|
Tungstate
In chemistry, a tungstate is a compound that contains an oxyanion of tungsten or is a mixed oxide containing tungsten. The simplest tungstate ion is , "orthotungstate". Many other tungstates belong to a large group of polyatomic ions that are termed polyoxometalates, ("POMs"), and specifically termed isopolyoxometalates as they contain, along with oxygen and maybe hydrogen, only one other element. Almost all useful tungsten ores are tungstates. Structures Orthotungstates feature tetrahedral W(VI) centres with short W–O distances of 1.79 Å. Structurally, they resemble sulfates. Six-coordinate, octahedral tungsten dominates in the polyoxotungstates. In these compounds, the W–O distances are elongated. Some examples of tungstate ions: * (hydrogentungstate) * polymeric ions of various structures in , and Wells A.F. (1984) ''Structural Inorganic Chemistry'' 5th edition Oxford Science Publications * (paratungstate A) * (tungstate Y)Jon A. McCleverty, N. G. Connelly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolated as a metal in 1783. Its important ores include scheelite and wolframite, the latter lending the element its alternate name. The free element is remarkable for its robustness, especially the fact that it has the highest melting point of all known elements barring carbon (which sublimes at normal pressure), melting at . It also has the highest boiling point, at . Its density is , comparable with that of uranium and gold, and much higher (about 1.7 times) than that of lead. Polycrystalline tungsten is an intrinsically brittle and hard material (under standard conditions, when uncombined), making it difficult to work. However, pure single-crystalline tungsten is more ductile and can be cut with a hard-steel hacksaw. Tungsten occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyoxometalate
In chemistry, a polyoxometalate (abbreviated POM) is a polyatomic ion, usually an anion, that consists of three or more transition metal oxyanions linked together by shared oxygen atoms to form closed 3-dimensional frameworks. The metal atoms are usually group 6 (Mo, W) or less commonly group 5 ( V, Nb, Ta) transition metals and Tc in their high oxidation states. Polyoxometalates are often colorless, orange or red diamagnetic anions. Two broad families are recognized, isopolymetalates, composed of only one kind of metal and oxide, and heteropolymetalates, composed of one metal, oxide, and a main group oxyanion (phosphate, silicate, etc.). Many exceptions to these general statements exist. Formation The oxides of d0 metals such as , , dissolve at high pH to give orthometalates, , , . For and , the nature of the dissolved species at high pH is less clear, but these oxides also form polyoxometalates. As the pH is lowered, orthometalates protonate to give oxide–hydroxide co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheelite
Scheelite is a calcium tungstate mineral with the chemical formula Ca W O4. It is an important ore of tungsten (wolfram). Scheelite is originally named after Swedish chemist K. Scheele (1742-1786). Well-formed crystals are sought by collectors and are occasionally fashioned into gemstones when suitably free of flaws. Scheelite has been synthesized using the Czochralski process; the material produced may be used to imitate diamond, as a scintillator, or as a solid-state lasing medium. It was also used in radium paint in the same fashion as was zinc sulphide, and Thomas Edison invented a fluoroscope with a calcium tungstate-coated screen, making the images six times brighter than those with barium platinocyanide; the latter chemical allowed Röntgen to discover X-rays in early November 1895. Properties Its crystals are in the tetragonal crystal system, appearing as dipyramidal pseudo-octahedra. Colors include golden yellow, brownish green to dark brown, pinkish to reddis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolframite
Wolframite is an iron, manganese, and tungstate mineral with a chemical formula of that is the intermediate between ferberite ( rich) and hübnerite ( rich). Along with scheelite, the wolframite series are the most important tungsten ore minerals. Wolframite is found in quartz veins and pegmatites associated with granitic intrusives. Associated minerals include cassiterite, scheelite, bismuth, quartz, pyrite, galena, sphalerite, and arsenopyrite. This mineral was historically found in Europe in Bohemia, Saxony, and Cornwall. China reportedly has the world's largest supply of tungsten ore with about 60%. Other producers are Spain, Canada, Portugal, Russia, Australia, Thailand, South Korea, Rwanda, Bolivia, the United States, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Name The name "wolframite" is derived from German "''wolf rahm''", the name given to tungsten by Johan Gottschalk Wallerius in 1747. This, in turn, derives from "''Lupi spuma''", the name Georg Agricola used for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdate
In chemistry a molybdate is a compound containing an oxoanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxoanions which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state. The larger oxoanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxoanions range in size from the simplest , found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, , , and ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten. Examples of molybdate anions Examples of molybdate oxoani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxyanion
An oxyanion, or oxoanion, is an ion with the generic formula (where A represents a chemical element and O represents an oxygen atom). Oxyanions are formed by a large majority of the chemical elements. The formulae of simple oxyanions are determined by the octet rule. The corresponding oxyacid of an oxyanion is the compound . The structures of condensed oxyanions can be rationalized in terms of AO''n'' polyhedral units with sharing of corners or edges between polyhedra. The oxyanions (specifically, phosphate and polyphosphate esters) adenosine monophosphate ( AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) are important in biology. Monomeric oxyanions The formula of monomeric oxyanions, , is dictated by the oxidation state of the element A and its position in the periodic table. Elements of the first row are limited to a maximum coordination number of 4. However, none of the first row elements has a monomeric oxyanion with that coordination number. Instead, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum Blue
Molybdenum blue is a term applied to: *reduced heteropolymolybdate complexes, polyoxometalates containing Mo(V), Mo(VI), and a hetero atom such as phosphorus or silicon *reduced isopolymolybdate complexes, polyoxometalates containing Mo(V), Mo(VI) formed when solutions of Mo(VI) are reduced *a blue pigment containing molybdenum(VI) oxide The "heteropoly-molybdenum blues", are used extensively in analytical chemistry and as catalysts. The formation of "isopoly-molybdenum blues" which are intense blue has been used as a sensitive test for reducing reagents. They have recently been shown to contain very large anionic species based on the so-called "big wheel" containing 154 Mo atoms, with a formula o154O462H14(H2O)70sup>14−.''From Scheele and Berzelius to MÜller: polyoxometalates (POMs) revisited and the "missing link" between the bottom up and top down approaches'' P. Gouzerh, M. Che; ''L'Actualité Chimique'', 2006, 298, 9 The molybdenum blue pigment is historically documented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powellite
Powellite is a calcium molybdate mineral with formula CaMoO4. Powellite crystallizes with tetragonal - dipyramidal crystal structure as transparent adamantine blue, greenish brown, yellow to grey typically anhedral forms. It exhibits distinct cleavage and has a brittle to conchoidal fracture. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and a specific gravity of 4.25. It forms a solid solution series with scheelite (calcium tungstate, CaWO4). It has refractive index values of nω=1.974 and nε=1.984. Powellite was first described by William Harlow Melville in 1891 for an occurrence in the Peacock Mine, Adams County, Idaho and named for American explorer and geologist, John Wesley Powell (1834–1902). It occurs in hydrothermal ore deposits of molybdenum within the near surface oxidized zones. It also appears as a rare mineral phase in pegmatite, tactite and basalt. Minerals found in association with powellite include molybdenite, ferrimolybdite, stilbite, laumontite and apophyllite Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidizer
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and the halogens. In one sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that undergoes a chemical reaction in which it gains one or more electrons. In that sense, it is one component in an oxidation–reduction (redox) reaction. In the second sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that transfers electronegative atoms, usually oxygen, to a substrate. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
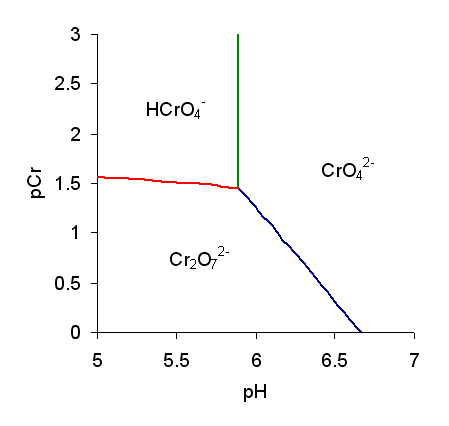
Chromate And Dichromate
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible. Chemical properties Potassium-chromate-sample.jpg, potassium chromate Potassium-dichromate-sample.jpg, potassium dichromate Chromates react with hydrogen peroxide, giving products in which peroxide, , replaces one or more oxygen atoms. In acid solution the unstable blue peroxo complex Chromium(VI) oxide peroxide, CrO(O2)2, is formed; it is an uncharged covalent molecule, which may be extracted into ether. Addition of pyridine results in the formation of the more stable complex CrO(O2)2py. Acid–base properties In aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate anions exist in a chemical equilibrium. :2 + 2 H+ + H2O The predominance diagram shows that the position of the equilibrium depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |