|
Willoughbyland
Surinam, also known as Willoughbyland, was a short-lived early English colony in South America in what is now Suriname. It was founded in 1650 by Lord Willoughby when he was the Royalist Governor of Barbados. History In 1598 Lawrence Kemys, leading an expedition to the Guianas on behalf of Walter Raleigh, passed a river he called "''Shurinama''". In 1613, a short-lived Dutch trading post had been established inside the mouth of the Suriname River, near an Amerindian village called " Parmurbo". In 1630, British settlers made the first European attempt at colonization at Marshall's Creek, a tributary of the Suriname. The Dutch navigator David Pietersz. de Vries wrote of traveling up the "''Sername''" river in 1634 until he encountered the English colony there, which did not last much longer. In 1650, Lord Francis Willoughby, a Parliamentarian turned Royalist, had been appointed Governor of Barbados by the exiled King Charles II. In view of his precarious position, he planned t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. On 12 July 927, the various Anglo-Saxon kings swore their allegiance to Æthelstan of Wessex (), unifying most of modern England under a single king. In 1016, the kingdom became part of the North Sea Empire of Cnut the Great, a personal union between England, Denmark and Norway. The Norman conquest of England in 1066 led to the transfer of the English capital city and chief royal residence from the Anglo-Saxon one at Winchester to Westminster, and the City of London quickly established itself as England's largest and principal commercial centre. Histories of the kingdom of England from the Norman conquest of 1066 conventionally distinguish periods named after successive ruling dynasties: Norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The crops that are grown include cotton, coffee, tea, cocoa, sugar cane, opium, sisal, oil seeds, oil palms, fruits, rubber trees and forest trees. Protectionist policies and natural comparative advantage have sometimes contributed to determining where plantations are located. In modern use the term is usually taken to refer only to large-scale estates, but in earlier periods, before about 1800, it was the usual term for a farm of any size in the southern parts of British North America, with, as Noah Webster noted, "farm" becoming the usual term from about Maryland northwards. It was used in most British colonies, but very rarely in the United Kingdom itself in this sense. There, as also in America, it was used mainly for tree plantation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Suriname
The early history of Suriname dates from 3000 BCE when Native Americans first inhabited the area. The Dutch acquired Suriname from the English, and European settlement in any numbers dates from the 17th century, when it was a plantation colony utilizing slavery for sugar cultivation. With abolition in the late 19th century, planters sought labor from China, Madeira, India, and Indonesia, which was also colonized by the Dutch. Dutch is Suriname's official language. Owing to its diverse population, it has also developed a creole language, Sranan Tongo. Indigenous settlement Suriname was populated millennia before the Europeans by many distinct indigenous cultures. The largest nations at the time of colonialization were the Arawaks, a nomadic coastal tribe that lived from hunting and fishing, and the Caribs. The Caribs conquered the Arawaks along much of the coast, and into the Caribbean, using sailing ships. They settled in Galibi (''Kupali Yumï'', meaning "tree of the forefather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global cultural, financial, entertainment, and media center with a significant influence on commerce, health care and life sciences, research, technology, education, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
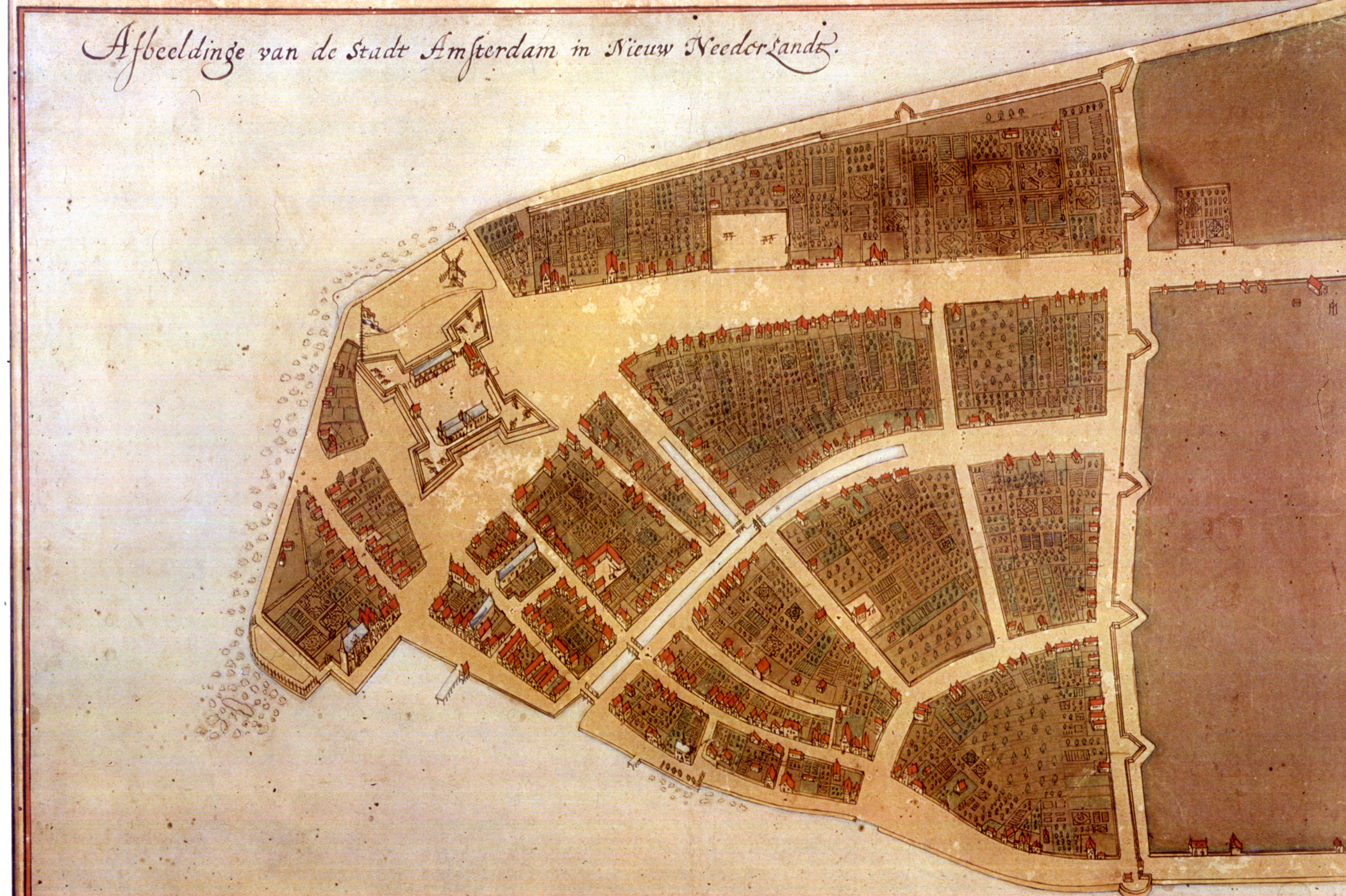
New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise to the settlement around Fort Amsterdam. The fort was situated on the strategic southern tip of the island of Manhattan and was meant to defend the fur trade operations of the Dutch West India Company in the North River (Hudson River). In 1624, it became a provincial extension of the Dutch Republic and was designated as the capital of the province in 1625. By 1655, the population of New Netherland had grown to 2,000 people, with 1,500 living in New Amsterdam. By 1664, the population of New Netherland had risen to almost 9,000 people, 2,500 of whom lived in New Amsterdam, 1,000 lived near Fort Orange, and the remainder in other towns and villages. In 1664, the English took over New Amsterdam and renamed it New York after the Duke o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Breda (1667)
The Peace of Breda, or Treaty of Breda was signed in the Dutch city of Breda, on 31 July 1667. It consisted of three separate treaties between England and each of its opponents in the Second Anglo-Dutch War: the Dutch Republic, France, and Denmark–Norway. It also included a separate Anglo-Dutch commercial agreement. Negotiations had been in progress since late 1666 but were slow, as both sides tried to improve their positions. This changed after the French invasion of the Spanish Netherlands in late May, which the Dutch viewed as a more serious threat. War-weariness in England was increased by the June Raid on the Medway. Both factors led to a rapid agreement of terms. Prior to 1667, the Anglo-Dutch relationship had been dominated by commercial conflict, which the treaty did not end entirely. However, tensions decreased markedly and cleared the way for the 1668 Triple Alliance between the Dutch Republic, England and Sweden. With the brief anomaly of the 1672 to 1674 Third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Crijnssen
Abraham Crijnssen (died 1 February 1669) was a Dutch naval commander, notable for capturing the English colony in Suriname in 1667 during the Second Anglo-Dutch War, resulting in the establishment of a long-term colony under Dutch control. The minesweeper and the frigate HNLMS ''Abraham Crijnssen'' have been named after him. Life 1632–1665 Crijnssen (also written as Krijnssen) was probably born in Vlissingen. His date of birth is unknown. In 1632 he commanded the ''Samson'' and the ''Vlissingen'', two ships belonging to a fleet of 12 privateers owned by the brothers Lampsins. Crijnssen inflicted much damage on the Dunkirk Privateers, and distinguished himself in 1639 during the Battle of the Downs. In 1665, he was commander at the Admiralty of Zeeland. First he served as first captain under Adriaan Banckert, but in the autumn he was appointed captain of ''Prins te Paard''. He fought at the Four Days' Battle and the St. James's Day Battle as commander of the frigate ''Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label= Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands— Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the two inhabited Îles des Saintes—as well as many uninhabited islands and outcroppings. It is south of Antigua and Barbuda and Montserrat, north of the Commonwealth of Dominica. The region's capital city is Basse-Terre, located on the southern west coast of Basse-Terre Island; however, the most populous city is Les Abymes and the main centre of business is neighbouring Pointe-à-Pitre, both located on Grande-Terre Island. It had a population of 384,239 in 2019.Populations légales 2019: 971 Guadeloupe INSEE Like the other overseas departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War or the Second Dutch War (4 March 1665 – 31 July 1667; nl, Tweede Engelse Oorlog "Second English War") was a conflict between England and the Dutch Republic partly for control over the seas and trade routes, where England tried to end the Dutch domination of world trade during a period of intense European commercial rivalry, but also as a result of political tensions. After initial English successes, the war ended in a Dutch victory. It was the second of a series of naval wars fought between the English and the Dutch in the 17th and 18th centuries. Background Anglo-Dutch relations Traditionally, many historians considered that the First and Second Anglo-Dutch Wars arose from commercial and maritime rivalry between England and the Netherlands. Although continuing commercial tensions formed the background to the second war, a group of ambitious English politicians and naval officers frustrated diplomatic efforts to reach any accommodation be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that the person is responsible for violating norms that warrant said punishment. The sentence ordering that an offender is to be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is ''condemned'' and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Crimes that are punishable by death are known as ''capital crimes'', ''capital offences'', or ''capital felonies'', and vary depending on the jurisdiction, but commonly include serious crimes against the person, such as murder, mass murder, aggravated cases of rape (often including child sexual abuse), terrorism, aircraft hijacking, war crimes, crimes against h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restoration (1660)
The Restoration of the Stuart monarchy in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland took place in 1660 when King Charles II returned from exile in continental Europe. The preceding period of the Protectorate and the civil wars came to be known as the Interregnum (1649–1660). The term ''Restoration'' is also used to describe the period of several years after, in which a new political settlement was established. It is very often used to cover the whole reign of King Charles II (1660–1685) and often the brief reign of his younger brother King James II (1685–1688). In certain contexts it may be used to cover the whole period of the later Stuart monarchs as far as the death of Queen Anne and the accession of the Hanoverian King George I in 1714. For example, Restoration comedy typically encompasses works written as late as 1710. The Protectorate After Richard Cromwell, Lord Protector from 1658 to 1659, ceded power to the Rump Parliament, Charles Fleetwood and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol (dated, standard English, Australian, and historically in Canada), penitentiary (American English and Canadian English), detention center (or detention centre outside the US), correction center, correctional facility, lock-up, hoosegow or remand center, is a facility in which inmates (or prisoners) are confined against their will and usually denied a variety of freedoms under the authority of the state as punishment for various crimes. Prisons are most commonly used within a criminal justice system: people charged with crimes may be imprisoned until their trial; those pleading or being found guilty of crimes at trial may be sentenced to a specified period of imprisonment. In simplest terms, a prison can also be described as a building in which people are legally held as a punishment for a crime they have committed. Prisons can also be used as a tool of political repression by authoritarian regimes. Their perceived opponents m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |