|
Titanium Isopropoxide
Titanium isopropoxide, also commonly referred to as titanium tetraisopropoxide or TTIP, is a chemical compound with the formula . This alkoxide of titanium(IV) is used in organic synthesis and materials science. It is a diamagnetic tetrahedral molecule. Titanium isopropoxide is a component of the Sharpless epoxidation, a method for the synthesis of chiral epoxides. The structures of the titanium alkoxides are often complex. Crystalline titanium methoxide is tetrameric with the molecular formula . Alkoxides derived from bulkier alcohols such as isopropyl alcohol aggregate less. Titanium isopropoxide is mainly a monomer in nonpolar solvents. Preparation It is prepared by treating titanium tetrachloride with isopropanol. Hydrogen chloride is formed as a coproduct: : TiCl4 + 4 (CH3)2CHOH → Ti4 + 4 HCl Properties Titanium isopropoxide reacts with water to deposit titanium dioxide: :Ti4 + 2 H2O → TiO2 + 4 (CH3)2CHOH This reaction is employed in the sol-gel synthesis of TiO2-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the synthesis of organic compounds, and as a fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world production of ethanol was , coming mostly from Brazil and the U.S. Etymology ''Ethanol'' is the systematic name defined by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called ''empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prochiral
In stereochemistry, prochiral molecules are those that can be converted from achiral to chiral in a single step. An achiral species which can be converted to a chiral in two steps is called proprochiral. If two identical substituents are attached to a sp3-hybridized atom, the descriptors ''pro''-R and ''pro''-S are used to distinguish between the two. Promoting the ''pro''-R substituent to higher priority than the other identical substituent results in an ''R'' chirality center at the original sp3-hybridized atom, and analogously for the ''pro''-S substituent. A trigonal planar sp2-hybridized atom can be converted to a chiral center when a substituent is added to the ''re'' or ''si'' () face of the molecule. A face is labeled ''re'' if, when looking at that face, the substituents at the trigonal atom are arranged in increasing Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority order (1 to 2 to 3) in a clockwise order, and ''si'' if the priorities increase in anti-clockwise order; note that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulinkovich Reaction
The Kulinkovich reaction describes the organic synthesis of cyclopropanols via reaction of esters with dialkyldialkoxytitanium reagents, generated in situ from Grignard reagents bearing hydrogen in beta-position and titanium(IV) alkoxides such as titanium isopropoxide. This reaction was first reported by Oleg Kulinkovich and coworkers in 1989. Titanium catalysts are ClTi(OiPr)3 or Ti(OiPr)4, ClTi(OtBu)3 or Ti(OtBu)4, Grignard reagents are EtMgX, PrMgX or BuMgX. Solvents can be Et2O, THF, toluene. Tolerated Functional Groups: Ethers R–O–R, R–S–R, Imines RN=CHR. Amides, primary and secondary amines. Carbamates typically do not tolerate the reaction conditions, but tert-butyl carbamates (N-Boc derivatives) survive the transformation. An asymmetric version of this reaction is also known with a TADDOL-based catalyst. Reaction mechanism The generally accepted reaction mechanism initially utilizes two successive stages of transmetallation of the committed Grignard reag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important chemical reagent and industrial chemical, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. The global demand for acetic aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
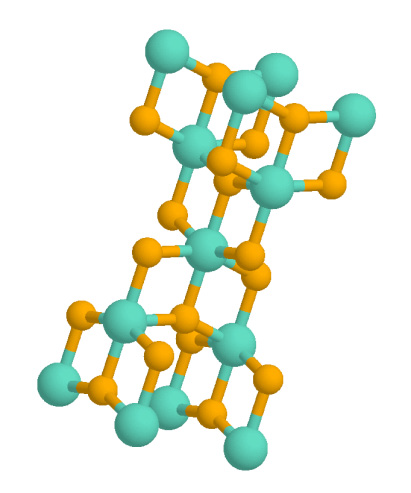
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble to water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structure of rutile is tetragonal in symmetry whereas anatase and brookite are orthorhombic. The oxygen substructures are all slight dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Tetrachloride
Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide () and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4" due to the phonetic resemblance of its molecular formula () to the word. Properties and structure is a dense, colourless distillable liquid, although crude samples may be yellow or even red-brown. It is one of the rare transition metal halides that is a liquid at room temperature, being another example. This property reflects the fact that molecules of weakly self-associate. Most metal chlorides are polymers, wherein the chloride atoms bridge between the metals. Its melting and boiling points are similar to those of . has a "closed" electronic shell, with the same numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl. Reactions Hydrogen chloride is a diatomic molecule, consisting of a hydrogen atom H and a chlorine atom Cl connected by a polar covalent bond. The chlorine atom is much more electronegative than the hydrogen atom, which makes this bond polar. Consequently, the molecule has a large dipole moment with a negative partial charge (δ−) at the chlorine atom and a positive partial charge (δ+) at the hydrogen atom. In part because of its high polarity, HCl is very soluble in water (and in other polar solvents). Upon contact, and HCl combine to form hydronium cations a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopropanol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. As an isopropyl group linked to a hydroxyl group (chemical formula ) it is the simplest example of a secondary alcohol, where the alcohol carbon atom is attached to two other carbon atoms. It is a structural isomer of propan-1-ol and ethyl methyl ether. It is used in the manufacture of a wide variety of industrial and household chemicals and is a common ingredient in products such as antiseptics, disinfectants, hand sanitizer and detergents. Well over one million tonnes is produced worldwide annually. Properties Isopropyl alcohol is miscible in water, ethanol, and chloroform as, like these compounds, isopropyl is a polar molecule. It dissolves ethyl cellulose, polyvinyl butyral, many oils, alkaloids, and natural resins. Unlike ethanol or methanol, isopropyl alcohol is not miscible with salt solutions and can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Tetrachloride
Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide () and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4" due to the phonetic resemblance of its molecular formula () to the word. Properties and structure is a dense, colourless distillable liquid, although crude samples may be yellow or even red-brown. It is one of the rare transition metal halides that is a liquid at room temperature, being another example. This property reflects the fact that molecules of weakly self-associate. Most metal chlorides are polymers, wherein the chloride atoms bridge between the metals. Its melting and boiling points are similar to those of . has a "closed" electronic shell, with the same numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |