|
Partial Correlation
In probability theory and statistics, partial correlation measures the degree of association between two random variables, with the effect of a set of controlling random variables removed. When determining the numerical relationship between two variables of interest, using their correlation coefficient will give misleading results if there is another confounding variable that is numerically related to both variables of interest. This misleading information can be avoided by controlling for the confounding variable, which is done by computing the partial correlation coefficient. This is precisely the motivation for including other right-side variables in a multiple regression; but while multiple regression gives unbiased results for the effect size, it does not give a numerical value of a measure of the strength of the relationship between the two variables of interest. For example, given economic data on the consumption, income, and wealth of various individuals, consider the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coefficient Of Determination
In statistics, the coefficient of determination, denoted ''R''2 or ''r''2 and pronounced "R squared", is the proportion of the variation in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variable(s). It is a statistic used in the context of statistical models whose main purpose is either the prediction of future outcomes or the testing of hypotheses, on the basis of other related information. It provides a measure of how well observed outcomes are replicated by the model, based on the proportion of total variation of outcomes explained by the model. There are several definitions of ''R''2 that are only sometimes equivalent. In simple linear regression (which includes an intercept), ''r''2 is simply the square of the sample ''correlation coefficient'' (''r''), between the observed outcomes and the observed predictor values. If additional regressors are included, ''R''2 is the square of the '' coefficient of multiple correlation''. In both such cases, the coeffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
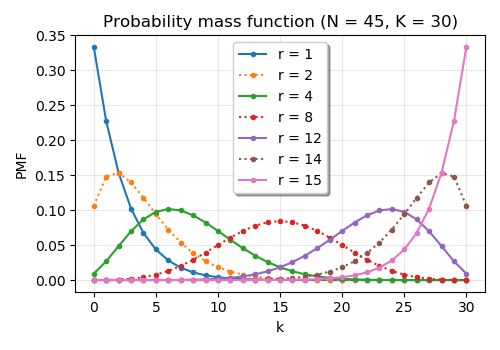
Negative Hypergeometric Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the negative hypergeometric distribution describes probabilities for when sampling from a finite population without replacement in which each sample can be classified into two mutually exclusive categories like Pass/Fail or Employed/Unemployed. As random selections are made from the population, each subsequent draw decreases the population causing the probability of success to change with each draw. Unlike the standard hypergeometric distribution, which describes the number of successes in a fixed sample size, in the negative hypergeometric distribution, samples are drawn until r failures have been found, and the distribution describes the probability of finding k successes in such a sample. In other words, the negative hypergeometric distribution describes the likelihood of k successes in a sample with exactly r failures. Definition There are N elements, of which K are defined as "successes" and the rest are "failures". Elements are drawn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
R (programming Language)
R is a programming language for statistical computing and Data and information visualization, data visualization. It has been widely adopted in the fields of data mining, bioinformatics, data analysis, and data science. The core R language is extended by a large number of R package, software packages, which contain Reusability, reusable code, documentation, and sample data. Some of the most popular R packages are in the tidyverse collection, which enhances functionality for visualizing, transforming, and modelling data, as well as improves the ease of programming (according to the authors and users). R is free and open-source software distributed under the GNU General Public License. The language is implemented primarily in C (programming language), C, Fortran, and Self-hosting (compilers), R itself. Preprocessor, Precompiled executables are available for the major operating systems (including Linux, MacOS, and Microsoft Windows). Its core is an interpreted language with a na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
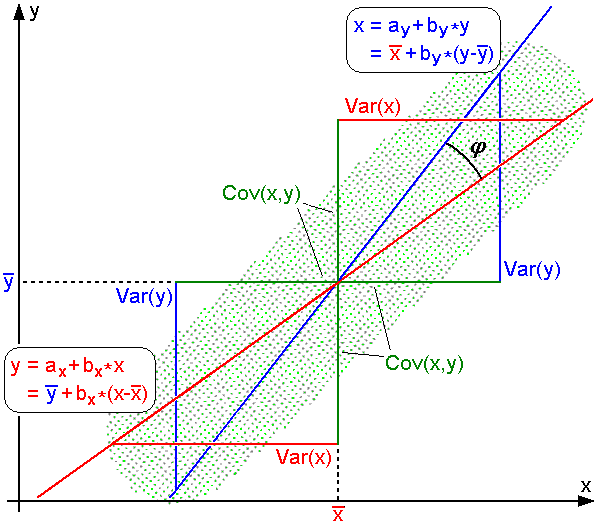
Pearson Correlation Coefficient
In statistics, the Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) is a correlation coefficient that measures linear correlation between two sets of data. It is the ratio between the covariance of two variables and the product of their standard deviations; thus, it is essentially a normalized measurement of the covariance, such that the result always has a value between −1 and 1. As with covariance itself, the measure can only reflect a linear correlation of variables, and ignores many other types of relationships or correlations. As a simple example, one would expect the age and height of a sample of children from a school to have a Pearson correlation coefficient significantly greater than 0, but less than 1 (as 1 would represent an unrealistically perfect correlation). Naming and history It was developed by Karl Pearson from a related idea introduced by Francis Galton in the 1880s, and for which the mathematical formula was derived and published by Auguste Bravais in 1844. The nami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ordinary Least Squares
In statistics, ordinary least squares (OLS) is a type of linear least squares method for choosing the unknown parameters in a linear regression In statistics, linear regression is a statistical model, model that estimates the relationship between a Scalar (mathematics), scalar response (dependent variable) and one or more explanatory variables (regressor or independent variable). A mode ... model (with fixed level-one effects of a linear function of a set of explanatory variables) by the principle of least squares: minimizing the sum of the squares of the differences between the observed dependent variable (values of the variable being observed) in the input dataset and the output of the (linear) function of the independent variable. Some sources consider OLS to be linear regression. Geometrically, this is seen as the sum of the squared distances, parallel to the axis of the dependent variable, between each data point in the set and the corresponding point on the regression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pearson Product-moment Correlation Coefficient
In statistics, the Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) is a correlation coefficient that measures linear correlation between two sets of data. It is the ratio between the covariance of two variables and the product of their standard deviations; thus, it is essentially a normalized measurement of the covariance, such that the result always has a value between −1 and 1. As with covariance itself, the measure can only reflect a linear correlation of variables, and ignores many other types of relationships or correlations. As a simple example, one would expect the age and height of a sample of children from a school to have a Pearson correlation coefficient significantly greater than 0, but less than 1 (as 1 would represent an unrealistically perfect correlation). Naming and history It was developed by Karl Pearson from a related idea introduced by Francis Galton in the 1880s, and for which the mathematical formula was derived and published by Auguste Bravais in 1844. The naming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dot Product
In mathematics, the dot product or scalar productThe term ''scalar product'' means literally "product with a Scalar (mathematics), scalar as a result". It is also used for other symmetric bilinear forms, for example in a pseudo-Euclidean space. Not to be confused with scalar multiplication. is an algebraic operation that takes two equal-length sequences of numbers (usually coordinate vectors), and returns a single number. In Euclidean geometry, the dot product of the Cartesian coordinates of two Euclidean vector, vectors is widely used. It is often called the inner product (or rarely the projection product) of Euclidean space, even though it is not the only inner product that can be defined on Euclidean space (see ''Inner product space'' for more). It should not be confused with the cross product. Algebraically, the dot product is the sum of the Product (mathematics), products of the corresponding entries of the two sequences of numbers. Geometrically, it is the product of the Euc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Joint Distribution
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Connect. Webp.274/ref> They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement (only during birth) in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally. Joints play a vital role in the human body, contributing to movement, stability, and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
McGraw-Hill
McGraw Hill is an American education science company that provides educational content, software, and services for students and educators across various levels—from K-12 to higher education and professional settings. They produce textbooks, digital learning tools, and adaptive technology to enhance learning experiences and outcomes. It is one of the "big three" educational publishers along with Houghton Mifflin Harcourt and Pearson Education. McGraw Hill also publishes reference and trade publications for the medical, business, and engineering professions. Formerly a division of The McGraw Hill Companies (later renamed McGraw Hill Financial, now S&P Global), McGraw Hill Education was divested and acquired by Apollo Global Management in March 2013 for $2.4 billion in cash. McGraw Hill was sold in 2021 to Platinum Equity for $4.5 billion. History McGraw Hill was founded in 1888, when James H. McGraw, co-founder of McGraw Hill, purchased the ''American Journal of Railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coefficient Of Alienation
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor involved in some term of a polynomial, a series, or any other type of expression. It may be a number without units, in which case it is known as a numerical factor. It may also be a constant with units of measurement, in which it is known as a constant multiplier. In general, coefficients may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the combination of variables and constants is not necessarily involved in a product, it may be called a ''parameter''. For example, the polynomial 2x^2-x+3 has coefficients 2, −1, and 3, and the powers of the variable x in the polynomial ax^2+bx+c have coefficient parameters a, b, and c. A , also known as constant term or simply constant, is a quantity either implicitly attached to the zeroth power of a variable or not attached to other variables in an expression; for example, the constant coefficients of the expressions above are the number 3 and the parameter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Linear Regression
In statistics, linear regression is a statistical model, model that estimates the relationship between a Scalar (mathematics), scalar response (dependent variable) and one or more explanatory variables (regressor or independent variable). A model with exactly one explanatory variable is a ''simple linear regression''; a model with two or more explanatory variables is a multiple linear regression. This term is distinct from multivariate linear regression, which predicts multiple correlated dependent variables rather than a single dependent variable. In linear regression, the relationships are modeled using linear predictor functions whose unknown model parameters are estimation theory, estimated from the data. Most commonly, the conditional mean of the response given the values of the explanatory variables (or predictors) is assumed to be an affine function of those values; less commonly, the conditional median or some other quantile is used. Like all forms of regression analysis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Errors And Residuals In Statistics
In statistics and optimization, errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of an observed value of an element of a statistical sample from its "true value" (not necessarily observable). The error of an observation is the deviation of the observed value from the true value of a quantity of interest (for example, a population mean). The residual is the difference between the observed value and the '' estimated'' value of the quantity of interest (for example, a sample mean). The distinction is most important in regression analysis, where the concepts are sometimes called the regression errors and regression residuals and where they lead to the concept of studentized residuals. In econometrics, "errors" are also called disturbances. Introduction Suppose there is a series of observations from a univariate distribution and we want to estimate the mean of that distribution (the so-called location model). In this case, the errors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |