians already called epidemic influenza the 'Chinese catarrh', the Germans called it the 'Russian pest', while the Italians in turn called it the 'German disease'. These epithet
An epithet (, ), also byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) known for accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It has various shades of meaning when applied to seemingly real or fictitious people, di ...
s were re-used in the 1918 pandemic, along with new ones.[
]
'Spanish' influenza
 Outside Spain, the disease was soon misnamed 'Spanish influenza'. In a 2 June 1918 ''
Outside Spain, the disease was soon misnamed 'Spanish influenza'. In a 2 June 1918 ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' ( ...
'' of London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
dispatch titled, "The Spanish Epidemic," a correspondent in Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
reported over 100,000 victims of, "The unknown disease…clearly of a gripal character," without referring to "Spanish influenza" directly. Three weeks later ''The Times'' reported that, "Everybody thinks of it as the 'Spanish' influenza to-day." Three days after that an advertisement appeared in ''The Times'' for Formamint tablets to prevent "Spanish influenza". When it reached Moscow, ''Pravda
''Pravda'' ( rus, Правда, p=ˈpravdə, a=Ru-правда.ogg, "Truth") is a Russian broadsheet newspaper, and was the official newspaper of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, when it was one of the most influential papers in the ...
'' announced, " (the Spanish lady) is in town," making 'the Spanish lady' another common name.
The outbreak did not originate in Spain (see below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
*Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
*Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
*Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
*Fred Below ( ...
),censorship
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governments ...
in belligerent
A belligerent is an individual, group, country, or other entity that acts in a hostile manner, such as engaging in combat. The term comes from the Latin ''bellum gerere'' ("to wage war"). Unlike the use of ''belligerent'' as an adjective meaning ...
nations. Spain was a neutral country
A neutral country is a state that is neutral towards belligerents in a specific war or holds itself as permanently neutral in all future conflicts (including avoiding entering into military alliances such as NATO, CSTO or the SCO). As a type ...
unconcerned with appearances of combat readiness
readiness is a condition of the armed forces and their constituent units and formations, warships, aircraft, weapon systems or other military technology and equipment to perform during combat military operations, or functions consistent with th ...
, and without a wartime propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
machine to prop up morale
Morale, also known as esprit de corps (), is the capacity of a group's members to maintain belief in an institution or goal, particularly in the face of opposition or hardship. Morale is often referenced by authority figures as a generic value ...
; so its newspapers freely reported epidemic effects, including King Alfonso XIII
Alfonso XIII (17 May 1886 – 28 February 1941), also known as El Africano or the African, was King of Spain from 17 May 1886 to 14 April 1931, when the Second Spanish Republic was proclaimed. He was a monarch from birth as his father, Alf ...
's illness, making Spain the apparent locus of the epidemic. The censorship was so effective that Spain's health officials were unaware its neighboring countries were similarly affected.Journal of the American Medical Association
''The Journal of the American Medical Association'' (''JAMA'') is a peer-reviewed medical journal published 48 times a year by the American Medical Association. It publishes original research, reviews, and editorials covering all aspects of b ...
'', a Spanish official protested, "we were surprised to learn that the disease was making ravages in other countries, and that people there were calling it the 'Spanish grip'. And wherefore Spanish? …this epidemic was not born in Spain, and this should be recorded as a historic vindication." But before this letter could be published, ''The Serbian Newspaper'' (Corfu
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The isl ...
) said, "Various countries have been assigning the origin of this imposing guest to each other for quite some time, and at one point in time they agreed to assign its origin to the kind and neutral Spain…"
Other exonyms
French press initially used 'American flu', but adopted 'Spanish flu' in lieu of antagonizing an ally.battlefield
A battlefield, battleground, or field of battle is the location of a present or historic battle involving ground warfare. It is commonly understood to be limited to the point of contact between opposing forces, though battles may involve troops ...
in Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
where many soldiers on both sides fell ill.Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 ...
it was named 'Brazilian flu', and in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, 'German flu'. In Spain it was also known as the 'French flu' (),zarzuela
() is a Spanish lyric-dramatic genre that alternates between spoken and sung scenes, the latter incorporating operatic and popular songs, as well as dance. The etymology of the name is uncertain, but some propose it may derive from the name of ...
.[ Spanish flu () is now a common name in Spain, but remains controversial there.]Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
disease',[ Some Africans called it a 'white man's sickness', but in ]South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, white men also used the ethnophaulism (lit. negro
In the English language, ''negro'' is a term historically used to denote persons considered to be of Black African heritage. The word ''negro'' means the color black in both Spanish and in Portuguese, where English took it from. The term can be ...
disease).[ Japan blamed ]sumo
is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a '' rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring ('' dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by t ...
wrestlers for bringing the disease home from a match in Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
by calling it 'sumo flu' (), even though three top wrestlers died there.
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
'best practices' first published in 2015 now aim to prevent social stigma
Social stigma is the disapproval of, or discrimination against, an individual or group based on perceived characteristics that serve to distinguish them from other members of a society. Social stigmas are commonly related to culture, gender, ra ...
by no longer associating culturally significant names with new diseases, listing "Spanish flu" under "examples to be avoided".[ Many authors now eschew calling this the Spanish flu,][ instead using variations of '1918–19/20 flu/influenza pandemic'.
]
Local names
Some language endonyms
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, o ...
did not name specific regions or groups of people. Examples specific to this pandemic include: nd, 'Malibuzwe' (let enquiries be made concerning it), sw, 'Ugonjo huo kichwa na kukohoa na kiuno' (the disease of head and coughing and spine),
Other names
This outbreak was also commonly known as the 'great influenza epidemic', after the 'great war', a common name for World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
before World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. French military doctors originally called it 'disease 11' ().children's song
A children's song may be a nursery rhyme set to music, a song that children invent and share among themselves or a modern creation intended for entertainment, use in the home or education. Although children's songs have been recorded and studied ...
from the 1889–90 flu pandemic was shortened and adapted into a skipping-rope rhyme
A skipping rhyme (occasionally skipping-rope rhyme or jump-rope rhyme), is a rhyme chanted by children while skipping. Such rhymes have been recorded in all cultures where skipping is played. Examples of English-language rhymes have been found g ...
popular in 1918. It is a metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide (or obscure) clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are often compared wi ...
for the transmissibility of 'Influenza', where that name was clipped to the apheresis
Apheresis ( ἀφαίρεσις (''aphairesis'', "a taking away")) is a medical technology in which the blood of a person is passed through an apparatus that separates out one particular constituent and returns the remainder to the circulation ...
'Enza':
History
Timeline
First wave of early 1918
The pandemic is conventionally marked as having begun on 4 March 1918 with the recording of the case of Albert Gitchell, an army cook at Camp Funston
Camp Funston is a U.S. Army training camp located on Fort Riley, southwest of Manhattan, Kansas. The camp was named for Brigadier General Frederick Funston (1865–1917). It is one of sixteen such camps established at the outbreak of World ...
in Kansas
Kansas () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its Capital city, capital is Topeka, Kansas, Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita, Kansas, Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebras ...
, United States, despite there having been cases before him. The disease had already been observed away in Haskell County as early as January 1918, prompting local doctor Loring Miner
Loring Vinton Miner (1860–1935) was an American physician who is most notable for being the first in the world to identify and describe the Spanish flu.
Early life and education
Loring Miner was born in 1860 in Kansas.
He graduated from Oh ...
to warn the editors of the U.S. Public Health Service's academic journal ''Public Health Reports''. Within days of the 4 March first case at Camp Funston, 522 men at the camp had reported sick. By 11 March 1918, the virus had reached Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
, New York. Failure to take preventive measures in March/April was later criticized.
As the U.S. had entered World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the disease quickly spread from Camp Funston, a major training ground for troops of the American Expeditionary Forces
The American Expeditionary Forces (A. E. F.) was a formation of the United States Army on the Western Front of World War I. The A. E. F. was established on July 5, 1917, in France under the command of General John J. Pershing. It fought along ...
, to other U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
camps and Europe, becoming an epidemic in the Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
, East Coast, and French ports by April 1918, and reaching the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
* Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a maj ...
by the middle of the month. It then quickly spread to the rest of France, Great Britain, Italy, and Spain and in May reached Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
and Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
. After the signing of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
(March 1918), Germany started releasing Russian prisoners of war, who then brought the disease to their country. It reached North Africa, India, and Japan in May, and soon after had likely gone around the world as there had been recorded cases in Southeast Asia in April. In June an outbreak was reported in China. After reaching Australia in July, the wave started to recede.
The first wave of the flu lasted from the first quarter of 1918 and was relatively mild. Mortality rates were not appreciably above normal; in the United States ~75,000 flu-related deaths were reported in the first six months of 1918, compared to ~63,000 deaths during the same time period in 1915.World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, with three-quarters of French troops, half the British forces, and over 900,000 German soldiers sick.
Deadly second wave of late 1918
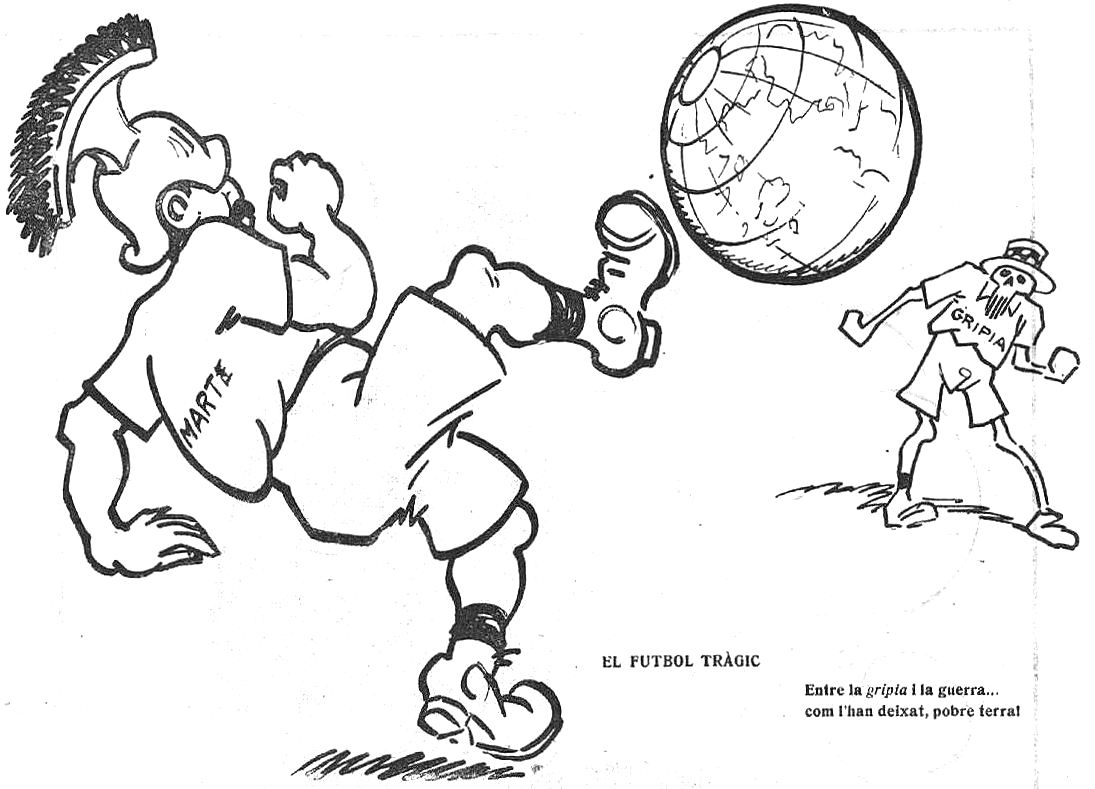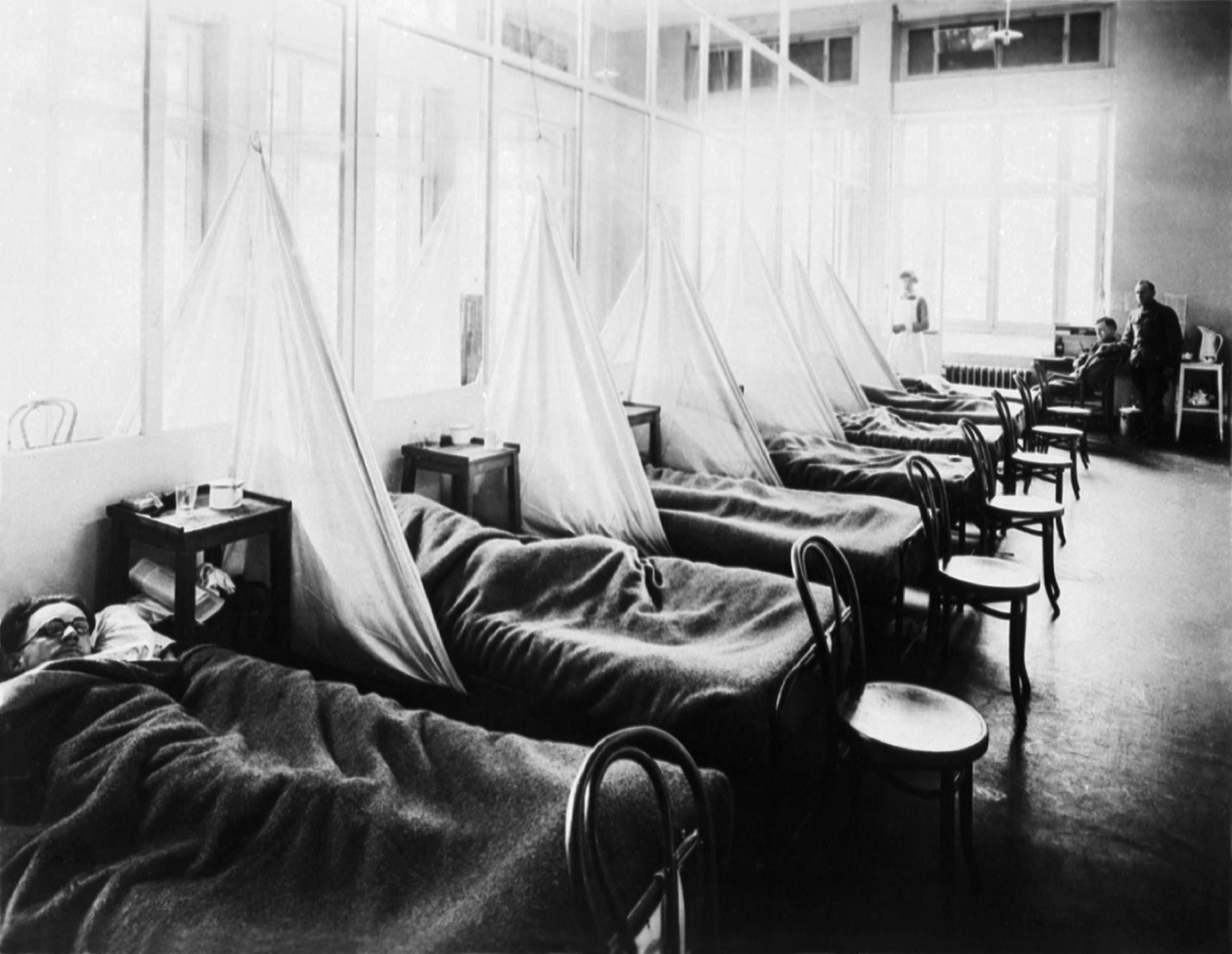
 The second wave began in the second half of August 1918, probably spreading to
The second wave began in the second half of August 1918, probably spreading to Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
and Freetown
Freetown is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educ ...
, Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ...
, by ships from Brest, France, Brest, where it had likely arrived with American troops or French recruits for naval training. From the Boston Navy Yard
The Boston Navy Yard, originally called the Charlestown Navy Yard and later Boston Naval Shipyard, was one of the oldest shipbuilding facilities in the United States Navy. It was established in 1801 as part of the recent establishment of t ...
and Camp Devens (later renamed Fort Devens
Fort Devens is a United States Army Reserve military installation in the towns of Ayer and Shirley, in Middlesex County and Harvard in Worcester County in the U.S. state of Massachusetts. Due to extensive environmental contamination it was li ...
), about 30 miles west of Boston, other U.S. military sites were soon afflicted, as were troops being transported to Europe. Helped by troop movements, it spread over the next two months to all of North America, and then to Central and South America, also reaching Brazil and the Caribbean on ships. In July 1918, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
saw its first cases in some soldiers.South African Native Labour Corps
The South African Native Labour Corps (SANLC) was a force of workers formed in 1916 in response to a British request for workers at French ports. About 25,000 South Africans joined the Corps. The SANLC was utilized in various menial noncombat tas ...
returning from France. From there it spread around southern Africa and beyond the Zambezi
The Zambezi River (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than ha ...
, reaching Ethiopia in November. On 15 September, New York City saw its first fatality from influenza. The Philadelphia Liberty Loans Parade, held in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, on 28 September 1918 to promote government bonds
A government bond or sovereign bond is a form of bond issued by a government to support public spending. It generally includes a commitment to pay periodic interest, called coupon payments'','' and to repay the face value on the maturity dat ...
for World War I, resulted in 12,000 deaths after a major outbreak of the illness spread among people who had attended the parade.
Third wave of 1919
In January 1919, the third wave of the flu hit Australia for the first time, where it killed around 12,000[
In the rest of the world, the third wave particularly affected Spain, Serbia, Mexico and Great Britain, resulting in hundreds of thousands of deaths.]
Fourth wave of 1920
 In the northern hemisphere, fears of a "recurrence" of the flu grew as fall approached. Experts cited the history of past flu epidemics, such as that of 1889–1890, to predict that such a recurrence a year later was not unlikely, though not all agreed. In September, Surgeon General of the United States, U.S. Surgeon General Rupert Blue said a return of the flu later in the year would "probably, but by no means certainly," occur. France had readied a public information campaign before the end of the summer, and Britain began preparations in the fall with the manufacture of vaccine.
In the United States, there were "almost continuously isolated or solitary cases" of flu throughout the spring and summer months.
In the northern hemisphere, fears of a "recurrence" of the flu grew as fall approached. Experts cited the history of past flu epidemics, such as that of 1889–1890, to predict that such a recurrence a year later was not unlikely, though not all agreed. In September, Surgeon General of the United States, U.S. Surgeon General Rupert Blue said a return of the flu later in the year would "probably, but by no means certainly," occur. France had readied a public information campaign before the end of the summer, and Britain began preparations in the fall with the manufacture of vaccine.
In the United States, there were "almost continuously isolated or solitary cases" of flu throughout the spring and summer months. The fourth wave in the United States subsided as swiftly as it had appeared, reaching a peak in early February. "An epidemic of considerable proportions marked the early months of 1920", the U.S. Mortality Statistics would later note; according to data at this time, the epidemic resulted in one third as many deaths as the 1918–1919 experience. New York City alone reported 6,374 deaths between December 1919 and April 1920, almost twice the number of the first wave in spring 1918.
The fourth wave in the United States subsided as swiftly as it had appeared, reaching a peak in early February. "An epidemic of considerable proportions marked the early months of 1920", the U.S. Mortality Statistics would later note; according to data at this time, the epidemic resulted in one third as many deaths as the 1918–1919 experience. New York City alone reported 6,374 deaths between December 1919 and April 1920, almost twice the number of the first wave in spring 1918.
End of the pandemic
By 1920, the virus that caused the pandemic evolved to become much less deadly and subsequently caused only ordinary seasonal flu. By 1921, deaths had returned to pre-pandemic levels.
Potential origins
Despite its name, historical and epidemiology, epidemiological data cannot identify the geographic origin of the Spanish flu. However, several theories have been proposed.
United States
The first confirmed cases originated in the United States. Historian Alfred W. Crosby stated in 2003 that the flu originated in Kansas
Kansas () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its Capital city, capital is Topeka, Kansas, Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita, Kansas, Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebras ...
, and author John M. Barry described a January 1918 outbreak in Haskell County, Kansas, as the point of origin in his 2004 article.
A 2018 study of tissue slides and medical reports led by evolutionary biology professor Michael Worobey found evidence against the disease originating from Kansas, as those cases were milder and had fewer deaths compared to the infections in New York City in the same period. The study did find evidence through phylogenetic analyses that the virus likely had a North American origin, though it was not conclusive. In addition, the Hemagglutinin (influenza), haemagglutinin glycoproteins of the virus suggest that it originated long before 1918, and other studies suggest that the reassortment of the H1N1 virus likely occurred in or around 1915.
Europe
The major UK troop staging and hospital camp in Étaples in France has been theorized by virologist John Oxford as being at the center of the Spanish flu.Aldershot
Aldershot () is a town in Hampshire, England. It lies on heathland in the extreme northeast corner of the county, southwest of London. The area is administered by Rushmoor Borough Council. The town has a population of 37,131, while the Alder ...
,
China
In 1993, Claude Hannoun, the leading expert on the Spanish flu at the Pasteur Institute, asserted the precursor virus was likely to have come from Republic of China (1912–1949), China and then mutated in the United States near Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
and from there spread to Brest, France, Brest, French Third Republic, France, Europe's battlefields, the rest of Europe, and the rest of the world, with Allies of World War I, Allied soldiers and sailors as the main disseminators.
Epidemiology and pathology
Transmission and mutation
 The basic reproduction number of the virus was between 2 and 3. The close quarters and massive troop movements of
The basic reproduction number of the virus was between 2 and 3. The close quarters and massive troop movements of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
hastened the pandemic, and probably both increased transmission and augmented mutation. The war may also have reduced people's resistance to the virus. Some speculate the soldiers' immune systems were weakened by malnourishment, as well as the stresses of combat and chemical attacks, increasing their susceptibility. A large factor in the worldwide occurrence of the flu was increased travel. Modern transportation systems made it easier for soldiers, sailors, and civilian travelers to spread the disease. Another was lies and denial by governments, leaving the population ill-prepared to handle the outbreaks.
Signs and symptoms
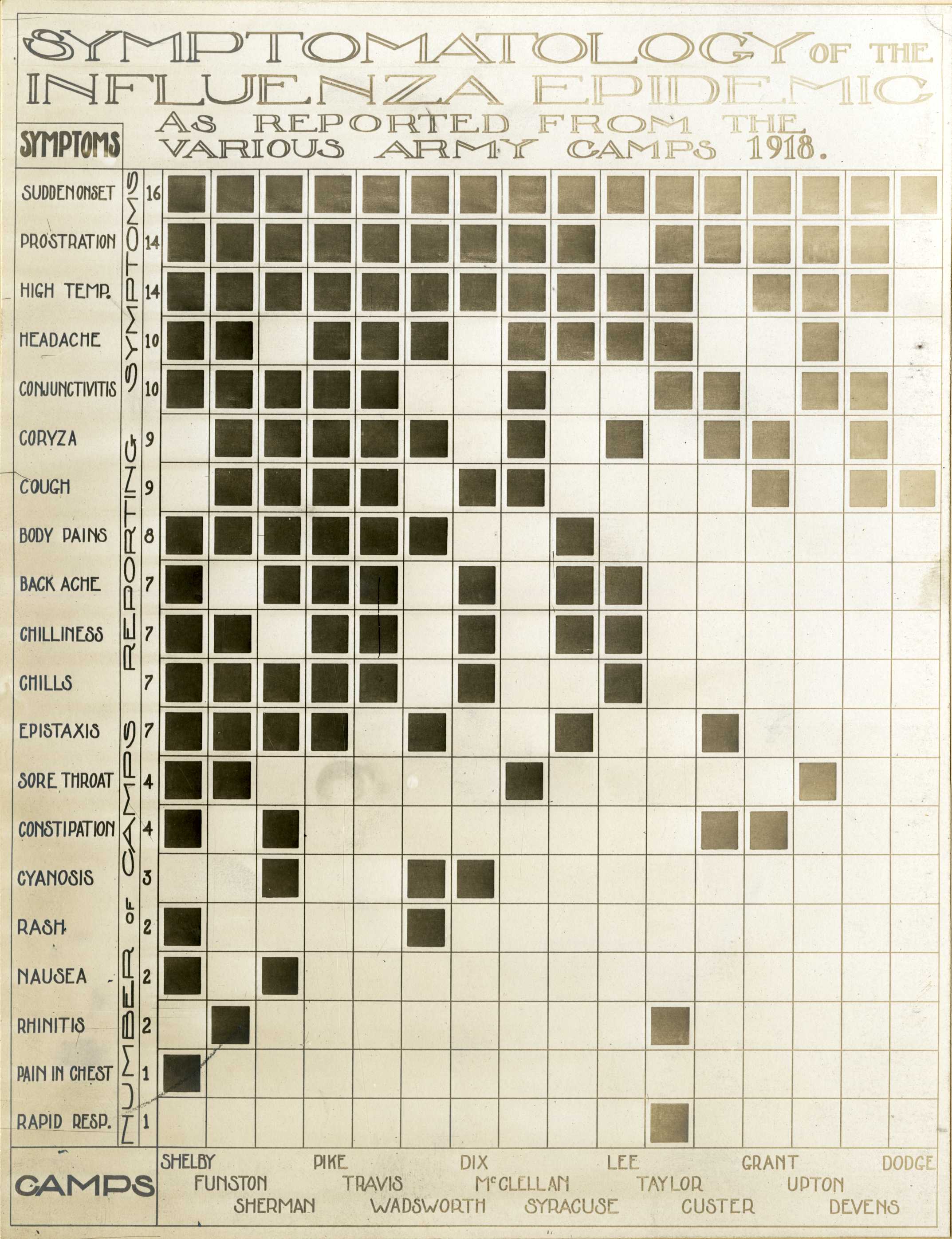 The majority of the infected experienced only the typical flu symptoms of sore throat, headache, and fever, especially during the first wave. However, during the second wave, the disease was much more serious, often complicated by bacterial pneumonia, which was often the cause of death. This more serious type would cause ''heliotrope cyanosis'' to develop, whereby the skin would first develop two mahogany spots over the cheekbones which would then over a few hours spread to color the entire face blue, followed by black coloration first in the extremities and then further spreading to the limbs and the torso. After this, death would follow within hours or days due to the lungs being filled with fluids. Other signs and symptoms reported included spontaneous mouth and nosebleeds, miscarriages for pregnant women, a peculiar smell, teeth, and hair falling, delirium, dizziness, insomnia, loss of hearing or smell, and impaired vision. One observer wrote, "One of the most striking of the complications was hemorrhage from mucous membranes, especially from the nose, stomach, and intestine. Bleeding from the ears and petechia, petechial hemorrhages in the skin also occurred". The severity of the symptoms was believed to be caused by
The majority of the infected experienced only the typical flu symptoms of sore throat, headache, and fever, especially during the first wave. However, during the second wave, the disease was much more serious, often complicated by bacterial pneumonia, which was often the cause of death. This more serious type would cause ''heliotrope cyanosis'' to develop, whereby the skin would first develop two mahogany spots over the cheekbones which would then over a few hours spread to color the entire face blue, followed by black coloration first in the extremities and then further spreading to the limbs and the torso. After this, death would follow within hours or days due to the lungs being filled with fluids. Other signs and symptoms reported included spontaneous mouth and nosebleeds, miscarriages for pregnant women, a peculiar smell, teeth, and hair falling, delirium, dizziness, insomnia, loss of hearing or smell, and impaired vision. One observer wrote, "One of the most striking of the complications was hemorrhage from mucous membranes, especially from the nose, stomach, and intestine. Bleeding from the ears and petechia, petechial hemorrhages in the skin also occurred". The severity of the symptoms was believed to be caused by cytokine storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a physiological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Norma ...
s.
The majority of deaths were from bacterial pneumonia,
Misdiagnosis
Because the virus that caused the disease was too small to be seen under a microscope at the time, there were problems with correctly diagnosing it. The bacterium ''Haemophilus influenzae'' was instead mistakenly thought to be the cause, as it was big enough to be seen and was present in many, though not all, patients. For this reason, a vaccine that was used against that bacillus did not make an infection rarer but did decrease the death rate.
During the deadly second wave there were also fears that it was in fact Plague (disease), plague, dengue fever, or cholera. Another common misdiagnosis was typhus, which was common in circumstances of social upheaval, and was therefore also affecting Russia in the aftermath of the October Revolution. In Chile, the view of the country's elite was that the nation was in severe decline, and therefore doctors assumed that the disease was typhus caused by poor hygiene, and not an infectious one, causing a mismanaged response which did not ban mass gatherings.
The role of climate conditions
 Studies have shown that the immune system of Spanish flu victims was weakened by adverse climate conditions which were particularly unseasonably cold and wet for extended periods of time during the duration of the pandemic. This affected especially WWI troops exposed to incessant rains and lower-than-average temperatures for the duration of the conflict, and especially during the second wave of the pandemic. Ultra-high-resolution climate data combined with highly detailed mortality records analyzed at Harvard University and the Climate Change Institute at the University of Maine identified a severe climate anomaly that impacted Europe from 1914 to 1919, with several environmental indicators directly influencing the severity and spread of the Spanish flu pandemic.
Studies have shown that the immune system of Spanish flu victims was weakened by adverse climate conditions which were particularly unseasonably cold and wet for extended periods of time during the duration of the pandemic. This affected especially WWI troops exposed to incessant rains and lower-than-average temperatures for the duration of the conflict, and especially during the second wave of the pandemic. Ultra-high-resolution climate data combined with highly detailed mortality records analyzed at Harvard University and the Climate Change Institute at the University of Maine identified a severe climate anomaly that impacted Europe from 1914 to 1919, with several environmental indicators directly influencing the severity and spread of the Spanish flu pandemic.
Responses
Public health management
While systems for alerting public health authorities of infectious spread did exist in 1918, they did not generally include influenza, leading to a delayed response. Nevertheless, actions were taken. Maritime quarantines were declared on islands such as Iceland, Australia, and American Samoa, saving many lives. Social distancing measures were introduced, for example closing schools, theatres, and places of worship, limiting public transportation, and banning mass gatherings. Wearing Surgical mask, face masks became common in some places, such as Japan, though there were debates over their efficacy. There was also some resistance to their use, as exemplified by the Anti-Mask League of San Francisco. Vaccines were also developed, but as these were based on bacteria and not the actual virus, they could only help with secondary infections. The actual enforcement of various restrictions varied. To a large extent, the New York City health commissioner ordered businesses to open and close on staggered shifts to avoid overcrowding on the subways.
A later study found that measures such as banning mass gatherings and requiring the wearing of face masks could cut the death rate up to 50 percent, but this was dependent on their being imposed early in the outbreak and not being lifted prematurely.
Medical treatment
As there were no antiviral drugs to treat the virus, and no antibiotics to treat the secondary bacterial infections, doctors would rely on a random assortment of medicines with varying degrees of effectiveness, such as aspirin, quinine, arsenics, digitalis, strychnine, Magnesium sulfate, epsom salts, castor oil, and iodine. Treatments of traditional medicine, such as bloodletting, ayurveda, and kampo were also applied.
Information dissemination
Due to World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, many countries engaged in wartime censorship, and suppressed reporting of the pandemic. For example, the Italian newspaper ''Corriere della Sera'' was prohibited from reporting daily death tolls. The newspapers of the time were also generally Paternalism, paternalistic and worried about mass panic. Misinformation also spread along with the disease. In Ireland there was a belief that Miasma theory, noxious gases were rising from the mass graves of Flanders Fields and being "blown all over the world by winds". There were also rumors that the Germans were behind it, for example by poisoning the aspirin manufactured by Bayer, or by Chemical weapons in World War I, releasing poison gas from U-boats.
Mortality
Around the globe
 The Spanish flu infected around 500 million people, about one-third of the world's population. Estimates as to how many infected people died vary greatly, but the flu is regardless considered to be one of the List of pandemics, deadliest pandemics in history. An early estimate from 1927 put global mortality at 21.6 million.
The Spanish flu infected around 500 million people, about one-third of the world's population. Estimates as to how many infected people died vary greatly, but the flu is regardless considered to be one of the List of pandemics, deadliest pandemics in history. An early estimate from 1927 put global mortality at 21.6 million.The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823.
The journal publishes original research articles ...
'' also noted that Indian provinces had excess mortality rates ranging from 2.1% to 7.8%, stating: "Commentators at the time attributed this huge variation to differences in nutritional status and diurnal fluctuations in temperature."
Devastated communities
 Even in areas where mortality was low, so many adults were incapacitated that much of everyday life was hampered. Some communities closed all stores or required customers to leave orders outside. There were reports that healthcare workers could not tend the sick nor the gravediggers bury the dead because they too were ill. Mass graves were dug by steam shovel and bodies buried without coffins in many places.
Bristol Bay, a region of Alaska populated by Alaska Natives, indigenous people, suffered a death rate of 40 percent of the total population, with some villages entirely disappearing.
Several Pacific island territories were hit particularly hard. The pandemic reached them from New Zealand, which was too slow to implement measures to prevent ships, such as , carrying the flu from leaving its ports. From New Zealand, the flu reached Tonga (killing 8% of the population), Nauru (16%), and Colony of Fiji, Fiji (5%, 9,000 people). Worst affected was Western Samoa, formerly German Samoa, which had been Occupation of German Samoa, occupied by New Zealand in 1914. 90% of the population was infected; 30% of adult men, 22% of adult women, and 10% of children died. By contrast, Governor of American Samoa, Governor John Martin Poyer prevented the flu from reaching neighboring American Samoa by imposing a blockade. The disease spread fastest through the higher social classes among the indigenous peoples, because of the custom of gathering oral tradition from chiefs on their deathbeds; many community elders were infected through this process.
In Qajar Iran, Iran, the mortality was very high: according to an estimate, between 902,400 and 2,431,000, or 8% to 22% of the total population died. The country was going through the Persian famine of 1917–1919 concurrently.
In History of Ireland (1801–1923), Ireland, during the worst 12 months, the Spanish flu accounted for one-third of all deaths.
In Union of South Africa, South Africa it is estimated that about 300,000 people amounting to 6% of the population died within six weeks. Government actions in the early stages of the virus' arrival in the country in September 1918 are believed to have unintentionally accelerated its spread throughout the country. Almost a quarter of the working population of Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley, consisting of workers in the diamond mines, died. In British Somaliland, one official estimated that 7% of the native population died. This huge death toll resulted from an extremely high infection rate of up to 50% and the extreme severity of the symptoms, suspected to be caused by
Even in areas where mortality was low, so many adults were incapacitated that much of everyday life was hampered. Some communities closed all stores or required customers to leave orders outside. There were reports that healthcare workers could not tend the sick nor the gravediggers bury the dead because they too were ill. Mass graves were dug by steam shovel and bodies buried without coffins in many places.
Bristol Bay, a region of Alaska populated by Alaska Natives, indigenous people, suffered a death rate of 40 percent of the total population, with some villages entirely disappearing.
Several Pacific island territories were hit particularly hard. The pandemic reached them from New Zealand, which was too slow to implement measures to prevent ships, such as , carrying the flu from leaving its ports. From New Zealand, the flu reached Tonga (killing 8% of the population), Nauru (16%), and Colony of Fiji, Fiji (5%, 9,000 people). Worst affected was Western Samoa, formerly German Samoa, which had been Occupation of German Samoa, occupied by New Zealand in 1914. 90% of the population was infected; 30% of adult men, 22% of adult women, and 10% of children died. By contrast, Governor of American Samoa, Governor John Martin Poyer prevented the flu from reaching neighboring American Samoa by imposing a blockade. The disease spread fastest through the higher social classes among the indigenous peoples, because of the custom of gathering oral tradition from chiefs on their deathbeds; many community elders were infected through this process.
In Qajar Iran, Iran, the mortality was very high: according to an estimate, between 902,400 and 2,431,000, or 8% to 22% of the total population died. The country was going through the Persian famine of 1917–1919 concurrently.
In History of Ireland (1801–1923), Ireland, during the worst 12 months, the Spanish flu accounted for one-third of all deaths.
In Union of South Africa, South Africa it is estimated that about 300,000 people amounting to 6% of the population died within six weeks. Government actions in the early stages of the virus' arrival in the country in September 1918 are believed to have unintentionally accelerated its spread throughout the country. Almost a quarter of the working population of Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley, consisting of workers in the diamond mines, died. In British Somaliland, one official estimated that 7% of the native population died. This huge death toll resulted from an extremely high infection rate of up to 50% and the extreme severity of the symptoms, suspected to be caused by cytokine storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a physiological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Norma ...
s.
Less-affected areas
In the Pacific, American Samoa Estimates for the death toll in China have varied widely,
Estimates for the death toll in China have varied widely,influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptom ...
among the Chinese population in 1918.
Patterns of fatality
 The pandemic mostly killed young adults. In 1918–1919, 99% of pandemic influenza deaths in the U.S. occurred in people under 65, and nearly half of deaths were in young adults 20 to 40 years old. In 1920, the mortality rate among people under 65 had decreased sixfold to half the mortality rate of people over 65, but 92% of deaths still occurred in people under 65. This is unusual since influenza is typically most deadly to weak individuals, such as infants under age two, adults over age 70, and the immunocompromised. In 1918, older adults may have had partial protection caused by exposure to the 1889–1890 flu pandemic, known as the "Russian flu".
The pandemic mostly killed young adults. In 1918–1919, 99% of pandemic influenza deaths in the U.S. occurred in people under 65, and nearly half of deaths were in young adults 20 to 40 years old. In 1920, the mortality rate among people under 65 had decreased sixfold to half the mortality rate of people over 65, but 92% of deaths still occurred in people under 65. This is unusual since influenza is typically most deadly to weak individuals, such as infants under age two, adults over age 70, and the immunocompromised. In 1918, older adults may have had partial protection caused by exposure to the 1889–1890 flu pandemic, known as the "Russian flu".[Hanssen, Olav. Undersøkelser over influenzaens optræden specielt i Bergen 1918–1922. Bg. 1923. 66 s. ill. (Haukeland sykehus. Med. avd. Arb. 2) (Klaus Hanssens fond. Skr. 3)] According to historian John M. Barry, the most vulnerable of all – "those most likely, of the most likely", to die – were pregnant women. He reported that in thirteen studies of hospitalized women in the pandemic, the death rate ranged from 23% to 71%. Of the pregnant women who survived childbirth, over one-quarter (26%) lost the child. Another oddity was that the outbreak was widespread in the summer and autumn (in the Northern Hemisphere); influenza is usually worse in winter.
There were also geographic patterns to the disease's fatality. Some parts of Asia had 30 times higher death rates than some parts of Europe, and generally, Africa and Asia had higher rates, while Europe and North America had lower ones. There was also great variation within continents, with three times higher mortality in Hungary and Spain compared to Denmark, two to three times higher chance of death in Sub-Saharan Africa compared to North Africa, and possibly up to ten times higher rates between the extremes of Asia. Cities were affected worse than rural areas. There were also differences between cities, which might have reflected exposure to the milder first wave giving immunity, as well as the introduction of social distancing measures.
Another major pattern was the differences between social classes. In Oslo, death rates were inversely correlated with apartment size, as the poorer people living in smaller apartments died at a higher rate. Social status was also reflected in the higher mortality among immigrant communities, with Italian Americans, a recently arrived group at the time, were nearly twice as likely to die compared to the average Americans. These disparities reflected worse diets, crowded living conditions, and problems accessing healthcare. Paradoxically, however, African Americans were relatively spared by the pandemic.
More men than women were killed by the flu, as they were more likely to go out and be exposed, while women would tend to Housewife, stay at home. For the same reason men also were more likely to have pre-existing tuberculosis, which severely worsened the chances of recovery. However, in India the opposite was true, potentially because Indian women were neglected with poorer nutrition, and were expected to care for the sick.
A study conducted by He ''et al''. (2011) used a mechanistic modeling approach to study the three waves of the 1918 influenza pandemic. They examined the factors that underlie variability in temporal patterns and their correlation to patterns of mortality and morbidity. Their analysis suggests that temporal variations in transmission rate provide the best explanation, and the variation in transmission required to generate these three waves is within biologically plausible values. Another study by He ''et al''. (2013) used a simple epidemic model incorporating three factors to infer the cause of the three waves of the 1918 influenza pandemic. These factors were school opening and closing, temperature changes throughout the outbreak, and human behavioral changes in response to the outbreak. Their modeling results showed that all three factors are important, but human behavioral responses showed the most significant effects.
Effects
World War I
Academic Andrew Price-Smith has made the argument that the virus helped tip the balance of power in the latter days of the war towards the Allied cause. He provides data that the viral waves hit the Central Powers before the Allied powers and that both morbidity and mortality in Weimar Republic, Germany and First Austrian Republic, Austria were considerably higher than in Britain and French Third Republic, France. A 2006 ''Lancet'' study corroborates higher excess mortality rates in Germany (0.76%) and Austria (1.61%) compared to Britain (0.34%) and France (0.75%).
Economic
 Many businesses in the entertainment and service industries suffered losses in revenue, while the healthcare industry reported profit gains. Historian Nancy Bristow has argued that the pandemic, when combined with the increasing number of women attending college, contributed to the success of women in the field of nursing. This was due in part to the failure of medical doctors, who were predominantly men, to contain and prevent the illness. Nursing staff, who were mainly women, celebrated the success of their patient care and did not associate the spread of the disease with their work.
A 2020 study found that US cities that implemented early and extensive non-medical measures (quarantine, etc.) suffered no additional adverse economic effects due to implementing those measures,
however, the validity of this study has been questioned because of the coincidence of WWI and other problems with data reliability.
Many businesses in the entertainment and service industries suffered losses in revenue, while the healthcare industry reported profit gains. Historian Nancy Bristow has argued that the pandemic, when combined with the increasing number of women attending college, contributed to the success of women in the field of nursing. This was due in part to the failure of medical doctors, who were predominantly men, to contain and prevent the illness. Nursing staff, who were mainly women, celebrated the success of their patient care and did not associate the spread of the disease with their work.
A 2020 study found that US cities that implemented early and extensive non-medical measures (quarantine, etc.) suffered no additional adverse economic effects due to implementing those measures,
however, the validity of this study has been questioned because of the coincidence of WWI and other problems with data reliability.
Long-term effects
A 2006 study in the ''Journal of Political Economy'' found that "cohorts ''in utero'' during the pandemic displayed reduced educational attainment, increased rates of physical disability, lower income, lower socioeconomic status, and higher transfer payments received compared with other birth cohorts." A 2018 study found that the pandemic reduced educational attainment in populations. The flu has also been linked to the outbreak of encephalitis lethargica in the 1920s.
Survivors faced an elevated mortality risk. Some survivors did not fully recover from physiological conditions resulting from infection.
Legacy
 Despite the high morbidity and mortality rates that resulted from the epidemic, the Spanish flu began to fade from public awareness over the decades until the arrival of news about Avian influenza, bird flu and other pandemics in the 1990s and 2000s. This has led some historians to label the Spanish flu a "forgotten pandemic". However, this label has been challenged by the historian Guy Beiner, who has charted a complex history of social and cultural forgetting, demonstrating how the pandemic was overshadowed by the commemoration of the First World War and mostly neglected in mainstream historiography, yet was remembered in private and local traditions across the globe.
There are various theories of why the Spanish flu was "forgotten". The rapid pace of the pandemic, which killed most of its victims in the United States within less than nine months, resulted in limited media coverage. The general population was familiar with patterns of pandemic disease in the late 19th and early 20th centuries: typhoid, yellow fever, diphtheria, and cholera all occurred near the same time. These outbreaks probably lessened the significance of the influenza pandemic for the public. In some areas, the flu was not reported on, the only mention being that of advertisements for medicines claiming to cure it.
Additionally, the outbreak coincided with the deaths and media focus on the First World War. Another explanation involves the age group affected by the disease. The majority of fatalities, from both the war and the epidemic, were among young adults. The high number of war-related deaths of young adults may have overshadowed the deaths caused by flu.
When people read the obituaries, they saw the war or postwar deaths and the deaths from the influenza side by side. Particularly in Europe, where the war's toll was high, the flu may not have had a tremendous psychological impact or may have seemed an extension of the war's tragedies. The duration of the pandemic and the war could have also played a role. The disease would usually only affect a particular area for a month before leaving. The war, however, had initially been expected to end quickly but lasted for four years by the time the pandemic struck.
Despite the high morbidity and mortality rates that resulted from the epidemic, the Spanish flu began to fade from public awareness over the decades until the arrival of news about Avian influenza, bird flu and other pandemics in the 1990s and 2000s. This has led some historians to label the Spanish flu a "forgotten pandemic". However, this label has been challenged by the historian Guy Beiner, who has charted a complex history of social and cultural forgetting, demonstrating how the pandemic was overshadowed by the commemoration of the First World War and mostly neglected in mainstream historiography, yet was remembered in private and local traditions across the globe.
There are various theories of why the Spanish flu was "forgotten". The rapid pace of the pandemic, which killed most of its victims in the United States within less than nine months, resulted in limited media coverage. The general population was familiar with patterns of pandemic disease in the late 19th and early 20th centuries: typhoid, yellow fever, diphtheria, and cholera all occurred near the same time. These outbreaks probably lessened the significance of the influenza pandemic for the public. In some areas, the flu was not reported on, the only mention being that of advertisements for medicines claiming to cure it.
Additionally, the outbreak coincided with the deaths and media focus on the First World War. Another explanation involves the age group affected by the disease. The majority of fatalities, from both the war and the epidemic, were among young adults. The high number of war-related deaths of young adults may have overshadowed the deaths caused by flu.
When people read the obituaries, they saw the war or postwar deaths and the deaths from the influenza side by side. Particularly in Europe, where the war's toll was high, the flu may not have had a tremendous psychological impact or may have seemed an extension of the war's tragedies. The duration of the pandemic and the war could have also played a role. The disease would usually only affect a particular area for a month before leaving. The war, however, had initially been expected to end quickly but lasted for four years by the time the pandemic struck.
In fiction and other literature
The Spanish flu has been represented in numerous works of fiction:
* Katherine Anne Porter's novella ''Pale Horse, Pale Rider'', published under the same title in a 1939 collection of three works
* 1918 (1985 film), ''1918'', a 1985 American drama film.
* ''The Last Town on Earth'', a 2006 novel.
* ''Spanish Flu: The Forgotten Fallen'', a 2009 British television series.
* ''Downton Abbey'', a 2010 British historical drama television series.
* ''Vampyr (video game), Vampyr'', a 2018 video game.
* ''The Pull of the Stars'', a 2020 novel by Emma Donoghue set in Dublin during the Spanish flu
* ''Resident Evil Village'', a 2021 video game.
* In ''Frankie Drake Mysteries'', series 4, episode 9, the plot revolves around an apparent outbreak of Spanish flu in a theatre where there is going to be a performance which some think risqué.
Mary McCarthy (author), Mary McCarthy referred to it in her memoir ''Memories of a Catholic Girlhood'' (1957), as she and her three brothers were orphaned by their parents' deaths from the Spanish flu.
Comparison with other pandemics
The Spanish flu killed a much lower percentage of the world's population than the Black Death, which lasted for many more years.
Research
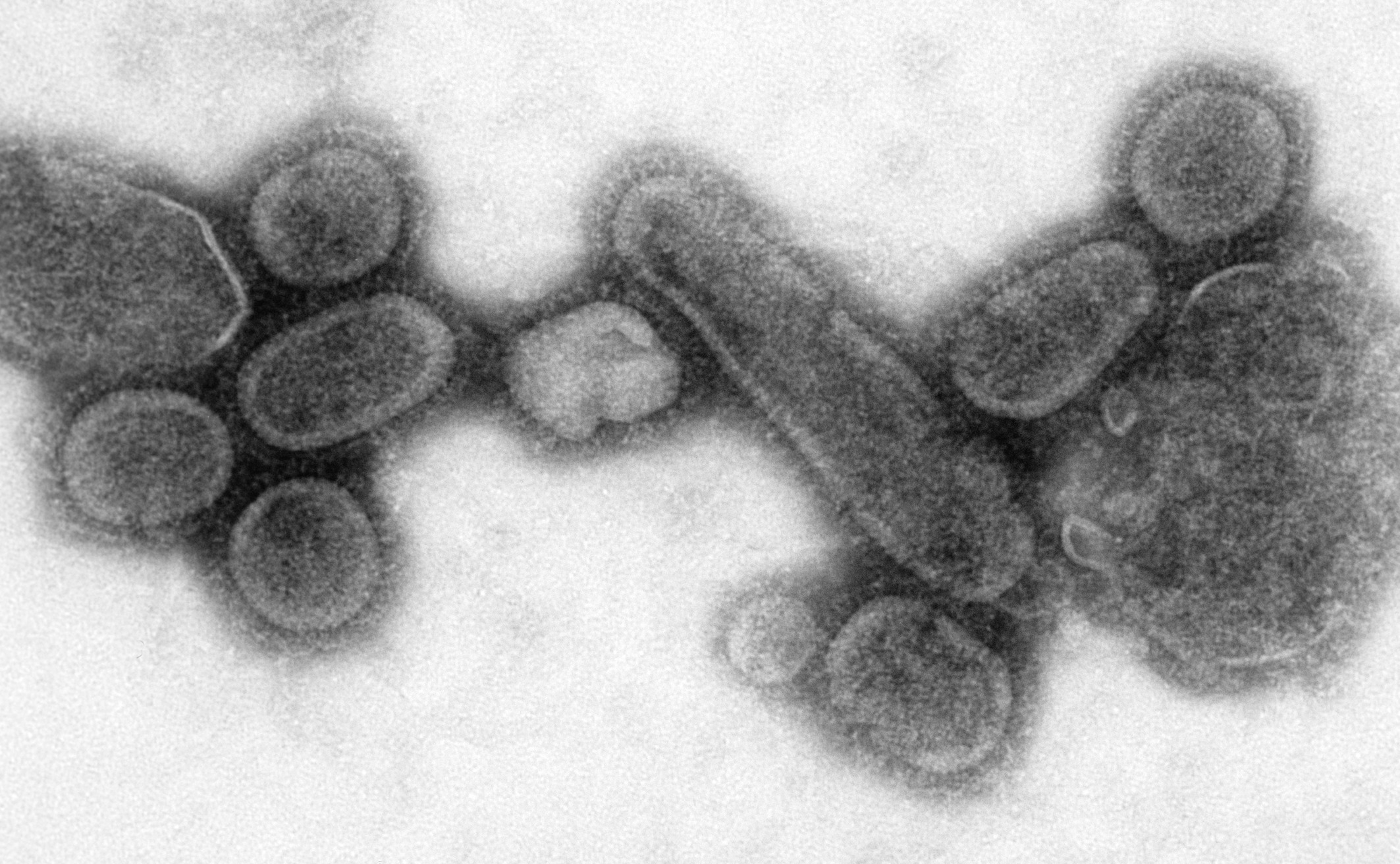 The origin of the Spanish flu pandemic, and the relationship between the near-simultaneous outbreaks in humans and swine, have been controversial. One hypothesis is that the virus strain originated at Fort Riley, Kansas, in viruses in poultry and swine which the fort bred for food; the soldiers were then sent from Fort Riley around the world, where they spread the disease. Similarities between a reconstruction of the virus and avian viruses, combined with the human pandemic preceding the first reports of influenza in swine, led researchers to conclude the influenza virus jumped directly from birds to humans, and swine caught the disease from humans.
The origin of the Spanish flu pandemic, and the relationship between the near-simultaneous outbreaks in humans and swine, have been controversial. One hypothesis is that the virus strain originated at Fort Riley, Kansas, in viruses in poultry and swine which the fort bred for food; the soldiers were then sent from Fort Riley around the world, where they spread the disease. Similarities between a reconstruction of the virus and avian viruses, combined with the human pandemic preceding the first reports of influenza in swine, led researchers to conclude the influenza virus jumped directly from birds to humans, and swine caught the disease from humans.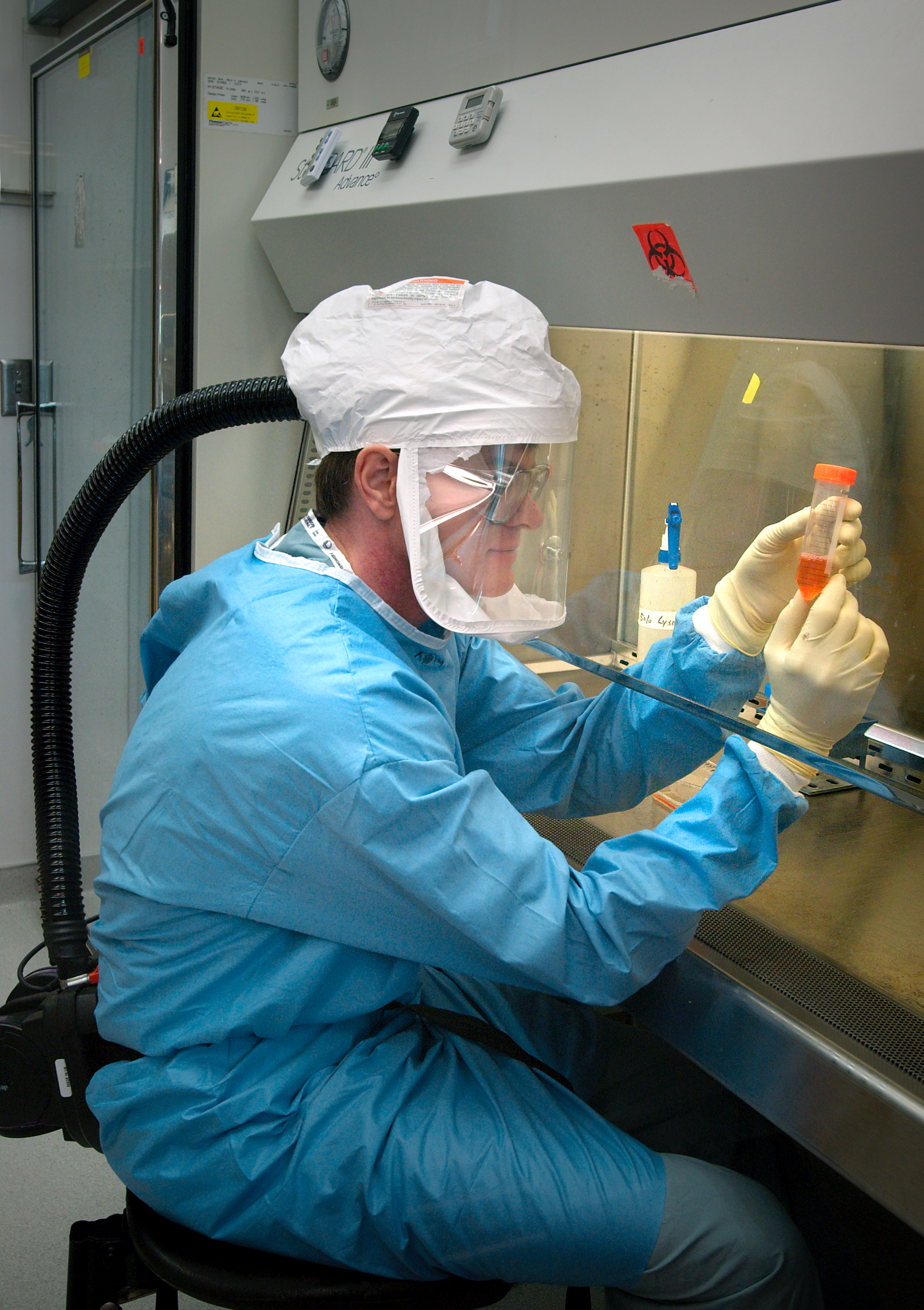 An effort to recreate the Spanish flu strain (a subtype of avian strain H1N1) was a collaboration among the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, the USDA Agricultural Research Service, ARS Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City. The effort resulted in the announcement (on 5 October 2005) that the group had successfully determined the virus's genetic sequence, using historic tissue samples recovered by pathologist Johan Hultin from an Inuit female flu victim buried in the Alaskan permafrost and samples preserved from American soldiers Roscoe Vaughan and James Downs.
On 18 January 2007, Kobasa et al. (2007) reported that monkeys (''Macaca fascicularis'') infected with the recreated flu strain exhibited classic symptoms of the 1918 pandemic, and died from cytokine storms – an overreaction of the immune system. This may explain why the Spanish flu had its surprising effect on younger, healthier people, as a person with a stronger immune system would potentially have a stronger overreaction.
On 16 September 2008, the body of British politician and diplomat Mark Sykes, Sir Mark Sykes was exhumed to study the RNA of the flu virus in efforts to understand the genetic structure of modern H5N1 bird flu. Sykes had been buried in 1919 in a lead coffin which scientists hoped had helped preserve the virus. The coffin was found to be split and the cadaver badly decomposed; nonetheless, samples of lung and brain tissue were taken.
In December 2008, research by Yoshihiro Kawaoka of the University of Wisconsin linked the presence of three specific genes (termed PA, PB1, and PB2) and a nucleoprotein derived from Spanish flu samples to the ability of the flu virus to invade the lungs and cause pneumonia. The combination triggered similar symptoms in animal testing.
In June 2010, a team at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine reported the 2009 flu pandemic vaccine provided some cross-protection against the Spanish flu pandemic strain.
One of the few things known for certain about influenza in 1918 and for some years after was that it was, except in the laboratory, exclusively a disease of human beings.
In 2013, the AIR Worldwide Research and Modeling Group "characterized the historic 1918 pandemic and estimated the effects of a similar pandemic occurring today using the AIR Pandemic Flu Model". In the model, "a modern-day 'Spanish flu' event would result in additional life insurance losses of between US$15.3–27.8 billion in the United States alone", with 188,000–337,000 deaths in the United States.
In 2018, Michael Worobey, an evolutionary biology professor at the University of Arizona who is examining the history of the 1918 pandemic, revealed that he obtained tissue slides created by William Rolland, a physician who reported on a respiratory illness likely to be the virus while a pathologist in the British military during World War One. Rolland had authored an article in the ''Lancet (journal), Lancet'' during 1917 about a respiratory illness outbreak beginning in 1916 in Étaples, France. Worobey traced recent references to that article to family members who had retained slides that Rolland had prepared during that time. Worobey extracted tissue from the slides to potentially reveal more about the origin of the pathogen.
An effort to recreate the Spanish flu strain (a subtype of avian strain H1N1) was a collaboration among the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, the USDA Agricultural Research Service, ARS Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City. The effort resulted in the announcement (on 5 October 2005) that the group had successfully determined the virus's genetic sequence, using historic tissue samples recovered by pathologist Johan Hultin from an Inuit female flu victim buried in the Alaskan permafrost and samples preserved from American soldiers Roscoe Vaughan and James Downs.
On 18 January 2007, Kobasa et al. (2007) reported that monkeys (''Macaca fascicularis'') infected with the recreated flu strain exhibited classic symptoms of the 1918 pandemic, and died from cytokine storms – an overreaction of the immune system. This may explain why the Spanish flu had its surprising effect on younger, healthier people, as a person with a stronger immune system would potentially have a stronger overreaction.
On 16 September 2008, the body of British politician and diplomat Mark Sykes, Sir Mark Sykes was exhumed to study the RNA of the flu virus in efforts to understand the genetic structure of modern H5N1 bird flu. Sykes had been buried in 1919 in a lead coffin which scientists hoped had helped preserve the virus. The coffin was found to be split and the cadaver badly decomposed; nonetheless, samples of lung and brain tissue were taken.
In December 2008, research by Yoshihiro Kawaoka of the University of Wisconsin linked the presence of three specific genes (termed PA, PB1, and PB2) and a nucleoprotein derived from Spanish flu samples to the ability of the flu virus to invade the lungs and cause pneumonia. The combination triggered similar symptoms in animal testing.
In June 2010, a team at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine reported the 2009 flu pandemic vaccine provided some cross-protection against the Spanish flu pandemic strain.
One of the few things known for certain about influenza in 1918 and for some years after was that it was, except in the laboratory, exclusively a disease of human beings.
In 2013, the AIR Worldwide Research and Modeling Group "characterized the historic 1918 pandemic and estimated the effects of a similar pandemic occurring today using the AIR Pandemic Flu Model". In the model, "a modern-day 'Spanish flu' event would result in additional life insurance losses of between US$15.3–27.8 billion in the United States alone", with 188,000–337,000 deaths in the United States.
In 2018, Michael Worobey, an evolutionary biology professor at the University of Arizona who is examining the history of the 1918 pandemic, revealed that he obtained tissue slides created by William Rolland, a physician who reported on a respiratory illness likely to be the virus while a pathologist in the British military during World War One. Rolland had authored an article in the ''Lancet (journal), Lancet'' during 1917 about a respiratory illness outbreak beginning in 1916 in Étaples, France. Worobey traced recent references to that article to family members who had retained slides that Rolland had prepared during that time. Worobey extracted tissue from the slides to potentially reveal more about the origin of the pathogen.
Sex differences in mortality
The high mortality rate of the influenza pandemic is one aspect that sets the pandemic apart from other disease outbreaks. Another factor is the higher mortality rate of men compared with women. Men with an underlying condition were at significantly more risk. Tuberculosis was one of the deadliest diseases in the 1900s, and killed more men than women. But with the spread of influenza disease, the cases of tuberculosis cases in men decreased. Many scholars have noted that tuberculosis increased the mortality rate of influenza in males, decreasing their life expectancy. During the 1900s tuberculosis was more common in males than females, but studies show that when influenza spread the tuberculosis mortality rate among females changed. The death rate of tuberculosis in females increased significantly and would continue to decline until post-pandemic.
Death rates were particularly high in those aged 20–35. The only comparable disease to this was the Black Death, black death, bubonic plague in the 1300s. As other studies have shown, tuberculosis and influenza had Comorbidity, comorbidities and one affected the other. The ages of males dying of the flu show that tuberculosis was a factor, and as males primarily had this disease at the time of the pandemic, they had a higher mortality rate. Life expectancy dropped in males during the pandemic but then increased two years after the pandemic.
Island of Newfoundland
One major cause of the spread of influenza was social behavior. Men had more social variation and were mobile more than women due to their work. Even though there was a higher mortality rate in males, each region showed different results, due to such factors as Malnutrition, nutritional deficiency. In Newfoundland and Labrador, Newfoundland, the pandemic spread was highly variable. Influenza did not discriminate who was infected, indeed it attacked the Socioeconomic status, socioeconomic status of people. Although social variability allowed the disease to move quickly geographically, it tended to spread faster and affect men more than women due to labor and social contact. Newfoundland's leading cause of death before the pandemic was tuberculosis and this is known to be a severe underlying condition for people and increases the , mortality rate when infected by the influenza disease. There was diverse labor in Newfoundland, men and women had various occupations that involved day-to-day interaction. But, fishing had a major role in the economy and so males were more mobile than females and had more contact with other parts of the world. The spread of the pandemic is known to have begun in the spring of 1918, but Newfoundland didn't see the deadly wave until June or July, which aligns with the high demand for employment in the fishery. The majority of men were working along the coast during the summer and it was typical for entire families to move to Newfoundland and work. Studies show a much higher mortality rate in males compared with females. But, during the first, second, and third waves of the pandemic, the mortality shifted. During the first wave, men had a higher mortality rate, but the mortality rate of females increased and was higher during the second and third waves. The female population was larger in certain regions of Newfoundland and therefore had a bigger impact on the death rate.
Influenza pandemic among Canadian soldiers
Records indicate the most deaths during the first wave of the pandemic were among young men in their 20s, which reflects the age of enlistment in the war. The mobility of young men during 1918 was linked to the spread of influenza and the biggest wave of the epidemic. In late 1917 and throughout 1918, thousands of male troops gathered at the Halifax port before heading to Europe. Any soldier that was ill and could not depart was added to the population of Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, which increased the case rate of influenza among men during the war. To determine the cause of the death during the pandemic, war scientists used the Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC), which reported under 2 million men and women died during the wars, with a record of those who died from 1917 to 1918. The movement of soldiers during this time and the transportation from United States between Canada likely had a significant effect on the spread of the pandemic.
See also
*
*
*
*
*
* List of epidemics
* List of Spanish flu cases
Footnotes
References
Citations
Bibliography
*
* – Open access material by the Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Health Sciences Research Commons.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
summary
by Infectious Diseases Society of America and ScienceDaily, 3 October 2009)
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
; Videos
We Heard the Bells: The Influenza of 1918
– NIH interviews with Spanish Flu survivors.
Presentation by Nancy Bristow on the Influenza Pandemic and World War I, November 1, 2019
C-SPAN
*
External links
*
The American Influenza Epidemic of 1918–1919: A Digital Encyclopedia
Largest digital collection of newspapers, archival manuscripts, and interpretive essays exploring the impact of the epidemic on 50 U.S. cities (Univ. of Michigan).
{{DEFAULTSORT:Spanish flu
Spanish flu
Pandemics
20th-century epidemics
1918 disease outbreaks
1919 disease outbreaks
1920 disease outbreaks
 This pandemic was known by many different names—some old, some new—depending on place, time, and context. The
This pandemic was known by many different names—some old, some new—depending on place, time, and context. The  Many alternative names are
Many alternative names are  Outside Spain, the disease was soon misnamed 'Spanish influenza'. In a 2 June 1918 ''
Outside Spain, the disease was soon misnamed 'Spanish influenza'. In a 2 June 1918 ''

 The second wave began in the second half of August 1918, probably spreading to
The second wave began in the second half of August 1918, probably spreading to  In the northern hemisphere, fears of a "recurrence" of the flu grew as fall approached. Experts cited the history of past flu epidemics, such as that of 1889–1890, to predict that such a recurrence a year later was not unlikely, though not all agreed. In September, Surgeon General of the United States, U.S. Surgeon General Rupert Blue said a return of the flu later in the year would "probably, but by no means certainly," occur. France had readied a public information campaign before the end of the summer, and Britain began preparations in the fall with the manufacture of vaccine.
In the United States, there were "almost continuously isolated or solitary cases" of flu throughout the spring and summer months. An increase in scattered cases became apparent as early as September, but Chicago experienced one of the first major outbreaks of the flu beginning in the middle of January. The Public Health Service announced it would take steps to "localize the epidemic", but the disease was already causing a simultaneous outbreak in Kansas City and quickly spread outward from the center of the country in no clear direction. A few days after its first announcement, PHS issued another assuring the disease was under the control of state health authorities and an outbreak of epidemic proportions was not expected.
It became apparent within days of the start of Chicago's explosive growth in cases that the flu was spreading in the city at an even faster rate than in winter 1919, though fewer were dying. Within a week, new cases in the city had surpassed its peak during the 1919 wave. Around the same time, New York City began to see its own sudden increase in cases, and other cities around the country were soon to follow. Certain pandemic restrictions, such as the closing of schools and theaters and staggered business hours to avoid congestion, were reimposed in cities like Chicago, Memphis, and New York City. As they had during the epidemic in fall 1918, schools in New York City remained open, while those in Memphis were shuttered as part of more general restrictions on public gatherings.
Amidst the spreading outbreak, Surgeon General Blue warned the public not to get "panicky" over the flu. Nevertheless, the United States Senate, Senate had sensed a turn in the tide (as the flu began to afflict their own families) and on 27 January passed an appropriations bill for $500,000 for the study of influenza. First introduced in July 1919 by Warren G. Harding, Senator Warren G. Harding after the third wave had subsided, the bill had been whittled down from $5 million. William H. King, Senator William H. King of Utah fundamentally opposed the bill, criticizing PHS for the "vast autocracy" it had become; James D. Phelan, Senator James D. Phelan of California sought to have the bill recommitted to the Committee on Public Health until there was an investigation into what previous flu funding had produced, but this failed. Ultimately, a letter from Carter Glass, United States Secretary of the Treasury, Secretary of the Treasury, regarding the outbreaks occurring in large cities and the threat they posed to the rest of the country persuaded many senators to vote for the package.
In the northern hemisphere, fears of a "recurrence" of the flu grew as fall approached. Experts cited the history of past flu epidemics, such as that of 1889–1890, to predict that such a recurrence a year later was not unlikely, though not all agreed. In September, Surgeon General of the United States, U.S. Surgeon General Rupert Blue said a return of the flu later in the year would "probably, but by no means certainly," occur. France had readied a public information campaign before the end of the summer, and Britain began preparations in the fall with the manufacture of vaccine.
In the United States, there were "almost continuously isolated or solitary cases" of flu throughout the spring and summer months. An increase in scattered cases became apparent as early as September, but Chicago experienced one of the first major outbreaks of the flu beginning in the middle of January. The Public Health Service announced it would take steps to "localize the epidemic", but the disease was already causing a simultaneous outbreak in Kansas City and quickly spread outward from the center of the country in no clear direction. A few days after its first announcement, PHS issued another assuring the disease was under the control of state health authorities and an outbreak of epidemic proportions was not expected.
It became apparent within days of the start of Chicago's explosive growth in cases that the flu was spreading in the city at an even faster rate than in winter 1919, though fewer were dying. Within a week, new cases in the city had surpassed its peak during the 1919 wave. Around the same time, New York City began to see its own sudden increase in cases, and other cities around the country were soon to follow. Certain pandemic restrictions, such as the closing of schools and theaters and staggered business hours to avoid congestion, were reimposed in cities like Chicago, Memphis, and New York City. As they had during the epidemic in fall 1918, schools in New York City remained open, while those in Memphis were shuttered as part of more general restrictions on public gatherings.
Amidst the spreading outbreak, Surgeon General Blue warned the public not to get "panicky" over the flu. Nevertheless, the United States Senate, Senate had sensed a turn in the tide (as the flu began to afflict their own families) and on 27 January passed an appropriations bill for $500,000 for the study of influenza. First introduced in July 1919 by Warren G. Harding, Senator Warren G. Harding after the third wave had subsided, the bill had been whittled down from $5 million. William H. King, Senator William H. King of Utah fundamentally opposed the bill, criticizing PHS for the "vast autocracy" it had become; James D. Phelan, Senator James D. Phelan of California sought to have the bill recommitted to the Committee on Public Health until there was an investigation into what previous flu funding had produced, but this failed. Ultimately, a letter from Carter Glass, United States Secretary of the Treasury, Secretary of the Treasury, regarding the outbreaks occurring in large cities and the threat they posed to the rest of the country persuaded many senators to vote for the package.
 The fourth wave in the United States subsided as swiftly as it had appeared, reaching a peak in early February. "An epidemic of considerable proportions marked the early months of 1920", the U.S. Mortality Statistics would later note; according to data at this time, the epidemic resulted in one third as many deaths as the 1918–1919 experience. New York City alone reported 6,374 deaths between December 1919 and April 1920, almost twice the number of the first wave in spring 1918. Other US cities including Detroit, Milwaukee, Kansas City, Minneapolis, and St. Louis were hit particularly hard, with death rates higher than all of 1918. The Territory of Hawaii experienced its peak of the pandemic in early 1920, recording 1,489 deaths from flu-related causes, compared with 615 in 1918 and 796 in 1919. Nenana, Alaska, had similarly avoided the extent of the pandemic for the previous two years, but by May 1920 an outbreak had consumed the town. Reports suggested that during the first two weeks of the month, the majority of the town's population became infected; 10% of the population were estimated to have died.
In winter and spring 1920, a fourth wave also occurred in various areas including Switzerland, Scandinavia, Mexico, and some South American islands. Poland experienced a devastating outbreak during the winter months, with its capital Warsaw reaching a peak of 158 deaths in a single week, compared to the peak of 92 reached in December 1918; however, the 1920 epidemic passed in a matter of weeks, while the 1918–1919 wave had developed over the entire second half of 1918. By contrast, the outbreak in western Europe was considered "benign", with the age distribution of deaths beginning to take on that of seasonal flu. Five countries in Europe (Spain, Denmark, Finland, Germany and Switzerland) recorded a late peak between January–April 1920. Peru experienced a late wave in early 1920, and Japan had one from late 1919 to 1920, with the last cases in March.
The fourth wave in the United States subsided as swiftly as it had appeared, reaching a peak in early February. "An epidemic of considerable proportions marked the early months of 1920", the U.S. Mortality Statistics would later note; according to data at this time, the epidemic resulted in one third as many deaths as the 1918–1919 experience. New York City alone reported 6,374 deaths between December 1919 and April 1920, almost twice the number of the first wave in spring 1918. Other US cities including Detroit, Milwaukee, Kansas City, Minneapolis, and St. Louis were hit particularly hard, with death rates higher than all of 1918. The Territory of Hawaii experienced its peak of the pandemic in early 1920, recording 1,489 deaths from flu-related causes, compared with 615 in 1918 and 796 in 1919. Nenana, Alaska, had similarly avoided the extent of the pandemic for the previous two years, but by May 1920 an outbreak had consumed the town. Reports suggested that during the first two weeks of the month, the majority of the town's population became infected; 10% of the population were estimated to have died.
In winter and spring 1920, a fourth wave also occurred in various areas including Switzerland, Scandinavia, Mexico, and some South American islands. Poland experienced a devastating outbreak during the winter months, with its capital Warsaw reaching a peak of 158 deaths in a single week, compared to the peak of 92 reached in December 1918; however, the 1920 epidemic passed in a matter of weeks, while the 1918–1919 wave had developed over the entire second half of 1918. By contrast, the outbreak in western Europe was considered "benign", with the age distribution of deaths beginning to take on that of seasonal flu. Five countries in Europe (Spain, Denmark, Finland, Germany and Switzerland) recorded a late peak between January–April 1920. Peru experienced a late wave in early 1920, and Japan had one from late 1919 to 1920, with the last cases in March.
 The basic reproduction number of the virus was between 2 and 3. The close quarters and massive troop movements of
The basic reproduction number of the virus was between 2 and 3. The close quarters and massive troop movements of  The majority of the infected experienced only the typical flu symptoms of sore throat, headache, and fever, especially during the first wave. However, during the second wave, the disease was much more serious, often complicated by bacterial pneumonia, which was often the cause of death. This more serious type would cause ''heliotrope cyanosis'' to develop, whereby the skin would first develop two mahogany spots over the cheekbones which would then over a few hours spread to color the entire face blue, followed by black coloration first in the extremities and then further spreading to the limbs and the torso. After this, death would follow within hours or days due to the lungs being filled with fluids. Other signs and symptoms reported included spontaneous mouth and nosebleeds, miscarriages for pregnant women, a peculiar smell, teeth, and hair falling, delirium, dizziness, insomnia, loss of hearing or smell, and impaired vision. One observer wrote, "One of the most striking of the complications was hemorrhage from mucous membranes, especially from the nose, stomach, and intestine. Bleeding from the ears and petechia, petechial hemorrhages in the skin also occurred". The severity of the symptoms was believed to be caused by
The majority of the infected experienced only the typical flu symptoms of sore throat, headache, and fever, especially during the first wave. However, during the second wave, the disease was much more serious, often complicated by bacterial pneumonia, which was often the cause of death. This more serious type would cause ''heliotrope cyanosis'' to develop, whereby the skin would first develop two mahogany spots over the cheekbones which would then over a few hours spread to color the entire face blue, followed by black coloration first in the extremities and then further spreading to the limbs and the torso. After this, death would follow within hours or days due to the lungs being filled with fluids. Other signs and symptoms reported included spontaneous mouth and nosebleeds, miscarriages for pregnant women, a peculiar smell, teeth, and hair falling, delirium, dizziness, insomnia, loss of hearing or smell, and impaired vision. One observer wrote, "One of the most striking of the complications was hemorrhage from mucous membranes, especially from the nose, stomach, and intestine. Bleeding from the ears and petechia, petechial hemorrhages in the skin also occurred". The severity of the symptoms was believed to be caused by  Studies have shown that the immune system of Spanish flu victims was weakened by adverse climate conditions which were particularly unseasonably cold and wet for extended periods of time during the duration of the pandemic. This affected especially WWI troops exposed to incessant rains and lower-than-average temperatures for the duration of the conflict, and especially during the second wave of the pandemic. Ultra-high-resolution climate data combined with highly detailed mortality records analyzed at Harvard University and the Climate Change Institute at the University of Maine identified a severe climate anomaly that impacted Europe from 1914 to 1919, with several environmental indicators directly influencing the severity and spread of the Spanish flu pandemic. Specifically, a significant increase in precipitation affected all of Europe during the second wave of the pandemic, from September to December 1918. Mortality figures follow closely the concurrent increase in precipitation and decrease in temperatures. Several explanations have been proposed for this, including the fact that lower temperatures and increased precipitation provided ideal conditions for virus replication and transmission, while also negatively affecting the immune systems of soldiers and other people exposed to the inclement weather, a factor proven to increase likelihood of infection by both viruses and pneumococcal co-morbid infections documented to have affected a large percentage of pandemic victims (one fifth of them, with a 36% mortality rate). A six-year climate anomaly (1914–1919) brought cold, marine air to Europe, drastically changing its weather, as documented by eyewitness accounts and instrumental records, reaching as far as the Gallipoli campaign, in Turkey, where ANZAC troops suffered extremely cold temperatures despite the normally Mediterranean climate of the region. The climate anomaly likely influenced the migration of H1N1 avian vectors which contaminate bodies of water with their droppings, reaching 60% infection rates in autumn. The climate anomaly has been associated with an anthropogenic increase in atmospheric dust, due to the incessant bombardment; increased nucleation due to dust particles (cloud condensation nuclei) contributed to increased precipitation.
Studies have shown that the immune system of Spanish flu victims was weakened by adverse climate conditions which were particularly unseasonably cold and wet for extended periods of time during the duration of the pandemic. This affected especially WWI troops exposed to incessant rains and lower-than-average temperatures for the duration of the conflict, and especially during the second wave of the pandemic. Ultra-high-resolution climate data combined with highly detailed mortality records analyzed at Harvard University and the Climate Change Institute at the University of Maine identified a severe climate anomaly that impacted Europe from 1914 to 1919, with several environmental indicators directly influencing the severity and spread of the Spanish flu pandemic. Specifically, a significant increase in precipitation affected all of Europe during the second wave of the pandemic, from September to December 1918. Mortality figures follow closely the concurrent increase in precipitation and decrease in temperatures. Several explanations have been proposed for this, including the fact that lower temperatures and increased precipitation provided ideal conditions for virus replication and transmission, while also negatively affecting the immune systems of soldiers and other people exposed to the inclement weather, a factor proven to increase likelihood of infection by both viruses and pneumococcal co-morbid infections documented to have affected a large percentage of pandemic victims (one fifth of them, with a 36% mortality rate). A six-year climate anomaly (1914–1919) brought cold, marine air to Europe, drastically changing its weather, as documented by eyewitness accounts and instrumental records, reaching as far as the Gallipoli campaign, in Turkey, where ANZAC troops suffered extremely cold temperatures despite the normally Mediterranean climate of the region. The climate anomaly likely influenced the migration of H1N1 avian vectors which contaminate bodies of water with their droppings, reaching 60% infection rates in autumn. The climate anomaly has been associated with an anthropogenic increase in atmospheric dust, due to the incessant bombardment; increased nucleation due to dust particles (cloud condensation nuclei) contributed to increased precipitation.
 The Spanish flu infected around 500 million people, about one-third of the world's population. Estimates as to how many infected people died vary greatly, but the flu is regardless considered to be one of the List of pandemics, deadliest pandemics in history. An early estimate from 1927 put global mortality at 21.6 million. An estimate from 1991 states that the virus killed between 25 and 39 million people. A 2005 estimate put the death toll at 50 million (about 3% of the global population), and possibly as high as 100 million (more than 5%). However, a 2018 reassessment in the ''American Journal of Epidemiology'' estimated the total to be about 17 million, though this has been contested. With a world population of 1.8 to 1.9 billion, these estimates correspond to between 1 and 6 percent of the population.
A 2009 study in ''Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses'' based on data from fourteen European countries estimated a total of 2.64 million excess deaths in Europe attributable to the Spanish flu during the major 1918–1919 phase of the pandemic, in line with the three prior studies from 1991, 2002, and 2006 that calculated a European death toll of between 2 million and 2.3 million. This represents a mortality rate of about 1.1% of the European population ( 250 million in 1918), considerably higher than the mortality rate in the US, which the authors hypothesize is likely due to the severe effects of the war in Europe. The excess mortality rate in the UK has been estimated at 0.28%–0.4%, far below this European average.
Some 12–17 million people died in 1918 flu pandemic in India, India, about 5% of the population. The death toll in British Raj, India's British-ruled districts was 13.88 million. Another estimate gives at least 12 million dead. The decade between 1911 and 1921 was the only census period in which India's population fell, mostly due to devastation of the Spanish flu pandemic. While India is generally described as the country most severely affected by the Spanish flu, at least one study argues that other factors may partially account for the very high excess mortality rates observed in 1918, citing unusually high 1917 mortality and wide regional variation (ranging from 0.47% to 6.66%). A 2006 study in ''
The Spanish flu infected around 500 million people, about one-third of the world's population. Estimates as to how many infected people died vary greatly, but the flu is regardless considered to be one of the List of pandemics, deadliest pandemics in history. An early estimate from 1927 put global mortality at 21.6 million. An estimate from 1991 states that the virus killed between 25 and 39 million people. A 2005 estimate put the death toll at 50 million (about 3% of the global population), and possibly as high as 100 million (more than 5%). However, a 2018 reassessment in the ''American Journal of Epidemiology'' estimated the total to be about 17 million, though this has been contested. With a world population of 1.8 to 1.9 billion, these estimates correspond to between 1 and 6 percent of the population.
A 2009 study in ''Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses'' based on data from fourteen European countries estimated a total of 2.64 million excess deaths in Europe attributable to the Spanish flu during the major 1918–1919 phase of the pandemic, in line with the three prior studies from 1991, 2002, and 2006 that calculated a European death toll of between 2 million and 2.3 million. This represents a mortality rate of about 1.1% of the European population ( 250 million in 1918), considerably higher than the mortality rate in the US, which the authors hypothesize is likely due to the severe effects of the war in Europe. The excess mortality rate in the UK has been estimated at 0.28%–0.4%, far below this European average.
Some 12–17 million people died in 1918 flu pandemic in India, India, about 5% of the population. The death toll in British Raj, India's British-ruled districts was 13.88 million. Another estimate gives at least 12 million dead. The decade between 1911 and 1921 was the only census period in which India's population fell, mostly due to devastation of the Spanish flu pandemic. While India is generally described as the country most severely affected by the Spanish flu, at least one study argues that other factors may partially account for the very high excess mortality rates observed in 1918, citing unusually high 1917 mortality and wide regional variation (ranging from 0.47% to 6.66%). A 2006 study in '' Even in areas where mortality was low, so many adults were incapacitated that much of everyday life was hampered. Some communities closed all stores or required customers to leave orders outside. There were reports that healthcare workers could not tend the sick nor the gravediggers bury the dead because they too were ill. Mass graves were dug by steam shovel and bodies buried without coffins in many places.
Bristol Bay, a region of Alaska populated by Alaska Natives, indigenous people, suffered a death rate of 40 percent of the total population, with some villages entirely disappearing.
Several Pacific island territories were hit particularly hard. The pandemic reached them from New Zealand, which was too slow to implement measures to prevent ships, such as , carrying the flu from leaving its ports. From New Zealand, the flu reached Tonga (killing 8% of the population), Nauru (16%), and Colony of Fiji, Fiji (5%, 9,000 people). Worst affected was Western Samoa, formerly German Samoa, which had been Occupation of German Samoa, occupied by New Zealand in 1914. 90% of the population was infected; 30% of adult men, 22% of adult women, and 10% of children died. By contrast, Governor of American Samoa, Governor John Martin Poyer prevented the flu from reaching neighboring American Samoa by imposing a blockade. The disease spread fastest through the higher social classes among the indigenous peoples, because of the custom of gathering oral tradition from chiefs on their deathbeds; many community elders were infected through this process.
In Qajar Iran, Iran, the mortality was very high: according to an estimate, between 902,400 and 2,431,000, or 8% to 22% of the total population died. The country was going through the Persian famine of 1917–1919 concurrently.
In History of Ireland (1801–1923), Ireland, during the worst 12 months, the Spanish flu accounted for one-third of all deaths.
In Union of South Africa, South Africa it is estimated that about 300,000 people amounting to 6% of the population died within six weeks. Government actions in the early stages of the virus' arrival in the country in September 1918 are believed to have unintentionally accelerated its spread throughout the country. Almost a quarter of the working population of Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley, consisting of workers in the diamond mines, died. In British Somaliland, one official estimated that 7% of the native population died. This huge death toll resulted from an extremely high infection rate of up to 50% and the extreme severity of the symptoms, suspected to be caused by
Even in areas where mortality was low, so many adults were incapacitated that much of everyday life was hampered. Some communities closed all stores or required customers to leave orders outside. There were reports that healthcare workers could not tend the sick nor the gravediggers bury the dead because they too were ill. Mass graves were dug by steam shovel and bodies buried without coffins in many places.
Bristol Bay, a region of Alaska populated by Alaska Natives, indigenous people, suffered a death rate of 40 percent of the total population, with some villages entirely disappearing.
Several Pacific island territories were hit particularly hard. The pandemic reached them from New Zealand, which was too slow to implement measures to prevent ships, such as , carrying the flu from leaving its ports. From New Zealand, the flu reached Tonga (killing 8% of the population), Nauru (16%), and Colony of Fiji, Fiji (5%, 9,000 people). Worst affected was Western Samoa, formerly German Samoa, which had been Occupation of German Samoa, occupied by New Zealand in 1914. 90% of the population was infected; 30% of adult men, 22% of adult women, and 10% of children died. By contrast, Governor of American Samoa, Governor John Martin Poyer prevented the flu from reaching neighboring American Samoa by imposing a blockade. The disease spread fastest through the higher social classes among the indigenous peoples, because of the custom of gathering oral tradition from chiefs on their deathbeds; many community elders were infected through this process.
In Qajar Iran, Iran, the mortality was very high: according to an estimate, between 902,400 and 2,431,000, or 8% to 22% of the total population died. The country was going through the Persian famine of 1917–1919 concurrently.
In History of Ireland (1801–1923), Ireland, during the worst 12 months, the Spanish flu accounted for one-third of all deaths.
In Union of South Africa, South Africa it is estimated that about 300,000 people amounting to 6% of the population died within six weeks. Government actions in the early stages of the virus' arrival in the country in September 1918 are believed to have unintentionally accelerated its spread throughout the country. Almost a quarter of the working population of Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley, consisting of workers in the diamond mines, died. In British Somaliland, one official estimated that 7% of the native population died. This huge death toll resulted from an extremely high infection rate of up to 50% and the extreme severity of the symptoms, suspected to be caused by  Estimates for the death toll in China have varied widely, a range which reflects the lack of centralized collection of health data at the time due to the Warlord Era, Warlord period. Republic of China (1912–1949), China may have experienced a relatively mild flu season in 1918 compared to other areas of the world. However, some reports from its interior suggest that mortality rates from influenza were perhaps higher in at least a few locations in China in 1918. At the very least, there is little evidence that China as a whole was seriously affected by the flu compared to other countries in the world.
The first estimate of the Chinese death toll was made in 1991 by Patterson and Pyle, which estimated a toll of between 5 and 9 million. However, this 1991 study was criticized by later studies due to flawed methodology, and newer studies have published estimates of a far lower mortality rate in China. For instance, Iijima in 1998 estimates the death toll in China to be between 1 and 1.28 million based on data available from Chinese port cities. The lower estimates of the Chinese death toll are based on the low mortality rates that were found in Chinese port cities (for example, Hong Kong) and on the assumption that poor communications prevented the flu from penetrating the interior of China. However, some contemporary newspaper and post office reports, as well as reports from missionary doctors, suggest that the flu did penetrate the Chinese interior and that influenza was severe in at least some locations in the countryside of China.
Although medical records from China's interior are lacking, extensive medical data were recorded in Chinese port cities, such as then British Empire, British-controlled British Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Guangzhou, Canton, Beijing, Peking, Harbin and Shanghai. These data were collected by the Chinese Maritime Customs Service, which was largely staffed by non-Chinese foreigners, such as the British, French, and other European Colonialism, colonial officials in China. As a whole, data from China's port cities show low mortality rates compared to other cities in Asia. For example, the British authorities at Hong Kong and Canton reported a mortality rate from influenza at a rate of 0.25% and 0.32%, much lower than the reported mortality rate of other cities in Asia, such as Kolkata, Calcutta or Mumbai, Bombay, where influenza was much more devastating. Similarly, in the city of Shanghai – which had a population of over 2 million in 1918 – there were only 266 recorded deaths from
Estimates for the death toll in China have varied widely, a range which reflects the lack of centralized collection of health data at the time due to the Warlord Era, Warlord period. Republic of China (1912–1949), China may have experienced a relatively mild flu season in 1918 compared to other areas of the world. However, some reports from its interior suggest that mortality rates from influenza were perhaps higher in at least a few locations in China in 1918. At the very least, there is little evidence that China as a whole was seriously affected by the flu compared to other countries in the world.
The first estimate of the Chinese death toll was made in 1991 by Patterson and Pyle, which estimated a toll of between 5 and 9 million. However, this 1991 study was criticized by later studies due to flawed methodology, and newer studies have published estimates of a far lower mortality rate in China. For instance, Iijima in 1998 estimates the death toll in China to be between 1 and 1.28 million based on data available from Chinese port cities. The lower estimates of the Chinese death toll are based on the low mortality rates that were found in Chinese port cities (for example, Hong Kong) and on the assumption that poor communications prevented the flu from penetrating the interior of China. However, some contemporary newspaper and post office reports, as well as reports from missionary doctors, suggest that the flu did penetrate the Chinese interior and that influenza was severe in at least some locations in the countryside of China.
Although medical records from China's interior are lacking, extensive medical data were recorded in Chinese port cities, such as then British Empire, British-controlled British Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Guangzhou, Canton, Beijing, Peking, Harbin and Shanghai. These data were collected by the Chinese Maritime Customs Service, which was largely staffed by non-Chinese foreigners, such as the British, French, and other European Colonialism, colonial officials in China. As a whole, data from China's port cities show low mortality rates compared to other cities in Asia. For example, the British authorities at Hong Kong and Canton reported a mortality rate from influenza at a rate of 0.25% and 0.32%, much lower than the reported mortality rate of other cities in Asia, such as Kolkata, Calcutta or Mumbai, Bombay, where influenza was much more devastating. Similarly, in the city of Shanghai – which had a population of over 2 million in 1918 – there were only 266 recorded deaths from  The pandemic mostly killed young adults. In 1918–1919, 99% of pandemic influenza deaths in the U.S. occurred in people under 65, and nearly half of deaths were in young adults 20 to 40 years old. In 1920, the mortality rate among people under 65 had decreased sixfold to half the mortality rate of people over 65, but 92% of deaths still occurred in people under 65. This is unusual since influenza is typically most deadly to weak individuals, such as infants under age two, adults over age 70, and the immunocompromised. In 1918, older adults may have had partial protection caused by exposure to the 1889–1890 flu pandemic, known as the "Russian flu".Hanssen, Olav. Undersøkelser over influenzaens optræden specielt i Bergen 1918–1922. Bg. 1923. 66 s. ill. (Haukeland sykehus. Med. avd. Arb. 2) (Klaus Hanssens fond. Skr. 3) According to historian John M. Barry, the most vulnerable of all – "those most likely, of the most likely", to die – were pregnant women. He reported that in thirteen studies of hospitalized women in the pandemic, the death rate ranged from 23% to 71%. Of the pregnant women who survived childbirth, over one-quarter (26%) lost the child. Another oddity was that the outbreak was widespread in the summer and autumn (in the Northern Hemisphere); influenza is usually worse in winter.
There were also geographic patterns to the disease's fatality. Some parts of Asia had 30 times higher death rates than some parts of Europe, and generally, Africa and Asia had higher rates, while Europe and North America had lower ones. There was also great variation within continents, with three times higher mortality in Hungary and Spain compared to Denmark, two to three times higher chance of death in Sub-Saharan Africa compared to North Africa, and possibly up to ten times higher rates between the extremes of Asia. Cities were affected worse than rural areas. There were also differences between cities, which might have reflected exposure to the milder first wave giving immunity, as well as the introduction of social distancing measures.
Another major pattern was the differences between social classes. In Oslo, death rates were inversely correlated with apartment size, as the poorer people living in smaller apartments died at a higher rate. Social status was also reflected in the higher mortality among immigrant communities, with Italian Americans, a recently arrived group at the time, were nearly twice as likely to die compared to the average Americans. These disparities reflected worse diets, crowded living conditions, and problems accessing healthcare. Paradoxically, however, African Americans were relatively spared by the pandemic.
More men than women were killed by the flu, as they were more likely to go out and be exposed, while women would tend to Housewife, stay at home. For the same reason men also were more likely to have pre-existing tuberculosis, which severely worsened the chances of recovery. However, in India the opposite was true, potentially because Indian women were neglected with poorer nutrition, and were expected to care for the sick.
A study conducted by He ''et al''. (2011) used a mechanistic modeling approach to study the three waves of the 1918 influenza pandemic. They examined the factors that underlie variability in temporal patterns and their correlation to patterns of mortality and morbidity. Their analysis suggests that temporal variations in transmission rate provide the best explanation, and the variation in transmission required to generate these three waves is within biologically plausible values. Another study by He ''et al''. (2013) used a simple epidemic model incorporating three factors to infer the cause of the three waves of the 1918 influenza pandemic. These factors were school opening and closing, temperature changes throughout the outbreak, and human behavioral changes in response to the outbreak. Their modeling results showed that all three factors are important, but human behavioral responses showed the most significant effects.
The pandemic mostly killed young adults. In 1918–1919, 99% of pandemic influenza deaths in the U.S. occurred in people under 65, and nearly half of deaths were in young adults 20 to 40 years old. In 1920, the mortality rate among people under 65 had decreased sixfold to half the mortality rate of people over 65, but 92% of deaths still occurred in people under 65. This is unusual since influenza is typically most deadly to weak individuals, such as infants under age two, adults over age 70, and the immunocompromised. In 1918, older adults may have had partial protection caused by exposure to the 1889–1890 flu pandemic, known as the "Russian flu".Hanssen, Olav. Undersøkelser over influenzaens optræden specielt i Bergen 1918–1922. Bg. 1923. 66 s. ill. (Haukeland sykehus. Med. avd. Arb. 2) (Klaus Hanssens fond. Skr. 3) According to historian John M. Barry, the most vulnerable of all – "those most likely, of the most likely", to die – were pregnant women. He reported that in thirteen studies of hospitalized women in the pandemic, the death rate ranged from 23% to 71%. Of the pregnant women who survived childbirth, over one-quarter (26%) lost the child. Another oddity was that the outbreak was widespread in the summer and autumn (in the Northern Hemisphere); influenza is usually worse in winter.
There were also geographic patterns to the disease's fatality. Some parts of Asia had 30 times higher death rates than some parts of Europe, and generally, Africa and Asia had higher rates, while Europe and North America had lower ones. There was also great variation within continents, with three times higher mortality in Hungary and Spain compared to Denmark, two to three times higher chance of death in Sub-Saharan Africa compared to North Africa, and possibly up to ten times higher rates between the extremes of Asia. Cities were affected worse than rural areas. There were also differences between cities, which might have reflected exposure to the milder first wave giving immunity, as well as the introduction of social distancing measures.
Another major pattern was the differences between social classes. In Oslo, death rates were inversely correlated with apartment size, as the poorer people living in smaller apartments died at a higher rate. Social status was also reflected in the higher mortality among immigrant communities, with Italian Americans, a recently arrived group at the time, were nearly twice as likely to die compared to the average Americans. These disparities reflected worse diets, crowded living conditions, and problems accessing healthcare. Paradoxically, however, African Americans were relatively spared by the pandemic.
More men than women were killed by the flu, as they were more likely to go out and be exposed, while women would tend to Housewife, stay at home. For the same reason men also were more likely to have pre-existing tuberculosis, which severely worsened the chances of recovery. However, in India the opposite was true, potentially because Indian women were neglected with poorer nutrition, and were expected to care for the sick.
A study conducted by He ''et al''. (2011) used a mechanistic modeling approach to study the three waves of the 1918 influenza pandemic. They examined the factors that underlie variability in temporal patterns and their correlation to patterns of mortality and morbidity. Their analysis suggests that temporal variations in transmission rate provide the best explanation, and the variation in transmission required to generate these three waves is within biologically plausible values. Another study by He ''et al''. (2013) used a simple epidemic model incorporating three factors to infer the cause of the three waves of the 1918 influenza pandemic. These factors were school opening and closing, temperature changes throughout the outbreak, and human behavioral changes in response to the outbreak. Their modeling results showed that all three factors are important, but human behavioral responses showed the most significant effects.
 Many businesses in the entertainment and service industries suffered losses in revenue, while the healthcare industry reported profit gains. Historian Nancy Bristow has argued that the pandemic, when combined with the increasing number of women attending college, contributed to the success of women in the field of nursing. This was due in part to the failure of medical doctors, who were predominantly men, to contain and prevent the illness. Nursing staff, who were mainly women, celebrated the success of their patient care and did not associate the spread of the disease with their work.
A 2020 study found that US cities that implemented early and extensive non-medical measures (quarantine, etc.) suffered no additional adverse economic effects due to implementing those measures,
however, the validity of this study has been questioned because of the coincidence of WWI and other problems with data reliability.
Many businesses in the entertainment and service industries suffered losses in revenue, while the healthcare industry reported profit gains. Historian Nancy Bristow has argued that the pandemic, when combined with the increasing number of women attending college, contributed to the success of women in the field of nursing. This was due in part to the failure of medical doctors, who were predominantly men, to contain and prevent the illness. Nursing staff, who were mainly women, celebrated the success of their patient care and did not associate the spread of the disease with their work.
A 2020 study found that US cities that implemented early and extensive non-medical measures (quarantine, etc.) suffered no additional adverse economic effects due to implementing those measures,
however, the validity of this study has been questioned because of the coincidence of WWI and other problems with data reliability.
 Despite the high morbidity and mortality rates that resulted from the epidemic, the Spanish flu began to fade from public awareness over the decades until the arrival of news about Avian influenza, bird flu and other pandemics in the 1990s and 2000s. This has led some historians to label the Spanish flu a "forgotten pandemic". However, this label has been challenged by the historian Guy Beiner, who has charted a complex history of social and cultural forgetting, demonstrating how the pandemic was overshadowed by the commemoration of the First World War and mostly neglected in mainstream historiography, yet was remembered in private and local traditions across the globe.
There are various theories of why the Spanish flu was "forgotten". The rapid pace of the pandemic, which killed most of its victims in the United States within less than nine months, resulted in limited media coverage. The general population was familiar with patterns of pandemic disease in the late 19th and early 20th centuries: typhoid, yellow fever, diphtheria, and cholera all occurred near the same time. These outbreaks probably lessened the significance of the influenza pandemic for the public. In some areas, the flu was not reported on, the only mention being that of advertisements for medicines claiming to cure it.
Additionally, the outbreak coincided with the deaths and media focus on the First World War. Another explanation involves the age group affected by the disease. The majority of fatalities, from both the war and the epidemic, were among young adults. The high number of war-related deaths of young adults may have overshadowed the deaths caused by flu.
When people read the obituaries, they saw the war or postwar deaths and the deaths from the influenza side by side. Particularly in Europe, where the war's toll was high, the flu may not have had a tremendous psychological impact or may have seemed an extension of the war's tragedies. The duration of the pandemic and the war could have also played a role. The disease would usually only affect a particular area for a month before leaving. The war, however, had initially been expected to end quickly but lasted for four years by the time the pandemic struck.
Despite the high morbidity and mortality rates that resulted from the epidemic, the Spanish flu began to fade from public awareness over the decades until the arrival of news about Avian influenza, bird flu and other pandemics in the 1990s and 2000s. This has led some historians to label the Spanish flu a "forgotten pandemic". However, this label has been challenged by the historian Guy Beiner, who has charted a complex history of social and cultural forgetting, demonstrating how the pandemic was overshadowed by the commemoration of the First World War and mostly neglected in mainstream historiography, yet was remembered in private and local traditions across the globe.
There are various theories of why the Spanish flu was "forgotten". The rapid pace of the pandemic, which killed most of its victims in the United States within less than nine months, resulted in limited media coverage. The general population was familiar with patterns of pandemic disease in the late 19th and early 20th centuries: typhoid, yellow fever, diphtheria, and cholera all occurred near the same time. These outbreaks probably lessened the significance of the influenza pandemic for the public. In some areas, the flu was not reported on, the only mention being that of advertisements for medicines claiming to cure it.
Additionally, the outbreak coincided with the deaths and media focus on the First World War. Another explanation involves the age group affected by the disease. The majority of fatalities, from both the war and the epidemic, were among young adults. The high number of war-related deaths of young adults may have overshadowed the deaths caused by flu.
When people read the obituaries, they saw the war or postwar deaths and the deaths from the influenza side by side. Particularly in Europe, where the war's toll was high, the flu may not have had a tremendous psychological impact or may have seemed an extension of the war's tragedies. The duration of the pandemic and the war could have also played a role. The disease would usually only affect a particular area for a month before leaving. The war, however, had initially been expected to end quickly but lasted for four years by the time the pandemic struck.
 The origin of the Spanish flu pandemic, and the relationship between the near-simultaneous outbreaks in humans and swine, have been controversial. One hypothesis is that the virus strain originated at Fort Riley, Kansas, in viruses in poultry and swine which the fort bred for food; the soldiers were then sent from Fort Riley around the world, where they spread the disease. Similarities between a reconstruction of the virus and avian viruses, combined with the human pandemic preceding the first reports of influenza in swine, led researchers to conclude the influenza virus jumped directly from birds to humans, and swine caught the disease from humans.
Others have disagreed, and more recent research has suggested the strain may have originated in a nonhuman, mammalian species. An estimated date for its appearance in mammalian hosts has been put at the period 1882–1913. This ancestor virus diverged about 1913–1915 into two clades (or biological groups each descended from a common ancestor), which gave rise to the classical swine and human H1N1 influenza lineages. The last common ancestor of human strains dates between February 1917 and April 1918. Because pigs are more readily infected with avian influenza viruses than are humans, they were suggested as the original recipients of the virus, passing the virus to humans sometime between 1913 and 1918.
The origin of the Spanish flu pandemic, and the relationship between the near-simultaneous outbreaks in humans and swine, have been controversial. One hypothesis is that the virus strain originated at Fort Riley, Kansas, in viruses in poultry and swine which the fort bred for food; the soldiers were then sent from Fort Riley around the world, where they spread the disease. Similarities between a reconstruction of the virus and avian viruses, combined with the human pandemic preceding the first reports of influenza in swine, led researchers to conclude the influenza virus jumped directly from birds to humans, and swine caught the disease from humans.
Others have disagreed, and more recent research has suggested the strain may have originated in a nonhuman, mammalian species. An estimated date for its appearance in mammalian hosts has been put at the period 1882–1913. This ancestor virus diverged about 1913–1915 into two clades (or biological groups each descended from a common ancestor), which gave rise to the classical swine and human H1N1 influenza lineages. The last common ancestor of human strains dates between February 1917 and April 1918. Because pigs are more readily infected with avian influenza viruses than are humans, they were suggested as the original recipients of the virus, passing the virus to humans sometime between 1913 and 1918.
 An effort to recreate the Spanish flu strain (a subtype of avian strain H1N1) was a collaboration among the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, the USDA Agricultural Research Service, ARS Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City. The effort resulted in the announcement (on 5 October 2005) that the group had successfully determined the virus's genetic sequence, using historic tissue samples recovered by pathologist Johan Hultin from an Inuit female flu victim buried in the Alaskan permafrost and samples preserved from American soldiers Roscoe Vaughan and James Downs.
On 18 January 2007, Kobasa et al. (2007) reported that monkeys (''Macaca fascicularis'') infected with the recreated flu strain exhibited classic symptoms of the 1918 pandemic, and died from cytokine storms – an overreaction of the immune system. This may explain why the Spanish flu had its surprising effect on younger, healthier people, as a person with a stronger immune system would potentially have a stronger overreaction.
On 16 September 2008, the body of British politician and diplomat Mark Sykes, Sir Mark Sykes was exhumed to study the RNA of the flu virus in efforts to understand the genetic structure of modern H5N1 bird flu. Sykes had been buried in 1919 in a lead coffin which scientists hoped had helped preserve the virus. The coffin was found to be split and the cadaver badly decomposed; nonetheless, samples of lung and brain tissue were taken.
In December 2008, research by Yoshihiro Kawaoka of the University of Wisconsin linked the presence of three specific genes (termed PA, PB1, and PB2) and a nucleoprotein derived from Spanish flu samples to the ability of the flu virus to invade the lungs and cause pneumonia. The combination triggered similar symptoms in animal testing.
In June 2010, a team at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine reported the 2009 flu pandemic vaccine provided some cross-protection against the Spanish flu pandemic strain.
One of the few things known for certain about influenza in 1918 and for some years after was that it was, except in the laboratory, exclusively a disease of human beings.
In 2013, the AIR Worldwide Research and Modeling Group "characterized the historic 1918 pandemic and estimated the effects of a similar pandemic occurring today using the AIR Pandemic Flu Model". In the model, "a modern-day 'Spanish flu' event would result in additional life insurance losses of between US$15.3–27.8 billion in the United States alone", with 188,000–337,000 deaths in the United States.
In 2018, Michael Worobey, an evolutionary biology professor at the University of Arizona who is examining the history of the 1918 pandemic, revealed that he obtained tissue slides created by William Rolland, a physician who reported on a respiratory illness likely to be the virus while a pathologist in the British military during World War One. Rolland had authored an article in the ''Lancet (journal), Lancet'' during 1917 about a respiratory illness outbreak beginning in 1916 in Étaples, France. Worobey traced recent references to that article to family members who had retained slides that Rolland had prepared during that time. Worobey extracted tissue from the slides to potentially reveal more about the origin of the pathogen.
In 2021 an investigation used the virus sequence to obtain the Hemagglutinin (influenza), Hemagglutinin (HA) antigen and observe the adaptive immunity in 32 survivors of the 1918 flu pandemic, all of them presented seroreactivity and 7 of 8 further tested presented memory B cells able to produce antibodies that bound to the HA antigen highlighting the ability of the immunological memory many decades after.
An effort to recreate the Spanish flu strain (a subtype of avian strain H1N1) was a collaboration among the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, the USDA Agricultural Research Service, ARS Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory, and Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City. The effort resulted in the announcement (on 5 October 2005) that the group had successfully determined the virus's genetic sequence, using historic tissue samples recovered by pathologist Johan Hultin from an Inuit female flu victim buried in the Alaskan permafrost and samples preserved from American soldiers Roscoe Vaughan and James Downs.
On 18 January 2007, Kobasa et al. (2007) reported that monkeys (''Macaca fascicularis'') infected with the recreated flu strain exhibited classic symptoms of the 1918 pandemic, and died from cytokine storms – an overreaction of the immune system. This may explain why the Spanish flu had its surprising effect on younger, healthier people, as a person with a stronger immune system would potentially have a stronger overreaction.
On 16 September 2008, the body of British politician and diplomat Mark Sykes, Sir Mark Sykes was exhumed to study the RNA of the flu virus in efforts to understand the genetic structure of modern H5N1 bird flu. Sykes had been buried in 1919 in a lead coffin which scientists hoped had helped preserve the virus. The coffin was found to be split and the cadaver badly decomposed; nonetheless, samples of lung and brain tissue were taken.
In December 2008, research by Yoshihiro Kawaoka of the University of Wisconsin linked the presence of three specific genes (termed PA, PB1, and PB2) and a nucleoprotein derived from Spanish flu samples to the ability of the flu virus to invade the lungs and cause pneumonia. The combination triggered similar symptoms in animal testing.
In June 2010, a team at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine reported the 2009 flu pandemic vaccine provided some cross-protection against the Spanish flu pandemic strain.
One of the few things known for certain about influenza in 1918 and for some years after was that it was, except in the laboratory, exclusively a disease of human beings.
In 2013, the AIR Worldwide Research and Modeling Group "characterized the historic 1918 pandemic and estimated the effects of a similar pandemic occurring today using the AIR Pandemic Flu Model". In the model, "a modern-day 'Spanish flu' event would result in additional life insurance losses of between US$15.3–27.8 billion in the United States alone", with 188,000–337,000 deaths in the United States.
In 2018, Michael Worobey, an evolutionary biology professor at the University of Arizona who is examining the history of the 1918 pandemic, revealed that he obtained tissue slides created by William Rolland, a physician who reported on a respiratory illness likely to be the virus while a pathologist in the British military during World War One. Rolland had authored an article in the ''Lancet (journal), Lancet'' during 1917 about a respiratory illness outbreak beginning in 1916 in Étaples, France. Worobey traced recent references to that article to family members who had retained slides that Rolland had prepared during that time. Worobey extracted tissue from the slides to potentially reveal more about the origin of the pathogen.
In 2021 an investigation used the virus sequence to obtain the Hemagglutinin (influenza), Hemagglutinin (HA) antigen and observe the adaptive immunity in 32 survivors of the 1918 flu pandemic, all of them presented seroreactivity and 7 of 8 further tested presented memory B cells able to produce antibodies that bound to the HA antigen highlighting the ability of the immunological memory many decades after.