|
Zoopagomycetes
The Zoopagomycotina are a subdivision (''incertae sedis'') of the fungal division Zygomycota ''sensu lato''. It contains 5 families and 20 genera.ygomycetes.orgurl=http://zygomycetes.org/index.php?id=8 Relationships among and within subphyla of Zygomycota are poorly understood, and their remains in question, so they are sometimes referred to by the informal name . Zoopagomycotina are microscopic and are typically obligate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with Arthropod, arthropods, Tardigrade, tardigrades and other moulting animalia, animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike platyhelminthe, flatworms, have tubular digestion, digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallus
Thallus (plural: thalli), from Latinized Greek (), meaning "a green shoot" or "twig", is the vegetative tissue of some organisms in diverse groups such as algae, fungi, some liverworts, lichens, and the Myxogastria. Many of these organisms were previously known as the thallophytes, a polyphyletic group of distantly related organisms. An organism or structure resembling a thallus is called thalloid, thallodal, thalliform, thalline, or thallose. A thallus usually names the entire body of a multicellular non-moving organism in which there is no organization of the tissues into organs. Even though thalli do not have organized and distinct parts (leaves, roots, and stems) as do the vascular plants, they may have analogous structures that resemble their vascular "equivalents". The analogous structures have similar function or macroscopic structure, but different microscopic structure; for example, no thallus has vascular tissue. In exceptional cases such as the Lemnoideae, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
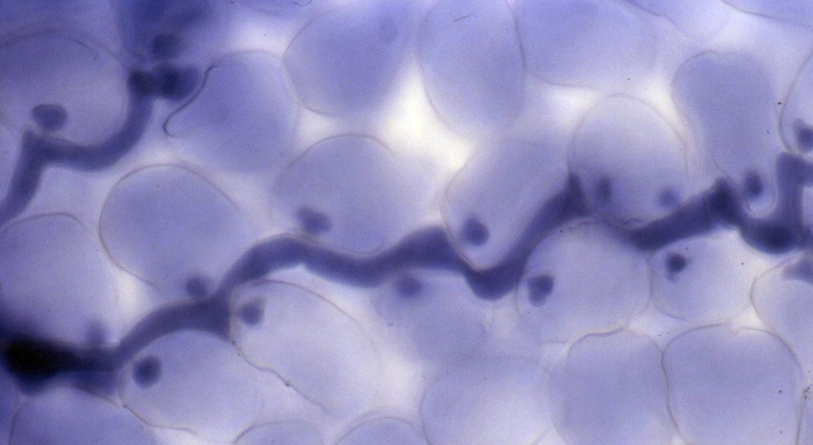
Hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenocytic
A coenocyte () is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without their accompanying cytokinesis, in contrast to a syncytium, which results from cellular aggregation followed by dissolution of the cell membranes inside the mass. The word syncytium in animal embryology is used to refer to the coenocytic blastoderm of invertebrates. A coenocytic colony is referred to as a coenobium (plural coenobia), and most coenobia are composed of a distinct number of cells, often as a multiple of two (4, 8, etc.). Research suggests that coenobium formation may be a defense against grazing in some species. Physiological examples Protists Diplomonads, like ''Giardia'', have two nuclei. Ciliates have cells that contain two nuclei: a macronucleus and a micronucleus. The schizont of apicomplexan parasites is a form of a coenocyte (i.e. a plasmodium in the general sense) as well as the plasmodia of microsporidian (Fungi) and myxosporidian (Metazoa) parasites. The tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chitin are produced each year in the biosphere. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi (especially basidiomycetes and filamentous fungi), the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans and insects, the radulae, cephalopod beaks and gladii of molluscs and in some nematodes and diatoms. It is also synthesised by at least some fish and lissamphibians. Commercially, chitin is extracted from the shells of crabs, shrimps, shellfishes and lobsters, which are major by-products of the seafood industry. The structure of chitin is comparable to cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or whiskers. It is functionally comparable to the protein keratin. Chitin has proved useful for several medicinal, industrial and biotechnological purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lineage (evolution)
An evolutionary lineage is a temporal series of populations, organisms, cells, or genes connected by a continuous line of descent from ancestor to descendant.The Oxford English Dictionary defines biological lineage as "a sequence of species each of which is considered to have evolved from its predecessorOED definition of lineage/ref> Lineages are subsets of the evolutionary tree of life. Lineages are often determined by the techniques of molecular systematics. Phylogenetic representation of lineages 299x299px, A rooted tree of life into three ancient monophyletic lineages: bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes">archaea.html" ;"title="bacteria, archaea">bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes based on rRNA genes Lineages are typically visualized as subsets of a phylogenetic tree. A lineage is a single line of descent or linear chain within the tree, while a clade is a (usually branched) monophyletic group, containing a single ancestor and all its descendants. Phylogenetic trees are typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotrophic
Symbiosis (from Ancient Greek, Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different Organism, biological organisms, be it Mutualism (biology), mutualistic, commensalism, commensalistic, or parasitism, parasitic. The organisms, each termed a symbiont, must be of different species. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term was subject to a century-long debate about whether it should specifically denote mutualism, as in lichens. Biologists have now abandoned that restriction. Symbiosis can be obligatory, which means that one or more of the symbionts depend on each other for survival, or facultative (optional), when they can generally live independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. When symbionts form a single body it is called conjunctive symbiosis, while all other arrangements are called disjunct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haustoria
In botany and mycology, a haustorium (plural haustoria) is a rootlike structure that grows into or around another structure to absorb water or nutrients. For example, in mistletoe or members of the broomrape family, the structure penetrates the host's tissue and draws nutrients from it. In mycology, it refers to the appendage or portion of a parasitic fungus (the hyphal tip), which performs a similar function. Microscopic haustoria penetrate the host plant's cell wall and siphon nutrients from the space between the cell wall and plasma membrane but do not penetrate the membrane itself. Larger (usually botanical, not fungal) haustoria do this at the tissue level. The etymology of the name corresponds to the Latin word ''haustor'' meaning ''the one who draws, drains or drinks'', and refers to the action performed by the outgrowth. In fungi Fungi in all major divisions form haustoria. Haustoria take several forms. Generally, on penetration, the fungus increases the surface ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectoparasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's body; a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |