|
Xinhai Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China (ROC). The revolution was the culmination of a decade of agitation, revolts, and uprisings. Its success marked the collapse of the Chinese monarchy, the end of over two millennia of imperial rule in China and the 200-year reign of the Qing, and the beginning of China's early republican era. The Qing had struggled for a long time to reform the government and resist foreign aggression, but the program of reforms after 1900 was opposed by conservatives in the Qing court as too radical and by reformers as too slow. Several factions, including underground anti-Qing groups, revolutionaries in exile, reformers who wanted to save the monarchy by modernizing it, and activists across the country debated how or whether to overthrow the Qing dynasty. The flash-point came on 10 October 1911, with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Qing Sentiment
Anti-Qing sentiment () refers to a sentiment principally held in China against the rule of the Manchu people, Manchu-led Qing dynasty (1644–1912), which was criticized by opponents as being "barbaric". Already hated by the Han Chinese because of the Manchus' ancestors, the Jurchen people, for the Jin–Song wars and the war crimes against them that followed (notably the Jingkang incident) centuries ago, the Qing was later accused of destroying traditional Han culture by enforcing policies such as Tifayifu, forcing Han to wear their hair in a Queue (hairstyle), queue in the Manchu style. It was blamed for suppressing Chinese science, Criticism of Qing dynasty's economic performance, causing China to be transformed from the world's premiere power to a poor, backwards nation. The people of the Eight Banners lived off Social welfare in China, government pensions unlike the general Han civilian population. The rallying slogan of anti-Qing activists was "Fǎn Qīng fù Míng" (; "Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huang Xing
Huang Xing or Huang Hsing (; 25 October 1874 – 31 October 1916) was a Chinese revolutionary leader and politician, and the first commander-in-chief of the Republic of China. As one of the founders of the Kuomintang (KMT) and the Republic of China, his position was second only to Sun Yat-sen. Together they were known as Sun-Huang during the Xinhai Revolution. He was also known as the "Eight Fingered General" because of wounds sustained during war. His tomb is on Mount Yuelu, in Changsha, Hunan, China. Huang was born in the village of Gaotang, now part of Changsha, Hunan. Like many other Chinese men born before 1949, Huang was known by many different names during his life. His birth name was "Huang Zhen", but this was later changed to "Huang Xing". He was also known as "Huang Keqiang" and "Qing Wu". In the period after 1911 he also used the names "Li Youqing" and "Zhang Shouzheng". Biography Early life Huang Xing was a descendant of Huang Tingjian, a Chinese artist, schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Qing Reforms
Late Qing reforms (), commonly known as New Policies of the late Qing dynasty (), or New Deal of the late Qing dynasty, simply referred to as New Policies, were a series of cultural, economic, educational, military, diplomatic, and political reforms implemented in the last decade of the Qing dynasty to keep the dynasty in power after the invasions of the great powers of the Eight Nation Alliance in league with the ten provinces of the Southeast Mutual Protection during the Boxer Rebellion. Late Qing reforms started in 1901, and since they were implemented with the backing of the Empress Dowager Cixi, they are also called Cixi's New Policies. The reforms were often considered more radical than the earlier Self-Strengthening Movement which came to an abrupt end with China's defeat in the First Sino-Japanese War in 1895. Despite the reforms and other political struggles the Revolution, revolutionaries led the 1911 Revolution which resulted in the fall of the Qing dynasty. Names In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beiyang Government
The Beiyang government was the internationally recognized government of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China between 1912 and 1928, based in Beijing. It was dominated by the generals of the Beiyang Army, giving it its name. Beiyang general Yuan Shikai gave Sun Yat-sen the military support he needed to overthrow the Qing dynasty and establish the Republic of China in 1912, following the 1911 Revolution. Through his control of the army, Yuan was quickly able to dominate the new Republic. Although the government and the state were nominally under civilian control through the Republic's constitution, Yuan and his generals were effectively in charge of it. After Yuan's death in 1916, the army split into various warlord factions competing for power, leading to a period of civil war called the Warlord Era. Nevertheless, the government maintained its legitimacy among the great powers, receiving diplomatic recognition, foreign loans, and access to tax and customs revenu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Empire
Chinese Empire (), or Empire of China, refers to the realm ruled by the Emperor of China during the era of Imperial China. It was coined by western scholars to describe the Ming dynasty, Ming and Qing dynasty, Qing dynasties (or imperial Dynasties of China, Chinese dynasties in general). Another term was the "Celestial Empire", in reference to the status of the emperor as the Son of Heaven. In 221 BC, China was unified under an emperor for the first time, and various imperial dynasties ruled China for a total of two millennia since then, including the Qin dynasty, Qin, Han dynasty, Han, Jin dynasty (266–420), Jin, Sui dynasty, Sui, Tang dynasty, Tang, Song dynasty, Song, Yuan dynasty, Yuan, Ming, and Qing, among others. Etymology and usage The word "China" has been used in English since the 16th century. China was previously known to Europeans as Cathay, as used in Marco Polo's book on The Travels of Marco Polo, his travels in the 13th century (during the Yuan dynasty), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchy Of China
China was a monarchy from prehistoric times up to 1912, when a republic was established. The succession of legendary monarchs of China were non-hereditary. Dynastic rule began when Yu the Great established the Xia dynasty, and monarchy lasted until 1912 when dynastic rule collapsed together with the monarchical government. Various attempts at preserving and restoring the Chinese monarchy occurred during and following the Xinhai Revolution, but these regimes were short-lived and lacked widespread recognition. The monarchy of China took the form of absolute monarchy during most of its existence, even though the actual power of the ruler varied depending on his/her ability to consolidate the rule and various other factors. On 3 November 1911, the Qing dynasty issued the constitutional Nineteen Creeds which limited the power of the emperor, marking the official transition to a constitutional monarchy. However, after only 3 months, the monarchy was abolished. During periods of po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of China (1912–1949)
The Republic of China (ROC) began on 1 January 1912 as a sovereign state in mainland China following the 1911 Revolution, which overthrew the Manchu people, Manchu-led Qing dynasty and ended China's imperial China, imperial history. From 1927, the Kuomintang (KMT) Northern expedition, reunified the country and initially ruled it as a one-party state with Nanjing as the national capital. In 1949, Nationalist government, the KMT-led government was defeated in the Chinese Civil War and lost control of the mainland to the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The CCP Proclamation of the People's Republic of China, established the People's Republic of China (PRC) while the ROC was forced to Retreat of the government of the Republic of China to Taiwan, retreat to Taiwan; the ROC retains control over the Taiwan Area, and political status of Taiwan, its political status remains disputed. The ROC is recorded as a founding member of both the League of Nations and the United Nations, and previous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
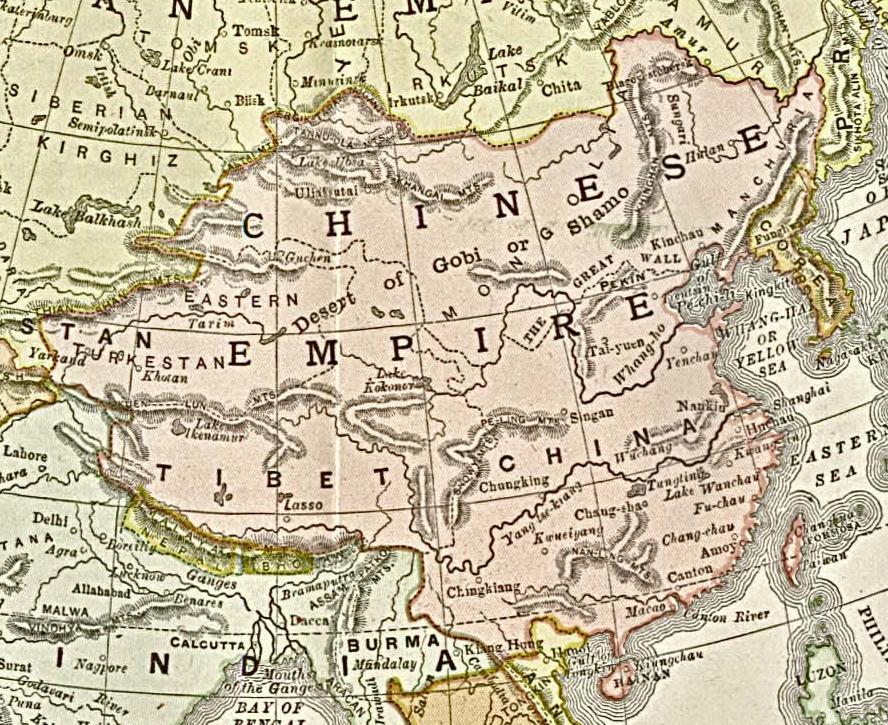
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
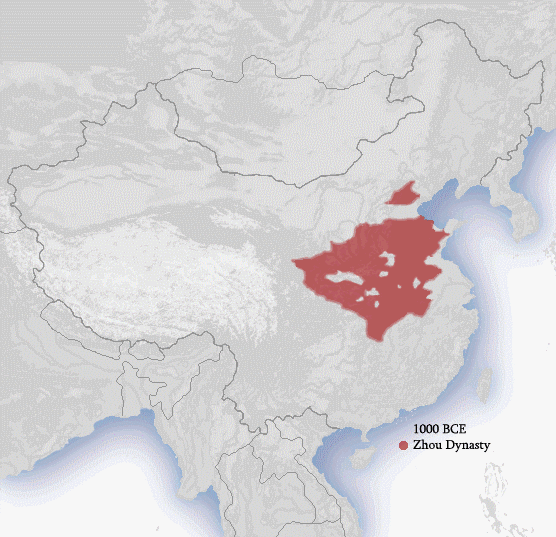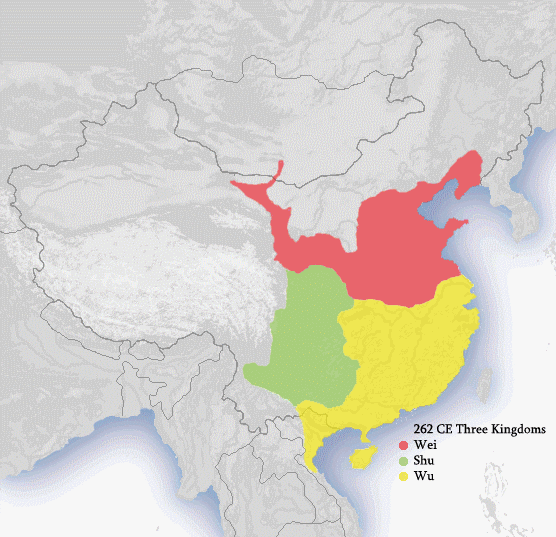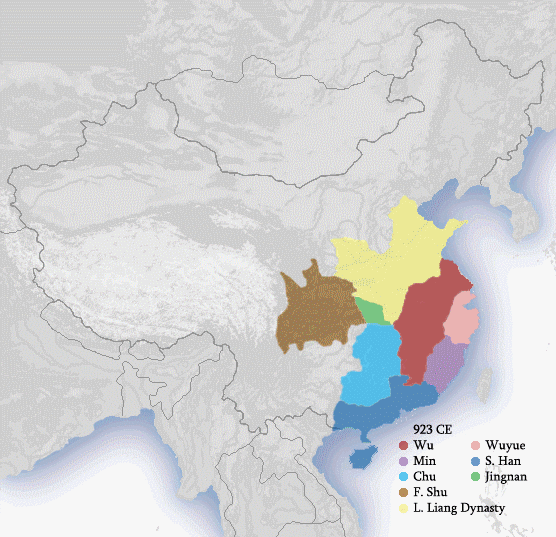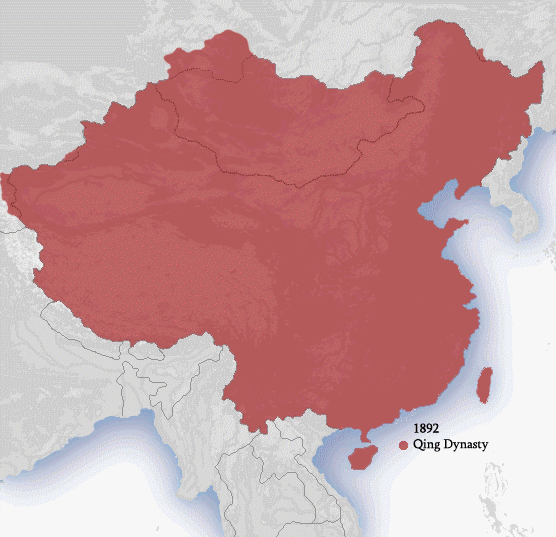
Dynasties Of China
For most of its history, China was organized into various dynastic states under the rule of hereditary monarchs. Beginning with the establishment of dynastic rule by Yu the Great , and ending with the abdication of the Xuantong Emperor in AD 1912, Chinese historiography came to organize itself around the succession of monarchical dynasties. Besides those established by the dominant Han ethnic group or its spiritual Huaxia predecessors, dynasties throughout Chinese history were also founded by non-Han peoples. Dividing Chinese history into dynastic epochs is a convenient and conventional method of periodization. Accordingly, a dynasty may be used to delimit the era during which a family reigned, as well as to describe events, trends, personalities, artistic compositions, and artifacts of that period. For example, porcelain made during the Ming dynasty may be referred to as "Ming porcelain". The longest-reigning orthodox dynasty of China was the Zhou dynasty, ruling for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexagenary Cycle
The sexagenary cycle, also known as the gānzhī (干支) or stems-and-branches, is a cycle of sixty terms, each corresponding to one year, thus amounting to a total of sixty years every cycle, historically used for recording time in China and the rest of the East Asian cultural sphere, as well as in Southeast Asia. It appears as a means of recording days in the first Chinese written texts, the oracle bones of the late second millennium BC Shang dynasty. Its use to record years began around the middle of the 3rd century BC. The cycle and its variations have been an important part of the traditional calendrical systems in Chinese-influenced Asian states and territories, particularly those of Japan, Korea, and Vietnam, with the old Chinese system still in use in Taiwan, and in Mainland China. In India, the Ahom people (descendants of the Dai people of Yunnan who migrated to Assam in the 13th century) also used the sexagenary cycle known as Lak-Ni. This traditional metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hu Hanmin
Hu Hanmin (; 9 December 1879 – 12 May 1936) was a Chinese philosopher and politician who was one of the early conservative right-wing faction leaders in the Kuomintang (KMT) during revolutionary China. Biography Hu was of Hakka descent from Ji'an, Jiangxi. Trần Xuân Sinh claimed that Hu Hanmin could be the descendant of Hồ Hán Thương, the second monarch of the Hồ dynasty of Vietnam. His father had moved to Panyu, Guangdong, to take up an official post. He qualified as a Juren at the age of 21. He studied in Japan from 1902 and joined the Tongmenghui (Chinese Revolutionary Alliance) in 1905 as editor of the newspaper Min Bao. From 1907 to 1910 he took part in several armed revolutions. Shortly after the Xinhai Revolution in 1911, he was appointed Governor of Guangdong and Chief Secretary of the Provisional Government. He took part in the Second Revolution of 1913 and, after its failure, followed Sun Yat-sen to Japan. There they founded the Kuomintang (Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cai E
Cai E (; 18 December 1882 – 8 November 1916) was a Chinese revolutionary leader and general. He was born Cai Genyin () in Shaoyang, Hunan, and his courtesy name was Songpo (). Cai eventually became an influential warlord in Yunnan ( Yunnan clique), and is best known for his role in challenging the imperial ambitions ( Hongxian emperor) of Yuan Shikai during the Anti-Monarchy War. Cai's name has also been romanised as Tsai Ao. Biography Early career Cai studied at the prestigious and progressive '' Shiwu Xuetang'' (School of Current Affairs), where he was taught by reformer faction intellectual Liang Qichao and Tang Caichang. He went to Japan in 1899. Cai returned to China in 1900, when he was only 18, and attempted to take part in an uprising against the Qing Dynasty as part of the Self-Support Army, a revolutionary militia led by Tang Caichang. When the rebellion failed, Cai returned to Japan. During this second sojourn in Japan he received military training at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |