$FONT.SYS on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
DOS/V is a Japanese computing initiative starting in 1990 to allow
 In 1993, Microsoft Japan released first retail versions of Windows (
In 1993, Microsoft Japan released first retail versions of Windows (
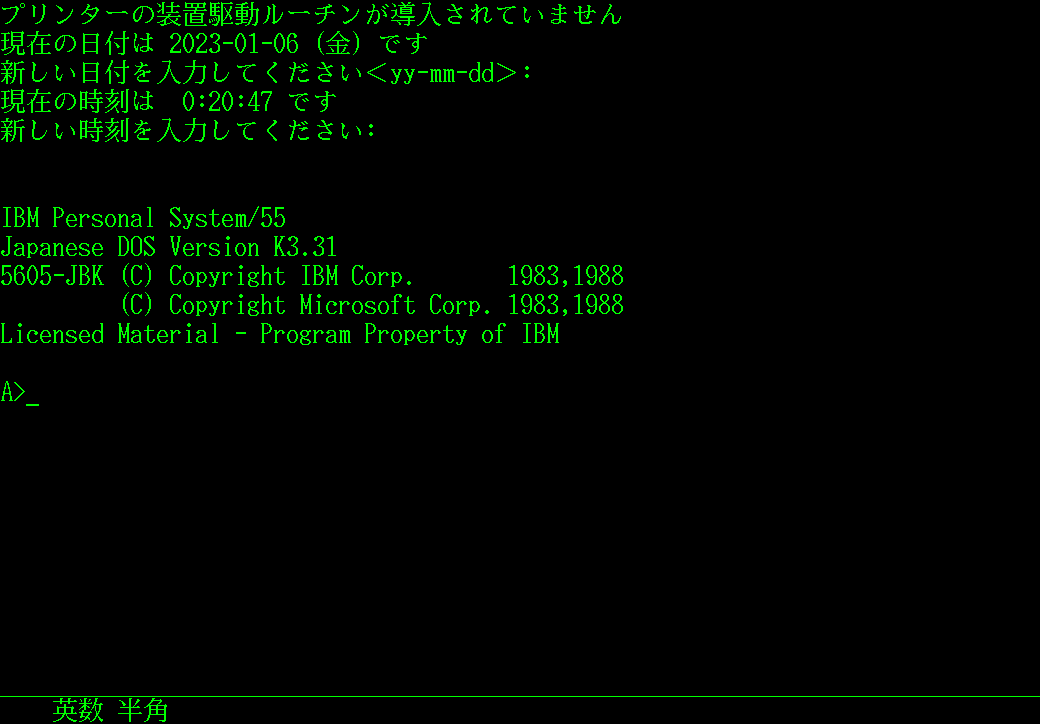 In 1988, IBM Japan released a new model of the PS/55 which was based on the PS/2 with Japanese language support. It is equipped with a proprietary video card, the Display Adapter, which has a high resolution
In 1988, IBM Japan released a new model of the PS/55 which was based on the PS/2 with Japanese language support. It is equipped with a proprietary video card, the Display Adapter, which has a high resolution  The first version of DOS/V, IBM DOS J4.0/V (J4.05/V), was released in the end of 1990. The word 'DOS/V' was quickly known to Japanese computer industry, but the DOS/V itself didn't spread quickly. As of 1991, some small companies sold American or Taiwanese computers in Japan, but DOS J4.0/V caused some issues on PC compatibles. Its EMS driver only supports IBM's Expanded Memory Adapter. The
The first version of DOS/V, IBM DOS J4.0/V (J4.05/V), was released in the end of 1990. The word 'DOS/V' was quickly known to Japanese computer industry, but the DOS/V itself didn't spread quickly. As of 1991, some small companies sold American or Taiwanese computers in Japan, but DOS J4.0/V caused some issues on PC compatibles. Its EMS driver only supports IBM's Expanded Memory Adapter. The
IBM DOS J5.02V disks.jpg, IBM DOS J5.02/V
MS-DOS 6.2V floppy disks.jpg, Japanese MS-DOS 6.2/V floppy disks
MS-DOS 6.2-V User's Guide Japanese cover 20130608.jpg, MS-DOS 6.2/V user's guide
DOS
DOS is shorthand for the MS-DOS and IBM PC DOS family of operating systems.
DOS may also refer to:
Computing
* Data over signalling (DoS), multiplexing data onto a signalling channel
* Denial-of-service attack (DoS), an attack on a communicat ...
on IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are similar to the original IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC, IBM Personal Computer XT, XT, and IBM Personal Computer/AT, AT, all from computer giant IBM, that are able to use the same software and expansion cards. Such ...
s with VGA cards to handle double-byte (DBCS) Japanese text via software alone. It was initially developed from PC DOS
PC or pc may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Player character or playable character, a fictional character controlled by a human player, usually in role-playing games or computer games
* '' Port Charles'', an American daytime TV soap opera
* ...
by IBM for its PS/55 machines (a localized version of the PS/2), but IBM gave the driver source code to Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washin ...
, who then licensed a DOS/V-compatible version of MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few ope ...
to other companies. Kanji
are the logographic Chinese characters taken from the Chinese family of scripts, Chinese script and used in the writing of Japanese language, Japanese. They were made a major part of the Japanese writing system during the time of Old Japanese ...
fonts and other locale information are stored on the hard disk rather than on special chips as in the preceding AX architecture. As with AX, its great value for the Japanese computing industry is in allowing compatibility with foreign software. This had not been possible under NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It provides IT and network soluti ...
's proprietary PC-98
The , commonly shortened to PC-98 or , is a lineup of Japanese 16-bit and 32-bit personal computers manufactured by NEC from 1982 to 2000. The platform established NEC's dominance in the Japanese personal computer market, and, by 1999, more th ...
system, which was the market leader before DOS/V emerged. DOS/V stands for "Disk Operating System/VGA
Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a video display controller and accompanying de facto graphics standard, first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, which became ubiquitous in the PC industry within three years. The term can no ...
" (not "version 5"; DOS/V came out at approximately the same time as DOS 5). In Japan, IBM compatible PCs became popular along with DOS/V, so they are often referred to as "DOS/V machine" or "DOS/V pasocom" even though DOS/V operating systems are no longer common.
The promotion of DOS/V was done by IBM and its consortium called PC Open Architecture Developers' Group (OADG).
Digital Research
Digital Research, Inc. (DR or DRI) was a company created by Gary Kildall to market and develop his CP/M operating system and related 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit systems like MP/M, Concurrent DOS, FlexOS, Multiuser DOS, DOS Plus, DR DOS and Gr ...
released a Japanese DOS/V-compatible version of DR DOS
DR-DOS (written as DR DOS, without a hyphen, in versions up to and including 6.0) is a disk operating system for IBM PC compatibles. Upon its introduction in 1988, it was the first DOS attempting to be compatible with IBM PC DOS and MS- ...
6.0 in 1992.
History
In the early 1980s,IBM Japan
IBM has had business internationally since before the company had a name. Early leaders of the companies that would eventually become IBM (Mr Hollerith, Mr Flint, and Mr Watson) all were involved in doing international business.
In those early day ...
developed two x86-based personal computer lines for the Asia-Pacific region, IBM 5550 and IBM JX. The 5550 reads Kanji fonts from the disk, and draws text as graphic characters on 1024×768 high resolution monitor. The JX extends IBM PCjr and IBM PC architecture. It supports English and Japanese versions of PC DOS
PC or pc may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Player character or playable character, a fictional character controlled by a human player, usually in role-playing games or computer games
* '' Port Charles'', an American daytime TV soap opera
* ...
with 720×512 resolution monitor. Both machines couldn't break dominant NEC's PC-98 in consumer market in Japan. Because the 5550 was expensive, it was mostly sold for large enterprises who used IBM's mainframe. The JX used 8088
The Intel 8088 ("''eighty-eighty-eight''", also called iAPX 88) microprocessor is a variant of the Intel 8086. Introduced on June 1, 1979, the 8088 has an eight-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers a ...
processor instead of faster 8086
The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-bit data bus (allowi ...
processor because IBM thought a consumer-class JX mustn't surpass a business-class 5550. It damaged buyer's reputations whatever the actual speed was. In another point, a software company said IBM was uncooperative for developing JX software. IBM Japan planned a 100% PC/AT
The IBM Personal Computer/AT (model 5170, abbreviated as IBM AT or PC/AT) was released in 1984 as the fourth model in the IBM Personal Computer line, following the IBM PC/XT and its IBM Portable PC variant. It was designed around the Intel 802 ...
compatible machine codenamed "JX2", but cancelled it in 1986.
Masahiko Hatori was a developer of JX's DOS. Through the development of JX, he learned the skills needed to localize an English computer into Japanese. In 1987, he started developing the DOS/V during spare time at IBM Yamato Development Laboratory. He thought the 480-line mode of VGA and a processor as fast as the 80386 would realize his idea, but they were expensive hardwares as of 1987. In this era, Toshiba
, commonly known as Toshiba and stylized as TOSHIBA, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, ...
released the J-3100 laptop computer, and Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washin ...
introduced the AX architecture. IBM Japan didn't join in the AX consortium. His boss, Tsutomu Maruyama , thought IBM's headquarters wouldn't allow to adopt the AX because they requested IBM Japan to use the same standard as worldwide IBM offices used. In October 1987, IBM Japan released the PS/55 Model 5535 which was a proprietary laptop using a special version of DOS. It was more expensive than the J-3100 because its LCD display used a non-standard 720×512 resolution. Hatori thought IBM needed to shift their own proprietary PC to IBM PC compatibles. Maruyama and Nobuo Mii thought Japan's closed PC market needed to be changed and this attempt couldn't be done by IBM alone. In summer of 1989, they decided to carry out the development of DOS/V, disclose the architecture of PS/55, and found the PC Open Architecture Developers' Group (OADG).
The DOS/V development team designed the DOS/V to be simple for better scalability and compatibility with original PC DOS. They had difficulty reducing text drawing time. "A stopwatch was a necessity for DOS/V development", Hatori said.
IBM Japan announced the first version of DOS/V, IBM DOS J4.0/V, on 11 October 1990, and shipped out in November 1990. At the same time, IBM Japan released the PS/55 Model 5535-S, a laptop computer with VGA resolution. The announcement letter stated DOS/V was designed for low-end desktops and laptops of PS/55, but users reported on BBS
BBS may refer to:
Ammunition
* BBs, BB gun metal bullets
* BBs, airsoft gun plastic pellets
Computing and gaming
* Bulletin board system, a computer server users dial into via dial-up or telnet; precursor to the Internet
* BIOS Boot Specificat ...
that they could run DOS/V on IBM PC clone
IBM PC compatible computers are similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT, all from computer giant IBM, that are able to use the same software and expansion cards. Such computers were referred to as PC clones, IBM clones or IBM PC clones. ...
s. The development team unofficially confirmed these comments, and modified incompatibilities of DOS/V. It was a secret inside the company because it would prevent sales of PS/55 and meet with opposition. Hatori said,
Maruyama and Mii had to convince IBM's branches to agree with the plan. In the beginning of December 1990, Maruyama went to IBM's Management Committee, and presented his plan "The low-end PC strategy in Japan". At the committee, a topic usually took 15 minutes, but his topic took an hour. The plan was finally approved by John Akers
John Fellows Akers (December 28, 1934 – August 22, 2014) was an American businessman. He was president (1983-1989), chief executive officer (1985-1993) and chairman (1986-1993) of IBM.
Education
Akers attended Yale, and while there became a bro ...
.
After the committee, Susumu Furukawa, a president of Microsoft Japan
Microsoft Japan, officially , is a subsidiary of Microsoft based in Japan. Their headquarters are near to Shinagawa station at Minato-ku district of Tokyo.
History
In 1978, Kazuhiko Nishi, co-founder of ASCII Publisher, partnered with Bill ...
, could make an appointment with IBM Japan to share the source code of DOS/V. On 20 December 1990, IBM Japan announced they founded OADG and Microsoft would supply DOS/V for other PC manufacturers. From 1992 to 1994, many Japanese manufacturers began selling IBM PC clones with DOS/V. Some global PC manufacturers entered into the Japanese market, Compaq
Compaq Computer Corporation (sometimes abbreviated to CQ prior to a 2007 rebranding) was an American information technology company founded in 1982 that developed, sold, and supported computers and related products and services. Compaq produced ...
in 1992 and Dell in 1993. Fujitsu released IBM PC clones (FMV series) in October 1993, and about 200,000 units were shipped in 1994.
The initial goal of DOS/V was to enable Japanese software to run on laptop computers based on the IBM global standards rather than the domestic computer architecture. As of 1989, the VGA was not common, but they expected the LCD panels with VGA resolution would be affordable within a few years. The DOS/V lacked its software library, so IBM Japan requested third-party companies to port their software to the DOS/V. The PS/55 Model 5535-S was released as a laptop terminal for the corporate sector. They only had to supply a few major business software to the DOS/V.
In March 1991, IBM Japan released the PS/55note
The IBM Personal System/55 Note (stylized as PS/55 note) is a series of notebooks manufactured by the IBM subsidiary IBM Japan as part of the IBM Personal System/55 series.
The international IBM PS/2 Note series was based on the PS/55 Note seri ...
Model 5523-S which was the lower-price laptop computer. It was a strategically important product to popularize the DOS/V into the consumer market, and led to the success of subsequent consumer products such as the ThinkPad
ThinkPad is a line of business-oriented laptop computers and tablets designed, developed and marketed by Lenovo, and formerly by IBM until 2005, when IBM's PC business was acquired by Lenovo. ThinkPads have a distinct black, boxy design la ...
. However, the DOS/V itself sold much better than the 5523S because advanced users purchased it to build a Japanese language environment on their IBM compatible PCs.
In 1992, IBM Japan released the PS/V (similar to the PS/ValuePoint) and the ThinkPad
ThinkPad is a line of business-oriented laptop computers and tablets designed, developed and marketed by Lenovo, and formerly by IBM until 2005, when IBM's PC business was acquired by Lenovo. ThinkPads have a distinct black, boxy design la ...
. They were based upon an architecture closer to PC compatibles, and intended to compete with rivals in the consumer market. As of December 1992, the PS/V was the most selling DOS/V computer. In January 1993, NEC released a new generation of the PC-98 to take back its initiative. NEC advertised that the scrolling speed of the word processor Ichitaro on the PC-9801BX was faster than on the PS/V 2405-W. Yuzuru Takemura of IBM Japan said, "Let us suppose the movement towards Windows is inevitability. Processors and graphics cards will become faster and faster. If the PC-98 holds its architecture, it never beat our machine at speed. Windows is developed for the PC/AT architecture. Kanji glyphs are also supplied as a software font. The only thing IBM have to do is tuning up it for the video card. On the different architecture, it will be hard to tune up Windows". In 1993, Microsoft Japan released first retail versions of Windows (
In 1993, Microsoft Japan released first retail versions of Windows (Windows 3.1
Windows 3.1 is a major release of Microsoft Windows. It was released to manufacturing on April 6, 1992, as a successor to Windows 3.0.
Like its predecessors, the Windows 3.1 series ran as a shell on top of MS-DOS. Codenamed Janus, Windows 3 ...
) for both DOS/V and PC-98. The DOS/V contributed the dawn of IBM PC clones in Japan, yet PC-98 had kept 50% of market share until 1996. It was turned round by the release of Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of operating systems. The first operating system in the 9x family, it is the successor to Windows 3.1x, and was released to manufacturi ...
.
Drivers
Three device drivers enable DBCS code page support in DOS on IBM PC compatibles with VGA; the font driver, the display driver and the input assisted subsystem driver. The font driver loads a complete set of the glyphs from a font file into theextended memory
In DOS memory management, extended memory refers to memory above the first megabyte (220 bytes) of address space in an IBM PC or compatible with an 80286 or later processor. The term is mainly used under the DOS and Windows operating systems. D ...
. The display driver sets the 640×480 graphics mode on the VGA, and allocates about 20 KB of the conventional memory
In DOS memory management, conventional memory, also called base memory, is the first 640 kilobytes of the memory on IBM PC or compatible systems. It is the read-write memory directly addressable by the processor for use by the operating system ...
for text, called the simulated video buffer. A DOS/V program writes the codes of the characters to the simulated video buffer through DOS output functions, or writes them directly and calls driver's function to refresh the screen. The display driver copies the font bitmap data from the extended memory to the actual video memory, corresponding to the simulated video buffer. The input assisted subsystem driver communicates with optional input method
An input method (or input method editor, commonly abbreviated IME) is an operating system component or program that enables users to generate characters not natively available on their input devices by using sequences of characters (or mouse o ...
s and enables the text editing in the on-the-spot or below-the-spot styles. Without installing these drivers, the DOS/V is equivalent to the generic MS-DOS without DBCS code page support.
* $FONT.SYS – Font driver
* $DISP.SYS – Display driver
* $IAS.SYS – Input assist subsystem (IAS) with front end processor (FEP) support driver
* $PRN.SYS – Printer driver
* $PRNUSER.SYS – Printer driver
* $PRNESCP.SYS – Printer driver for Epson
Seiko Epson Corporation, or simply known as Epson, is a Japanese multinational electronics company and one of the world's largest manufacturers of computer printers and information- and imaging-related equipment. Headquartered in Suwa, Nagano ...
ESC/P J84
Versions
 In 1988, IBM Japan released a new model of the PS/55 which was based on the PS/2 with Japanese language support. It is equipped with a proprietary video card, the Display Adapter, which has a high resolution
In 1988, IBM Japan released a new model of the PS/55 which was based on the PS/2 with Japanese language support. It is equipped with a proprietary video card, the Display Adapter, which has a high resolution text mode
Text mode is a computer display mode in which content is internally represented on a computer screen in terms of characters rather than individual pixels. Typically, the screen consists of a uniform rectangular grid of ''character cells'', each ...
and a Japanese character set stored in a ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
on the card. It supports Japanese DOS K3.3, PC DOS 3.3 (English) and OS/2
OS/2 (Operating System/2) is a series of computer operating systems, initially created by Microsoft and IBM under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci. As a result of a feud between the two companies over how to position OS/2 r ...
.
IBM DOS J4.0 was released in 1989. It combines Japanese DOS and PC DOS, which runs Japanese DOS as the Japanese mode (PS/55 mode) and PC DOS as the English mode (PS/2 mode). Although it had two separated modes that needed a reboot to switch between them, IBM Japan called it ''bilingual''. This version requires the PS/55 display adapter.
 The first version of DOS/V, IBM DOS J4.0/V (J4.05/V), was released in the end of 1990. The word 'DOS/V' was quickly known to Japanese computer industry, but the DOS/V itself didn't spread quickly. As of 1991, some small companies sold American or Taiwanese computers in Japan, but DOS J4.0/V caused some issues on PC compatibles. Its EMS driver only supports IBM's Expanded Memory Adapter. The
The first version of DOS/V, IBM DOS J4.0/V (J4.05/V), was released in the end of 1990. The word 'DOS/V' was quickly known to Japanese computer industry, but the DOS/V itself didn't spread quickly. As of 1991, some small companies sold American or Taiwanese computers in Japan, but DOS J4.0/V caused some issues on PC compatibles. Its EMS driver only supports IBM's Expanded Memory Adapter. The input method
An input method (or input method editor, commonly abbreviated IME) is an operating system component or program that enables users to generate characters not natively available on their input devices by using sequences of characters (or mouse o ...
doesn't support the US keyboard nor the Japanese AX keyboard, so it locates some keys at the wrong place. PS/55 keyboards were available from IBM, but it must be used with an AT to PS/2 adapter because AX machines (thus PC/AT clones) generally have the older 5-pin DIN connector. Scrolling text with the common Tseng Labs ET4000
The Tseng Labs ''ET4000'' was a line of SVGA graphics controller chips during the early 1990s, commonly found in many 386/ 486 and compatible systems, with some models, notably the ''ET4000/W32'' and later chips, offering graphics acceleration. Of ...
graphics controller makes the screen unreadable. This issue can be fixed by the new /HS=LC switch of $DISP.SYS in DOS J4.07/V. "Some VGA clones did not correctly implement the CRTC address wraparound. Most likely those were Super VGAs with more video memory than the original VGA (i.e. more than 256 KB). Software relying on the address wraparound was very rare and therefore the functionality was not necessarily correctly implemented in hardware. On the other hand, the split screen technique was relatively well documented and well understood, and commercial software (especially games) sometimes used it. It was therefore likely to be tested and properly implemented in hardware."
IBM Japan released DOS J5.0/V in October 1991, and DOS J5.0 in December 1991. DOS J5.0 combines Japanese DOS and DOS/V. This is the last version developed for the PS/55 display adapter. DOS J5.02/V was released in March 1992. It added official support for the IBM PS/2 and the US English layout keyboard.
The development of MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few ope ...
5.0/V was delayed because IBM and Microsoft disputed how to implement the API
An application programming interface (API) is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how ...
for input methods. It took a few months to make an agreement that the OEM
An original equipment manufacturer (OEM) is generally perceived as a company that produces non-aftermarket parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. It is a common industry term recognized and used by many professional or ...
adaptation kit (OAK) of MS-DOS 5.0/V provided both IAS (Input Assist Subsystem) and MKKC (Microsoft Kana-Kanji Conversion). Microsoft planned to add the AX application support into DOS/V, but cancelled it because its beta release was strongly criticized by users for lacking compatibility. Some PC manufacturers couldn't wait Microsoft's DOS/V. Toshiba developed a DOS/V emulator that could run DOS/V applications on a VGA-equipped J-3100 computer. AST Research
AST Research, Inc., later doing business as AST Computer, was a personal computer manufacturer. It was founded in 1980 in Irvine, California by Albert Wong, Safi Qureshey, and Thomas Yuen, as an initialism of their first names. In the 1980s, AST ...
Japan and Sharp
Sharp or SHARP may refer to:
Acronyms
* SHARP (helmet ratings) (Safety Helmet Assessment and Rating Programme), a British motorcycle helmet safety rating scheme
* Self Help Addiction Recovery Program, a charitable organisation founded in 19 ...
decided to bundle IBM DOS J5.0/V. Compaq developed own DOS/V drivers, and released their first DOS/V computers in April 1992.
On 10 December 1993, Microsoft Japan and IBM Japan released new versions of DOS/V, MS-DOS 6.2/V Upgrade and PC DOS J6.1/V. Although both were released at the same time, they were separately developed. MS-DOS 6.2/V Upgrade is the only Japanese version of MS-DOS released by Microsoft under its own brand for retail sales. Microsoft Japan continued selling it after Microsoft released MS-DOS 6.22 to resolve patent infringement of DoubleSpace
DriveSpace (initially known as DoubleSpace) is a disk compression utility supplied with MS-DOS starting from version 6.0 in 1993 and ending in 2000 with the release of Windows Me. The purpose of DriveSpace is to increase the amount of data the ...
disk compression.
IBM Japan ended support for PC DOS 2000 on 31 January 2001, and Microsoft Japan ended support for MS-DOS on 31 December 2001.
Japanese versions of Windows 2000
Windows 2000 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft and oriented towards businesses. It was the direct successor to Windows NT 4.0, and was released to manufacturing on December 15, 1999, and was officiall ...
and XP have a DOS/V environment in NTVDM
Virtual DOS machines (VDM) refer to a technology that allows running 16-bit/32-bit DOS and 16-bit Windows programs when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware.
Overview
Virtual DOS machines can operate eit ...
. It was removed in Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years before, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of ...
.
PC DOS versions
PC DOS versions of DOS/V (J for Japanese, P for Chinese (PRC), T for Taiwanese, H for Korean (Hangul)): * IBM DOS J4.0/V "5605-PNA" (version 4.00 – 4.04 were not released for DOS/V) ** IBM DOS J4.05/V for PS/55 (announced 1990-10-11, shipped 1990-11-05) ** IBM DOS J4.06/V (1991-04) ** IBM DOS J4.07/V (1991-07) * IBM DOS J5.0/V "5605-PJA" (1991-10), IBM DOS T5.0/V, IBM DOS H5.0/V ** IBM DOS J5.02/V for PS/55 (1992-03) ** IBM DOS J5.02A/V ** IBM DOS J5.02B/V ** IBM DOS J5.02C/V ** IBM DOS J5.02D/V (1993-05) ** Sony OADG DOS/V (includes IBM DOS J5.0/V and drivers for AX machines) * PC DOS J6.1/V "5605-PTA" (1993-12), PC DOS P6.1/V, PC DOS T6.10/V ** PC DOS J6.10A/V (1994-03) * PC DOS J6.3/V "5605-PDA" (1994-05) ** PC DOS J6.30A/V ** PC DOS J6.30B/V ** PC DOS J6.30C/V (1995-06) * PC DOS J7.0/V "5605-PPW" (1995-08), PC DOS P7/V, PC DOS T7/V, PC DOS H7/V ** PC DOS J7.00A/V ** PC DOS J7.00B/V ** PC DOS J7.00C/V (1998-07) * PC DOS 2000 Japanese Edition "04L5610" (1998-07)MS-DOS versions
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few ope ...
versions of DOS/V:
* Toshiba Nichi-Ei (日英; Japanese-English) MS-DOS 5.0
* Compaq MS-DOS 5.0J/V (1992-04)
* MS-DOS 5.0/V (OEM, generic MS-DOS 5.0/V)
* MS-DOS 6.0/V
* MS-DOS 6.2/V (Retail, 1993-12)
* MS-DOS 6.22/V (1994-08)
* Fujitsu Towns OS
The is a Japanese personal computer, built by Fujitsu from February 1989 to the summer of 1997. It started as a proprietary PC variant intended for multimedia applications and PC games, but later became more compatible with IBM PC compatibles. ...
for FM Towns (only late issues had DOS/V compatibility added)
DR DOS versions
DR DOS
DR-DOS (written as DR DOS, without a hyphen, in versions up to and including 6.0) is a disk operating system for IBM PC compatibles. Upon its introduction in 1988, it was the first DOS attempting to be compatible with IBM PC DOS and MS- ...
versions of DOS/V:
* DR DOS 6.0/V (Japanese) (1992-07), DR DOS 6.0/V (Korean)
** ViewMAX 2 (Japanese) (1991–1992)
** NetWare Lite 1.1J (Japanese) (1992–1997)
* Novell DOS 7
DR-DOS (written as DR DOS, without a hyphen, in versions up to and including 6.0) is a disk operating system for IBM PC compatibles. Upon its introduction in 1988, it was the first DOS attempting to be compatible with IBM PC DOS and MS-D ...
(Japanese)?
** Personal NetWare J 1.0 (Japanese) (1994–1995)
* (DR-DOS 7.0x/V) (2001–2006) (an attempt to build a DR-DOS/V from existing components)
Extensions
IBM DOS/V Extension extends DOS/V drivers to set up a variety of text modes for certain video adapters. The High-quality Text Mode is the default 80 columns by 25 rows with 12×24 pixels large characters. The High-density Text Mode (Variable Text; V-Text) offers large text modes with various font sizes. DOS/V Extension V1.0 included drivers for VGA, XGA, PS/55 Display Adapter,SVGA
Super VGA (SVGA) is a broad term that covers a wide range of computer display standards that extended IBM's VGA specification.
When used as shorthand for a resolution, as VGA and XGA often are, SVGA refers to a resolution of 800×600.
History
I ...
(800×600) and ET4000 (1024×768). Some of its drivers were included in PC DOS J6.1/V and later.
* IBM DOS/V Extension V1.0 (1993-01) includes V-Text support
* IBM DOS/V Extension V2.0 "5605-PXB"
See also
*Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, wh ...
* List of DOS commands
This article presents a list of commands used by DOS operating systems, especially as used on x86-based IBM PC compatibles (PCs). Other DOS operating systems are not part of the scope of this list.
In DOS, many standard system commands were pro ...
* Kanji CP/M-86 (1984)
* (A Japanese magazine on IBM clones)
Notes
References
}Further reading
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:DOS V DOS on IBM PC compatibles 1990 software