|
Understeer
Understeer and oversteer are vehicle dynamics terms used to describe the sensitivity of a vehicle to steering. Oversteer is what occurs when a car turns (steers) by more than the amount commanded by the driver. Conversely, understeer is what occurs when a car steers less than the amount commanded by the driver. Automotive engineers define understeer and oversteer based on changes in steering angle associated with changes in lateral acceleration over a sequence of steady-state circular turning tests. Car and motorsport enthusiasts often use the terminology more generally in magazines and blogs to describe vehicle response to steering in a variety of maneuvers. Vehicle dynamics terminology Standard terminology used to describe understeer and oversteer are defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in document J670SAE International Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice, "Vehicle Dynamics Terminology", SAE Standard J670, Rev. 2008-01-24 and by the International Organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundorf Analysis
A Bundorf analysis is a measure of the characteristics of a vehicle that govern its understeer balance. The understeer is measured in units of degrees of additional yaw per g of lateral acceleration. An imaginary example Hence the total under-steer is 11.0 deg/g minus 6.9 deg/g, or 4.1 deg/g. Negative values are over-steering, positive values are under-steering, for that axle. If the under-steer contribution of the rear axle is greater than that of the front axle you get negative under-steer, which is known as oversteer. The analysis is only applicable while the parameters remain constant, and thus only up to about 0.4 g. Explanation of terms Load transfer effect and cornering stiffness of tire. As load transfers across the vehicle the tire's ability to provide cornering force for a given slip angle changes. The latter is known as the cornering stiffness of the tire. See also Tire load sensitivity Aligning torque. The tire does not just generate a lateral force, it gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Dynamics
For motorized vehicles, such as automobiles, aircraft, and watercraft, vehicle dynamics is the study of vehicle motion, e.g., how a vehicle's forward movement changes in response to driver inputs, propulsion system outputs, ambient conditions, air/surface/water conditions, etc. Vehicle dynamics is a part of engineering primarily based on classical mechanics. Factors affecting vehicle dynamics The aspects of a vehicle's design which affect the dynamics can be grouped into drivetrain and braking, suspension and steering, distribution of mass, aerodynamics and tires. Drivetrain and braking * Automobile layout (i.e. location of engine and driven wheels) * Powertrain * Braking system Suspension and steering Some attributes relate to the geometry of the suspension, steering and chassis. These include: * Ackermann steering geometry * Axle track * Camber angle * Caster angle * Ride height * Roll center * Scrub radius * Steering ratio * Toe * Wheel alignment * Wheelbase Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinout (driving)
An automobile skid is an automobile handling condition where one or more tires are slipping relative to the road, and the overall handling of the vehicle has been affected. Subtypes of skid include: * fishtailing, where the vehicle yaws back and forth across the direction of motion. * ''spin'' or ''spinout'' where a vehicle rotates in one direction during the skid. * understeer and oversteer where front or rear wheels lose traction during cornering, causing a vehicle to follow a larger or smaller turning radius. * ''burnout'' where a vehicle slips or spins its tires during acceleration. * skidding during braking (with or without directional or yaw changes). __TOC__ Slip and skid Tire slip, and related slip angle (angle of motion relative to tire), describe the performance of an individual tire. Important concepts about slip and skid include circle of forces or circle of traction, and cornering force. To a first approximation, the tire can withstand approximately the same absolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tire Load Sensitivity
Tire load sensitivity describes the behaviour of tires under load. Conventional pneumatic tires do not behave as classical friction theory would suggest. The load sensitivity of most real tires in their typical operating range is such that the coefficient of friction decreases as the vertical load, Fz, increases. The maximum lateral force that can be developed does increase as the vertical load increases, but at a diminishing rate. Behaviour Coulomb friction theory says that the maximum horizontal force developed should be proportional to the vertical load on the tire. In practice, the maximum horizontal force Fy that can be generated is proportional, roughly, to the vertical load Fz raised to the power of somewhere between 0.7 and 0.9, typically. Production car tires typically develop this maximum lateral force, or cornering force, at a slip angle of 6-10 degrees, although this angle increases as the vertical load on the tire increases. Formula 1 car tires may reach a peak si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving Techniques
Driving is the controlled operation and movement of a vehicle, including cars, motorcycles, trucks, buses, and bicycles. Permission to drive on public highways is granted based on a set of conditions being met and drivers are required to follow the established road and traffic laws in the location they are driving. The word driving, has etymology dating back to the 15th century and has developed as what driving has encompassed has changed from working animals in the 15th to automobiles in the 1800s. Driving skills have also developed since the 15th century with physical, mental and safety skills being required to drive. This evolution of the skills required to drive have been accompanied by the introduction of driving laws which relate to not only the driver but the driveability of a car. Etymology The origin of the term ''driver'', as recorded from the 15th century, refers to the occupation of driving working animals, especially pack horses or draft horses. The verb ' ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automotive Safety
Automotive safety is the study and practice of design, construction, equipment and regulation to minimize the occurrence and consequences of traffic collisions involving motor vehicles. Road traffic safety more broadly includes roadway design. One of the first formal academic studies into improving motor vehicle safety was by Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory of Buffalo, New York. The main conclusion of their extensive report is the crucial importance of seat belts and padded dashboards. However, the primary vector of traffic-related deaths and injuries is the disproportionate mass and velocity of an automobile compared to that of the predominant victim, the pedestrian. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 80% of cars sold in the world are not compliant with main safety standards. Only 40 countries have adopted the full set of the seven most important regulations for car safety. In the United States, a pedestrian is injured by a motor vehicle every 8 minutes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drifting (motorsport)
Drifting is a driving technique where the driver intentionally oversteers, with loss of traction, while maintaining control and driving the car through the entirety of a corner. The technique causes the rear slip angle to exceed the front slip angle to such an extent that often the front wheels are pointing in the opposite direction to the turn (e.g. car is turning left, wheels are pointed right or vice versa, also known as opposite lock or counter-steering). Drifting is traditionally done by clutch kicking (where the clutch is rapidly disengaged and re-engaged with the intention of upsetting the grip of the rear wheels), then intentionally oversteering and countersteering. This sense of ''drift'' is not to be confused with the ''four wheel drift'', a classic cornering technique established in Grand Prix and sports car racing. As a motoring discipline, drifting competitions were first popularized in Japan in the 1970s and further popularized by the 1995 manga series ''Init ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opposite Lock
Opposite lock, also commonly known as counter-steering, is a colloquial term used to mean the steering associated with the deliberate use of oversteer to turn a vehicle rapidly without losing momentum. It is typified by the classic rallying style of rear-wheel drive cars, where a car travels around a bend with a large drift angle. The terms "opposite lock" and "counter-steering" refer to the position of the steering wheel during the maneuver, which is turned in the opposite direction to that of the bend. The technique works best on loose or wet surfaces where the friction between the tires and the road is not too high, but can also be used on asphalt or other surfaces with high friction if the vehicle has enough power to maintain speed. Before entry to the bend, the car is turned towards the bend slightly, but quickly, so as to cause a rotating motion that induces the rear of the car to slide outwards. Power is applied which applies further sideways movement. At the same ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brake Bias
The brake balance or brake bias of a vehicle is the distribution of brake force at the front and rear tires, and may be given as the percentage distributed to the front brakes (e.g. 52%) or as the ratio of front and rear percentages (e.g. 52/48). The braking balance affects the driving characteristics in terms of how fast the vehicle can brake, how the vehicle can take corners, and tire wear. The optimal brake balance can vary between circuits, weather conditions and driving styles. On race cars, the brake balance is often part of the racing setup, and in formula car racing it is regularly adjusted during the course of an entire lap. In some cases, the brake balance may be adjusted to match the traction (grip) of the vehicle during braking, which usually means distributing a greater braking force to the front (for example 55/45). In other cases, it may be desirable for the brake balance to be the more similar at the front and rear (e.g. 50/50) for the tires to last longer, which m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishtailing
Fishtailing is a vehicle handling problem which occurs when the rear wheels lose traction, resulting in oversteer. This can be caused by low friction surfaces (sand, gravel, rain, snow, ice, etc.). Rear-drive vehicles with sufficient power can induce this loss of traction on any surface, which is called power-oversteer. During fishtailing, the rear end of the car skids to one side, which must be offset by the driver counter-steering, which is turning the front wheels in the same direction as the skid, (e.g. left if the rear swings left) and reducing engine power. Over-correction will result in a skid in the opposite direction; hence the name. Without a proper driver's reaction, the fishtailing vehicle will spin completely. Friction is the main reason this action is effective. If a car is moving across a surface in any direction other than the direction it is pointed, it is skidding (or sliding), and a sideways load is being imposed against the tires. This causes a lot of frict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
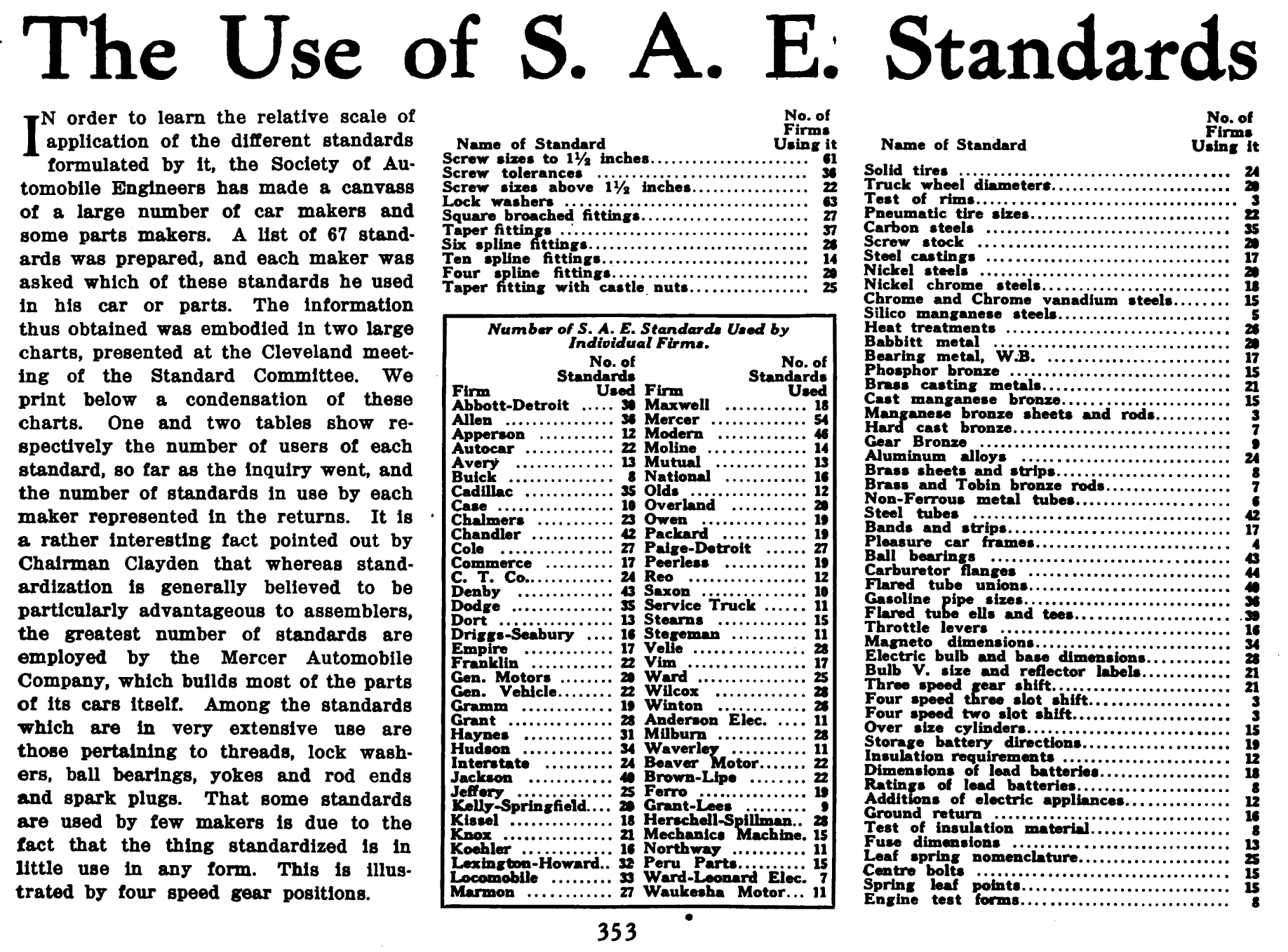
SAE International
SAE International, formerly named the Society of Automotive Engineers, is a United States-based, globally active professional association and standards developing organization for engineering professionals in various industries. SAE International's world headquarters is in Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 20 miles north of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Principal emphasis is placed on global transport industries such as aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicles. The organization adopted the name SAE International to reflect the broader emphasis on mobility. SAE International has over 138,000 global members. Membership is granted to individuals, rather than companies. Aside from its standardization efforts, SAE International also devotes resources to projects and programs in STEM education, professional certification, and collegiate design competitions. For historical legacy reasons, the label "SAE" is commonly used on tools and hardware in North America to indicate United States c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)