|
Time Preference
In behavioral economics, time preference (or time discounting,. delay discounting, temporal discounting, long-term orientation) is the current relative valuation placed on receiving a good at an earlier date compared with receiving it at a later date. Applications for these preferences include finance, health, and climate change. Time preferences are captured mathematically in the discount function. The main models of discounting include exponential, hyperbolic, and quasi hyperbolic. The higher the time preference, the higher the discount placed on returns receivable or costs payable in the future. Several factors correlate with an individual’s time preference, including age, income, race, risk, and temptation. On a larger level, ideas such as sign effects, sub-additivity, and the elicitation method can influence how people display time preference. Time preference can also inform wider preferences about real world behavior and attitudes, such as pro-social behavior. Cultura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Behavioral Economics
Behavioral economics is the study of the psychological (e.g. cognitive, behavioral, affective, social) factors involved in the decisions of individuals or institutions, and how these decisions deviate from those implied by traditional economic theory. Behavioral economics is primarily concerned with the bounds of rationality of economic agents. Behavioral models typically integrate insights from psychology, neuroscience and microeconomic theory. Behavioral economics began as a distinct field of study in the 1970s and 1980s, but can be traced back to 18th-century economists, such as Adam Smith, who deliberated how the economic behavior of individuals could be influenced by their desires. The status of behavioral economics as a subfield of economics is a fairly recent development; the breakthroughs that laid the foundation for it were published through the last three decades of the 20th century. Behavioral economics is still growing as a field, being used increasingly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Decision Making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either rational or irrational. The decision-making process is a reasoning process based on assumptions of values, preferences and beliefs of the decision-maker. Every decision-making process produces a final choice, which may or may not prompt action. Research about decision-making is also published under the label problem solving, particularly in European psychological research. Overview Decision-making can be regarded as a problem-solving activity yielding a solution deemed to be optimal, or at least satisfactory. It is therefore a process which can be more or less rational or irrational and can be based on explicit or tacit knowledge and beliefs. Tacit knowledge is often used to fill the gaps in complex decision-making processes. Usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions Theory
Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory is a framework for cross-cultural psychology, developed by Geert Hofstede. It shows the effects of a society's culture on the values of its members, and how these values relate to behavior, using a structure derived from factor analysis. Hofstede developed his original model as a result of using factor analysis to examine the results of a worldwide survey of employee values by International Business Machines between 1967 and 1973. It has been refined since. The original theory proposed four dimensions along which cultural values could be analyzed: individualism- collectivism; uncertainty avoidance; power distance (strength of social hierarchy) and masculinity-femininity (task-orientation versus person-orientation). The Hofstede Cultural Dimensions factor analysis is based on extensive cultural preferences research conducted by Gert Jan Hofstede and his research teams. Hofstede based his research on national cultural preferences rather than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dynamic Inconsistency
In economics, dynamic inconsistency or time inconsistency is a situation in which a decision-maker's preferences change over time in such a way that a preference can become inconsistent at another point in time. This can be thought of as there being many different "selves" within decision makers, with each "self" representing the decision-maker at a different point in time; the inconsistency occurs when not all preferences are aligned. The term "dynamic inconsistency" is more closely affiliated with game theory, whereas "time inconsistency" is more closely affiliated with behavioral economics. In game theory In the context of game theory, dynamic inconsistency is a situation in a dynamic game where a player's best plan for some future period will not be optimal when that future period arrives. A dynamically inconsistent game is subgame imperfect. In this context, the inconsistency is primarily about commitment and credible threats. This manifests itself through a violation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
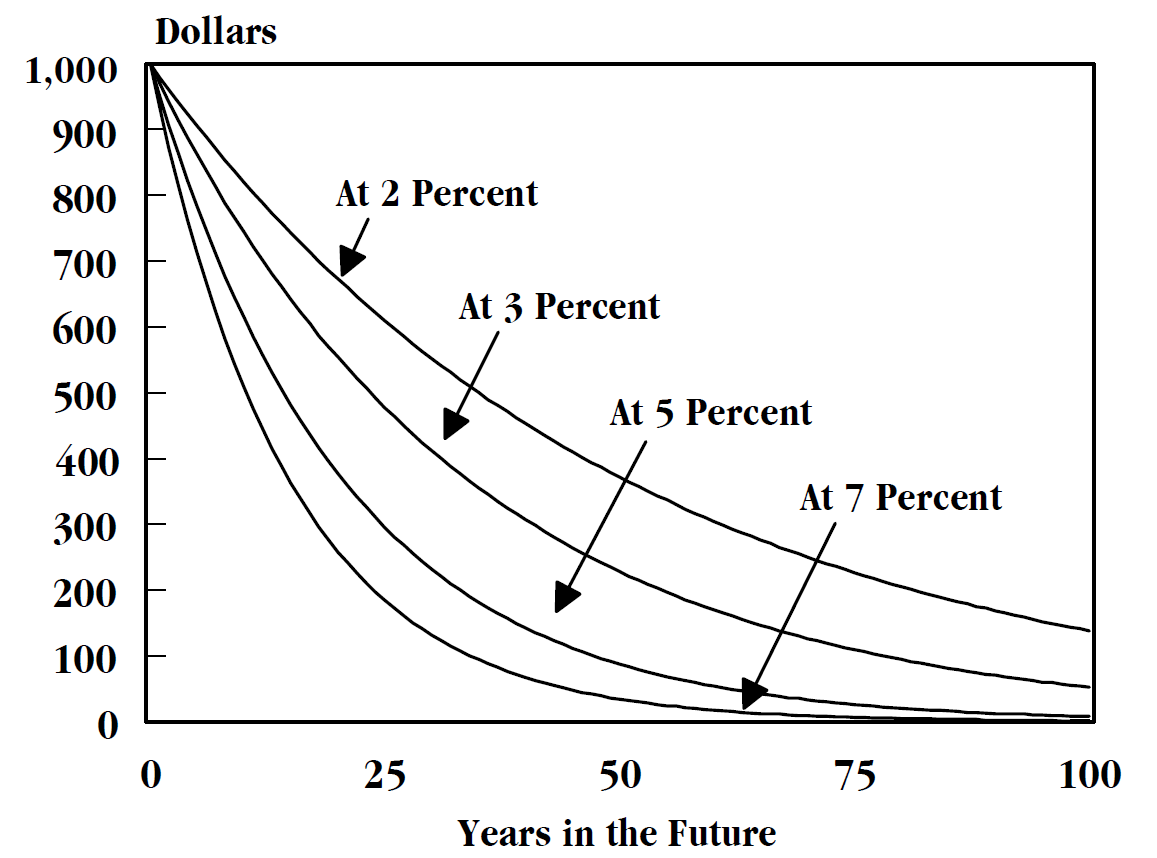
Discounting
In finance, discounting is a mechanism in which a debtor obtains the right to delay payments to a creditor, for a defined period of time, in exchange for a charge or fee.See "Time Value", "Discount", "Discount Yield", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Market", "Market Value" and "Opportunity Cost" in Downes, J. and Goodman, J. E. ''Dictionary of Finance and Investment Terms'', Baron's Financial Guides, 2003. Essentially, the party that owes money in the present purchases the right to delay the payment until some future date.See "Discount", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Markets Hypothesis", "Efficient Resource Allocation", "Pareto-Optimality", "Price", "Price Mechanism" and "Efficient Market" in Black, John, ''Oxford Dictionary of Economics'', Oxford University Press, 2002. This Financial transaction, transaction is based on the fact that most people prefer current interest to delayed interest because of Mortality salience, mortality effects, impatience effects, and Motivational sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Discounted Utility
In economics, discounted utility is the utility (desirability) of some future event, such as consuming a certain amount of a good, as perceived at the present time as opposed to at the time of its occurrence. It is calculated as the present discounted value of future utility, and for people with time preference for sooner rather than later gratification, it is less than the future utility. The utility of an event occurring at future time under utility function , discounted back to the present (time 0) using discount factor , is \beta ^t u(x_t). Since more distant events are less liked, . Discounted utility calculations made for events at various points in the future as well as at the present take the form \sum_^T \beta ^t u(x_t), where is the utility of some choice at time and is the time of the most distant future satisfaction event. Here, since utility comparisons are being made across time when the utilities are combined in a single evaluation, the utility functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Discount Function
In economics, a discount function is used in economic models to describe the weights placed on rewards received at different points in time. For example, if time is discrete and utility is time-separable, with the discount function having a negative first derivative and with (or in continuous time) defined as consumption at time , total utility from an infinite stream of consumption is given by: U\Bigl( \_^\infty \Bigr) = \sum_^\infty Total utility in the continuous-time case is given by: U \Bigl( \_^\infty \Bigr) = \int_^\infty {f(t)u(c(t)) dt} provided that this integral exists. Exponential discounting and hyperbolic discounting are the two most commonly used examples. See also *Discounted utility In economics, discounted utility is the utility (desirability) of some future event, such as consuming a certain amount of a good, as perceived at the present time as opposed to at the time of its occurrence. It is calculated as the present dis ... * Inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Delayed Gratification
Delayed gratification, or deferred gratification, is the ability to resist the temptation of an immediate reward in favor of a more valuable and long-lasting reward later. It involves forgoing a smaller, immediate pleasure to achieve a larger or more enduring benefit in the future. A growing body of literature has linked the ability to delay gratification to a host of other positive outcomes, including academic success, physical health, psychological health, and social competence. A person's ability to delay gratification relates to other similar skills such as patience, impulse control, self-control and willpower, all of which are involved in self-regulation. Broadly, self-regulation encompasses a person's capacity to adapt the self as necessary to meet demands of the environment. Delaying gratification is the reverse of delay discounting, which is "the preference for smaller immediate rewards over larger but delayed rewards" and refers to the "fact that the subjective value of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |