|
Lycopodiopsida
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants also known as lycopsids, lycopods, or lycophytes. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching stems bearing simple leaves called microphylls and reproduce by means of spores borne in sporangia on the sides of the stems at the bases of the leaves. Although living species are small, during the Carboniferous, extinct tree-like forms ( Lepidodendrales) formed huge forests that dominated the landscape and contributed to coal deposits. The nomenclature and classification of plants with microphylls varies substantially among authors. A consensus classification for extant (living) species was produced in 2016 by the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group (PPG I), which places them all in the class Lycopodiopsida, which includes the classes Isoetopsida and Selaginellopsida used in other systems. (See Table 2.) Alternative classification systems have used ranks from di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group
The Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group (PPG) is an informal international group of systematic botanists who collaborate to establish on the classification of pteridophytes ( lycophytes and ferns) that reflects knowledge about plant relationships discovered through phylogenetic studies. In 2016, the group published a classification for extant pteridophytes, termed "PPG I". The paper had 94 authors (26 principal and 68 additional). The classification was presented as a consensus classification supported by the community of fern taxonomists. Alternative classifications of ferns exist and are preferred by some. PPG I A first classification, PPG I, was produced in 2016, covering only extant (living) pteridophytes. The classification was rank-based, using the ranks of class, subclass, order, suborder, family, subfamily and genus. Phylogeny The classification was based on a consensus phylogeny, shown below to the level of order. The very large order Polypodiales was divided into two subord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lycopodiales
The Lycopodiaceae (class Lycopodiopsida, order Lycopodiales) are an old family of vascular plants, including all of the core clubmosses and firmosses, comprising 17 accepted genera and about 500 known species. This family originated about 380 million years ago in the early Devonian, though the diversity within the family has been much more recent. "Wolf foot" is another common name for this family due to the resemblance of either the roots or branch tips to a wolf's paw. Description Members of Lycopodiaceae are not spermatophytes and so do not produce seeds. Instead they produce spores, which are oily and flammable, and are the most economically important aspects of these plants. The spores are of one size (i.e. the plants are isosporous) and are borne on a specialized structure at the apex of a shoot called a strobilus (plural: strobili), which resembles a tiny battle club, from which the common name derives. Members of the family share the common feature of having a microphy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
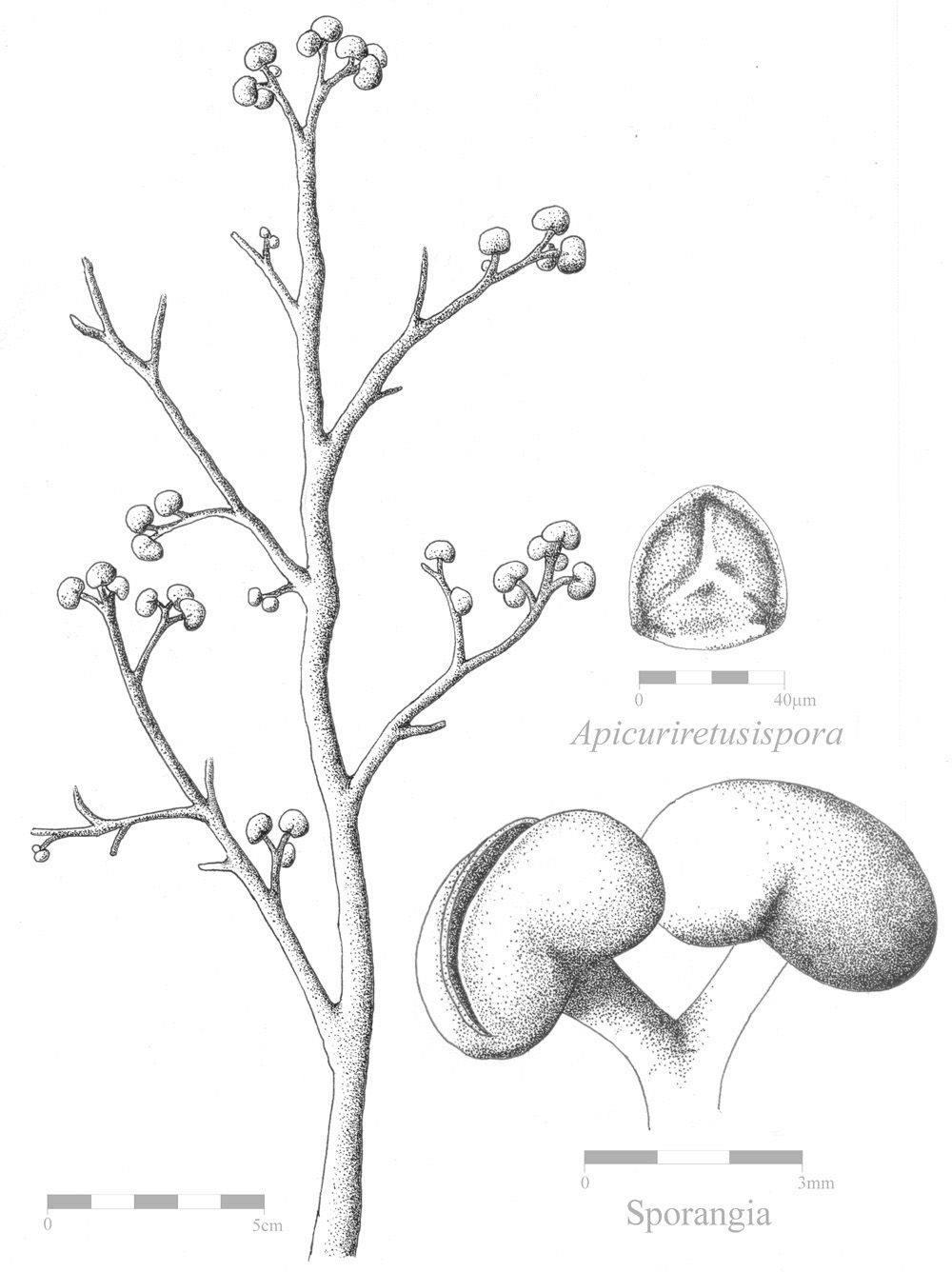
Isoetes
''Isoetes'', commonly known as the quillworts, is a genus of lycopod. It is the only living genus in the family Isoetaceae and order Isoetales. , there were about 200 recognized species, with a cosmopolitan distribution mostly in aquatic habitats but with the individual species often scarce to rare. Species virtually identical to modern quillworts have existed since the Jurassic epoch, though the timing of the origin of modern ''Isoetes'' is subject to considerable uncertainty. The name of the genus may also be spelled ''Isoëtes''. The diaeresis (two dots over the e) indicates that the o and the e are to be pronounced in two distinct syllables. Including this in print is optional; either spelling (''Isoetes'' or ''Isoëtes'') is correct. Description Quillworts are mostly aquatic or semi-aquatic in clear ponds and slow-moving streams, though several (e.g. '' I. butleri'', '' I. histrix'' and '' I. nuttallii'') grow on wet ground that dries out in the summer. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vascular Plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes (, ) or collectively tracheophyta (; ), are plants that have lignin, lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified Tissue (biology), tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. The group includes most embryophyte, land plants ( accepted known species) excluding mosses. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, Equisetum, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). They are contrasted with nonvascular plants such as mosses and green algae. Scientific names for the vascular plants group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida sensu lato, Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zosterophyll
The zosterophylls are a group of extinct land plants that first appeared in the Silurian period. The taxon was first established by Banks in 1968 as the subdivision Zosterophyllophytina; they have since also been treated as the division Zosterophyllophyta or Zosterophyta and the class or plesion Zosterophyllopsida or Zosteropsida. They were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and had a world-wide distribution. They were probably stem-group lycophytes, forming a sister group to the ancestors of the living lycophytes. By the late Silurian (late Ludlovian, about ) a diverse assemblage of species existed, examples of which have been found fossilised in what is now Bathurst Island in Arctic Canada. Morphology The stems of zosterophylls were either smooth or covered with small spines known as enations, branched dichotomously, and grew at the ends by unrolling, a process known as circinate vernation. The stems had a central vascular column in which the protox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lepidodendrales
Lepidodendrales (from the Greek for "scale tree") or arborescent lycophytes are an extinct order of primitive, vascular, Heterospory, heterosporous, arborescent (tree-like) plants belonging to Lycopodiopsida. Members of Lepidodendrales are the best understood of the fossil lycopsids due to the vast diversity of Lepidodendrales specimens and the diversity in which they were preserved; the extensive distribution of Lepidodendrales specimens as well as their well-preservedness lends paleobotanists exceptionally detailed knowledge of the coal-swamp giants’ reproductive biology, vegetative development, and role in their paleoecosystem. The defining characteristics of the Lepidodendrales are their secondary xylem, extensive periderm development, three-zoned Cortex (botany), cortex, rootlike appendages known as stigmarian rootlets arranged in a spiralling pattern, and megasporangium each containing a single functional megaspore that germinates inside the sporangium. Many of these differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vascular Plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes (, ) or collectively tracheophyta (; ), are plants that have lignin, lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified Tissue (biology), tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. The group includes most embryophyte, land plants ( accepted known species) excluding mosses. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, Equisetum, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). They are contrasted with nonvascular plants such as mosses and green algae. Scientific names for the vascular plants group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida sensu lato, Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients, and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaf, leaves called megaphylls that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled Fiddlehead fern, fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate (Polypodiidae (plant), Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, Psilotaceae, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid ferns. The fern crown group, consisting of the leptosporangiates and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bryophyte
Bryophytes () are a group of embryophyte, land plants (embryophytes), sometimes treated as a taxonomic Division (taxonomy), division referred to as Bryophyta ''Sensu#Common qualifiers, sensu lato'', that contains three groups of non-vascular plant, non-vascular land plants: the Marchantiophyta, liverworts, hornworts, and mosses. In the Sensu#Common qualifiers, strict sense, the division Bryophyta consists of the mosses only. Bryophytes are characteristically limited in size and prefer moist habitats although some species can survive in drier environments. The bryophytes consist of about 20,000 plant species. Bryophytes produce enclosed reproductive structures (gametangia and sporangia), but they do not produce flowers or seeds. They reproduce sexually by spores and asexually by fragmentation or the production of Gemma (botany), gemmae. Though bryophytes were considered a paraphyletic group in recent years, almost all of the most recent phylogenetics, phylogenetic evidence support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Selaginella Apoda
''Selaginella apoda'', commonly known as meadow spikemoss, is a perennial lycophyte native to much of the eastern United States and parts of northeastern Mexico. The life cycle is the shortest of the genus ''Selaginella'', as well as one of the shortest among the lycophytes. ''Selaginella apoda'' is found primarily in damp soils in habitats such as swamps, wet fields, open woods and along stream banks. ''Selaginella apoda'' presents the potential for case studies involving the plant's adaptability to environmental toxins. It is closely related to '' Selaginella eclipes'' and '' S. ludoviciana'', with both of which it has been reported to form hybrids. This group is characterized by relatively flat strobili and large megasporophylls which occur in the same plane as the lateral leaves. The plant was originally described, and named ''Lycopodium apodum'' by Carl Linnaeus in his ''Species Plantarum'' (1753). Description ''Selaginella apoda'' stems have smaller leaves in two rows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Selaginella
''Selaginella'', also known as spikemosses or lesser clubmosses, is a genus of lycophyte. It is usually treated as the only genus in the family Selaginellaceae, with over 750 known species. This family is distinguished from Lycopodiaceae (the clubmosses) by having scale-leaves bearing a ligule and by having spores of two types. They are sometimes included in an informal paraphyletic group called the " fern allies". The species '' S. moellendorffii'' is an important model organism. Its genome has been sequenced by the United States Department of Energy's Joint Genome Institute. The name ''Selaginella'' was erected by Palisot de Beauvois solely for the species '' Selaginella selaginoides'', which turns out (with the closely related '' Selaginella deflexa'') to be a clade that is sister to all other ''Selaginellas'', so any definitive subdivision of the species into separate genera leaves two taxa in ''Selaginella'', with the hundreds of other species in new or resurrected gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Microphylls And Megaphylls
In plant anatomy and evolution a microphyll (or lycophyll) is a type of plant leaf with one single, unbranched leaf vein. Plants with microphyll leaves occur early in the fossil record, and few such plants exist today. In the classical concept of a microphyll, the leaf vein emerges from the protostele without leaving a leaf gap. Leaf gaps are small areas above the node of some leaves where there is no vascular tissue, as it has all been diverted to the leaf. Megaphylls, in contrast, have multiple veins within the leaf and leaf gaps above them in the stem. Leaf vasculature The clubmosses and horsetails have microphylls, as in all extant species there is only a single vascular trace in each leaf. These leaves are narrow because the width of the blade is limited by the distance water can efficiently diffuse cell-to-cell from the central vascular strand to the margin of the leaf. Despite their name, microphylls are not always small: those of '' Isoëtes'' can reach 25 centimetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |