|
Trematode
Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. Infection by trematodes can cause disease in all five traditional vertebrate classes: mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. Etymology Trematodes are commonly referred to as flukes. This term can be traced back to the Old English name for flounder, and refers to the flattened, rhomboidal shape of the organisms. Taxonomy There are 18,000 to 24,000 known species of trematodes, divided into two subclasses — the Aspidogastrea and the Digenea. Aspidogastrea is the smaller subclass, comprising 61 species. These flukes mainly infect bivalves and bony fishes.https://www.biotaxa.org/Zootaxa/article/view/zootaxa.3918.3.2 Digenea — which comprise the majority of trematodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspidogastrea
The Aspidogastrea (Ancient Greek: ' “shield”, ' “stomach/pouch”) is a small group of flukes comprising about 80 species. It is a subclass of the trematoda, and sister group to the Digenea. Species range in length from approximately one millimeter to several centimeters. They are parasites of freshwater and marine molluscs and vertebrates ( cartilaginous and bony fishes and turtles). Maturation may occur in the mollusc or vertebrate host. None of the species has any economic importance, but the group is of very great interest to biologists because it has several characters which appear to be archaic. Morphology Shared characteristics Shared characteristics of the group are a large ventral disc with a large number of small alveoli ("suckerlets") or a row of suckers and a tegument with short protrusions, so-called "microtubercles". Larval physiology Larvae of some species have ciliated patches. Those of ''Multicotyle purvisi'' have four patches on the anteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digenea
Digenea (Gr. ''Dis'' – double, ''Genos'' – race) is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms (known as ''flukes'') with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date. Morphology Key features Characteristic features of the Digenea include a syncytial tegument; that is, a tegument where the junctions between cells are broken down and a single continuous cytoplasm surrounds the entire animal. A similar tegument is found in other members of the Neodermata; a group of platyhelminths comprising the Digenea, Aspidogastrea, Monogenea and Cestoda. Digeneans possess a vermif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed '' schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Organization as the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease (after malaria), with hundreds of millions infected worldwide. Adult flatworms parasitize blood capillaries of either the mesenteries or plexus of the bladder, depending on the infecting species. They are unique among trematodes and any other flatworms in that they are dioecious with distinct sexual dimorphism between male and female. Thousands of eggs are released and reach either the bladder or the intestine (according to the infecting species), and these are then excreted in urine or feces to fresh water. Larvae must then pass through an intermediate snail host, before the next larval stage of the parasite emerges that can infect a new mammalian host by dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
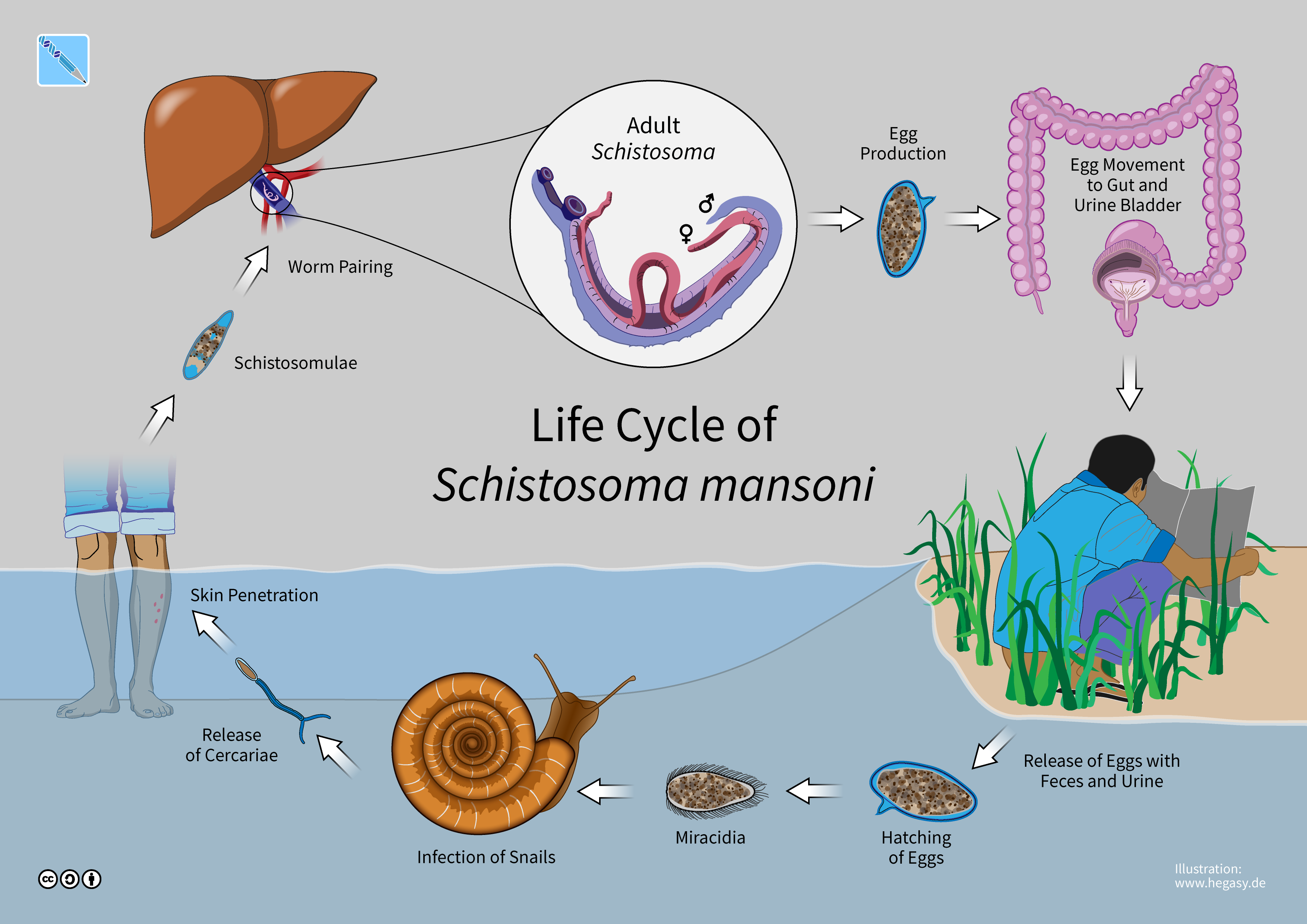
Schistosoma Mansoni
A paired couple of ''Schistosoma mansoni''. ''Schistosoma mansoni'' is a water-borne parasite of humans, and belongs to the group of blood flukes ''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed ''schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Organi ... (''Schistosoma''). The adult lives in the blood vessels ( mesenteric veins) near the human intestine. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis (similar to '' S. japonicum'', '' S. mekongi'', ''S. guineensis'', and '' S. intercalatum''). Clinical symptoms are caused by the eggs. As the leading cause of schistosomiasis in the world, it is the most prevalent parasite in humans. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease. As of 2021, the World Health Organization reports that 236.6 million people have schistosomiasis and most of it is due to ''S. mansoni''. It is found in Africa, the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatworm
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates (having no body cavity), and have no specialized circulatory and respiratory organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion (intake of nutrients) and egestion (removal of undigested wastes); as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously. In traditional medicinal texts, Platyhelminthes are divided into Turbellaria, which are mostly non- parasitic animals such as planarians, and three entirely parasitic groups: Cestoda, Trematoda and Monogenea; however, since the turbellarians have since been proven not to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercaria
A cercaria (plural cercariae) is the larval form of the trematode Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive h ... class of parasites. It develops within the germinal cells of the sporocyst or redia. A cercaria has a tapering head with large penetration glands. It may or may not have a long swimming "tail", depending on the species. The motile cercaria finds and settles in a host where it will become either an adult, or a mesocercaria, or a metacercaria, according to species. Rotifers ('' Rotaria rotatoria'') produce a chemical, Schistosome Paralysis Factor, suppressing cercaria swimming and reducing infections.{{cite journal , editor1-last=Khosla , editor1-first=Chaitan , last1=Gao, first1=Jiarong, last2=Yang, first2=Ning, last3=Lewis, first3=Fred A., last4=Yau, first4=Peter, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma Mekongi
''Schistosoma mekongi'' is a species of trematodes, also known as flukes. It is one of the five major schistosomes that account for all human infections, the other four being ''S. haematobium'', ''S. mansoni, S. japonicum, and S. intercalatum''. This trematode causes schistosomiasis in humans. Freshwater snail ''Neotricula aperta'' serves as an intermediate host for ''Schistosoma mekongi''. History Schistosomiasis was first reported in the Mekong River's Lower Basin region in 1957, from Laotian island of Khong to Cambodian province of Kratié, specifically. It was believed that the cause of these cases was ''Schistosoma japonicum'' until 1978, when ''Neotricula aperta'' was discovered and it was determined that the Schistosome was a unique species, ''Schistosoma mekongi''. In 1967, a WHO-mission was sent to Champasack, confirming the infections, and putting focus on how it was being transferred. In 1989, the Ministry of Health in Laos initiated its first medicational inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic flatworms called schistosomes. The urinary tract or the intestines may be infected. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stool, or blood in the urine. Those who have been infected for a long time may experience liver damage, kidney failure, infertility, or bladder cancer. In children, it may cause poor growth and learning difficulty. The disease is spread by contact with fresh water contaminated with the parasites. These parasites are released from infected freshwater snails. The disease is especially common among children in developing countries, as they are more likely to play in contaminated water. Other high-risk groups include farmers, fishermen, and people using unclean water during daily living. It belongs to the group of helminth infections. Diagnosis is by finding eggs of the parasite in a person's urine or stool. It can also be confirmed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host (biology)
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an association is much larger than the other, it is generally known as the host. In parasitism, the parasite benefits a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichobilharzia Regenti
''Trichobilharzia regenti'' is a neuropathogenic parasitic flatworm of birds which also causes cercarial dermatitis in humans. The species was originally described in 1998 in the Czech Republic and afterwards it was detected also in other European countries, e.g. Denmark, Germany, France, Iceland, Poland, Switzerland, or Russia, and even in Iran. For its unique neurotropic behaviour in vertebrate hosts, the host-parasite interactions are extensively studied in terms of molecular biology, biochemistry and immunology. Life cycle The life cycle of ''T. regenti'' is analogous to that of human schistosomes. Adult flukes mate in a nasal mucosa of anatid birds (e.g. ''Anas platyrhynchos, Spatula clypeata'' or '' Cairina moschata'') and produce eggs with miracidia which hatch directly in the host tissue and leak outside when the bird is drinking/feeding. Once in water, the miracidia swim using their cilia and actively search for a proper molluscan intermediate host (''Radix lagotis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma Intercalatum
''Schistosoma intercalatum'' is a parasitic worm found in parts of western and central Africa. There are two strains: the Lower Guinea strain and the Zaire strain. ''S. intercalatum'' is one of the major agents of the rectal form of schistosomiasis, also called bilharzia. It is a trematode, and being part of the genus ''Schistosoma'', it is commonly referred to as a blood-fluke since the adult resides in blood vessels. Humans are the definitive host and two species of freshwater snail make up the intermediate host, ''Bulinus forskalii'' for the Lower Guinea strain and '' Bulinus africanus'' for the Zaire strain.Tchuem Tchuenté LA, Southgate, VR, Jourdane J, Webster BL, Vercruysse J (2003) ''Schistosoma intercalatum'': an endangered species in Cameroon? ''Trends Parasitol'' 19: 141-153. Morphology The clinically defining characteristic of most schistosome species are their eggs' size and shape. The eggs of ''Schistosoma intercalatum'' have a terminal spine and tend to be modera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)