|
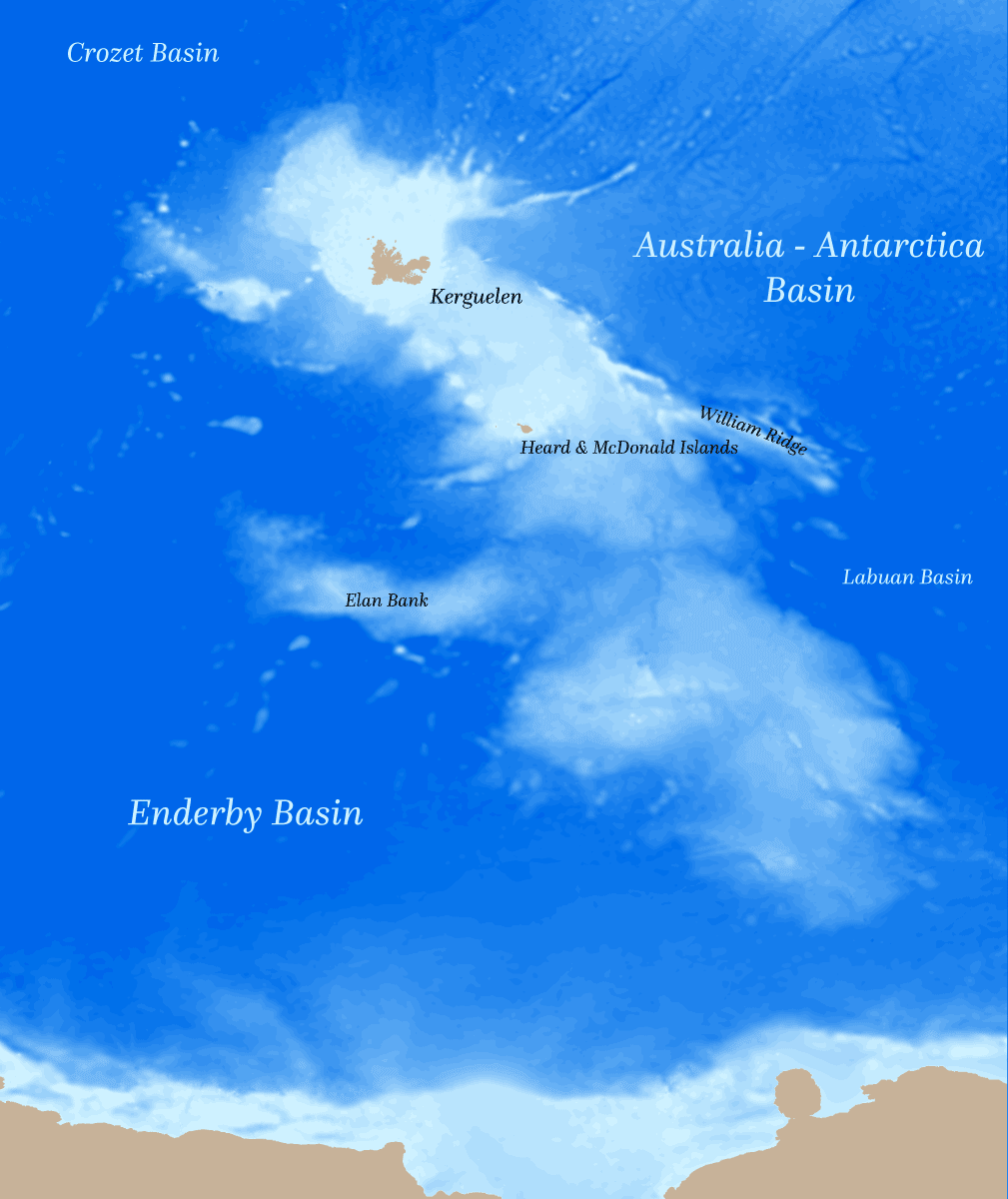
Kerguelen Plateau
The Kerguelen Plateau (, ), also known as the Kerguelen–Heard Plateau, is an oceanic plateau and a large igneous province (LIP) located on the Antarctic Plate, in the southern Indian Ocean. It is about to the southwest of Australia and is nearly three times the size of California. The plateau extends for more than in a northwest–southeast direction and lies in deep water. The plateau was produced by the Kerguelen hotspot, starting with or following the breakup of Gondwana about 130 million years ago. A small portion of the plateau breaks sea level, forming the Kerguelen Islands (a French overseas territory) plus the Heard and McDonald Islands (an Australian external territory). Intermittent volcanism continues on the Heard and McDonald Islands. Geographical extent Symmetrically across the Indian Ocean ridge and due west of Australia is the Broken Ridge underwater volcanic plateau, which at one time was contiguous with the Kerguelen Plateau before rifting by the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory
Lamont or LaMont may refer to: People *Lamont (name), people with the surname or given name ''Lamont'' or ''LaMont'' * Clan Lamont, a Scottish clan Places Canada *Lamont, Alberta, a town in Canada *Lamont County, a municipal district in Alberta United States *Lamont, California *Lamont, Florida *Lamont, Iowa *Lamont, Kansas * Lamont, Kentucky *Lamont, Nebraska *Lamont, Oklahoma *Lamont, Washington *Lamont, Wisconsin, a town **Lamont (community), Wisconsin, an unincorporated community *Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory, New York Music *Lamont Harp, one of only three surviving medieval Gaelic harps Other uses *Lamont (lunar crater), a crater on the Moon *Lamont (Martian crater), a crater on Mars *Lamont Gallery, an art gallery in Exeter, New Hampshire *Lamonts, a chain department store See also *Lamonte (other) LaMonte, Lamonte or La Monte may refer to the following people: Surname * Bob LaMonte, American sports agent * Collene Lamonte, American politician from M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labuan Basin
Labuan (), officially the Federal Territory of Labuan ( ms, Wilayah Persekutuan Labuan), is a Federal Territory of Malaysia. Its territory includes and six smaller islands, off the coast of the state of Sabah in East Malaysia. Labuan's capital is Victoria and is best known as an offshore financial centre offering international financial and business services via Labuan IBFC since 1990 as well as being an offshore support hub for deepwater oil and gas activities in the region. It is also a tourist destination for people travelling through Sabah, nearby Bruneians and scuba divers. The name Labuan derives from the Malay word ''labuhan'' which means harbour. History For three centuries from the 15th century, the north and west coast of Borneo including the island of Labuan was part of the Sultanate of Brunei. In 1775, Labuan was temporarily occupied by the British East India Company after the failure of the company's station at Balambangan Island. The Sultan of Brunei, Omar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooperation Sea
Cooperation Sea, also called Commonwealth Sea (erratum) or Sodruzhestvo Sea (russian: Море Содружества), is a proposed sea name for part of the Southern Ocean, between Enderby Land (the eastern limit of which is 59°34'E) and West Ice Shelf (85°E), off the coast of MacRobertson Land and Princess Elizabeth Land. It would stretch over an area of 258,000 km². It would be bordered by the Davis Sea on the east, and by another Russian proposal to the 2002 International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) draft, a Cosmonauts Sea to the west. The Cooperation Sea was named in 1962 by the Soviet Antarctic Expedition in honor of international science cooperation in Antarctica. The name first appeared as a proposal to the IHO in the IHO 2002 draft. This draft was never approved by the IHO (or any other organization), and the 1953 IHO document (which does not contain the name) remains currently in force. Leading geographic authorities and atlases do not use the name, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Elizabeth Trough
Princess is a regal rank and the feminine equivalent of prince (from Latin ''princeps'', meaning principal citizen). Most often, the term has been used for the consort of a prince, or for the daughter of a king or prince. Princess as a substantive title Some princesses are reigning monarchs of principalities. There have been fewer instances of reigning princesses than reigning princes, as most principalities excluded women from inheriting the throne. Examples of princesses regnant have included Constance of Antioch, princess regnant of Antioch in the 12th century. Since the President of France, an office for which women are eligible, is ''ex-officio'' a Co-Prince of Andorra, then Andorra could theoretically be jointly ruled by a princess. Princess as a courtesy title Descendants of monarchs For many centuries, the title "princess" was not regularly used for a monarch's daughter, who, in English, might simply be called "Lady". Old English had no female equivalent of "prince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigues Triple Point
The Rodrigues Triple Junction (RTJ), also known as the Central Indian ceanTriple Junction (CITJ) is a geologic triple junction in the southern Indian Ocean where three tectonic plates meet: the African Plate, the Indo-Australian Plate, and the Antarctic Plate. The triple junction is named for the island of Rodrigues which lies north-west of it. The RTJ was first recognized in 1971, then described as a stable R-R-R (ridge-ridge-ridge) triple junction based on coarse ship data. Boundaries The boundaries of the three plates which meet at the Rodrigues Triple Junction are all oceanic spreading centers, making it an R-R-R type triple junction. They are: the Central Indian Ridge (CIR, between the African and Indo-Australian plates) with a spreading rate of 50 mm/yr; the Southwest Indian Ridge (SWIR, between the African and Antarctic plates) 16 mm/yr; and the Southeast Indian Ridge (SEIR, between the Indo-Australian and Antarctic plates) 60 mm/yr. The SEIR has the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Indian Ridge
The Southwest Indian Ridge (SWIR) is a mid-ocean ridge located along the floors of the south-west Indian Ocean and south-east Atlantic Ocean. A divergent tectonic plate boundary separating the Somali Plate to the north from the Antarctic Plate to the south, the SWIR is characterised by ultra-slow spreading rates (only exceeding those of the Gakkel Ridge in the Arctic) combined with a fast lengthening of its axis between the two flanking triple junctions, Rodrigues () in the Indian Ocean and Bouvet () in the Atlantic Ocean. Geological setting Spreading rates The spreading rate along the SWIR varies: the transition between slow (30 mm/yr) and ultra-slow (15 mm/yr) spreading occur at magnetic anomaly C6C (ca. 24 Ma). This occurs between 54°–67°E, the deepest, and perhaps coldest and most melt-poor, part of Earth's mid-ocean ridge system. Crustal thickness decreases quickly as spreading rates drop below c. 20 mm/yr and in the SWIR there is an absence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeast Indian Ridge
The Southeast Indian Ridge (SEIR) is a mid-ocean ridge in the southern Indian Ocean. A divergent tectonic plate boundary stretching almost between the Rodrigues Triple Junction () in the Indian Ocean and the Macquarie Triple Junction () in the Pacific Ocean, the SEIR forms the plate boundary between the Australian and Antarctic plates since the Oligocene ( anomaly 13). The SEIR is the spreading centre closest to the Kerguelen and Amsterdam– Saint-Paul hotspot. The SEIR has an intermediate full spreading rate of 65 mm/yr, and, because Antarctica is virtually stationary, this results in a northward ridge migration of half that rate. Spreading rates along the SEIR varies from 69 mm/yr near 88°E to 75 mm/yr near 120°E. Geology Amsterdam−St. Paul hotspot During the past 1 Ma the Amsterdam–St. Paul hotspot (ASP) has produced a 150×200 km plateau straddling on the SEIR. The ASP Plateau covers and area of 30,000 km2 and rises 500 m a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
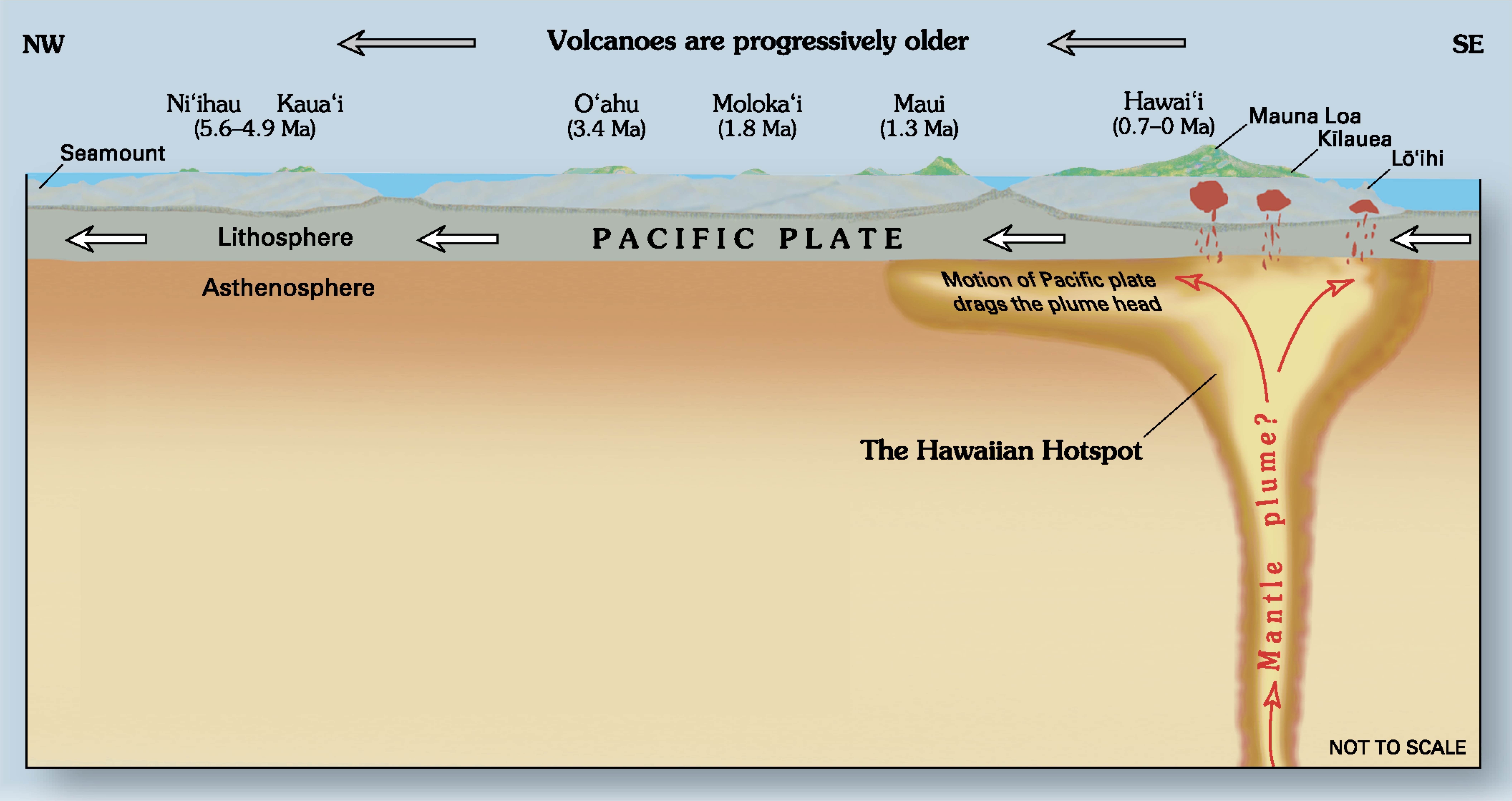
Hotspot (geology)
In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The alternative plate theory is that the mantle source beneath a hotspot is not anomalously hot, rather the crust above is unusually weak or thin, so that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. Origin The origins of the concept of hotspots lie in the work of J. Tuzo Wilson, who postulated in 1963 that the formation of the Hawaiian Islands resulted from the slow movement of a te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between Sangaman Kanda, Sri Lanka, and the north westernmost point of Sumatra, Indonesia. It is the largest water region called a bay in the world. There are countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal in South Asia and Southeast Asia. During the existence of British India, it was named as the Bay of Bengal after the historic Bengal region. At the time, the Port of Kolkata served as the gateway to the Crown rule in India. Cox's Bazar, the longest sea beach in the world and Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest and the natural habitat of the Bengal tiger, are located along the bay. The Bay of Bengal occupies an area of . A number of large rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal: the Ganges– Hooghly, the Padma, the Brahmaputra–Yamuna, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninety East Ridge
The Ninety East Ridge (also rendered as Ninetyeast Ridge, 90E Ridge or 90°E Ridge) is a mid-ocean ridge on the Indian Ocean floor named for its near-parallel strike along the 90th meridian at the center of the Eastern Hemisphere. It is approximately in length and can be traced topographically from the Bay of Bengal southward towards the Southeast Indian Ridge (SEIR), though the feature continues to the north where it is hidden beneath the sediments of the Bengal Fan. The ridge extends between latitudes 33°S and 17°N and has an average width of 200 km. Description The ridge divides the Indian Ocean into the West and East Indian Ocean. The northeastern side is named the Wharton Basin and ceases at the western end of the Diamantina Fracture Zone which passes to the east and almost to the Australian continent.Stow, D. A. V. (2006) ''Oceans : an illustrated reference'' Chicago : University of Chicago Press, - page 127 for map of Indian Ocean and ridges The ridge is primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |