|
Telicity
In linguistics, telicity (; ) is the property of a verb or verb phrase that presents an action or event as having a specific endpoint. A verb or verb phrase with this property is said to be ''telic''; if the situation it describes is ''not'' heading for any particular endpoint, it is said to be ''atelic''. Testing for telicity in English One common way to gauge whether an English verb phrase is telic is to see whether such a phrase as ''in an hour'', in the sense of "within an hour", (known as a ''time-frame adverbial'') can be applied to it. Conversely, a common way to gauge whether the phrase is atelic is to see whether such a phrase as ''for an hour'' (a ''time-span adverbial'') can be applied to it. This can be called the ''time-span/time-frame test''. According to this test, the verb phrase ''built a house'' is telic, whereas the minimally different ''built houses'' is atelic: : Fine: "John built a house in a month." : Bad: *"John built a house for a month." :: → ''bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Language
Finnish ( endonym: or ) is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland (the other being Swedish). In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. The Kven language, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian county Troms og Finnmark by a minority group of Finnish descent. Finnish is typologically agglutinative and uses almost exclusively suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numerals and verbs are inflected depending on their role in the sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, although the extensive use of inflection allows them to be ordered differently. Word order variations are often reserved for differences in information structure. Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Aspect
In linguistics, aspect is a grammatical category that expresses how an action, event, or state, as denoted by a verb, extends over time. Perfective aspect is used in referring to an event conceived as bounded and unitary, without reference to any flow of time during ("I helped him"). Imperfective aspect is used for situations conceived as existing continuously or repetitively as time flows ("I was helping him"; "I used to help people"). Further distinctions can be made, for example, to distinguish states and ongoing actions ( continuous and progressive aspects) from repetitive actions ( habitual aspect). Certain aspectual distinctions express a relation between the time of the event and the time of reference. This is the case with the perfect aspect, which indicates that an event occurred prior to (but has continuing relevance at) the time of reference: "I have eaten"; "I had eaten"; "I will have eaten". Different languages make different grammatical aspectual distinction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
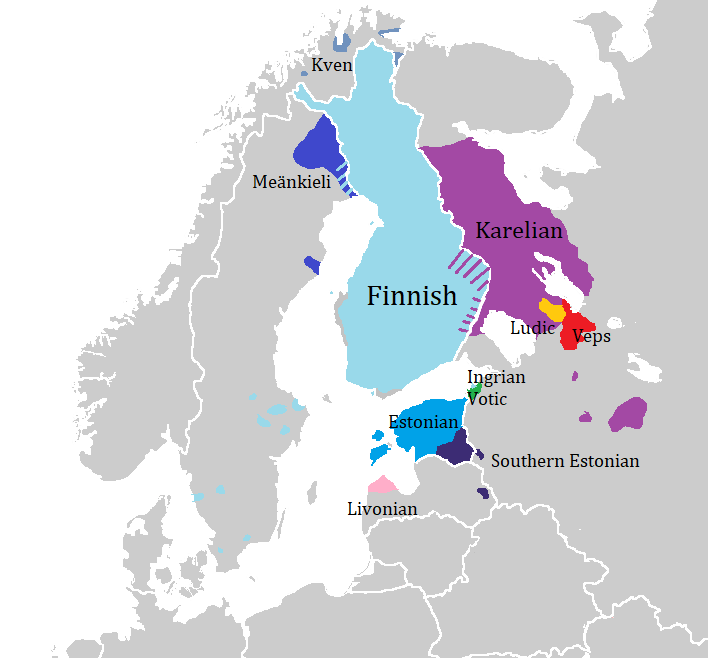
Finnic Languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prepositions
Prepositions and postpositions, together called adpositions (or broadly, in traditional grammar, simply prepositions), are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in'', ''under'', ''towards'', ''before'') or mark various semantic roles (''of'', ''for''). A preposition or postposition typically combines with a noun phrase, this being called its complement, or sometimes object. A preposition comes before its complement; a postposition comes after its complement. English generally has prepositions rather than postpositions – words such as ''in'', ''under'' and ''of'' precede their objects, such as ''in England'', ''under the table'', ''of Jane'' – although there are a few exceptions including "ago" and "notwithstanding", as in "three days ago" and "financial limitations notwithstanding". Some languages that use a different word order have postpositions instead, or have both types. The phrase formed by a preposition or postposition together with its co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulativity
In linguistic semantics, an expression X is said to have cumulative reference if and only if the following holds: If X is true of both of ''a'' and ''b'', then it is also true of the combination of ''a'' and ''b''. Example: If two separate entities can be said to be "water", then combining them into one entity will yield more "water". If two separate entities can be said to be "a house", their combination cannot be said to be "a house". Hence, "water" has cumulative reference, while the expression "a house" does not. The plural form "houses", however, ''does'' have cumulative reference. If two (groups of) entities are both "houses", then their combination will still be "houses". Cumulativity has proven relevant to the linguistic treatment of the mass/count distinction and for the characterization of grammatical telicity. Formally, a cumulative predicate ''CUM'' can be defined as follows, where capital ''X'' is a variable over sets, ''U'' is the universe of discourse, ''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantization (linguistics)
In formal semantics, a predicate is quantized if it being true of an entity requires that it is ''not'' true of any proper subparts of that entity. For example, if something is an "apple", then no proper subpart of that thing is an "apple". If something is "water", then many of its subparts will also be "water". Hence, the predicate "apple" is quantized, while "water" is not. Formally, a quantization predicate ''QUA'' can be defined as follows, where U is the universe of discourse, F is a variable over sets, and p is a mereological part structure on U with <_p the mereological part-of relation: Quantization was first propose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the science, scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the Cognition, cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manfred Krifka
Manfred Krifka (born 26 April 1956 in Dachau) is a German linguist. He is the director of the Leibniz Centre for General Linguistics (Leibniz-Zentrum Allgemeine Sprachwissenschaft, ZAS) in Berlin, a professor at the Humboldt University of Berlin, and editor of the academic journal ''Theoretical Linguistics''. See staff bio and journal web pages in External links below. Career and education Krifka graduated from the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich in 1986 in Theoretical Linguistics, Philosophy and Theory of Science, and Psycholinguistics. He consequently held positions at the University of Tübingen 1986 - 1989, at the University of Texas at Austin 1990 - 2000, and at Humboldt University of Berlin 2000 - current. He has been the director of the Leibniz Centre for General Linguistics (ZAS) since 2001. Work Krifka's main areas of research are linguistic semantics, pragmatics, language typology and Melanesian languages, especially languages of Ambrym. He has done substan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitive
In linguistics, the partitive is a word, phrase, or case that indicates partialness. Nominal partitives are syntactic constructions, such as "some of the children", and may be classified semantically as either set partitives or entity partitives based on the quantifier and the type of embedded noun used. Partitives should not be confused with '' quantitives'' (also known as pseudopartitives), which often look similar in form, but behave differently syntactically and have a distinct meaning. In many Romance and Germanic languages, nominal partitives usually take the form: DP_Det._+_''of''_+_[DP_Det._+_NP.html" ;"title="sub>DP Det. + ''of'' + [DP Det. + NP">sub>DP Det. + ''of'' + [DP Det. + NPMartí i Girbau, M. N. (2010). The syntax of partitives. where the first determiner is a Quantifier (linguistics), quantifier word, using a prepositional element to link it to the larger set or whole from which that quantity is partitioned. The partitive constructions of the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accusative
The accusative case (abbreviated ) of a noun is the grammatical case used to mark the direct object of a transitive verb. In the English language, the only words that occur in the accusative case are pronouns: 'me,' 'him,' 'her,' 'us,' and ‘them’. The spelling of those words will change depending on how they are used in a sentence. For example, the pronoun ''they'', as the subject of a sentence, is in the nominative case ("They wrote a book"); but if the pronoun is instead the object, it is in the accusative case and ''they'' becomes ''them'' ("The book was written by them"). The accusative case is used in many languages for the objects of (some or all) prepositions. It is usually combined with the nominative case (for example in Latin). The English term, "accusative", derives from the Latin , which, in turn, is a translation of the Greek . The word may also mean "causative", and this may have been the Greeks' intention in this name, but the sense of the Roman translation h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine ( Subcarpathia), central and western Romania ( Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia (Prekmurje), and eastern Austria. It is also spoken by Hungarian diaspora communities worldwide, especially in North America (particularly the United States and Canada) and Israel. With 17 million speakers, it is the Uralic family's largest member by number of speakers. Classification Hungarian is a member of the Uralic language family. Linguistic connections between Hungarian and other Uralic languages were noticed in the 1670s, and the family itself (then called Finno-Ugric) was established in 1717. Hungarian has traditionally been assigned to the Ugric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Language
Czech (; Czech ), historically also Bohemian (; ''lingua Bohemica'' in Latin), is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. Spoken by over 10 million people, it serves as the official language of the Czech Republic. Czech is closely related to Slovak, to the point of high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish to a lesser degree. Czech is a fusional language with a rich system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval period, and the standardization of Czech and Slovak within the Czech–Slovak dialect continuum emerged in the early modern period. In the later 18th to mid-19th century, the modern written standard became codified in the context of the Czech National Revival. The main non-standard variety, known as Common Czech, is based on the vernacular of Prague, but is now spoken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |