|
William Ellery Channing
William Ellery Channing (April 7, 1780 – October 2, 1842) was the foremost Unitarianism, Unitarian preacher in the United States in the early nineteenth century and, along with Andrews Norton (1786–1853), one of Unitarianism's leading theologians. Channing was known for his articulate and impassioned sermons and public speeches, and as a prominent thinker in the liberal theology of the day. His religion and thought were among the chief influences on the New England Transcendentalists although he never countenanced their views, which he saw as extreme. His espousal of the developing philosophy and theology of Unitarianism was displayed especially in his "Baltimore Sermon" of May5, 1819, given at the ordination of the theologian and educator Jared Sparks (1789–1866) as the first minister of the newly organized First Unitarian Church (Baltimore, Maryland), First Independent Church of Baltimore. Life and work Early life Channing, the son of William Channing and Lucy Ellery, wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Newport, Rhode Island
Newport is a seaside city on Aquidneck Island in Rhode Island, United States. It is located in Narragansett Bay, approximately southeast of Providence, Rhode Island, Providence, south of Fall River, Massachusetts, south of Boston, and northeast of New York City. It is known as a New England summer resort and is famous for its historic Newport Mansions, mansions and its rich sailing history. The city has a population of about 25,000 residents. Newport hosted the first U.S. Open tournaments in both US Open (tennis), tennis and US Open (golf), golf, as well as every challenge to the America's Cup between 1930 and 1983. It is also the home of Salve Regina University and Naval Station Newport, which houses the United States Naval War College, the Naval Undersea Warfare Center, and an important Navy training center. It was a major 18th-century port city and boasts many buildings from the Colonial history of the United States, colonial era. Newport is the county seat of Newport C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
United States Declaration Of Independence
The Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America in the original printing, is the founding document of the United States. On July 4, 1776, it was adopted unanimously by the Second Continental Congress, who convened at Pennsylvania State House, later renamed Independence Hall, in the Colonial history of the United States, colonial capital of Philadelphia. These delegates became known as the nation's Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Fathers. The Declaration explains why the Thirteen Colonies regarded themselves as independent sovereign states no longer subject to British colonization of the Americas, British colonial rule, and has become one of the most circulated, reprinted, and influential documents in history. On June 11, 1776, the Second Continental Congress appointed the Committee of Five, including John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Robert R. Livingston, and Roger Sherman, who were charged w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fellow
A fellow is a title and form of address for distinguished, learned, or skilled individuals in academia, medicine, research, and industry. The exact meaning of the term differs in each field. In learned society, learned or professional society, professional societies, the term refers to a privileged member who is specially elected in recognition of their work and achievements. Within institutions of higher education, a fellow is a member of a highly ranked group of teachers at a particular college or university or a member of the governing body in some universities. It can also be a specially selected postgraduate student who has been appointed to a post (called a fellowship) granting a stipend, research facilities and other privileges for a fixed period (usually one year or more) in order to undertake some advanced study or research, often in return for teaching services. In the context of medical education in North America, a fellow is a physician who is undergoing a supervised, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Federal Street Church (Boston)
The Federal Street Church (established 1729) was a congregational Unitarian church in Boston, Massachusetts. Organized in 1727, the originally Presbyterian congregation changed in 1786 to "Congregationalism", then adopted the liberal theology of its fifth senior minister, William Ellery Channing, (1780–1842). For most of the 18th century the church was known as the Long Lane Meeting-House. In 1788, state leaders met in the relatively spacious building to determine Massachusetts' ratification of the United States Constitution. Thereafter the church renamed itself the Federal Street Church in honor of the event. In 1803, it called Channing as its minister who defined "Unitarian Christianity" and launched the Unitarian movement, making the Federal Street Church one of the first to define itself as Unitarian. History 1727–1803 The congregation began as a group of Scots-Irish Calvinists gathered in a converted barn on Long Lane in Boston on November 15, 1729. The inhospitable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
David Meade Randolph
Mary Randolph (August 9, 1762 – January 23, 1828) was a Southern American cook and author, known for writing ''The Virginia House-Wife; Or, Methodical Cook'' (1824), one of the most influential housekeeping and cook books of the 19th century. Many of the recipes used local Virginia ingredients including '' Tanacetum vulgare virginia'' pudding, pickled nasturtiums and desserts with the native gooseberry. She was the first person known to be buried at what would become known as Arlington National Cemetery. Early life Mary Randolph was born on August 9, 1762, at Ampthill Plantation in Chesterfield County, Virginia. Her parents were Thomas Mann Randolph Sr. (1741–1794) and Anne Cary Randolph (1745–1789). The extended Randolph family was one of the richest and most political significant families in 18th century Virginia. Mary's father was orphaned at a young age and raised by Thomas Jefferson's parents who were distant cousins. Her father also served in the Virginia Hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), U.S. commonwealth of Virginia. Incorporated in 1742, Richmond has been an independent city (United States), independent city since 1871. The city's population in the 2020 United States census was 226,610, up from 204,214 in 2010, making it Virginia's List of cities and counties in Virginia#Largest cities, fourth-most populous city. The Greater Richmond Region, Richmond metropolitan area, with over 1.3 million residents, is the Commonwealth's Virginia statistical areas, third-most populous. Richmond is located at the Atlantic Seaboard fall line, James River's fall line, west of Williamsburg, Virginia, Williamsburg, east of Charlottesville, Virginia, Charlottesville, east of Lynchburg, Virginia, Lynchburg and south of Washington, D.C. Surrounded by Henrico County, Virginia, Henrico and Chesterfield County, Virginia, Chesterfield counties, Richmond is at the intersection o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reformed Christianity
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterian, Congregational, and Waldensians traditions, as well as parts of the Methodist, Anglican (known as "Episcopal" in some regions) and Baptist traditions. Reformed theology emphasizes the authority of the Bible and the sovereignty of God, as well as covenant theology, a framework for understanding the Bible based on God's covenants with people. Reformed churches emphasize simplicity in worship. Several forms of ecclesiastical polity are exercised by Reformed churches, including presbyterian, congregational, and some episcopal. Articulated by John Calvin, the Reformed faith holds to a spiritual (pneumatic) presence of Christ in the Lord's Supper. Emerging in the 16th century, the Reformed tradition developed over several generation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
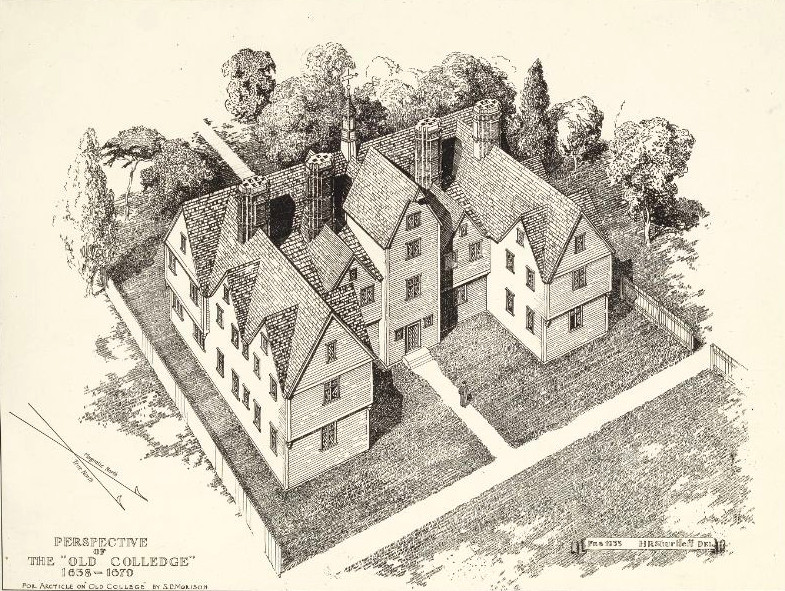
Harvard College
Harvard College is the undergraduate education, undergraduate college of Harvard University, a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Part of the Harvard Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Harvard College is Harvard University's traditional undergraduate program, offering BA (Bachelor of Arts) and BS (Bachelor of Science) degrees. It is highly selective, with fewer than four percent of applicants being offered admission as of 2022. Harvard College students participate in over 450 extracurricular organizations and nearly all live on campus. First-year students reside in or near Harvard Yard while upperclass students reside in other on-campus housing. History Harvard College was founded in 1636 by vote of the Massachusetts General Court, Great and General Court of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Two years later, the college became home to North America's first known printing press, carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Divine Election
In Christianity, particularly within the theological framework of Calvinism, election involves God choosing a particular person or group of people to a particular task or relationship, especially eternal life. Election to eternal life is viewed by some as conditional on a person's faith, and by others as unconditional. According to Calvinist theology, before the foundation of the world, God chose certain individuals, known as the "elect", to receive his saving grace and be predestined for eternal salvation; Calvinists view this election as unconditional, based not on human merit or works but solely on God's sovereign will and purpose. In the Old Testament The Old Testament applies the term "elect" (; ) to the Israelites insofar as they are called to be the chosen people, people of God, or faithful to their divine call. The idea of such an election is common in Deuteronomy and in Isaiah 40-66. In the New Testament The New Testament transfers the meaning of the term from its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Total Depravity
Total depravity (also called radical corruption or pervasive depravity) is a Protestant theological doctrine derived from the concept of original sin Original sin () in Christian theology refers to the condition of sinfulness that all humans share, which is inherited from Adam and Eve due to the Fall of man, Fall, involving the loss of original righteousness and the distortion of the Image .... It teaches that, as a consequence of the Fall, every person born into the world is enslaved to the service of sin as a result of their fallen nature and, apart from the Irresistible grace, efficacious (irresistible) or Prevenient grace, prevenient (enabling) Grace in Christianity, grace of God, is completely unable to choose by themselves to follow God in Christianity, God, refrain from evil, or accept the gift of Salvation in Christianity, salvation as it is offered. The doctrine is advocated to various degrees by many Protestant denominations, including Lutheranism and all Calv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Calvinism
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterian, Congregational, and Waldensians traditions, as well as parts of the Methodist, Anglican (known as "Episcopal" in some regions) and Baptist traditions. Reformed theology emphasizes the authority of the Bible and the sovereignty of God, as well as covenant theology, a framework for understanding the Bible based on God's covenants with people. Reformed churches emphasize simplicity in worship. Several forms of ecclesiastical polity are exercised by Reformed churches, including presbyterian, congregational, and some episcopal. Articulated by John Calvin, the Reformed faith holds to a spiritual (pneumatic) presence of Christ in the Lord's Supper. Emerging in the 16th century, the Reformed tradition developed over several genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |