|
Zhang Chunqiao
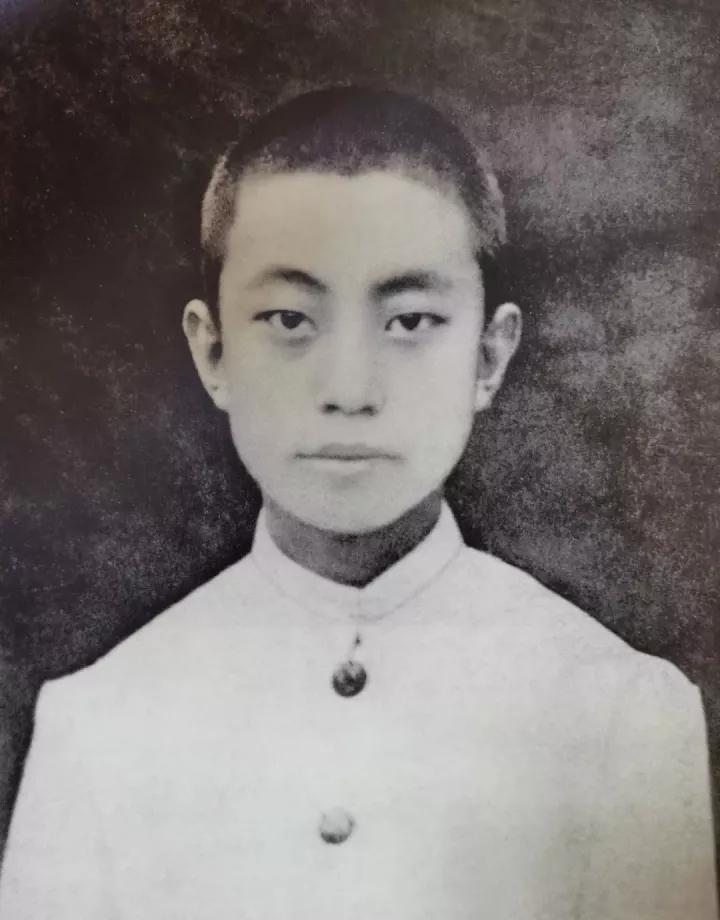
Zhang Chunqiao (; 1 February 1917 – 21 April 2005) was a prominent Chinese political theorist, writer, and politician. He came to the national spotlight during the late stages of the Cultural Revolution, and was a member of the ultra-Maoist group dubbed the "Gang of Four". Biography Born in Juye County, Shandong, Zhang worked as a writer in Shanghai in the 1930s and became closely associated with the city. After the Yan'an conference in 1938, he joined the Communist Party of China. With the creation of the People's Republic of China, he became a prominent journalist in Shanghai in charge of the ''Liberation Daily'' newspaper. He met Jiang Qing in Shanghai and helped to launch the Cultural Revolution. Zhang first came to prominence as the result of his October 1958 ''Jiefang'' ("Liberation") magazine entitled “Destroy the Ideology of Bourgeois Right.” Mao Zedong ordered the reproduction of the article in ''People’s Daily'', and personally wrote an accompanying “Edito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang (surname)
Zhang () is the third most common surname in China and Taiwan (commonly spelled as "Chang" in Taiwan), and it is one of the most common surnames in the world. Zhang is the pinyin romanization of the very common Chinese surname written in simplified characters and in traditional characters. It is spoken in the first tone: ''Zhāng''. It is a surname that exists in many languages and cultures, corresponding to the surname 'Archer' in English for example. In the Wade-Giles system of romanization, it is romanized as "Chang", which is commonly used in Taiwan; "Cheung" is commonly used in Hong Kong as romanization. It is also the pinyin romanization of the less-common surnames (''Zhāng''), which is the 40th name on the '' Hundred Family Surnames'' poem. There is the even-less common (''Zhǎng''). was listed 24th in the famous Song-era '' Hundred Family Surnames'', contained in the verse 何呂施張 (He Lü Shi Zhang). Today, it is one of the most common surnames in the worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Revolution Group
The (Central) Cultural Revolution Group (CRG or CCRG; ) was formed in May 1966 as a replacement organisation to the Central Committee Secretariat and the "Five Man Group", and was initially directly responsible to the Standing Committee of the Politburo. It consisted mainly of radical supporters of Mao, including Chen Boda, the Chairman's wife Jiang Qing, Kang Sheng, Yao Wenyuan, Zhang Chunqiao, Wang Li and Xie Fuzhi. The CRG played a central role in the Cultural Revolution's first few years, and for a period of time the group replaced the Politburo Standing Committee (PSC) as the ''de facto'' top power organ of China. Its members were also involved in many of the major events of the Cultural Revolution. Background In January 1965, at a meeting of the Politburo, Mao Zedong called on the leaders of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) to implement a "Cultural Revolution" in China. (The Oxford English Dictionary traces the English-language phrase "cultural revolution" (defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
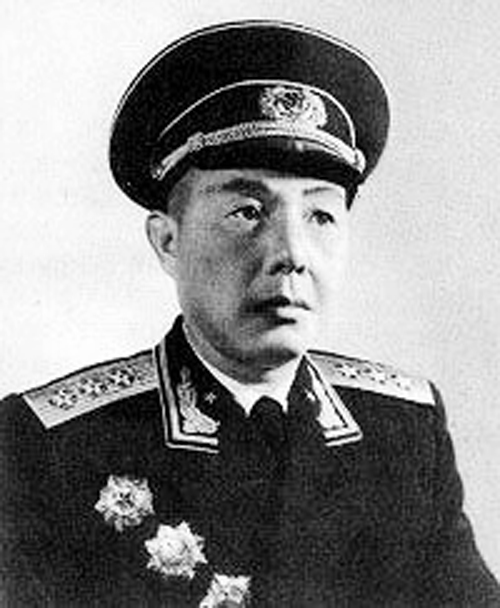
Su Zhenhua
Su Zhenhua (; June 2, 1912 – February 7, 1979), born Su Qisheng (蘇七生), was a Chinese Communist general and politician. He fought for the Communists in the Chinese civil war. After the founding of the People's Republic, Su became an admiral in the People's Liberation Army Navy, the Party Secretary of Guizhou province, the First Secretary of Shanghai, and a member of the Politburo of the Chinese Communist Party. Su was born in Pingjiang County, Hunan province. Su joined a guerrilla fighting force in 1926 at age 14, and entered the Communist Youth League three years later. He joined the Red Army in June 1930 and the Communist Party several years later. He participated in the Long March and was instrumental in the Communist takeover of Zunyi. He then served successively in a series of roles as political commissar. In December 1949, following the Communist takeover of Guizhou province, Su became the Party Committee Secretary of Guizhou.徐行,《明報月刊》 (''Ming P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayor Of Shanghai
This is a list of mayors of Shanghai, China. In the People's Republic of China, the mayor is subordinate to the Communist Party Secretary of Shanghai. Republic of China Mayor of the Shanghai Special Municipal Government # Huang Fu (July 7, 1927 – August 14, 1927) # Wu Zhenxiu (August 15, 1927 – September 16, 1927) # Zhang Dingfan (September 17, 1927 – March 31, 1929) # Zhang Qun (April 1, 1929 – June 29, 1930) Mayor of the Shanghai Municipal Government # Zhang Qun (July 1, 1930 – January 6, 1932) # Wu Tieh-cheng (January 7, 1932 – March 31, 1937) # Yu Hung-chun (April 1, 1937 – August 13, 1945) Mayors under Japanese occupation Mayor of the Great Way Municipal Government of Shanghai # Su Xiwen (December 5, 1937 – April 27, 1938) Supervisor of the Shanghai Municipal Great Way Office # Su Xiwen (April 28, 1938 – October 15, 1938) Mayor of the Shanghai Special Municipal Government # Fu Xiaoan (October 16, 1938 – October 11, 1940) # Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hua Guofeng
Hua Guofeng (; born Su Zhu; 16 February 1921 – 20 August 2008), alternatively spelled as Hua Kuo-feng, was a Chinese politician who served as Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party and Premier of the People's Republic of China. The designated successor of Mao Zedong, Hua held the top offices of the government, party, and the military after the deaths of Mao and Premier Zhou Enlai, but was gradually forced out of supreme power by a coalition of party leaders between December 1978 and June 1981, and subsequently retreated from the political limelight, though still remaining a member of the Central Committee until 2002. Born and raised in Jiaocheng, Shanxi, Hua was educated at the Jiaocheng County Commercial School and joined the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) in 1938, seeing action in both the Second Sino–Japanese War and the Chinese Civil War as a guerrilla fighter.Ye Yonglie, 邓小平改变中国——1978:中国命运大转折 (Deng Xiaoping Changed China-1978: Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Xiannian
Li Xiannian (pronounced ; 23 June 1909 – 21 June 1992) was a Chinese Communist military and political leader, President of the People's Republic of China (''de jure'' head of state) from 1983 to 1988 under Paramount Leader Deng Xiaoping and then Chairman of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference from 1988 until his death. He was a full member of the Politburo from 1956 to 1987, and of its Standing Committee from 1977 to 1987.''Li Xiannian (1909–1992)'', in Christopher R. Lew, Edwin Pak-wah Leung: ''Historical Dictionary of the Chinese Civil War'', p.p. 120-121, Scarecrow Press, 2013Holley, David"Li Xiannian, Ex-President of China, Dies at 83: Old Guard: He was one of a ruling clique of ‘8 elders’ who ordered the army to repress the pro-democracy movement in 1989".''Los Angeles Times'', 23 June 1992. Li worked as an apprentice carpenter in his teenage years to support his family. He joined the Communist Party in December 1927 and became a soldier in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ye Jianying
Ye Jianying (; 28 April 1897 – 22 October 1986) was a Chinese Communist revolutionary leader and politician, one of the founding Ten Marshals of the People's Republic of China. He was the top military leader in the 1976 coup that overthrew the Gang of Four and ended the Cultural Revolution, and was the key supporter of Deng Xiaoping in his power struggle with Hua Guofeng. After Deng ascended power, Ye served as China's head of state as Chairman of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress from 1978 to 1983. Life Born Ye Yiwei () into a wealthy Christian Hakka merchant family in an old rural village at Jiaying county (modern-day renamed as Meixian District), his courtesy name was Cangbai () and most of Ye Jianying's siblings died before being adults due to severe illness. After graduation from the Yunnan Military Academy in 1919, he joined the Kuomintang (KMT). He taught at the Whampoa Military Academy, and in 1927 joined the Communist Party. That year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping (22 August 1904 – 19 February 1997) was a Chinese revolutionary leader, military commander and statesman who served as the paramount leader of the People's Republic of China (PRC) from December 1978 to November 1989. After CCP chairman Mao Zedong's death in 1976, Deng gradually rose to supreme power and led China through a series of far-reaching market-economy reforms earning him the reputation as the "Architect of Modern China". He contributed to China becoming the world's second largest economy by GDP nominal in 2010. Born in the province of Sichuan in the Qing dynasty, Deng studied and worked in France in the 1920s, where he became a follower of Marxism–Leninism and joined the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) in 1924. In early 1926, Deng travelled to Moscow to study Communist doctrines and became a political commissar for the Red Army upon returning to China. In late 1929, Deng led local Red Army uprisings in Guangxi. In 1931, he was demoted within the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politburo Standing Committee
The Politburo Standing Committee (PSC), officially the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the Communist Party of China Central Committee, is a committee consisting of the top leadership of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Historically it has been composed of five to eleven members, and currently has seven members. Its officially mandated purpose is to conduct policy discussions and make decisions on major issues when the Politburo, a larger decision-making body, is not in session. According to the party's constitution, the General Secretary of the Central Committee must also be a member of the Politburo Standing Committee. According to the party's Constitution, the party's Central Committee elects the Politburo Standing Committee. In practice, however, this is only a formality. The method by which membership is determined has evolved over time. During the Mao Zedong era, Mao himself selected and expelled members, while during the Deng Xiaoping era consultation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politburo Of The Communist Party Of China
The Politburo of the Chinese Communist Party, formally known as the Political Bureau of the Communist Party of China Central Committee and known as the Central Bureau before 1927, is the decision-making body of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Currently, it is a group of 24 top officials who oversee the CCP and headed by the general secretary. Unlike politburos of other Communist parties, power within the Chinese politburo is further centralized in the Politburo Standing Committee, a group of 7 individuals from among the larger Politburo. The Politburo is nominally elected by the Central Committee. In practice, however, scholars of Chinese elite politics believe that the Politburo is a self-perpetuating body, with new members of both the Politburo and its Standing Committee chosen through a series of deliberations by current Politburo members and retired Politburo Standing Committee members. The current and former Politburo members conduct a series of informal straw polls to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutionary Committee (China)
Revolutionary committees () were tripartite bodies established during the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976) in the People's Republic of China to facilitate government by the three mass organisations in China — the people, the People's Liberation Army (PLA), and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). They were originally established in the power-seizure movement as a replacement system of government to the old Party apparatus, but quickly became subordinate to it. Background As the spirit of the Cultural Revolution spread across China in the latter half of 1966, it soon became clear to the Maoist leadership in Beijing that the ability of local party organizations and officials to resist the attempts by the Red Guards to remove them from power was greater than had been thought. As a result, Mao Zedong proposed dramatic seizures of power by the various Red Guard and workers' groups and the establishment of new local governments based on Karl Marx's Paris Commune model. The fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yao Wenyuan
Yao Wenyuan (January 12, 1931 – December 23, 2005) was a Chinese literary critic, a politician, and a member of the Gang of Four during China's Cultural Revolution. Biography Yao Wenyuan was born in Zhuji, Zhejiang, to an intellectual family. His father, Yao Pengzi () was a writer, translator and art critic. He began his career in Shanghai as a literary critic, where he became known for his sharp attacks against colleagues, such as in June 1957 against the newspaper '' Wenhuibao''. Since that time, he began to closely collaborate with leftist Shanghai politicians, including the head of the city's Propaganda Department, Zhang Chunqiao. His article "On the New Historical Beijing Opera 'Hai Rui Dismissed from Office, published in ''Wenhuibao'' on November 10, 1965, launched the Cultural Revolution. The article was about a popular opera by Wu Han, who was deputy mayor of Beijing. Zhang Chunqiao and Jiang Qing feared the play could be counter-revolutionary because parallel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)