|
High German Consonant Shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development (sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic languages, West Germanic dialect continuum. The shift is used to distinguish High German from other continental West Germanic languages, namely Low Franconian (including standard Dutch language, Dutch) and Low German, which experienced no shift. The shift resulted in the affrication or spirantization of the West Germanic voiceless stop consonants /t/, /p/, and /k/, depending on position in a word. A related change, the devoicing of the voiced stopped consonants /d/, /b/ and /g/, was less widespread, with only the devoicing of /d/ being found in most dialects. There is no consensus on when the High German consonant shift occurred; it probably began between the 3rd and 5th centuries and was complete before the first written examples in Old High German, the earliest recorded stage of High ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
German Dialectal Map
German(s) may refer to: * Germany, the country of the Germans and German things **Germania (Roman era) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizenship in Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman era) *German diaspora * German language * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (disambiguat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Proto-West Germanic
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into three branches: Ingvaeonic, which includes English, the Low German languages, and the Frisian languages; Istvaeonic, which encompasses Dutch and its close relatives; and Irminonic, which includes German and its close relatives and variants. English is by far the most-spoken West Germanic language, with more than 1 billion speakers worldwide. Within Europe, the three most prevalent West Germanic languages are English, German, and Dutch. Frisian, spoken by about 450,000 people, constitutes a fourth distinct variety of West Germanic. The language family also includes Afrikaans, Yiddish, Low Saxon, Luxembourgish, Hunsrik, and Scots. Additionally, several creoles, patois, and pidgins are based on Dutch, English, or German. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Moselle Franconian
Moselle Franconian (; ) is a West Central German language, part of the Central Franconian languages area, that includes Luxembourgish. Overview Moselle Franconian is spoken in the southern Rhineland and along the course of the Moselle, in the Siegerland of North Rhine-Westphalia, throughout western Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland, Luxembourg, the south of the German-speaking Community of Belgium and in the neighboring French département of Moselle (in Arrondissement of Boulay-Moselle). The Transylvanian Saxon dialect spoken in the Transylvania region of Romania Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ... is derived from this dialect as a result of the emigration of numerous " Transylvanian Saxons" between 1100 and 1300, primarily from areas in which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Germanic Strong Verb
In the Germanic languages, a strong verb is a verb that marks its past tense by means of Indo-European ablaut, changes to the stem vowel. A minority of verbs in any Germanic language are strong; the majority are ''Germanic weak verb, weak verbs'', which form the past tense by means of a dental consonant, dental suffix. In modern English, strong verbs include ''sing'' (present ''I sing'', simple past, past ''I sang'', past participle ''I have sung'') and ''drive'' (present ''I drive'', past ''I drove'', past participle ''I have driven''), as opposed to weak verbs such as ''open'' (present ''I open'', past ''I opened'', past participle ''I have opened''). Not all verbs with a change in the stem vowel are strong verbs, however: they may also be irregular weak verbs such as ''bring, brought, brought'' or ''keep, kept, kept''. The key distinction is that the system of strong verbs has its origin in the earliest sound system of Proto-Indo-European, whereas weak verbs use a dental ending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lexical Diffusion
Lexical diffusion is the hypothesis that a sound change is an abrupt change that spreads gradually across the words in a language to which it is applicable. It contrasts with the Neogrammarian view that a sound change results from phonetically-conditioned articulatory drift acting uniformly on all applicable words, which implies that sound changes are regular, with exceptions attributed to analogy and dialect borrowing. Similar views were expressed by Romance dialectologists in the late 19th century but were reformulated and renamed by William Wang and coworkers studying varieties of Chinese in the 1960s and the 1970s. William Labov found evidence for both processes but argued that they operate at different levels. Neogrammarians A key assumption of historical linguistics is that sound change is regular. The principle was summarized by the Neogrammarians in the late 19th century in the slogan "sound laws suffer no exceptions" and forms the basis of the comparative method of reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wermelskirchen
Wermelskirchen (; Ripuarian language, Ripuarian: ''Wärmelßkirrshe'') is a town in the Rheinisch-Bergischer Kreis, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, southeast of Remscheid. It is home to one of Europe's biggest live Christmas trees (measuring 26m). Geography The distance to Cologne is about 35 kilometers, to Düsseldorf about 45 kilometers. The neighboring municipalities are Remscheid, Hückeswagen, Wipperfürth, Kürten, Odenthal, Burscheid and Solingen. The townscape is characterized by Altberg slate and half-timbered houses. The city area of Wermelskirchen (area: 74,74 km²) composed out of three district's: the initial Wermelskirchen and the incorporated, previously independent municipalities, Dhünn and Dabringhausen. Coat of arms The coat-of-arms of the city of Wermelskirchen looks like a silver shield split into thirds. In the left field is an oak tree. In the right field there is a Swan and pictured in the middle field there is a church. History From 1822 to 1945, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Uerdingen Line
The Uerdingen Line (, ; named after Uerdingen by Georg Wenker) is the isogloss within West Germanic languages that separates dialects which preserve the ''-k'' sound in the first person singular pronoun word "ik" (north of the line) from dialects where the word-final ''-k'' has changed to word final ''-ch'' in the word "ich" (IPA ) (south of the line). This sound shift is the one that progressed the furthest north among the consonant shifts which characterize High German and Middle German dialects. The line passes through Belgium, the Netherlands, and Germany. North of the line Low German and Dutch language, Dutch are spoken. South of the line Central German is spoken. In the area between the Uerdingen line and the Benrath line to its south, which includes parts of Belgium and the Netherlands, the Germanic dialect Limburgish is spoken. In eastern Germany, the regional languages have been largely replaced by standard German language, German since the 20th century. The western en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
South Low Franconian
South Low Franconian is a group of transitional dialects between Low Franconian and Ripuarian, part of the so-called Rhenish fan, a much larger transitional area between Low Franconian and Rhine Franconian. Linguists hold different opinions about the classification of South Low Franconian: the consensus view among Dutch and Belgian linguists is that South Low Franconian is a part of Low Franconian, whereas German linguists either agree with its inclusion within Low Franconian or instead position South Low Franconian within Central Franconian, either as part of its Ripuarian branch or as a sister group of it. In the Netherlands, dialects included within in this group (commonly referred to as "Limburgish") have gained recognition as a regional language in the province of Limburg. Terminology Usage of the name "South Low Franconian" (, ) for this dialect group was originally restricted to German dialectology, while Dutch dialectologists generally employ the terms Limburgish (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
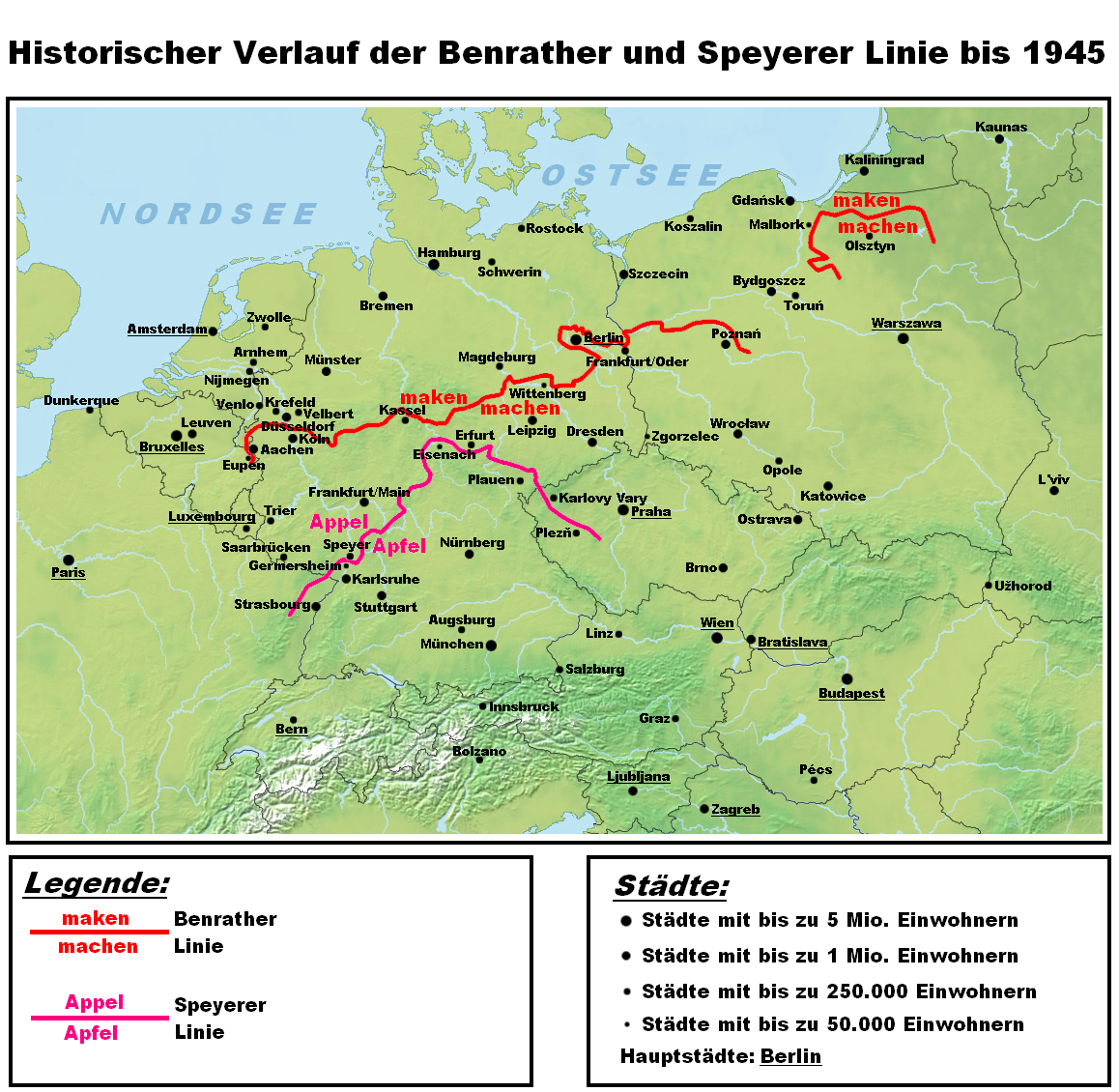
Benrath Line
In German linguistics, the Benrath line () is the isogloss: dialects north of the line have the original in (to make), while those to the south have the innovative (). The line runs from Aachen in the west via Benrath (south of Düsseldorf) to eastern Germany near Frankfurt an der Oder in the area of Berlin and Dessau and through former East Prussia dividing Low Prussian dialect and High Prussian dialect. It is called Benrath line because Benrath is the place where it crosses the Rhine. The High German consonant shift (3rd to 9th centuries AD), in which the (northern) Low German dialects for the most part did not participate, affected the southern varieties of the West Germanic dialect continuum. This shift is traditionally seen to distinguish the High German varieties from the other West Germanic languages The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic languages, Germanic family of languages (the others being the North German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
German Dialects
German dialects are the various traditional local varieties of the German language. Though varied by region, those of the southern half of Germany beneath the Benrath line are dominated by the geographical spread of the High German consonant shift, and the dialect continuum that connects High German to the neighboring varieties of Low Franconian ( Dutch) and Low German. The varieties of German are conventionally grouped into Upper German, Central German and Low German; Upper and Central German form the High German subgroup. Standard German is a standardized form of High German, developed in the early modern period based on a combination of Central German and Upper German varieties. Etymology and nomenclature Traditionally, all of the major dialect groupings of German dialects are typically named after so-called " stem duchies" or "tribal duchies" (German: ''Stammesherzogtümer'') by early German linguists, among whom the Brothers Grimm were especially influential. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
West Germanic Gemination
West Germanic gemination was a sound change that took place in all West Germanic languages around the 3rd or 4th century AD. It affected consonants directly followed by , which were generally lengthened or geminated in that position. Because of Sievers' law, only consonants immediately after a short vowel were affected by the process. Overview When followed by , consonants were lengthened (doubled). The consonant , whether original or from earlier through rhotacization, was generally not affected; it occasionally shows gemination in Old High German, but inconsistently and this may be an analogical change. In contrast, the second element of the diphthongs ''iu'' and ''au'' was still underlyingly the consonant at this time, and therefore was lengthened as well. In Proto-Germanic, only appeared at the beginning of a syllable, primarily as the onset of a variety of suffixes and endings. It alternated with its syllabic counterpart in accordance with a phonological rule known as S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |