|
Tech Model Railroad Club
The Tech Model Railroad Club (TMRC) is a student organization at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Historically it has been a wellspring of hacker culture and the oldest such hacking group in North America. Formed in 1946, its HO scale layout specializes in automated operation of model trains. History The first meeting of the Tech Model Railroad Club was organized by John Fitzallen Moore and Walter Marvin in November of 1946. Moore and Marvin had membership cards #0 and #1 and served as the first president and vice-president respectively. They then switched roles the following year. Circa 1948, the club obtained official MIT campus space in Room 20E-214, on the third floor of Building 20, a "temporary" World War II-era structure, sometimes called "the Plywood Palace", which had been home to the MIT Radiation Lab during World War II. The club's members, who shared a passion to find out how things worked and then to master them, were among the first Hacker (term), ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tech Model Railroad Green Building
Tech or The Tech may refer to: * An abbreviation of technology or technician *Tech Dinghy, an American sailing dinghy developed at MIT *Tech (mascot), the mascot of Louisiana Tech University, U.S. * Tech (river), in southern France * "Tech" (''Smash''), a 2012 episode of TV series ''Smash'' * ''The Tech'' (newspaper), newspaper at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology * The Tech Interactive, formerly The Tech Museum of Innovation, or The Tech, a museum in San Jose, California, U.S. * Tech Tower, a building at the Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. See also * USS ''Tech Jr.'' (SP-1761), a United States Navy patrol boat in commission in 1917 * USS ''Tech III'' (SP-1055), a United States Navy patrol boat in commission in 1917 *Technical (other) *Technique (other) Technique or techniques may refer to: Music * The Techniques, a Jamaican rocksteady vocal group of the 1960s *Technique (band), a British female synth pop band in the 1990s * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaginary Unit
The imaginary unit or unit imaginary number () is a solution to the quadratic equation x^2+1=0. Although there is no real number with this property, can be used to extend the real numbers to what are called complex numbers, using addition and multiplication. A simple example of the use of in a complex number is 2+3i. Imaginary numbers are an important mathematical concept; they extend the real number system \mathbb to the complex number system \mathbb, in which at least one root for every nonconstant polynomial exists (see Algebraic closure and Fundamental theorem of algebra). Here, the term "imaginary" is used because there is no real number having a negative square. There are two complex square roots of −1: and -i, just as there are two complex square roots of every real number other than zero (which has one double square root). In contexts in which use of the letter is ambiguous or problematic, the letter or the Greek \iota is sometimes used instead. For example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
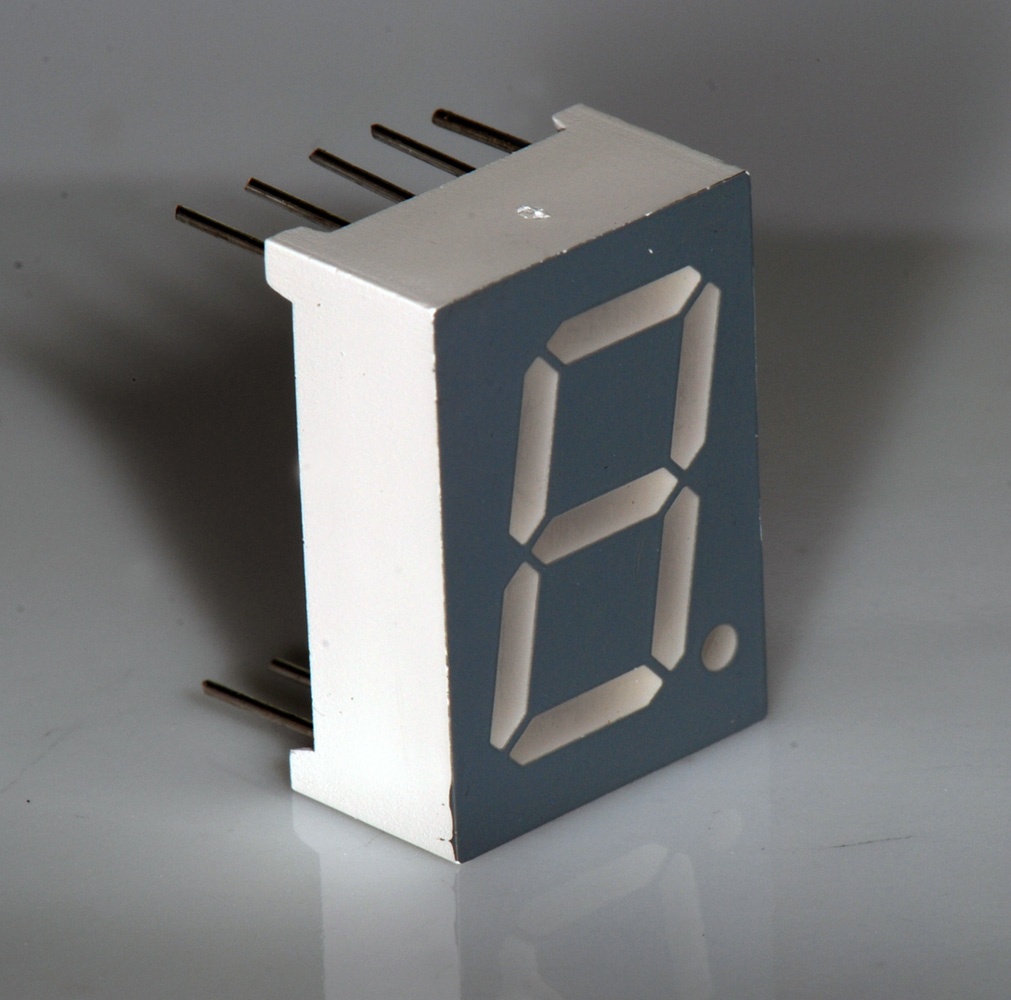
Seven-segment Display
A seven-segment display is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an alternative to the more complex dot matrix displays. Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, and other electronic devices that display numerical information. History Seven-segment representation of figures can be found in patents as early as 1903 (in ), when Carl Kinsley invented a method of telegraphically transmitting letters and numbers and having them printed on tape in a segmented format. In 1908, F. W. Wood invented an 8-segment display, which displayed the number 4 using a diagonal bar (). In 1910, a seven-segment display illuminated by incandescent bulbs was used on a power-plant boiler room signal panel. They were also used to show the dialed telephone number to operators during the transition from manual to automatic telephone dialing. They did not achieve widespread use until the advent of LEDs in the 1970 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scram
A scram or SCRAM is an emergency shutdown of a nuclear reactor effected by immediately terminating the fission reaction. It is also the name that is given to the manually operated kill switch that initiates the shutdown. In commercial reactor operations, this type of shutdown is often referred to as a "scram" at boiling water reactors (BWR), a "reactor ''trip''" at pressurized water reactors and at a CANDU reactor. In many cases, a scram is part of the routine shutdown procedure, which serves to test the emergency shutdown system. The etymology of the term is a matter of debate. United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission historian Tom Wellock notes that ''scram'' is English-language slang for leaving quickly and urgently, and cites this as the original and most likely accurate basis for the use of ''scram'' in the technical context. A persistent alternative explanation posits that ''scram'' is an acronym for "safety control rod axe man", which was supposedly coined by Enrico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relay
A relay Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off A relay is an electrically operated switch. It consists of a set of input terminals for a single or multiple control signals, and a set of operating contact terminals. The switch may have any number of contacts in multiple contact forms, such as make contacts, break contacts, or combinations thereof. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by an independent low-power signal, or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. Relays were first used in long-distance telegraph circuits as signal repeaters: they refresh the signal coming in from one circuit by transmitting it on another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations. The traditional form of a relay uses an electromagnet to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hacker
A hacker is a person skilled in information technology who uses their technical knowledge to achieve a goal or overcome an obstacle, within a computerized system by non-standard means. Though the term ''hacker'' has become associated in popular culture with a '' security hacker''someone who utilizes their technical know-how of bugs or exploits to break into computer systems and access data which would otherwise be inaccessible to them – hacking can also be utilized by legitimate figures in legal situations. For example, law enforcement agencies sometimes use hacking techniques in order to collect evidence on criminals and other malicious actors. This could include using anonymity tools (such as a VPN, or the dark web) to mask their identities online, posing as criminals themselves. Likewise, covert world agencies can employ hacking techniques in the legal conduct of their work. On the other hand, hacking and cyber-attacks are used extra- and illegally by law enforcemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back Orifice
Back Orifice (often shortened to BO) is a computer program designed for remote system administration. It enables a user to control a computer running the Microsoft Windows operating system from a remote location.Richtel, Matt.Hacker Group Says Program Can Exploit Microsoft Security Hole" ''The New York Times'' August 4, 1998. Retrieved April 24, 2007. The name is a play on words on Microsoft BackOffice Server software. It can also control multiple computers at the same time using imaging. Back Orifice has a client–server architecture. A small and unobtrusive server program is on one machine, which is remotely manipulated by a client program with a graphical user interface on another computer system. The two components communicate with one another using the TCP and/or UDP network protocols. In reference to the Leet phenomenon, this program commonly runs on port 31337. The program debuted at DEF CON 6 on August 1, 1998 and was the brainchild of Sir Dystic, a member of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frob
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mung (computer Term)
Mung is computer jargon for a series of potentially destructive or irrevocable changes to a piece of data or a file. It is sometimes used for vague data transformation steps that are not yet clear to the speaker. Common munging operations include removing punctuation or HTML tags, data parsing, filtering, and transformation. The term was coined in 1958 in the Tech Model Railroad Club at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. In 1960 the backronym "Mash Until No Good" was created to describe Mung, and by 1976 it was revised to "Mung Until No Good", making it one of the first recursive acronyms. It lived on as a recursive command in the editing language Text Editor and Corrector, TECO. It differs from the very similar term munged password, munge, because munging usually implies destruction of data, while mungeing usually implies modifying data (simple passwords) in order to create protection related to that data. Munging may also describe the constructive operation of tying to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jargon File
The Jargon File is a glossary and usage dictionary of slang used by computer programmers. The original Jargon File was a collection of terms from technical cultures such as the MIT AI Lab, the Stanford AI Lab (SAIL) and others of the old ARPANET AI/ LISP/PDP-10 communities, including Bolt, Beranek and Newman, Carnegie Mellon University, and Worcester Polytechnic Institute. It was published in paperback form in 1983 as ''The Hacker's Dictionary'' (edited by Guy Steele), revised in 1991 as ''The New Hacker's Dictionary'' (ed. Eric S. Raymond; third edition published 1996). The concept of the file began with the Tech Model Railroad Club (TMRC) that came out of early TX-0 and PDP-1 hackers in the 1950s, where the term hacker emerged and the ethic, philosophies and some of the nomenclature emerged. 1975 to 1983 The Jargon File (referred to here as "Jargon-1" or "the File") was made by Raphael Finkel at Stanford in 1975. From that time until the plug was finally pulled on the SAIL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Greenblatt (programmer)
Richard D. Greenblatt (born December 25, 1944) is an American computer programmer. Along with Bill Gosper, he may be considered to have founded the hacker community,) and holds a place of distinction in the communities of the programming language Lisp and of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. Early life Greenblatt was born in Portland, Oregon on December 25, 1944. His family moved to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania when he was a child. He later moved to Columbia, Missouri with his mother and sister when his parents divorced. Career Becoming a hacker Greenblatt enrolled in MIT in the fall of 1962, and around his second term as an undergraduate student, he found his way to MIT's famous Tech Model Railroad Club. At that time, Peter Samson had written a program in Fortran for the IBM 709 series machines, to automate the tedious business of writing the intricate timetables for the Railroad Club's vast model train layout. Greenblatt felt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keypunch
A keypunch is a device for precisely punching holes into stiff paper cards at specific locations as determined by keys struck by a human operator. Other devices included here for that same function include the gang punch, the pantograph punch, and the stamp. The term was also used for similar machines used by humans to transcribe data onto punched tape media. For Jacquard looms, the resulting punched cards were joined together to form a paper tape, called a "chain", containing a program that, when read by a loom, directed its operation.Bell, T.F. (1895) '' Jacquard Weaving and Designing'', Longmans, Green And Co. For Hollerith machines and other unit record machines the resulting punched cards contained data to be processed by those machines. For computers equipped with a punched card input/output device the resulting punched cards were either data or programs directing the computer's operation. Early Hollerith keypunches were manual devices. Later keypunches were electrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
