|
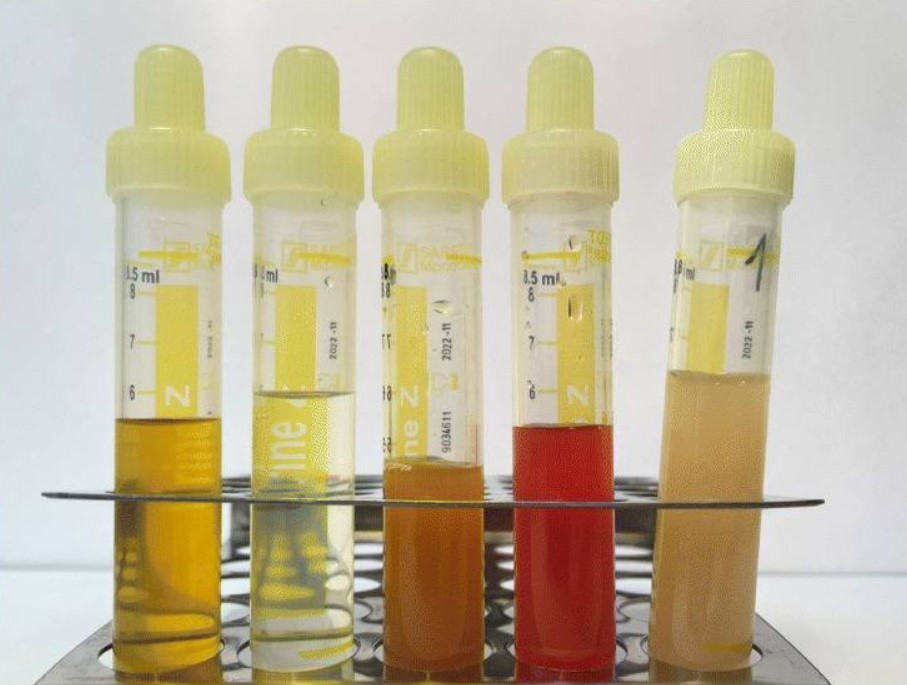
Urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and microscopic examination. Macroscopic examination targets parameters such as color, clarity, odor, and specific gravity; urine test strips measure chemical properties such as pH, glucose concentration, and protein levels; and microscopy is performed to identify elements such as cells, urinary casts, crystals, and organisms. Background Urine is produced by the filtration of blood in the kidneys. The formation of urine takes place in microscopic structures called nephrons, about one million of which are found in a normal human kidney. Blood enters the kidney though the renal artery and flows through the kidney's vasculature into the glomerulus, a tangled knot of capillaries surrounded by Bowman's capsule. The glomerulus and Bowman's capsule together form the renal corpus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine Test Strip
A urine test strip or dipstick is a basic diagnostic tool used to determine pathological changes in a patient's urine in standard urinalysis. A standard urine test strip may comprise up to 10 different chemical pads or reagents which react (change color) when immersed in, and then removed from, a urine sample. The test can often be read in as little as 60 to 120 seconds after dipping, although certain tests require longer. Routine testing of the urine with multiparameter strips is the first step in the diagnosis of a wide range of diseases. The analysis includes testing for the presence of proteins, glucose, ketones, haemoglobin, bilirubin, urobilinogen, acetone, nitrite and leucocytes as well as testing of pH and specific gravity or to test for infection by different pathogens. The test strips consist of a ribbon made of plastic or paper of about 5 millimetre wide, plastic strips have pads impregnated with chemicals that react with the compounds present in urine producing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine Test Strips
A urine test strip or dipstick is a basic diagnostic tool used to determine pathological changes in a patient's urine in standard urinalysis. A standard urine test strip may comprise up to 10 different chemical pads or reagents which react (change color) when immersed in, and then removed from, a urine sample. The test can often be read in as little as 60 to 120 seconds after dipping, although certain tests require longer. Routine testing of the urine with multiparameter strips is the first step in the diagnosis of a wide range of diseases. The analysis includes testing for the presence of proteins, glucose, ketones, haemoglobin, bilirubin, urobilinogen, acetone, nitrite and leucocytes as well as testing of pH and specific gravity or to test for infection by different pathogens. The test strips consist of a ribbon made of plastic or paper of about 5 millimetre wide, plastic strips have pads impregnated with chemicals that react with the compounds present in urine producing a char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
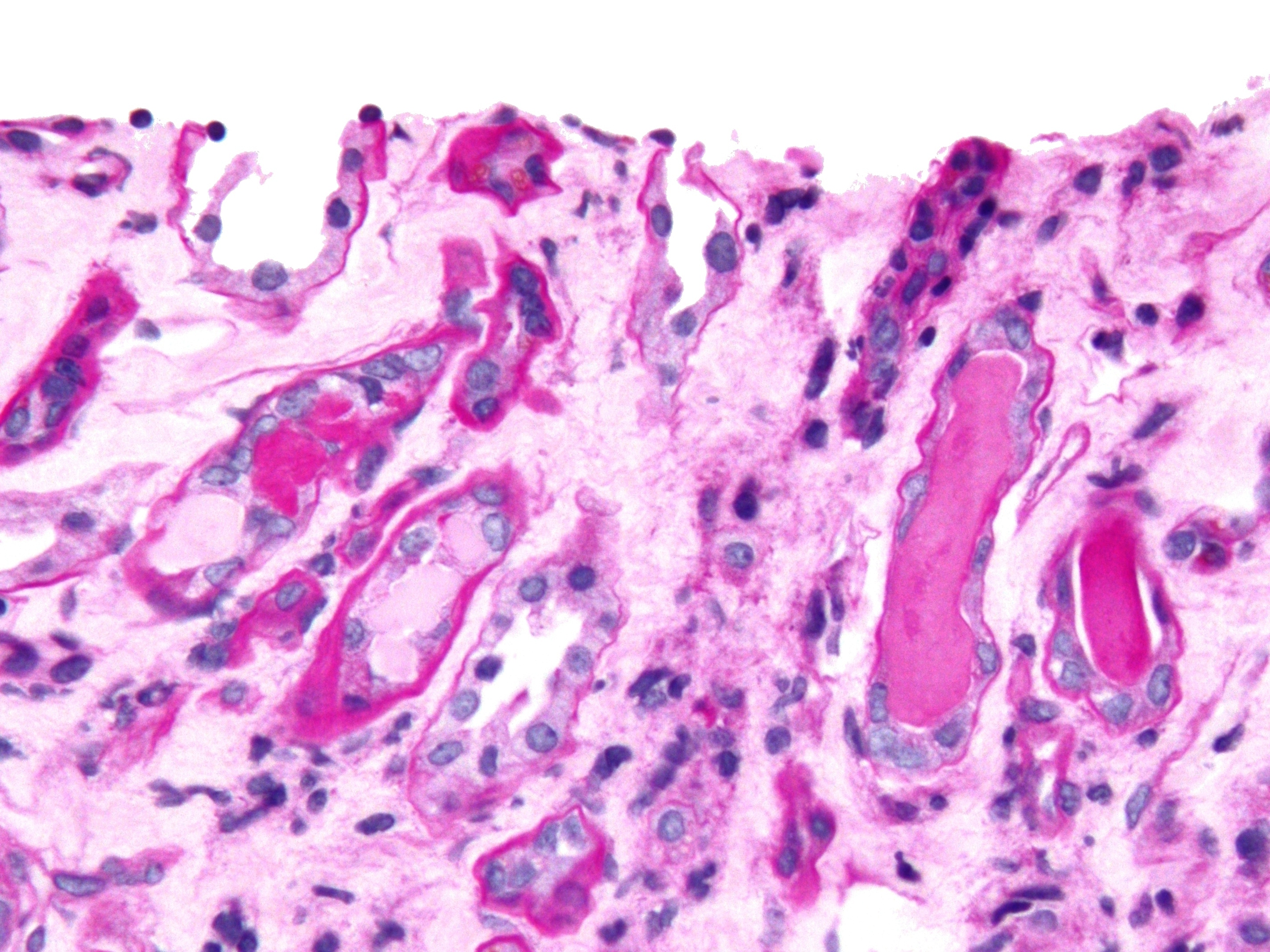
Crystalluria
Crystalluria refers to crystals found in the urine when performing a urine test. Crystalluria is considered often as a benign condition and as one of the side effects of sulfonamides and penicillins. The main reason for the identification of urinary crystals is to detect the presence of the relatively few abnormal types that may represent a disease. Clinical significance It can be an indication of urolithiasis. It may be relevant when there is presence of specific abnormal types of crystals (cystine, cholesterol, leucine, tyrosine, etc.) and that may be a sign of metabolic or liver disorders such as cystinuria Cystinuria is an inherited autosomal recessive disease characterized by high concentrations of the amino acid cystine in the urine, leading to the formation of cystine stones in the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. It is a type of aminoaciduria. .... It leads to formation of stones. References External links Abnormal clinical and laboratory findings for ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates many by-products that are rich in nitrogen and must be cleared from the bloodstream, such as urea, uric acid, and creatinine. These by-products are expelled from the body during urination, which is the primary method for excreting water-soluble chemicals from the body. A urinalysis can detect nitrogenous wastes of the mammalian body. Urine plays an important role in the earth's nitrogen cycle. In balanced ecosystems, urine fertilizes the soil and thus helps plants to grow. Therefore, urine can be used as a fertilizer. Some animals use it to mark their territories. Historically, aged or fermented urine (known as lant) was also used for gunpowder production, household cleaning, tanning of leather and dyeing of text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Cast
Urinary casts are microscopic cylindrical structures produced by the kidney and present in the urine in certain disease states. They form in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts of nephrons, then dislodge and pass into the urine, where they can be detected by microscopy. They form via precipitation of Tamm–Horsfall mucoprotein, which is secreted by renal tubule cells, and sometimes also by albumin in conditions of proteinuria. Cast formation is pronounced in environments favoring protein denaturation and precipitation (low flow, concentrated salts, low pH). Tamm–Horsfall protein is particularly susceptible to precipitation in these conditions. Casts were first described by Henry Bence Jones (1813–1873). As reflected in their cylindrical form, casts are generated in the small distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts of the kidney, and generally maintain their shape and composition as they pass through the urinary system. Although the most common form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomerulus (kidney)
The glomerulus (plural glomeruli) is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a ''tuft'', located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney. Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons. The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium (the space between the blood vessels), composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells. The blood is filtered across the capillary walls of this tuft through the glomerular filtration barrier, which yields its filtrate of water and soluble substances to a cup-like sac known as Bowman's capsule. The filtrate then enters the renal tubule of the nephron. The glomerulus receives its blood supply from an afferent arteriole of the renal arterial circulation. Unlike most capillary beds, the glomerular capillaries exit into efferent arterioles rather than venules. The resistance of the efferent arterioles causes sufficient hydrostatic pressure within the glomerulus to provide the force for ultrafiltration. The glomerul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Panel
A test panel is a predetermined group of medical tests used in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Test panels (sometimes called profiles) are typically composed of individual laboratory tests which are related in some way: by the medical condition they are intended to help diagnose (cardiac risk panel), by the specimen type ( complete blood count, CBC), by the tests most frequently requested by users (comprehensive chemistry profile), by the methodology employed in the test (viral panel by polymerase chain reaction), or by the types of components included (urine drug screen). Advantages of diagnostic test panels over individual diagnostic tests Test panels offer various advantages to laboratories performing the tests (labor efficiency, potential for automation and reduced costs through performing large numbers of the same kinds of tests each day) as well as to end users such as ordering physicians and hospitals (more comprehensive testing, rapid turn-around, and lower prices) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrons
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the foot processes of the podocytes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged (some are added, others are removed); first with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Other variables include the pH of extracellular fluid, the concentrations of sodium, potassium and calcium ions, as well as that of the blood sugar level, and these need to be regulated despite changes in the environment, diet, or level of activity. Each of these variables is controlled by one or more regulators or homeostatic mechanisms, which together maintain life. Homeostasis is brought about by a natural resistance to change when already in the optimal conditions, and equilibrium is maintained by many regulatory mechanisms: it is thought to be the central motivation for all organic action. All homeostatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Tubule
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the foot processes of the podocytes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged (some are added, others are removed); first with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filtrate
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a ''filter medium'' that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as ''oversize'' and the fluid that passes through is called the ''filtrate''. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as ''blinding''. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective ''pore size'' of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles (depending on the pore size, filter thickness and biological activity). Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms. Filtration is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |