|
Wothorpe
Wothorpe is a village and civil parish in the Peterborough unitary authority of Cambridgeshire, England. It is in the far north-west of the district, and to the south of Stamford (in Lincolnshire). The parish borders Northamptonshire to the west. Overview Wothorpe Priory was a "small Benedictine nunnery", founded apparently around 1160. All but one of the nuns died in the outbreak of Plague in 1349, with the survivor becoming part of the Priory of St Michael in Stamford. The property was dissolved by Henry VIII, being granted to Richard Cecil. As a parish, it was considered a hamlet within the parish of Stamford Baron, becoming a separate civil parish once more in 1866. Historically the parish was part of the Soke of Peterborough, associated with Northamptonshire. Administratively, it became part of the Stamford rural sanitary district in the 19th century, then later the Barnack Rural District of the administrative county of the Soke, then passing to Huntingdon and Peterb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamford, Lincolnshire
Stamford is a town and civil parish in the South Kesteven District of Lincolnshire, England. The population at the 2011 census was 19,701 and estimated at 20,645 in 2019. The town has 17th- and 18th-century stone buildings, older timber-framed buildings and five medieval parish churches. It is a frequent film location. In 2013 it was rated a top place to live in a survey by ''The Sunday Times''. Its name has been passed on to Stamford, Connecticut, founded in 1641. History Roman and Medieval Stamford The Romans built Ermine Street across what is now Burghley Park and forded the River Welland to the west of Stamford, eventually reaching Lincoln. They also built a town to the north at Great Casterton on the River Gwash. In 61 CE Boudica followed the Roman legion Legio IX Hispana across the river. The Anglo-Saxons later chose Stamford as the main town, being on a larger river than the Gwash. The place-name Stamford is first attested in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, where it app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
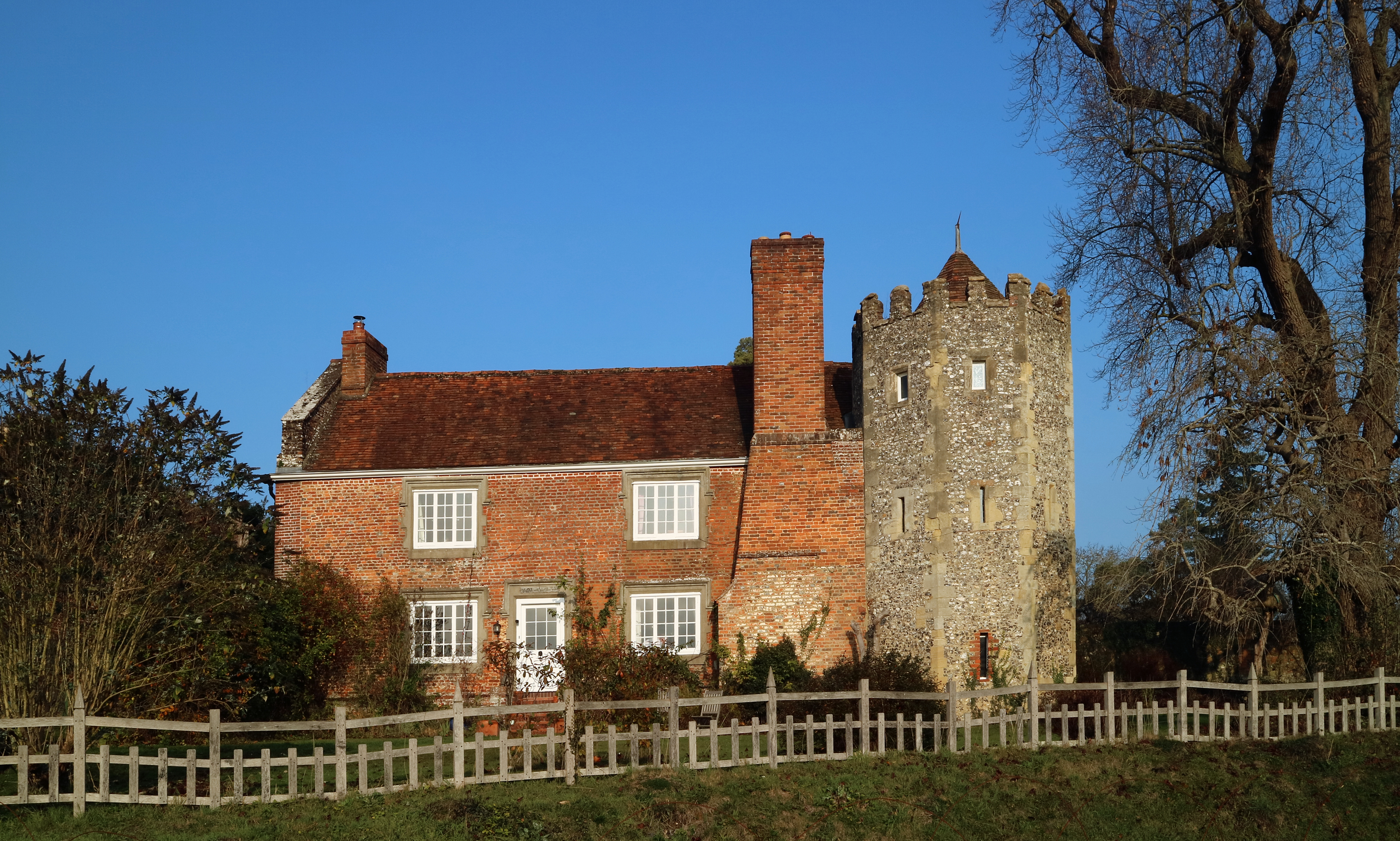
Wothorpe Priory
Wothorpe Priory was a monastic house in Northamptonshire, England but adjacent to Stamford, Lincolnshire Stamford is a town and civil parish in the South Kesteven District of Lincolnshire, England. The population at the 2011 census was 19,701 and estimated at 20,645 in 2019. The town has 17th- and 18th-century stone buildings, older timber-framed .... It was a "small Benedictine nunnery", founded apparently around 1160. All but one of the nuns died in the outbreak of plague in 1349, with the survivor becoming part of the Priory of Stamford. The property was dissolved by Henry VIII, being granted to Richard Cecil. References Monasteries in Northamptonshire {{UK-Christian-monastery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Cecil, 1st Earl Of Exeter
Thomas Cecil, 1st Earl of Exeter, KG (5 May 1542 – 8 February 1623), known as Lord Burghley from 1598 to 1605, was an English politician, courtier and soldier. Family Thomas Cecil was the elder son of William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley, by his first wife, Mary Cheke (d. February 1543), daughter of Peter Cheke of Cambridge, Esquire Bedell of the University from 1509 until his death in 1529 (and sister of Sir John Cheke). He was the half-brother of Robert Cecil, 1st Earl of Salisbury, Anne Cecil, and Elizabeth Cecil. William Cecil declared the young Thomas to be like, "a spendyng sott, mete to kepe a tenniss court" (a spendthrift soak, suited merely to govern a tennis court), although the same source notes that "Thomas Cecil became an improved character as he advanced in life". Whilst Thomas's career may have been overshadowed by those of his illustrious father and half-brother, he was a fine soldier and a useful politician and had a good deal of influence on the build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamford Baron
Stamford Baron St Martin was a civil parish in Stamford, England, including the southern part of Stamford, south of the River Welland, and therefore historically part of Northamptonshire. It remains an ecclesiastical parish used by the Church of England; the parish church is St Martin's. The ''Baron'' part of the name comes from the fact that the area was granted as a barony to the Abbot of Peterborough in the 15th Century. It expanded at an early stage to include Wothorpe, which was split out civilly in 1866. The parish was divided again in 1889, under the Local Government Act 1888. The area of the parish which was inside the boundary of the municipal borough of Stamford became considered part of Lincolnshire along with the rest of Stamford, and retained the name Stamford Baron St Martin, whilst the outer part became the parish of St Martin's Without remaining in the Soke of Peterborough associated with Northamptonshire. The rump of civil parish was abolished in 1930 w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
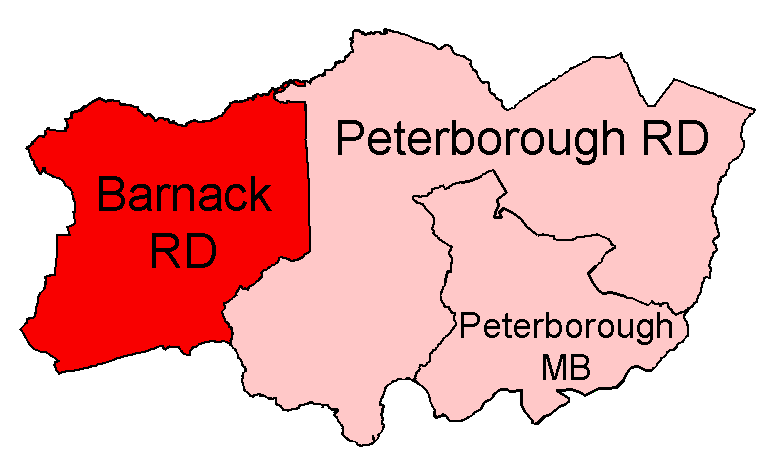
Barnack Rural District
Barnack was a rural district in the Soke of Peterborough and later Huntingdon and Peterborough from 1894 to 1974. It was created in 1894 under the Local Government Act 1894, from that part of the Stamford rural sanitary district which was in the Soke (the rest formed either Ketton Rural District in Rutland, Easton on the Hill Rural District in Northamptonshire proper, or Uffington Rural District in Lincolnshire, Parts of Kesteven). It included the parishes of Bainton, Barnack, Southorpe, Stamford Baron, St Martins Without, Thornhaugh, Ufford, Wansford, Wittering and Wothorpe in the Soke. It also had administrative responsibility for the parish of Sibson cum Stibbington, which was over the border in Huntingdonshire. This was made part of the Norman Cross Rural District in 1935.The County of Huntingdon Review Order 1934, Ministry of Health Order No. 79915 It was abolished in 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972, becoming part of the larger Peterborough distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Peterborough
The City of Peterborough is a unitary authority district with city status in the ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire, England. The area is named after its largest settlement, Peterborough but also covers a wider area of outlying villages and hamlets. Historically the area was split into parts between the counties of Northamptonshire, Isle of Ely and Huntingdonshire until 1974 when it became part of the short-lived county of Huntingdon and Peterborough before becoming part of the ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire. Located in the East Anglia region of England, the area borders the surrounding counties of Lincolnshire and Northamptonshire. The population of the district was 202,259 making it the second-largest district by population in East Anglia (After Norwich). The district was also part of the Soke of Peterborough and was a Saxon settlement during the Anglo-Saxon era. The district also includes outlying villages such as Thorney, Old Fletton, Werrington, Parnwell, Dogs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Counties Of England And Wales In 1964 By Highest Point
List of counties of England and Wales in 1964 by highest point. In 1964 they are more or less the ancient counties, with the addition of the County of London and a number of historic divisions in place as administrative counties: Cambridgeshire into the Isle of Ely and Cambridgeshire; Hampshire into the Isle of Wight and Hampshire; Lincolnshire into the Parts of Holland, Kesteven and Lindsey; Northamptonshire into Soke of Peterborough and Northamptonshire; Suffolk into East and West; Sussex into East and West; and Yorkshire into the East, North and West Ridings. Footnotes #The foot measurement is derived from the Ordnance Survey metre measurement, multiplied by 3.2808. References External linksCounty topsof the British Isles on Wikishire (by traditional counties)Hill Bagging {{Mountains of Great Britain and Ireland Counties Counties Highest points Historic counties by highest point Highest points A list of highest points typically contains the name, elevation, and locati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Villiers, 2nd Duke Of Buckingham
George Villiers, 2nd Duke of Buckingham, 20th Baron de Ros, (30 January 1628 – 16 April 1687) was an English statesman and poet. Life Early life George was the son of George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham, favourite of James I and Charles I, and his wife Katherine Manners. He was only seven months old when his father was assassinated at Portsmouth by the disaffected officer John Felton. Subsequently, he was brought up in the royal household of Charles I, together with his younger brother Francis and the King's own children, the future Charles II and James II. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he obtained the degree of Master of Arts in 1642. For a time he was taught geometry by Thomas Hobbes. During this time he was also acquainted with George Aglionby, whose influence he later accredited with persuading him to follow the English King in the Civil War. Involvement in the English Civil War In the Civil War he fought for the King, and too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley
William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley (13 September 15204 August 1598) was an English statesman, the chief adviser of Queen Elizabeth I for most of her reign, twice Secretary of State (1550–1553 and 1558–1572) and Lord High Treasurer from 1572. In his description in the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Eleventh Edition, Albert Pollard wrote, "From 1558 for forty years the biography of Cecil is almost indistinguishable from that of Elizabeth and from the history of England." Cecil set as the main goal of English policy the creation of a united and Protestant British Isles. His methods were to complete the control of Ireland, and to forge an alliance with Scotland. Protection from invasion required a powerful Royal Navy. While he was not fully successful, his successors agreed with his goals. In 1587, Cecil persuaded the Queen to order the execution of the Roman Catholic Mary, Queen of Scots, after she was implicated in a plot to assassinate Elizabeth. He was the father of Rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritage At Risk Register
An annual ''Heritage at Risk Register'' is published by Historic England. The survey is used by national and local government, a wide range of individuals and heritage groups to establish the extent of risk and to help assess priorities for action and funding decisions. This heritage-at-risk data is one of the UK government's official statistics. ''Heritage at risk'' is term for cultural heritage assets that are at risk as a result of neglect, decay, or inappropriate development; or are vulnerable to becoming so. England's ''Heritage at Risk Register'' The ''Heritage at Risk Register'' covers: * Grade I and II* listed buildings (the baseline register is 1999); Grade II listed buildings in London only (the baseline register is 1991) * Structural scheduled monuments (base year is 1999) and scheduled monuments (base year is 2009) * Registered parks and gardens (base year is 2009) * Registered historic battlefields (base year is 2008) * Protected wreck sites * Conservation areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dower House
A dower house is usually a moderately large house available for use by the widow of the previous owner of an English, Scottish or Welsh estate. The widow, often known as the "dowager", usually moves into the dower house from the larger family house on the death of her husband if the heir is married, and upon his marriage if he was single at his succession. The new heir occupies the now vacated principal house. The dower house might also be occupied by an elder son after his marriage, or simply rented to a tenant. Examples The British royal family maintains a dower house in London as well as one in the country. Well-known royal dower-houses in London have included Clarence House, Marlborough House, and (for a time during the 18th century) Buckingham Palace (then known as "Buckingham House"). Rappaport, Helen (2003)''Queen Victoria: A Biographical Companion'' p. 83. ABC-CLIO, Inc. Frogmore House has served as Windsor Castle's dower house. The Dukes of Devonshire kept Har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyecatchers
An eyecatcher is something artificial that has been placed in the landscape as a focal point to "catch the eye" or gain a viewer's attention. It is used to decorate or ornament landscapes for aesthetic reasons, and are typically found in gardens, parks and the grounds of stately homes. Many of these can be found in various forms. Devices or objects These can be anything but typically they tend to be *boulders *rockery * trees Or on a grander scale they can be structures such as a * bridge over a river, a stream or lake as an ornamental feature * conservatory - glasshouses, orangeries, vineries * exedra *folly * gloriettes * grottoes **shell grottos *mausoleums *monopteros * monuments (whether they commemorate anything or just for decoration) * nymphaea * pavilions * reflecting pools *shooting Shooting is the act or process of discharging a projectile from a ranged weapon (such as a gun, bow, crossbow, slingshot, or blowpipe). Even the acts of launching flame, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |