|
Tube (fluid Conveyance)
A tube, or tubing, is a long hollow cylinder used for moving fluids (liquids or gases) or to protect electrical or optical cables and wires. The terms "pipe" and "tube" are almost interchangeable, although minor distinctions exist — generally, a tube has tighter engineering requirements than a pipe. Both pipe and tube imply a level of rigidity and permanence, whereas a hose is usually portable and flexible. A tube and pipe may be specified by standard pipe size designations, ''e.g.'', nominal pipe size, or by nominal outside or inside diameter and/or wall thickness. The actual dimensions of pipe are usually not the nominal dimensions: A 1-inch pipe will not actually measure 1 inch in either outside or inside diameter, whereas many types of tubing are specified by actual inside diameter, outside diameter, or wall thickness. Manufacture There are three classes of manufactured tubing: seamless, as-welded or electric resistant welded (ERW), and drawn-over-mandr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic Tubing
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to its widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives. 9.2 billion tonnes of plastic are estimated to have been made between 1950 and 2017. More than half this plastic has been produced since 2004. In 2020, 400 million tonnes of plastic were produced. If global trends on plastic demand continue, it is estimated that by 2050 annual global plastic production will reach over 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outside Diameter
This page lists the standard US nomenclature used in the description of mechanical gear construction and function, together with definitions of the terms. The terminology was established by the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA), under accreditation from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). Addendum The addendum is the height by which a tooth of a gear projects beyond (outside for external, or inside for internal) the standard pitch circle or pitch line; also, the radial distance between the pitch diameter and the outside diameter. Addendum angle Addendum angle in a bevel gear, is the angle between face cone and pitch cone. Addendum circle The addendum circle coincides with the tops of the teeth of a gear and is concentric with the standard (reference) pitch circle and radially distant from it by the amount of the addendum. For external gears, the addendum circle lies on the outside cylinder while on internal gears the addendum circle lies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piping
Within industry, piping is a system of pipes used to convey fluids (liquids and gases) from one location to another. The engineering discipline of piping design studies the efficient transport of fluid. Industrial process piping (and accompanying in-line components) can be manufactured from wood, fiberglass, glass, steel, aluminum, plastic, copper, and concrete. The in-line components, known as fittings, valves, and other devices, typically sense and control the pressure, flow rate and temperature of the transmitted fluid, and usually are included in the field of piping design (or piping engineering), though the sensors and automatic controlling devices may alternatively be treated as part of instrumentation and control design. Piping systems are documented in piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs). If necessary, pipes can be cleaned by the tube cleaning process. ''Piping'' sometimes refers to piping design, the detailed specification of the physical piping layout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestic Water System
Tap water (also known as faucet water, running water, or municipal water) is water supplied through a tap, a water dispenser valve. In many countries, tap water usually has the quality of drinking water. Tap water is commonly used for drinking, cooking, washing, and toilet flushing. Indoor tap water is distributed through "indoor plumbing", which has existed since antiquity but was available to very few people until the second half of the 19th century when it began to spread in popularity in what are now developed countries. Tap water became common in many regions during the 20th century, and is now lacking mainly among people in poverty, especially in developing countries. Governmental agencies commonly regulate tap water quality. Household water purification methods such as water filters, boiling, or distillation can be used to treat tap water's microbial contamination to improve its potability. The application of technologies (such as water treatment plants) involved in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
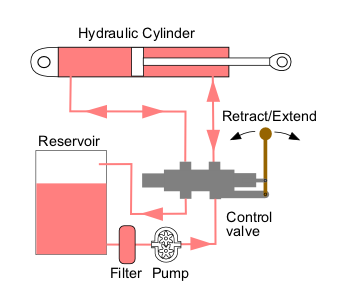
Hydraulic Machinery
Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurized according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, or pipes. Hydraulic systems, like pneumatic systems, are based on Pascal's law which states that any pressure applied to a fluid inside a closed system will transmit that pressure equally everywhere and in all directions. A hydraulic system uses an incompressible liquid as its fluid, rather than a compressible gas. The popularity of hydraulic machinery is due to the very large amount of power that can be transferred through small tubes and flexible hoses, the high power density and a wide array of actuators that can make use of this power, and the huge multiplication of forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Piping
Hydrogen pipeline transport is a transportation of hydrogen through a pipe as part of the hydrogen infrastructure. History *1938 - Rhine-Ruhr The first hydrogen pipes that are constructed of regular pipe steel, compressed hydrogen pressure , diameter . Still in operation. *1973 – pipeline in Isbergues, France. *1985 - Extension of the pipeline from Isbergues to Zeebrugge *1997 - Connection of the pipeline to Rotterdam *1997 - 2000: Development of two hydrogen networks, one near Corpus Christi, Texas, and one between Freeport and Texas City. *2009 - extension of the pipeline from Plaquemine to Chalmette. Economics Hydrogen pipeline transport is used to transport hydrogen from the point of production or delivery to the point of demand. Although hydrogen pipeline transport is technologically mature, and the transport costs are similar to those of CNG, most hydrogen is produced in the place of demand, with an industrial production facility every Piping For process meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Tubing
Copper tubing is most often used for heating systems and as a refrigerant line in HVAC systems. Copper tubing is slowly being replaced by PEX tubing in hot and cold water applications. There are two basic types of copper tubing, soft copper and rigid copper. Copper tubing is joined using flare connection, compression connection, pressed connection, or solder. Copper offers a high level of corrosion resistance but is becoming very costly. Types Soft copper Soft (or ductile) copper tubing can be bent easily to travel around obstacles in the path of the tubing. While the work hardening of the drawing process used to size the tubing makes the copper hard or rigid, it is carefully annealed to make it soft again; it is, therefore, more expensive to produce than non-annealed, rigid copper tubing. It can be joined by any of the three methods used for rigid copper, and it is the only type of copper tubing suitable for flare connections. Soft copper is the most popular choice for refriger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Factor
In engineering, a factor of safety (FoS), also known as (and used interchangeably with) safety factor (SF), expresses how much stronger a system is than it needs to be for an intended load. Safety factors are often calculated using detailed analysis because comprehensive testing is impractical on many projects, such as bridges and buildings, but the structure's ability to carry a load must be determined to a reasonable accuracy. Many systems are intentionally built much stronger than needed for normal usage to allow for emergency situations, unexpected loads, misuse, or degradation (reliability). Definition There are two definitions for the factor of safety (FoS): * The ratio of a structure's absolute strength (structural capability) to actual applied load; this is a measure of the reliability of a particular design. This is a calculated value, and is sometimes referred to, for the sake of clarity, as a ''realized factor of safety''. * A constant required value, imposed by law, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal (unit)
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI), and is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is defined as one newton per square metre and is equivalent to 10 barye (Ba) in the CGS system. The unit of measurement called standard atmosphere (atm) is defined as 101,325 Pa. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), which is equal to one centibar. Meteorological observations typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals per the recommendation of the World Meteorological Organization, thus a standard atmosphere (atm) or typical sea-level air pressure is about 1013 hPa. Reports in the United States typically use inches of mercury or millibars (hectopascals). In Canada these reports are given in kilop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensile Strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials the ultimate tensile strength can be higher. The ultimate tensile strength is usually found by performing a tensile test and recording the engineering stress versus strain. The highest point of the stress–strain curve is the ultimate tensile strength and has units of stress. The equivalent point for the case of compression, instead of tension, is called the compressive strength. Tensile strengths are rarely of any consequence in the design of ductile members, but they are important with brittle members. They are tabulated for common materials such as alloys, composite materials, ceramics, plastics, and wood. Definition The ultimate tensile st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wall Thickness
A wall is a structure and a surface that defines an area; carries a load; provides security, shelter, or soundproofing; or, is decorative. There are many kinds of walls, including: * Walls in buildings that form a fundamental part of the superstructure or separate interior rooms, sometimes for fire safety *Glass walls (a wall in which the primary structure is made of glass; does not include openings within walls that have glass coverings: these are windows) * Border barriers between countries * Brick walls * Defensive walls in fortifications * Permanent, solid fences * Retaining walls, which hold back dirt, stone, water, or noise sound * Stone walls * Walls that protect from oceans (seawalls) or rivers ( levees) Etymology The term ''wall'' comes from Latin ''vallum'' meaning "...an earthen wall or rampart set with palisades, a row or line of stakes, a wall, a rampart, fortification..." while the Latin word ''murus'' means a defensive stone wall. English uses the same wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |