|
Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon to the southwest, Nigeria to the southwest (at Lake Chad), and Niger to the west. Chad has a population of 16 million, of which 1.6 million live in the capital and largest city of N'Djamena. Chad has several regions: a desert zone in the north, an arid Sahelian belt in the centre and a more fertile Sudanian Savanna zone in the south. Lake Chad, after which the country is named, is the second-largest wetland in Africa. Chad's official languages are Arabic and French. It is home to over 200 different ethnic and linguistic groups. Islam (55.1%) and Christianity (41.1%) are the main religions practiced in Chad. Beginning in the 7th millennium BC, human populations moved into the Chadian basin in great number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N'Djamena
N'Djamena ( ) is the capital and largest city of Chad. It is also a special statute region, divided into 10 districts or ''arrondissements''. The city serves as the centre of economic activity in Chad. Meat, fish and cotton processing are the chief industries, and it is a regional market for livestock, salt, dates, and grains. It is a port city located at the confluence of the Logone River with the Chari River, forming a transborder agglomeration with the city of Kousséri (in Cameroon), capital of the Department of Logone-et-Chari, which is on the west bank of both rivers. It had 1,093,492 inhabitants in 2013. History N'Djamena was founded as Fort-Lamy by French commander Émile Gentil on 29 May 1900, and named after Amédée-François Lamy, an army officer who had been killed in the Battle of Kousséri about a month earlier. It was a major trading city and became the capital of the region and nation. During the Second World War, the French relied upon the city's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
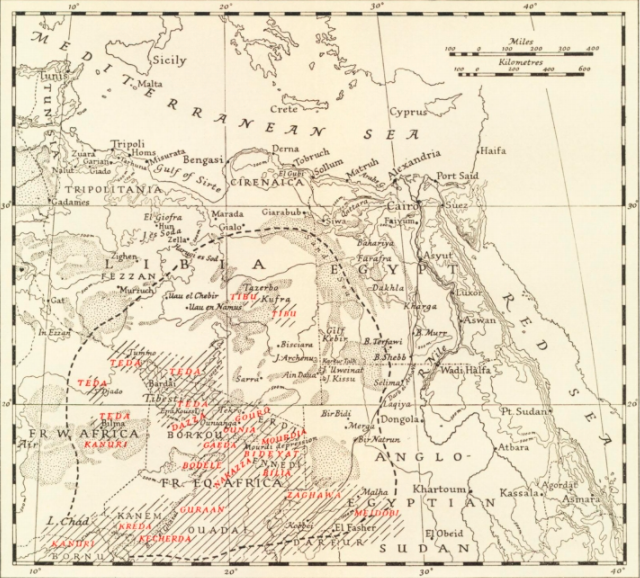
Toubou People
The Toubou or Tubu (from Old Tebu, meaning "rock people") are an ethnic group native to the Tibesti Mountains that inhabit the central Sahara in northern Chad, southern Libya and northeastern Niger. They live either as herders and nomads or as farmers near oases. Their society is clan-based, with each clan having certain oases, pastures and wells. The Toubou are generally divided into two closely related groups: the Teda (or Téda, Toda) and the Dazagara (or Dazzaga, Dazagada, Daza). They are believed to share a common origin and speak the Tebu languages, which are from the Saharan branch of the Nilo-Saharan language family. Tebu is divided further into two closely related languages, called '' Tedaga'' (Téda Toubou) and '' Dazaga'' (Dazaga Gouran). Of the two groups, the Daza, found to the south of the Teda, are more numerous. The Toubou people are also referred to as the Tabu, Tebu, Tebou, Tibu, Tibbu, Toda, Todga, Todaga, Tubu, Tuda, Tudaga, or Gorane people. The Daza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
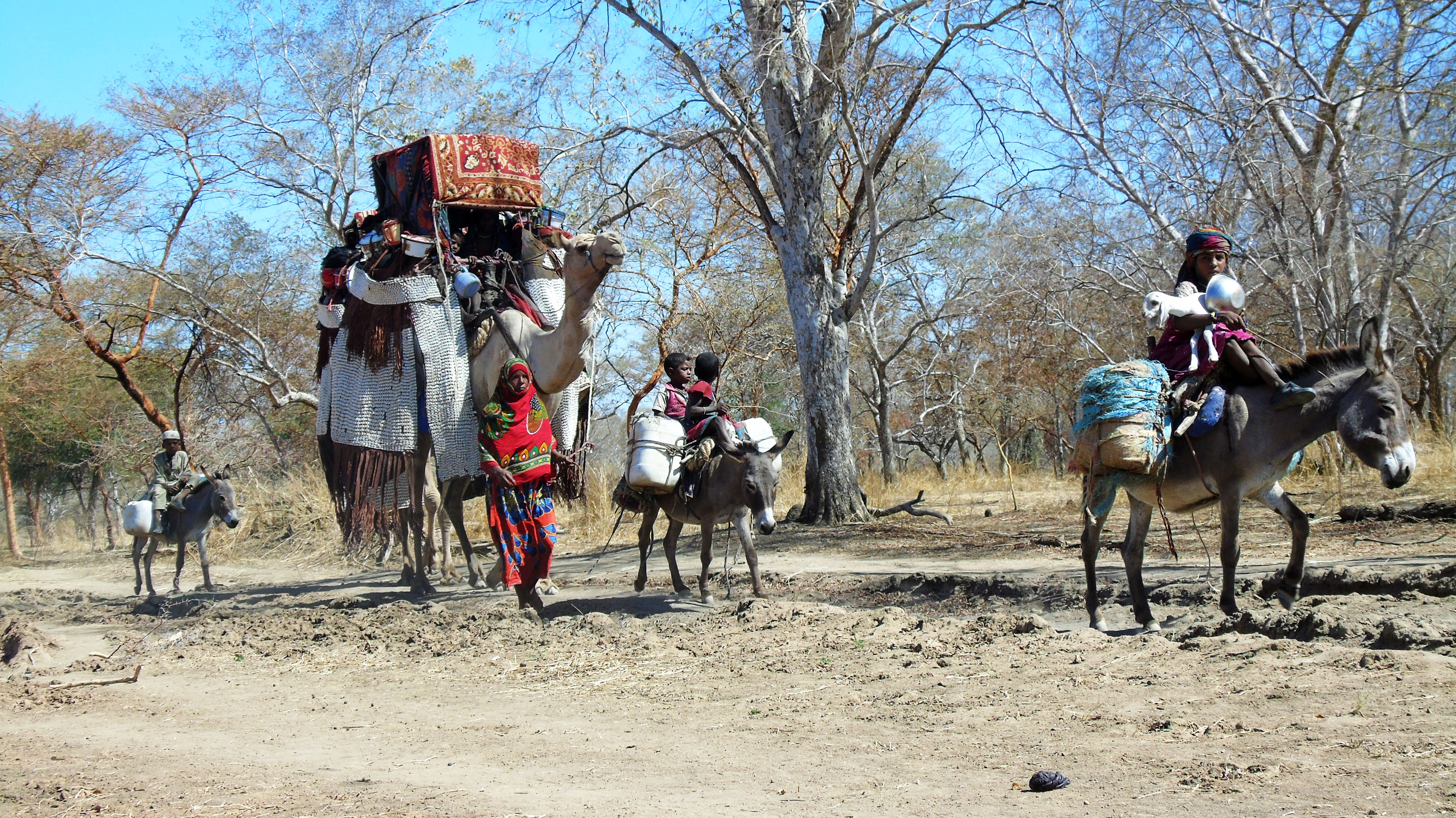
Ethnic Groups In Chad
__NOTOC__ The population of Chad has numerous ethnic groups. SIL Ethnologue reports more than 130 distinct languages spoken in Chad. History and demographics The 14 million Chad people belong to some 200 ethnicities, who speak numerous languages. The peoples of Chad carry significant ancestry from Eastern, Central, Western, and Northern Africa. The population can be broadly divided between those in the east, north and west who follow Islam, and the peoples of the south, the five southernmost prefectures, who are mostly Christian or animist. The southern part of the country was historically the cross roads of the caravan routes below the Sahara, forming a link between West Africa and the Arabic region, as well as one between North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa. The slave trade between sub-Saharan Africa and the Middle East passed through the slave markets of Chad and Western Sudan, slave-trading was a key component of Chad's historic economy, and this brought people of various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sara People
The Sara people are a Central Sudanic ethnic group native to southern Chad, the northwestern areas of the Central African Republic, and the southern border of North Sudan. They speak the Sara languages which are a part of the Central Sudanic language family. They are also the largest ethnic group in Chad. Sara oral histories add further details about the people. In summary, the Sara are mostly animists (veneration of nature), with a social order made up of several patrilineal clans formerly united into a single polity with a national language, national identity, and national religion. Many Sara people have retained their ethnic religion, but some have converted to Christianity and Islam. Overview In Chad The Sara (Kameeni) are the largest ethnic group in the Republic of Chad, they're concentrated in the Moyen-Chari, the Logone Oriental, the Logone Occidental, and parts of the Tandjile regions. After their arrival, they continued to be the target of violent raids by northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In Chad
Christianity arrived in Chad more recently than other religions, with the arrival of Europeans. Its followers are divided into Roman Catholics and Protestants (including several denominations) and collectively represent 45% of population.https://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/FR90/FR90.pdf Protestantism The Protestants came to southern Chad in the 1920s. The American organization Baptist Mid-Missions was the first Protestant mission to settle in the country in 1925 in Sarh.J. Gordon Melton, Martin Baumann, ''Religions of the World: A Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Beliefs and Practices'', ABC-CLIO, USA, 2010, p. 534 Missionaries of other denominations and nationalities soon followed. Many of the American missions were northern offshoots of missionary networks founded farther south in the Ubangi-Chari colony (now Central African Republic) of French Equatorial Africa (Afrique Equatoriale Franchise — AEF). The organizational ties between the missions in southern Chad and Ubangi-Chari were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula People
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide. A significant proportion of the Fula – a third, or an estimated 12 to 13 million – are pastoralists, and their ethnic group has the largest nomadic pastoral community in the world., Quote: The Fulani form the largest pastoral nomadic group in the world. The Bororo'en are noted for the size of their cattle herds. In addition to fully nomadic groups, however, there are also semisedentary Fulani � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaghawa People
The Zaghawa people, also called Beri or Zakhawa, are a Sahelian Muslim ethnic group primarily residing in Fezzan North-eastern Chad, and western Sudan, including Darfur. Zaghawas speak the Zaghawa language, which is an eastern Saharan language. They are pastoralists, and a breed of sheep that they herd is called Zaghawa by the Arabs. They are nomadic and obtain much of their livelihood through herding cattle, camels and sheep and harvesting wild grains. It has been estimated that there are 307,000 Zaghawas. Names The Kanemite royal history, the Girgam, refers to the Zaghawa people as the Duguwa. Today, Zaghawa refer to themselves as the ''Beri'', while the Arab people and literature refers to them as "Zaghawa". In literature related to African ethnic groups, the term ''Beri'' (sometimes ''Kegi'') includes Zaghawas, Bideyat and Bertis peoples, each clustered in different parts of Chad, Sudan and Libya. History The Zaghawa are mentioned in classical Arabic language tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baggara Arabs
The Baggāra ( ar, البَقَّارَة "heifer herder") or Chadian Arabs are a nomadic confederation of people of mixed Arab and Arabized indigenous African ancestry, inhabiting a portion of the Sahel mainly between Lake Chad and the Nile river near south Kordofan, numbering over six million. They are known as Baggara and Abbala in Sudan, and as Shuwa Arabs in Cameroon, Nigeria and Western Chad. The term Shuwa is said to be of Kanuri origin. The Baggāra mostly speak their distinct dialect, known as Chadian Arabic. However the Baggāra of Southern Kordofan, due to contact with the sedentary population and the Sudanese Arab camel herders of Kordofan, has led to some Sudanese Arabic influence on the dialect of that zone. They also have a common traditional mode of subsistence, nomadic cattle herding, although nowadays many lead a settled existence. Nevertheless, collectively they do not all necessarily consider themselves one people, i.e., a single ethnic group. The term "b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In Chad
The earliest presence of Islam in Chad can be traced back to Uqba ibn Nafi, whose descendants can be found settled in the Lake Chad region to this day. By the time Arab migrants began arriving from the east in the fourteenth century in sizeable numbers, the creed was already well established. Islamization in Chad was gradual, the effect of the slow spread of Islamic civilization beyond its political frontiers.Library of Congress., and Thomas Collelo. Chad, a country study. 2nd ed. Washington D.C.: Federal Research Division Library of Congress ;For sale by the Supt. of Docs. U.S. G.P.O, 1990. Among Chadian Muslims, 48% professed to be Sunni, 21% Shia, 23% just Muslim and 4% Other. Islam in Chad was not influenced much by the great mystical movements of the Islamic Middle Ages, nor the fundamentalist upheavals that affected other countries. Consistent contact with West African Muslim traders and pilgrims may be the reason Chadian Muslims identify with the Tijaniyya order. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tchadienne
"" (, ) is the national anthem of Chad Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic .... Written by Louis Gidrol and his student group and composed by Paul Villard, it has been the official state anthem of Chad since it gained independence from France in January 1960. History The anthem was written, following a competition, by Jesuit father Louis Gidrol and his student group from the Saint Paul Boarding School in Fort-Archambault (the current city of Sarh). The music was composed by another Jesuit father, Paul Villard. It was adopted as the official state anthem of Chad upon gaining independence from France in January 1960. Lyrics The anthem comprises a chorus and four verses. Only the chorus and first verse constitute the official national anthem. The other three vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tchadienne (instrumental)
"" (, ) is the national anthem of Chad. Written by Louis Gidrol and his student group and composed by Paul Villard, it has been the official state anthem of Chad since it gained independence from France in January 1960. History The anthem was written, following a competition, by Jesuit father Louis Gidrol and his student group from the Saint Paul Boarding School in Fort-Archambault Semi-active radar homing (SARH) is a common type of missile guidance system, perhaps the most common type for longer-range air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems. The name refers to the fact that the missile itself is only a passive de ... (the current city of Sarh). The music was composed by another Jesuit father, Paul Villard. It was adopted as the official state anthem of Chad upon gaining independence from France in January 1960. Lyrics The anthem comprises a chorus and four verses. Only the chorus and first verse constitute the official national anthem. The other three verses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tama People
Tama are a non-Arab, African ethnic group of people who live in eastern Chad and western Sudan. They speak Tama, a Nilo-Saharan language. The population is 200,000–300,000 people and they practice Islam. Many Tama are subsistence farmers who live in permanent settlements and some raise livestock. In the civil war in Chad (2005–2010) the Tama were involved in ethnic conflicts with the Zaghawa tribe. Culture The Tama people are a non-ArabHuman Rights Watch, p. 11 (i.e., "Indigenous African" ) tribe that live in Dar Tama in northeastern Chad and Darfur in western Sudan. They number 200,000–300,000. They speak Tama, a Nilo-Saharan language. Many of the Tama are subsistence farmersOlson, p. 42 who live in permanent settlements and raise millet, beans, cucumbers, gumbo, and sesame. They also raise cattle, camels and goats. The majority of Tama are Muslims, but they also have some animistic beliefs. Subgroups The Tama are made up of a number of subgroups: Abu Sharib (approximat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |