|
Relay
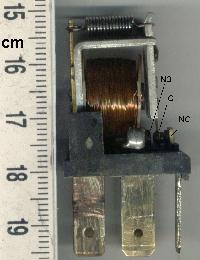
A relay Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off A relay is an electrically operated switch. It has a set of input terminals for one or more control signals, and a set of operating contact terminals. The switch may have any number of contacts in multiple contact forms, such as make contacts, break contacts, or combinations thereof. Relays are used to control a circuit by an independent low-power signal and to control several circuits by one signal. They were first used in long-distance telegraph circuits as signal repeaters that transmit a refreshed copy of the incoming signal onto another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations. The traditional electromechanical relay uses an electromagnet to close or open the contacts, but relays using other operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protective Relay
In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a relay device designed to trip a circuit breaker when a Electrical fault, fault is detected. The first protective relays were electromagnetic devices, relying on coils operating on moving parts to provide detection of abnormal operating conditions such as over-current, overvoltage, reverse electric power, power flow, over-frequency, and under-frequency. Microprocessor-based Solid-state electronics, solid-state digital protection relays now emulate the original devices, as well as providing types of protection and supervision impractical with electromechanical relays. Relay, Electromechanical relays provide only rudimentary indication of the location and origin of a fault. In many cases a single microprocessor relay provides functions that would take two or more electromechanical devices. By combining several functions in one case, numerical relays also save capital cost and maintenance cost over electromechanical relays. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Relay Animation Without Flyback Diode
A relay Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off A relay is an electrically operated switch. It has a set of input terminals for one or more control signals, and a set of operating contact terminals. The switch may have any number of contacts in multiple contact forms, such as make contacts, break contacts, or combinations thereof. Relays are used to control a circuit by an independent low-power signal and to control several circuits by one signal. They were first used in long-distance telegraph circuits as signal repeaters that transmit a refreshed copy of the incoming signal onto another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations. The traditional electromechanical relay uses an electromagnet to close or open the contacts, but relays using other operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electrical Contact
An electrical contact is an Electronic component, electrical circuit component found in electrical switches, relays, Electrical connector, connectors and circuit breakers. Each contact is a piece of electrically conductive material, typically metal. When a pair of contacts touch, they can pass an electrical current with a certain contact resistance, dependent on surface structure, surface chemistry and contact time; when the pair is separated by an insulator (electricity), insulating gap, then the pair does not pass a electric current, current. When the contacts touch, the switch is ''closed''; when the contacts are separated, the switch is ''open''. The gap must be an insulating medium, such as air, vacuum, oil, SF6, SF6. Contacts may be operated by humans in push-buttons and switches, by mechanical pressure in sensors or machine cams, and Electromechanics, electromechanically in relays. The surfaces where contacts touch are usually composed of metals such as silver or gold alloysM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Solid-state Relay
file:Solid-state-contactor.jpg, Solid state contactor file:Solid-state relay.jpg, PCB mount solid-state DIL relay A solid state relay (SSR) is an Electronic switch, electronic switching device that switches on or off when an external voltage (AC or DC) is applied across its control terminals. They serve the same function as an electromechanical relay, but solid-state electronics contain no moving parts and have a longer operational lifetime. Solid state relays were invented in 1971 by the Crydom Controls division of International Rectifier. SSRs consist of a sensor which responds to an appropriate input (control signal), an electronic switching device which switches power to the load circuitry, and a coupling mechanism to enable the control signal to activate this switch without mechanical parts. They may be designed to switch either Alternating current, AC or Direct current, DC loads. Packaged SSRs use power semiconductor devices such as thyristors and transistors, to switch cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Safety Relay
Safety relays are devices that generally implement safety functions. History Relays and contactors were used to control plant and machinery in the early days of control technology. In the event of a hazardous situation, the actuator was simply isolated from the energy supply. This type of protection system could be manipulated in the event of a malfunction, disabling the protective function. Special relay circuits, such as the three-contactor combination, were the first designs to come out of deliberations into how this could be avoided. These device combinations led to the development of the first safety relay from the German automation manufacturer Pilz, the PNOZ. Description In the event of a hazard, the task of safety functions (e.g. E-STOP, safety gate or standstill monitoring) is to use appropriate measures to reduce the existing risk to an acceptable level. These many safety functions include: * Emergency stop pushbuttons * Safety gates * Light beam devices * Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electromechanical
Electromechanics combine processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focus on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each other. This process is especially prominent in systems such as those of DC or AC rotating electrical machines which can be designed and operated to generate power from a mechanical process ( generator) or used to power a mechanical effect ( motor). Electrical engineering in this context also encompasses electronics engineering. Electromechanical devices are ones which have both electrical and mechanical processes. Strictly speaking, a manually operated switch is an electromechanical component due to the mechanical movement causing an electrical output. Though this is true, the term is usually understood to refer to devices which involve an electrical signal to create mechanical movement, or vice versa mechanical movement to create an ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Samuel Morse
Samuel Finley Breese Morse (April 27, 1791 – April 2, 1872) was an American inventor and painter. After establishing his reputation as a portrait painter, Morse, in his middle age, contributed to the invention of a Electrical telegraph#Morse system, single-wire telegraph system based on European telegraphs. He was a co-developer of Morse code in 1837 and helped to develop the commercial use of telegraphy. Personal life Samuel F. B. Morse was born in Charlestown, Boston, Massachusetts, the first child of the pastor Jedidiah Morse, who was also a geographer, and his wife Elizabeth Ann Finley Breese. His father was a great preacher of the Calvinism, Calvinist faith and supporter of the Federalist Party. He thought it helped preserve Puritan traditions (strict observance of Christian Sabbath, Sabbath, among other things), and believed in the Federalist support of an alliance with Britain and a strong central government. Morse strongly believed in education within a Federalist f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of switch is an electromechanical device consisting of one or more sets of movable electrical contacts connected to external circuits. When a pair of contacts is touching current can pass between them, while when the contacts are separated no current can flow. Switches are made in many different configurations; they may have multiple sets of contacts controlled by the same knob or actuator, and the contacts may operate simultaneously, sequentially, or alternately. A switch may be operated manually, for example, a light switch or a keyboard button, or may function as a sensing element to sense the position of a machine part, liquid level, pressure, or temperature, such as a thermostat. Many specialized forms exist, such as the toggle swit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Repeater
In telecommunications, a repeater is an electronic device that receives a signal and retransmits it. Repeaters are used to extend transmissions so that the signal can cover longer distances or be received on the other side of an obstruction. Some types of repeaters broadcast an identical signal, but alter its method of transmission, for example, on another frequency or baud rate. There are several different types of repeaters; a telephone repeater is an amplifier in a telephone line, an optical repeater is an optoelectronic circuit that amplifies the light beam in an optical fiber cable; and a radio repeater is a radio receiver and transmitter that retransmits a radio signal. A broadcast relay station is a repeater used in broadcast radio and television. Overview When an information-bearing signal passes through a communication channel, it is progressively degraded due to loss of power. For example, when a telephone call passes through a wire telephone line, some of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |